Abstract
Rapid expansion of global transportation infrastructure leads to the accumulation of vast quantities of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP). Recycling RAP is essential for reducing environmental impacts. However, current recycling practices typically limit RAP content to below 30%. Increasing RAP content in asphalt mixtures—especially beyond 50%—offers a more sustainable approach, but also introduces challenges in performance, design, and implementation. This study presents a case in which the hot central plant recycling asphalt mixture containing 50% RAP, enhanced with an active rejuvenating agent, was used for the lower layer of the Jianghe Expressway. The aggregate gradation was designed using the Marshall method, with the optimal asphalt–aggregate ratio determined to be 3%. The average compaction degree was 98.9%, the infiltration coefficient ranged from 6.43 mL/min to 23.77 mL/min, and the standard deviation of flatness did not exceed 1.0. However, material shoving was observed during paving, suggesting that, with appropriate adjustments, the technique can be optimized for large-scale implementation. The gradation of the RAP material showed minimal deviation from the design gradation, remaining within ±5%. The compaction scheme with eight roller passes and a loose paving coefficient of 1.35 yielded superior compaction performance.
1. Introduction
Global road networks are expanding rapidly, increasing the length of highways needing annual maintenance. This process generates roughly 120 million tons of discarded asphalt mixture each year [1]. Consequently, the accumulation and idle storage of asphalt pavement waste has led to growing concerns regarding land use and environmental issues [2,3]. To address these problems, extensive experiments and research have been conducted on asphalt pavement reuse [4,5,6]. The application of asphalt pavement recycling technologies has significantly reduced construction costs and conserved large quantities of natural aggregates, asphalt binder, and other raw materials, thus offering notable environmental and economic benefits [7,8,9,10]. In hot central plant recycling, RAP content typically ranges from 10% to 30% [11,12,13]. Within this range, the plant-mixed recycled asphalt mixture can achieve road performance comparable to that of virgin mixtures [14,15], with significantly improved rutting resistance [12,16,17,18]. Therefore, asphalt pavement recycling is considered a feasible and sustainable method for modern road construction.
Increasing the proportion of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) significantly enhances the economic and environmental benefits of hot recycling [19,20,21,22,23]. As a result, the research and application of high-RAP-content mixtures (RAP ≥ 30%) have become a major focus in the development of hot recycling technologies [24,25,26,27]. The use of RAP technology enables the effective recycling of asphalt resources, and also reduces the consumption of non-renewable materials such as virgin asphalt. Research reported that producing asphalt mixtures with 30% RAP content requires only 84% of the energy and results in 80% of the CO2 emissions compared to virgin mixtures [28]. Through the high-speed reconstruction case from Bengbu to Hefei, Li found that 30% RAP materials can save approximately 1.5 to 18 million CNY and reduced ash emissions by 17.6 tons per kilometer of pavement [29]. Therefore, it is promising to study high-RAP-content asphalt mixtures, which can significantly reduce energy consumption and construction funds and can generate significant economic benefits [19].
However, high proportions of RAP in asphalt mixtures can adversely affect crack resistance [30], fatigue resistance [31], and water-damage resistance [31]. While elevated RAP content has been associated with improvements in rutting resistance [31], it compromises long-term durability by increasing susceptibility to embrittlement and surface spalling [32]. In addition, current guidelines do not adequately address the variability of high RAP content and the proportion of newly introduced asphalt mixtures. Although prior studies have demonstrated feasibility in laboratory settings, uncertainties persist regarding the consistency of mechanical properties and constructability when RAP content exceeds 30% [33]. These knowledge gaps are especially critical given the need to scale sustainable paving practices in settings.
Asphalt recycling is conventionally classified into four principal methods: hot central plants recycling, hot in-place recycling, cold recycling at central facilities, and cold in-place recycling [34]. By testing key parameters, such as the aging degree of the reused asphalt, asphalt content, moisture content, and aggregate gradation, and conducting reasonable mix design, hot central plant recycling effectively control of the quality of the recycled asphalt mixture can be effectively ensured [13,35,36,37]. Therefore, compared to other recycling methods, hot central recycling is more suitable for high-content RAP while maintaining the quality of the mixture, making it the preferred method for sustainable pavement construction and rehabilitation [34]. In addition, combining laboratory and field testing in the evaluation of asphalt mixtures is essential to ensure that material design translates into reliable in-service performance. As noted by Jin, cold in-place recycling (CIR) asphalt pavements often exhibit high air void content due to residual moisture during field construction, which plays a critical role in determining their service life [38,39].
Despite its limitations, the Marshall method remains one of the most widely used approaches for asphalt mixture design and evaluation [40,41]. Extensive engineering practice has demonstrated that Marshall stability and flow values effectively reflect the shear deformation resistance of mixtures under ambient conditions, making the method particularly suitable for the quality control of dense-graded asphalt mixtures. Its statistical correlation with pavement rutting has been confirmed by numerous studies [42,43]. As a classic method for asphalt mixture design, the Marshall method has been incorporated into well-established standard systems, such as ASTM D6927 [44] and JTG E20-2011 [45]. Its testing procedures—including specimen preparation, compaction, and measurement of stability and flow—are highly repeatable, facilitating reliable inter-laboratory comparisons.
Based on the above background, this research explores high-RAP-asphalt recycling for pavement construction. There is no consensus on the widespread use of high-content RAP asphalt materials. The Jianghe Expressway expansion project provides 50% RAP empirical data, which provides a reference for large-scale construction. The primary objectives of this research are as follows:
- (1)
- Mix design of hot mix asphalt with high RAP content. Based on the material composition analysis of recycled mixtures, a 50% RAP incorporation scheme is designed using the Marshall method to evaluate the engineering performance of the recycled mixture.
- (2)
- Evaluation of aggregate gradation and asphalt content in high-RAP-content asphalt mixtures.
- (3)
- Assessment of field performance indicators of the high-RAP-content asphalt test section, including surface smoothness, layer thickness, and permeability coefficient.
2. Materials
The asphalt mixture produced and studied in this project is hot central plant recycling ATB-25 dense-graded asphalt-treated base (ATB) mixture, incorporating 50% reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP).
2.1. Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement
The characteristics of RAP, such as the aging degree of the aged binder and the fragmentation of coarse aggregates, have a significant impact on the performance of recycled asphalt mixtures [46]. In this study, RAP was obtained from the milled surface of the Jiangmen–Heshan section of the Jianghe Expressway (Jiangmen, Guangdong, China). According to the test method specified in JTG 5521-2019, the maximum particle size of the RAP material was 19.0 mm, meeting the specification requirements. The RAP material was pretreated using an XCMG XPSL25 crushing and screening unit, and separated into three size ranges: 0–6 mm, 6–12 mm, and 12–22 mm. The gradation results of the RAP are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
RAP gradation results.
During construction, the gradation and aged binder content of RAP materials may fluctuate. Therefore, it is necessary to adjust the production mix ratio to ensure the stability of the recycled mixture and the asphalt–aggregate ratio. The technical specifications of the RAP-recycled asphalt are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Physical properties of the recycled asphalt.
The penetration of the recycled asphalt is 32, and its ductility is only 10 cm, indicating severe aging of the asphalt binder after more than a decade of use.
2.2. Asphalt
The asphalt is Esso Grade A 70# road petroleum asphalt provided by Dongguan Taihe Co., Ltd (Dongguan, Guangdong, China). The properties of the asphalt were evaluated in accordance with the Chinese standard JTG E20-2011. The properties are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Properties of asphalt.
2.3. Aggregate
The coarse and fine aggregates were sourced from Guangxi Guohao Building Materials Co., Ltd. (Laibing, Guangxi, China), consisting of crushed stone and manufactured sand. The specifications for the coarse aggregates were 10–25 mm, 10–20 mm, 5–10 mm, and 3–5 mm, while the fine aggregates had a size range of 0–3 mm. The coarse and fine aggregates test results are shown in Table 4 and Table 5.

Table 4.
Properties of the coarse aggregate.

Table 5.
Properties of the fine aggregate.
2.4. Mineral Powder
The mineral powder used was produced by Xinda Quarry in Jinji Town, Luoding City, Guangdong Province, China. The apparent density, moisture content, gradation composition, hydrophilicity, and plasticity of the mineral powder were tested, as shown in Table 6.

Table 6.
Properties of the mineral powder.
2.5. Additive
The asphalt additive used is the OP-1100 type produced by Shenzhen Haichuan New Materials Technology Co., Ltd., (Shenzhen, Guangdong, China). It is a brown liquid composed primarily of modified alkyl amine polyamine, exhibiting a viscous-flow state at room temperature. It is an active additive, with an addition ratio of 5% based on the recommendation of the regenerator manufacturer. The effectiveness of the regenerant has been confirmed in previous studies [47]. The properties of the additive are presented in Table 7.

Table 7.
Properties of additive.
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Plan
The test section constructed during this study is part of the highway renovation and expansion project in Jiangmen City, Guangdong Province, China. The total length of the test section is 800 m, with a paving width of 11.25 m. The project utilized a hot central plant recycling ATB-25 asphalt mixture with a thickness of 12 cm and 50% RAP content, with an estimated volume of approximately 675 m3. The test section was used to validate whether the technical properties and production mix ratio of the asphalt mixture met the required standards, providing guidance for large-scale construction.
As shown in Figure 1, an XCMG XARP325H hot recycling asphalt mixing plant (Xuzhou Construction Machinery Group Co., Ltd., Xuzhou, Jiangsu, China) was used during the construction of the test section. Each mixing batch produced 4.5 tons, with an hourly production capacity of approximately 261 tons. During the asphalt mixture mixing phase, the heating temperature of the asphalt was maintained between 155 °C and 165 °C, with the new material heated to approximately 190 °C and the RAP material heated to around 130 °C. The mixing process of the hot central plant recycling asphalt mixture is presented in Table 8.

Figure 1.
XCMG XARP325H asphalt mixing equipment used in this study.

Table 8.
Mixing process of ATB-25 recycled mixture.
During the construction of the test section, the heating temperature of the RAP material was 130 °C. In the production process, the emission of white smoke was considered normal, while the blue smoke indicated an abnormal condition. In such cases, the temperature should be checked to ensure compliance with the requirements. Figure 2 presents the mix production temperature. If the temperature is too high or if carbonization occurs, mixtures with bubbling or moisture content are discarded. The temperature of the hot central plant recycling ATB-25 mixture is shown in Table 9.

Figure 2.
Measure the mix production temperature.

Table 9.
Mix production temperature standard.
After the paving was completed, core samples were taken from the site to detect key indicators such as layer thickness, stratification, compaction, and air voids, ensuring the uniformity of the samples and evaluating whether the construction quality met the design requirements. For laboratory testing, asphalt samples were directly collected from the asphalt plant for analysis and testing.
3.2. Testing Methods
The selection of test methods was guided by the “Technical Specifications for Construction of Highway Asphalt Pavements”—JTG F40-2004 [48]. To ensure consistency with the primary objectives of this study, Chinese standard testing methods were employed. The testing of asphalt mixtures was conducted in three main phases. The first phase focused on the mix design, where the Marshall mix design method was employed, which included both the production mix and the target mix. The goal was to calculate the optimal proportions of various materials and to determine the optimum asphalt content through the Marshall mix design method. The second phase involved quality testing of the asphalt mixture using samples taken from the paved material. The testing focused on both Marshall specimen indicators and the road performance of the asphalt mixture. Marshall stability and flow values were measured in accordance with Chinese Standard T 0709-2011. The third phase was the in situ pavement quality assessment conducted after completion of the 800 m test section. This evaluation focused on three aspects: pavement thickness and compaction, water permeability coefficient, and surface smoothness.
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Marshall Mix Design Method
The Marshall mix design method has become the most widely adopted and technically mature approach for hot mix asphalt (HMA) design globally, owing to its straightforward theoretical framework, clear specification requirements, and relatively affordable testing equipment [49]. As a typical volumetric design method, it optimizes asphalt mixtures by evaluating key parameters such as flow value, density, and air voids while accounting for rheological properties under high-temperature conditions. However, this method is only applicable to continuously graded asphalt mixtures.
The Marshall design system comprises three sequential phases: target mix design, production mix design, and production mix verification. This comprehensive framework addresses critical factors including aggregate selection, gradation optimization, and asphalt content determination.
4.1.1. Grading Curve Design
This study adopted the Marshall design method, controlled the content of RAP material at 50%, and carried out mix design for the hot central plant recycling ATB-25 asphalt mixture. At the same time, the current “Technical Specifications for Highway Asphalt Pavement Construction” (JTG F40-2004) was referred to determine the gradation curve. The RAP gradation and aggregate gradation are presented in Table 10. The gradation curve is shown in Figure 3.

Table 10.
Aggregate gradation for target mix ratio.
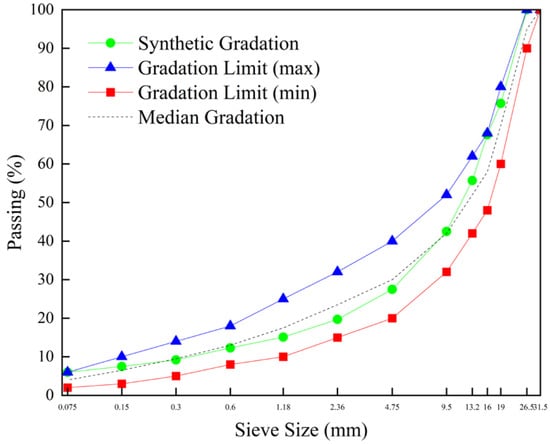
Figure 3.
Gradation curve of the aggregate for the target mix design.
The target mix proportion was determined as follows (by mass ratio): 12~22 mm (RAP): 6~12 (RAP) mm: 0~6 mm (RAP): 10~25 mm: 10~20 mm: 5~10 mm: 3~5 mm: 0~3 mm: mineral filler = 36:3:11:30:4:7:5:3:1. A rejuvenator was added at 5% of the aged asphalt binder weight. Following Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering (T 0623), the target mix design was validated by preparing slab specimens (300 mm × 300 mm × 50 mm) for wheel tracking tests. Under a wheel pressure of 0.7 MPa and a temperature of 60 °C, the dynamic stability reached 5733 passes/mm, confirming compliance with design and specification requirements. The Marshall test results of the target mix design are shown in Table 11.

Table 11.
Marshall test results for the target mix design.
4.1.2. Determination of the Optimal Asphalt Dosage
This study employed the Marshall design method to determine the optimal asphalt content. In accordance with the current Technical Specifications for Construction of Highway Asphalt Pavements (JTG F40-2004), the mix design requirements typically adopt a flexible approach for establishing the optimum asphalt content. Throughout this process, particular emphasis was placed on incorporating proven local construction experience.
Based on the synthesized gradation of the mixture, this study referenced both the specification guidelines and practical engineering experience to establish an appropriate asphalt content range for the ATB-25 asphalt mixture. Laboratory Marshall tests were conducted, from which the optimal asphalt–aggregate ratio was determined to be 3.0%, with a corresponding air void content of 4.9%.
According to the target mix design, the blending ratios of newly added aggregates were determined through sieving analysis. The gradation of each aggregate component was tested, and based on the specification requirements the production mix gradation curve was adjusted to closely match the target mix gradation curve. This principle was followed to determine the proportions of materials in each hot bin, which were then provided to the mixing plant control room for implementation. The determined proportions for each bin in the production mix were as follows: 12–22 mm (RAP): 6–12 mm (RAP): 0–6 mm (RAP): 10–25 mm: 10–20 mm: 5–10 mm: 3–5 mm: 0–3 mm: mineral filler = 30:17:3:21:18:5:5:5:1. The corresponding gradation curve is illustrated in Figure 4.
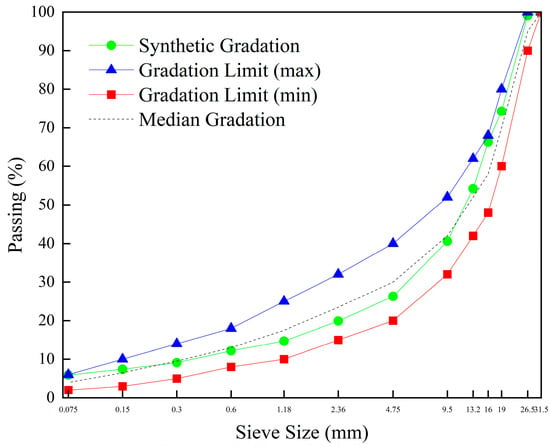
Figure 4.
Gradation curve of the aggregate for the production mix design.
Based on the Marshall test results, the optimum asphalt–aggregate ratio was determined to be 3%, considering only the proportion of newly added asphalt. The corresponding air void content was 4.3%. Detailed Marshall test data are presented in Table 12.

Table 12.
Marshall test results for the production mix design.
4.2. Mixture Gradation and Performance Testing
4.2.1. Combustion Test and Screening Test of Asphalt Mixture
On the day of paving the hot central plant recycling ATB-25 asphalt mixture, two samples were collected for ignition and sieve analyses to determine the gradation and asphalt content of the mixture. The results of the two tests were then compared. The main procedure involved heating the asphalt mixture in an ignition furnace. Since asphalt is primarily composed of hydrocarbons, it decomposes into gases under high-temperature combustion, allowing for the separation of asphalt from the mineral aggregates. Figure 5 and Table 13 present the ignition test results for aggregate gradation and asphalt–aggregate ratio, respectively.
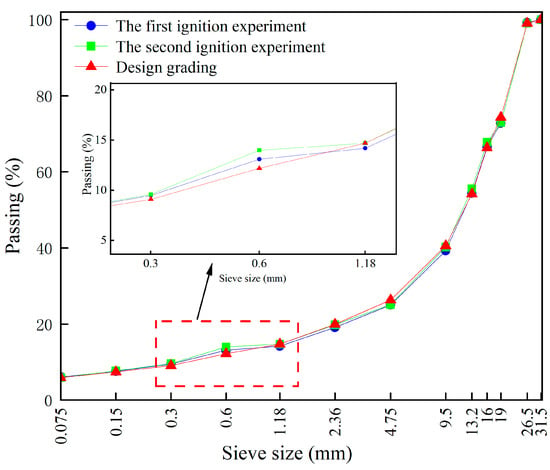
Figure 5.
Aggregate gradation results after ignition of pavement samples.

Table 13.
Asphalt–aggregate ratio results from the ignition test.
The results indicate that sampling and testing of the hot central plant recycling ATB-25 mixture confirmed that key quality indicators, including aggregate gradation and asphalt–aggregate ratio, complied with the design requirements specified in the Technical Specifications for Construction of Highway Asphalt Pavements (JTG F40-2004) for ATB-25 mixtures. Specifically, in terms of gradation control the measured passing rates for key sieves (including 31.5 mm, 26.5 mm, 19 mm, 16 mm, 13.2 mm, 9.5 mm, 4.75 mm, 2.36 mm, 1.18 mm, 0.6 mm, 0.3 mm, 0.15 mm, and 0.075 mm) deviated by no more than ±3% from the target gradation curve. Moreover, fluctuations in the passing rates of the critical control sieves (4.75 mm, 2.36 mm, and 0.075 mm) were strictly maintained within ±2%. The test results for the asphalt–aggregate ratio showed that the absolute deviation between the measured and designed values did not exceed ±5%, meeting the specification requirements. The deviation of the gradation is lower than 5% to ensure the RAP material integrates effectively with virgin materials. This control is particularly significant in high-RAP-content mixtures, where variability can have amplified effects on long-term performance and durability.
4.2.2. Marshall Test
Therefore, on the day of paving the hot central plant recycling ATB-25 test section, representative samples were uniformly collected from the mixture for the preparation of Marshall specimens. Their volumetric and mechanical properties were subsequently tested, and the results are presented in Table 14.

Table 14.
Marshall test results of asphalt mixture.
4.3. Road Quality Inspection
4.3.1. Material Shoving
Compaction is a critical process to ensure the density, smoothness, and structural load-bearing capacity of asphalt mixtures. During compaction, shoving of asphalt mixtures typically occurs around the contact area between the roller and the asphalt surface, where horizontal forces cause the mixture to flow forward and laterally. This results in visible wheel marks and bulges, and in severe cases, wave-like deformations, heaving, and fine surface cracks. Shoving is commonly observed in dense-graded asphalt mixtures during compaction, primarily due to insufficient interlocking between aggregates to resist the horizontal forces exerted by the roller.
After the occurrence of pavement shoving deformation, as shown in Figure 6a, on-site investigations and structural evaluations identified two primary causes: (1) The tamper frequency of the paver was too low, resulting in insufficient compaction energy and an excessively high loose paving coefficient. (2) The asphalt mixture was excessively hot, which increased its fluidity and reduced its cohesion. The following corrective measures were implemented: (1) adopting a lower loose paving coefficient; (2) reducing the production temperature of the asphalt mixture. As shown in Figure 6b, these measures effectively reduced shoving deformation and significantly improved pavement smoothness.

Figure 6.
Pavement shoving. (a) Effects before taking measures. (b) Effects after taking measures.
4.3.2. Pavement Thickness Detection
As a key indicator of highway construction quality, compaction degree directly reflects potential construction issues. Asphalt pavement construction requires strict control of compaction; insufficient compaction may prevent the asphalt mixture from forming an effective aggregate skeleton, which can lead to a range of pavement defects, compromising both safety and service life and ultimately reducing the overall economic and social benefits of the highway project. In this study, two paving schemes were implemented: Scheme I used a loose paving coefficient of 1.30 and seven passes of compaction while Scheme II adopted a loose paving coefficient of 1.35 and eight passes. After paving, six core samples were extracted from each scheme, with samples No. 1–6 corresponding to Scheme I, and No. 7–12 to Scheme II. Based on laboratory tests, the maximum theoretical density of the hot central plant recycling ATB-25 asphalt mixture was 2.580 g/cm3, while the Marshall test density was 2.460 g/cm3. The compaction degree and air void ratio of the core samples were calculated accordingly, and the results are presented in Figure 7.
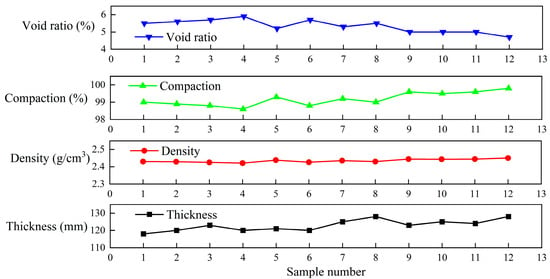
Figure 7.
Pavement thickness and compaction test results.
The trends observed in void ratio, compaction, density, and thickness are mechanistically consistent with established principles of asphalt mixture behavior. As compaction increased, the void ratio correspondingly decreased. This inverse relationship is a direct result of improved aggregate packing and reduced entrapped air. For example, Sample 12 exhibited the highest compaction (99.8%) and the lowest void ratio (4.7%), while Samples 3–4 showed lower compaction (98.6%) and the highest void ratios (5.9%). This trend underscores the role of compaction effort in controlling internal air voids, which directly influences mixture durability and mechanical performance.
Density, another key indicator of mixture integrity, was positively correlated with compaction and negatively with void ratio. Samples with higher compaction levels consistently exhibited increased density values, indicating enhanced structural uniformity. This behavior reflects improved aggregate interlock and minimized porosity under effective compaction. For instance, the density increased steadily from ~2.42 g/cm3 in Sample 1 to ~2.45 g/cm3 in Sample 12, aligning closely with observed improvements in compaction and reductions in void content.
Thickness also played a crucial mechanistic role. Thicker asphalt layers retained heat longer during construction, allowing for more effective and prolonged compaction. This resulted in better densification and lower void content. In contrast, thinner layers cooled rapidly, limiting compaction time and leading to higher void ratios. Notably, Sample 1, with the lowest thickness (118 mm), displayed both a high void ratio and low compaction, whereas Sample 12, with a thickness of 128 mm, demonstrated the most favorable performance across all measured parameters.
To further quantify these observations, statistical measures were applied to the experimental data. The standard deviations of the key parameters—void ratio (0.37), compaction (0.38), and density (0.001)—demonstrated relatively low variability, indicating consistent construction quality and validating the observed mechanistic trends. The standard deviation in thickness (3.23) was slightly higher, likely reflecting minor variations in paving practices rather than material behavior.
4.3.3. Water Permeability Coefficient
Early damage to asphalt pavements is closely related to water. When water infiltrates the surface layer of the asphalt pavement it generates repeated dynamic water pressure under heavy traffic loads, causing the asphalt film to gradually detach from the aggregate surface. As water infiltrates downwards it exists as free water, weakening the bonding strength between aggregates. In the first rainy season after opening to traffic, asphalt pavements may experience varying degrees of bleeding, cracking, loosening, rutting, and potholes. The permeability of the pavement structure is a critical parameter in the waterproofing and drainage design of asphalt pavements. In practice, the permeability is represented by the infiltration coefficient. In accordance with the T0730-2011 (JTG E20-2011) standards, three spaced test points at each test location were selected and subsequently the infiltration performance of the hot central plant recycling ATB-25 test section was tested, and the results are presented in Figure 8.
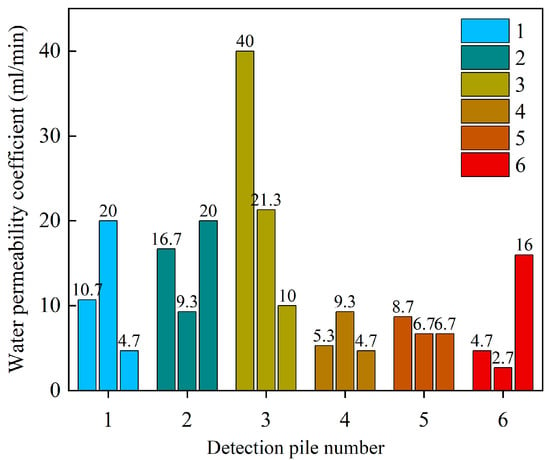
Figure 8.
Water permeability test results.
The results show that the infiltration coefficient was tested at six locations in the sublayer of the test section, with three points tested at each location. According to the specification, the infiltration coefficient at each location should not exceed 200 mL/min. The average infiltration coefficient at each test point met the design requirements, with a pass rate of 100%. The infiltration coefficient ranged from 6.43 mL/min to 23.77 mL/min. This indicates that the test section exhibits a low water permeability coefficient, suggesting adequate compaction, high mixture density, and low void connectivity, which collectively imply satisfactory resistance to moisture-induced damage.
4.3.4. Continuous Flatness Tester
Smoothness is one of the important indicators of pavement construction quality and service level. It refers to the measurement of surface irregularities using a specified standard gauge, either intermittently or continuously, indicating the level of roughness. The smoothness of the pavement is related to the evenness of the various structural layers of the pavement. The effect of smoothness at each layer accumulates and is reflected on the surface of the pavement. As the surface layer directly contacts vehicles and the atmosphere, an uneven surface increases driving resistance and causes additional vibrations in the vehicle. These vibrations can cause vehicle jolting, affecting driving speed, safety, driving smoothness, and passenger comfort. Moreover, the vibrations exert impact forces on the pavement, accelerating damage to the road and vehicle components, as well as tire wear, and increasing fuel consumption. Additionally, uneven pavement can trap rainwater, accelerating pavement deterioration. Therefore, the detection and evaluation of smoothness is a crucial aspect of highway construction and maintenance.
A continuous smoothness tester was used to assess the smoothness of the hot central plant recycling ATB-25 sublayer in the test section, and the section included four lanes, each 500 m long. Testing intervals were set at 10 cm, with each calculation section being 100 m long, and results were outputted for each section, with the results presented in Figure 9.
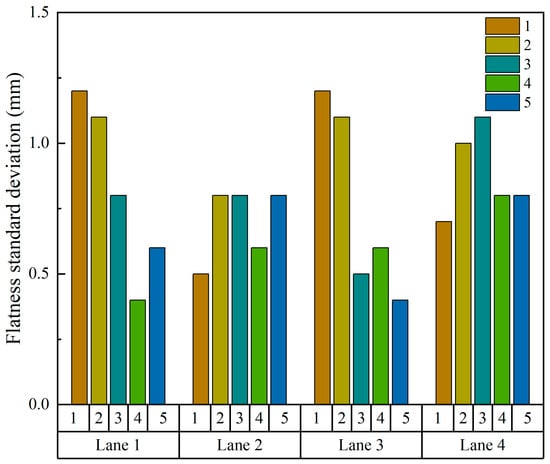
Figure 9.
Road surface smoothness test results.
The test results show that the smoothness of the four lanes was good, with average standard deviations of 0.82 mm, 0.7 mm, 0.76 mm, and 0.88 mm, respectively.
5. Conclusions
Field investigations and laboratory tests of the test section demonstrated that hot central plant recycling ATB-25 asphalt mixtures are technically feasible even with a high RAP content of 50%. In this study, the Marshall mix design method was employed to analyze re-compacted samples and core specimens extracted from the site. Various parameters, including construction temperature, gradation, Marshall stability, and in situ pavement quality, were tested. The key findings are summarized as follows:
- (1)
- The hot central plant recycling ATB-25 asphalt mixture and corresponding engineering indicators met the specification requirements, providing a practical reference for large-scale construction projects.
- (2)
- According to the Marshall mix design, the optimum asphalt–aggregate ratio for the ATB-25 mixture containing 50% RAP was determined to be 3.0%. Burn-off tests on the test section indicated a slight increase in this ratio, although it remained below 4.0%.
- (3)
- A loose paving coefficient of 1.35 with eight passes of compaction resulted in better densification than a coefficient of 1.30 with seven passes. However, the resulting core thickness was relatively large.
The findings may not directly apply to other regions or RAP materials with different aging or composition. Only Marshall-based performance and basic field quality metrics were evaluated; long-term durability under traffic (e.g., fatigue, cracking, aging effects) was not assessed. Future research will investigate economic and environmental impacts, and this will support decision-making.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Z. and H.Y.; methodology, H.Z., Y.H. and H.Y.; validation, H.Z. and Z.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.M. and H.Y.; investigation, X.X., H.Z. and Y.H.; writing—review and editing, H.Y., Z.M. and M.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant No. 52408481].
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Haiqi Zhang, Yimin Huang, Zhengquan Zhang, Xiaomiao Xiang and Mingkun Luo were employed by the company Jiangmen Jianghe Expressway Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Zahoor, M.; Nizamuddin, S.; Madapusi, S.; Giustozzi, F. Sustainable asphalt rejuvenation using waste cooking oil: A comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Bird, R.N.; Heidrich, O. A review of the use of recycled solid waste materials in asphalt pavements. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2007, 52, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victory, W. A review on the utilization of waste material in asphalt pavements. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 27279–27282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarsi, G.; Tataranni, P.; Sangiorgi, C. The challenges of using reclaimed asphalt pavement for new asphalt mixtures: A review. Materials 2020, 13, 4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadgoleh, M.A.; Mohammadi, M.M.; Ghodrati, A.; Sharifi, S.S.; Palizban, S.M.M.; Ahmadi, A.; Vahidi, E.; Ayar, P. Characterization of contaminant leaching from asphalt pavements: A critical review of measurement methods, reclaimed asphalt pavement, porous asphalt, and waste-modified asphalt mixtures. Water Res. 2022, 219, 118584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, B.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, X. Performance evaluation and feasibility study on reuse of reclaimed epoxy asphalt pavement (REAP). Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 450, 138653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkins, A.E.; Lane, B.; Kazmierowski, T. Sustainable Pavements: Environmental, Economic, and Social Benefits of In Situ Pavement Recycling. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2008, 2084, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, A. Life-Cycle Environmental and Economic Assessment of Using Recycled Materials for Asphalt Pavements. 2003. Available online: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/5jz3x91z (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- Yao, L.; Leng, Z.; Lan, J.; Chen, R.; Jiang, J. Environmental and economic assessment of collective recycling waste plastic and reclaimed asphalt pavement into pavement construction: A case study in Hong Kong. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 336, 130405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, L.F.; Mendes, L.P.T.; de Medeiros Melo Neto, O.; de Figueiredo Lopes Lucena, L.C.; de Figueiredo Lopes Lucena, L. Economic and environmental benefits of recycled asphalt mixtures: Impact of reclaimed asphalt pavement and additives throughout the life cycle. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 32, 11269–11291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ren, H.; Jin, A. Low-temperature fracture resistance of plant-mixed heat recycled asphalt mixture based on SCB. Mater. Res. Express 2023, 10, 115101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, R.S.; Shah, A.; Huber, G.A.; Copeland, A. Effects of reclaimed asphalt pavement content and virgin binder grade on properties of plant produced mixtures. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2012, 13, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, K.; Das, A. Pavement design with central plant hot-mix recycled asphalt mixes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, R.S.; Anderson, R.M. Recommended Use of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement in the Superpave Mix Design Method: Technician’s Manual; National Research Council (US): Washington, DC, USA; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. Available online: https://rosap.ntl.bts.gov/view/dot/15417 (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- Edwards, A.C.; Mayhew, H.C. Recycled Asphalt Wearing Courses. 1989. Available online: https://trid.trb.org/View/313917 (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- Servas, V.P.; Ferreira, M.A.; Curtayne, P.C. Fundamental properties of recycled asphalt mixes. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Structural Design of Asphalt Pavements, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 13–17 July 1987; pp. 455–465. [Google Scholar]
- Kandhal, P.S. Performance of Recycled Hot Mix Asphalt Mixtures, National Center for Asphalt Technology. 1995. Available online: https://books.google.com/books?hl=zh-CN&lr=&id=kYGhDODQ6ccC&oi=fnd&pg=PA19&dq=Kandhal+PS,+Rao+SS,+Watson+DE,+Young+B.+Performance+of+recycled+hot+mix+asphalt+mixtures.+NCAT+Report+No.+95-1.+National+Center+for+Asphalt+Technology,+Auburn+University,+Alabama%3B+1995.&ots=bCMtvRNW0f&sig=zAP2qE5QaXIt_vt0UmMzlcLfvbY (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- Malpass, G.A. The Use of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement in New Superpave Asphalt Concrete Mixtures, North Carolina State University. 2003. Available online: https://search.proquest.com/openview/8541e0c12491948bfdbc20ff1fb6a844/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=18750&diss=y (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- Aurangzeb, Q.; Al-Qadi, I.L.; Ozer, H.; Yang, R. Hybrid life cycle assessment for asphalt mixtures with high RAP content. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 83, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Kang, S.; Ozer, H.; Al-Qadi, I.L. Environmental and economic analyses of recycled asphalt concrete mixtures based on material production and potential performance, Resources. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 104, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaumanis, M.; Mallick, R.B.; Frank, R. 100% hot mix asphalt recycling: Challenges and benefits. Transp. Res. Procedia 2016, 14, 3493–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaumanis, M.; Mallick, R.B.; Frank, R. 100% recycled hot mix asphalt: A review and analysis. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 92, 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariyappan, R.; Palammal, J.S.; Balu, S. Sustainable use of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) in pavement applications—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 45587–45606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, G.; Pérez-Jiménez, F.; Miró, R.; Martínez, A.; Botella, R. Experimental study of recycled asphalt mixtures with high percentages of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP). Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Lim, J.; Labuz, J.F. Cyclic Triaxial Testing of Recycled Asphalt Pavement and Aggregate Base. 2009. Available online: https://trid.trb.org/View/881267 (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- Bueche, N.; Dumont, A.-G.; Vanelstraete, A.; De Visscher, J.; Vansteenkiste, S.; Vervaecke, F.; Gaspar, L.; Thogersen, F. Laboratory and ALT-Evaluation of high stiffness underlayers with high percentage of re-use as developed in the NR2C-project. In Proceedings of the 4th Eurasphalt and Eurobitume Congress, Copenhagen, Denmark, 21–23 May 2008; Available online: https://infoscience.epfl.ch/entities/publication/312a3228-2d69-4f64-9d76-b32369e00917/full (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- West, R.; Kvasnak, A.; Tran, N.; Powell, B.; Turner, P. Testing of Moderate and High Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement Content Mixes: Laboratory and Accelerated Field Performance Testing at the National Center for Asphalt Technology Test Track. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2009, 2126, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Chou, C.-P.; Chen, K.-Y. Benefits in Energy Savings and CO2 Reduction by Using Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement. 2012. Available online: https://trid.trb.org/View/1129304 (accessed on 30 July 2025).
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S. A High Proportion Reuse of RAP in Plant-Mixed Cold Recycling Technology and Its Benefits Analysis. Coatings 2022, 12, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.; Cao, J.; Feng, D.; Gao, L.; Hu, W.; Yi, J. Performance evaluation of recycled asphalt mixtures with various percentages of RAP from the rotary decomposition process. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 321, 126406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Yang, F.; Cheng, M.; Wang, Y.; Amirkhanian, S.; Wu, S.; Wei, M.; Xie, J. Multi-scale performance evaluation and correlation analysis of blended asphalt and recycled asphalt mixtures incorporating high RAP content. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 317, 128278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Xu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Hou, X. Recent applications and developments of reclaimed asphalt pavement in China, 2010–2021. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2023, 37, e00697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Shen, Z.; Hao, S.; Du, M.; Hu, J. Mitigating RAP variability through detailed particle size classification: Applications in high RAP content asphalt mixtures. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 23, e04993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Chang, Z.; Jiang, W.; Han, Z.; Li, M. Hot central-plant recycling technology: A systematic review on raw materials and performance-influencing factors. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. (Engl. Ed.) 2025, 12, 1040–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, B.F.; Powell, R.B. Use of a Hot-Mix Asphalt Plant to Produce a Cold Central Plant Recycled Mix: Production Method and Performance. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2021, 2675, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, Y. Optimal percentage of reclaimed asphalt pavement in central plant hot recycling mixture. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 2010, 25, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Du, M.; Shen, Z.; Yang, F.; Han, C. RAP Variability Intelligent Control Framework for Hot in-Plant Recycling of Asphalt Pavement. Results Eng. 2025, 26, 105339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Yin, L.; Malburg, L.; You, Z. Laboratory evaluation and field demonstration of cold in-place recycling asphalt mixture in Michigan low-volume road. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e02923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Ge, D.; Chen, S.; Che, T.; Liu, H.; Malburg, L.; You, Z. Cold In-Place Recycling Asphalt Mixtures: Laboratory Performance and Preliminary M-E Design Analysis. Materials 2021, 14, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Deng, C.; Xue, J.; Chen, Z. Investigation into the performance of asphalt mixture designed using different methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 177, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakroborty, P.; Das, A.; Ghosh, P. Determining Reliability of an Asphalt Mix Design: Case of Marshall Method. J. Transp. Eng. 2010, 136, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, M.P.; Nguyen, Q.P.; Vo, H.L.; Du Nguyen, V. Marshall and Balanced mix design in determining the asphalt content for hot mix asphalt mixture: A comparative study. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Wei, L.; Zhang, J. Experimental study on performance of asphalt mixture designed by different method. Procedia Eng. 2016, 137, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D6927–15; Materials Standard Test Method for Marshall Stability and Flow of Asphalt Mixtures. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- JTG E20-2011; Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering. People’s Communication Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Gao, J.; Yao, Y.; Song, L.; Xu, J.; Yang, J. Determining the maximum permissible content of recycled asphalt pavement stockpile in plant hot-mix recycled asphalt mixtures considering homogeneity: A case study in China. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T. Development on recycling, aging simulation and regeneration methods of reclaimed styrene-butadiene-styrene modified asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG F40-2004; Technical Specifications for Construction of Highway Asphalt Pavements. The Industry Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2004.
- Asi, I.M. Performance evaluation of SUPERPAVE and Marshall asphalt mix designs to suite Jordan climatic and traffic conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).