Abstract
Accurate brain tumor segmentation from 3D Magnetic Resonance Imaging (3D-MRI) is an important method for obtaining information required for diagnosis and disease therapy planning. Variation in the brain tumor’s size, structure, and form is one of the main challenges in tumor segmentation, and selecting the initial contour plays a significant role in reducing the segmentation error and the number of iterations in the level set method. To overcome this issue, this paper suggests a two-step dragonfly algorithm (DA) clustering technique to extract initial contour points accurately. The brain is extracted from the head in the preprocessing step, then tumor edges are extracted using the two-step DA, and these extracted edges are used as an initial contour for the MRI sequence. Lastly, the tumor region is extracted from all volume slices using a level set segmentation method. The results of applying the proposed technique on 3D-MRI images from the multimodal brain tumor segmentation challenge (BRATS) 2017 dataset show that the proposed method for brain tumor segmentation is comparable to the state-of-the-art methods.
1. Introduction
The American national brain tumor society noted that approximately 700,000 humans suffered from brain tumors in 2017 [1]. A brain tumor is an abandoned growth of cancerous cells inside or around the brain. These tumors are classified into two main types, i.e., benign (noncancerous) and malignant (cancerous) [2]. Knowing the tumor type can, therefore, help to understand the patient’s condition. In medical practice, the early detection and accurate recognition of brain tumors are vital. A timely diagnosis helps in the treatment procedure.
Brain biopsy and brain imaging systems are the common techniques used for the diagnosis of tumors and their cause. In open biopsies, a small hole is drilled into the skull and a tiny piece of tissue is extracted to examine the tumor under a microscope to determine its type, composition, and cause (see Figure 1). This technique is highly risky to human life. The development of medical imaging technologies has revolutionized medical diagnosis allowing doctors to detect tumors earlier and improving the prognosis. Tumor type, size, and position are now able to be determined using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans. Furthermore, MRI can differentiate soft tissue and detect small changes in tissue density and physiological mutations associated with tumors [3,4]. Moreover, an advantage of the use of MRI scans for brain tumor diagnosis is that the procedure does not rely on the use of ionizing radiation [5,6]. In general, an MRI image of the brain consists of 3D scans of the human brain or a sampling of the brain structure in three different dimensions (see Figure 2). Accurate MRI segmentation requires precise labeling of MRI image pixels, and segmentation information helps in brain tumor treatment and radiation therapy. For infected tumor tissue detection in medical imaging modalities, segmentation is employed.
Figure 1.
(Left) Example of brain image with a tumor, (right) example of biopsy process.
Figure 2.
Example of 3D Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) volume scans.
Image segmentation is one of the most popular research areas in the medical imaging domain. Because of manual contouring is time consuming, research has focused on automated contouring methods. The segmentation task attempts to obtain the location of the object of interest by contouring that object. The more variations in the appearance of the object of interest and the greater the number of irregular boundaries, the greater the difficulty of the segmentation task. Based on previous studies, there is an overlap in the intensity range of healthy and unhealthy tissues. Three dimensional images provide greater benefits than 2D images since they can provide complete information in all directions rather than having only a single 2D view [7].
Tumor detection is a challenging task due to the overlap in intensity between tumor and normal tissue, the deformation of nearby healthy tissues, and the large heterogeneity of tumors in terms of shape, position, size, and appearance [8]. Despite many exciting advances over the last decade for 3D brain tumor segmentation, numerous key problems and challenges remain. High-resolution MRI scanning requires a significant amount of memory and computational resources because of its large data size, which is issue for 3D segmentation [9].
A variety of approaches have been attempted to tackle the problem of brain tumor segmentation of 3D MRI. Two methods have been proposed to deal with volumetric input. The first of these uses the idea of natural image segmentation, where the 3D volume is cut into 2D slices, and a 2D network is then trained to process each slice individually or sequentially. The second method involves cutting the volume into patches, then training a 3D network to process these patches. In the following stage, the two methods use a sliding window to test the original volume. Both methods have advantages and disadvantages [10]. Due to varying resolutions in the third dimension of the MRI dataset, 3D-MRI images are converted into 2D slices. Within the second category, level set based segmentation is broadly used. The level set method provides a direct way to estimate the geometric properties of the evolving structure. Figure 3 shows an example of brain tumor segmentation using level set after initializing the initial contour [11,12]. The advantage of using a level set representation is its ability to represent contours of complex topology and handle various topological changes, such as merging and splitting, in a natural and efficient way. To solve this optimization problem, gradient descent is used as an effective search method within the level set technique. However, the main drawbacks of gradient descent methods are their sensitivity to local optima and slow convergence.
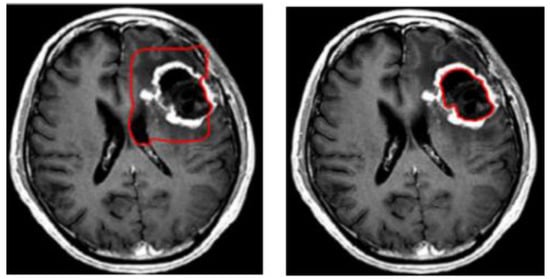
Figure 3.
Example of brain tumor segmentation using the level set method.
Recently, numerous papers have proposed an umbrella deployment of swarm algorithms for medical imaging applications. The dragonfly algorithm (DA) is one of the most recently developed swarm optimization algorithms. Many studies have shown that DA is highly effective in convergence to the optimal solution in various problems. To guarantee convergence during the optimization process, dragonflies should adaptively change their weights to transform from intensification to diversification. The neighborhood area is expanded to adjust the flying path during the progress of the optimization process and, accordingly, the swarm is unified in one group to converge to the global optimum at the final stage of the optimization process. In DA, the best solution will represent food, while the worst solution will represent the enemy. The main advantage of DA over other swarm algorithms is that DA is stable and could easily be merged with other optimization techniques. However, a lack of internal memory may lead to convergence to a local optimum. A lack of correlation between position updating and the centroid of the algorithm is one of the difficulties the user may find while using DA. This property may lead DA to converge to a local optimum and fail to locate an optimal solution [13,14,15].
1.1. Problem Statement and Motivation
Brain cancer is one of the dangerous diseases globally. Thus, early diagnosis of cancer is key to its cure. As the human brain is highly complex, the structure analysis of tumors in this region is a difficult process. Existing systems use different algorithms, such as threshold-based, model-based, and hybrid-based segmentation, which have numerous disadvantages; in particular, they are time-consuming and more inclined to mistakes. The motivation for the current work is to enhance the physician’s perception of targeted objects (i.e., tumors in the brain) because this process is subject to a number of obstacles, including a lack of detection accuracy. In order to overcome the drawbacks of existing brain tumor segmentation systems, the work presented in this paper aimed to provide an efficient model that combines two-step dragonfly algorithm-based clustering and the level set method for segmenting 3D-MRI scans.
1.2. Contribution and Methodology
This paper offers a modified bio-inspired level set segmentation technique to extract brain tumors in MRI images. The suggested model utilizes a two-step clustering technique to determine the accurate initial contour points of the level set segmentation method. This clustering technique integrates k-means and the dragonfly algorithm. In DA, instead of using a random initial position for the population centroid, k-means is used to identify the initial position. Due to the variability in the tumor’s size, form, and structure, the initial position is crucial for handling topological changes in contours. This paper suggests a two-step dragonfly algorithm clustering technique to extract initial contour points accurately. The brain is extracted from the head in the preprocessing step, then tumor edges are extracted using the two-step DA, and these extracted edges are used as an initial contour for the MRI sequence. Lastly, the tumor region is extracted from all volume slices using a level set segmentation method.
The remainder of the paper is structured as follows. In Section 2 some of the recent related works are presented. The proposed two-step DA model is described in detail in Section 3. In Section 4, we interpret our results using the multimodal brain tumor segmentation challenge (BRATS)2017 dataset. Finally, conclusions are drawn in Section 5.
2. Related Work
Over many decades, a large number of brain image segmentation approaches have been developed to find a solution to the associated optimization problem. Researchers have also made significant efforts to improve the performance of the segmentation algorithms. However, complicated image segmentation remains a difficult problem to solve. From the literature, the current brain segmentation approaches can be broadly grouped into five major categories [16,17]: (a) intensity-based segmentation, which categorizes individual pixels/voxels based on their intensity; (b) atlas-based segmentation, which labels the desired anatomy or set of anatomy from images generated by medical imaging modalities; (c) deep learning approaches, which extract representative features using convolution and pooling operations to learn the relationships between the pixels of input images; (d) model-based segmentation, which involves the formulation of a propagating interface (a closed curve in 2D and a closed surface in 3D) that changes under a speed function determined by local, global, and sovereign properties; and (e) hybrid segmentation, which combines different techniques to achieve the segmentation goal. Within the model-based segmentation category, the level set method allows segmentation to easily follow shapes that change topology [18]. Several studies have been conducted by researchers regarding MRI brain tumor segmentation techniques. An brief review of some of the recent studies is presented here; these studies used different methods, including Neural Network Models, Deformable Models, Fuzzy C-Means (FCM), Genetic Algorithms, Level Set Models, Differential Evolutionary Algorithms, Hybrid Clustering, and Artificial Intelligence [19,20].
The authors in [21] suggested a 3D-MRI brain tumor detection method based on symmetry analysis using the fast-bounding box technique followed by region growing and geodesic level set methods to acquire the final tumor. This algorithm is efficient and completely unsupervised and does not necessitate any training phase. The limitations of this method are that volumes with very low tumor size and multiple tumors have not been tested. Similarly, the authors in [22] presented an automated segmentation technique for a brain tumor in MRI by combining a rough fuzzy c-means algorithm and shape-based topological features to detect the tumor region. The advantage of the rough-fuzzy c-means approach is that it can appropriately handle the uncertainty and overlapping partitions in the datasets. However, this method requires high computation time, and the experiments were conducted on one type of tumor.
Furthermore, the authors in [23] contributed a robust system that segments brain MRI using the adaptive pillar k-means algorithm. This type of segmentation overcomes k-means clustering limitations as it shows strong sensitivity to outliers and noise. Their system used the Euclidean distance to determine the distance between an object and its cluster centroid. This robust system can determine the best initial clusters for the k-means by deploying all centroids discretely among the clusters in the data distribution. Using a similar approach, to track the poor convergence of the traditional level set segmentation towards the tumor boundary, a k-means and level set-based hybrid brain tumor segmentation technique was proposed in [24]. Despite the importance of contour initialization to the accuracy of that approach, it was randomly determined in most cases. The limitation of this method is that k-means clustering is sensitive to outliers and noise due to the random initialization of centroids.
In [25], the authors presented a new level set signed pressure function for MRI brain tumor segmentation that utilized the region-based method for the segmentation of the targeted object. Herein, the manual calculation is not needed. Therefore, it reduces the segmentation error by eliminating human error. This model can efficiently stop the contours at weak or blurred edges and works well, even if the image has an inhomogeneous region. However, this model fails to work in all tumor regions for the 3D volume and the level set’s iteration number is large, and the method is thus time consuming. The authors in [26] suggested a novel framework that provides a solution for automatic brain tumor segmentation using deep recurrent level sets. This type of level set segmentation integrates the advantages of both deep learning and level set. Overall, on the 2017 BRATS dataset, their algorithm achieved average dice scores of 0.86, 0.89, and 0.77 for the Whole Tumor (WT), Core Tumor (CT), and Enhancing core tumor (ET) regions, respectively. Moreover, the authors in [27] suggested a novel framework that combines a Deep Neural Network (DNN) with a level set method to perform sub-region segmentation for MRI brain tumor scans. They trained the DNN to classify the center pixel of the image patches according to four MRI modalities (T1, T1c, T2, and flair). The output of the DNN was then used as the initial contour for the level set method. The level set method improves the MRI image segmentation accuracy, however, DNN requires time for training.
The authors in [28] combined k-means clustering, fuzzy c-means, and active contour by level set in a unified framework for brain tumor segmentation. Herein, employing the intensity adjustment process improved the segmentation accuracy. The authors in [29] applied the same concept and compared their results with k-means, expectation-maximization, mean shift, and fuzzy c-means. Furthermore, the authors in [30] enhanced the previous work by adding an extra layer that was based on an integrated set of image processing algorithms, while the other method was based on a modified and improved probabilistic neural network structure. Simulation results showed the efficiency of this algorithm to accurately detect and identify the tumor. However, multiple tumors were not tested. The authors in [31] merged random forests and an active contour model (level set method) for segmenting volumetric MRI images. Specifically, they utilized a feature representation learning strategy to effectively explore both contextual and local information from multimodal images. Finally, a novel multi-scale patch driven active contour model was exploited to refine the inferred structure by taking advantage of sparse representation techniques. The limitation of this model is that it requires several labeled training data that were annotated by the fusion of clinical experts’ annotation and segmentation results from algorithms. Thus, the ground truth labels could be systematically biased by the algorithm results.
In recent years, optimization techniques have received significant attention from researchers. For instance, the authors in [32] contributed a new brain tumor segmentation methodology based on the ABC algorithm. Genetic algorithm-, k-means-, and fuzzy c-means-based MRI image segmentation methods were compared with the ABC-based segmentation method, and results showed that ABC-based methods performed better in both visual and numerical terms. However, ABC performs well at exploration but performs poorly at exploitation. Moreover, its convergence speed is also an issue and initial cluster centers are selected randomly. In [33], the authors suggested a new sophisticated brain tumor segmentation algorithm named the Clown Fish Queuing and Switching Optimization Algorithm (CFQSOA). The MRI scan is segmented using CFQSOA by characterizing the ecological behavior of clownfish. The results were compared with well-known other optimization algorithms. The results showed that their algorithm is a promising method for segmenting brain tumors accurately. In general, selecting the appropriate algorithm to solve a certain problem depends on the knowledge of the different algorithms available, and it should be appreciated that there is no unique optimization algorithm that can be used to solve all optimization problem. Furthermore, different configurations of an algorithm may provide better performance compared with standard values. Moreover, an adverse configuration may lead the algorithm to be trapped at a local optimum instead of the global optimum.
With the active development of deep learning, many deep learning approaches have been proposed to improve the performance of MRI image processing and analysis [34,35,36]. In [36], a Deep Neural Network (DNN) was used to automatically segment brain tumors. The DNNs are customized to segment glioblastomas (high and low grade) in MRI scans. The network exploits both global and local contextual features simultaneously. The networks use a final fully connected convolutional layer. The results from applying this approach to the BRATS 2013 dataset showed that the network architecture surpasses the state-of-the-art methods of the time. Numerous studies have been devoted to developing deep learning-based MRI segmentation applications, with some yielding promising results, Nonetheless, many challenges remain that require innovative solutions. The most challenging limitations are (1) class imbalance and small dataset size, and (2) selecting a suitable Deep Learning (DL) architecture with the consistent hyperparameters for an application.
The conducted survey showed that the 3D-MRI brain tumor detection systems have the following limitations: (a) These systems showed low accuracy when dealing with heterogeneous tumors. (b) Cluster-based segmentation systems yielded inaccurate segmentation results when processing noisy images but worked well with non-noisy images. (c) Bio-inspired techniques may be slow to converge, and are good at exploration but poor at exploitation. (d) The learning process in NN-based segmentation is poor when dealing with noisy images with a weak border of the tumor. (e) Inaccurate segmentation results are found when using level set segmentation method separately, whereas combining it with other initialization techniques improves the segmentation results. To the best of our knowledge, little attention has been paid to devising a new bio-inspired clustering technique for a brain tumor detection system that relies on a 3D-MRI.
3. Materials and Methods
In order to detect 3D-MRI brain tumors accurately, contours should be determined correctly. To achieve this goal, the proposed model fuses semantically k-means and DA optimization. Herein, the semantic fusion is achieved using k-means inside DA clustering, i.e., rather than using a random center of the mass of the neighborhood (cluster centers) within DA clustering, k-means regulate these accurately. Figure 4 shows the main model’s components and the way they are linked to each other. Our proposed brain tumor segmentation model consists of three main steps: pre-processing, two-step dragonfly algorithm clustering, and the last phase, level set segmentation. The following subsections discuss these components in detail.
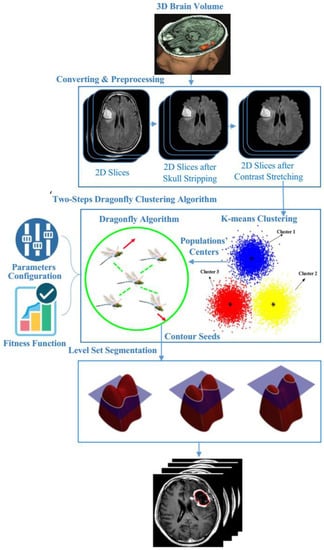
Figure 4.
The proposed 3D-MRI brain tumor detection model.
3.1. Preprocessing Phase
Segmentation of MRI brain tumor scans always challenged by poor image quality, the main cause for image degradation in MRI is the contamination of the MRI images with noises like irregularities [37]. Pre-processing operations are required to enhance the image quality, the target for these procedures is to reduce the contaminated noise and improve segmentation of image edges by eliminating inhomogeneous areas of the image. In the proposed model, four steps were applied: conversion of the 3D-MRI into 2D slices, skull-stripping, anisotropic diffusion, and contrast enhancement. Figure 5 shows an example of one patient’s 2D slices after pre-processing. Herein, the conversion process was applied using 3D Slicer, which is an open- source software web application for medical image informatics, image processing, and three-dimensional visualization.
Figure 5.
Example of one volume after pre-processing.
Skull-stripping comprises three steps involving morphological operations: Step 1: The input 2D-MRI slices are converted to binary images using Otsu’s thresholding. Step 2: Dilation and erosion operations are undertaken to preserve the minute features of the brain in the resultant 2D-MRI slices (creation of the mask). By filling the holes, the brain becomes a complete connected component. Step 3: (Superimposition): The final skull stripped image is obtained by superimposing the mask on the input image [37]. An anisotropic diffusion filter is employed to diminish the noise in the image and homogenize it in regions having a similar grey level by preserving regions’ edges. As a generalization of the diffusion process, anisotropic diffusion filter creates a set of parameterized images, such that each image in the resulting images is a fusion of the original image and an original image local content-based filter. Therefore, anisotropic diffusion is a space variant and non-linear transformation of the original image. See reference [38] for more information. Finally, contrast enhancement is applied using a histogram equalization technique in which the tumor conspicuity is improved by redistributing the greyscale of the images in a non-linear way to advance the separation of latent or hidden variations in pixel intensity into a more visually discernible distribution, thus taking advantage of the human vision physiological attributes [37,38].
3.2. Two Steps Dragonfly-Based Clustering Phase
Clustering is a powerful tool in machine learning systems, it uses predefined similarity criterion for grouping unlabeled group of data objects or clusters [39,40]. The clustering problem can be formulated as an optimization problem as follow: given a set is a set of objects is a data matrix consisting of rows and columns where represents the number of objects of a dataset, and represents the number of attributes (features) or dimensions of a given dataset. The -th data object is defined using a real-valued -dimensional vector where each object denotes the -th feature of the -th object . The objective of the clustering algorithm is to create a set of partition for the given data matrix and satisfying the following conditions:
In our model, to accelerate the convergence rate and preserve the stability during exploration and exploitation, a two-step DA algorithm is used to improve it for clustering problems using the k-means algorithm [40]. The main steps of the DA clustering algorithm are shown in Algorithm 1. Herein, to handle randomization of the selection of the center of the mass of the neighborhood within the DA algorithm, k-means is used to generate accurate centers.
| Algorithm 1: Two-step Dragonfly Clustering. |
| Input: dataset contains MRI brain images Output: Best solution of final cluster center () Begin Initialization phase Initialize the position of dragonfly population Xi (i = 1 2, ..., n). Initialize step vectors Δ Xi For /* is the total number of food sources (number of clusters) */ Initialize the food source within the boundary of given dataset in random order; Evaluate the better potions of food sources by applying the k-means algorithm / *Algorithm 2*/ Send the dragonflies to the food sources; / * Computed centers */ End For Dragonfly algorithm Phase Iteration = 0; Do While (the end condition is not satisfied) For i = 1:n Calculate the fitness of each dragonfly Update the food source and enemy Update w, s, a, c, f, and e Calculate S, A, C, F, and E using Equations (4) to (8) Update neighboring radius If (a dragonfly has at least one neighboring dragonfly) Update step vector (ΔX) using Equation (9) Update position vector X using Equation (10) Else Update position vector using Equation (11) End if Check and correct the new positions based on the boundaries of variables End For For Compute the probability. /* Calculate the probability for each one */ End For For If (rand ( ) < ) /* denotes the probability associated with food source */ Calculate the new fitness of the new food source using Equation (14); Select the best food source by using a greedy selection between the old and new food source; Else ; End If End For End While Output: Final clusters‘ centers. End |
Initialization stage: The K-means algorithm (see Algorithm 2) is used to find the initial food sources (center of the mass of the neighborhood). Herein, four clusters representing background (), gray matter (), white matter (), and tumor () as stated in [41] are identified. Each point is then assigned to the nearest centroid. In this paper, the Euclidean distance is used as a measure to the proximity which used to assign objects to the nearest centroids. The clusters are created by assigning each object to the suitable cluster based on the proximity measure, the centroids then updated based on the average of the object proximity measures in each cluster. The reassigning process and centroids updating are repeated until there is no change in each cluster’s objects [42].
| Algorithm 2: K-means clustering [42]. |
| Input: . // the number of clusters; dataset contains MRI brain images (2D slices). Begin Arbitrary choose objects from as the initial cluster centers; Repeat - (re) group the most similar objects into a cluster, based on the Euclidian distance between the object and the cluster centroid (mean); - Update the cluster centroid, i.e., calculate the mean value of the objects for each cluster. Until no change. |
Determine initial segmentation points using dragonfly algorithm
The behavior of swarms follows three primitive principles [14,15,43,44]: (1) Separation principle, this principle relies on the fact that the swarm individuals tries to avoid static collision with other individuals in the neighborhood. (2) Alignment principle, this principle reflects the attitude of the each individual in the swarm to match its velocity with other individuals in the neighborhood; and (3) Cohesion principle, this principle refers to the tendency of swarm individuals to centralized around the neighborhood mass center. In order to survive, all the swarm individuals should be attracted towards food sources and repelled from enemies. Each of these behaviors is mathematically formulated as follows:
Separation is calculated as follows [44]:
where X is the position of the current individual, represents the position j-th neighboring individual, and N is the number of neighboring individuals.
Alignment is calculated as follows:
where is the velocity of j-th neighboring individual.
Cohesion is calculated as follows:
where N is the number of neighborhoods, and Xj shows the position j-th neighboring individual.
Attraction towards a food source is calculated as follows:
where is the position of the food source.
Repulsion from an enemy is calculated as follows:
where is the position of the enemy.
The behavior of dragonflies is assumed to comprise the combination of these five corrective patterns. To update the location of artificial dragonflies in a search space and simulate their movements, two vectors are considered: step (X) and position (X). The step vector shows the direction of the movement of the dragonflies and is defined as follows:
where s, a, and c are the weights of separation, alignment, and cohesion respectively. Si, Ai, and Ci represent separation, alignment, and cohesion of the i-th individual respectively f is the food factor, is the food source of the i-th individual, e is the enemy factor, is the position of enemy of the i-th individual, w is the inertia weight, and t is the iteration counter. After calculating the step vector, the position vectors are calculated as follows:
With separation, alignment, cohesion, food, and enemy factors (s, a, c, f, and e), during dragonfly optimization, different explorative and exploitative behaviors can be reached. Neighbors of dragonflies are very important, so a neighborhood (circle in a 2D) with a certain radius is assumed around each artificial dragonfly. Dragonflies tend to align their flying while keep proper separation and cohesion in a dynamic swarm. In a static swarm, however, alignments are very low while cohesion is high to attack prey. Therefore, while exploring the search space, dragonflies with high alignment and low cohesion weights were assigned, on the other hand dragonflies with low alignment and high cohesion when exploiting the search space. Due to switching between exploration and exploitation, the radii of neighborhoods are increased proportionally to the number of iterations. Another way to balance exploration and exploitation is to adaptively tune the swarming factors during optimization. While converging to the global optimum in the final stage of the algorithm, the neighborhood area became larger as the swarm becomes one group. The best and the worthiest reached solutions are used as the food source and enemy. This causes convergence towards promising areas of the search space and divergence from non-promising regions of the search space. Figure 6 shows the flowchart of the dragonfly algorithm.
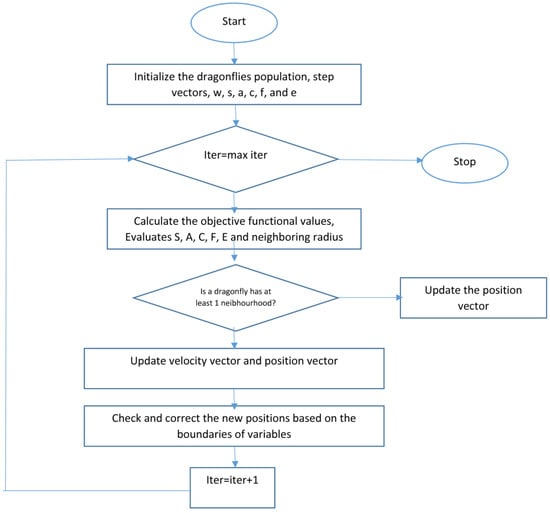
Figure 6.
Dragonfly algorithm flowchart [43].
When there are no neighboring solutions, dragonflies must travel around the search space. Dragonflies use a random walk ( flight) to boost the randomness, stochastic behavior, and. In this case, the position of dragonflies is updated using the following equation [44]:
where d is the dimension of the position vectors. are two random numbers in [0,1], is a constant, and . Herein, the fitness function is calculated as:
is the number of data instances that are used to normalize the sum, and is the class which data instances belong to.
3.3. Level Set Segmentation
Level set (LS) techniques are powerful tools for modelling time varying objects, by using level set techniques it is not difficult to follow topological changes in the object shape. They use deformable models with active contour energy minimization techniques without parametrizing the surface to find a solution for the minimal distance curves problem. LS methods are controlled by curvature-dependent speeds of moving curves or fronts [21,45,46]. The initial position of the contour is always a key challenge in some LS methods while solving segmentation problems. The contour can move inward or outward and its initial position determines the target for segmentation. In segmenting images with poorly defined boundaries, some methods replace the initial contour with a region-based active contour and the re-initialization step has been eliminated by including a term in the Partial Differential Equation (PDE) that penalizes the deviation of level set function from a contour based signed distance function. Different level set methods differ either in how to form an initial contour or the energy functional to be minimized or some combination of both. There are still key challenges in using level set in image segmentation and there is no general level set method that can solve segmentation problem for all applications. In our case, the deformable model initialization uses the cluster centers that are computed using the previous phase for each slice as the initial placement for final tumor segmentation.
Level set segmentation techniques are based on two main stages: first, the insertion of the interface as the zero level set of a higher dimensional function, and, second, the interface’s speed to this higher dimensional level set function. The evolvement of the contour or surface is managed by a level set equation. The solution to which this partial differential equation tends to is determined iteratively by updating φ at each time interval. The level set method is a numerical algorithm that gradually tracks the motion of a curve (in 2D slices) implicitly by embedding a propagating interface Γ as the zero level set of a higher dimensional function , where , and represents time. The level set function , defined over the image space, is a surface which is positive inside the region , negative outside , and zero on the interfaces between and other regions. The general form of the level set equation is [21]:
where is the evolution of , is the field for speed, is the normal interface vector, is a curvature controlled term with the parameter , is a velocity term weighted by , is equal to the scale of the image outline, and is the variance of the Gaussian . Finally, represent a local advection force that pulls the level set towards the tumor boundaries; this force is weighted by the parameter . After some repetitions of the PDE or once has converged, the final level set function is achieved. Algorithm 3 illustrates the main steps of the level set segmentation procedure. Figure 7 shows the result of applying the level set segmentation to a set of images.
| Algorithm 3: Level set segmentation. |
| 1: Insert initial contour points using two-step DA clustering output (ROI indexes). 2: Construct a signed distance function. 3: Calculate feature image using Gaussian filter and gradient. 4: Obtain the curve’s narrow band. 5: Obtain curvature and use gradient descent to minimize energy. 6: Evolve the curve. 7: Repeat step number two and stop after obtaining the segmented region. |
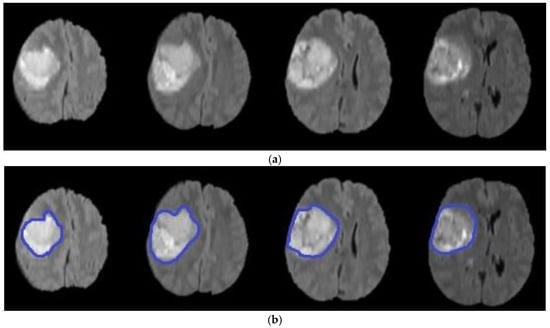
Figure 7.
Brain tumor segmentation using level set (a) original images (b) segmented tumors.
In summary, in the traditional level set algorithm, if the initial contour is far from the actual contour, the algorithm will require a greater number of iterations, and significant computation is needed. In contrast, two-step DA clustering places the initial contour set near the actual tumor contour, resulting in good convergence and requiring fewer iterations.
4. Experimental Results
In this section, the performance of the proposed model is validated on MRI volumes from 285 subjects with different forms of cerebral tumors in terms of form, position, size, and intensity. These 3D-MRI brain tumor data were obtained from the BRATS 2017 (Brain Tumor Segmentation) test and challenge dataset [47,48]. The experiment was carried out using an Intel, Core i3 CPU with 8.00 GB of RAM using MATLAB software R2018a. Herein, accuracy, recall, and precision are used as an evaluation metrics.
4.1. Experiment 1: Comparison with Existing Methods
The first group of experiments was performed to validate the efficiency of the proposed model compared to the state-of-the-art brain tumor segmentation methods listed in Table 1 using the BRATS 2017 dataset. The proposed method in [21] is based on a hybrid approach that uses a brain symmetry analysis method and a combination of region-based and boundary-based segmentation methods. However, region segmentation has the drawback of being applied only to closed boundaries. The model in [22] utilizes fuzzy C-means and rough fuzzy C-means with shape-based topological properties to handle uncertainty in MRI data by utilizing fuzzy membership and a rough set. However, the construction of the membership function and determination of the upper and lower boundaries for the rough set remain the main challenges. In [24], the combination of region-based k-means clustering and variational level sets is introduced to deal with poor convergence towards the concavities of the tumor boundary. However, it is difficult to predict the k-value and different initial partitions can result in different final clusters. In addition, to compare the suggested model with other known algorithms for segmentation purposes, the models in [49,50] were chosen. However, training a large number of deep trees can have high computational costs and use a lot of memory, and the Support Vector Machine (SVM) does not perform well when the data set has more noise, i.e., when target classes are overlapping. The default level set parameters were assigned to the same values suggested by [51] (σ = 1.5, ρ = 1, ε = 1.5, λ = 5), the time step () was set 1 to assure the stability of the curve evolution, and the velocity term α = 15. This experiment was performed based on the default values of each method’s parameters. See [21,22,24,49,50] for more information regarding default values for each method.

Table 1.
Results of the comparison between the proposed model and state-of-the-art brain segmentation methods (average over 285 subjects).
The results confirm the superiority of the suggested model as it increases the accuracy by 5.27% compared with the SVM-based brain segmentation algorithm. One possible explanation of this result is that using a two-step DA approach enhances segmentation accuracy as it detects an accurate initial contour rather than choosing it randomly or less accurately, as is done in the compared methods. The search mechanism of DA is maintained by the utilization of the information obtained from k-means. In other words, the connection between k-means and DA helps to increase accuracy and decrease the error rate. Figure 8 shows a sample of segmentation results.
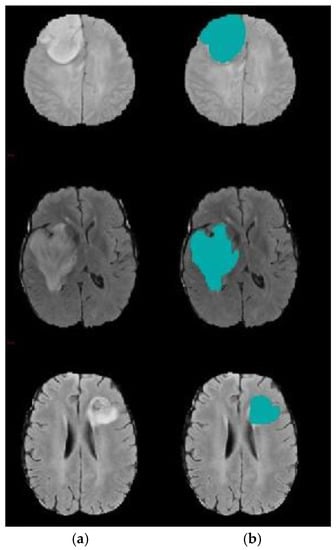
Figure 8.
Brain tumor segmentation (a) 2D slice (b) final segmentation using DA.
Furthermore, to verify the efficiency of the proposed model, the results of the proposed model was compared to the results of other methods that rely on the use of Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) as one of the up to date tools for segmenting brains tumors; another group of experiments was implemented to compare the proposed model with the recent works in [26] and [36] as illustrated in Table 2. These two methods differ from each other in that the first incorporates the Variational Level Set (VLS) into deep learning to address the sensitivity of the level set to initial settings and its dependence on the number of iterations. The second uses a novel two-pathway Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architecture that learns about the local details of the brain in addition to the larger context. Although results largely converged with those of the method in [36]. one of the CNN drawbacks is the problem of overfitting, which make it computationally expensive and requires a large database for training.

Table 2.
Results of the comparison between the proposed model and Deep Neural Network (DNN)-based brain segmentation methods (average over 285 subjects).
Another group of experiments was carried out to compare the efficiency of the combination of DA clustering and the level set algorithm in the field of brain tumor segmentation with a combination of some nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithms with level set. We replaced the DA module in the proposed model with well-known metaheuristic modules, via a BlackBox, with their default configurations. These metaheuristic algorithms include Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), the Artificial Bee Colony (ABC) Algorithm, and the Clown Fish (CF) Algorithm [33]. The results in Table 3 confirm the research hypothesis that using the DA classifier based on accurate center points extracted using k-means will enhance the segmentation accuracy. The suggested combination achieved a 1% increase in accuracy compared to the nearest combination that shields between the CF and the level set segmentation. In PSO, ABC, and CF, the convergence rate is affected by the main parameters that affect the individual’s movement toward the best position obtained thus far by individuals and others in the group; this consequently affects their tendency to be explorative or exploitative. In DA, the convergence rate is not affected by any parameters. DA tends to be explorative, which is shown by the lowest convergence rate the compared methods. In a comparison of the time taken, PSO, ABC, and CF took about 95–100 s, whereas DA took about 40–45 s to complete the segmentation process. Figure 9 shows a sample of segmentation results using DA and CF combined with level set segmentation.

Table 3.
Results of the comparison between combinations of different nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithms with level set for brain tumor segmentation (average over 285 subjects).
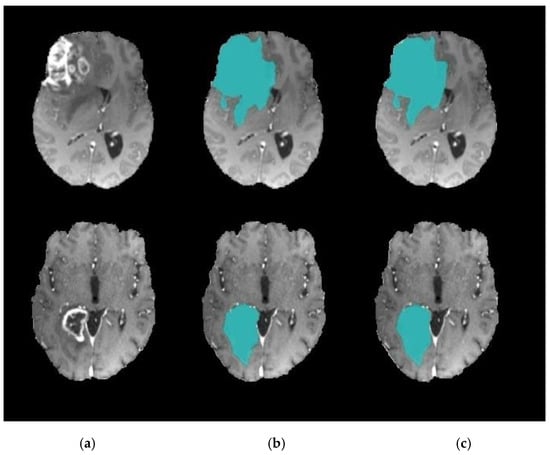
Figure 9.
Brain tumor segmentation. (a) 2D slice. (b) Final segmentation based on the Dragonfly Algorithm (DA). (c) Final segmentation based on the Clown Fish (CF) Algorithm.
4.2. Experiment 2: Model Accuracy with and without k-Means
This group of experiments was conducted to validate the role of k-means to enhance segmentation accuracy. Table 4 reveals the power of the suggested model that utilizes k-means to get the initial DA population, which raises the accuracy by 13% relative to the model with random initialization of DA. This result could be explained as that utilizing a two-step DA accelerates the convergence rate and preserve the balance between exploration and exploitation. In this research, the DA clustering algorithm results are enhanced with the k-means algorithm rather than with random initialization because k-means is used to determine the appropriate locations in a random search space of food sources. In this case, cluster centers extracted by k-means act as the initial food source positions in the DA algorithm. As revealed from the table, a low standard deviation was obtained, which means that the data points tend to centralized around the mean, i.e., there were no outliers. This implies that the measurements of the model’s accuracy are stable for the variety of the MRI images.

Table 4.
Comparison of accuracy with and without k-means (average over 285 subjects with repeating each experiment 5 times).
4.3. Experiment 3: Role of DA to Reduce Level Set Iteration
The goal of this experiment was to emphasize the role of DA in reducing the level-set segmentation iteration number. Herein, to reduce time cost and increase accuracy, the initial contour of the region of interest (ROI) target was automatically generated based on the two-step DA clustering result. Table 5 shows the comparative results of the suggested model and traditional level set segmentation algorithms in terms of the number of iterations required for level set to complete the segmentation process. These group of experiments were conducted 10 times to ensure the robustness of the proposed model against random factors, which may affect the stability of the algorithm. Herein, five MRI volumes were randomly chosen. It can be inferred that utilizing the DA algorithm reduces the number of level set iterations dramatically. Using the best-designed two-step DA parameters, the contour was positioned very close to the tumor region. Figure 10 and Figure 11 show a sample of the segmentation process using the modified level set.

Table 5.
Level set iteration number with and without DA clustering.
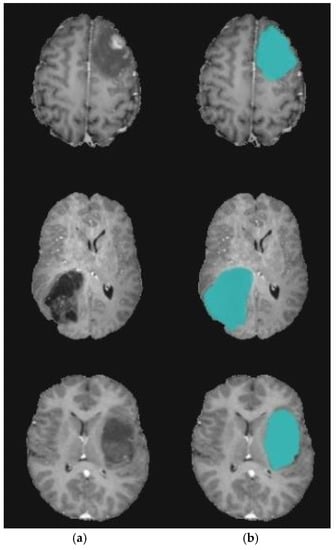
Figure 10.
Brain tumor segmentation for BRATS 2017 dataset. (a) 2D slice. (b) Final segmentation with the modified level set.
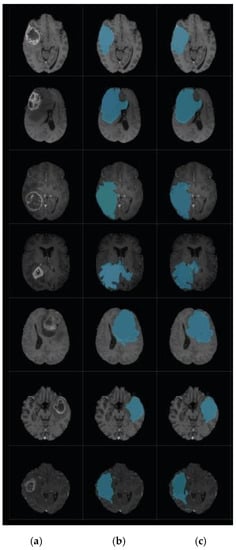
Figure 11.
Brain tumor segmentation for BRATS 2017 dataset. (a) 2D slice. (b) Final segmentation with the modified level set. (c) Ground truth.
5. Conclusions and Future Work
This paper suggests an accurate model for segmenting tumors from 3D-MRI medical images. The proposed model uses a modified version of the level set segmentation technique. This version utilizes DA-based clustering to regulate the initial contour accurately rather than in a random manner. The utilized bio-cluttering algorithm uses k-means to select an initial source food, rather than random sources, to be applied to DA, with the aim of enhancing clustering accuracy. Thus, the suggested model addresses two types of randomness: one within the DA classifier by utilizing k-means, and one within the level set procedure. The suggested model helps to locate accurate tumors’ contours compared to the commonly used trial-and-error contour detection methods. In addition, it aids the rapid extraction of tumor edges by reducing the number of iterations needed in segmentation. Our experiments assessed the accuracy of the proposed model. The suggested model achieves about a 5% increase in accuracy compared with related works; furthermore, it reduces complexity in terms of the consumed time by an average of 7% compared with the traditional level set-based tumor segmentation methods. The limitations of the suggested model are that it has not been tested on volumes containing more than one tumor per one slice; this paper concentrates only on the whole tumor segmentation. Future work includes utilizing the parallel segmentation approach to further reduce the complexity of the suggested model. Furthermore, future work could include extending the suggested model to deal with different parts of tumors, and studying the effect of variables (parameters) of both level set segmentation and the dragonfly algorithm on the model’s accuracy. Finally, a Deep Neural Network may be used with the suggested model to extract salient features for segmentation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.D., H.A.K. and O.F.H.; Methodology, S.D. and H.A.K.; Software, Y.M.I.; Validation, S.D., H.A.K. and O.F.H.; Formal Analysis, H.A.K. and S.D.; Investigation, S.D. and Y.M.I.; Resources, H.A.K., S.D. and O.F.H.; Data Curation, Y.M.I., O.F.H.; Writing—original draft preparation, H.A.K., S.D. and Y.M.I.; Writing—review and editing, S.D. and O.F.H.; Visualization, Y.M.I. and O.F.H.; Supervision, H.A.K., S.D. and O.F.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- El-Melegy, M.T.; El-Magd, K.M.A.; Ali, S.A.; Hussain, K.F.; Mahdy, Y.B. Ensemble of Multiple Classifiers for Automatic Multimodal Brain Tumor Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovative Trends in Computer Engineering (ITCE), Aswan, Egypt, 2–4 February 2019; pp. 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Aparna, R.M.; Shanmugavadivu, P. A Survey of Medical Imaging, Storage and Transfer Techniques. In Proceedings of the International Conference on ISMAC in Computational Vision and Bio-Engineering, Coimbatore, India, 16–17 May 2018; pp. 17–29. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Xu, Z.; Ye, X. Evaluation of Intraoperative MRI-Assisted Stereotactic Brain Tissue Biopsy: A Single-Center Experience in China. Chin. Neurosurg. J. 2019, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, S.; Wiest, R.; Nolte-P, L.; Reyes, M. A Survey of MRI-Based Medical Image Analysis For Brain Tumor Studies. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mild, K.H.; Lundström, R.H.; Wilén, J.H. Non-ionizing Radiation in Swedish Health Care Exposure and Safety Aspects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuge, Y.; Krauze, A.V.; Ning, H.; Cheng, J.Y.; Arora, B.C.; Camphausen, K.; Miller, R.W. Brain tumor segmentation using holistically nested neural networks in MRI images. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, 5234–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Mitra, S. Novel Volumetric Sub-region Segmentation in Brain Tumors. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, J.J.; Godson, T.E.; Olasoji, Y.O.; Adu, M.R. Study on Capabilities of Different Segmentation Algorithms in Detecting and Reducing Brain Tumor Size in Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Effective Telemedicine Services. Eur. J. Eng. Res. Sci. 2019, 4, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulakshmi, M.; Priya, G.L. Automated Brain Tumor Segmentation Techniques—A Review. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2017, 27, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirly, S.; Ramesh, K. Review on 2D and 3D MRI Image Segmentation Techniques. Curr. Med. Imaging Former. Curr. Med. Imaging Rev. 2019, 15, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, S.; Hussain, S.; Sarwar, A. Brain Tumor Detection and Segmentation in MR Images Using Deep Learning. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 9249–9261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D. Efficient Level-Set Segmentation Model Driven by The Local GMM and Split Bregman Method. IET Image Process. 2019, 13, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, C.; Rashid, T. Dragonfly Algorithm and Its Applications in Applied Science Survey. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2019, 2019, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedali, M. Dragonfly Algorithm: A New Meta-Heuristic Optimization Technique for Solving Single-Objective, Discrete, and Multi-Objective Problems. Neural Comput. Appl. 2016, 27, 1053–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjini, K.; Murugan, S. Memory Based Hybrid Dragonfly Algorithm for Numerical Optimization Problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 83, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saman, S.; Narayanan, S.J. Survey on brain tumor segmentation and feature extraction of MR images. Int. J. Multimed. Inf. Retr. 2018, 8, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Srivastava, S.; Pant, M. Brain tumor segmentation and classification from magnetic resonance images: Review of selected methods from 2014 to 2019. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 131, 244–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Baz, A.; Suri, J.S. Level Set Method in Medical Imaging Segmentation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Rifaie, M.; Aber, A.; Hemanth, J. Deploying Swarm Intelligence in Medical Imaging; Identifying Metastasis, Micro-Calcifications and Brain Image Segmentation. IET Syst. Biol. 2015, 9, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupika, N.; Menon, H.; Vikram, K. A Survey on Advanced Segmentation Techniques for Brain MRI Image Segmentation. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2017, 7, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermi, A.; Andjouh, K.; Zidane, F. Fully automated brain tumor segmentation system in 3D-MRI using symmetry analysis of brain and level-sets. IET Image Process. 2018, 12, 1964–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, A.; Banerjee, M.; Chakrabarti, A.; Sharma, P. MRI Brain Tumor Segmentation and Analysis using Rough-Fuzzy C-Means and Shape Based Properties. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, V.; Murugavalli, S. Brain Tumor Classification using Two-Tier Classifier with Adaptive Segmentation Technique. IET Comput. Vis. 2016, 10, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalakshmi, A.; Krishnappa, H.; Jayadevappa, D. A Hybrid Approach for the Segmentation of Brain Tumor using K-Means Clustering and Variational Level Set. J. Adv. Res. Dyn. Control. Syst. 2018, 10, 258–264. [Google Scholar]
- Thapaliya, K.; Pyun, J.-Y.; Park, C.-S.; Kwon, G.-R. Level Set Method with Automatic Selective Local Statistics for Brain Tumor Segmentation in MR Images. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2013, 37, 522–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.; Gummadi, R.; Savvides, M. Deep Recurrent Level Set for Segmenting Brain Tumors. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2018, 11072, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, J.; Liu, H.; Cui, Y. A Framework Combining DNN and Level-Set Method to Segment Brain Tumor in Multi-Modalities MR Image. Soft Comput. 2019, 19, 9237–9251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, P.G.; Sundar, C. Brain Tumor Detection and Segmentation by Intensity Adjustment. J. Med. Syst. 2019, 43, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Maksoud, E.; Elmogy, M.; Al-Awadi, R. Brain Tumor Segmentation Based on A Hybrid Clustering Technique. Egypt. Inform. J. 2015, 16, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ural, B. A Computer-Based Brain Tumor Detection Approach with Advanced Image Processing and Probabilistic Neural Network Methods. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2017, 38, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Luo, G.; Wang, K. Concatenated and Connected Random Forests with Multiscale Patch Driven Active Contour Model for Automated Brain Tumor Segmentation of MR Images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1943–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancer, E.; Ozturk, C.; Karaboga, D. Extraction of Brain Tumors from MRI Images with Artificial Bee Colony-Based Segmentation Methodology. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ELECO), Bursa, Turkey, 28–30 November 2019; pp. 516–520. [Google Scholar]
- Christ, J.; Subramanian, R. Clown Fish Queuing and Switching Optimization Algorithm for Brain Tumor Segmentation. Biomed. Res. 2016, 27, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan, B.; Hardie, R. A Computationally Efficient U-Net Architecture for Lung Segmentation in Chest Radiographs. In Proceedings of the IEEE National Aerospace and Electronics Conference (NAECON), Dayton, OH, USA, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 279–284. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.; Pan, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, Z.; Tang, L.; Lu, C.; Wang, J. Applications of Deep Learning to MRI Images: A Survey. Big Data Min. Anal. 2018, 1, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, H.; Davy, A.; Warde-Farley, D.; Biard, A.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y.; Pal, C.; Jodoin, P.-M.; Larochelle, H. Brain Tumor Segmentation with Deep Neural Networks. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 35, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, J.E.; Liu, C.-Y.; Thompson, P.; Tu, Z. Robust brain extraction across datasets and comparison with publicly available methods. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2011, 30, 1617–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.; David, E.; Rajagopal, S. A robust anisotropic diffusion filter with low arithmetic complexity for images. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2019, 48, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gong, Y. Particle swarm optimization for two-echelon location-routing problem. J. Comput. Appl. 2013, 33, 2261–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Sahoo, G. A two-step artificial bee colony algorithm for clustering. Neural Comput. Appl. 2015, 28, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shen, X.; Cheng, H.; Qian, Q. Brain tumor segmentation based on hybrid clustering and morphological operations. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2019, 2019, 1–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armano, G.; Farmani, M.R. Clustering analysis with combination of artificial bee colony algorithm and k-means technique. Int. J. Comput. Theory Eng. 2014, 6, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunprasath, S. Internet of medical things-load optimization of power flow based on hybrid enhanced grey wolf optimization and dragonfly algorithm. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 98, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Jia, H.; Lang, C. Dragonfly algorithm with opposition-based learning for multilevel thresholding Color Image Segmentation. Symmetry 2019, 11, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xu, C.; Gui, C.; Fox, M.D. Distance regularized level set evolution and its application to image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 3243–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belaid, A.; Boukerroui, D.; Maingourd, Y.; Lerallut, J.F. Phase-based level set segmentation of ultrasound images. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 15, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menze, B.; Jakab, A.; Bauer, S.; Cramer, J.K.; Farahani, K.; Kirby, J.; Burren, Y.; Porz, N.; Slotboom, J.; Wiest, R.; et al. The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 1993–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, J.A.; Dasarathy, B. Medical image fusion: A survey of the state of the art. Int. J. Inf. Fusion 2014, 19, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefkovits, L.; Lefkovits, S.; Vaida, M. Brain tumor segmentation based on random forest. Mem. Sci. Sect. Rom. Acad. 2016, 39, 83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Ayachi, R.; Amor, N.B. Brain tumor segmentation using support vector machines. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. Book Ser. (LNCS) 2009, 5590, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.; Song, H.; Zhou, W. Active contours with selective local or global segmentation: A new formulation and level set method. Image Vis. Comput. 2010, 28, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).