Abstract
Existing assessment tools have not been successfully used to evaluate the performance of the remedial treatment of concrete flat roofs by building users or building management personnel because they are complicated and difficult to be applied by non-experts. In this study, a semi-quantitative method has been developed to assess the quality of remedial treatment on concrete flat roofs of multiple buildings. A 10-point scale weighting was calculated based on the results of ranking, and then the score assessment scheme was developed. Results revealed that the repairing principles included protection against ingress (W = 7.25), physical resistance against ingress (W = 5.23), concrete restoration (W = 8.22), structural strengthening (W = 8.22), moisture control (W = 6.59), and chemical resistance (W = 4.57). The grouped principles included physical resistance (W = 6.24), structural stability (W = 8.22), and chemical resistance (W = 5.58). The scoring assessment scheme was applied to a remedial treatment on multilayer concrete flat roof which was treated with bituminous membrane. The assessment scheme was revised based on the surveyors’ comments and then verified by the experts. This assessment method secured and improved the quality of the remedial treatment, since the building management staff/owner successfully evaluated, controlled, and monitored the quality of remedial treatments.
1. Introduction
A flat concrete roof is one of the most complex and challenging building elements because it is consistently exposed to harmful agents from the external environment. Concrete flat roofs may consist of many functional defects, including cracking, disintegration, and others [1,2]. As such, remedial treatments are necessary to improve the performance of concrete flat roof and to extend its service life [3]. Remedial treatments are conducted not only on old concrete structures but also on newly constructed structures because of many influencing factors. Diverse industrial products have been developed to repair concrete flat roofs. However, building codes and standards for the evaluation of remedial treatments are yet to be established. Issues on questionable quality of remedial treatments have also been raised.
The performance of flat roofs has been studied. Carretero-Ayuso et al. [4] identified the factors that influence defects and found that design is the most important parameter. Carretero-Ayuso and de Brito [5] investigated the effect of third-party monitoring on flat roof construction and observed that third-party monitoring can improve the quality of flat roofs. Also, Conceição et al. [6] developed a system to inspect, maintain, and rehabilitate flat roofs.
Remedial treatments on concrete have also received considerable research attention. Jumaat et al. [7] reviewed the repair treatments for concrete beams and discussed the advantages and disadvantages of each repairing attempt, such as using cement grout, mortar, concrete, sprayed concrete or shotcrete, epoxy, ferrocement with mortar, fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP), and sprayed FRP. Bhaskaran et al. [8] reviewed and compared the estimated cost of anti-corrosion approaches, such as Uhlig method, Hoar method, NBS-BCL input/output method, and the net present value method. However, the assessment methods for the remedial treatments of concrete flat roofs have yet to be investigated comprehensively. Garrido et al. [9] compared and examined the performance of combined techniques to repair bituminous waterproofing and observed that heating is essential for repairing bituminous waterproofing. However, it should be noted that the above-mentioned studies mainly focused on technical issues and parameters, while not providing emphasis on the quality assessment of on-site remedial work. In this aspect, several techniques to evaluate and analyze the quality of concrete flat roofs have been looked into. In general, three types of assessment methods are applied in current practice: qualitative, quantitative, and semi-quantitative methods. Among them, the qualitative method is the most common, where surveyors or inspectors use their experience, knowledge, and intuition to evaluate the quality of concrete flat roofs. While this method can be convenient and straightforward, the findings can be subjective and different among individual users. Nevertheless, Walter et al. [10] developed a checklist to identify the defects of a bituminous waterproofing system. Kenai and Bahar [11] designed an assessment method for the new Algiers airport building with visual inspection, seismic parallel technique, and nondestructive equipment [12]. Moreover, Mosa et al. [13] developed an expert system to identify the causes of problems and their expected effects on pavement as well as applying suitable remedies.
Several techniques have also been developed to quantify the performance of concrete flat roofs. One of the most common quantifying methods is through laboratory experiments. In laboratory experiments, the effects of factors on the performance of a waterproofing system are examined. For example, Weigel and Stephan [14] used Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and multivariate analysis methods to correlate the chemical and physical characteristics of bitumen samples, and their results are based on refineries, grades, and aging states to predict chemical, conventional, and rheological parameters. These methods provide highly accurate results, but they are expensive and may be unsuitable for existing buildings. Morgado et al. [15] supported the approach of Weigel and Stephan [14], and they found that the replacement of a waterproofing system should be undertaken earlier than the expected year (20 years) because damage mostly occurs in waterproofing systems. Skominas et al. [16] performed a laboratory experiment to evaluate concrete mortar as a repair material for hydraulic structures. Furthermore, Che-Ani et al. [17] monitored and controlled water ponding problems with etape-sensors. More advanced and novel quantitative techniques are those such as big data analysis, simulation, and modeling. Bailey and Bradford [18] conducted big data analysis to examine a large army of roof inspection record and to identify defects and their impacts. Tamas et al. [19] also developed a simulation model to select waterproofing rehabilitation for a church and a castle. These novel quantitative techniques can provide more accurate and precise results, but their implementation requires large and detailed data. However, most existing maintenance record systems of buildings are confidential and different among buildings. Other associated problems are like insufficient recorded data, especially for construction methods and materials that were used in old existing buildings, and numerous unauthorized structures that have been constructed. These uncertainties may increase the difficulties in evaluating the performance of concrete flat roofs.
Semi-quantitative assessment methods are uncommon in evaluating the quality of concrete flat roofs, but they are commonly used for fire risk assessments, such as fire safety rankings [20]. Moradi-Marani et al. [12] designed a similar method to investigate the corrosion damage and repair system in a concrete jetty structure, while Che-Ani et al. [21] developed a condition survey protocol matrix to assess the condition of buildings, where they produced a checklist and assigned weighting to each attribute. They categorized the proposed condition assessment into five scales, i.e., as good, fair, poor, very poor, and dilapidated; and ranked the priority of maintenance work into four classes of normal, routine, urgent, and emergency. The semi-quantitative assessment method may involve some nondestructive equipment to provide precise data. Although the accuracy of its assessment results is lower than that of quantitative methods, the former is more convenient and user-friendly than the latter when analysis is conducted on site.
In this study, the authors have developed a semi-quantitative method to assess the quality of the remedial treatments on concrete flat roofs of multiple buildings, to save money and resources, and to prevent the possibility of performing the remedial treatment again in a short period. An ideal assessment method should be user-friendly, suitable for spaces, easily documented for future monitoring, accurate, and precise. The advantages and characteristics of the proposed method are similar to those of other methods to the features of ideal assessment methods. This paper highlights the problems and limitations associated with the existing remedial treatments on concrete flat roofs and discusses the development of a semi-quantitative assessment method to analyze the quality of the remedial treatments for concrete flat roofs of multiple buildings, where a 10-point weighting is calculated based on the results of ranking, and the score assessment scheme is developed.
2. Methodology
This paper discusses the development of a semi-quantitative assessment method to evaluate the quality of remedial treatment for concrete flat roofs in multiple buildings. The overall procedure of the development is presented in Figure 1.
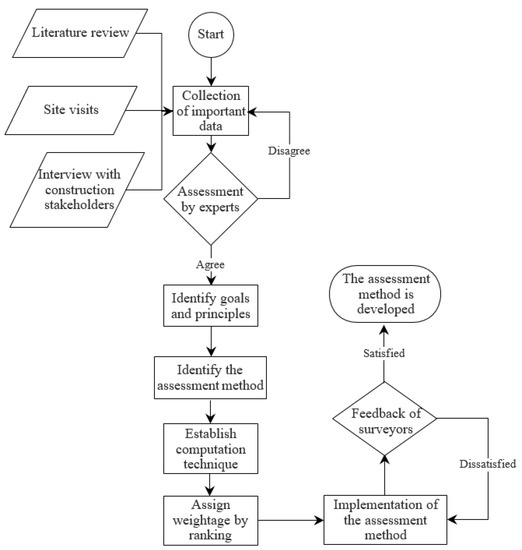
Figure 1.
Overall flow chart to develop assessment method for remedial treatment.
Important information was collected first through a comprehensive literature review, followed by a preliminary study on the case with a performed remedial treatment, and an assessment of construction stakeholders. Subsequently, the repairing principles were identified based on the collected information, grouped, and verified through the assessment of experts. The experts involved in this process were from diverse backgrounds, such as researchers and academic staff, specialist contractors, consultants, and government staff. They had at least 2 years of working experience in dealing with concrete flat roof-related issues. This process was repeated unless (and until) all experts agreed with the grouping and verification of attributes. After that, the point-scheme was developed and obtained according to the analyzed results ranked by the experts. Finally, the assessment scheme was applied on a completed remedial treatment of concrete flat roof.
The assessment scheme was further revised according to the feedback of surveyors. The details of these procedures have been explained and discussed in Section 3 of the paper, considering that these procedures are part of the development of an assessment method for the evaluation of the quality of remedial treatment on concrete flat roofs.
3. Results and Discussion
The procedure of developing semi-quantitative assessment scheme was divided into several phases. The findings of each phase have been reported and discussed below.
3.1. Preliminary Study
Understanding existing remedial treatment procedures is necessary prior to developing an assessment method to help elucidate the remedial treatment assessment scheme, identify the characteristics of an ideal assessment tool, and determine the challenges in currently available assessment tools. A typical assessment process is illustrated in Figure 2.
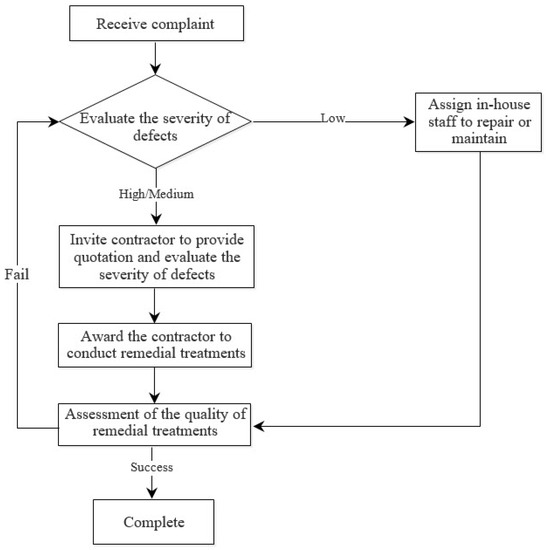
Figure 2.
General approach to perform remedial treatment.
High-rise buildings are maintained by the appointed building management team. This process is not periodic civil maintenance because most preventive maintenance treatments focus on mechanical and electrical aspects [1]. However, the remedial treatments begin if a complaint is received. First, the defect severity is evaluated by a representative from building management/owners. If the defect severity is low, in-house technical staff are assigned to repair or maintain concrete flat roofs. Otherwise, a contractor is invited to evaluate the defect severity, propose remedial treatments, and provide a quotation. If the quoted contract cost is too high, tendering is open to all contractors to bid. After the awarded contractor conducts remedial treatments, the output is assessed by a representative from building management/owners. The completion of remedial treatments depends on their effectiveness. If these treatments are successful, then they are completed. If not, the contractor provides extra services to solve problems until the building management team is satisfied with their performance.
Preliminary studies revealed that an ideal assessment scheme on remedial treatments should have the following characteristics: (1) nondestructive to building structures, (2) minimized disturbance on the operation of buildings, (3) user-friendly, (4) easily understood and interpreted, (5) standardized results, and (6) highly accurate and valid results. Most of these characteristics are satisfied by semi-quantitative assessment methods. One of the reasons to develop semi-quantitative assessment methods is that most maintenance staff [1] and building owners do not have strong knowledge in civil and structural engineering.
3.2. Identifying Repairing Principles and Examination Methods
The repairing principles and examination methods of the assessment scheme were identified as information was collected. The repairing principles and examination methods were grouped, verified, and validated through the assessment by the experts from diverse backgrounds. The overall flowchart to identify the repairing principles and examination methods is illustrated in Figure 3. The six identified repairing principles were adopted based on the repairing principles described in BS EN 1504 [22] and they included protection against ingress, moisture control, concrete restoration, structural strengthening, increasing physical resistance, and chemical resistance.
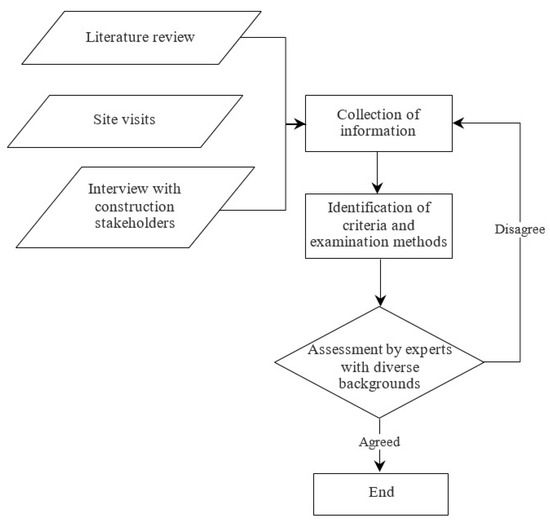
Figure 3.
Identifying attributes and examination method.
The study presented in this paper was based on the opinion of experts to group repairing principles in order to reduce the complication of assessment and to increase the convenience of surveyors. Therefore, three groups of repairing principles were further clustered based on the characteristics of problems (Figure 4): physical resistance principles, chemical resistance principles, and structural stability principles. Protection against ingress and increasing physical resistance were grouped into physical resistance principles. Moisture control and resistance to chemicals were categorized under chemical resistance principles. Concrete restoration and structural strengthening were considered under structural stability principles.
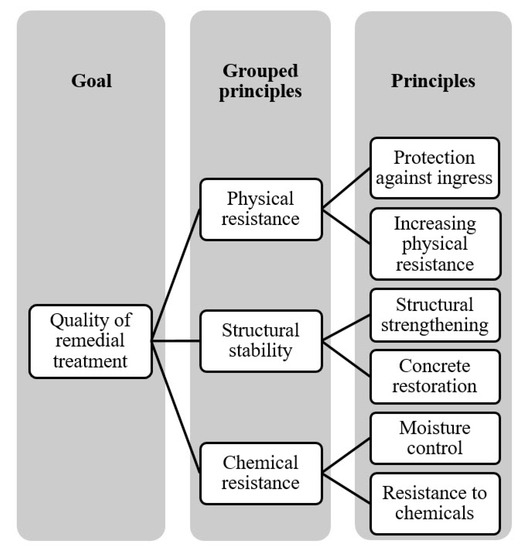
Figure 4.
Classification of repairing principles.
A flowchart to determine the use of the repairing principles is presented in Figure 5. Three central questions determine the repairing principles: (1) Are physical damage problems available? (2) Are moisture and chemical attack problems available? (3) Are structural problems available? In other words, the remedial treatments involving physical resistance were conducted to solve physical problems. The remedial treatments applying chemical resistance principles are suitable to resolve chemical problems. Structural problems should be solved with the remedial treatments that use structural stability principles.
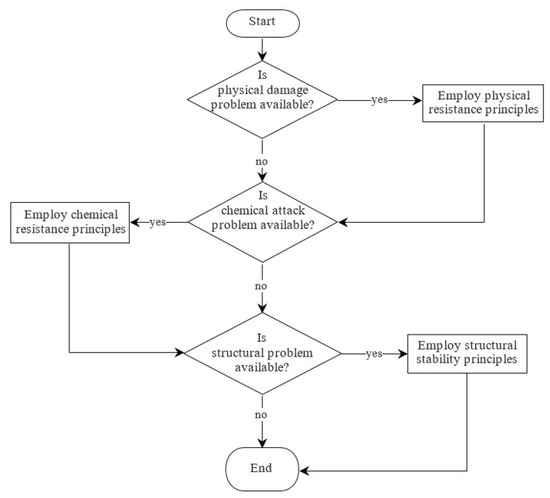
Figure 5.
Flowchart to determine employable repairing principles.
The examination methods for the grouped repairing principles are summarized in Table 1. First, the surveyors used visual observation to identify the physical damage problems. If such a problem was detected, a 58-C0218ELE crack microscope was used to measure the width of cracks and their growth. Then, the water pouring technique was used to identify and assess the water ponding problems. Visual observation was performed to detect the signs of chemical attacks, such as salting and discoloration. Finally, visual observation was performed to detect the characteristics of structural failures, such as deflation, whereas a calibrated TMT106B-TMH-225 rebound hammer was utilized to determine the compressive strength of concrete structures because it resulted in a limited effect on concrete structures.

Table 1.
Examination methods for different grouped repairing principles.
3.3. Mathematical Operations in the Assessment
The repairing principles used in this study vary among different instances of remedial treatment and depend on the severity of defects and the complications in remedial treatments. In other words, more principles are applied to more complicated remedial treatments with more severe defects, thereby possibly increasing the difficulty in assessing these treatments. The assessment scheme should be formulated to provide the comparable and standardized results by using Equations (1) to (5).
where
- G = Overall assessment score of the quality of remedial treatments
- Ci = Assigned scores of the grouped repairing principles involved in the remedial treatments
- Wi = Assigned weighting of the grouped repairing principles involved in the remedial treatments
- Cmax = Maximum score of the grouped repairing principles involved in the remedial treatments
- Wmax = Maximum weighting of the grouped repairing principles involved in the remedial treatments
- n = Number of the grouped repairing principles involved in the remedial treatments
The point-scheme (Ci) was developed based on Equations (1) and (2) for all grouped repairing principles, assigning the points (scores) from 0 to 2 based on the condition of remedial treatments. The evaluation scheme is shown in Table 2. Cracking or any visual sign of physical damage was the main criterion for physical resistance. Water ponding or any visual sign of chemical attack was the main criterion for chemical resistance. Compressive strength or any visual characteristic of structural failure was the main criterion for structural stability.

Table 2.
Point-scheme for grouped repairing principles.
Weighting accuracy strongly influences the evaluation accuracy. An expert panel is required to determine the weighting accuracy. In this study, a preference ranking scale was used because of its various advantages, such as convenience, quick result generation, and fatigue reduction [23]. The method presented in this paper was developed based on the grouped repairing principles that were identified from preliminary results and experts’ assessment. These principles were then ranked by the experts in the order of importance based on their experience and knowledge.
The repairing principles with higher rankings were assigned with a higher score. Then, the weighting of repairing principles was obtained by a method adopted from Abalo et al. [23]. n raters were presented with s repairing principles, and numbers 1 (most preferred) to k (least preferred) were used to rank their top k preferences without allowance of ties. Only the top three ranked attributes were considered to avoid repairing principles with low aggregate rank scores, resulting in crowding at the bottom, especially for a high number of attributes. Furthermore, this method reduced the difficulty in reporting and comparing data.
Raw ranking (gij), which is the rank assigned to the i-th repairing principle by the j-th rater, was recorded to ranking scores (hij) by using Equation (3) to increase the degree of preference, and then assign 0 to all the repairing principles not mentioned by the rater. Table 3 lists hij if the values of k and gij are up to 6. The weight of the repairing principles was obtained using Equation (4). However, the repairing principles were calculated using Equation (5) because of the grouping of the repairing principles.

Table 3.
Ranking score hij for raw ranking gij of the rater’s most preferred k attributes.
The weighting results of the grouped repairing principles along with the weighting of their component principles are reported in Table 4. In addition, the weighting results of the overall repairing principles are presented in Figure 6 for better comparison. The most critical repairing principles were concrete restoration (W = 8.22) and structural strengthening (W = 8.22). The chemical resistance of the remedial treatment was selected as the principle with the lowest weighting (W = 4.57). The other repairing principles were protection against ingress (W = 7.25), increasing physical resistance (W = 5.23), and moisture control (W = 6.59).

Table 4.
Weighting of grouped and component repairing principles.
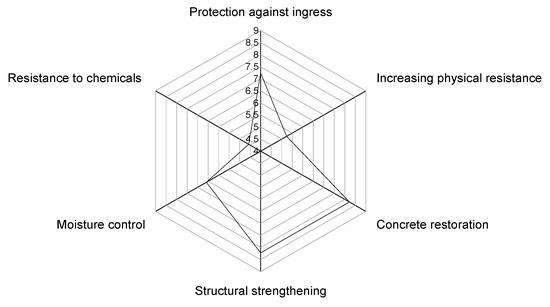
Figure 6.
Weighting of overall repairing principles.
The ranking of different grouped repairing principles has been illustrated in Figure 7 based on their weighting results. In Figure 7, the weighting of the structural stability (W = 8.22) is the highest because the repairing principles were involved in the severely damaged concrete flat roofs. If the repairing principle fails, then concrete flat roofs could harm the safety of building users and their properties. The weighting of chemical resistance (W = 5.58) is the lowest. The remedial treatment with this repairing principle was recommended and conducted on the concrete flat roofs near areas with high amounts of aggressive chemical agents, such as the marine environment. However, most concrete flat roofs are seldom exposed to aggressive chemical agents. Therefore, the chemical resistance is less critical than the other principles. Furthermore, the weighting of physical resistance (W = 6.24) indicates that the associated repairing principles were less critical than those of structural stability.
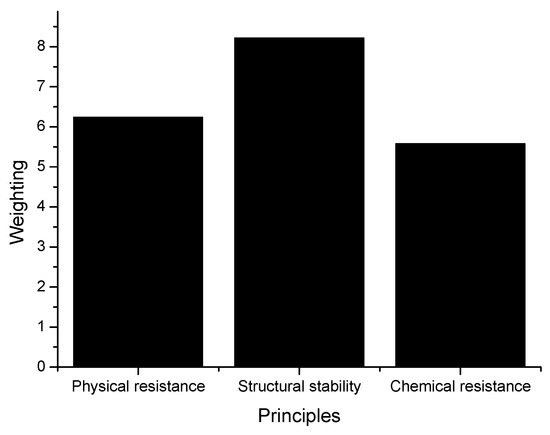
Figure 7.
Ranking of different grouped repairing principles.
The overall weighting of the remedial treatment principles is presented in Figure 8. After the assessment score and the weighting were obtained by using Equations (1) to (5), the results from Equation (1) were further interpreted based on the percentage scores given in Table 5. Five main categories of assessment score were used: excellent, good, fair, weak, and fail.
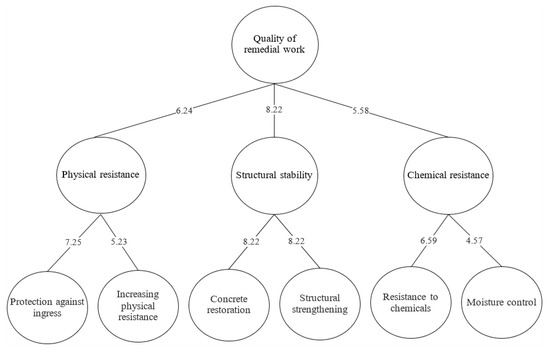
Figure 8.
Overall framework for remedial treatment.

Table 5.
Categories of percentage score.
3.4. Implementing the Assessment Method
The surveyed building was a multi-story reinforced concrete structure with multiple concrete flat roofs. The waterproofing system was replaced with bituminous waterproofing membranes because of water leakage problems and cracking. Cracking was repaired with epoxy resins. After the remedial treatments were completed, three surveyors, namely, the author, the building manager, and a contractor’s representative applied the assessment method to evaluate the quality of remedial treatments. During surveying, the assessment scheme was revised based on the surveyors’ feedback and then it was verified by the experts having diverse backgrounds.
The principles involved were first identified by the procedures shown in Figure 9. The remedial treatments involved repairing cracks and increasing resistance against moisture and chemicals. The maximum score of this assessment calculated using Equation (6) was 23.64. The involved principles included physical resistance and chemical resistance. In these remedial treatments, all the surveyors identified many defects. The overall assessment quality score of the remedial treatments was determined using Equation 2. The calculation is shown in Equation (6) and Equation (7).
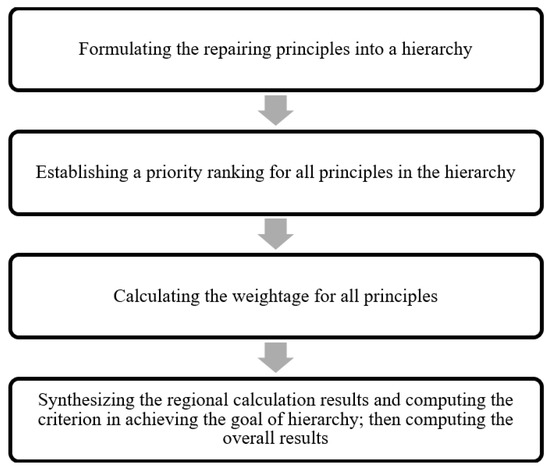
Figure 9.
Weighting the repairing principles with priority ranking.
In the assessment process, the quality of the remedial treatments was under the fail category because the surveyors identified many defects (Figure 10). The surveyors found many cracks (Figure 10a) and vegetation (Figure 10b) growing on the waterproofing membrane. Some cracks were more than 5 mm in width. Disintegration (Figure 10c,d) led to thinning and affected the durability and service life of the waterproofing system. At the same time, the signs of chemical attack on the waterproofing system were detected (Figure 10e). The poor remedial treatments were caused by the low quality of workmanship and could be identified based on their application defects.
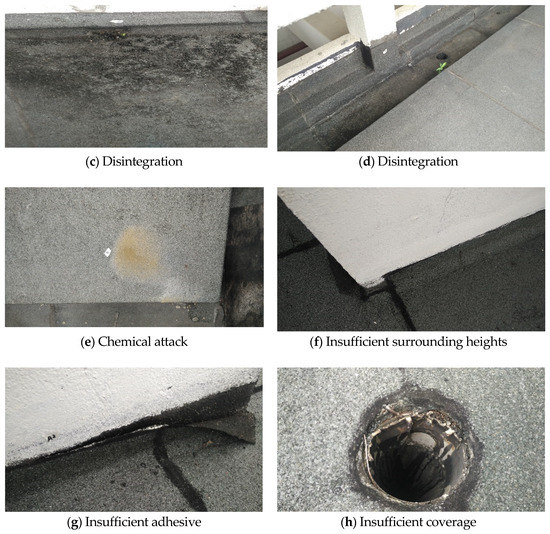


Figure 10.
Defects identified in remedial treatment.
Improper application defects, such as insufficient surrounding heights (Figure 10f), insufficient adhesive (Figure 10g), and insufficient coverage (Figure 10h) were identified. Mailvaganam and Collins [24], Bailey and Bradford [18], and Mailvaganam and Collins [25] emphasized the considerable effects of workmanship on the performance of waterproofing systems. Bailey and Bradford [18] investigated the relationship between low sloped roofing issues and deduced that the 75% of defects were caused by the factors stated above, rather not by natural degradation. Among those factors, the quality of workmanship during installation was the most critical factor, which influences the performance of roof. In addition, Mailvaganam and Collins [24] found that at ambient weather conditions, the quality of workmanship and preparation of the substrate strongly affects the performance of elastomeric waterproofing membrane. In other words, the workmanship is highly related to the quality of remedial treatments.
4. Concluding Remarks
Concrete flat roofs are one of the building components that are most prone to degradation. Remedial treatments are necessary to extend the service life of concrete flat roofs. However, limited research has been conducted to assess the quality of remedial treatments of concrete flat roofs. In this study, a semi-quantitative assessment method to analyze the quality of the remedial treatments on concrete flat roofs of multiple buildings has been proposed. The development of the assessment method was initiated with the identification and grouping of repairing principles and assessment criteria, which were identified through literature survey, case studies, and interviews with construction stakeholders. Score values were assigned to the grouped principles after analyzing the assessment results and taking the opinions of the experts. The remedial treatment on a selected concrete flat roof was assessed with the developed assessment method. The assessment method was further revised according to the feedback from the surveyors.
The proposed method is advantageous compared to other quantitative methods. It is user-friendly and easily applicable. Also, it does not require expertise to assess the quality of the remedial treatments of concrete flat roofs. However, the results from semi-quantitative methods can be less precise and accurate compared to quantitative methods. However, this technique may provide a more precise and accurate results than qualitative methods, which are subjective and may vary based on the prediction of users.
The performance of the remedial treatments of concrete flat roofs can be appropriately examined with the proposed method. Through this approach, it is practical for stakeholders, especially non-experts to understand, monitor, and control the performance of remedial treatments of concrete flat roofs. This process can prevent the wastage of resources and time, and even minimize the safety hazards to building users and their valuable properties. However, this method is unsuitable for remedial treatments of other building components due to varying repairing principles, factors, conditions, and materials. Further research is required to comprehensively study the influencing factors and performance of the remedial treatments of other building components.
Author Contributions
The data collection, assessment, and analysis were performed by C.-O.W. under the guidance and supervision of S.N.R., M.J., and M.F.M.Z. S.N.R., C.-O.W., and M.J. designed the research program for the research. M.S. significantly assisted in the analysis of research findings to facilitate the present study and planned the framework for this paper. The manuscript was written by C.-O.W. and S.N.R., and was supplemented by the contributions of M.J. and M.F.M.Z. M.S. critically reviewed the paper and provided valuable technical inputs to improve its overall quality.
Funding
This research was funded by UKM (Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia) Research University Grant (GUP-2018-101).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Suffian, A. Some common maintenance problems and building defects: Our experiences. Procedia Eng. 2013, 54, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarman, A.M.; Nawi, M.; Nasrun, M.; Che-Ani, A.I.; Mazlan, E.M. Concrete flat roof defects in equatorial climates. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2015, 10, 7319–7324. [Google Scholar]
- ACI 562M-13. Code Requirements for Assessment, Repair, and Rehabilitation of Existing Concrete Structures and Commentary; ACI Committee 562; American Concrete Institute: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Carretero-Ayuso, M.J.; García-Sanz-Calcedo, J.; Reyes-Rodríguez, A.M. Qualitative and quantitative analyses on project deficiencies in flat-roof design in Extremadura, Spain. J. Constr. Eng. Mang. 2016, 142, 4016061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero-Ayuso, M.J.; de Brito, J.V. Analysis of the execution deficiencies of flat roofs with bituminous membranes. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2016, 30, 4016049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, J.; Poça, B.; de Brito, J.; Flores-Colen, I.; Castelo, A. Inspection, diagnosis, and rehabilitation system for flat roofs. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2017, 31, 04017100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumaat, M.; Kabir, M.; Obaydullah, M. A review of the repair of reinforced concrete beams. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2006, 2, 317–326. [Google Scholar]
- Bhaskaran, R.; Palaniswamy, N.; Rengaswamy, N. A review of differing approaches used to estimate the cost of corrosion, anti-corrosion method and materials. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2013, 52, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, M.; António, D.; Lopes, J.; Correia, J. Performance of different joining techniques used in the repair of bituminous waterproofing membranes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 158, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, A.; de Brito, J.; Grandão Lopes, J. Current flat roof bituminous membranes waterproofing systems—Inspection, diagnosis and pathology classification. Constr. Build. Mater. 2005, 19, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenai, S.; Bahar, R. Evaluation and repair of Algiers new airport building. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2003, 25, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi-Marani, F.; Shekarchi, M.; Dousti, A.; Mobasher, B. Investigation of corrosion damage and repair system in a concrete jetty structure. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2009, 24, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosa, A.M.; Ismail, N.N.; Yusoff, N.I.M.; Mubaraki, M.A.; Memon, N.A.; Taha, M.R.; Hainin, M.R. An expert system to remedy concrete imperfections and their effects on rigid pavements. J. Teknol. 2015, 76, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigel, S.; Stephan, D. The prediction of bitumen properties based on FTIR and multivariate analysis methods. Fuel 2017, 208, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgado, J.; Morgado, J.; Flores-Colen, I.; Flores-Colen, I.; de Brito, J.; de Brito, J.; Silva, A.; Silva, A. Maintenance programmes for flat roofs in existing buildings. Prop. Manag. 2017, 35, 339–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skominas, R.; Gurskis, V.; Sadzevicius, R.; Damulevicius, V.; Radzevicius, A. Evaluation of cement mortar suitability for repairing concrete in hydraulic structures. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2017, 21, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che-Ani, A.; Johar, S.; Mohamad-Idin, M.; Abdullah, M.; Maruzuki, M. Development of transduction circuit for flat roof water ponding monitoring system using etape sensor. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2015, 10, 24–34. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, D.M.; Bradford, D. Membrane and flashing defects in low-slope roofing: Causes and effects on performance. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2005, 19, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamas, F.-L.; Mizgan, P.; Muntean, R.; Cazacu, C.; Galatanu, T. Optimization of a technological solution used to waterproofing rehabilitation for building infrastructure. Procedia Eng. 2017, 181, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.M. A fire safety assessment system for existing buildings. J. Fire Technol. 1999, 35, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che-Ani, A.I.; Tazilan, A.S.M.; Kosman, K.A. The development of a condition survey protocol matrix. J. Struct. Surv. 2011, 29, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BS EN 1504-9. Products and Systems for the Protection and Repair of Concrete Structures—Definitions, Requirements, Quality Control and Evaluation of Conformity. General Principles for Use of Products and Systems; British Standard Institution: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Abalo, J.; Varela, J.; Manzano, V. Importance values for importance–performance analysis: A formula for spreading out values derived from preference rankings. J. Bus. Res. 2007, 60, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailvaganam, N.; Collins, P. Workmanship factors influencing quality of installed parking garage waterproofing membranes. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2004, 18, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailvaganam, N.P.; Collins, P. Effective Installation of Membranes on Parking Garage Decks; Institute for Research in Construction, National Research Council of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1999. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).