Abstract
To enhance the microstructure and mechanical properties and to optimize the formulations of high-strength and high-flow ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC), the effects of different quartz powder contents, fineness, and curing temperatures of UHPC were systematically studied. It was hypothesized that using the appropriate content and fineness of quartz powder can improve the microstructure of UHPC and, thus, improve its mechanical properties, especially at higher curing temperatures. To test this hypothesis, the flowability, compressive strength, flexural strength, and tensile strength of UHPC mixtures with different quartz powder dosages (0%, 15%, 30%) and fineness (4 µm, 8 µm), cured at 20 °C, 45 °C, and 90 °C, were investigated. The results indicate that as the dosage of quartz powder increases and the particle size decreases, the flowability of UHPC decreases. The compressive strength of UHPC first increases and then decreases with an increase in quartz powder dosage. Finer quartz powder usage considerably enhances packing density and pore structure. When the content of quartz powder is 15%, UHPC achieves optimal mechanical properties and pore structure, showing an improvement of 3.6% to 14.4% compared to UHPC with a coarse particle size. Additionally, an increase in curing temperature leads to the consistent growth of the compressive strength of UHPC. Under 90 °C steam curing, UHPC incorporating 15% fine quartz powder (4 μm) achieved a peak compressive strength of 182.1 MPa, increased by 19.8% compared to that under 20 °C, which is attributed to the enhanced pozzolanic activity of fine quartz powder. These findings provide valuable guidance for the mix design of UHPC in precast concrete components, long-span bridges, and marine structures, where high early strength and durability are critical.
1. Introduction
Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) has emerged as a transformative material in modern civil engineering, being characterized by exceptional compressive strength (>150 MPa), durability, and resistance to environmental degradation [,,]. Its applications include high-rise buildings, long-span bridges, and marine infrastructure, where superior mechanical performance and longevity are critical [,,]. The performance of UHPC is strongly influenced by its composition [,]. A typical UHPC mix incorporates binder materials with various particle sizes, including cement, silica fume (SF), fly ash, and so on [,]. Fine aggregates are incorporated to enhance packing density [,], while fibers are added to improve strength and toughness [,]. Previous studies [,,,] indicate that increasing the steel fiber content of UHPC enhances its mechanical performance, although this also reduces flowability. Additionally, achieving optimal performance typically needs the incorporation of significant quantities of supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) in UHPC [,]. Shi et al. [] found that under standard curing conditions, SF exhibited a greater impact on compressive strength. Feng et al. [] demonstrated that high-strength quartz sand could replace river sand when preparing UHPC. However, the widespread adoption of UHPC still remains constrained by high material costs, primarily due to the extensive use of cement, SF, and specialty additives [,,].
To address this issue, researchers have increasingly focused on optimizing SCMs like quartz powder to reduce costs while enhancing performance [,]. Quartz powder has been extensively studied as a filler and potential pozzolan in cementitious systems. Its fine particle size (typically < 100 µm) enables improved packing density by occupying interparticle voids between cement particles, thereby reducing porosity and enhancing its mechanical properties []. Benezet et al. [] demonstrated that quartz powder particles that are smaller than 5 µm exhibit partial pozzolanic activity under specific conditions, reacting with calcium hydroxide (CH) to form calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) gel. This reactivity is highly dependent on particle fineness and curing regimes, with elevated temperatures accelerating pozzolanic reactions []. The appropriate incorporation of quartz powder (10–20%) can significantly enhance the compressive strength of concrete. According to Sobuz et al. [], quartz powder accelerates hydration through its filling effect and nucleation, resulting in a maximum increase of 14.3% in 28 d compressive strength. In UHPC, the synergistic effect of quartz powder with steel fibers and SF can improve fracture toughness by up to 6.6%. However, excessive additions (>30%) may lead to increased porosity due to uneven particle packing, resulting in a decrease in strength [].
Although the role of quartz powder as a filler has previously been recognized, the effects of its particle fineness and dosage on the hydration behavior and microstructure of UHPC are still not fully understood. In particular, the potential pozzolanic activity of fine quartz powder under elevated curing temperatures and the interaction between quartz powder and other SCMs, such as fly ash microbeads (FAMs), remain unexplored. Therefore, this study addresses two critical research questions: (1) How do quartz powder fineness and dosage influence the mechanical properties and microstructural evolution of UHPC? (2) Can elevated curing temperatures enhance the pozzolanic reactivity of quartz powder to achieve superior early-age strength? To answer these questions, the influence of both quartz powder dosage and particle fineness on the flowability, mechanical performance, and microstructure of UHPC was systematically investigated. In addition, the effects of different curing temperatures on the hydration process and compressive strength were explored through advanced tests. The novelty of this research includes systematically comparing the influence of quartz powder dosage and fineness on UHPC performance, providing evidence of quartz powder’s pozzolanic reaction at elevated temperatures, and offering a comprehensive experimental framework for optimizing UHPC mix design in both normal and steam curing environments. These findings provide valuable insights into the role of quartz powder in enhancing UHPC performance.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
For this study, the main raw materials used in the experiments included cement, SF, FAMs, quartz powder, steel fibers, a water-reducing agent, and water. Among these materials, two particle sizes of quartz powder were utilized. The cement used was PI 52.5 Portland cement, with a measured specific surface area of 378 m2/kg. The compressive strengths at 3 d and 28 d were 31.8 MPa and 58.6 MPa, respectively. The chemical compositions, as presented in Table 1, were obtained through X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analysis, and represent the mass percentage of major oxide components in each material. The mineral compositions of the cement were as shown in Figure 1, with a median diameter (D50) of 15 μm; the particle size distribution is detailed in Figure 2. The chemical composition and particle size distribution of the SF can be found in Table 1 and Figure 2, with a SiO2 content of 91.9% and a D50 particle size of 0.5 μm. The primary mineral composition of the quartz powder was predominantly SiO2, as shown in Figure 1. The particle size distributions of the two types of quartz powder are detailed in Figure 2, with D50 particle sizes of 4 μm and 8 μm, smaller than that of the cement. The chemical composition is detailed in Table 1, primarily consisting of SiO2 and Al2O3, with an amorphous structure. The particle size distribution is shown in Figure 2, with a D50 particle size of 1.5 μm, approximately 1/13 of the median diameter of ordinary fly ash. Microspheres with particle sizes of between 0.5 and 2 μm accounted for 65%, while those larger than 10 μm made up 15% of the distribution.

Table 1.
Main oxide components of cement, SF, quartz powder, and FAM (%).
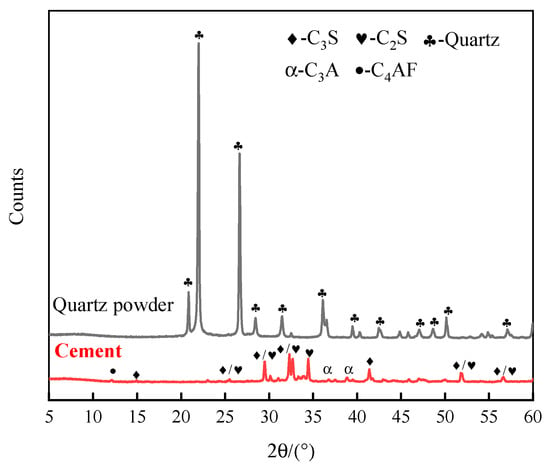
Figure 1.
XRD analysis patterns of cement and quartz powder.
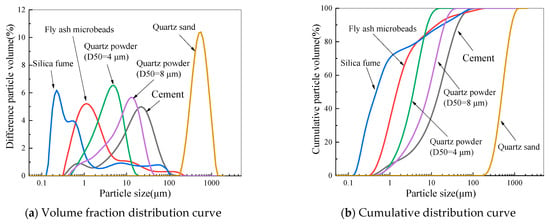
Figure 2.
Particle size distribution of cement, SF, quartz powder, FAMs, and quartz sand.
The particle morphology of the quartz powder used in this study is shown in Figure 3a. It can be observed that the particles of quartz powder have an irregular shape, are uneven in size, and possess a relatively smooth and dense surface. The particle morphology of the FAMs is presented in Figure 3b, which illustrates that the microspheres have a smooth, glass-like appearance. This morphology is beneficial for the “rolling” treatment of the paste, greatly enhancing the flowability of UHPC. The particle size distribution of the quartz powder ranges from 40 to 80 mesh; further details are provided in Figure 2. The steel fibers used in the experiments have a length of 13 mm, a diameter of 0.2 mm, and a tensile strength of ≥2850 MPa. The water-reducing agent employed in the experiments was a polycarboxylic acid-based high-performance water reducer, with a water reduction rate of ≥35%.
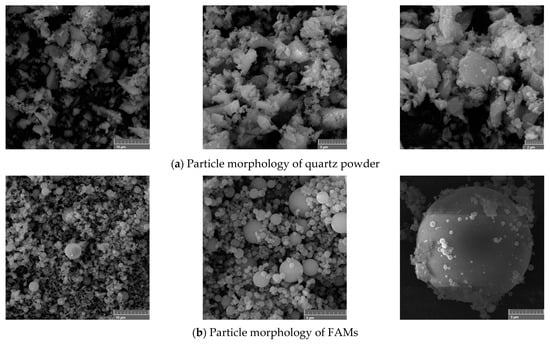
Figure 3.
Microscopic morphology of the raw materials used.
2.2. Sample Preparation and Curing
2.2.1. Mix Design
The water-to-binder ratio for UHPC is typically low, generally ranging from 0.13 to 0.20 [,,]. In this study, a water-to-binder ratio of 0.15 was used, with SF being incorporated at 10% of the total binder material. FAMs are commonly employed in UHPC to enhance its flowability, due to their spherical morphology. Therefore, FAMs were added at replacement levels of 15% and 30% by weight of the binder material to understand the contribution of quartz powder in both low- and high-FAM systems. Two types of quartz powder with different particle sizes were utilized, with replacement rates of 0%, 15%, and 30% for the cement content. Steel fibers were incorporated at 2.5% by volume. The specific quantities of materials in the mix are detailed in Table 2. In the numbering of the mix designs, the first digit “1” indicates the inclusion of fine quartz powder (D50 = 4 μm), while “2” denotes the inclusion of coarse quartz powder (D50 = 8 μm).

Table 2.
Mix proportion of UHPC.
2.2.2. Sample Preparation
Materials were weighed according to the mix design, and then quartz sand, quartz powder, cement, SF, and FAMs were added sequentially into the concrete mixer. The mixture was blended for 2 min, after which water and the water-reducing agent were added and mixed for an additional 3 to 5 min. Finally, steel fibers were added, and mixing continued for another 1 min. The mixture was then poured into molds, followed by vibration forming.
2.2.3. Specimen Dimensions and Curing
The compressive strength tests for the concrete were conducted using cubes with side lengths of 100 mm. The specimens were demolded 24 h after casting and then placed in a standard curing chamber (temperature 20 °C ± 2 °C, relative humidity ≥ 95%) for curing for 3 d, 7 d, 28 d, and 56 d. The flexural and tensile strength specimens were also demolded 24 h after casting and placed in the standard curing environment (20 °C ± 2 °C, relative humidity ≥ 95%) until 28 d had passed. The steam curing temperatures were set at 45 °C and 90 °C. The specimens were demolded 24 h after casting and then placed in a steam curing chamber, where the temperature was raised over a period of 4 h to either 45 °C or 90 °C, maintained at that temperature for 40 h, and then cooled over 4 h to reach the standard curing temperature. They were then cured for 7 d before conducting the compressive strength tests.
2.3. Testing Methods
2.3.1. Flowability Test
The flowability of the UHPC was tested according to the procedure described in the Chinese standard GB/T 2419-2005 (method for testing the fluidity of cement mortar) []. When testing the flowability of UHPC, the mixed UHPC was first placed into a slump cone. After lifting the cone, measurements were taken when the UHPC no longer spread or when the spreading time reached 50 s. A steel ruler was used to measure the maximum diameter of the spread surface of the UHPC mixture and the diameter in the direction perpendicular to the maximum diameter. The arithmetic mean of these two measurements was then calculated to determine the result of the flowability test.
2.3.2. Compressive Strength Test
This testing method refers to the Chinese standard GB/T50081-2019 (Standard for the Testing Methods of the Physical and Mechanical Properties of Concrete) []. A HYE-2000-type compression testing machine was used to evaluate the compressive strength of UHPC after 3 d, 7 d, 28 d, and 56 d. The steam-cured UHPC specimens only tested for compressive strength after 7 days.
2.3.3. Flexural Toughness Test
The three-point bending test was conducted in accordance with the ASTM-C 1018 standard []. The dimensions of the specimen were 40 mm × 40 mm in cross-section and 160 mm in length, with a span distance of 100 mm, as shown in Figure 4a. The bending load was applied at the midspan of the specimen, equidistant between the two supports (span length = 100 mm). Deflection was measured at the midspan, using a linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) to capture vertical displacement during loading. A servo-controlled testing machine applied a displacement-controlled load at a rate of 0.2 mm/min until failure. The loading test was carried out after standard curing for 28 d. The formula for calculating flexural strength is:
where fcf is the UHPC bending strength (MPa); Fcf is the peak load of UHPC; l is the span between the specimen beam supports (mm); h is the beam height (mm); b is the beam width (mm).
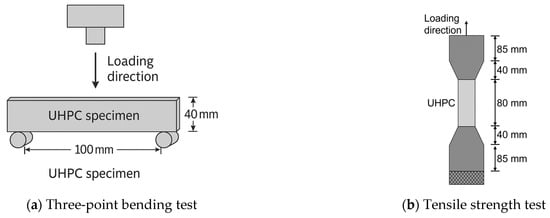
Figure 4.
Illustrative diagrams of the three-point bending test and tensile strength test.
2.3.4. Tensile Strength Test
The tensile strength test was carried out as depicted in Figure 4b, conducted according to standard JC/T 2461-2018 [], and the tensile test was carried out after 28 d of standard curing. The calculation formula for tensile strength is as follows:
where is the tensile strength (MPa); is the maximum tension value of the specimen (N); is the cross-sectional area (mm2).
2.3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy Test
The micro-morphology of the tested material was observed using a G300 scanning electron microscope (SEM) produced by Carl Zeiss AG, Germany. To prepare the samples, small segments were first immersed in anhydrous ethanol to stop hydration and then dried in a vacuum oven at 50 °C for 48 h. Then, the samples were coated with a thin layer of gold using a sputter coater to ensure conductivity. The SEM observations were performed under an accelerating voltage of 5 kV.
2.3.6. Thermogravimetric Analysis Test
Thermal analysis of the phases in UHPC containing 0%, 15%, and 30% quartz powder was performed by combining thermogravimetric analysis (TG) and derivative thermogravimetry (DTG). The procedure followed was based on ASTM E1131-20 (Standard Test Method for Compositional Analysis by Thermogravimetry) []. For this test, the UHPC samples were crushed, followed by immersion in anhydrous ethanol for 48 h to stop hydration. The samples were then dried in a vacuum oven at 50 °C for 48 h and ground finely enough to pass through a 45 μm sieve. Approximately 20 mg of each sample was loaded into a platinum crucible and tested using a TG/TGA 7300 analyzer (Seiko Instruments Inc., Tokyo, Japan). The test was carried out under a nitrogen atmosphere with a flow rate of 50 mL/min, and the temperature was ramped from 30 °C to 1000 °C at a constant heating rate of 10 °C/min. Mass loss in specific temperature ranges was attributed to the decomposition of hydration products: 100–200 °C for C-S-H dehydration, 400–500 °C for CH decomposition, and 600–750 °C for CaCO3 decarbonation.
2.3.7. Pore Structure Test
The pore structure of UHPC was analyzed using mercury intrusion porosimetry (MIP), based on ASTM D4404-10 []. UHPC specimens were extracted from the fractured core after mechanical testing. To stop hydration, the samples were immersed in anhydrous ethanol for 48 h and then vacuum-dried at 50 °C for 48 h. A Micromeritics AutoPore IV 9500 porosimeter was used, covering a pressure range from 0.01 to 60,000 psi, corresponding to pore diameters from ~10 μm to 5 nm.
2.3.8. X-Ray Diffraction Test
The phase composition of the hydrated UHPC matrix was determined using X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis according to ASTM C1365-18 []. Powdered samples (<45 μm) were prepared using ethanol and vacuum-drying procedures, as described earlier. The measurements were conducted on a Bruker D8 Advance diffractometer using Cu-Kα radiation, operating at 40 kV and 40 mA. The scanning was performed in the 2θ range of 5° to 60°, with a step size of 0.02° and a scan rate of 2°/min.
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Effect of FAMs and Quartz Powder on the Extensibility of UHPC
The effect of different FAM contents on the flowability of UHPC is shown in Figure 5. It can be seen from the figure that, with the same quartz powder content, the flowability increases with increasing FAM content. When the fine particle size quartz powder content is 15%, the flowability of UHPC is 820 mm and 840 mm for FAM contents of 15% and 30%, respectively. The flowability of UHPC with a FAM content of 30% is 20 mm greater than that with a content of 15%. This increase in flowability is attributed to the morphology of FAMs, which resemble fine glass beads, facilitating the “rolling” of the paste and thereby enhancing the fluidity of the UHPC.
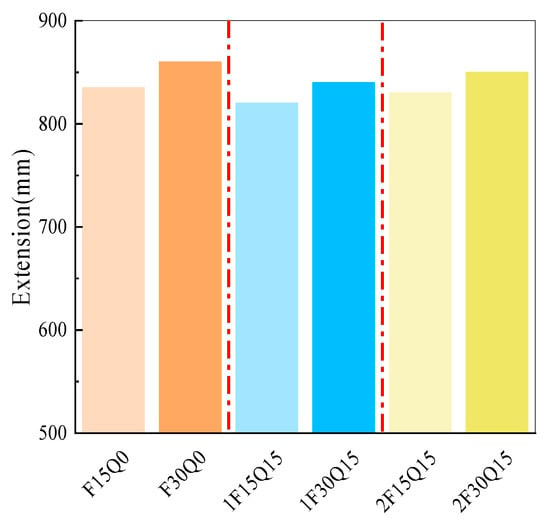
Figure 5.
The effect of FAMs on the extension of UHPC.
The effect of different quartz powder contents on the flowability of UHPC is illustrated in Figure 6. It can be observed that with the same FAM content, as the quartz powder content increases, the flowability decreases. For instance, the flowability of 1F30Q15 and 2F30Q15 is reduced by 20 mm and 10 mm, respectively, compared to F30Q15. This is primarily attributable to the increased specific surface area associated with higher quartz powder dosage, which leads to higher water demand and greater internal friction. Moreover, the cement and quartz powder have similar zeta potentials and chemical properties, which result in comparable electrostatic repulsion between the cement–quartz powder particles and between the cement particles themselves []. Furthermore, it is evident that the finer quartz powder (4 μm) results in lower flowability than the coarser powder (8 μm) at the same replacement rate. The finer particles possess greater surface energy and absorb more free water, thereby reducing the effective water available for lubrication between particles [,].
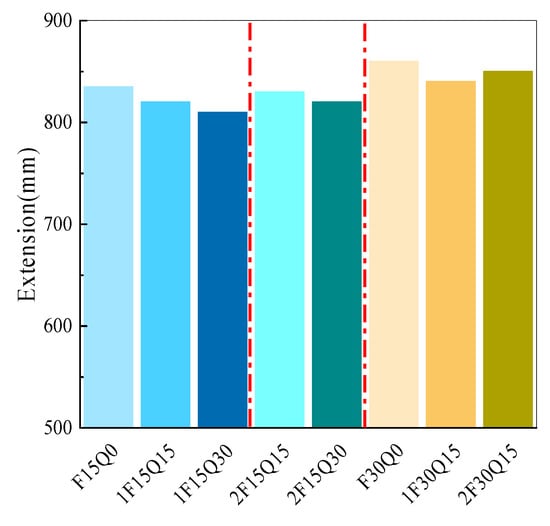
Figure 6.
The effect of quartz powder on the extension of UHPC.
3.2. Compressive Strength of UHPC Incorporating Quartz Powder
3.2.1. Influence of Quartz Powder Content and Fineness on Compressive Strength
The compressive strength of UHPC samples with different quartz powder contents is illustrated in Figure 7. As shown in the figure, in UHPC samples with the same quartz powder content, the compressive strength increases with the curing age, indicating that the incorporation of quartz powder does not hinder the hydration of cement. At the same age, the compressive strength of the UHPC varies with the content and fineness of quartz powder. At a curing age of 3 d, as the quartz powder content increases, the strength of UHPC gradually decreases. This is mainly due to the reduction in hydration products with the increase in quartz powder content, leading to the lower early strength performance of the concrete. When the FAM content is 15%, after 7 d of curing, the compressive strength of UHPC with fine particle size quartz powder is greater than that of UHPC without quartz powder. However, as the quartz powder content increases, the compressive strength of the UHPC initially rises and then declines, as depicted in Figure 7a. At a curing age of 56 d, for UHPC samples with a FAM content of 15% and quartz powder contents of 0%, 15%, and 30%, the compressive strengths are 121.5 MPa, 155.5 MPa, and 149.4 MPa, respectively. After 7 d of curing, the strength of UHPC incorporating 15% coarse particle size quartz powder is greater than the strength of UHPC without quartz powder, whereas the compressive strength of UHPC with 30% coarse particle size quartz powder is lower than that of UHPC without quartz powder, as shown in Figure 7b. The initial increase in compressive strength is primarily attributable to the filler effect of quartz powder, which improves particle packing density and refines the pore structure, thereby enhancing the compressive strength [,]. However, excessive quartz powder content dilutes the cement content, leading to a reduction in the amount of hydration products such as C-S-H gel. This dilution effect results in a weakened microstructure and, ultimately, a decrease in strength []. After 56 days of curing, the compressive strengths of 2F15Q15 and 2F15Q30 are 1.5% higher and 6.4% lower, respectively, compared to the compressive strength of F15Q0. When the FAM content is 30%, after 3 d of curing, the compressive strengths of 1F30Q15 and 2F30Q15 are 4.5% and 24.0% lower, respectively, than that of F30Q15, as shown in Figure 7c. After 28 d and 56 d of curing, the compressive strengths of UHPC incorporating 15% of both coarse and fine particle sizes of quartz powder are greater than that of UHPC without quartz powder.
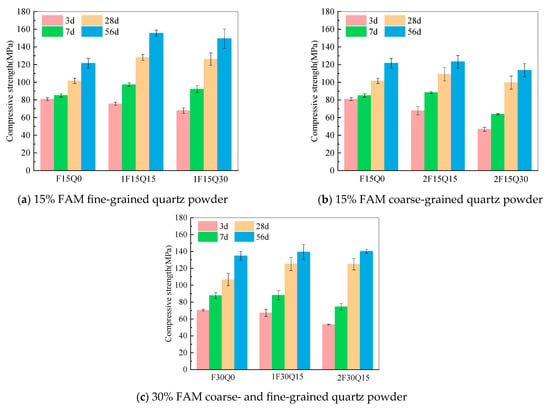
Figure 7.
Compressive strength of UHPC samples with different quartz powder contents.
Figure 8 shows the effect of quartz powder fineness on the compressive strength of UHPC after 28 d. As can be seen from the figure, when the FAM content is 15%, the compressive strength of UHPC with 15% and 30% coarse particle size quartz powder is 14.8% and 21.4% lower, respectively, than that of UHPC with a fine particle size of quartz powder. However, when the FAM content is 30%, the difference in compressive strength between UHPC containing 15% fine particle size quartz powder and the same amount of coarse particle size quartz powder is negligible. Figure 9 illustrates the impact of FAM content on the compressive strength of UHPC. It is evident from the figure that as the curing age increases, the compressive strength of UHPC continues to rise, indicating that the incorporation of FAMs does not hinder the later hydration of the cement. The early compressive strength of UHPC with 15% FAM content is higher than that of UHPC samples with 30% FAM content. However, at later ages, the UHPC samples with 15% FAM content exhibit lower compressive strength compared to those with 30% FAM content. The higher early strength of UHPC with 15% FAM content is primarily due to the higher cement content, which accelerates early hydration reactions and contributes to faster strength gain. In contrast, 30% FAM content replacement reduces the amount of clinker hydration at an early stage, resulting in lower early strength. However, at later ages, UHPC samples with 30% FAM content exhibit higher compressive strength, due to the ongoing pozzolanic reactions of the FAMs. These reactions consume CH and form additional C-S-H gel, further densifying the microstructure and improving strength over time. This is consistent with the results of Ghazy et al. [] and Ding et al. []. Although UHPC with a larger FAM content exhibits greater later strength, at 56 d, the compressive strength of UHPC with 30% FAM content improved by approximately 12.5% compared to that with 15% FAM content. This improvement is due to the continued and vigorous pozzolanic reactions of FAMs, which surpass the hydration reactions of cement. The substances generated from the pozzolanic reactions further fill the internal pores of UHPC, enhancing its strength.
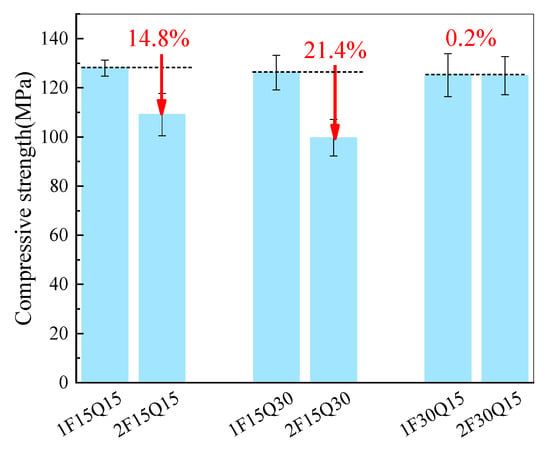
Figure 8.
Influence of quartz powder fineness on the compressive strength of UHPC.
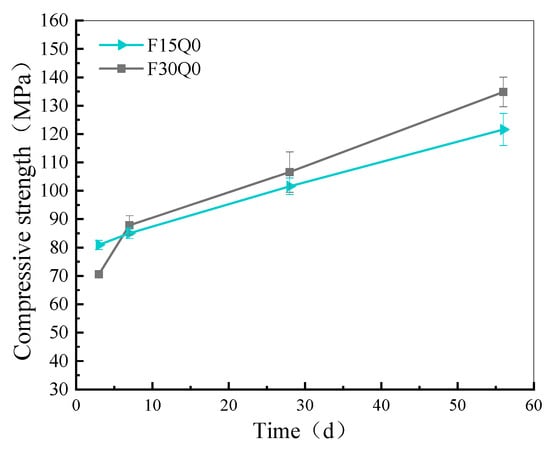
Figure 9.
Influence of FAM content on UHPC compressive strength.
3.2.2. Influence of Curing Temperature on Compressive Strength
Figure 10 illustrates the effect of curing temperature on the compressive strength of UHPC with quartz powder. As shown in the figure, as the curing temperature increases, the compressive strength of quartz-powder UHPC continuously rises. The compressive strength of quartz powder UHPC at a curing temperature of 45 °C shows a significant improvement compared to that at 20 °C. At a curing temperature of 90 °C, the 7-day compressive strength of quartz powder UHPC ranges from 152.0 MPa to 182.1 MPa. This improvement is primarily due to the acceleration of cement hydration kinetics at higher temperatures, which promotes the early formation of C-S-H gel. Additionally, steam curing at 90 °C stimulates the pozzolanic activity of fine quartz powder, which indicates further C-S-H formation and the consumption of CH. This contributes to microstructural densification, thereby enhancing mechanical performance. As demonstrated by Bolina et al. [], the thermal behavior of UHPC is closely linked to its composition, further underscoring the significance of microstructure tuning through fine particle additives such as quartz powder. As the quartz powder content increases, the compressive strength of quartz powder UHPC initially rises and then declines, peaking at a quartz powder content of 15%. Thus, it can be observed that a quartz powder content of approximately 15% is optimal, with the compressive strength of UHPC containing 15% fine particle size quartz powder being 182.1 MPa. Comparing Figure 10a and Figure 10b, it is evident that when the quartz powder content is 15%, the compressive strength of the mixture with a fine particle size is improved by 3.6% to 14.4%, compared to the mixture with a coarse particle size. At a quartz powder content of 30%, the compressive strength of the fine particle size mixture is enhanced by 9.7% to 19.3% over that of the coarse particle size mixture. This indicates that a finer particle size of quartz powder has a better pore-filling effect in UHPC, effectively improving its compressive strength.
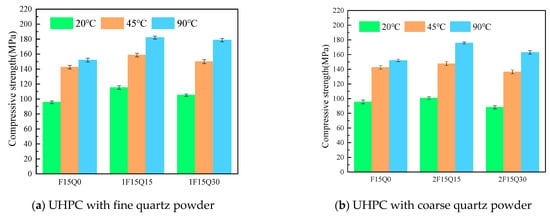
Figure 10.
Effect of curing temperatures on the compressive strength of UHPC.
3.3. Flexural Performance
Steel-fiber-reinforced UHPC retains higher load-bearing capacity during bending, even after the initial cracking, indicating the significant enhancement and toughening effect of including steel fibers in UHPC [,]. Figure 11 presents the flexural strength of quartz powder UHPC, showing that the flexural strength ranges from 15.8 MPa to 24.6 MPa. The addition of 30% coarse quartz powder results in a 35.7% reduction in flexural strength compared to that of UHPC without quartz powder. The deflection of the quartz powder UHPC ranges from 0.726 mm to 0.958 mm, and the deflection of the 30% coarse quartz powder UHPC is 24.2% lower than that of UHPC without quartz powder.
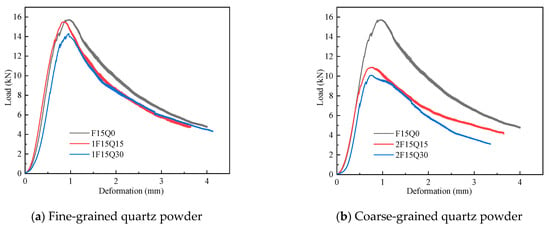
Figure 11.
Flexural strength of quartz powder UHPC.
As shown in Figure 11a,b, with increasing quartz powder content, both the flexural strength and deflection of quartz powder UHPC decrease, which is related to the primary component of quartz powder being SiO2. A comparison of Figure 11a and Figure 11b reveals that the flexural strength of the UHPC with fine quartz powder is higher than that of the UHPC with coarse quartz powder in terms of both flexural strength and deflection. The incorporation of coarse quartz powder significantly reduces the flexural strength and deflection of UHPC, suggesting that fine quartz powder provides a better filling effect in the pores of UHPC than coarse quartz powder. The flexural strength of UHPC with 15% fine quartz powder is close to that of UHPC without quartz powder. Although the addition of quartz powder can reduce flexural strength, with the inclusion of fine rather than coarse quartz powder, UHPC can still maintain relatively high flexural strength and deflection.
3.4. Tensile Strength
Figure 12 shows the tensile strength of UHPC samples with different fineness gauges and contents of quartz powder. The tensile strength of quartz powder UHPC samples ranges from 8.9 MPa to 12.7 MPa, and the tensile strength of UHPC with 15% quartz powder is 42.7% higher compared to that of UHPC without quartz powder. This indicates that the incorporation of quartz powder significantly enhances the tensile strength of UHPC. From the figure, it can be observed that as the quartz powder content increases, the tensile strength of quartz powder UHPC initially increases and then decreases. The tensile strength of UHPC with added quartz powder remains higher than that of UHPC without quartz powder. This can be attributed to the effective pore-filling of UHPC by the appropriate amount of quartz powder, which improves its tensile strength. Figure 12c shows that the fine quartz powder exhibits higher tensile strength, indicating that fine quartz powder fills the pores of UHPC more effectively than coarse quartz powder, which is consistent with previous findings on compressive strength.
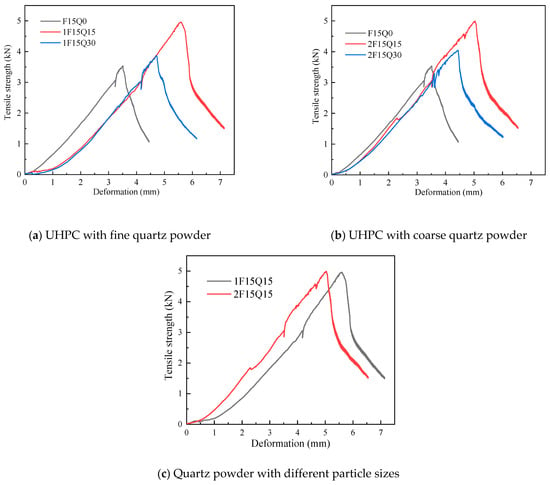
Figure 12.
Load displacement under tension.
3.5. Mechanism Analysis of Influence of Quartz Powder on the Mechanical Properties of UHPC
3.5.1. Hydration Product Analysis
- (1)
- XRD Test Results
Figure 13 shows the XRD pattern of quartz slurry of varying fineness and dosages after 28 d. From Figure 13a,b, it can be observed that in the paste with 15% FAM content, the mineral phases of the hydration products are largely consistent, featuring unhydrated cement clinker C3S and C2S, as well as CH and AFt. As the dosage of quartz powder increases, the intensity of the SiO2 diffraction peaks gradually increases, which correlates with the primary component of the quartz powder. Meanwhile, the contents of AFt and CH gradually decrease, along with a reduction in unhydrated C3S and C2S, primarily due to the increased quartz powder dosage replacing part of the cement, which reduces the formation of hydration products such as AFt and CH.
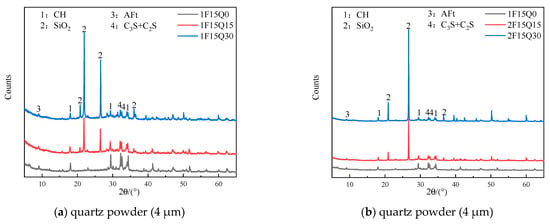
Figure 13.
XRD patterns of quartz powder pastes of different fineness and contents (28d).
Figure 14 presents the XRD patterns of paste samples containing different fineness of quartz powder and the same amount of FAMs after 28 d. From Figure 14a,b, it can be seen that in the paste samples F15Q15, F15Q30, and F30Q15, the only variable is the fineness of the quartz powder, while the types of hydration products are consistent. The contents of AFt and CH are also fairly similar. However, in the paste containing the fine particle size of quartz powder, the content of SiO2 is lower, and the SiO2 peak at 2θ = 21.99° is more pronounced in the fine particle size paste.
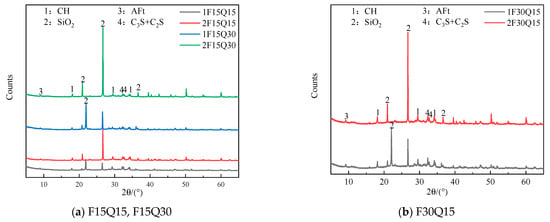
Figure 14.
XRD pattern of samples including silica powder-FAMs of different fineness and the same quartz powder contents (after 28 d).
Figure 15 presents the XRD patterns of paste samples with different amounts of FAMs and the same amounts of quartz powder after 28 d. From Figure 15, it can be observed that in the pastes with quartz powder contents of 0% and 15%, the types of hydration products are essentially the same, with the SiO2 peak from the quartz powder visible in the paste with 15% quartz powder. As the amount of FAMs increases, the content of the hydration product CH decreases. This can be attributed to two factors: first, the equivalent replacement of cement by FAMs reduces the amount of cement used, thereby decreasing the production of hydration products; second, the pozzolanic activity of the FAMs becomes more effective in the later stages of hydration, which also generates a certain amount of hydration products [].
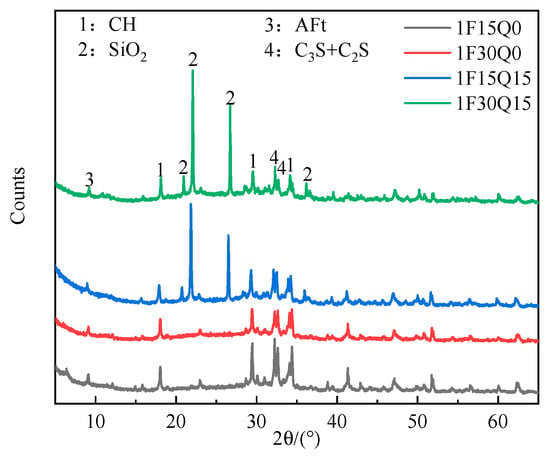
Figure 15.
XRD pattern of FAMs at different contents and the same quartz powder contents (28 d).
Figure 16 presents the XRD patterns of UHPC samples at different steam curing temperatures and varying fineness of quartz powder. The labels 20, 45, and 90 represent the curing temperatures, with 1F15Q15-90 indicating that the steam curing temperature for the 1F15Q15 specimen is 90 °C. From Figure 16a,b, it can be observed that as the steam curing temperature increases, the intensity of the diffraction peaks for CH continuously decreases. This reduction can be attributed to the elevated temperature, which enhances the pozzolanic effect of the FAMs, leading to the consumption of some CH []. Furthermore, as shown in Figure 16a,d, the content of SiO2 in the UHPC with the content of SiO₂ in the UHPC with finer quartz powder is lower under 90 °C curing conditions, indicating that at higher temperatures, the SiO2 in the quartz powder demonstrates some level of activity, reacting with CH to form C-S-H gel, thereby consuming CH. This phenomenon also contributes to the increase in compressive strength of UHPC with the same dosage of quartz powder as the curing temperature rises. As seen in Figure 16b, the SiO2 content remains relatively unchanged with increasing curing temperatures and coarser quartz powder, indicating that the coarse quartz powder does not exhibit significant pozzolanic activity. Additionally, Figure 16a,c demonstrates that under 45 °C steam curing conditions, samples using finer quartz powder do not exhibit pozzolanic activity. Therefore, the pozzolanic activity of quartz powder is related to its particle size and the curing temperature. Under 90 °C steam curing conditions, XRD analysis shows reduced CH peaks in the finer quartz powder mixtures, indicating that finer quartz powder exhibits pozzolanic activity, reacting with CH to form additional C-S-H gel material.
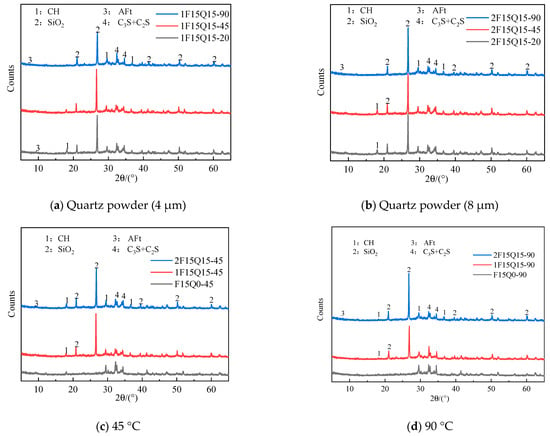
Figure 16.
XRD of quartz powder UHPC samples under different steam temperature treatments.
- (2)
- DTG test results
Figure 17 shows the DTG patterns of pastes of different fineness and with varying dosages of quartz powder after 28 d of curing. From Figure 17a,b, it can be observed that the DTG curves exhibit three mass loss peaks. The mass loss between 50 °C and 200 °C is primarily due to the decomposition of hydration products such as AFt and the loss of bound water in C-S-H gel. The mass loss occurring between 400 °C and 500 °C is related to the decomposition of CH. Additionally, the mass loss between 600 °C and 700 °C is attributable to the thermal decomposition of CaCO3 formed by the carbonation of CH [,,]. After 28 d of hydration, with an increased dosage of quartz powder, the contents of AFt/C-S-H and CH decrease correspondingly, which is consistent with the observations from the XRD patterns. Figure 18 shows the DTG curves of paste samples with different fineness grades of quartz powder. From the figure, it can be observed that UHPC with finer quartz powder content exhibits greater mass loss at 50–200 °C (indicative of AFt/C-S-H content) compared to that with coarser quartz powder. This is due to the fact that finer quartz powder provides a greater surface area, acting as nucleation sites for C-S-H gel formation and accelerating early hydration.
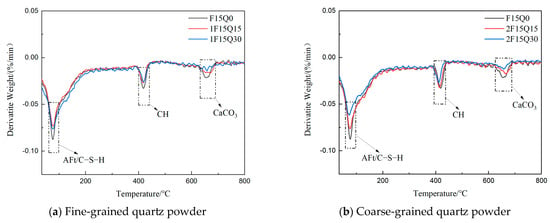
Figure 17.
DTG spectra of quartz slurry with different fineness and different dosages at 28 d age.
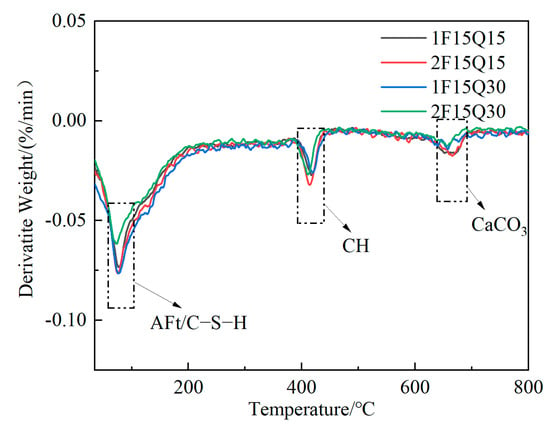
Figure 18.
DTG spectra of 15% FAM coarse- and fine-grained quartz powder samples (28 d).
3.5.2. Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry Results
Figure 19a,b illustrates the pore size distribution and porosity of paste specimens with different fineness and dosages of quartz powder, along with a constant dosage of FAMs after 28 d of curing. From Figure 19b, it can be seen that the porosities of the 1F15Q15, 1F15Q30, 2F15Q15, and 2F15Q30 mixtures are 9.93%, 9.22%, 10.21%, and 11.92%, respectively. These results indicate that fine quartz powder provides a superior filling effect, enhancing the pore structure of the slurry. However, as the dosage of quartz powder increases, the paste with fine quartz becomes denser, while the coarser quartz powder adversely affects the stability of the paste. Additionally, it is noticeable that those pores smaller than 10 nm in the fine quartz powder samples of UHPC are significantly reduced compared to those with coarse quartz powder. The incorporation of fine quartz powder refines the internal micropores of the UHPC and effectively fills those pores smaller than 10 nm, improving packing density. When analyzed in conjunction with Figure 19a, the 2F15Q30 paste exhibits significantly more numerous large pores compared to the 2F15Q15 paste. Under loading conditions, these large pores are more likely to become initiation points for cracking in the paste, leading to a reduction in concrete strength, which is consistent with the observed macroscopic mechanical performance.
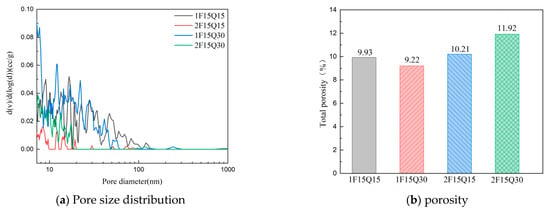
Figure 19.
Pore structure results for the UHPC samples.
3.5.3. SEM
Figure 20 shows SEM images of the different steam curing temperatures and different fineness of quartz powder mortar at 7 d, where QP represents quartz powder. From Figure 20a, it can be observed that a large amount of flocculent C-S-H gel has formed under standard curing conditions after 7 d. When comparing the SEM results across different curing temperatures, it is evident that as the curing temperature increases, the microstructure of the UHPC becomes denser. Additionally, some unhydrated FAMs and quartz powder particles can be observed, as shown in Figure 20b. Under the condition of 90 °C steam curing, some honeycomb or network-like C-S-H gel structures can be observed, as illustrated in Figure 20c. This formation is attributed to the increased degree of cement hydration at elevated temperatures, leading to an increase in the chain length of the C-S-H gel [], thereby making the paste structure denser []. This finding is consistent with the results regarding the effect of curing temperature on the compressive strength of quartz powder UHPC. Figure 20d shows that finer quartz powder contributes to a denser and more homogeneous matrix, with fewer large voids and a better integration of hydration products. In contrast, coarser particles leave behind more unreacted grains and lead to a more porous and heterogeneous structure.
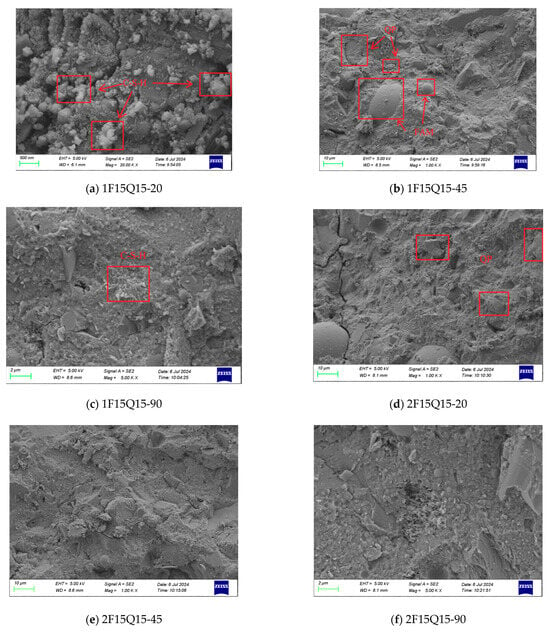
Figure 20.
SEMs after 7 d, showing samples of FAM slurry with the same contents at different evaporation temperatures.
Figure 21 presents the SEM images of UHPC samples with varying amounts of quartz powder. It can be seen that as the content of fine quartz powder increases, the microstructure initially becomes denser before slightly loosening at higher dosages. However, the microstructure remains denser than that of UHPC samples without quartz powder. This improvement can be attributed to the quartz powder’s ability to refine the internal pore structure and effectively fill the internal voids. This finding is consistent with the observed improvement in compressive strength resulting from the addition of quartz powder.
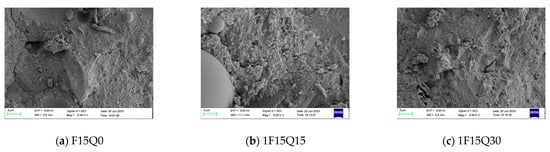
Figure 21.
SEMs of samples with different quartz powder and FAM contents over 28 days.
4. Conclusions
This study systematically investigated the influence of quartz powder content, fineness, and curing temperature on the mechanical and microstructural performance of UHPC. Based on a comprehensive set of flowability, strength, pore structure, and hydration analyses, the following key conclusions can be drawn:
(1) Flowability decreases with increasing quartz powder content and with decreasing particle size. The use of finer powder (4 μm) increases the specific surface area and internal friction of the mix, leading to a more significant reduction in workability.
(2) An optimal quartz powder dosage of 15% with 4 μm fineness yielded the best balance of packing density and pozzolanic contribution. This combination significantly enhanced the samples’ mechanical properties, achieving a compressive strength of 182.1 MPa under 90 °C steam curing.
(3) Steam curing effectively accelerated cement hydration and activated the pozzolanic reactivity of fine quartz powder, as confirmed by the DTG and XRD results. The secondary formation of C-S-H gel and the consumption of CH contributed to a denser microstructure and increased strength.
(4) Pore structure analysis revealed a refinement in pore size distribution and a reduction in total porosity with both an increasing curing temperature and decreasing quartz powder size. The use of both fine quartz powder and steam curing treatment resulted in a highly compacted microstructure.
This work provides a clearer understanding of the combined influence of quartz powder content, fineness, and curing conditions on UHPC performance. The findings also offer valuable guidance for optimizing UHPC formulations in precast, high-performance, and accelerated construction applications.
Author Contributions
Methodology, J.X., Y.H., Z.C., Y.Z. and X.M.; Software, G.Y. and Z.C.; Validation, H.Z.; Investigation, J.X. and Y.L.; Resources, X.M.; Data curation, G.Y.; Writing—original draft, J.X. and Y.L.; Writing—review & editing, J.X., Y.H., W.Z., H.Z. and Y.Z.; Project administration, M.L.; Funding acquisition, M.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is part of a series of projects financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Project (2022YFE0133800), Fund project of CCCC First Habor Engineering Company Ltd.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the corresponding author on request.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Jianguang Xu, Yongsheng Li, Zhonglu Cao were employed by the company CCCC First Harbor Engineering Company Ltd. And author Jianguang Xu, Yongsheng Li, Guojian Yuan were employed by the company No.2 Engineering Company Ltd. of CCCC First Harbor Engineering Company Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. Jianguang Xu, Yongsheng Li, Zhonglu Cao are employee of CCCC First Habor Engineering Company Ltd, who provided funding and teachnical support for the work. The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Lai, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Q. Properties and modeling of ultra-high-performance concrete subjected to multiple bullet impacts. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018256.1–04018256.11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habert, G.; Arribe, D.; Dehove, T.; Espinasse, L.; Le Roy, R. Reducing environmental impact by increasing the strength of concrete: Quantification of the improvement to concrete bridges. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 35, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Wen, X.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y. Thermal and mechanical properties of ultra-high performance concrete incorporated with microencapsulated phase change material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 273, 121714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allena, S.; Newtson, C.M.; Weldon, B.D.; Jauregui, D.V. Mechanical properties and durability issues of ultra-high performance concrete-an overview. Int. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2018, 10, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, Z.B.; Graybeal, B.A. Performance of Grouted Connections for Prefabricated Bridge Deck Elements; United States. Federal Highway Administration. Office of Infrastructure Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- Xue, J.; Briseghella, B.; Huang, F.; Nuti, C.; Tabatabai, H.; Chen, B. Review of ultra-high performance concrete and its application in bridge engineering. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, X.; Sun, M. Synergistic effect of microfibers and oriented steel fibers on mechanical properties of UHPC. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 91, 109742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.B.; Biswas, R.K.; Sen, D.; Tasnim, S. Flexural and Shear Strengthening of Reinforced-Concrete Beams with Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC). Constr. Mater. 2024, 4, 468–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkaysi, M.; El-Tawil, S. Effects of variations in the mix constituents ofultra high performance concrete (UHPC) on costand performance. Mater. Struct. 2016, 49, 4185–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Zhou, F.; Yin, T.; Wang, Z.; Ding, M.; Liu, Z.; Leng, Y.; Gao, X.; Shui, Z. Uncovering the approach to develop ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) with dense meso-structure based on rheological point of view: Experiments and modeling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 271, 121500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Yu, R.; Shui, Z.; Wu, C.; Song, Q.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Gao, X.; He, Y. A new design approach of steel fibre reinforced ultra-high performance concrete composites: Experiments and modeling. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 110, 103597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Yu, R.; Shui, Z.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Su, Q. A novel approach for developing a green ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) with ad-vanced particles packing meso-structure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 265, 120339. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, Y.; Pyo, S. Effect of steel fiber content on structural and electrical properties of ultra high performance concrete (UHPC) sleepers. Eng. Struct. 2020, 222, 111131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Shi, C.; He, W.; Wu, L. Effects of steel fiber content and shape on mechanical properties of ultra high performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 103, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.Y.; Kim, S.; Park, G.J.; Park, J.J.; Kim, S.W. Effects of fiber shape, aspect ratio, and volume fraction on flexural behavior of ul-tra-high-performance fiber-reinforced cement composites. Compos. Struct. 2017, 174, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Yoon, Y.S. Effect of fiber content on mechanical and fracture properties of ultra high performance fiber reinforced cementitious composites. Compos. Struct. 2013, 106, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.Y.; Shin, H.O.; Yang, J.M.; Yoon, Y.S. Material and bond properties of ultra performance fiber reinforced concrete with micro steel fibers. Compos. Part B 2014, 58, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrokhinasab, E.; Looney, T.; Floyd, R.; Garber, D. Effect of Fiber, Cement, and Aggregate Type on Mechanical Properties of UHPC. Civ. Eng. J. 2021, 7, 1290–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazıcı, H. The effect of curing conditions on compressive strength of ultra high strength concrete with high volume mineral admixtures. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 2083–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Spiesz, P.; Brouwers, H. Development of an eco-friendly ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) with efficient cement and mineral admixtures uses. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 55, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.L.; Zhao, P. Study on the Compressive Strength and Mixing of Ultra-High Performance Concrete. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 357–360, 825–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graybeal, B.; Brühwiler, E.; Kim, B.S.; Toutlemonde, F.; Voo, Y.L.; Zaghi, A. International perspective on UHPC in Bridge Engineering. J. Bridge Eng. 2020, 25, 04020094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Fang, Z.; Wang, K. Design and behavior of super-long span cable-stayed bridge with CFRP cables and UHPC members. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 164, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, J.; Qin, J.; Liu, D.; Yalçınkaya, Ç.; He, Y. Effect of silica fume on the performance of high-early-strength UHPC prepared with mag-nesium ammonium phosphate cement. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03351. [Google Scholar]
- Tabrizi, N.M.; Mostofinejad, D.; Eftekhar, M.R. Effects of Different Fibers and Cement Substituting Minerals on Mechanical Properties of Ultra-High-Performance Fiber-Reinforced Concrete. ACI Mater. J. 2023, 120, 15–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Lu, W.; Song, J.; Lee, G.C. Application of Ultra-High performance concrete in bridge engineering. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 186, 1256–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berodier, E.; Scrivener, K. Understanding the Filler Effect on the Nucleation and Growth of C-S-H. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 97, 3764–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benezet, J.; Benhassaine, A. The influence of particle size on the pozzolanic reactivity of quartz powder. Powder Technol. 1999, 103, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadri, E.H.; Aggoun, S.; De Schutter, G.; Ezziane, K. Combined effect of chemical nature and fineness of mineral powders on Portland cement hydration. Mater. Struct. 2010, 43, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobuz, M.H.; Kabbo, M.K.; Khatun, M.; Alahmari, T.S.; Jameel, M.; Khan, M.M. Microstructural assessment and supervised machine learning-aided modeling to explore the potential of quartz powder as an alternate binding material in concrete. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathirvel, P.; Murali, G. Effect of using available GGBFS, silica fume, quartz powder and steel fibres on the fracture behavior of sustainable reactive powder concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 375, 130997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wille, K.; Naaman, A.E.; Tawlls, E.I. Optimizing ultra-high-performance fiber reinforced concrete. Concr. Int. 2011, 33, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wille, K.; Naaman, A.E.; El-Tawil, S.; Parra-Montesinos, G.J. Ultra-high performance concrete and fiber reinforced concrete: Achieving strength and ductility without heat curing. Mater. Struct. 2012, 45, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.H.; Cho, A.R.; Song, J.K. Effect of water-binder ratio on the mechanical properties of calcium hydroxide-based alka-li-activated slag concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 2419-2005; Test Method for Fluidity of Cement Mortar. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2005.
- GB/T50081-2019; Standard for Test Method of Concrete Physical and Mechanical Properties. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- ASTM C 1018; Flexural Toughness and First-Crack Strength of Fiber-Reinforced Concrete (Using Beam With Third-Point Loading). American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1997.
- JC/T 2461-2018; Standard Test Method for the Mechanical Properties of Ductile Fiber Reinforced Cementitious Composites. China Building Materials Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- ASTM E1131-20; Standard Test Method for Compositional Analysis by Thermogravimetry. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- ASTM D4404-10; Standard Test Method for Determination of Pore Volume and Pore Volume Distribution of Soil and Rock by Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.
- ASTM C1365-18; Standard Test Method for Determination of the Proportion of Phases in Portland Cement and Portland-Cement Clinker Using X-Ray Powder Diffraction Analysis. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- Xu, S.D. Study on the Effect of Micro-and Nano-Scale Stone Powder on the Properties of Cement-Based Materials. Master’s Thesis, Guangdong University, Guangzhou, China, 2021. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemi, Y.; Emborg, M.; Cwirzen, A. Exploring the relation between the flow of mortar and specific surface area of its con-stituents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdipour, I.; Khayat, K.H. Effect of particle-size distribution and specific surface area of different binder systems on packing density and flow characteristics of cement paste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 78, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, Q.; Zhan, B.; Gao, P.; Guo, B.; Chu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Bian, P. Activity quantification and assessment of recycled concrete powder based on the contributions of the dilution effect, physical effect and chemical effect. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 442, 140918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazy, A.; Bassuoni, M.T.; Shalaby, A. Nano-modified fly ash concrete: A repair option for concrete pavements. ACI Mater. J. 2016, 113, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Du, H.; Wu, E.; Yi, P.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; Liu, W. Investigating the hydration, mechanical properties, and pozzolanic activity of cement paste con-taining co-combustion fly ash. Buildings 2024, 14, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolina, F.L.; Lago, B.D.; Rodríguez, E.D. Effects of thermal properties on temperature field of UHPC structures under fire conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Mezari, B.; Hensen, E.; Yu, R.; Schollbach, K.; Brouwers, H.; Yu, Q. Effect of highly dispersed colloidal olivine nano-silica on early age properties of ultra-high performance concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 131, 104564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oinam, Y.; Dahal, M.; Mesfin, M.; Park, S.; Kim, H.-K.; Pyo, S. On improved microstructure properties of slag-based UHPC incorporating calcium formate and calcium chloride. J. Build. Mater. 2024, 90, 109551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; He, T.; Yang, R.; Ma, X. New insights into the impact of inorganic salt on cement pastes mixed with alkali free liquid accelerator in low temperature. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 70, 106419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruben, S.; Hadi, K.K.; Peter, N.; Van den Abeele, L. Classification and Milling Increase Fly Ash Pozzolanic Reactivity. Front. Built Envi-Ronment 2021, 7, 670996. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z. Effects of ultrafine fly ash on the properties of high-strength concrete. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 121, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.M.; Liu, J.Z.; Zhang, K.W. Influence of Mineral Admixtures on the Short and Long-term Performance of Steam-cured Concrete. Energy Procedia 2012, 16, 836–841. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, L.; Gao, X.; Chen, T. Influence of mineral admixtures on carbonation curing of cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 212, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Guan, X. Effect and mechanism of coal gangue concrete modification by fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 294, 123563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. Mechanical properties and microstructure of cement-based materials by different high-temperature curing methods: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 96, 110464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).