Abstract
Insider threats that occur within organizations cause more serious damage than external threats. However, there are many factors that are difficult to determine, such as the definition, classification, and severity of security breaches; hence, it is necessary to analyze system logs and user behavior-based scenarios within organizations. The reality is that qualitative judgment criteria are different for everyone to apply, and there is no detailed verification procedure to compare them objectively. In this study, realistic insider threats were examined through the definition, classification, and correlation/association analysis of various human–machine logs of acts associated with security breaches that occur in an organization. In addition, a quantitative process and decision-making tool were developed for insider threats by establishing various internal information leakage scenarios. As a result, insider threats were assessed quantitatively and a decision-making process was completed that enabled case analysis based on several insider threat scenarios. This study will enable precise modeling of insider threats that occur in real organizations and will support an objective process and a decision-making system to establish a range of required information for security protection measures.
1. Introduction
Security incidents related to internal data leaks in the private, public, and military sectors have recently emerged as social issues. Multinational companies in particular are making great efforts to develop new technologies to address these issues to secure customers and gain a competitive edge in the global market. Meanwhile, there are ongoing technology and personal information leaks. More security incidents have been attributed to insiders that are legally recognized by organizations, through the infiltration of internal systems, than to outsiders (or hackers) [1,2]. An insider [3,4] is an individual who has legitimate access rights to personnel, facilities, and information assets in an organization. Hence, insiders include former and current permanent employees, contract workers, and partner employees working internally. However, people who are given access to internal information in accordance with laws and regulations are also insiders, such as those who are responsible for transfers, takeovers and mergers, and commissioned researchers. Insiders are all individuals who are able to gain access to information in the company under different circumstances. They access internal assets or systems more easily than outsiders with malicious intent and often cause serious damage to organizations [5,6]. This characteristic presents considerable challenges in dealing with insider threats.
According to a recent survey, 27% of all cybercrimes are suspected of being committed by insiders, and 30% of respondents reported that damage incurred by insiders was much more serious than that by external attackers [7]. Furthermore, it was reported that 23% of all e-crimes were suspected or known to be caused by insiders [8], and 45% of participants reported that the damage caused was worse than that caused by external attackers. A survey conducted by Vormetric Inc. [9] found that only 11% of respondents felt that their organizations were not vulnerable to insider attacks. Security incidents on IT assets in organizations caused by intentional or unintentional malicious physical acts committed by insiders continue to occur. However, traditional network and system-centered security control systems, such as F/W, IPS, Web F/W, DRM, DLP, and so on, require more advanced countermeasures because they only deal with and analyze general security incidents. In other words, it is necessary to clarify the different types of threats to organizations and to develop a series of appropriate processes to analyze, detect, identify, and respond to these threats.
The objectives of this study were to identify various scenarios related to insider threats and to develop a method to detect the threats. Insider threats require a description beyond analyzing network traffic by business type. They need to be determined by considering the number of cases for all threats occurring inside organizations. Thus, security logs (e.g., unauthorized access logs and communication details, unauthorized device use) need to be collated from conventional legacy security systems, and a process and model must be developed to detect malicious acts by applying them to insider threat scenarios [10,11].
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces various reports and detection studies that analyze conventional insider threats. Section 3 presents a decision-making model and methodology to detect the occurrence of actual threats by applying the detection logs of the conventional legacy security system to the separation system of various insider threats. Section 4 identifies the information protection measures that are adoptable by defining and analyzing the typical cases of insider threats based on probable scenarios. Section 5 respectively presents and discusses the results. Finally, Section 6 concludes with future research directions.
2. Related Studies
Traditionally, the machine/non-machine learning approach to an insider threat-related detection methodology stems from defining the configuration of malicious or unintentional random insider problems as anomalous detection tasks. Therefore, in performing scenario analysis related to the definition, identification, and detection of insider threats proposed in this paper, the approaches and unique features of related previous studies are discussed based on two main classifications of “machine learning” and “non-machine learning.”
2.1. Insider Threats Based on Machine Learning Approach
From previous research [12,13,14] and descriptions related to insider threat detection and analysis based on machine learning methodology, we selected the classification and clustering concepts as well as the related techniques [15,16] for anomaly detection and misuse as the main scope of this research.
Focusing on the classification technique (supervised learning), Li et al. [17] proposed the concept of a collaborative intrusion detection network (CIDN) using supervised learning as an integrated anomaly detection-based machine learning methodology to attenuate complex insider threats in the real world. As a feature of the study, in order for the distributed intrusion detection systems (IDSs) to collect and learn the main insider threat patterns collaboratively, intrusion sensitivity values were calculated using classification learning algorithms (such as the K nearest neighbor, backpropagation neural network, and decision tree algorithms) and were configured to be applied automatically in the CIDN according to each major factor by organization and insider type. As functional/structural evaluation of the network for the implemented classifier, in-depth comparative analysis was performed according to the type of detailed insider threats, such as betrayal, newcomer (re-entry), and so-called Sybil attacks [18]. This assessment provided enhanced detection accuracy, increased execution speed, and reduced overhead compared to the distributed systems operations and management approach [19] and Dirichlet-based model [20] presented as a CIDN-focused approach. Azaria et al. [21] derived an improved comparison group compared to the previous insider threat detection mechanism by proposing a support vector machine (SVM) and naïve Bayes-based behavioral analysis of the insider threat framework. The authors also proposed an algorithm that analyzed threats caused by intentional or unintentional insiders by learning all categories of normal and malicious acts (e.g., network print, email, and HTTP service) within the organization network in real-time semi-supervised environments [22,23,24]. Mathew et al. [25] detected attacks such as masquerading insider attack, data exfiltration, and sabotage attack in the relational database management system (RDBMS) by proposing a role-based masquerader profile module applied with supervised learning based on an SVM, a J48 decision tree, and a naïve Bayes classifier. Ronao et al. [26] also derived an improved comparison performance group for each dataset pre-presented in the study by proposing a random forest-based recognition and principal component analysis (PCA)-based function selection process. They detected malicious insider threat acts after building a normal behavioral profile for each role in the access control model to address insider threat problems in the RDBMS.
Focusing on the clustering technique (unsupervised learning), Lo et al. [27] identified the unique characteristics of mathematically non-deterministic insider threat acts and considered that the learning process presented in the previous studies did not improve the detection accuracy of actual insider threats. Therefore, the authors proposed distance measurement methods (such as the Damerau--Levenshtein, Jaccard, and cosine distance methods) with low algorithmic complexity as they are specified in the insider threat detection dataset, CERT [28], based on the hidden Markov model. Tabash et al. [29] proposed a latent variable model based on complex probability distributions by applying the Gaussian mixture model (GMM) as a detailed component to formalize the normal acts of an insider. The authors calculated the shared probability model that clustered observations in a linear combination, as well as the automatic rating model, to estimate insider threat-related scores. Moustafa et al. [30] improved the data fitting and boundary definition results for statistical analysis and probability distribution sets related to the NSL-KDD, KDD CUP 99, and UNSW-NB15 datasets. The authors proposed an anomaly detection system that was a framework configured with detailed modules, such as the Dirichlet multinomial mixture model, GMM, and beta mix model, which were very effective in detecting statistical outliers and anomalies related to complex insider threat data. Tuor et al. [31] proposed a deep neural network as a methodology for real-time detection and adaptive analysis of insider threat-related anomalies based on the threshold in a large network log stream. After learning the normal activities of each user, it was configured with a detailed network based on the recurrent neural network in the form of long short-term memory for further security of the reliability of sequential vector delivery for insider threats, achieving performance improvement based on loss and recall, compared to the previous studies using SVM, PCA, etc.
2.2. Insider Threats Based on Non-Machine Learning Approach: Statistical Scheme
From the previous studies related to insider threat detection and analysis based on a non-machine learning methodology, a number of different access control types and means [32,33], insider threat-specific game theory, and various decision strategies, modeling and simulation approaches, and graphing techniques were selected as the main focuses of this work.
Focusing on game theory and decision strategy, Liu et al. [34] proposed an insider game model to formalize interactions between internal users and system administrators as a probabilistic methodology for deriving meaningful associations and correlations between malicious insider motives and multiple decision-making processes. As a feature of the study, based on competitive responses between insiders and administrators, as well as detailed case studies, it was possible to calculate a Nash equilibrium for insiders to infer strategies for taking and determining the best counterattacks by the defenders. The authors also derived adaptive modeling and analysis and determined the possibility for scenarios that administrators could not recognize and respond to in a system in which potential internal breaches existed. Based on this naive approach, Kantzavelou et al. [35] proved the complexity of insider threats by proposing a theoretical type of IDS and rationality determination and distribution/prediction modeling strategy based on the quantal response equilibrium (QRE) [36] in the form of adding an iterative game concept. Tang et al. [37] reported achieving improved precision by utilizing a newly proposed dynamic Bayesian network structure to predict insider acts in advance before calculating the QRE balance in order to alleviate the theoretical limitations of the IDS system in the previous studies (e.g., unproven time complexity, realism, and identity). As a separate research method based on game theory, Zhang et al. [38] proposed a multiple defender reputation setting algorithm for the internal system that defined a hierarchical insider who established a conspiracy system between specialized independent malicious insiders or external attackers as a manipulation variable and improved the trade-off relationship between true and false positives.
Focusing on modeling and simulation based on graph theory, Chinchani et al. [39] proposed the concept of a key challenge graph with physical entities such as a host computer or server as peaks by applying the attack graph concept [40]. This [39] contained network communication channels as singular or plural trunks depending on the number. The authors not only divided vertices with specific resources that could potentially cause insider threats, but also proved that it was easy to construct a theoretical traceback system of malicious internal attackers for pre-defined trunks. They also provided a heuristic algorithm related to a unique algorithm for calculating successful internal breaches close to the minimum cost. Based on this naive approach, Eberle et al. [41] proposed a detector algorithm that applied the graph-based anomaly detection technique, as well as an anomalous insertion, modification, and deletion environment. The authors derived the main features, such as the calculation of real intelligence specific [42] to malicious insiders, and directed their focus towards the capture of insiders in the real world. The authors also derived the formation of synthetic security data applicable to each organization, involving reasonable computational overhead due to the improved algorithm. Other studies on insider threats based on graph theory have been conducted in connection with learning factors such as supervised and non-supervised learning, as well as classification and clustering, in machine learning.
The conventional methodologies of insider threat analysis based on machine or non-machine learning approaches have their own advantages and disadvantages, yet the applicability in real world environments and intuition of analysis is difficult to ensure. It is meaningful to analyze human or machine acts through learning (machine learning) or statistical (non-machine learning) processing, yet exceptional analysis results could arise since various factors such as situation descriptions of various scenarios, human-machine interests, and work types should be considered. Therefore, in order to maximize the effectiveness of these analyses, internal threats were classified as actual work environment-oriented, and related risk values were defined in this study. Based on the risk values of these figures, various internal threat scenarios were applied for analysis. Thus, we propose an analytic hierarchy decision-making process that determines the insider threat detection and response priority for each risk-based threat scenario, which is applicable to the working environment.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Proposed Model
To design an analytic hierarchy process (AHP) [43] model for artifacts related to cyber-attack types, we analyzed various threat logs generated in conventional information and communication technology (ICT) systems in detail. Several inside threat acts were detected by inducing different combinations of these logs. As shown in Figure 1, we classified threats and divided the acts for each threat criterion to establish various scenarios that could occur in the inside and outside environments and to estimate the risk for each attack type.
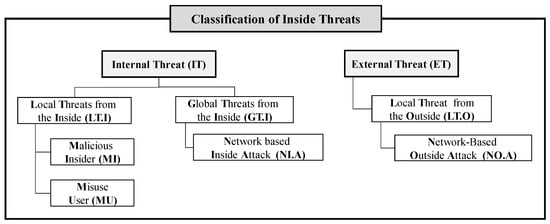
Figure 1.
Classification of inside threats.
As illustrated in Figure 1, inside threats are divided into internal threats (ITs) and external threats (ETs). In particular, they are divided into local and global threats that occur internally. In addition, external local threats are classified as inside threats. In other words, internal local threats (LT.Is) are divided into malicious insiders (MIs) (individuals with a malicious nature that threatens the real internal information system) and misuse users (MUs) (ordinary users who make simple mistakes that are expressed as internal threats). Moreover, infected nodes can be classified as network-based internal attacks (NI.As) targeted at neighboring nodes by malicious codes introduced from the outside into internal global threats (GT.Is). Finally, a typical external network-based attack (NO.A) is defined with a local threat (LT.O) occurring from the outside.
In this paper, we firstly define the internal threats occurring within an organization as local and global threats and explain the factors by dividing the threats into insiders and outsiders. Based on these, as shown in Figure 2, the threats are classified in detail into human and machine factors, and more detailed scenarios are generated as follows.
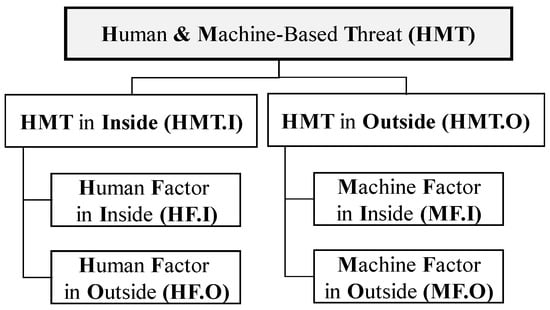
Figure 2.
Classification of human and machine threats.
We establish the possible scenarios that could occur at the center of the internal environment of an organization for each attack type in the following subsections.
3.2. Internal Threats from Inside the Organization
As described in Table 1, the possible cyber threats that arise from within organizations are classified in terms of the threat type/attack type/main act. This classification is analyzed along with internal information leakage factors as in Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4. Quantitatively definition of the absolute importance (1–9) of these factors according to the situation within an organization enables the calculation of various scenario-based risks considering the association between threats. However, the following tables were defined based on the quantitative risks observed in a typical organization.

Table 1.
Possible cyber threats that could arise inside organizations.

Table 2.
Information subject and whether authorized or not.

Table 3.
Business type according to spatio-temporal information.

Table 4.
Leakage means and main paths by information type.
3.3. Internal Threats from Outside the Organization
As shown in Table 5, the possible cyber threats that arise from the outside are classified in terms of threat type/attack type/main act. As in Section 3.2, based on the absolute importance (1–9), this classification can be analyzed with the external security breach factors given below.

Table 5.
Examples of internal attacks from the outside and inside the organization.
As shown in Table 6 and Table 7, external attacks that infiltrate into the inside through internal vulnerabilities must be viewed from the perspective of internal threats, since malicious acts are performed internally with regard to security breaches. Therefore, in this study, the external view is crucial because external threats also begin with malicious acts on the inside from the beginning. The viewpoint of actual insiders (e.g., members of an organization) and outsiders (e.g., hackers) should be properly divided and investigated in understanding this. Therefore, Table 6 and Table 7 can also be made up from the main features related to internal malicious acts, and the absolute importance (1–9) of these factors was quantitatively defined according to the situation within an organization.

Table 6.
Main path and spatio-temporal information in the event of internal infiltration.

Table 7.
Main malicious acts targeting information systems in the organization.
3.4. Human and Machine-Focused Insider Threats Scenario
Section 3.2 and Section 3.3 summarize the internal threat types that are usually observed in internal organizations from the perspective of the inside and outside and define appropriate risks (importance). They represent estimations of the most important indicators for describing the scenario-based, dynamically occurring internal threats. It should be noted that the threats are related to the unique characteristics of individual organizations.
As shown in Table 8, the cyber threats arising based on humans and machines can be divided into external security breach scenarios and internal information leakage scenarios and analyzed as follows.

Table 8.
Attack type and main act of human and machine threats.
3.4.1. External Security Breach Scenario
To prepare the scenarios caused by external security breaches, they should be defined assuming that there are various situations, as shown in Table 9. In other words, various threat scenarios are created based on the network and system implementation of the actual organization, and there are interworking systems (e.g., VPNs, server/DB/PC logs, firewalls, and intrusion protection systems (IPSs)/IDS) that can be referenced to recognize them.

Table 9.
External security breach scenario.
3.4.2. Internal Information Leakage Scenario
When external security breaches are successful, internal information is collected. Internal information is captured through various leakage paths, and as shown in Table 10 there are interworking security systems (e.g., PC security, DLP, disaster risk management (DRM), mail/messenger, vaccine, and network access control (NAC) systems) that can be referenced to recognize them.

Table 10.
Threat scenarios and interworking security system according to the leakage path.
3.5. Application of the Proposed Framework by AHP
We calculated the weight through hierarchical analysis based on the structural analysis and quantitative risk values of the internal threats from inside the organization, as described in Section 3.2, and the internal threats from outside the organization, as described in Section 3.3.
In particular, to define the modeling of analytic hierarchy security threats, we classified threats by associating various security threat scenarios with the characteristics of ICT assets. Hence, we derived the final priorities by defining and analyzing the hierarchy for decision-making and modeling and by performing pairwise comparison between the decision-making factors in each hierarchy as follows. We estimated and used the relative weights between the proposed AHP [43] factors. It is important to calculate the consistency index (CI) when applying the AHP process, which is critical to determine whether the results of quantitative assessment are logical inconsistencies from the perspective of security experts or system administrators.
We obtain the weight value w through IT ∙ w = n ∙ w (w = [w1, w2, …, wn]T: right eigenvector of matrix IT, n: eigenvalue of matrix IT, λmax > n) (the matrix IT can be expressed the same as the matrix HMT that corresponds to a human and machine threat). Therefore, it can be re-expressed as IT ∙ w = λmax∙ w and summarized for w as follows:
Equation (1) represents a linear system of n equations, and to obtain a non-trivial solution for w, |IT − λI| = 0 in Equation (4) must be established. The estimated IT matrix of the relative importance of element i to element j that is subjected to pairwise comparison is defined as ITij = (1 + δij) wi/wj. Here, the difference between the largest eigenvalue λmax obtained from the observed pairwise comparison matrix and the maximum eigenvalue n of the pairwise comparison matrix with complete consistency can be expressed as follows:
In Equation (2), if the estimate ITij matches exactly wi/wj, then δij = 0; thus, λmax − n = 0. Therefore, the closer λmax of the pairwise comparison matrix of a specific evaluation result is to n, the more consistent the judgment is. Based on this characteristic, we define the CI of the response as follows:
Here, we use the consistency ratio (CR) divided by the average random index to test the consistency. The hypothesis regarding the consistency of the test statistic is that if it is less than 0.1, then it is accepted that consistency is maintained.
Thus, the basic IT matrix for insider threats consists of features defined in Table 1 and Table 4 as follows. These are in reference to [43], where values in a pairwise comparison matrix were inserted based on surveys by security experts, with numerical judgments such as 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9 in the table of the logic of properties.
Equation (4) is a pairwise comparison matrix based on the relative importance, and the result of hierarchy analysis is the weight that satisfies the CI index (based on 0.1 or less), as shown in Table 11.

Table 11.
Weight by internal threat, attack type, and main act.
Based on the human and machine-focused insider threat scenarios described in Section 3.4, we set the weights as follows through analytic hierarchy based on structural analysis and quantitative risk values to apply to external security breach scenarios and internal information leakage scenarios. The HMT matrix produced at this time consists of features defined in Table 11 and can be expressed as follows:
Equation (5) is a pairwise comparison matrix based on the relative importance, and the result of the analytic hierarchy is the weight that satisfies the CI index (based on 0.1 or less), as shown in Table 12.

Table 12.
Weight by human and machine-focused threat type, attack type, and main act.
4. Scenario-Based Insider Threats and Case Analysis
Note that in the scenarios described below, the numbers in brackets refer to risk values as defined in the tables in Section 3.
4.1. Scenario (a): Internal Information Leakage by Insiders (IT.I)
Bob, an authorized (9) internal staff (9) in a specific company, decides to pass on the secrets of the company (9) to a competitor. He collects and summarizes the secrets over time (3) within the company (9) during non-working hours (5) on non-business days (3). He copies the information to an external hard drive (9) and prints out some of the information as offline documents (7). When transfer is not possible with these means, he uses his smartphone, that is, using the camera and video functions of his mobile phone (9). As he shares the ID and password with his superior, who has handling rights (9) to the information, he is able to decrypt and store the document without attracting any attention from others.
In this scenario, to find the main point of internal information leakage, we performed the analysis based on the above results to obtain the weight values in Table 13. In summary, starting with the management of data handling rights according to each job level of the company, a document management system needs to be monitored intensively. Using this approach, acts were established according to each job level and a safe document management system is maintained accordingly. In addition, by introducing systems such as data loss prevention (DLP) and mobile device management to control portable devices such as external hard drives and smartphones, which are storage media, an information protection system could be established that enables “choice and focus.”

Table 13.
Weight by main act for intentional internal information leakage by an insider.
4.2. Scenario (b): Internal Information Leakage by Outsiders Using Malware
In order to hack employee Alice at a specific company to collect the secrets of her company, the attacker (hacker) collects various types of information, such as her personal digital information (e.g., portal email, social networking service account, and activity) and her main business activities displayed on the homepage.
She is an authorized (9) internal staff member (9) in a specific company (9) and is responsible for international affairs (9). In particular, she starts her morning work routine (7) on Monday (9) and starts working based on the emails (9) related to international orders and deliveries received over the weekend. Over the weekend, the hacker sent a hacking email with malware (9) disguised as an international delivery related to her work. Alice read the email without any suspicion because of the high-quality content of the email and executed the attachment. Then, malware code was executed through the vulnerability of Windows 7, which was the OS on her PC, and the root authority of the PC was seized by the hacker. The executed malware bypassed the vaccine (9) because it was variant malware, and it periodically communicated (5) with the command and control (C & C) server of the hacker. By scanning other servers and PCs in the same network, the attacker searched the network equipment ports (9), server ports (9), and PC ports (7) and discovered the shared folder. Afterward, the attacker was able to obtain the research information (9), IT asset information (9), and personnel information (9) of the company from the shared folder.
In scenario (b), we also performed the analysis based on the weight value to find the main point of internal information leakage. The greatest risk factor in this scenario is the ripple effect of vaccine bypass (VS in Table 14). Therefore, it is critical to update the vaccine patterns to the latest versions, increasing the probability of having adequate defense against the latest malware. In addition, as the inflow of malware decreases, scanning will also decrease, and the leakage of important company data, such as personnel information, will also be controlled.

Table 14.
Weight by main act for internal information leakage using malware by an outsider.
4.3. Scenario (c): Internal Information Leakage Due to Misuse of Internal System by Insiders
Eve, an authorized internal staff member (9) at a specific company, operates and maintains the external services of a 24 h information system (IT). She does not have major problems in IT service operation, but she feels that maintenance is burdensome. Because of the large amount of work and the need for urgent maintenance, she needs to take care of the work despite taking business trips or do it after normal work. She has extensive access rights to the IT system; hence, she installs and uses the remote program (7) on her business laptop (9) for convenience and links to the operating server of the company. This program allows access not only to the internal system from the outside, but also to the internal system from the inside.
In addition, because there are many servers to be managed in the internal network (5) and a password must be changed periodically every month, she creates a separate password file (9) and attempts to connect frequently to the servers to check them. The hacker succeeded in hacking Eve using a social engineering approach (9) and was able to access the operational servers of the company through her business laptop. The hacker was able to browse her password file and control traces of intrusions and thus could plan on conducting long-term intrusion campaigns. Then, the hacker disabled the vaccine (9) function on the servers and laptop and captured various types of company secrets by installing malware (9) to communicate periodically with the C & C server of the hacker (9) through a backdoor.
In this scenario, to find the main point of internal information leakage due to misuse of internal system by an insider, we performed the analysis based on the above results to obtain the weight values in Table 15. There are a few information system personnel in most organizations whose workloads, such as those involving systems operation and maintenance, are excessively high in this scenario. Therefore, remote programs are used to increase the efficiency of tasks routinely or for convenience. Under the premise that the system is infected by malware, it is assumed that the leakage of company secrets occurs while it periodically communicates with the C & C server (9). The damage incurred by these security breaches varies depending on the malware type. Moreover, as most malware is zero-day or variant malware, it bypasses the vaccine. Subsequently, through various social engineering attacks, the hacker launches additional attacks. Therefore, to determine whether there is a remote program installed in an organization, the relevant software list registered in the NAC system should be regularly updated. In addition, through the detection log of the IDS/IPS or advanced persistent threat information protection solutions, periodic communication from “the inside to the inside” or “the inside to the outside” should be identified and anomalies should be distinguished from normal acts. Through this process, it is also crucial to identify the type and status of data distributed in an organization in periodic communications, that is, the payload in the communication packets. It is also important to note that data leaking malware has been recently detected in organizations and to pay attention to the trends of similar malware. As this risk is related to the update of the vaccine server, the server should always be kept up to date, and related cyber threat intelligence should be collected.

Table 15.
Weight by main act for internal information leakage according to misuse of internal system by an insider.
5. Discussion
Most existing information protection solutions (or research reports) have offered methods of detecting malicious insider behavior through precise analysis of network traffic (IP, port, specific communication protocols, etc.) but have shown very high misuse detection results. This finding indicates that between WEB/WAS and other servers and PCs, various normal traffic occurs for numerous reasons, and there are many mistakes involving detecting normal traffic as malicious.
In contrast, many features that could pose internal threats were extracted in this study, and the risks of those features were prioritized in specific scenarios. If this approach enables identification of the most important malicious internal threats in a given scenario, a clear malicious insider can be found by correlating the logs of related information protection solutions. Therefore, we attempted to interpret logically the differences between this study and the existing papers and research methods with this perspective.
The following sentences provide various environmental information and prerequisites for final analysis to clarify the main findings of this study.
- -
- This study was based on internal information leakage scenarios arising from a specific organization, and the analysis can be performed differently according to the information security solution, internal/external security policy, business type, and cyber security response capability of each organization.
- -
- The analysis method proposed in this paper is a decision-making tool that supports the development of a response strategy according to the priority of the finally estimated importance of various features. Therefore, from a relative instead of an absolute perspective, it will support the establishment of information protection measures for organizations in the future.
- -
- The scenarios mentioned above can occur independently or be transformed into new or extended interdependent scenarios. Therefore, the proposed method is not intended to be used to establish a standardized policy, but rather is an adaptive and flexible method of analyzing inside threats.
6. Conclusions
In this study, in order to model leakage scenarios related to various possible insider threats from within an organization accurately, we analyzed scenarios by dividing them into “internal threats from inside the organization,” “internal threats from outside the organization,” and a “human and machine-focused internal threat scenario.” There were composed of highly probable features that could arise from a specific organization, and we used the AHP technique to quantify them. This approach substantially aided the understanding of the various scenarios and, consequently, long-term information leak scenarios. In other words, the final importance value calculated through attempts to quantify the entire stage for each scenario is likely to support decision-making regarding which stage to choose and focus on as a security administrator or manager. This information offers insight into the sensitive problem of internal data leakage in organizations and facilitates the development of active countermeasures against intelligent internal data leakage.
In future decision-making modeling, we intend to work on analyzing the internal threat sources in an organization in advance, as well as various security events collected through this approach, with the ultimate objective of patternizing the sources. Based on this information, we plan to make precise and active security measures easier for organizations through machine learning. Furthermore, to create realistic internal threat scenarios, we intend to prove various causal relationships between humans and machines by increasing the complexity through association/correlation analysis between scenarios.
Author Contributions
D.K. designed the plan of the proposed model, conducted the experiments, analyzed the insider threat data, and wrote the paper. S.S. designed the test plan of the proposed model, collected the experimental data, analyzed the result of experiment and wrote the paper together with D.K. All authors have read and approved the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Kyonggi University Research Grant (2019).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Insider Threat Report. 2019. Available online: https://www.fortinet.com/content/dam/fortinet/assets/threat-reports/insider-threat-report.pdf (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- Insider Threat Intelligence Report. 2018. Available online: https://nationalinsiderthreatsig.org/itrmresources/DTex%202018%20Insider%20Threat%20Intelligence%20Report.pdf (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- Bishop, M.; Gates, C. Defining the insider threat. In Proceedings of the 4th Annual Workshop on Cyber Security and Information Intelligence Research, Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 12–14 May 2008; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Kandias, M.; Mylonas, A.; Virvilis, N.; Theoharidou, M.; Gritzalis, D. An insider threat prediction model. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Trust, Privacy and Security in Digital Business, Bilbao, Spain, 30–31 August 2010; pp. 26–37. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, M.B.; Hershkop, S.; Stolfo, S.J. A survey of insider attack detection research. Adv. Inf. Secur. 2008, 39, 69–70. [Google Scholar]
- Homoliak, I.; Toffalini, F.; Guarnizo, J.; Elovici, Y.; Ochoa, M. Insight into insiders and IT: A survey of insider threat taxonomies, analysis, modeling, and countermeasures. ACM Comput. Surv. 2019, 52, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEI Cyber Minute: Insider Threats. April 2017. Available online: http://resources.sei.cmu.edu/library/asset-view.cfm?assetid=496626 (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- Cappelli, D.; Moore, A.; Trzeciak, R.; Shimeall, T.J. Common Sense Guide to Prevention and Detection of Insider Threats, 3rd ed.; Version 3.1; CyLab; Carnegie Mellon University; Software Engineering Institute: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2009; pp. 1–88. [Google Scholar]
- Vormetric Insider Threat Report. Technical Report. 2015. Available online: https://dtr.thalesesecurity.com/insiderthreat/2015/pdf/2015-vormetric-insider-threat-press-deck-v3.pdf (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- Young, W.T.; Memory, A.; Goldberg, H.G.; Senator, T.E. Detecting unknown insider threat scenarios. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Security and Privacy Workshops, San Jose, CA, USA, 18–21 May 2014; pp. 277–288. [Google Scholar]
- Legg, P.A.; Buckley, O.; Goldsmith, M.; Creese, S. Automated insider threat detection system using user and role-based profile assessment. IEEE Syst. J. 2015, 11, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, M.; Kim, H.; Cho, S.; Kang, P. Insider threat detection based on user behavior modeling and anomaly detection algorithms. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Woo, S.; Moon, D.; Choi, H. Secure cyber deception architecture and decoy injection to mitigate the insider threat. Symmetry 2018, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.M.; Monge, M.A.S. Obfuscation of malicious behaviors for thwarting masquerade detection systems based on locality features. Sensors 2020, 20, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, R.; Jhaveri, R.; Borrego, C. Applications in security and evasions in machine learning: A survey. Electronics 2020, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alom, M.Z.; Taha, T.M.; Yakopcic, C.; Westberg, S.; Sidike, P.; Nasrin, M.S.; Hasan, M.; Van Essen, B.C.; Awwal, A.A.S.; Asari, V.K. A state-of-the-art survey on deep learning theory and architectures. Electronics 2019, 8, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Meng, W.; Kwok, L.F.; Horace, H.S. Enhancing collaborative intrusion detection networks against insider attacks using supervised intrusion sensitivity-based trust management model. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2017, 77, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, J.M.; Vallejo, J.C.; Fraga, D.; Araujo, Á.; Villanueva, D.; de Goyeneche, J.M. Using reputation systems and non-deterministic routing to secure wireless sensor networks. Sensors 2009, 9, 3958–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, C.J.; Baysal, O.; Zhang, J.; Aib, I.; Boutaba, R. Trust management for host-based collaborative intrusion detection. Int. Work. Distrib. Syst. Oper. Manag. 2008, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, C.J.; Zhang, J.; Aib, I.; Boutaba, R. Robust and scalable trust management for collaborative intrusion detection. In Proceedings of the 2009 IFIP/IEEE International Symposium on Integrated Network Management, Long Island, NY, USA, 1–5 June 2009; pp. 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Azaria, A.; Richardson, A.; Kraus, S.; Subrahmanian, V.S. Behavioral analysis of insider threat: A survey and bootstrapped prediction in imbalanced data. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2014, 1, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greitzer, F.L.; Frincke, D.A. Combining traditional cyber security audit data with psychosocial data: Towards predictive modeling for insider threat mitigation. Insid. Threat. Cyber Secur. 2010, 49, 85–113. [Google Scholar]
- Maloof, M.A.; Stephens, G.D. Elicit: A system for detecting insiders who violate need-to-know. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Recent Advances in Intrusion Detection, Gold Coast, Australia, 5–7 September 2007; pp. 146–166. [Google Scholar]
- Caputo, D.D.; Maloof, M.A.; Stephens, G.D. Detecting insider theft of trade secrets. IEEE Secur. Priv. 2009, 7, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, S.; Petropoulos, M.; Ngo, H.Q.; Upadhyaya, S. A data-centric approach to insider attack detection in database systems. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Recent Advances in Intrusion Detection, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 15–17 September 2010; pp. 382–401. [Google Scholar]
- Ronao, C.A.; Cho, S.B. Anomalous query access detection in RBAC-administered databases with random forest and PCA. Inf. Sci. 2016, 369, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, O.; Buchanan, W.J.; Griffiths, P.; Macfarlane, R. Distance measurement methods for improved insider threat detection. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2018, 2018, 5906368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindauer, B.; Glasser, J.; Rosen, M.; Wallnau, K. Generating test data for insider threat detectors. J. Wirel. Mob. Netw. Ubiquitous Comput. Dependable Appl. 2014, 5, 80–94. [Google Scholar]
- Tabash, K.A.; Happa, J. Insider-threat detection using Gaussian mixture models and sensitivity profiles. Comput. Secur. 2018, 77, 838–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, N.; Creech, G.; Slay, J. Big data analytics for intrusion detection system: Statistical decision-making using finite dirichlet mixture models. In Data Analytics and Decision Support for Cybersecurity; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 127–156. [Google Scholar]
- Tuor, A.; Kaplan, S.; Hutchinson, B.; Nichols, N.; Robinson, S. Deep learning for unsupervised insider threat detection in structured cybersecurity data streams. In Proceedings of the Workshops at the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–5 February 2017; pp. 224–234. [Google Scholar]
- Ndibanje, B.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, S.G. Security analysis and improvements of authentication and access control in the internet of things. Sensors 2014, 14, 14786–14805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, N.; Choi, B.J. State of the art authentication, access control, and secure integration in smart grid. Energies 2015, 8, 11883–11915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, X.F.; Camp, J. Game-theoretic modeling and analysis of insider threats. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. Prot. 2008, 1, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantzavelou, I.; Katsikas, S. A game-based intrusion detection mechanism to confront internal attackers. Comput. Secur. 2010, 29, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berninghaus, S.K.; Neumann, T.; Vogt, B. Learning in networks-An experimental study using stationary concepts. Games 2014, 5, 140–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, M. Cyber insider threats situation awareness using game theory and information fusion-based user behavior predicting algorithm. J. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2011, 8, 529–545. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Yu, W.; Fu, X.; Das, S.K. Maintaining defender’s reputation in anomaly detection against insider attacks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. Part B Cybern. 2010, 40, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinchani, R.; Iyer, A.; Ngo, H.Q.; Upadhyaya, S. Towards a theory of insider threat assessment. In Proceedings of the 2005 International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks, Yokohama, Japan, 28 June–1 July 2005; pp. 108–117. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.; Dong, M.; Ota, K.; Wu, J.; Li, J. A security assessment mechanism for software-defined networking-based mobile networks. Sensors 2015, 15, 31843–31858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberle, W.; Graves, J.; Holder, L. Insider threat detection using a graph-based approach. J. Appl. Secur. Res. 2010, 6, 32–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serketzis, N.; Katos, V.; Ilioudis, C.; Baltatzis, D.; Pangalos, G. Improving forensic triage efficiency through cyber threat intelligence. Futur. Internet 2019, 11, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. Int. J. Ser. Sci. 2008, 1, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).