Abstract
In recent years, cross-regional waste management has garnered significant academic interest, yet systematic reviews of related research remain scarce. Therefore, this study employed the PRISMA methodology to conduct a systematic review of 58 papers from the Web of Science and Scopus databases, aiming to clarify the current state of research in this field and explore future directions. Through analysis, five research themes were identified: management characteristics, core challenges, policy and regulation, technological innovation, and impact assessment. Research findings indicate that quantitative analysis constitutes 60% of the literature, representing the core methodology used in studies of cross-regional waste management. The challenges encountered in cross-regional waste management primarily manifest in three areas: environmental impacts, stakeholder relationships, and policy frameworks. Achieving cross-regional coordination necessitates collaborative efforts from governments, corporations, and society. This study further proposes future research directions providing support for future investigations by governments, universities, and corporate personnel.
1. Introduction
Among the environmental challenges facing the twenty-first century, waste management has profound implications for resource conservation. The World Bank indicates that total solid waste production will increase to 3.88 billion tons by 2050 [1]. Regrettably, approximately 23% of global waste remains uncollected, whereas 33% is disposed of through open dumping [2]. Improper waste management not only pollutes the environment [3,4], but also results in the squandering of substantial resources that could otherwise be recycled and reintroduced into the circular economy [5]. Consequently, implementing appropriate waste management measures has become a crucial component of ecological and environmental governance.
However, owing to the sheer volume and complexity of waste streams, coupled with limited waste management infrastructure in certain regions, it has proven challenging for local authorities to effectively manage locally generated waste through their own resources alone. In response to this situation, some local governments have begun exploring cross-regional collaborative treatment measures, offering a direction for waste management. Statistics indicate that Australia achieved a construction and demolition waste diversion rate of 91% in 2018 [6], surpassing the recycling rates of developed countries, including the United States [7]. Greece and Albania jointly established the Waste React project to address waste recycling challenges across their borders, enabling cross-border recycling and composting to achieve sustainable waste management [8].
In practice, compared with single-region management, the distinctiveness of cross-regional waste management lies in its involvement of multiple regions and stakeholders, necessitating the breakdown of administrative barriers to achieve interregional departmental coordination. This significantly increases the implementation difficulty compared with single-region approaches. Moreover, the current division of responsibilities and collaborative oversight present significant obstacles to cross-regional waste management [9]. Inadequate coordination may inadvertently encourage illegal cross-regional dumping, thereby undermining the overall effectiveness of regional cooperation. Therefore, identifying the unique challenges inherent in cross-regional management is a critical prerequisite for enhancing the efficiency of cross-regional waste cooperation.
Scholars have engaged in multifaceted discussions on cross-regional waste management and produced many research findings. However, no systematic literature review has been conducted in this field. As an emerging area of study, cross-regional waste management has a considerable scope for exploration. However, the absence of a systematic literature review on this subject may hinder researchers’ ability to grasp the current overarching framework within this domain.
This research addresses this gap by undertaking a systematic literature review of cross-regional waste management, aiding researchers in comprehensively understanding the current state and themes within this field. In this systematic review, the methodologies applied in cross-regional waste management research are summarized, the characteristics of different waste management types are compared, and the policy and governance mechanisms underpinning cross-regional waste management are analyzed. Consequently, our analysis focuses on the following research questions: (1) What challenges and opportunities currently confront cross-regional waste management? (2) What future research directions exist for cross-regional waste management?
This research aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state of cross-regional waste management, while examining existing issues and challenges. By examining the research status and development of transboundary collaborative waste management, this study systematically summarizes core research themes in cross-regional waste management under the Sustainable Development Goals. This research contributes the following points: (1) By synthesizing the latest developments in the literature, key research areas, technological advancements, and policy developments driving cross-regional waste management can be identified. This work establishes a foundation for future research, thereby advancing the field of cross-regional waste management. (2) Unlike previous studies focusing on specific waste streams or nations, this research represents the first detailed exploration of the theme of cross-regional waste management without sectoral limitations, providing a theoretical foundation for constructing a more holistic cross-regional waste management framework. (3) Through a systematic literature review, this study highlights underexplored themes and future research directions to address existing gaps, thereby contributing promising inspirations for researchers, industry stakeholders, and policymakers.
2. Methodology
2.1. Methods
The PRISMA method is a popularly adopted systematic review method [10]. To systematically and comprehensively present the research landscape of cross-regional waste management, this study adheres to the PRISMA statement for literature retrieval, screening, and analytical processing. Additionally, Table S1: The PRISMA checklist facilitated the scientific preparation and reporting of this study. This study has been registered in the OSF Registry with the DOI: https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/KEW8C.
Web of Science (WOS) and Scopus are the most commonly accessed databases, covering diverse disciplines, including humanities, social sciences, and management economics, making them suitable for interdisciplinary research topics [11,12]. Therefore, this review conducted a literature search on cross-regional waste management within both the WOS and Scopus databases. Following expert deliberation, the primary keywords employed to retrieve bibliometric information within the relevant research domain. Initial searches were conducted in the WOS and Scopus databases, with the search scopes set to ‘topic’ and ‘Title, Abstract, and Keywords’, respectively. To ensure the completeness of the analysis, this study follows the approach of scholars [13,14,15] by setting the date criterion to ‘All years to date’.
2.2. Data Resources
To eliminate irrelevant articles, several screening criteria were established to ensure the quality and relevance of the papers. First, conference papers, books, and other nonresearch materials offer limited contributions to research findings and complicate the analytical process [16,17]. Consequently, the search was restricted to articles and reviews specifically concerning cross-regional waste management [18]. Second, given that English is the most prevalent language in global scientific research, publications were limited to English-language sources. To reflect the quality of the papers, this study adopts the methodology of Suárez et al. [17], selecting only journals with JCR or SJR (Scopus) impact factors and publishing articles in Q1, Q2, and Q3 journals. Furthermore, drawing upon the steps of Tripathy et al. [19] and García-Herrera et al. [20], the following retrieval strategy was adopted: (1) Accept only essays that appeared in peer-reviewed journals; (2) where the title, abstract, and keywords provided insufficient clarity, full-text reading was utilized to assess textual quality. Table 1 outlines the screening criteria applied in this research.

Table 1.
Search Protocol: Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria.
This study predefines the inclusion criteria for core concepts as follows:
- (1)
- Cross-regional: Covers both domestic cross-regional scenarios between different provincial or municipal administrative divisions and international cross-border scenarios between different countries;
- (2)
- Waste stream types: There are no specific restrictions. The scope includes municipal solid waste, construction and demolition waste, electronic waste, food waste, medical waste, wastewater, and other categories;
- (3)
- Governance Tools: Regulatory assessment, policy and legislation, technological innovation measures, and market-based mechanisms;
- (4)
- Outcome Types: Emission reduction quantities, waste treatment effectiveness, and policy implementation effectiveness.
A comprehensive evaluation of the articles was conducted. Based on the retrieval criteria outlined in Table 1, duplicate entries were first removed from the search results assembled in both the WOS and Scopus databases, followed by the exclusion of papers that could not be accessed in full text. When uncertain whether certain paper titles or abstracts should be included in this analysis, the full text should be reviewed to ensure thorough consideration before making inclusion or exclusion decisions [21,22]. Conduct full-text review for documents whose eligibility for inclusion is difficult to determine based on title or abstract [23]. In cases of disagreement between reviewers, consensus was reached through discussion. Ultimately, 58 papers met all criteria.
In terms of research reliability, Taghizadeh et al. [24] and Landa-Oregi et al. [25] conducted systematic literature reviews of 29 and 27 studies, respectively, yielding research conclusions endorsed by experts within the field. The present study’s sample size significantly exceeds those of the aforementioned investigations, sufficiently demonstrating its adequacy. Two reviewers conducted a quality assessment of the collected results, indicating a low risk of bias. The final extracted literature information is presented in tabular form in Table S2. Figure 1 illustrates the PRISMA workflow, summarizing the screening process for this study.
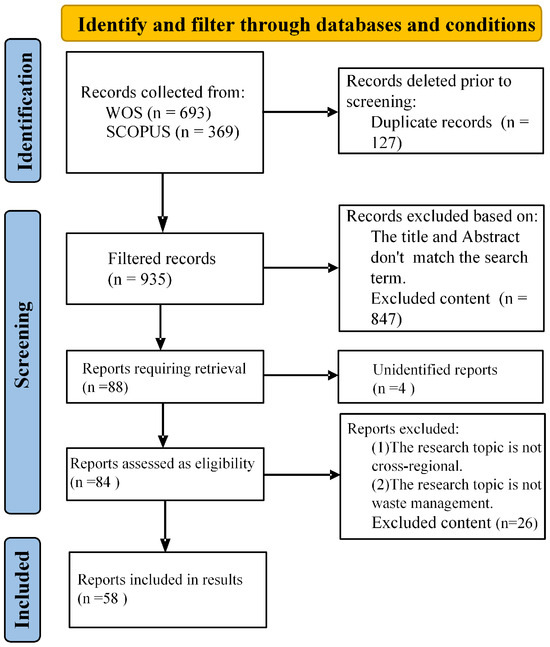
Figure 1.
Literature search flowchart under the PRISMA framework.
3. Descriptive Analysis of the Article
This section presents a systematic analysis of the 58 papers selected in the review. The analysis encompasses several key aspects: the year of publication, the primary research domain, type of methodology employed, and the correspondence between subjects and governance tools. An examination of these dimensions provides an overview of the collected articles and illustrates prevalent tendencies.
3.1. Publication Year
The first article on cross-regional waste management appeared in 2013, with the number of publications on this topic remaining fairly low from 2012 to 2019. From 2020 to 2024, there was a marked increase in the volume of publications. The number published in 2021 and 2022 alone equalled the sum of those articles published over the preceding six years. Moreover, the number of publications in 2023 reached a record high to date, accounting for approximately 25% of all articles. The distribution of articles by publication year is illustrated in Figure 2.
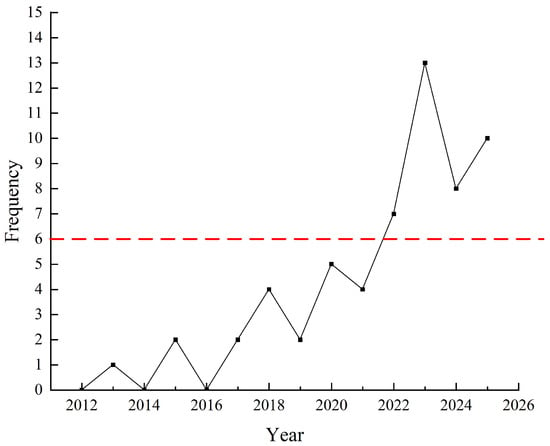
Figure 2.
Distribution of articles by publication year.
As shown in Figure 2, the amount of literature on this topic has increased, particularly since 2020. The numbers of articles published on transboundary waste management in 2023 and 2024 were 13 and 8, respectively. As of 12 November 2025, nine papers had been published that year. This indicates that the volume of literature in 2025 is on an upward trend. Furthermore, the number of publications in each of the past three years has exceeded the levels observed in 2022 and earlier. This indicates a growing interest in and heightened focus among scholars on cross-regional waste management. The rise in this research boom is inseparable from the advancement of relevant policies and technological progress worldwide. At the policy level, regional strategies such as China’s “Zero-Waste Cities” initiative [26] and the Circular Economy Action Plan under the EU Green New Deal [27] have designated cross-regional collaboration as a key pathway for waste management. Simultaneously, international regulatory frameworks such as the Basel Convention [28] amendments have spurred greater academic focus on compliance in transboundary waste movements. Technologically, the maturity of blockchain technology [29,30] and digital tools such as route optimization algorithms [31] has made real-time tracking and scheduling of cross-regional waste feasible. In recent years, articles concerning cross-regional waste management have focused on various aspects, such as stakeholder relationships [32,33], management mechanisms for the waste life cycle [34,35], waste material flow analysis [36,37], and waste trade mechanisms [30,38].
3.2. Types of Methods Employed
This section presents a Sankey diagram based on the authors’ countries of affiliation, methodological approaches, and research themes, as shown in Figure 3.
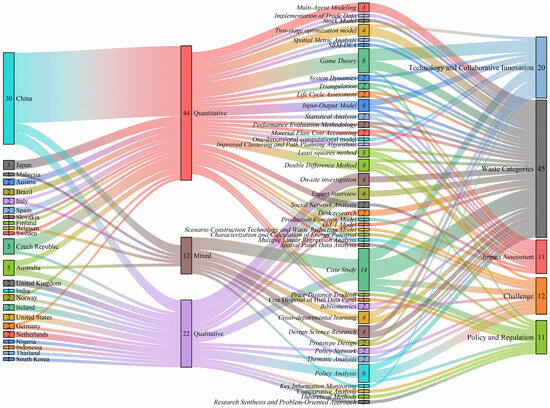
Figure 3.
Correspondence between authors’ countries, methodologies, and themes in the literature. Note: Countries, methods, and themes overlap in the figure, so the total count does not equal the number of retrieved articles.
Among the studies concerning cross-regional waste management, over half of the articles employed quantitative methodologies. Scholars have quantified and validated relationships by collecting data and analyzing interrelationships. From the perspective of methodological and thematic trends, quantitative methods are employed primarily to explore innovations in technologies and collaborative models [31,33,39] for cross-regional waste governance and to assess the economic, social, and environmental impacts [40,41] of waste. Given that current research examines the drivers, barriers, and management mechanisms of cross-regional waste management, these issues typically require rigorous quantitative analysis to examine such complex problems. As shown in Figure 3, game theory, difference-in-differences analysis, and input-output models are the most widely applied quantitative methods. Conversely, most qualitative studies employ policy analysis, case studies, and interviews to assess the applicability of cross-regional management policies and analyze key challenges [42,43,44,45]. Studies employing mixed methods constitute the smallest proportion. Given that transboundary waste management involves cross-cutting issues between governance and related industries, this field could potentially leverage mixed methods to address more complex challenges associated with transboundary waste management. For instance, when studying the siting of waste treatment facilities, one may first conduct quantitative assessments through spatial analysis or cost–benefit models to identify the most economically and technically optimal solutions. Subsequently, qualitative analysis can be performed using methods such as field surveys and interviews to evaluate the regulatory coordination challenges each proposed site actually faces. By integrating quantitative and qualitative approaches, the solutions can be both economically optimal and aligned with practical realities, thereby enhancing the scientific rigor and feasibility of the research outcomes.
3.3. Keyword Analysis
Following the aforementioned analysis of temporal and methodological types, this section performs keyword analysis. VOSviewer 1.6.20 was employed to visualize the keywords within the papers. This software uses text mining to statistically analyze keyword frequency, which represents interkeyword relationships through link distance. A greater distance indicates a stronger correlation [46]. Following data cleaning and the replacement of duplicate terms, a network visualization of keywords from the research titles was generated, as depicted in Figure 4.
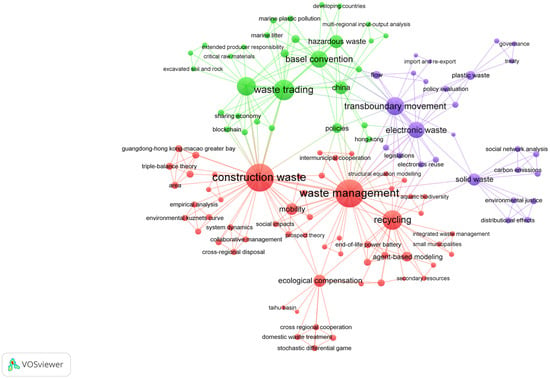
Figure 4.
Thematic network analysis diagram.
The three research clusters depicted in Figure 4 provide clear guidance for policies and practices in cross-regional waste management from different dimensions. The purple cluster focuses on the characteristics of cross-regional waste flows and their performance impacts, offering empirical evidence for identifying key logistics pathways and evaluating management effectiveness. This assists policymakers in optimizing regional coordination mechanisms based on data to enhance resource allocation efficiency. The green cluster centers on cross-regional waste trade and policy evaluation across its stages, revealing market dynamics and institutional requirements for resource circulation. This necessitates a policy framework encompassing trade access, process control, and responsibility allocation to mitigate trade risks. The red cluster primarily involves life-cycle assessments of cross-regional waste management and simulation analyses of stakeholder behaviors related to the circular economy. Based on life-cycle assessment outcomes, differentiated compensation mechanisms and responsibility allocation systems can be established. Furthermore, this theme facilitates the development of more effective incentives and coordination measures, promoting a shift in governance models from rigid controls to systemic regulation.
As evident from Figure 4, the top five most frequently occurring terms are construction waste, waste management, waste trading and recycling. This aligns with the research focus of this study. Notably, construction waste reflects the construction sector as a key area of concern in cross-regional waste management. Moreover, within the context of sustainable development, waste is increasingly recognized as a resource in the wrong bin [47,48,49]. Consequently, the recycling and processing of waste for commercial trade has gained significant attention within academic circles. Based on this, targeted support policies can be introduced, such as increasing investment in research and development of construction waste recycling technologies to promote efficient resource circulation.
3.4. Analysis of Subjects and Governance Tools
This section organizes the key actors and governance tools involved in transboundary waste management research and presents them in a chord diagram, as shown in Figure 5. The actors specifically include governments, transport enterprises, and disposal enterprises. Owing to variations in the literature descriptions of entities involved in waste treatment, this section consistently categorizes all entities directly engaged in final waste disposal as disposal enterprises to ensure analytical consistency. The core categories encompass enterprises focused on landfilling and incineration, as well as resource recovery enterprises. Governance tools are summarized into four types: regulatory assessment, policy and legislation, market mechanisms, and technological innovation. Figure 5 shows that government actors flow into three types of governance tools. Among these tools, policy assessment is the most frequently discussed governance tool for government actors in existing research. Transport enterprises utilize three types of governance tools, although policy evaluation is absent from their portfolio, with technological innovation being the most prevalent. Disposal enterprises comprehensively employ all four governance tools, with technological innovation also being the most frequently utilized. This finding demonstrates that technological capability serves as a critical indicator of corporate competitiveness. Therefore, enterprises should intensify innovation investments while enhancing brand reputation and fostering collaborative linkages across regions.
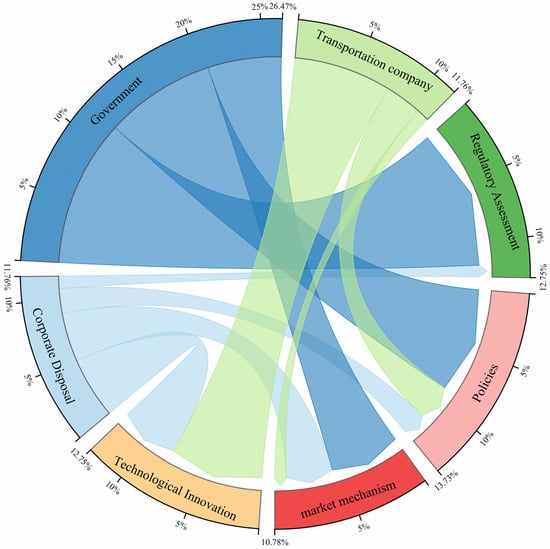
Figure 5.
String diagram of the relationship between governance actors and tools.
4. Thematic Analysis
Against the backdrop of heightened waste mobility in the era of globalization, cross-regional waste management has emerged as a pivotal issue requiring attention. Its core objective lies in addressing several critical challenges: the mismatch between waste generation and disposal capacity, insufficient regulatory coordination across administrative boundaries, and the imbalance between environmental and economic benefits. Cross-regional waste management encompasses diverse waste streams, methodologies, and differentiated policy research frameworks. This study systematically examines relevant research themes and practical experiences across four dimensions: core challenges, key characteristics of waste stream management, and others. Table 2 presents a comparative overview of the research themes in cross-regional waste management.

Table 2.
Research themes in cross-regional waste management.
4.1. Key Management Characteristics of Cross-Regional Waste Streams
In studies on cross-regional waste management, various waste streams exhibit distinct flow patterns and management characteristics shaped by their physical properties, economic value, and environmental impacts. As shown in Table 2, existing research on cross-regional waste management primarily focuses on construction waste, electronic waste, medical hazardous waste, food waste, and wastewater. While existing research provides preliminary analyses of cross-regional waste flows and management characteristics, further exploration is warranted in areas such as the underlying driving mechanisms.
In research on cross-regional waste management, construction waste constitutes a significant segment. Construction waste is characterized by its substantial weight and low unit value. Transportation and aggregate screening represent the two stages with the highest carbon emissions and economic costs throughout the entire lifecycle of construction waste, from generation to disposal [94]. Therefore, given the inherent properties of construction waste and the critical stages in its management, balancing cost-effectiveness is a key consideration in cross-regional construction waste management. Consequently, scholars have focused on coordinating responsibility allocation among stakeholders, using modeling approaches to explore and propose cooperative optimization strategies. For example, research confirms that at different market scales, when profit distribution coefficients range between 0.3–0.35, 0.25–0.3, and 0.25–0.3, respectively, construction recycling enterprises shift from non-cooperative to cooperative behavior [33]. This provides a theoretical basis for cross-regional waste management. Case studies further validate the practical value of cross-regional coordination. For example, cross-state flows of construction waste in Australia primarily occur through interstate recycling, interstate landfilling, and overseas exports [50]. Hong Kong and Shenzhen, which are constrained by insufficient local processing capacity, have established a cross-regional collaborative governance model where most construction waste is transported to neighboring cities for treatment [51]. With respect to the evolutionary trends of construction waste flows, studies analyzing carbon emission reduction effects in China’s construction sector reveal that China’s construction waste exhibits a growth-decline-regrowth pattern [52]. Regional carbon emission reduction levels show a gradual convergence trend, with the number of large-scale construction enterprises being the primary driver of variation [53]. However, existing research has focused primarily on describing cross-regional waste flow patterns and modeling cooperative mechanisms, and empirical studies on specific cooperative mechanisms for cost allocation and benefit distribution are lacking. Furthermore, analyses of the overall regional characteristics of construction waste flows and the interconnections between local linkages remain insufficient.
Compared with construction waste, electronic waste flows from developed regions to low-to-medium development regions with strong dismantling and recycling capabilities and is considered one of the world’s fastest-growing waste streams [95]. This characteristic also presents complex governance challenges. Case studies indicate that, owing to insufficient processing facilities, most electronic waste received by Macao, China, from developed countries is subsequently exported to other countries or regions [59]. Projections indicate that between 2020 and 2030, 23.11 million units of e-waste are expected to be transported from developed regions to less developed regions in Guangdong Province, China [9]. Therefore, on the basis of this flow pattern, dismantling capacities across regions should be optimized according to e-waste distribution patterns [96]. Larger countries should develop targeted policies; for instance, regions with low recycling rates could adopt cross-regional coordination strategies [61]. Scholars have begun focusing on specific categories, such as power batteries and lead-acid batteries, revealing the complex coexistence of formal and informal systems [97]. In some developing countries, informal recycling has hindered the successful implementation of e-waste regulations [98]. Therefore, it is necessary to address the relationship between formal and informal systems to facilitate the transition from informal to formal practices and enhance e-waste management efficiency [99]. Research analyzing cross-regional lead-acid battery recycling in eastern China revealed that regulatory enforcement exceeding subsidy levels reduced illegal recycling activities by 84% [60]. Notably, battery waste processing carries risks of heavy metal leakage, necessitating cross-regional management that balances resource efficiency with risk control. However, existing studies on these issues often remain at the level of principled advocacy, lacking actionable technical pathways.
The imbalance between supply and demand for medical waste during the pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in its management system. Scholars have begun employing more sophisticated models, such as a two-level optimization approach to quantify infection probability, to address this challenge. Through a case study in Maharashtra, India, this model achieved dual objectives: reducing infection probability while lowering economic costs [71]. An analysis of the case study from Wuhan, China, indicates that sorting different types of medical waste at the source can significantly enhance processing efficiency. This encourages local governments to develop differentiated strategies for establishing disposal centers [70]. Consequently, proposals include establishing regional shared disposal centers and implementing dynamic penalty mechanisms to regulate transportation companies’ behavior. These studies mark a shift from an emergency response to a resilient system design, although existing models still fall short in capturing the suddenness and uncertainty of outbreaks.
The synergistic management of food waste and agricultural residues, along with the NIMBY effect in wastewater treatment, highlights the critical role of resource coordination and social acceptance in cross-regional governance [100,101]. Food waste treatment plants in urban areas face energy conversion barriers due to insufficient agricultural waste feedstock. Huang and Xu proposed that regulatory authorities should facilitate partnerships between plants and rural areas to ensure sustainable waste flows [72]. In cross-regional wastewater management, public NIMBYism stems from environmental externalities, necessitating regional coordination mechanisms to jointly oversee waste flows [102]. Consequently, studies advocate reinstating joint water commissions and establishing unified wastewater treatment standards to mitigate public health risks from groundwater contamination [103]. To address this, China has developed a cross-administrative compensation mechanism for urban living facilities that integrates economic and ecological considerations [104]. While these studies focus on resource integration and institutional coordination, establishing effective interest linkage mechanisms to ensure stable cross-regional cooperation remains an unexplored area in current research.
4.2. Core Challenges in Cross-Regional Waste Management
Throughout the entire process of cross-regional waste management, numerous challenges arise, including the diverse nature of waste streams, differences in administrative systems, uneven regional development, and divergent stakeholder demands. Given the complexity of these circumstances, the challenges of cross-regional waste management are articulated at the macro, meso, and microlevels as three primary issues: inadequate policy frameworks; inefficient coordination among stakeholders; and environmental externalities. Table 2 presents the policy tools proposed and developed by managers and scholars to address existing challenges.
- Incomplete policy systems
On the one hand, differences in how countries or jurisdictions define reusable equipment versus waste, coupled with policy misunderstandings stemming from language barriers [66], often result in inefficient cross-regional waste flows and frequent illegal dumping incidents [42]. On the other hand, policymakers may harbor suspicions that cross-regional cooperation benefits only the other party due to differing perspectives, thereby undermining collaborative management efforts [43]. Furthermore, when waste recycling operations are outsourced, responsibility shifts, creating significant challenges in determining accountability [67]. Additionally, policy discrepancies within certain jurisdictions may lead to environmental impacts from cross-regional waste flows. For example, China’s “One Country, Two Systems” policy has created legal loopholes concerning illegal cross-regional waste dumping [62,105]. Similarly, in Ghana, the lack of coordination among local governments and the absence of dedicated waste management authority have slowed the implementation of waste management policies [76]. In Israel and Palestine, the absence of a joint water committee has prevented the effective improvement of wastewater in Palestinian-origin areas [103]. The negative externalities generated during waste transportation necessitate compensation from polluters to affected parties. Poor coordination may increase local governments’ financial burdens, potentially driving illegal dumping [57]. These administrative barriers stemming from policy and standard discrepancies directly hinder regional coordination efficiency. To address these challenges, implementing extended producer responsibility (EPR) systems and clarifying responsibility allocation among stakeholders can facilitate interregional cooperation in waste management.
- Governance actors lack smooth coordination
To achieve efficient waste utilization, Brazil has issued the National Solid Waste Policy, encouraging cooperation between two or more cities [106]. However, the implementation of this policy may be significantly undermined by the lack of participation from municipal public administrators in local decision-making processes, thereby limiting the effectiveness of cross-regional collaboration [80]. Furthermore, transportation distances not only significantly impact economic costs and the environment but also may increase communication and coordination expenses between parties. Consequently, regions consider geographical proximity when seeking cross-regional partners. Only when geographical proximity is optimal can a foundation be laid for advancing cross-regional cooperation [79]. The heterogeneous demands among local governments may undermine cooperation stability, necessitating agreements that maximize mutual satisfaction [81]. During cross-regional transactions, critical information such as the specific composition of waste and the environmental risks it poses remains opaque [38]. This lack of transparency is a key factor contributing to the inefficiency in matching supply and demand across regions. Traditional cooperation processes and processing platforms struggle to ensure information authenticity and transparency, further exacerbating trust costs among cross-regional cooperation entities [30,107]. Consequently, reaching a consensus on cost-sharing levels and establishing information-sharing platforms to guarantee information symmetry among cooperation entities are crucial measures for achieving sustainable interregional cooperation.
- Environmental externalities
Owing to factors such as revenue costs and environmental externalities, conflicts of interest among entities involved in cross-regional waste management cooperation can affect the willingness to collaborate, thereby impacting the overall efficiency of waste governance. Scholars assessing the economic impact of waste flows in Australia have reported that Queensland may lose A$223 million in industry revenue because of cross-border waste movements within its borders [41]. Another study using input-output modeling to quantify China’s agricultural chemical oxygen demand (COD) reported that 68.8% of agricultural COD originates from long-distance transfers flowing from west to east [73]. This cross-regional transfer phenomenon exacerbates water resource crises. This model of pollution transfer rather than cooperative governance has little effect on improving waste management efficiency or reducing environmental pollution. Therefore, close intergovernmental cooperation and strengthened regulation are essential to achieve environmentally sustainable development.
In summary, the core challenges in current cross-regional waste management can be categorized into three types: inadequate policy frameworks, a lack of stakeholder coordination, and environmental externalities. To address these challenges effectively, policymakers, administrators, and academics have proposed numerous solutions. Section 4.3 and Section 4.4 review and analyze the optimization measures proposed by scholars to address these challenges. These tools primarily include policy tools such as interregional coordination agreements and unified regulation, as well as technical improvement recommendations for achieving information sharing and establishing cost-sharing mechanisms.
4.3. Policy and Governance Mechanisms for Cross-Regional Waste Management
To address the core challenges in cross-regional cooperative waste management, scholars have evaluated and analyzed existing policies across two dimensions: regional policy assessment and international treaty analysis. With respect to environmental externalities, regional coordination has proposed optimization recommendations. To address the challenge of policy inadequacies, research has focused on extended producer responsibility systems, landfill fees, tax rebate policies, and international convention analysis.
4.3.1. Regional Policy Analysis
- Extended producer responsibility system
The extended producer responsibility system achieves effective management by assigning specific responsibilities to relevant entities. It indirectly supports market-based waste strategies by treating waste as a resource for exchange, thereby advancing the circular economy [65]. Current research on cross-regional waste management proposes consumer extended responsibility systems and producer extended responsibility systems. In 2003, California enacted the Electronic Waste Recycling Act, which requires electronics retailers to collect recycling fees [108]. By 2025, the law will mandate expanded public participation to increase e-waste management effectiveness [109]. California has also implemented extended producer responsibility in household waste management, improving overall waste handling practices [110]. As waste sorting has become increasingly widespread in China, consumer responsibility in waste management has increased. Extended responsibility systems can enhance environmental awareness among the public and consumers, influencing the behaviors of friends and family to reduce non-eco-friendly actions [9]. However, existing research primarily describes institutional frameworks through policy analysis, with limited exploration of implementation pathways for responsibility allocation. Future studies could compare different system types within complex regional contexts to propose optimization strategies.
- Landfill fees and tax rebate policies
Landfill fees and tax rebate policies, among other economic incentives, can directly guide the cross-regional collaborative management of waste. However, their effectiveness depends on the precision of regional coordination and institutional design. For example, two regions must collaboratively establish a reasonable landfill fee charging system to enhance the efficiency of joint oversight [56]. Tax incentives are widely recognized as among the most effective policies for stimulating waste recycling [111,112]. Nevertheless, when implementing rebate policies, setting appropriate rebate rate thresholds is crucial [83]. Research indicates that lower thresholds may enhance policy effectiveness. While these studies contribute to the development of economic incentives for policymakers, it should be noted that landfill fee pricing is influenced by factors such as waste type and physical properties. Future research could therefore establish standardized methodologies for landfill fee calculation. Furthermore, existing studies on tax rebate policies have not considered the possibility of illegal dumping, nor have they accounted for regional variations in rebate incentives. These limitations may impact the actual implementation outcomes of such policies [83]. Consequently, future research should build upon these findings to explore these areas further.
- Regional coordination
Cross-regional collaboration practices further reveal challenges in policy implementation. China’s zero-waste city pilot program aims to reduce solid waste and CO2 emissions. However, the dual environmental effects have not demonstrated significant spatial spillover. Scholars believe that this may stem from weak cross-regional coordination, uneven resource allocation, and the policy’s urban-centric implementation [84]. Therefore, regional linkages require further strengthening. The United States, which is overly reliant on cross-regional emission transfers, tends to transport waste to regions with lower disposal costs. Local residents suffer health impacts from excessive pollutant emissions. Consequently, U.S. jurisdictions have enacted NIMBY laws to restrict cross-border waste shipments. Scholars note that implementing such laws in isolated jurisdictions may paradoxically increase total waste volume. While coordinated implementation across all jurisdictions could reduce costs, it does not address the underlying imbalance in waste distribution [82]. This highlights the need for a policy design that balances local efficiency with systemic integrity. Future research should move beyond describing individual policies or case studies, focusing instead on systematic analysis of policy combinations, regional variations, and institutional feasibility.
4.3.2. Analysis of International Conventions
To curb the illegal cross-border transfer of waste to low-income and lower-middle-income countries, EU member states have signed regulations such as the WEEE Directive and the Waste Shipment Regulation to safeguard the ecological environment and maintain international environmental stability. The Basel Convention is the primary international treaty governing the transboundary movement of waste, including hazardous waste, established to protect public safety and health [113]. Within this regulatory framework, industrialized nations account for the largest share of waste imports, whereas the least developed countries, with their limited openness to waste trade, remain vulnerable to illegal smuggling activities [85]. To address illegal shipments, scholars have analyzed South Korea’s Hazardous Waste Transboundary Movement and Disposal Act to propose legal improvements for all nations. These include timely updates to Basel Convention data, as accurate information provides critical insights into global waste flows [86]. Additionally, platforms should be established to monitor waste transportation routes [45,64]. In transboundary shipments, clarifying responsibilities among stakeholders is crucial [87]. Integrating accountability theories to establish a system where those with power bear responsibility can advance circular economy models. Additionally, China’s Import Ban has effectively prevented waste from entering its territory, yielding relatively positive outcomes. For example, it has fostered the development of legitimate waste management industries while effectively combating informal activities [63].
The aforementioned research offers valuable insights for optimizing global cross-regional waste governance. However, in-depth institutional design remains necessary for delineating specific responsibilities among stakeholders. Future studies could employ quantitative methods to quantify elements within responsibility allocation and propose actionable recommendations.
4.4. Technological and Collaborative Innovation in Cross-Regional Waste Management
To address the challenge of inadequate coordination among stakeholders, existing research has pioneered innovative technologies and collaborative models for cross-regional waste management. These innovations can be categorized into three areas: stakeholder collaboration models, transportation and scheduling, and transaction and traceability systems.
4.4.1. Innovation in Collaborative Models
Cross-regional waste management involves multiple stakeholders, including governments, enterprises, and the public. The behavioral choices of different actors can constrain one another, thereby affecting the efficiency of waste treatment. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct an in-depth exploration of the reasons behind stakeholder decision-making and the underlying influence mechanisms. Existing research employs various modeling tools to address this issue. For example, scholars have utilized complex network evolutionary game models to analyze strategic adjustments by recycling enterprises in two regions under market mechanisms versus government regulatory frameworks, proposing corresponding policy recommendations that lay the groundwork for promoting coordinated interregional development [33]. Such modeling research reveals how policy environments at the microlevel shape corporate behavior. Other scholars propose that enterprises should incorporate environmental advocacy into their operational decisions to enhance their public image [114]. Practically, Spain’s intermunicipal cooperation case demonstrates that outsourcing management can address certain quality deficiencies, maximizing local public service efficiency [90]. This provides empirical support for intergovernmental cooperation models. Additionally, research employing system dynamics methods analyzes the factors influencing cross-regional collaborative waste management, which is validated through a case study in Guangdong Province, China. A previous study revealed that establishing reasonable landfill fee schemes on the basis of disposal capacity enhances cross-regional collaborative management efficiency [56]. However, these studies face limitations in revealing the behavioral mechanisms among actors in detail. On the one hand, while evolutionary game models simulate strategic interactions, their construction and conclusions are often influenced by assumptions that simplify real-world bounded rationality and heterogeneity. On the other hand, while case studies offer practical relevance, their specific contexts may limit the generalizability of conclusions.
Ecological compensation serves as a policy tool for balancing environmental and economic benefits. Early approaches primarily determined compensation standards on the basis of pollutant proportions and wastewater treatment costs to address cross-regional sewage management issues [88]. As practices matured, the application scenarios and design concepts of ecological compensation expanded. For example, to counter environmental externalities during waste transfers, China established a cross-administrative compensation system for urban domestic wastewater, setting compensation standards. By clarifying interregional cooperation’s benefit and responsibility distribution, this system promotes sustainable regional development [104]. Notably, Guangdong Province’s 2024 issuance of ecological compensation management measures for cross-regional construction waste transfers signifies the mechanism’s transition from theoretical discussion to practical policy implementation [115]. In recent years, scholars have begun exploring the use of ecological compensation to develop mechanisms for cross-regional waste management. Some researchers have categorized ecological compensation on the basis of different municipal solid waste management scenarios and have concluded that fully shared compensation represents the optimal approach [89]. Others have proposed an ecological compensation distribution scheme through evolutionary game theory that benefits all stakeholders in the cross-regional collaborative management of construction waste [32,57]. These studies mark a shift in the field from why compensation is necessary to how it can be optimized. Nevertheless, current ecological compensation mechanisms still hold room for further refinement. First, regarding fiscal issues, funding sources and the sustainability of payment guarantees have not been fully considered. Second, the implementation outcomes, encountered resistance, and genuine feedback from stakeholders concerning the ecological compensation policy proposed in Guangdong Province, China, have yet to be evaluated or empirically studied, leaving valuable space for future research.
4.4.2. Transportation and Dispatch
The efficiency and cost of cross-regional waste management are largely determined by its transportation and scheduling systems. Research indicates that waste collection, operations, and storage account for 60–80% of the total lifecycle costs [116]. Consequently, how to plan waste transportation routes properly has drawn significant attention from scholars. However, various uncertainties in cross-regional transportation make it difficult to conduct quantitative analysis via traditional methods. To address this, scholars actively employ computer simulation techniques to seek optimal solutions. Specifically, in emergency scenarios, research has employed digital twin technology to construct a virtual system for selecting temporary disposal center locations based on the physical world. Using a case study of medical waste treatment in India, the model was evaluated to ultimately develop targeted cross-regional transportation strategies [71]. For routine operations, to address the challenge of excessive waste influx into disposal sites, scholars employed an improved hierarchical clustering algorithm to establish an optimization model balancing transport distance and capacity. This model innovatively proposed intelligent waste transport route planning, enabling flexible task allocation based on dynamic waste volumes and terminal processing capacities. This approach helps reduce vehicle transport distances and quantities while improving utilization rates of vehicle carrying capacity [31]. Additionally, scholars have decomposed Japan’s two-region input-output table into three regions via input-output modeling, revealing distinct waste distribution patterns between regions with and without cross-transport [39]. From an environmental sustainability perspective, studies indicate that selecting appropriate transportation modes can substantially reduce negative externalities. Researchers have proposed coordinating logistics operations and utilizing rail transport for cross-border shipments to minimize carbon emissions from transportation [55].
The aforementioned studies present cutting-edge solutions for cross-regional waste transportation, effectively reducing carbon emissions in the transport process. However, this field warrants further in-depth exploration. While digital twin technology holds great promise, its high implementation costs mean that current research remains largely in the conceptual validation phase, lacking practical supply chain applications and benefit assessments. Furthermore, most algorithmic models often simplify uncertainties such as traffic conditions and policy changes for quantitative convenience, potentially weakening their applicability. Future research should therefore focus on developing more resilient adaptive algorithms and promoting deeper integration between advanced algorithms and grassroots operations.
4.4.3. Transactions and Traceability
Cross-regional management is not merely a logistics issue but also fundamentally a matter of information and trust. Regional disparities in resource endowments drive cross-regional waste trade [117]. This innovative reuse approach theoretically creates a win-win scenario for both suppliers and consumers. However, transaction processes may encounter obstacles due to mismatches between supply and demand. Consequently, scholars are dedicated to building trustworthy trading environments through innovative technologies. Some scholars have drawn upon smart grid concepts to analyze the performance of construction waste transactions across production, flow, market, distribution, and consumption scenarios. Building on this analysis, they have innovatively proposed transaction arrangements to achieve rational cross-regional allocation of waste [58]. Additionally, blockchain technology facilitates waste traceability to address information asymmetry in regional cooperation processes [118], thereby achieving effective waste management [29,30]. To date, this technology has undergone continuous refinement and application in cross-regional waste management. Waste passports help bridge the information gap between buyers and suppliers [38], and their integration enhances governance effectiveness [38]. Scholars have integrated blockchain with nonfungible token (NFT) passports enhances information transparency in the cross-regional construction waste trade, thereby fostering interregional collaboration [38]. Additionally, researchers have incorporated details such as type, quantity, properties, and origin into waste passport systems to achieve upstream-downstream information symmetry, enabling stakeholders to access more comprehensive lifecycle histories of materials [30]. Nevertheless, the application of blockchain technology remains underexplored in terms of cost analysis, energy consumption, and stakeholders’ willingness to share information. Future research should delve into the governance costs of these new mechanisms within specific institutional contexts.
4.5. Impact Assessment
4.5.1. Environmental Impact
The environmental benefits of cross-regional waste management, particularly its carbon footprint, are central to sustainability assessments [119]. Existing research primarily quantifies environmental impacts through life cycle assessment and spatial analysis methodologies. Some scholars argue, on the basis of the whole-life-cycle approach, that if cross-regional management can increase recycling rates, it can encourage the cross-regional flow of construction waste [40]. Analysis of the spatial characteristics and influencing factors of carbon emissions from municipal solid waste over 15 years reveals that the spatial correlation of carbon emissions has spillover effects not only on neighboring cities but also on non-neighboring cities, filling a gap in previous research that considered only the impact of geographical proximity on neighboring cities [91]. Additionally, scholars employing multiregional input-output models have revealed the chemical oxygen demand footprints of wastewater across China’s regions and their interrelationships, providing a scientific basis for formulating coordinated emission reduction policies [73].
However, while spatial spillover effects confirm the existence of correlations, they fail to clearly analyze underlying mechanisms—such as the roles of technology diffusion and industrial relocation. Future research must therefore establish more inclusive environmental impact assessment frameworks and delve into the driving pathways of cross-regional environmental effects.
4.5.2. Economic Impact
Cost effectiveness may be the primary factor driving local governments to consider cooperation, making economic impact assessments crucial for helping managers and policymakers determine the efficacy of cross-regional collaboration. On this basis, studies have examined the cross-regional transport of construction waste in Australia and evaluated the economic implications of waste flows [41]. Research has also demonstrated a significant positive correlation between intermunicipal cooperation and cost savings [54], with municipal decisions potentially impacting costs in neighboring jurisdictions [93]. Thus, enterprises may explore cross-regional collaboration for mutual benefit [92]. However, some scholars note that annual gains from interregional construction waste management may not sufficiently offset associated costs [34]. This discrepancy likely stems from variations in study regions and research focuses. Given the substantial volume of construction waste, transportation constitutes a significant portion of the overall cost. This discrepancy indicates that economic impact assessments depend on a range of contextual factors, including waste physical properties, geographic distance, market scale, and resource recovery pathways. Future research should therefore extend beyond evaluating overall benefits to conduct in-depth analyses of cost–benefit allocation mechanisms under different models.
4.5.3. Social Impact
Some argue that overreliance on waste export for disposal will lead to significant job losses. Therefore, to preserve more employment opportunities, reducing cross-regional waste export activities is recommended [41]. This reflects the trade-off between environmental efficiency and social stability. By examining the social composition of the recycling industry, scholars have focused on informal organizations within the waste recycling system and their societal value. Recyclers can be categorized by legal status into formal and informal recyclers. Although the latter are not recognized by waste management authorities, they play a vital role in the secondary market. Research indicates that abandoning informal recycling would ultimately results in substantial waste [68]. Therefore, given this social reality, a holistic and inclusive strategy should be adopted, fully considering its social value to avoid the negative impacts of outright rejection. Current research highlights the impact of cross-regional waste governance on social employment. Future studies can build upon this foundation to further explore the design of employment security mechanisms, striving to establish a more equitable and inclusive transition pathway.
5. Research Status and Future Directions in Cross-Regional Waste Management
5.1. Research Status of Cross-Regional Waste Management
Cross-regional waste management has become an indispensable core issue in advancing the global circular economy. With accelerating urbanization and deepening regional industrial specialization, the movement of waste streams such as construction waste, electronic waste, medical waste and wastewater across administrative boundaries and even internationally has increased in frequency. The efficiency of their disposal directly impacts the coordinated development of environmental, social and economic dimensions.
A significant portion of research has centered on establishing governance frameworks for cross-regional waste management, addressing stakeholder dynamics and rules for cross-regional cooperation [32,33,57]. However, and current input-output models are predominantly constructed using static data [39,69,73] and measure the inflow and outflow of different waste streams at a single point in time. Their key limitation lies in failing to adequately account for disruptions to waste flow pathways and management strategies caused by unforeseen events such as natural disasters or epidemics. Neglecting these uncertainties may lead to results that deviate from actual governance scenarios, thereby hindering local governments from formulating appropriate policies for cross-regional waste management. Consequently, further exploration of the dynamic mechanisms involved in cross-regional coordination is warranted.
Numerous studies have focused on quantifying the environmental, economic, and social impacts [40,61], alongside optimizing the sequencing of policy instruments [78]. These efforts aim to mitigate negative externalities arising from cross-regional flows while maximizing the circular value of resources. However, further research into the adaptability of regional strategies across different developmental levels is needed. Although studies have identified spontaneous flows of electronic waste from developed regions toward concentrated dismantling industries [9], systematic approaches for technology transfer and benefit compensation mechanisms targeting less developed regions remain underdeveloped. As demonstrated by supplementary case studies, certain regions, such as China’s Yangtze River Delta and the Gulf of Bothnia in the European Union, have achieved some success in cross-regional waste facility sharing and mutual recognition of regulatory standards. Nevertheless, further theoretical refinement and broader dissemination of these experiences remain necessary [104,120].
The recovery and reutilization of waste materials to transform them into valuable commodities is gaining recognition among the public and consumers. To enhance cross-regional cooperation, current research focuses primarily on implementing logistics traceability and transport route planning to address information asymmetry issues [30,31,38].
Future research may further deepen work across three dimensions: governance, strategy, and technology. Specifically, at the governance level, the implementation of cross-regional compensation mechanisms for benefits and responsibility sharing must be advanced. At the strategic level, differentiated approaches should be developed according to waste type and regional development level. Technologically, deep integration of blockchain, digital twins, and traditional management models can be pursued to overcome the core obstacles of information asymmetry and low collaborative efficiency.
5.2. Future Research Directions and Recommendations
According to projections by the United Nations Environment Programme, global municipal solid waste generation will reach 3.8 billion tons in 2050, an increase of 1 billion tons compared with that in 2025 [121]. However, significant disparities exist between regional waste generation levels and treatment capacities, implying that portions of waste are transported elsewhere for disposal. The high logistical costs associated with cross-regional transfers and issues such as the illegal cross-regional movement of hazardous waste underscore the urgent need for integrated regional waste management. Given that the relationship between recycling efficiency and cost plays a pivotal role in cross-regional cooperation, system optimization with technology innovation is a critical component of circular economy transformation. Since waste types are complex, improper handling can cause ecological damage. Consequently, advanced waste recycling technologies and infrastructure can facilitate more effective waste management.
Further work is needed to optimize cross-regional governance mechanisms and foster multistakeholder collaborative innovation to promote effective interaction among actors. This encompasses a multistakeholder collaborative model involving government leadership, corporate operations, NGO oversight, and public participation. Specifically, this entails examining administrative coordination processes among local governments, market-driven operational pathways for enterprises in cross-regional waste transportation and treatment, and the oversight of cross-regional transfer processes by NGOs and the public. Specifically, multi-agent modeling methods can be employed to simulate the behavioral evolution of various stakeholders under different policy scenarios, thereby providing a basis for designing compensation mechanisms.
Efforts should be made to enhance intelligent logistics systems and digital tracking technology for cross-regional waste management, thereby achieving visualization, efficient operation, and traceability throughout the transfer process. Future research could develop a unified data collection and transmission protocol. By using IoT sensors to monitor the locations of transport vehicles, the quantity of waste loaded and the integrity of seals in real time prevent leakage and illegal dumping during transit. A tamper-proof traceability chain spanning the entire cross-regional waste lifecycle—from source to transport, processing, and recycling—should be established via blockchain technology, clearly defining responsibility at each stage. Furthermore, research must assess the feasibility of implementing digital systems. This includes evaluating compatibility between regional digital platforms, the technological access costs for SMEs, and specific mechanisms for data security and privacy protection. Such measures will ensure that technological innovations tangibly enhance the efficiency of cross-regional waste transfers. Furthermore, these studies should be grounded in thorough pilot verification, such as the selection of specific urban clusters to conduct practical explorations of digital waste passports, thereby increasing experience for broader implementation.
It is worth emphasizing that the most critical and urgent gap in this field lies in the failure to incorporate risk as a factor into the full life-cycle assessment system for transboundary waste management. This includes evaluating the contamination risks to soil and water bodies along transport routes in the event of leakage during the illegal shipment of hazardous waste, as well as the long-term ecological consequences arising from the concentration of treatment facilities in specific regions. Previous studies have examined the impact of risk factors on the recycling of construction waste within local contexts [122], but no research has yet analyzed the role of risk in cross-regional scenarios. Comparing the environmental risks between traditional regionally independent management and transboundary collaborative management can help provide policymakers with decision-making support centered on safety priorities. Importantly, integrating machine learning technologies with real-time monitoring data to establish an environmental risk early warning platform with predictive capabilities can provide a scientific basis for the precise allocation of regulatory resources.
For cross-regional waste management to operate efficiently, robust infrastructure support is indispensable. Future research should prioritize the coordinated planning and intelligent upgrading of cross-regional infrastructure. Research should optimize site selection models for cross-regional waste transfer hubs, comprehensively considering regional waste generation volumes, transport accessibility, the distribution of environmentally sensitive areas, and land use costs to prevent hubs from becoming either too dispersed or excessively concentrated. In terms of specific implementation pathways, multi-agent optimization models can be employed to consider multiple factors, such as economic costs, environmental impacts, and social benefits, holistically. Furthermore, sustainable models such as public–private partnerships (PPPs) should be proposed to address issues in infrastructure development, including funding arrangements and the allocation of operational and maintenance responsibilities. Solutions tailored to the specific characteristics of each project must be thoroughly designed.
6. Conclusions
6.1. Conclusion
This study reviewed 58 papers by adhering to the PRISMA framework. Notably, quantitative research constitutes the predominant methodology in this field, with increasing applications of empirical studies and modeling analyses. This methodological evolution reflects the growing complexity and interdisciplinary nature of the field. Single methodologies are increasingly inadequate for comprehensively addressing the multidimensional challenges in transregional waste management. Consequently, this review recommends that scholars employ mixed methods to elucidate issues in transregional waste management that cannot be adequately explained by quantitative analysis or qualitative approaches alone.
This study further indicates that challenges in cross-regional waste management primarily manifest in three areas: inadequate policy frameworks, inefficient coordination among stakeholders, and environmental externalities. The cross-regional management of construction waste largely necessitates collaborative efforts among local governments, relevant corporate entities, and the public. Regardless of whether technological efficiency or management capabilities are enhanced, cooperation with all stakeholders is essential to address social, economic, and environmental issues. Moreover, this research conducted a systematic review across five themes, offering valuable insights for shaping future research directions. These findings broaden the theoretical foundations of transregional waste management research, guiding academia in identifying unexplored avenues while laying the groundwork for policymakers to formulate effective transregional coordination policies.
6.2. Theoretical Significance
This research answers the questions posed and contributes to the present literature by conducting a visual analysis and systematic thematic categorization of existing studies on cross-regional waste management. Overall, the literature review on cross-regional waste management reinforces the perspective that cross-regional collaboration constitutes an effective strategy for achieving sustainable development. This systematic literature review provides the research community with a novel framework and insight into cross-regional waste management.
First, this study analyses the management characteristics of various waste streams and the current state of cross-regional research, thereby broadening the knowledge base. The study employed VOSviewer 1.6.20 to visualize keywords from relevant literature, providing enhanced and more profound insights into the bibliometric findings concerning research priorities. Second, this study serves as a foundation for future scholars to delve deeper into cross-regional waste management, offering influential insights to facilitate progress in collaborative waste handling across jurisdictions. An examination of the research themes highlights existing gaps in the literature, providing crucial reference points for academics. Fundamentally, research into cross-regional waste management necessitates exploring issues hitherto neglected across the entire waste lifecycle—from generation to recycling. These include responsibility allocation, flow risks, secondary pollution during manufacturing, market barriers, and long-term versus short-term cooperative mechanisms.
6.3. Practical Implications
This study holds significant importance for industry leaders and provides them with valuable insights. By focusing on the challenges of cross-regional cooperation, organizations and corporations can formulate corresponding strategic measures. The collaborative barriers to cross-regional waste management identified in this study can be translated into concrete strategic initiatives. For example, to address risks stemming from information asymmetry and trust deficits, enterprises can pioneer the adoption of blockchain technology to transform transportation and disposal data into credible green credentials. This approach enhances corporate reputation and fosters greater trust among partners. Concurrently, businesses should proactively engage in establishing industrial infrastructure for cross-regional waste management. By sharing processing facilities, they can scale up cross-regional waste management models into large-scale operations. These findings help guide corporations in developing more informed and appropriate cross-regional cooperation strategies on the basis of identified obstacles, thereby aligning their sustainability initiatives with industry dynamics.
For policymakers, this research provides a robust foundation for establishing regulations governing cross-regional collaborative waste management across different regions. Key recommendations include incentivizing cross-regional corporate collaboration through subsidies or tax relief, standardizing waste classification protocols, and strengthening penalties for illegal dumping to foster regional cooperation. This study recommends that policymakers first promote the standardization of waste sorting and measurement across regions to prevent interregional cooperation from being disrupted by inconsistent standards. Building on this foundation, a unified ecological compensation mechanism for waste transfer should be negotiated, incorporating comprehensive assessments based on transportation distance and waste characteristics. Compensation should be provided by waste-generating regions to receiving regions, thereby mitigating the NIMBY effect caused by the unfair distribution of benefits. For enterprises engaged in cross-regional illegal dumping, regions should implement joint disciplinary actions. Violating enterprises should be included in cross-regional credit records, increasing the cost of noncompliance and thereby establishing institutional constraints. By reviewing existing policies and governance tools, policymakers can enhance their understanding of cross-regional waste management and develop tailored governance measures on the basis of their specific circumstances, building upon the existing policy framework.
6.4. Limitations
This review is not without limitations. On the one hand, although the authors have attempted to consider as many search terms related to transregional waste management as possible, it may still be impossible to avoid omitting some relevant literature. Therefore, future research could employ more synonyms to ensure more comprehensive retrieval results. On the other hand, the scope of this study’s literature focuses on English peer-reviewed journal articles from the Web of Science and Scopus databases, excluding document types such as conference papers, books, and newspapers. This may result in the exclusion of relevant research in other languages or publication formats, which future studies could incorporate into their search scope. Furthermore, while transregionality encompasses both geographical scale and administrative hierarchy, this study focused on analyzing research related to transregional management and thus did not make detailed distinctions. Since different studies emphasize varying aspects of transregional waste management, the metrics used differ, and this study lacks an analysis of these variations. This may somewhat affect the precision of the results.
To enhance comparability in research on transregional waste management, this study proposes the following minimum reporting standards for future research: First, clearly identify the flow information being tracked. This includes all stages from generation to disposal, such as transportation, collection, and recycling, while specifying the direction of waste flows and data sources. Second, clearly define boundaries, which may involve both geographic and administrative boundaries. Third, the functional units should be standardized. Adherence to these reporting standards will help reduce the interference of heterogeneity in future research.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/buildings15244459/s1, Table S1: PRISMA checklist [123]; Table S2: Data extraction table template.
Author Contributions
Methodology, validation, formal analysis, investigation, resources, data curation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, visualization, Y.Z.; conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft, supervision, project administration, X.L.; project administration, supervision, writing—review and editing L.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 72204178, 71963033 and 72364037), Sichuan Science and Technology Program and Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan, China (grant number 2023NSFSC1053).
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- More Growth, Less Garbage. Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/entities/publication/ba7feea4-0abe-59fb-bc60-ce6b60eb1ceb (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- How the World Bank is Tackling the Growing Global Waste Crisis. Available online: https://blogs.worldbank.org/zh/voices/how-the-world-bank-is-tackling-the-growing-global-waste-crisis (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Siddiqua, A.; Hahladakis, J.N.; Al-Attiya, W.A.K.A. An overview of the environmental pollution and health effects associated with waste landfilling and open dumping. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 58514–58536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Liu, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Guo, Q.; Zhou, S. Analysis of industrial solid waste and the possibility of recycling and utilization. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2025, 18, 2493155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damayanti, D.; Saputri, D.R.; Marpaung, D.S.S.; Yusupandi, F.; Sanjaya, A.; Simbolon, Y.M.; Asmarani, W.; Ulfa, M.; Wu, H.S. Current prospects for plastic waste treatment. Polymers 2022, 14, 3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- South Australia’s Circular Economy Resource Recovery Performance. Available online: https://www.greenindustries.sa.gov.au/SArecycling (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- National Waste Report 2018. Available online: https://www.environment.gov.au/protection/waste-resource-recovery/national-waste-reports/national-waste-report-2018 (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Boosting Cross-Border Recycling and Composting in Greece & Albania. Available online: https://futurium.ec.europa.eu/en/border-focal-point-network/good-practices/boosting-cross-border-recycling-and-composting-greece-albania (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Yuan, Q.; Gu, Y.; Yang, M.; Wu, Y.; Hu, G.; Zhou, G. Synergistic utilization mechanism of e-waste in regions with different levels of development: A case study of Guangdong Province. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 134855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonzo, D.; Abril, J.M.V.; Villonez, G.; Armstrong, R.; Dalona, I.M.; Beltran, A.; Orbecido, A.; Tabelin, C.B.; Villacorte-Tabelin, M.; Promentilla, M.A.; et al. Integrating indigenous knowledge and skills in mining operations: A systematic literature review. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2025, 24, 101706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, J.; Pereira, D.; Gonçalves, Â.; Oliveira, T. Digitalizing the pillars of Hybrid Civic Universities: A bibliometric analysis and new taxonomy proposal. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2023, 9, 100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, E.; Leitao, J.; Alves, H. Screening and enhancing intellectual capital consistency: A scoping review of systematised literature reviews. J. Innov. Knowl. 2025, 10, 100664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebl, W.I.; Theis, I.P.; Guisard, T.; Madera, J.M. The hospitality & tourism frontline employee: A bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2026, 133, 104451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, M.; Svejvig, P. Taking stock of project value creation: A structured literature review with future directions for research and practice. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2016, 34, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbük, R.M.Y.; Coşkun, A. Factors affecting food waste at the downstream entities of the supply chain: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.R.; Martek, I.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Aibinu, A.A.; Arashpour, M.; Chileshe, N. Critical evaluation of off-site construction research: A Scientometric analysis. Autom. Constr. 2018, 87, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, E.; Calvo-Mora, A.; Roldán, J.L.; Periáñez-Cristóbal, R. Quantitative research on the EFQM excellence model: A systematic literature review (1991–2015). Eur. Res. Manag. Bus. Econ. 2017, 23, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Fan, L.; Mahabir, R. Building carbon emissions (2016–2025): A PRISMA-based systematic review of definitions, quantification methods and policies. Environ. Dev. 2025, 57, 101345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, P.; Jena, P.K.; Mishra, B.R. Systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis of energy efficiency. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 200, 114583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Herrera, A.; Serrano-Hernandez, A.; Faulin, J. Understanding the dynamics of crowdshipping in last-mile distribution within urban mobility: A comprehensive framework. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2025, 101, 102249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Cao, X.; Yang, X. Assessment and reduction of embodied carbon emissions in buildings: A systematic literature review of recent advances. Energy Build. 2025, 345, 116058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, A.K.; Choudhary, S.K.; Singh, V.K. How can artificial intelligence impact sustainability: A systematic literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 134120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, V.; Castagnoli, A.; Pecorini, I.; Chiarello, F. Identifying technologies in circular economy paradigm through text mining on scientific literature. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0312709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh, M.; Gentile, N.; Mattsson, P.; Dubois, M.C. Energy impact of integrative lighting: A systematic literature review. Energy Build. 2025, 344, 115920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa-Oregi, I.; Gonzalez-Ochoantesana, I.; Anaya-Rodriguez, M. Understanding the engagement of citizens in the regeneration of urban spaces through human-centered design: A systematic literature review. Cities 2025, 168, 106414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notice of the General Office of the State Council on Issuing the Pilot Work Plan for “Waste-Free City” Construction. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2019-01/21/content_5359620.htm (accessed on 27 November 2025).
- Circular Economy Action Plan. Available online: https://www.eeas.europa.eu/sites/default/files/ce_action_plan_2.0_cn_0.pdf (accessed on 27 November 2025).
- Basel Convention. Available online: https://www.bcrc.cn/col/1256348829590/index.html (accessed on 27 November 2025).
- Lin, Y.H.; Wang, J.; Niu, D.; Tao, X. Blockchain-driven framework for construction waste recycling and reuse. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 89, 109355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Peng, Z.; Webster, C.; Wu, L. Developing a construction waste material ‘passport’for cross-jurisdictional trading. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 137509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Liang, C.; Tang, H. A Cross-Regional Scheduling Strategy of Waste Collection and Transportation Based on an Improved Hierarchical Agglomerative Clustering Algorithm. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 7412611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, W. Can ecological compensation promote cross-regional collaborative governance of construction and demolition waste? Evidence from prospect theory. Dev. Built Environ. 2025, 22, 100679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Han, C.; Shao, Z.; Meng, L. Exploring the evolutionary mechanism of the cross-regional cooperation of construction waste recycling enterprises: A perspective of complex network evolutionary game. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 139972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, N.; Duan, H.; Dong, L. Pathways to sound management of excavated soil and rock: A case study in Shenzhen. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 458, 142383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Yuan, H. Investigating waste reduction potential in the upstream processes of offshore prefabrication construction. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 28, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wen, Z.; Wang, Y. Nitrogen flow patterns in the food system among cities within urban agglomeration: A case study of the Pearl River Delta region. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, L.A.T.; Soulier, M. Defining regional recycling indicators for metals. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 129, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Lu, W.; Peng, Z.; Webster, C. A blockchain non-fungible token-enabled ‘passport’for construction waste material cross-jurisdictional trading. Autom. Constr. 2023, 149, 104783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, S.; Nishimura, K. A nonsurvey multiregional input–output estimation allowing cross-hauling: Partitioning two regions into three or more parts. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2013, 50, 935–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zuo, J.; Zillante, G.; Wang, J.; Duan, H. Environmental impacts of cross-regional mobility of construction and demolition waste: An Australia Study. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 174, 105805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zuo, J.; Yuan, H.; Zillante, G.; Wang, J. Investigation of the social and economic impacts of cross-regional mobility of construction and demolition waste in Australia. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 190, 106814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovantseva, N.; Fitzpatrick, C. Barriers to electronics reuse of transboundary e-waste shipment regulations: An evaluation based on industry experiences. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 102, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridho, H.; Thamrin, M.H.; Nasution, F.A.; Indainanto, Y.I. Disposition of Waste Management Policy Implementers Through the Regional Cooperation Scheme. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2023, 18, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vomacka, V. Desperate, Determined, Dumped: Fight against illegal waste treatment in the Czech Republic. J. Agric. Environ. Law 2024, 19, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, N.; Park, Y.S.; Jeon, T.W. An improved strategy for effectively managing the transboundary movement of waste based on the basel convention: A case study in South Korea. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, A.; Shahzad, F.; Rehman, I.U.; Sergi, B.S. A systematic literature review of blockchain technology and environmental sustainability: Status quo and future research. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2023, 88, 1602–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, B.; Zou, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, Z.; He, Y.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, X. Coevolution mechanism of remanufacturer–construction enterprise–public in construction and demolition waste resource utilization projects under green value co-creation. Buildings 2024, 14, 2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Liu, S.; Zeng, L.; Peng, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, X. Leader and employee behavioral decision-making in construction and demolition waste recycling projects under psychological contract theory. Buildings 2024, 14, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Li, X. Operational Decisions of Construction and Demolition Waste Recycling Supply Chain Members under Altruistic Preferences. Systems 2024, 12, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zuo, J.; Yuan, H.; Zillante, G.; Wang, J. Cross-regional mobility of construction and demolition waste in Australia: An exploratory study. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 156, 104710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Wong, A.B.; Liao, Y.; Zuo, J. Self-fulfillment degree of construction and demolition waste management capability based on the Triple-balance theory: A case study of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Waste Manag. 2021, 133, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, X.; Xie, J.; Zheng, M.; Chen, L.; Yu, F. Examining the evolution trajectory of construction and demolition waste in China: An empirical analysis based on spatial metrology and the environmental Kuznets curve. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 478, 143847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, N. Towards synergistic effect: Spatiotemporal evolution and convergence of construction waste and carbon reduction efficiency. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2025, 12, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struk, M.; Bakoš, E. Long-term benefits of intermunicipal cooperation for small municipalities in waste management provision. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borbon-Galvez, Y.; Curi, S.; Dallari, F.; Ghiringhelli, G. International industrial symbiosis: Cross-border management of aggregates and construction and demolition waste between Italy and Switzerland. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 25, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Yuan, H.; Wu, H. Collaborative mechanism for promoting the cross-regional management of construction and demolition waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 372, 133706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yin, W.; Yi, B.; Xu, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, X. Evolutionary mechanism of government green development behavior in construction and demolition waste recycling projects: A perspective of ecological compensation. Buildings 2023, 13, 1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Lee, W.M.; Bao, Z.; Chi, B.; Webster, C. Cross-jurisdictional construction waste material trading: Learning from the smart grid. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Duan, H.; Yu, D.; Zeng, X. Characterizing the transboundary movements of UEEE/WEEE: Is Macau a regional transfer center? J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 157, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Tan, H.; Xie, J.; Xia, Z.; Liu, Y. Design and simulation of a cross-regional collaborative recycling system for secondary resources: A case of lead-acid batteries. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Peng, F.; Xie, J.; Liu, Y. Agent-based modeling for an end-of-life power battery cross-regional recycling system and subregional policy analysis: A case study in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 441, 141054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.W. Electronic waste governance under “one country, two systems”: Hong Kong and mainland China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuly, K.; Fitzpatrick, C. Understanding the Impacts of Transboundary waste shipment policies: The case of plastic and electronic waste. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, P.; Kumar, S. Evaluation of e-waste status, management strategies, and legislations. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 6957–6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagnoni, M.; Grazzi, M.; Pieri, F.; Tomasi, C. Extended producer responsibility and trade flows in waste: The case of batteries. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2025, 88, 43–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faradillah, P.; Sultan, A.A.M.; Samat, K.F.; Kamarulzaman, T. Strengthening e-waste governance: A decision framework for sustainable transboundary movements under the Swiss-Ghana Amendments. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2025, 23, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Sun, X.; Hao, H. Transboundary trade poses regulatory challenges for EV battery recycling. Environ. Res. Lett. 2025, 20, 091006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramusch, R.; Pertl, A.; Scherhaufer, S.; Schmied, E.; Obersteiner, G. Modelling informally collected quantities of bulky waste and reusable items in Austria. Waste Manag. 2015, 44, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, M.; Shan, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J.; Fang, W.; Ma, Z.; Wang, J.; et al. Large virtual transboundary hazardous waste flows: The case of China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 8161–8173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Chou, M.C.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y. Location and transportation joint decisions for infectious medical waste in sustainable supply chains during a pandemic: A bi-level optimization approach. Ann. Oper. Res. 2025; 1–49, early online. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, M. Digital twin-driven robust bi-level optimisation model for COVID-19 medical waste location-transport under circular economy. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 186, 109107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, J. Bi-level multi-objective programming approach for bioenergy production optimization towards co-digestion of kitchen waste and rice straw. Fuel 2022, 316, 123117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, L.; Li, F.; Kharrazi, A.; Bai, Y. Regional footprints and interregional interactions of chemical oxygen demand discharges in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 132, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukopová, J.; Mikušová-Meričková, B.; Nemec, J.; Šumpíková, M. Institutional factors determining costs of municipal waste management in the Czech Republic. Waste Manag. 2022, 144, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guggisberg, S. Finding equitable solutions to the land-based sources of marine plastic pollution: Sovereignty as a double-edged sword. Mar. Policy 2024, 159, 105960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andoh, C.N.; Donkor, P.; Aboagye, J. Ghana’s environmental law and waterbody protection: A critical assessment of plastic pollution regulations. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 380, 125172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smakgahn, K. Transboundary Trade in Plastic Waste and Environmental Concerns: A Case Study from Thailand. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2025, 24, D1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, E.; Tiller, R.; Oftebro, T.L.; Throne-Holst, M.; Normann, A.K. Orchestration within plastics governance–From global to Arctic. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 197, 115635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deus, R.M.; Battistelle, R.A.G.; Silva, G.H.R. Scenario evaluation for the management of household solid waste in small Brazilian municipalities. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2017, 19, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmo, F.C.; Simao, N.; Nebra, S.; Santana, P.D.M. Energy recovery from municipal solid waste of intermunicipal public consortia identified in São Paulo State. Waste Manag. Res. 2019, 37, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukopová, J.; Vaceková, G. Internal factors of intermunicipal cooperation: What matters most and why? Local Gov. Stud. 2018, 44, 105–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P. The costs and environmental justice concerns of NIMBY in solid waste disposal. J. Assoc. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2023, 10, 607–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Yuan, H. Impacts of tax refund on enterprise’s decisions on recycled materials production: A cross-regional perspective. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 167, 108035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.; Zhu, X.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X. Evaluating Pollution Reduction and Carbon Mitigation in China’s Zero-Waste Cities. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S. Trade for the environment: Transboundary hazardous waste movements after the Basel Convention. Rev. Policy Res. 2020, 37, 713–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, K.; Vermeulen, W.J.; Deutz, P.; Olayide, O.E. Transboundary movement of waste review: From binary towards a contextual framing. Waste Manag. Res. 2023, 41, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijethilake, C.; Adhikari, P.; Upadhaya, B. Regulatory Capture in Transboundary Waste Dumping:(Lack of) Accountability in the Global North–South Context. Organ. Environ. 2024, 37, 84–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shen, C.; Wei, J.; Niu, Y. Study of ecological compensation in complex river networks based on a mathematical model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 22861–22871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Han, C.; Meng, L.; Shao, Z.; Liu, P. Ecological compensation for cross-regional domestic waste treatment: A stochastic differential game perspective. Waste Manag. Res. 2025, 43, 1301–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafra-Gómez, J.L.; López-Pérez, G.; Garrido-Montañés, M.; Zafra-Gómez, E. Cost efficiency in municipal solid waste (MSW): Different alternatives in service delivery for small and medium sized Spanish local governments. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gao, M. Spatial correlation network of municipal solid waste carbon emissions and its influencing factors in China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 106, 107490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, H.; Asami, Y. Estimating the minimal efficient scale and the effect of intermunicipal cooperation on service provision areas for waste treatment in Japan. Asia-Pac. J. Reg. Sci. 2020, 4, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafra-Gómez, J.L.; Chica-Olmo, J. Spatial spillover effect of delivery forms on cost of public services in small and medium-sized Spanish municipalities. Cities 2019, 85, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Kong, L. Evaluation of carbon and economic benefits of producing recycled aggregates from construction and demolition waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 425, 138946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankhi, I.J.; Hossain, G.A.; Faisal, A.K.M.; Hasan, M.R.U.; Barua, S.; Masud, M.H. Material flow analysis and risk evaluation of informal and formal E-waste recycling processes in Bangladesh: Towards sustainable management strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 497, 145090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Song, X.; Yang, D.; Li, B.; Lu, B. Simulating the interprovincial movements of waste mobile phones in China based on the current disassembly capacity. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, N.; Hossain, M.I. Structure, actors, and interdependencies between informal and formal e-waste management supply chain in Bangladesh. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 522, 146146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Shukla, O.J. Unravelling sustainable impediments in E-waste supply chain management: A Fuzzy-WINGS decision approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 389, 126208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.L.; Behdad, S. From present to future: A review of e-waste recycling processes. Waste Manag. 2025, 204, 114863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, R.J.; Nixon, J.D.; Brusey, J. Using multi-objective optimisation with ADM1 and measured data to improve the performance of an existing anaerobic digestion system. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padilla-Rivera, A.; Morgan-Sagastume, J.M.; Noyola, A.; Güereca, L.P. Addressing social aspects associated with wastewater treatment facilities. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2016, 57, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Shi, S. Resolving the dilemma of wastewater treatment plants: An empirical study on public acceptance for publicly accessible WWTPs. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 475, 143674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotan, P.; Yeshayahu, M.; Odeh, W.D.; Gordon-Kirsch, N.; Groisman, L.; Al-Khateeb, N.; Rabbo, A.A.; Tal, A.; Arnon, S. Endocrine disrupting compounds in streams in Israel and the Palestinian West Bank: Implications for transboundary basin management. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 204, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Jiang, L.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y. Cross-Administrative Integrated Compensation for Urban Domestic Wastewater Treatment Facilities: A Theoretic Framework and Case Study in China. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Water Resource and Environment, Matsue, Japan, 21–24 November 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.W.M.; Ho, L.K.K. Environmental collaboration within a country? Tackling cross-border electronic waste movement between Mainland China and Hong Kong. China Int. J. 2021, 19, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law No.12305-Brazilian National Policy on Solid Waste. Available online: https://braziliannr.com/brazilian-environmental-legislation/law-no-12305-brazilian-national-policy-solid-waste/ (accessed on 27 November 2025).
- Ahmad, Z.; Esposito, P. Collaborative Governance for Social Change and Environmental Sustainability: A Case Study of Campania Region. Adm. Sci. 2025, 15, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Electronic Waste Recycling Act of 2003. Available online: https://calrecycle.ca.gov/electronics/statutes/ (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Battery Stewardship. Available online: https://calrecycle.ca.gov/EPR/batteries/ (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Mim, S.J.; Richter, A.; Gitifar, A.; Chowdhury, R.; Ng, K.T.W. The use of efficiency metrics for cross-jurisdictional assessment of household hazardous waste collection and recycling. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 503, 145420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Zuo, J.; Li, J. Key policies to the development of construction and demolition waste recycling industry in China. Waste Manag. 2020, 108, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Peng, J.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Gao, P.; Zhu, X.; Li, X. Pricing decisions in construction and demolition waste recycling supply chains under carbon tax scenarios. Systems 2024, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, J.; She, S. Green governance of global shipbreaking: Key problems and reform pathways. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 533, 146995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, Z.; Khan, F. The effects of green human resource management practices on sustainable performance: The mediating role of green climat and green employee empowerment. Turk. Online J. Qual. Inq. 2021, 12, 1381–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notice Concerning the Issuance of the Administrative Measures for Construction Waste Transfer Consignment Notes in Guangdong Province. Available online: https://www.gd.gov.cn/zwgk/gongbao/2024/24/content/post_4518585.html (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Lou, C.X.; Shuai, J.; Luo, L.; Li, H. Optimal transportation planning of classified domestic garbage based on map distance. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 254, 109781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, P.H.; Keuschnigg, C. Resource dependence, recycling, and trade. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2024, 128, 103064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, X. Optimizing on-site sorting of construction and demolition waste with blockchain and subsidy policy: A differential game approach. Eng. Constr. Arch. Manag. 2025; 1–30, early online. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zuo, J.; Zillante, G.; Wang, J.; Yuan, H. Status quo and future directions of construction and demolition waste research: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 118163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmi, O.; Hukkinen, J.; Heino, J.; Pajunen, N.; Wierink, M. Governing the Interplay between industrial ecosystems and environmental regulation: Heavy industries in the Gulf of Bothnia in Finland and Sweden. J. Ind. Ecol. 2012, 16, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Longfor, N.R.; Dong, L.; Qian, X. Beyond theory of planned behavior: A meta-analysis of psychological and contextual determinants of household waste separation. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2026, 116, 108087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Ding, Z. Optimal supply chain performance: Risk aversion to green innovation. Manag. Decis. 2024, 62, 3996–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
