Spatial Gradient Effects of Landscape Pattern on Ecological Quality Along the Grand Canal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sources
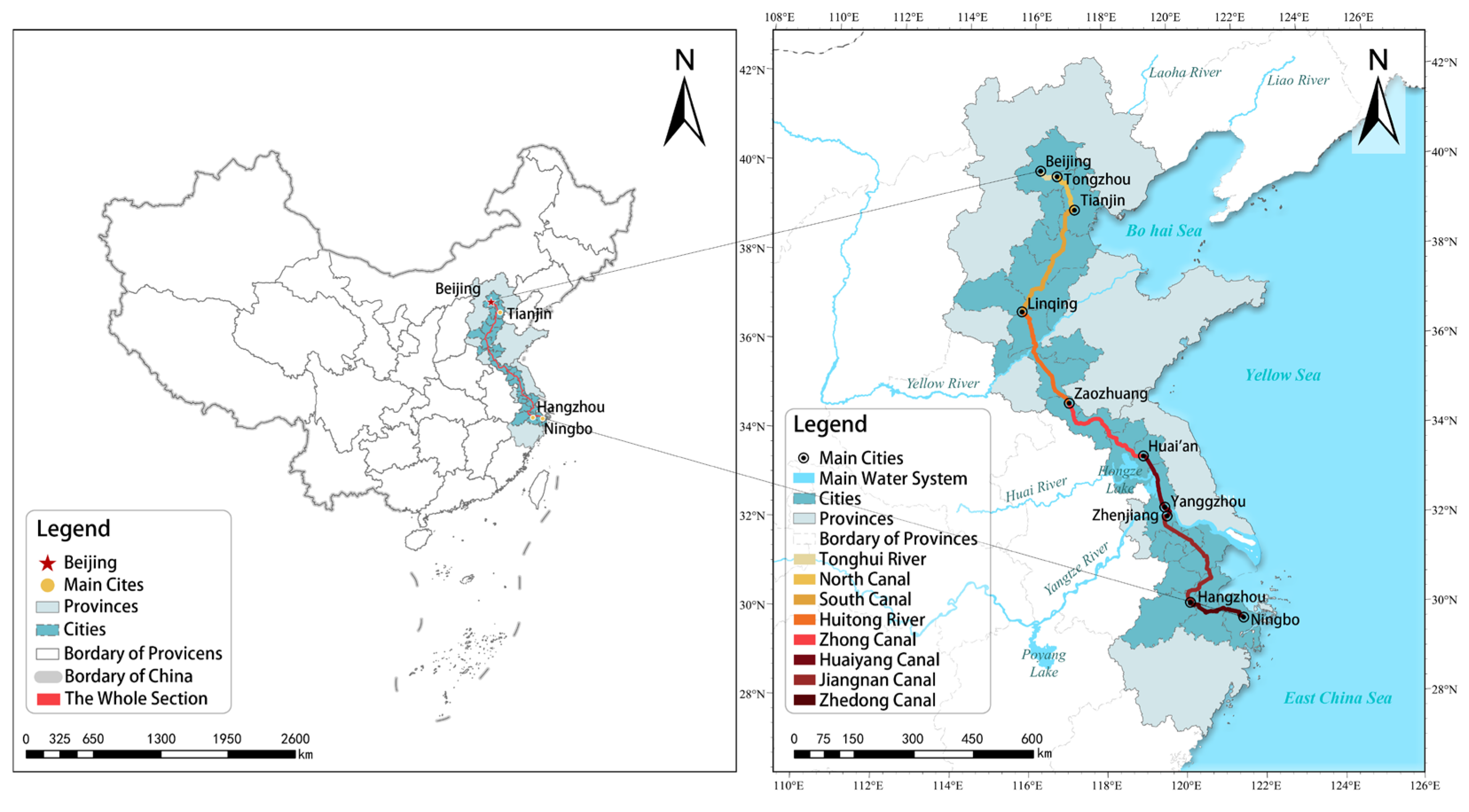
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Pre-Processing
3. Methods
3.1. Landscape Pattern Metrics
3.2. Ecological Quality Assessment
3.3. Spatial Correlation Between Landscape Patterns and Ecological Quality
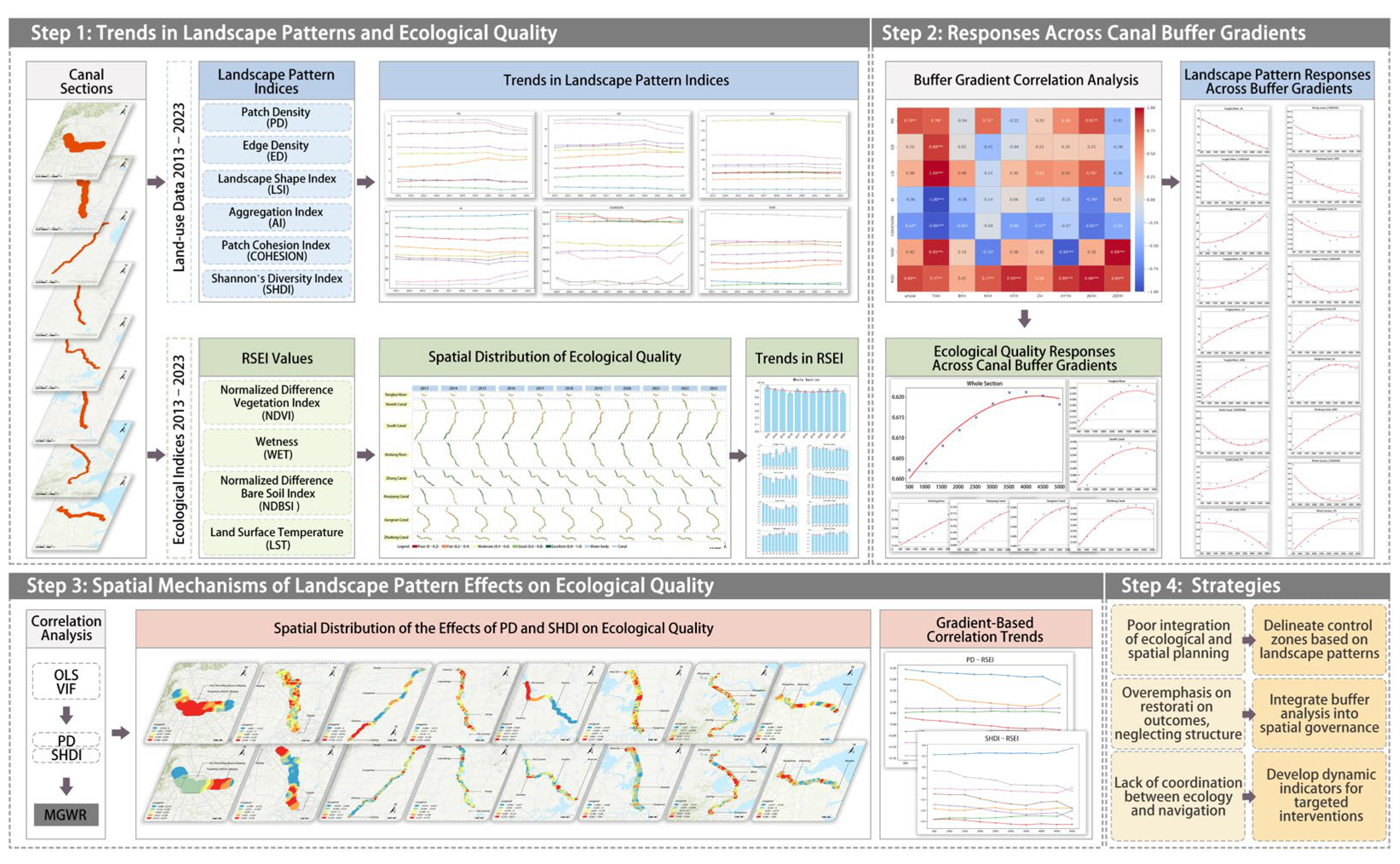
4. Results
4.1. Trends in Landscape Pattern and Ecological Quality
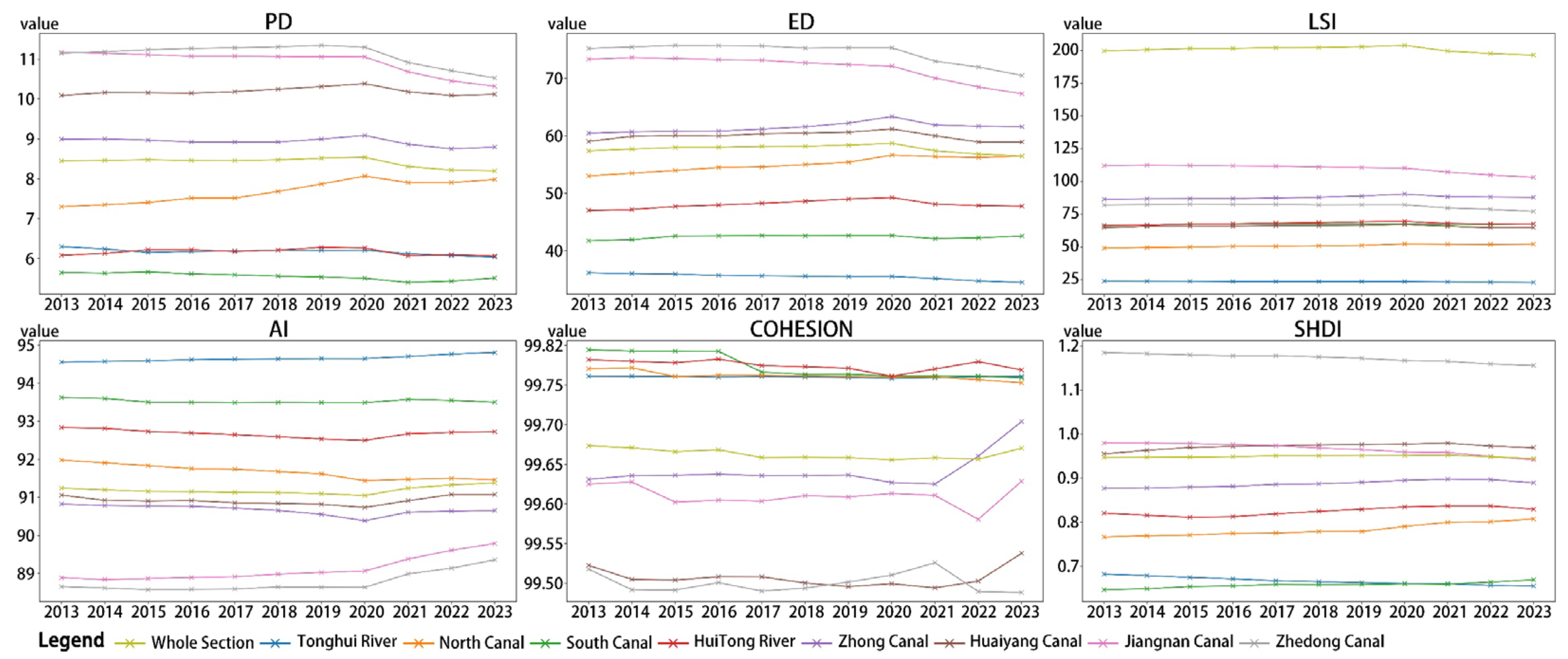
4.1.1. Trends in Landscape Pattern Changes
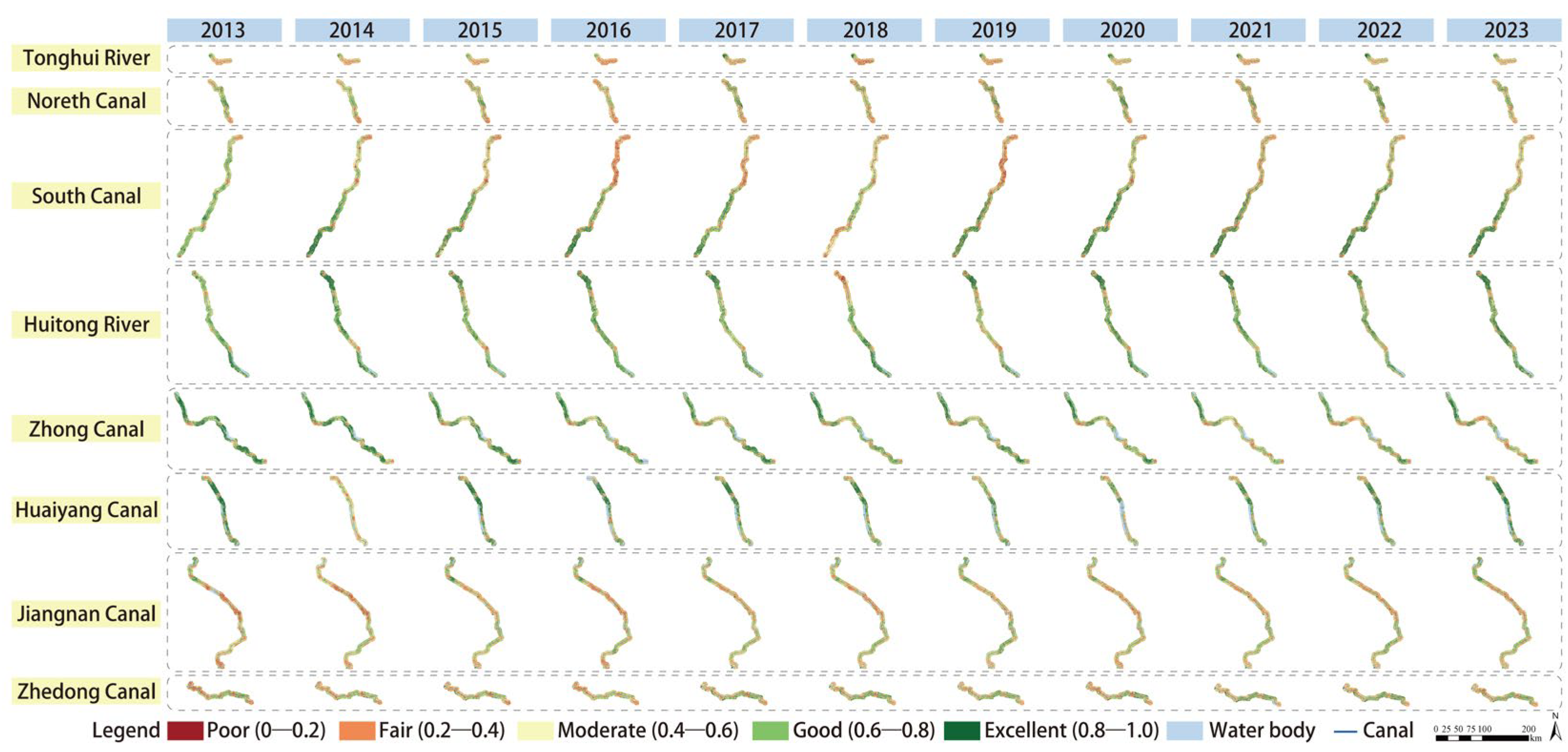
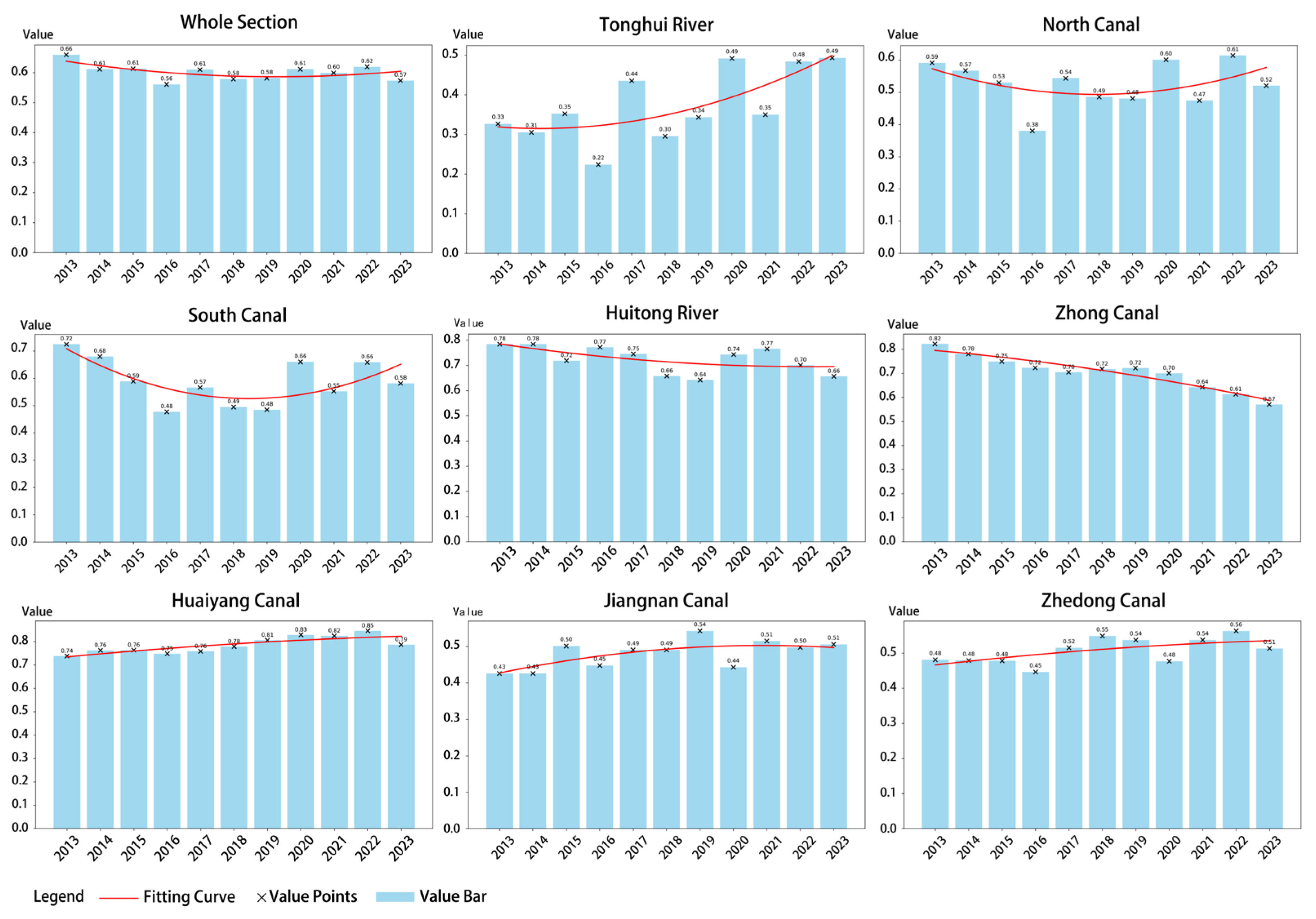
4.1.2. Trends in Ecological Quality Changes
4.2. Landscape Pattern and Ecological Quality Responses Across Canal Buffer Gradients
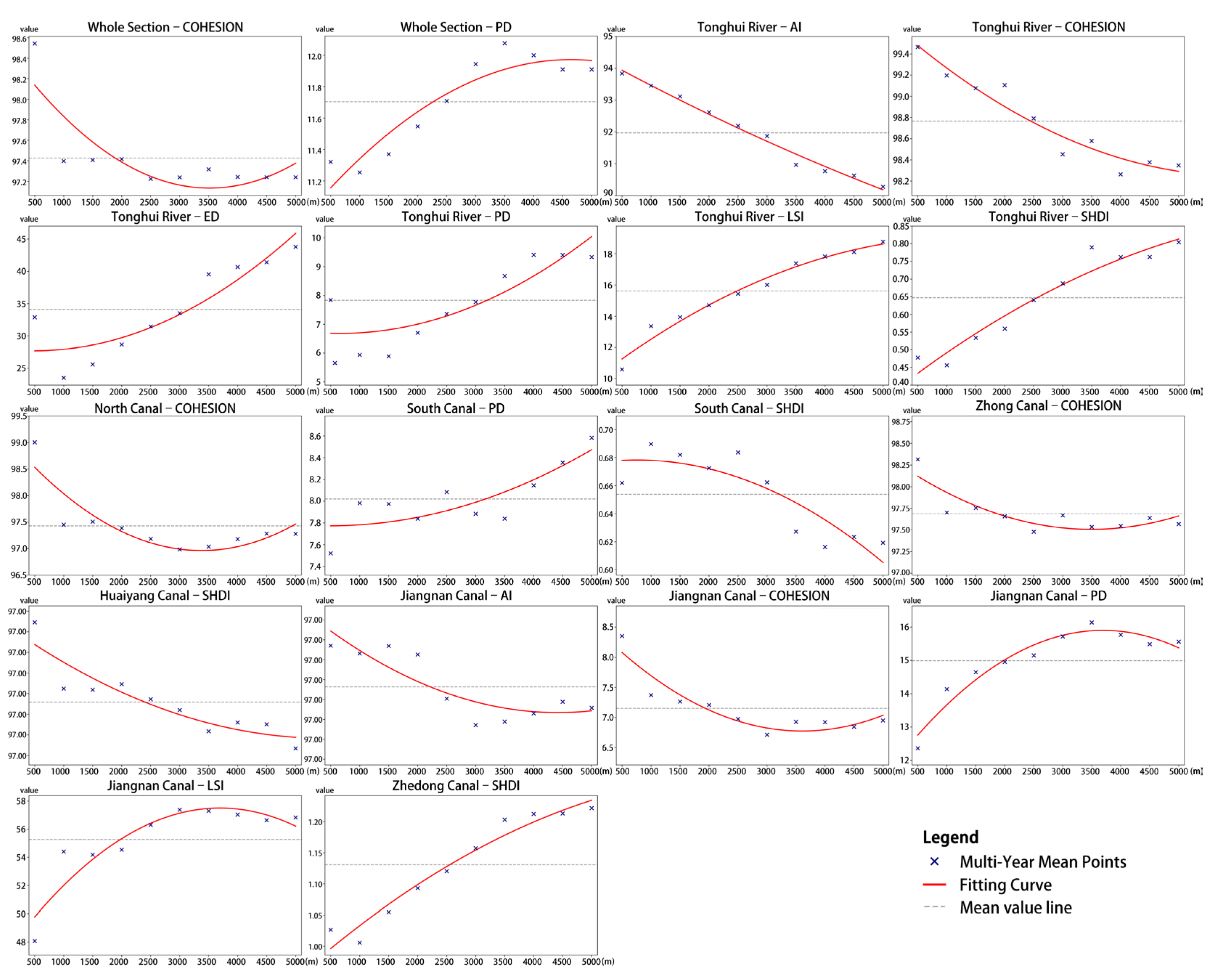
4.2.1. Landscape Pattern Index Responses Across Canal Buffer Gradients
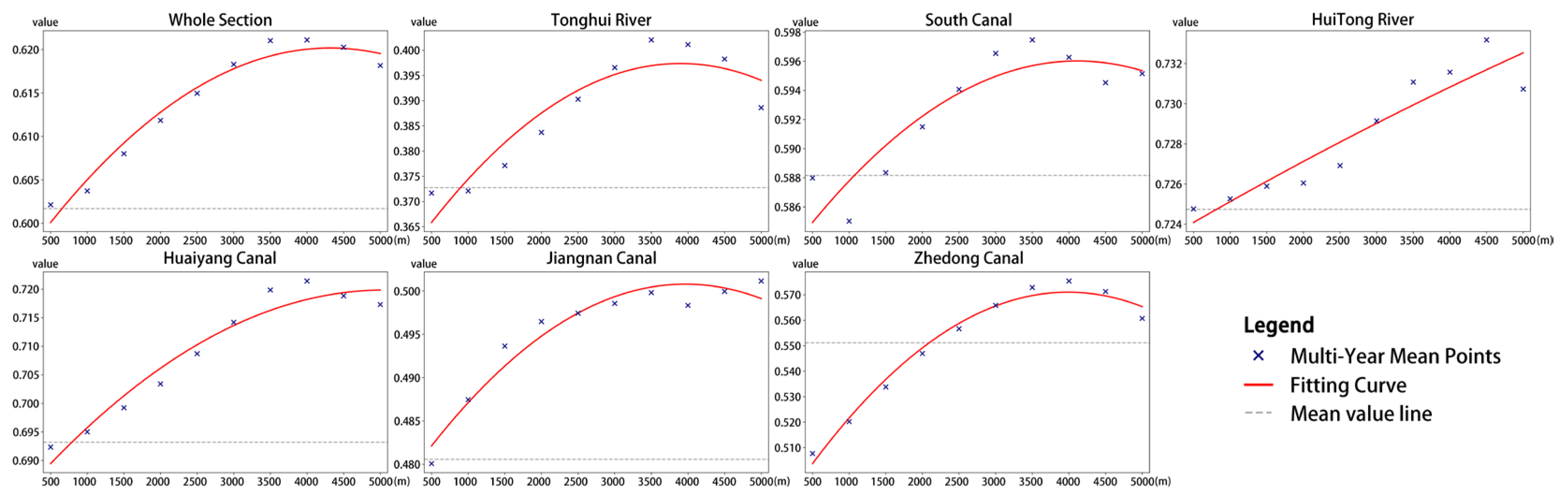
4.2.2. Ecological Quality Responses Across Canal Buffer Gradients
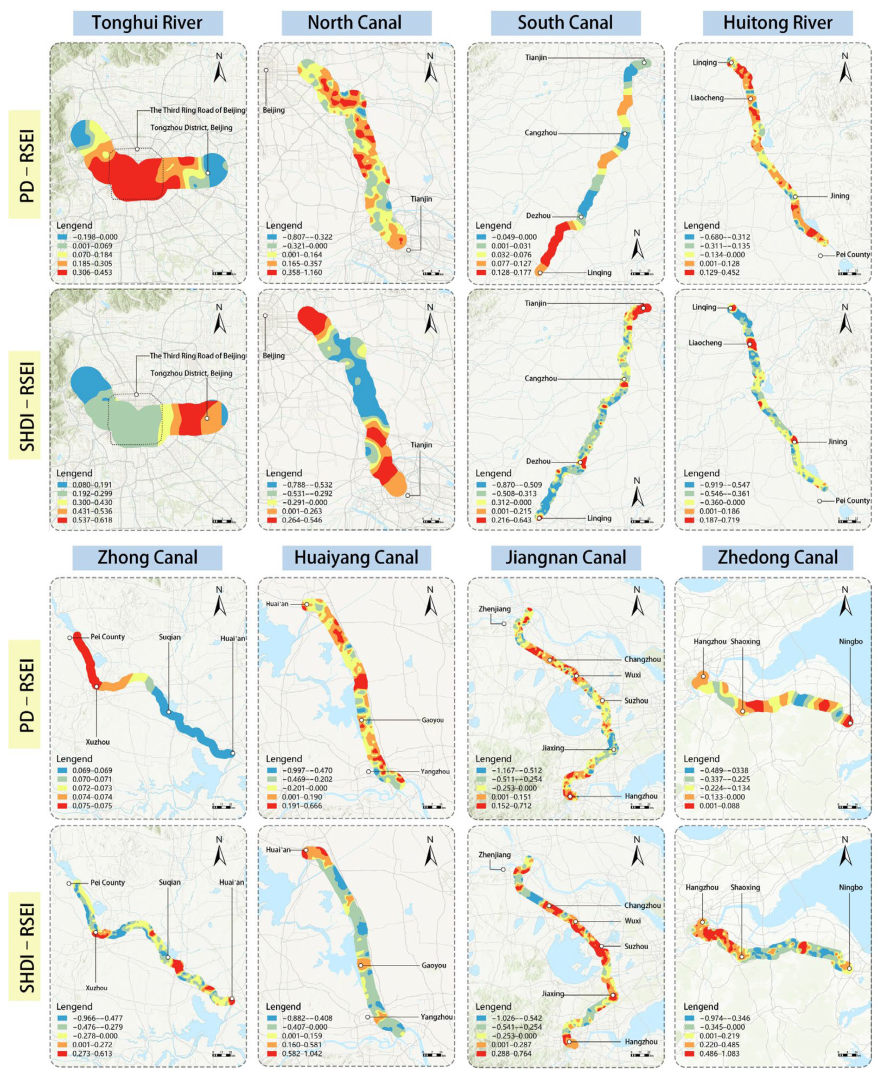
4.3. Spatial Mechanisms of Landscape Pattern Effects on Ecological Quality
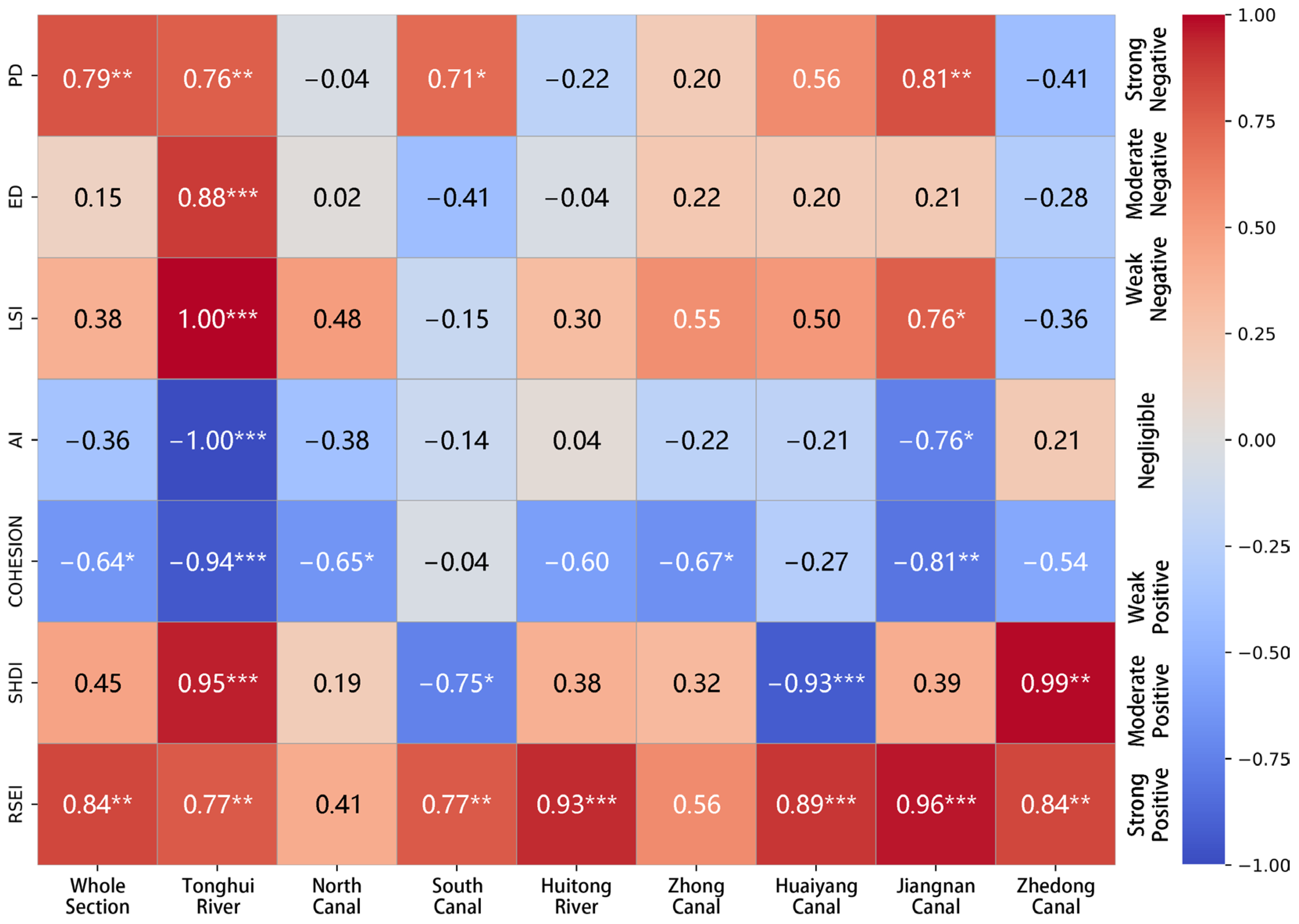
4.3.1. Spatial Effects of Landscape Pattern on Ecological Quality
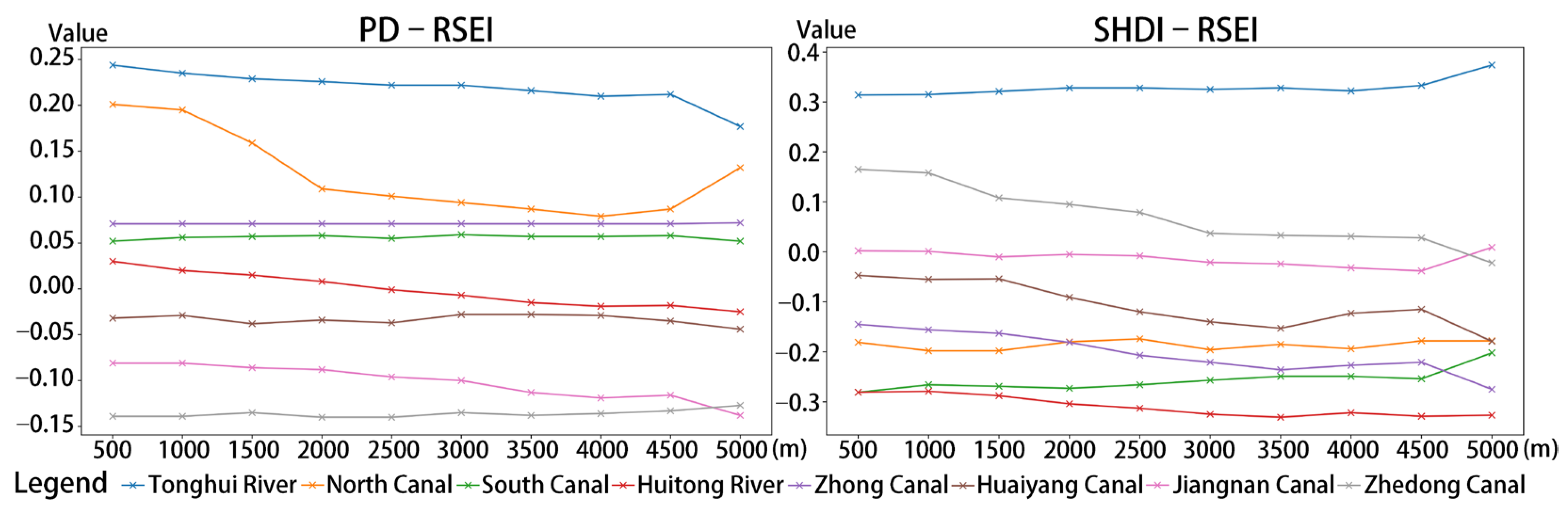
4.3.2. Landscape Pattern Effects on Ecological Quality Across Buffer Gradients
5. Discussion
5.1. Mechanistic Analysis of the Evolution of Landscape Pattern and Ecological Quality
5.2. Differential Responses of Ecological Quality to Landscape Pattern
5.3. Ecological Planning Strategies and Policy Implications
5.4. Limitations and Future Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, J.; Zhao, T.; Cao, L.; Bijecki, F. Semantic Riverscapes: Perception and evaluation of linear landscapes from oblique imagery using computer vision. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 228, 104569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Chen, S. Rebel on the Canal: Disrupted Trade Access and Social Conflict in China. 1650–1911. Am. Econ. Rev. 2022, 112, 1555–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y.; Fu, M.; Huang, N.; Duan, W.; Luo, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Song, W. Spatio-temporal variation and coupling coordination relationship between urbanisation and habitat quality in the Grand Canal, China. Land Use Policy 2022, 117, 106119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, L.; Han, Q.; Wang, X.; Zou, T.; Fan, C. Estimation of remote sensing based ecological index along the Grand Canal based on PCA-AHP-TOPSIS methodology. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Ye, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Duan, Y. Identifying intrinsic drivers to changes in riparian ecosystem services by using PSR framework: A case study of the Grand Canal in Jiangsu, China. Environ. Dev. 2022, 43, 100728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Pei, T.; Chan, C.; Wang, M.; Meng, B. Tourism value assessment of linear cultural heritage: The case of the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal in China. Curr. Issues Tour. 2023, 26, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Song, W. Ecological function regionalization of the core area of the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal based on the leading ecological function perspective. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Wu, J. Coupling coordination degree and obstacle factors between the tourism industry and ecological environment in the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal Basin, China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 2589–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Xiao, X.; Chen, F.; Huang, Y.; Kang, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Gao, M.; Du, Y. Satellite-Based Water Quality Assessment of the Beijing Section of the Grand Canal: Implications for SDG11.4 Evaluation. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, A.; Sun, F.; Zhang, B.; Wu, Q.; Cai, S.; Yang, Z.; Chang, Y.; Han, R.; Yu, S. Spatiotemporal dynamics and driving factors of vegetation coverage around linear cultural heritage: A case study of the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 119431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Peng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Lyu, J.; Pan, M. From nature-based to engineering-based: The interaction process and turning point of the city-water system relationship in the North China plain. Appl. Geogr. 2021, 135, 102556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, S. Spatio-temporal evolution and distribution of cultural heritage sites along the Suzhou canal of China. Herit. Sci. 2023, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jing, Z.; Huang, Q.; Wang, X.; Sun, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, J.; Tan, L. On conservation of world heritage Beijing-Hangzhou grand canal for enhancing cultural ecosystem services. Herit. Sci. 2023, 11, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Dang, Q.; Li, C.; Fan, Y. Analysis of Landscape Fragmentation Evolution Characteristics and Driving Factors in the Wei River Basin, China. Land 2025, 14, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jin, X.; Lin, J.; Liang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y. Identification and characteristic analysis of semi-natural habitats in China’s economically developed areas: New insights to inform cultivated land system ecological conservation. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Bai, H.; He, H.; Zhang, Y. Combining ecosystem service value and landscape ecological risk to subdivide the riparian buffer zone of the Weihe River in Shaanxi. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.C.P.; Martins, L.M.D.; Pacheco, F.A.L.; Fernandes, L.F.S. The consequences for stream water quality of long-term changes in landscape patterns: Implications for land use management and policies. Land Use Policy 2021, 109, 105679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Liu, Z.; Kang, W.; Su, J.; Zhang, R.; Xu, X. Historical Spatial Radiation Range of the Yongding River Corridor in Beijing Plain Section: Implications for Landscape Patterns and Ecological Restoration. Land 2023, 12, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Yan, X.; Li, X.; Huang, Z.; Yan, X.; Xia, Y. Significant differences in optimal riparian buffer zone on water quality between different segments within the same river. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 381, 125306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H.; Cheng, J. Spatiotemporal Variations of Ecosystem Service Indicators and the Driving Factors Under Climate Change in the Qinghai-Tibet Highway Corridor. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 935713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Darvishan, A.K.; Dinelli, E.; Bahramifar, N.; Alavi, S.J. How does land use configuration influence on sediment heavy metal pollution? Comparison between riparian zone and sub-watersheds. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 36, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, L. Spatial effect of river landscape on housing price: An empirical study on the Grand Canal in Hangzhou, China. Habitat Int. 2017, 63, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Jing, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Yin, W.; Zhao, S. Identification of Ecological Security Pattern and Ecological Restoration Zoning Strategy in the Shandong Section of the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal. Land 2025, 14, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, G. Effects of transport infrastructures and climate change on ecosystem services in the integrated transport corridor region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 885, 163961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Hui, Z. Landscape ecological risk assessment of Chinese coastal cities based on land use change. Appl. Geogr. 2020, 117, 102174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Ahmed, Z.; Majeed, A.; Huang, B. An environmental impact assessment of economic complexity and energy consumption: Does institutional quality make a difference? Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 89, 106603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, A.; Pata, U.K. The role of ICT, R&D spending and renewable energy consumption on environmental quality: Testing the LCC hypothesis for G7 countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 135038. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Xu, H. A new remote sensing index for assessing the spatial heterogeneity in urban ecological quality: A case from Fuzhou City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizizi, Y.; Kasimu, A.; Liang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, B. Evaluation of ecological space and ecological quality changes in urban agglomeration on the northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.; Jin, X.; Ren, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z. Ecological environment quality assessment based on remote sensing data for land consolidation. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 118126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firozjaei, M.K.; Fatholoumi, S.; Kiavvarz, M.; Biswas, A.; Homaee, M. Land Surface Ecological Status Composition Index (LSESCI): A novel remote sensing-based technique for modeling land surface ecological status. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 123, 107375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.; Hu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal Changes and Driving Analysis of Ecological Environmental Quality along the Qinghai–Tibet Railway Using Google Earth Engine—A Case Study Covering Xining to Jianghe Stations. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Jia, P.; Huang, X.; Yang, J.; Mao, Z.; Shen, S. Highway Ecological Environmental Assessment Based on Modified Remote Sensing Index—Taking the Lhasa–Nyingchi Motorway as an Example. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Qiao, J.; Li, M.; Dun, Y.; Zhu, X. Spatiotemporal evolution of ecological environmental quality and its dynamic relationships with landscape pattern in the Zhengzhou Metropolitan Area: A perspective based on nonlinear effects and spatiotemporal heterogeneity. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 480, 144102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xu, W.; Yu, J.; Xie, X.; Xie, Z.; Lei, X.; Wu, Z.; Ding, Z. Exploring the impact of changing landscape patterns on ecological quality in different cities: A comparative study among three megacities in eastern and western China. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 77, 102255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Zhan, L.; Yao, M.; Yang, L. A geographically weighted regression model augmented by Geodetector analysis and principal component analysis for the spatial distribution of PM2.5. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 56, 102106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.; Al Kindi, A.; Al-Said, A.; Al-Said, A.; Atkinson, P. Sociodemographic determinants of COVID-19 incidence rates in Oman: Geospatial modelling using multiscale geographically weighted regression (MGWR). Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 65, 102627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Majumder, S.; Bose, A.; Chowdhury, I.R. The rich-poor divide: Unravelling the spatial complexities and determinants of wealth inequality in India. Appl. Geogr. 2024, 166, 103267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, S.; Lu, Y.; Yang, H.; Yang, L. Multiscale impacts of urban nature on land surface temperature over two decades in a city with cloudy and foggy climates. Urban Clim. 2025, 61, 102389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Qiu, A.; Cao, A.; Zhang, W.; Xu, M. Spatial Responses of Ecosystem Service Trade-offs and Synergies to Impact Factors in Liaoning Province. Environ. Manag. 2025, 75, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zan, Y.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Sun, F.; Zhang, C.; Lu, C. Evaluation of Water Replenishment in the Northern Segment of the Yellow River Within the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal, China. Water 2025, 17, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Hu, Z.; Wang, P.; Han, J.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, X.; Cao, Y. Crop Classification and Growth Monitoring in Coal Mining Subsidence Water Areas Based on Sentinel Satellite. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakoto, P.Y.; Delami, K.; Hurley, J.; Amati, M.; Sun, Q. Revisiting the cooling effects of urban greening: Planning implications of vegetation types and spatial configuration. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 64, 127266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yu, j.; Xu, W.; Wu, Y.; Lei, X.; Ye, j.; Geng, J.; Ding, Z. Long-time series ecological environment quality monitoring and cause analysis in the Dianchi Lake Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Fu, L.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Li, F.; Deng, Z.; Xie, Y. Spatiotemporal change detection of ecological quality and the associated affecting factors in Dongting Lake Basin, based on RSEI. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 302, 126995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; She, J.; Long, X.; Zhang, M. Spatio-temporal evolution and driving factors of eco-environmental quality based on RSEI in Chang-Zhu-Tan metropolitan circle, central China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Xu, W.; Lu, N.; Huang, S.; Wu, C.; Wang, L.; Dai, F.; Kou, W. Assessment of spatial–temporal changes of ecological environment quality based on RSEI and GEE: A case study in Erhai Lake Basin, Yunnan province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Guo, C.; Marinello, F. Instability of remote sensing based ecological index (RSEI) and its improvement for time series analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wei, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, H. Spatiotemporal variation of land use and its impact on ecosystem service value in the Beiyun River Basin from 1980 to 2015. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2021, 41, 301–310. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zou, Y.; Liu, B. Evolution mechanisms and development strategies of local human residential environment landscape in the Jiangnan Canal Basin. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2025, 41, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Fu, B. Historical social connectivity of the Tonghui River system in Beijing from an urban spatial perspective. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2022, 38, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Lu, Y.; Cao, M.; Wang, R.; Chen, J. Assessing accessibility to peri-urban parks considering supply, demand, and traffic conditions. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2025, 257, 105313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Chen, X.; Yuan, Z.; Ye, C.; Liang, Y. Impact of landscape patterns on water quality in urbanized rivers at characteristic scale: A case of Pearl River Delta, China. Environ. Manag. 2024, 74, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatayu, A.; Rustiadi, E.; Juanda, B.; Pribadi, D.O. Metric-based approach for quantifying urban expansion impact on urban form changes in the JBMUR south conurbation corridor. Land 2023, 12, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlier, J.; Moran, J. Landscape typology and ecological connectivity assessment to inform Greenway design. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 3241–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Qin, K.; Dai, S.; Lu, H.; Lu, M.; Ji, J.; Yang, Z.; Chen, C.; Jia, P. Long-term dynamic monitoring and driving force analysis of eco-environmental quality in China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Yang, J.; Yu, H.; Ren, J.; Yu, W.; Cong, N.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J.; Li, X.; Qiao, Z. Towards ecological civilization: Spatiotemporal heterogeneity and drivers of ecological quality transitions in China (2001–2020). Appl. Geogr. 2024, 173, 103439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Peng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, D.; Dong, J. Zoning for ecosystem restoration based on ecological network in mountainous region. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yu, X.; Ng, N.; Li, K.; Fang, L. Exploring the dynamic correlation of landscape composition and habitat fragmentation with surface water quality in the Shenzhen river and deep bay cross-border watershed, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 90, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cui, Y.; Qin, Y.; Qin, H.; Dong, J. Construction land allocation in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and Yangtze River Delta urban agglomerations. J. Geogr. Sci. 2025, 35, 501–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Qian, Y.; Fang, Y.; Shi, X.; Yao, S.; Dong, B.; Ji, K.; Wang, Z. Road network expansion and landscape dynamics in the Chaohu Lake wetland: A 20-year analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 173, 113443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Shen, A.; Liu, C.; Wen, B. Impacts of ecological land fragmentation on habitat quality in the Taihu Lake basin in Jiangsu Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ao, Y.; Ke, J.; Lu, Y.; Liang, Y. To walk or not to walk? Examining non-linear effects of streetscape greenery on walking propensity of older adults. J. Transp. Geogr. 2021, 94, 103099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Tan, L.; Yan, Y.; Tian, Y.; Shen, Y.; Cao, H.; Dong, M. Measures and planning for wetland restoration of Xianghe Segment of China’s Grand Canal. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2016, 23, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurora, R.M.; Furuya, K. Spatiotemporal analysis of urban sprawl and ecological quality study case: Chiba Prefecture, Japan. Land 2023, 12, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, H.; Yu, B.; Lu, Y.; Cui, J.; Lin, D. Exploring non-linear and synergistic effects of green spaces on active travel using crowdsourced data and interpretable machine learning. Travel Behav. Soc. 2024, 34, 100673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, G.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, J. Exploring Characteristics and Patterns of In Situ Space Morphology: Perspective of the Historical and Cultural Canal Settlement. Land 2024, 13, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Bian, G.; Sun, T.; Yan, J. The In-Situ Spatial-Temporal Evolution of the Settlement Space along the Grand Canal Tianjin Section from the Perspective of Cultural Heritage. Land 2023, 12, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, M.; Zhang, P. Linking Ecosystem Service and MSPA to Construct Landscape Ecological Network of the Huaiyang Section of the Grand Canal. Land 2021, 10, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Wang, Z. Construction of recreation opportunity spectrum of Grand Canal National Cultural Park based on scene theory—Taking the Yuhe River section of Beijing as an example. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2022, 38, 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Dai, L. Exploring the construction path of the Grand Canal National Cultural Park based on territorial spatial planning. J. Nat. Resour. 2023, 38, 2312–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, L.; Magalhães, M.R. Assessing the ecological suitability of land-use change. Lessons learned from a rural marginal area in southeast Portugal. Land Use Policy 2022, 122, 106381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Xiao, D.; Zhou, K. Corridor effect of the spatial changes of landscape patterns in and areas: A case study of the river corridor areas in the middle and lower reaches of Tarim River. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51 (Suppl. 1), 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin, C.; Mistry, I.; Young, N. Collaborative knowledge mapping to inform environmental policy-making: The case of Canada’s Rideau Canal National Historic Site. Environ. Sci. Policy 2022, 128, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Bobbink, I.; Chouairi, A. Water narratives exploring the convergence of the Canal du Midi and its coastal landscape. Shima 2023, 17, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data | Resolution | Year | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Land-use data | 30 m | 2013–2023 | https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.12779975 (accessed on 12 February 2025) |
| Landsat 8 OLI | 30 m | 2013–2023 | https://www.usgs.gov/landsat (accessed on 13 February 2025) |
| Canals and rivers | − | 2021 | https://www.webmap.cn (accessed on 13 February 2025) |
| Index | Description |
|---|---|
| Patch Density (PD) | Quantifies landscape fragmentation; a higher number of patches indicates greater fragmentation. |
| Edge Density (ED) | Captures boundary complexity; longer total edge length suggests more intricate patch boundaries. |
| Landscape Shape Index (LSI) | Measures patch shape irregularity, normalized to remove area influence. |
| Aggregation Index (AI) | Indicates the degree of clustering among patches of the same type; higher values imply stronger aggregation. |
| Patch Cohesion Index (COHESION) | Reflects spatial connectivity of similar patches; higher values denote more continuous landscapes. |
| Shannon’s Diversity Index (SHDI) | Represents landscape diversity in terms of richness and evenness of patch types, indicating overall heterogeneity. |
| Index | Formula |
|---|---|
| NDVI | |
| LST | |
| WET | |
| NDBSI | |
| Year | Loading of NDVI | Loading of LST | Loading of WET | Loading of NDBSI | Contribution Ratio of PC1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | −0.605 | −0.381 | 0.410 | 0.566 | 77.14 |
| 2014 | −0.617 | −0.386 | 0.380 | 0.571 | 78.79 |
| 2015 | −0.603 | −0.404 | 0.370 | 0.580 | 78.98 |
| 2016 | −0.600 | −0.431 | 0.353 | 0.573 | 80.78 |
| 2017 | −0.600 | −0.416 | 0.336 | 0.595 | 77.36 |
| 2018 | −0.600 | −0.426 | 0.357 | 0.576 | 74.50 |
| 2019 | −0.597 | −0.432 | 0.358 | 0.573 | 79.59 |
| 2020 | −0.597 | −0.393 | 0.401 | 0.574 | 80.11 |
| 2021 | −0.582 | −0.417 | 0.388 | 0.580 | 80.05 |
| 2022 | −0.616 | −0.395 | 0.352 | 0.583 | 77.70 |
| 2023 | −0.599 | −0.414 | 0.381 | 0.569 | 79.31 |
| Canal Sections | Moran’s I | Z-Score | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tonghui River | 0.756 | 42.803 | 0.000 |
| North Canal | 0.692 | 56.488 | 0.000 |
| South Canal | 0.762 | 105.278 | 0.000 |
| Huitong River | 0.696 | 116.113 | 0.000 |
| Zhong Canal | 0.750 | 95.144 | 0.000 |
| Huaiyang Canal | 0.726 | 70.513 | 0.000 |
| Jiangnan Canal | 0.732 | 71.388 | 0.000 |
| Zhedong Canal | 0.724 | 98.891 | 0.000 |
| Canal Sections | OLS | MGWR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AICc | R2 | Adj.R2 | AICc | R2 | Adj.R2 | |
| Tonghui River | 3899.508 | 0.389 | 0.388 | 2114.404 | 0.826 | 0.810 |
| North Canal | 9726.510 | 0.020 | 0.019 | 5491.568 | 0.780 | 0.750 |
| South Canal | 27,821.192 | 0.042 | 0.042 | 12,619.346 | 0.839 | 0.819 |
| Huitong River | 21,105.191 | 0.095 | 0.095 | 10,451.657 | 0.828 | 0.804 |
| Zhong Canal | 21,406.759 | 0.060 | 0.060 | 11,500.445 | 0.789 | 0.767 |
| Huaiyang Canal | 10,757.009 | 0.057 | 0.057 | 5263.762 | 0.834 | 0.808 |
| Jiangnan Canal | 26,015.883 | 0.037 | 0.037 | 13,281.209 | 0.817 | 0.790 |
| Zhedong Canal | 13,292.110 | 0.091 | 0.090 | 7308.020 | 0.799 | 0.771 |
| Canal Sections | Landscape Pattern Indices | Average Value | Minimum Value | Median Value | Maximum Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tonghui River | PD | 0.222 | −0.198 | 0.282 | 0.453 |
| SHDI | 0.324 | 0.080 | 0.265 | 0.618 | |
| North Canal | PD | 0.125 | −1.003 | 0.132 | 1.392 |
| SHDI | −0.186 | −0.789 | −0.307 | 0.545 | |
| South Canal | PD | 0.057 | −0.051 | 0.047 | 0.177 |
| SHDI | −0.262 | −0.958 | −0.350 | 0.741 | |
| Huitong River | PD | −0.002 | −0.707 | 0.029 | 0.503 |
| SHDI | −0.313 | −0.985 | −0.373 | 0.768 | |
| Zhong Canal | PD | 0.071 | 0.068 | 0.071 | 0.075 |
| SHDI | −0.204 | −1.022 | −0.251 | 0.634 | |
| Huaiyang Canal | PD | −0.032 | −1.065 | −0.025 | 0.880 |
| SHDI | −0.105 | −0.934 | −0.150 | 1.087 | |
| Jiangnan Canal | PD | −0.102 | −1.255 | −0.069 | 0.867 |
| SHDI | −0.014 | −1.048 | 0.026 | 0.797 | |
| Zhedong Canal | PD | −0.138 | −0.497 | −0.135 | 0.089 |
| SHDI | 0.075 | −1.150 | 0.076 | 1.166 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, Y.; Jin, A. Spatial Gradient Effects of Landscape Pattern on Ecological Quality Along the Grand Canal. Land 2025, 14, 1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061310
Xiong Y, Jin A. Spatial Gradient Effects of Landscape Pattern on Ecological Quality Along the Grand Canal. Land. 2025; 14(6):1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061310
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Yonggeng, and Aibo Jin. 2025. "Spatial Gradient Effects of Landscape Pattern on Ecological Quality Along the Grand Canal" Land 14, no. 6: 1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061310
APA StyleXiong, Y., & Jin, A. (2025). Spatial Gradient Effects of Landscape Pattern on Ecological Quality Along the Grand Canal. Land, 14(6), 1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061310







