An Assessment of the N Load from Animal Farms in Saline Wetland Catchments in the Ebro Basin, NE Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
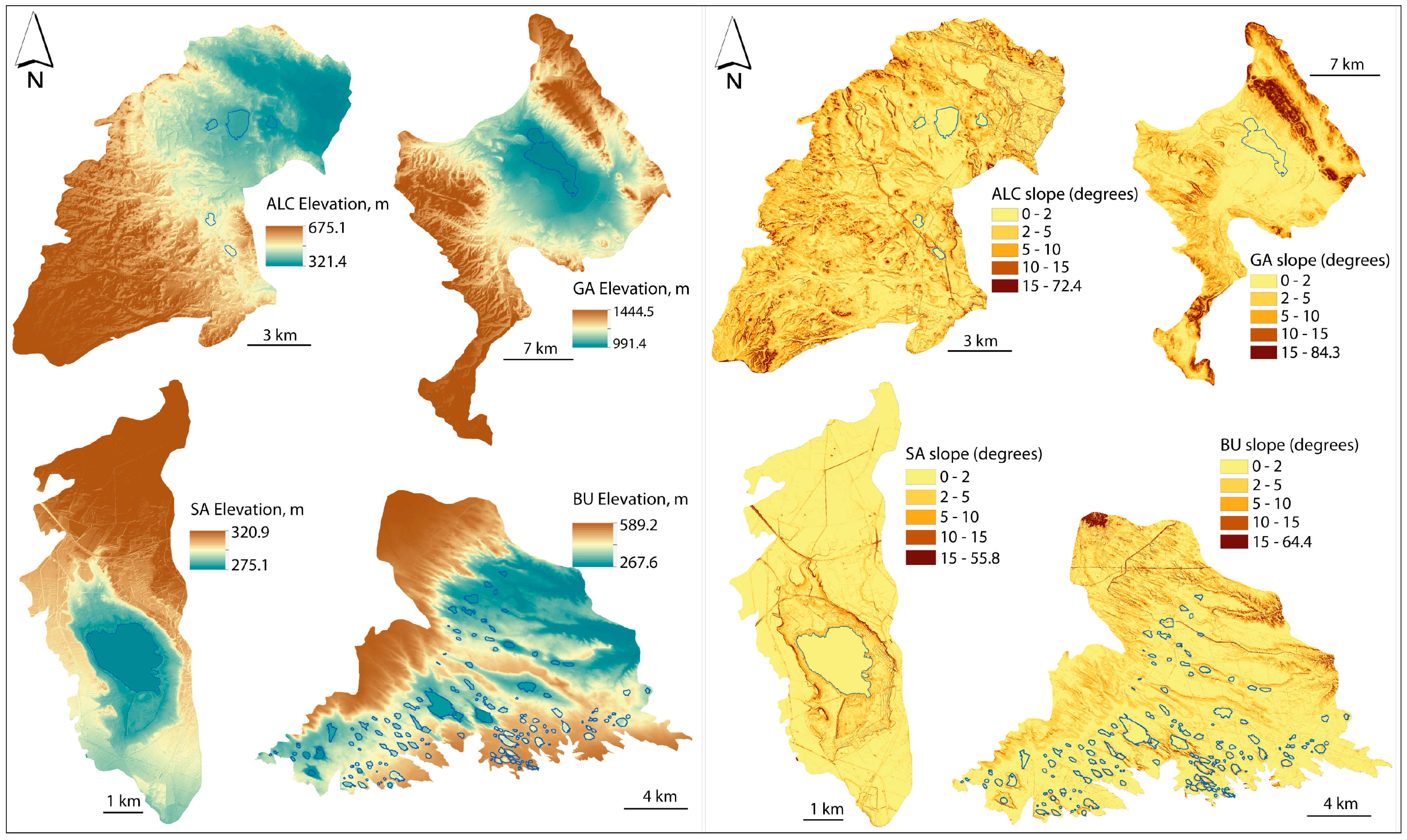
2.1. Study Areas
2.2. Wetland Watershed Delimitation
2.3. Livestock Census and N Produced
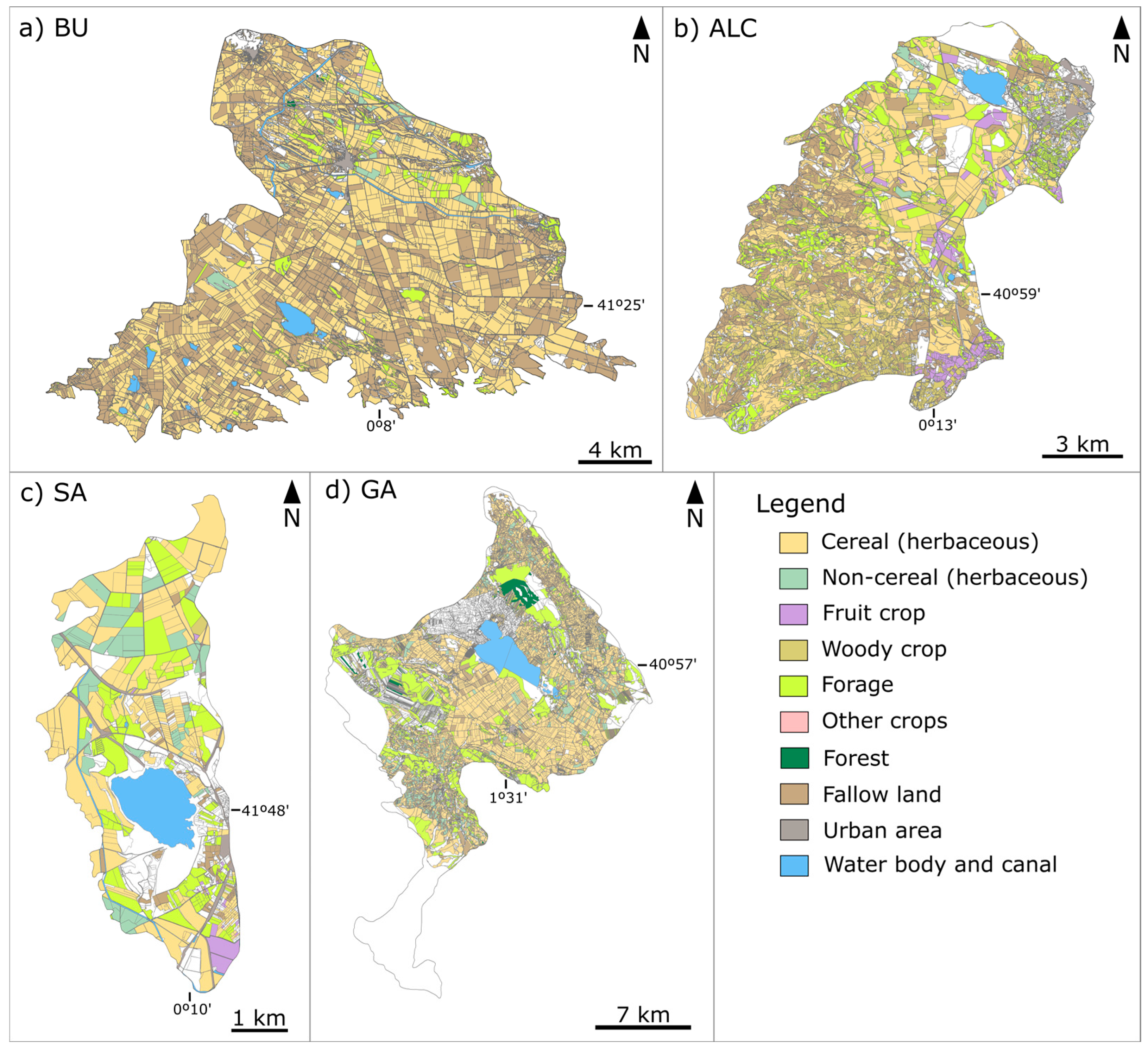
2.4. Crop and Plot Information
2.5. Areas and Doses of Application of Animal Excreta
2.6. N Pressure Balances and Indexes
| N balance Index | Index Value | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| N Balance (NB) | NB ≥ 0 | Excess N from organic sources |
| NB < 0 | Still available N capacity | |
| NB/7.6 < 0 | Still available capacity (number of fattening pigs) | |
| Livestock Load Index (LLI) adapted from [34] | 0.5 < LLI ≤ 0.8 | Capacity to absorb more organics |
| 0.8 < LLI ≤ 1.0 | Compatible | |
| 1.0 < LLI ≤ 1.2 | Moderate | |
| LLI > 1.2 | Saturated | |
| Saturation Index (SI) adapted from [34] | SI ≤ 0 | Compatible |
| 0 < SI ≤ 25 | Moderate | |
| 25 < SI ≤ 50 | Severe | |
| SI > 50 | Critical |
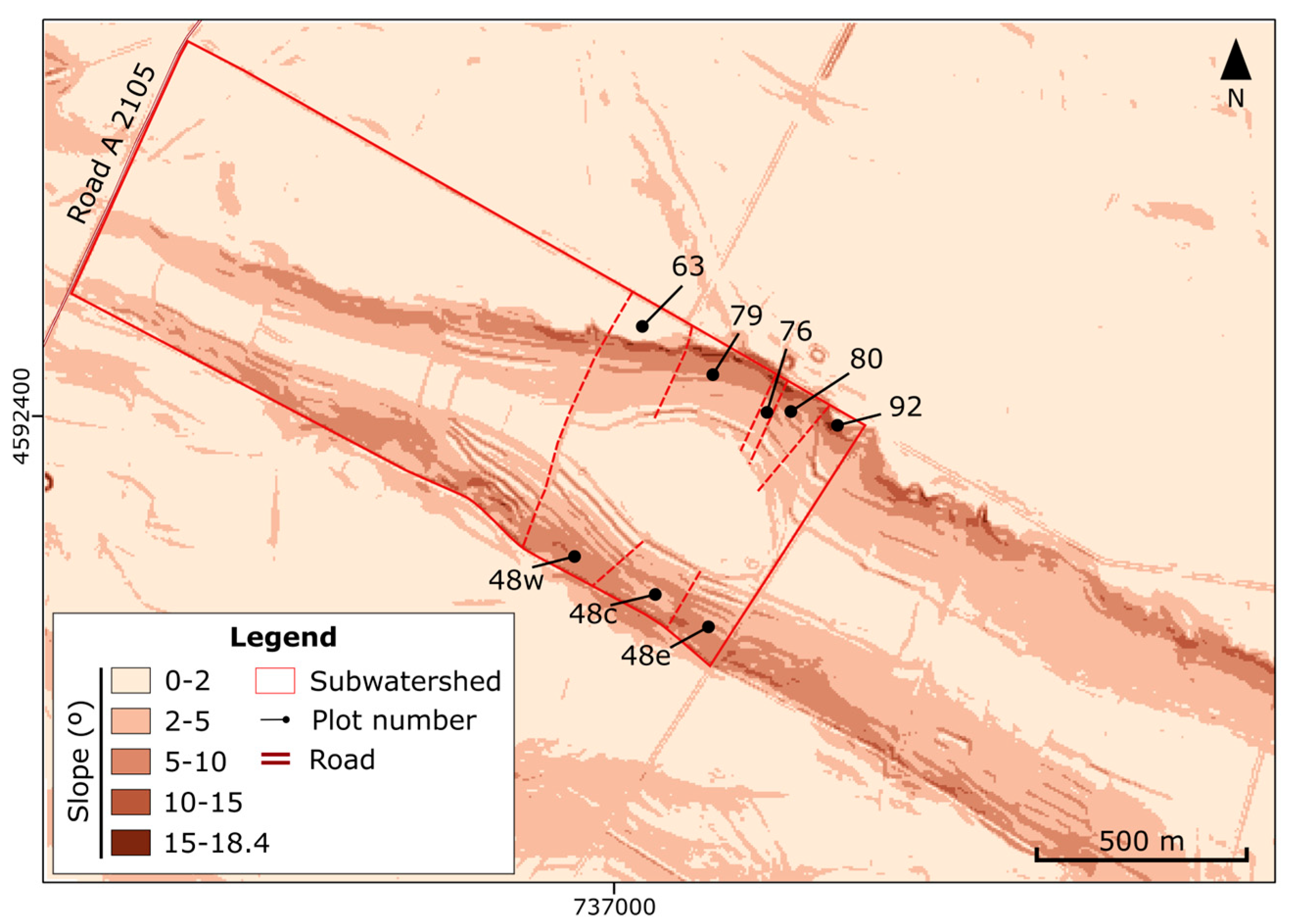
2.7. Application of the WEPP Model to the Farnaca Wetland
3. Results
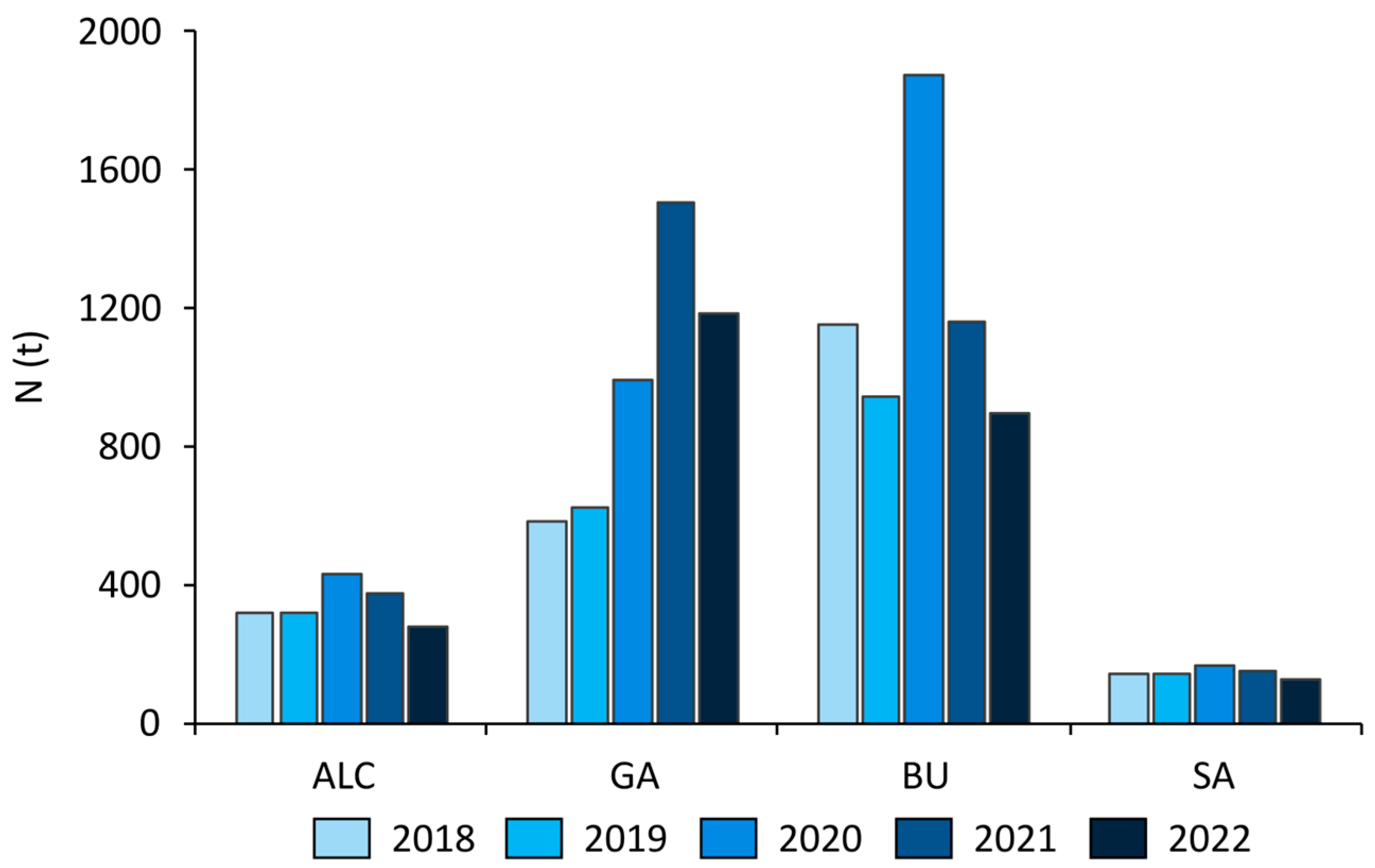
3.1. Crop Distribution and Yield from 2018 to 2022
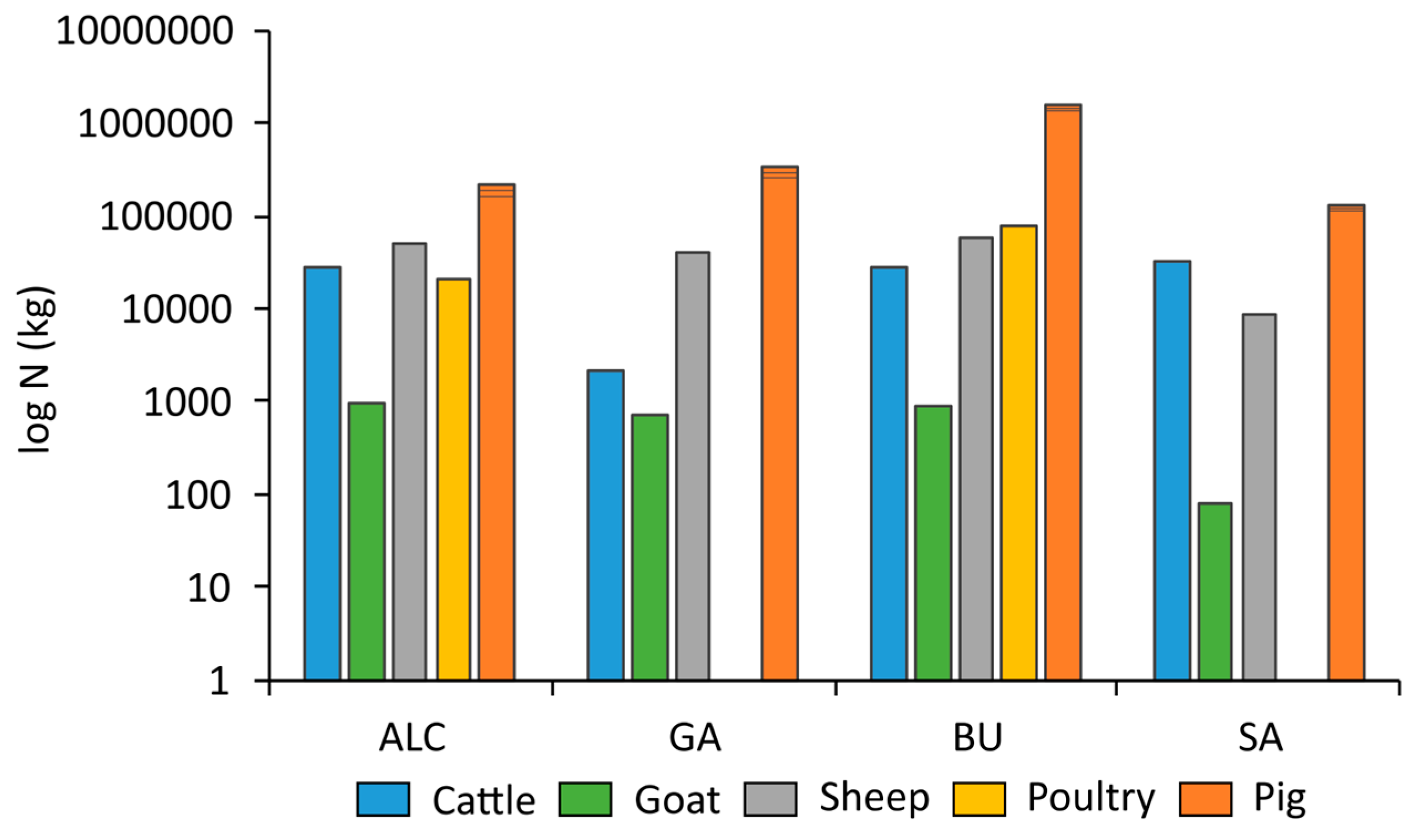
3.2. Livestock Density and N Excreted
3.3. Crop Requirements as Organic Fertilizers
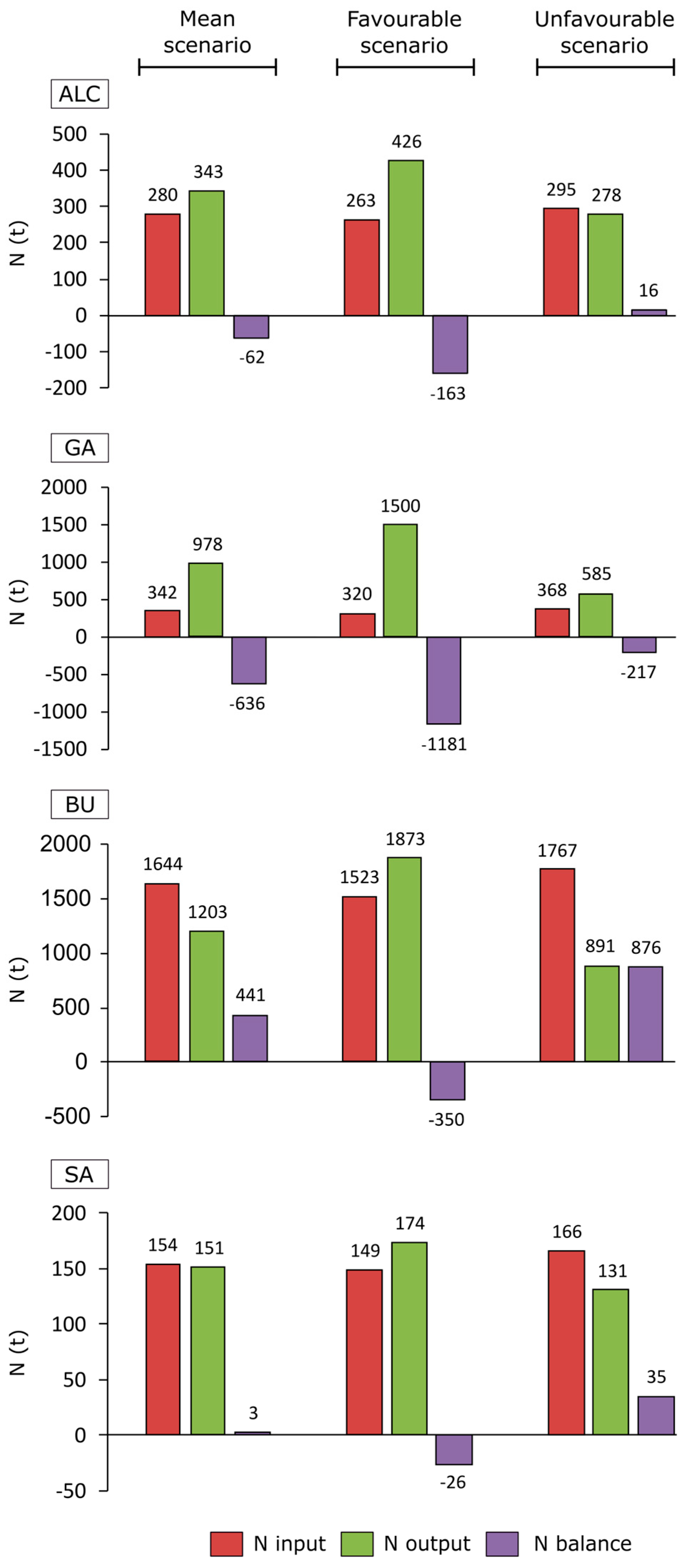
3.4. Nitrogen Balances and Indexes
3.5. Runoff and Sediments in the Farnaca Watershed
4. Discussion
4.1. Organic N Load in the Basins
4.2. Runoff and Nutrients Reaching Farnaca Wetland
4.3. The Protection of the Basins from Pollution
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NVZs | Nitrate Vulnerable Zones |
| WEPP | Water Erosion Prediction Project |
| ND | Nitrate Directive |
| UAA | Utilized Agricultural Area |
| ALC | Saladas de Alcañiz-Calanda |
| GA | Gallocanta Lake |
| BU | Saladas de Sástago-Bujaraloz |
| SA | Sariñena Lake |
| WFD | Water Framerwork Directive |
| CAP | Common Agricultural Policy |
| GSSA | GeoSpatial Aid Application |
| NB | Nitrogen Balance |
| LLI | Livestock Load Index |
| SI | Saturation Index |
References
- Wood, A.; Van Halsema, G. Scoping agriculture-wetland interactions: Towards a sustainable multiple-response strategy. FAO Water Rep. 2008, 33, 155. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fileadmin/user_upload/faowater/docs/WaterReports33.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- Wu, W.; Ma, B. Integrated nutrient management (INM) for sustaining crop productivity and reducing environmental impact: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MITECO (Ministerio para la Transición Ecológica y el Reto Demográfico). Informe de Seguimiento de la Directiva 91/676/CEE. In Contaminación del Agua por Nitratos Utilizados en la Agricultura. Cuatrienio 2016–2019; MTERD: Madrid, Spain, 2020; p. 308. Available online: https://www.miteco.gob.es/content/dam/miteco/es/agua/temas/estado-y-calidad-de-las-aguas/informe-2016-2019_tcm30-518402.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- MITECO (Ministerio para la Transición Ecológica y el Reto Demográfico). Real Decreto 35/2023, de 24 de enero, por el que se Aprueba la Revisión de los Planes Hidrológicos de las Demarcaciones Hidrográficas del Cantábrico Occidental, Guadalquivir, Ceuta, Melilla, Segura y Júcar, y de la parte española de las demarcaciones hidrográficas del Cantábrico Oriental. Miño-Sil, Duero, Tajo, Guadiana y Ebro; 2023; nº 35, p. 19510. Available online: https://www.boe.es/boe/dias/2023/02/10/pdfs/BOE-A-2023-3511.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- Eurostat. Pig Population–Annual Data, Online Data Code: Apro_mt_lspig; Eurostat: Luxembourg, 2024; Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/databrowser/product/page/APRO_MT_LSPIG (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- Masaka, J.; Wuta, M.; Nyamangara, J.; Themba-Mugabe, F. Effect of manure quality on nitrate leaching and groundwater pollution in wetland soil under field tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum, Mill var. Heinz) rape (Brassica napus, L. var. Giant). Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2013, 96, 149–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Hou, M.; Zhang, Q.; Bellingrath-Kimura, S.D. Critical livestock densities and manure management for the typical paddy rice and corn cropping systems in an intensive livestock watershed, Japan. Agric. Syst. 2020, 177, 102722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, J.W.; Groenestein, C.M.; De Boer, I.J.M. Environmental consequences of processing manure to produce mineral fertilizer and bio-energy. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 102, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinnawo, S.O. Eutrophication: Causes, consequences, physical, chemical and biological techniques for mitigation strategies. Environ. Chall. 2023, 12, 100733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.N.; McDowell, R.W.; Kleinman, P.J.A. Phosphorus loss from land to water: Integrating agricultural and environmental management. Plant Soil 2001, 237, 287–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Leavitt, P.R.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B. Anthropogenic eutrophication of shallow lakes: Is it occasional? Water Res. 2022, 221, 118728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Martín, M.A. Understanding Nutrient Loads from Catchment and Eutrophication in a Salt Lagoon: The Mar Menor Case. Water 2023, 15, 3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemly, A.D.; Finger, S.E.; Nelson, M.K. Sources and impacts of irrigation drainwater contaminants in arid wetlands. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1993, 12, 2265–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Carrillo, S.; Álvarez-Cobelas, M. Nutrient Dynamics and Eutrophication Patterns in a Semi-Arid Wetland: The Effects of Fluctuating Hydrology. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2001, 131, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Cobelas, M.; Sánchez-Carrillo, S.; Cirujano, S.; Angeler, D.G. A Story of the Wetland Water Quality Deterioration: Salinization, Pollution, Eutrophication and Siltation. In Ecology of Threatened Semi-Arid Wetlands. Wetlands: Ecology, Conservation and Management, 2nd ed.; Sánchez-Carrillo, S., Angeler, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez-Serra, M.; Triadó-Margarit, X.; Castañeda, C.; Herrero, J.; Casamayor, E.O. Microbial composition, potential functional roles and genetic novelty in gypsum-rich and hypersaline soils of Monegros and Gallocanta (Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourhane, Z.; Cagnon, C.; Castañeda, C.; Rodríguez-Ochoa, R.; Álvaro-Fuentes, J.; Cravo-Laureau, C.; Duran, R. Vertical organization of microbial communities in Salineta hypersaline wetland, Spain. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 869901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, S.; Viso, R.; Borrego-Ramos, M.; López-flores, R.; Mota-Echadía, D.; Tierra, M.; Herrero, J.; Castañeda, C. The Ecology of Benthic Diatom Assemblages in Saline Wetlands of the Ebro Basin, NE Spain. Microb. Ecol. 2025, 88, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, W.D. Environmental threats to salt lakes and the likely status of inland saline ecosystems in 2025. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, C.; Herrero, J. Assessing the degradation of saline wetlands in an arid agricultural region in Spain. Catena 2008, 72, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Beisiegel, M.; Herrero, J.; Castañeda, C. Saline wetlands’ fate in inland deserts: An example of 80years’ decline in monegros, spain. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 250–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, C.; López-Flores, R.; Román, A.; Mota, D.; Tierra, M.; Abdelrazek, A.; Navarro, G. Uso de drones para muestreo de agua y adquisición de datos multiespectrales en humedales protegidos de Aragón afectados por intensificación agrícola. In Actas XX Congreso de la Asociación Española de Teledetección; Universidad de Cádiz: Cádiz, Spain, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsar Convention Secretariat. Designating Ramsar Sites: Strategic Framework and guidelines for the future development of the List of Wetlands of International Importance. In Ramsar Handbooks for the Wise Use of Wetlands, 4th ed.; Ramsar Convention Secretariat: Gland, Switzerland, 2010; Volume 17, p. 120. Available online: https://www.ramsar.org/sites/default/files/documents/pdf/lib/hbk4-17.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- Castañeda, C.; Gracia, F.J.; Luna, E.; Rodríguez-Ochoa, R. Edaphic and geomorphic evidences of water level fluctuations in Gallocanta Lake, NE Spain. Geoderma 2015, 239-240, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragüés, R.; Puy, J.; Royo, A.; Espada, J.L. Three-year field response of young olive trees (Olea europaea L., cv. Arbequina) to soil salinity: Trunk growth and leaf ion accumulation. Plant Soil 2005, 271, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberto, F.; Aragüés, R. La problemática general de la salinidad en la Cuenca del Ebro. 1983. Available online: https://explore.openaire.eu/search/publication?pid=10261%2F132182 (accessed on 27 May 2025). (In Spanish).
- Lecina, S.; Isidoro, D.; Playán, E.; Aragüés, R. Irrigation Modernization in Spain: Effects on Water Quantity and Quality-A Conceptual Approach. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2010, 26, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirantes, J. Estudio Sedimentológico y Estratigráfico del Terciario Continental de los Monegros; Institución Fernando El Católico: Zaragoza, Spain, 1978; p. 208. Available online: https://ifc.dpz.es/publicaciones/ebooks/id/0792 (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- MAPA (Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación). Balance de nitrógeno en la Agricultura Española (Años 1990–2021). Criterios Utilizados; MAPA: Madrid, Spain, 2023; p. 282. Available online: https://www.mapa.gob.es/es/agricultura/temas/medios-de-produccion/a00_metodologia_bn2021_tcm30-674948.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2025). (In Spanish)
- DGA (Diputación General de Aragón). Order AGM/83/2021, from February 15, por la que se Designan y Modifican las Zonas Vulnerables a la Contaminación de las Aguas por Nitratos Procedentes de Fuentes Agrarias en la Comunidad Autónoma de Aragón y por la que se Aprueba el V Programa de Actuación sobre las Zonas Vulnerables de Aragón; DGA: Zaragoza, Spain, 2021; BOA nº 47; pp. 9286–9330. Available online: https://www.boa.aragon.es/cgi-bin/EBOA/BRSCGI?CMD=VEROBJ&MLKOB=1151989261212&type=pdf (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- MAPA (Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación). Informe anual de implantación anual de mejores técnicas disponibles en el sector porcino intensivo. 2022. In Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación. Dirección General de Producciones y Mercados Agrarios; MAPA: Madrid, Spain, 2022; p. 147. Available online: https://www.mapa.gob.es/en/ganaderia/temas/ganaderia-y-medio-ambiente/informeanualdeimplantacionmtdporcino2022def1_tcm38-661837.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- BOE (Boletín Oficial del Estado). Royal Decree RD47/2022, from January 18, Sobre Protección de las Aguas Contra la Contaminación Difusa Producida por los Nitratos Procedentes de Fuentes Agrarias; BOE: Madrid, Spain, 2022; BOE nº 17; p. 5664. Available online: https://www.boe.es/boe/dias/2022/01/20/pdfs/BOE-A-2022-860.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- Orús, F.; Quílez Sáez De Viteri, D.; Betrán Aso, J. El código de Buenas Prácticas Agrarias (I): Fertilización nitrogenada y contaminación por nitratos. In Informaciones Técnicas; Gobierno de Aragón, Centro de Transferencia Tecnológica en Producción Vegetal, Eds.; Gobierno de Aragón: Zaragoza, Spain, 2000; Volume 93, p. 21. Available online: https://bibliotecavirtual.aragon.es/i18n/catalogo_imagenes/grupo.cmd?path=3705254 (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- DOGC (Diari Oficial de la Generalitat de Catalunya). Decree 153/2019, from July 3, of Department of Presidency, de Gestión de la Fertilización del Suelo y de las Deyecciones Ganaderas y de Aprobación del Programa de Actuación en las Zonas Vulnerables en Relación con la Contaminación por Nitratos Procedentes de Fuentes Agrarias; DOGC: Catalunya, Spain, 2019; nº 7911; p. 101. Available online: https://residus.gencat.cat/web/.content/home/consultes_i_tramits/normativa/normativa_catalana_en_materia_de_residus/decret_153_2019_es.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- DGA (Diputación General de Aragón). Order AGM/900/2021, from June 29, of Department of Agriculture, Livestock and Environment, por la que se Establece la Herramienta de Cálculo del Contenido en Nitrógeno de los Estiércoles Generados en Explotaciones Porcinas de la Comunidad Autónoma de Aragón y se Determina el Procedimiento de Reconocimiento de la Reducción del Contenido de Nitrógeno en el Estiércol Generado por Dichas Explotaciones Respecto a los Valores Estándar; DGA: Zaragoza, Spain, 2021; BOA nº 160; pp. 34691–34698. Available online: https://www.boa.aragon.es/cgi-bin/EBOA/BRSCGI?CMD=VEROBJ&MLKOB=1178479463636&type=pdf (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- USDA-ARS; NSERL; Purdue University. WEPP Hillslope Model. In Windows Interface; Version 2012.8; National Soil Erosion Research Laboratory; USDA-ARS: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Daverede, I.C.; Kravchenko, A.N.; Hoeft, R.G.; Nafziger, E.D.; Bullock, D.G.; Warren, J.J.; Gonzini, L.C. Phosphorus runoff from incorporated and surface-applied liquid swine manure and phosphorus fertilizer. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.J.; Olson, E.C.S.; Chanasyk, D.S.; Beasley, B.W.; Larney, F.J.; Olson, B.M. Phosphorus and nitrogen in rainfall simulation runoff after fresh and composted beef cattle manure application. J. Environ. Qual. 2006, 35, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.J.; Chanasyk, D.S.; Curtis, T.W.; Olson, B.M. Phosphorus and nitrogen in runoff after phosphorus- or nitrogen-based manure applications. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volf, C.A.; Ontkean, G.R.; Bennett, D.R.; Chanasyk, D.S.; Miller, J.J. Phosphorus losses in simulated ranifall runoff from manured soils of Alberta. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzari, M.; Antognelli, S.; Pauselli, M.; Benincasa, P.; Farneselli, M.; Morbidini, L.; Borghi, P.; Bodo, G.; Santucci, A. Potential nitrogen load from crop-livestock systems: A spatial database for a multi-scale assessment and mapping. Int. J. Agric. Environ. Inf. Syst. 2016, 7, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huezo, L.; Jones, D.; Edwards, E.; Sharara, M. Manure nutrient cycling in US animal agriculture basins-North Carolina case study. J. Environ. Qual. 2023, 53, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oenema, O.; Oudendag, D.; Velthof, G.L. Nutrient losses from manure management in the European Union. Livest. Sci. 2007, 112, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asman, W.A.H.; Sutton, M.A.; Schjørring, J.K. Ammonia: Emission, atmospheric transport and deposition. New Phytol. 1998, 139, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAPA (Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación). Estadística de Consumo de Fertilizantes en la Agricultura 2023; MAPA: Madrid, Spain, 2024; p. 282. Available online: https://www.mapa.gob.es/es/estadistica/temas/estadisticas-agrarias/fertilizantes2023_definitivoswebpdf_tcm30-694345.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- Raclot, D.; Albergel, J. Runoff and water erosion modelling using WEPP on a Mediterranean cultivated catchment. Phys. Chem. Earth 2006, 31, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; McGehee, R.P.; Guo, T.; Flanagan, D.C.; Engel, B.A. Calibration, validation, and evaluation of the Water Erosion Prediction Project (WEPP) model for hillslopes with natural runoff plot data. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2022, 11, 669–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samper-Calvete, F.J.; García-Vera, M.A. Inverse modeling of groundwater flow in the semiarid evaporitic closed basin of Los Monegros, Spain. Hydrogeol. J. 1998, 6, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmas, C.; Danalatos, N.; Cammeraat, L.H.; Chabart, M.; Diamantopoulos, J.; Farand, R.; Gutiérrez, L.; Jacob, A.; Marques, H.; Martínez-Fernández, J.; et al. The effect of land use on runoff and soil erosion rates under Mediterranean conditions. Catena 1997, 29, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santisteban, L.M.; Casalí, J.; López, J.J. Assessing soil erosion rates in cultivated areas of Navarre (Spain). Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2006, 31, 487–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, E.; Jouany, C.; Castañeda, C. Soil composition and plant nutrients at the interface between crops and saline wetlands in arid environments in NE Spain. Catena 2019, 173, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MPRCMD (Ministerio de la Presidencia, Relaciones con las Cortes y Memoria Democrática). Real Decreto 1051/2022, de 27 de Diciembre, por el que se Establecen Normas Para la Nutrición Sostenible en los Suelos Agrarios; MPRCMD: Madrid, Spain, 2022; BOE nº 312; p. 188873. Available online: https://www.boe.es/boe/dias/2022/12/29/pdfs/BOE-A-2022-23052.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- Kreiling, R.M.; Thoms, M.C.; Richardson, W.B. Beyond the edge: Linking agricultural landscapes, stream networks, and best management practices. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 47, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, J.; Marques-dos-Santos, C.; Marinheiro, J.; Cruz, S.; Cameira, M.R.; de Vries, W.; Dalgaard, T.; Hutchings, N.J.; Graversgaard, M.; Giannini-Kurina, F.; et al. Assessing nitrate groundwater hotspots in Europe reveals an inadequate designation of Nitrate Vulnerable Zones. Chemosphere 2024, 355, 141830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHE (Confederación Hidrográfica del Ebro). Estrategia de la Confederación Hidrográfica del Ebro Para la Lucha Contra el Elevado Contenido de Nitratos en las Aguas de la Cuenca (Estrategia NITRACHE). In Adaptación a Nueva Normativa y Criterio Interpretativo, 12 de diciembre de 2024; CHE: Zaragoza, Spain, 2024; Available online: https://portal.chebro.es/documents/20121/972743/20241212%27+Estrategia_NITRACHE.pdf/75c39850-1196-2ef1-73f5-d2fbd968381b?t=1734089387380 (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- CHE (Confederación Hidrográfica del Ebro). Plan Hidrológico de la Demarcación Hidrográfica del Ebro, Cuarto Ciclo (2028–2033). In Documentos Iniciales. Anejo 14: Evaluación Preliminar de Impactos en las Masas de Agua Subterránea; CHE: Zaragoza, Spain, 2024; Available online: https://www.chebro.es/documents/20121/2459045/PHE4_pDDII_Anejo14_Impac-MSBT_V04.pdf/cfc78dc3-e4cb-9ef1-620f-72d2b0f2174e?t=1734622236305 (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- Jiménez-Aguirre, M.T.; Isidoro, D. Hydrosaline balance in and nitrogen loads from an irrigation district before and after modernization. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 208, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, R.; Isidoro, D.; Aragüés, R. Long-term water balances in La Violada irrigation district (Spain): I. sequential assessment and minimization of closing errors. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 102, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
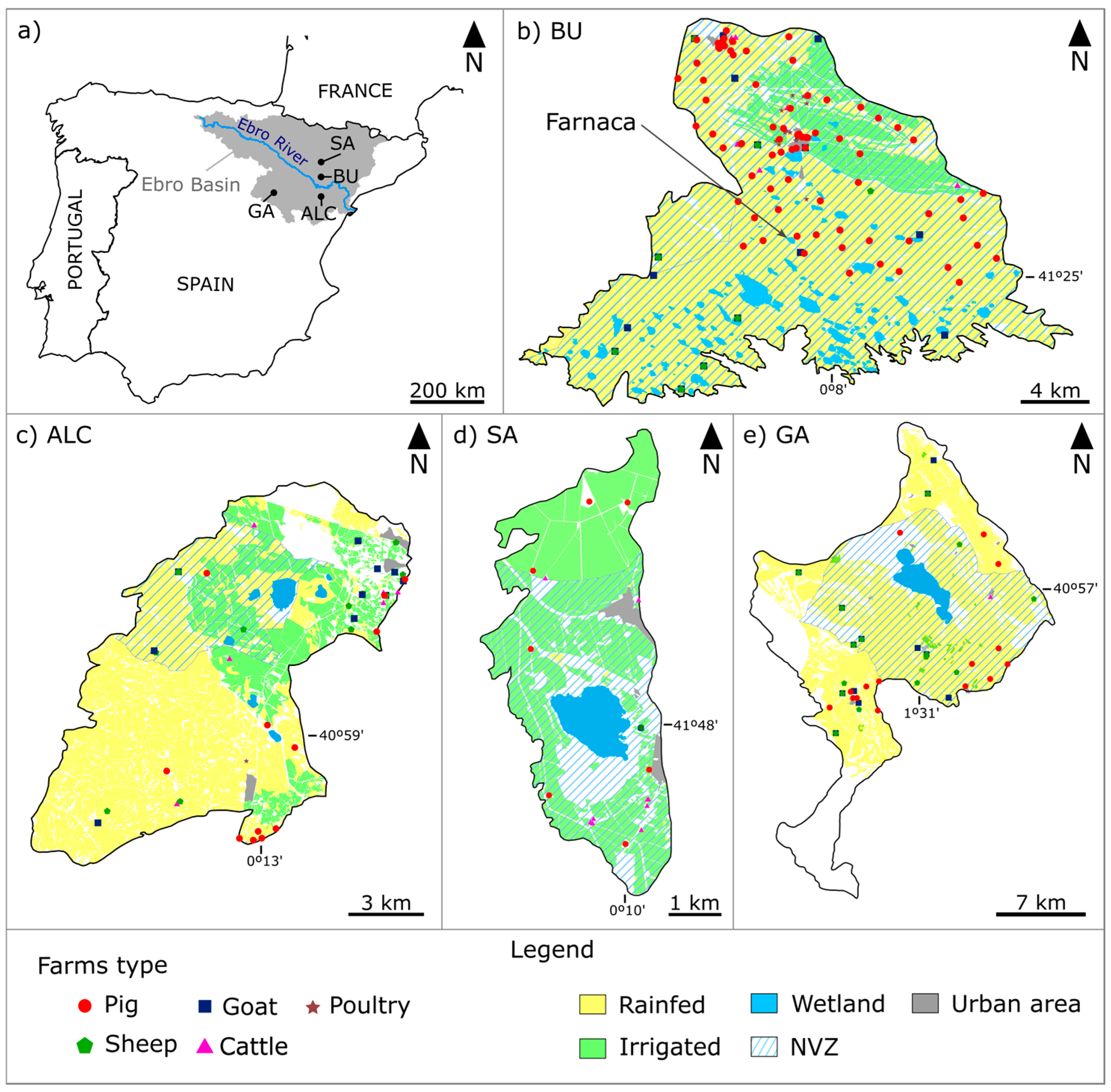
| Main Characteristics | Wetland Basin | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALC | GA | BU | SA | |
| Wetland basin | ||||
| Basin area (ha) | 12,925 | 35,187 | 35,519 | 1959 |
| Mean annual rainfall (mm) | 366 | 487 | 359 | 378 |
| Mean annual ET0 (mm) | 1312 | 1100 | 1262 | 1217 |
| Agriculture | Rainfed and Irrigated | Rainfed | Rainfed and Irrigated | Irrigated |
| Wetland | ||||
| Surface area (ha) | 179 | 1400 | 1917 | 141 |
| Elevation (m a.s.l.) | 350 | 990 | 325 | 330 |
| Hydrological regime | Fluctuating until dry | Fluctuating until dry | Fluctuating until dry | Permanent |
| Depth of water column (m) | <0.5 | <2.8 | <0.5 | <3 |
| Water salinity (dS m−1) | 4–90 | 16−>100 | Up to 400 | 2.5–3 |
| Pig Type | Excreted N (kg Place−1 y−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Regional Regulation [30] (1) | National Regulation [31] | ||
| Mean for Aragón (2) | Mean for Spain (3) | ||
| Sow with piglets up to 20 kg | 18.00 | ||
| Replacement sow | 8.50 | ||
| Piglets from 6 to 20 kg | 1.19 | ||
| Pigs from 20 to 100 kg | 7.25 | ||
| Boars | 18.00 | ||
| Weaned piglets 6–20 kg | 2.10 | 2.40 | |
| Fattening pigs 20–100 kg | 7.60 | 8.40 | |
| Breeding sows/Sow with piglets < 6 kg | 21.80 | 20.50 | |
| Parameter/Criteria | Source | Upper Threshold (kg N ha−1)/Class |
|---|---|---|
| Designation of Nitrates Vulnerable Zones (NVZs) | General reference upper limits [16] | 170 (rainfed) 210 (irrigated) |
| Type of production area | Annex XIV [30] | Type 1: Arid rainfed Type 2: Humid rainfed Type 3: Irrigated |
| N output (N ha−1) based on expected production in vulnerable areas: 30 kg N t−1 winter cereal 25 kg N t−1 sprinkler corn | Annex III [30] | Winter cereal (Type 1): 90 Winter cereal (Type 2): 150 Sprinkler corn: 380 |
| N output (N ha−1) in non-vulnerable areas (kg N t−1) | Own crop production data and [32] | Own data up to 210 |
| Slope of agricultural plot | GSAA dataset attributes | 15% |
| Parameter | Wetland Basin | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALC | GA | BU | SA | |
| Agricultural area (AA) (ha) | 10,548 | 16,885 | 33,142 | 1383 |
| Irrigated area (ha) | 2644.4 | 136.4 | 4116.8 | 1365.8 |
| Nitrates Vulnerable Zone (ha) | 2955.6 | 18,492.8 | 35,339.6 | 1468.3 |
| Cereal area with <15% slope (ha) | 4203.0 | 11,461.7 | 18,944.5 | 756.2 |
| Cereal Type | Yield (t ha−1) per Wetland Basin | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALC | GA | BU | SA | |||||
| I | R | I | R | I | R | I | R | |
| Barley | 6.9 (±0.5) | 2.3 (±1.0) | 4.6 (±0.9) | 3.9 (±0.8) | 7.6 (±0.5) | 1.9 (±1.0) | 7.0 (±0.5) | 2.2 (±1.1) |
| Common wheat | 6.7 (±0.3) | 2.1 (±1.3) | 4.3 (±0.8) | 3.6 (±1.1) | 6.5 (±0.7) | 1.4 (±1.1) | 5.6 (±1.0) | 1.7 (±0.9) |
| Corn | 13.4 (±1.1) | 7.5 (±0.5) | 13.4 (±1.1) | 7.5 (±0.5) | 12.3 (±2.9) | 8.8 (±2.9) | 13.4 (±1.1) | 7.5 (±0.5) |
| Durum wheat | 5.6 (±0.5) | 1.5 (±1.1) | 3.8 (±0.9) | 3.2 (±1.0) | 6 (±0.0) | 1.3 (±1.0) | 5.0 (±1.4) | 1.7 (±0.7) |
| Rye | - | 0.7 (±0.0) | 4 (±0.6) | 3.4 (±1.1) | - | 1 (±0.7) | 3.0 (±0.0) | 1.6 (±0.5) |
| Oat | 3.8 (±0.4) | 2.2 (±1.0) | 3.3 (±0.8) | 2.9 (±0.8) | - | 1.6 (±0.9) | 3.0 (±0.0) | 2.2 (±0.6) |
| Animal Type | ALC | GA | BU | SA | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA: 3472.3 | AA: 8780.9 | AA: 16,606.6 | AA: 869.2 | |||||||||
| Farm | Places | Places ha−1 | Farm | Places | Places ha−1 | Farm | Places | Places ha−1 | Farm | Places | Places ha−1 | |
| Cattle | 5 | 100 | 0.03 | 1 | 1 | - | 9 | 1400 | 0.08 | 9 | 1278 | 1.2 |
| Goat | 10 | 121 | 0.03 | 9 | 90 | 0.01 | 12 | 110 | 0.01 | 1 | 10 | 0.01 |
| Pig | 12 | 24,678 | 7.1 | 15 | 39,403 | 4.5 | 75 | 199,592 | 12.02 | 7 | 14,923 | 17.2 |
| Poultry | 2 | 53,524 | 15.4 | - | - | - | 14 | 344,000 | 33.3 | - | - | - |
| Sheep | 14 | 9196 | 2.7 | 14 | 7237 | 0.8 | 12 | 10,255 | 0.6 | 1 | 1530 | 1.8 |
| N Requirements of the Crop | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | Watershed | Medium | High | Low |
| LLI | ALC | 0.9 Compatible | 0.7 C. abs | 1.0 Moderate |
| GA | 0.4 C. abs | 0.3 C. abs | 0.6 C. abs | |
| BU | 1.4 Saturated | 0.9 Compatible | 1.9 Saturated | |
| SA | 1.0 Moderate | 0.9 Compatible | 1.2 Moderate | |
| SI | ALC | −18.2 Compatible | −34.2 Compatible | 0.7 Moderate |
| GA | −65.0 Compatible | −77.2 Compatible | −41.5 Compatible | |
| BU | 36.7 Severe | −12.2 Compatible | 84.5 Critic | |
| SA | 1.8 Moderate | −11.6 Compatible | 17.9 Moderate | |
| Slope/ Subwatershed | Area (ha) | Runoff (mm y−1) | Sediments (kg y−1) | Organic Matter (kg y−1) | Nitrogen (kg y−1) | Phosphorus (kg y−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76 | 0.66 | 15.02 | 604 | 11 | 0.6 | 0.2 |
| 80 | 2.16 | 14.06 | 4656 | 84 | 2.1 | 0.7 |
| 92 | 2.16 | 14.45 | 8690 | 147 | 2.2 | 0.7 |
| 48e | 2.65 | 17.27 | 6496 | 132 | 3.4 | 1.1 |
| 48c | 2.77 | 12.65 | 2158 | 45 | 2.1 | 0.7 |
| 48w | 4.11 | 15.38 | 6742 | 134 | 3.6 | 1.1 |
| Subwatershed | 74.18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 63 | 4.70 | 13.82 | 16,426 | 332 | 5.5 | 1.7 |
| 79 | 3.88 | 15.42 | 8317 | 167 | 4.0 | 1.3 |
| Aragon Provinces | N from Animal Farms (t) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 2016 | 2021 | |||||||
| Avail. | Used | Excess | Avail. | Used | Excess | Avail. | Used | Excess | |
| Huesca | 15,594 | 15,594 | 10,535 | 29,373 | 29,373 | 20,921 | 35,884 | 35,884 | 25,099 |
| Teruel | 3792 | 3792 | 0 | 7741 | 7741 | 5330 | 9117 | 9117 | 5892 |
| Zaragoza | 8576 | 8576 | 1040 | 20,512 | 20,512 | 11,486 | 24,309 | 24,309 | 14,692 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tierra, M.; Olarieta, J.R.; Castañeda, C. An Assessment of the N Load from Animal Farms in Saline Wetland Catchments in the Ebro Basin, NE Spain. Land 2025, 14, 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061170
Tierra M, Olarieta JR, Castañeda C. An Assessment of the N Load from Animal Farms in Saline Wetland Catchments in the Ebro Basin, NE Spain. Land. 2025; 14(6):1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061170
Chicago/Turabian StyleTierra, María, José R. Olarieta, and Carmen Castañeda. 2025. "An Assessment of the N Load from Animal Farms in Saline Wetland Catchments in the Ebro Basin, NE Spain" Land 14, no. 6: 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061170
APA StyleTierra, M., Olarieta, J. R., & Castañeda, C. (2025). An Assessment of the N Load from Animal Farms in Saline Wetland Catchments in the Ebro Basin, NE Spain. Land, 14(6), 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14061170






