Abstract
International heritage management approaches have developed into a more inclusive process wherein public participation is identified as a pivotal tool. Thus, determining how to assess public interests and include the public’s ideas in heritage protection has become a technical issue, but relevant research still remains limited. This paper aims to test the digital footprints of social media users as a public participatory tool, with the objectives of identifying industrial heritage landscape attributes and assessing associated values. Targeting the Sanxian industrial heritage landscape of Liangdancheng in China as a case study, in this research the data from user-generated content on social media platforms Ctrip, Weibo, and Meituan were collected and processed with ROST CM 6 and NVivo 12, and content analysis (CA) and importance-performance analysis (IPA) were conducted. Results revealed that the industrial heritage landscape of Liangdancheng encompasses various built, cultural, and natural environmental resources, including both tangible and intangible attributes such as architectural constructions, historic artifacts, cultural events, and plants. These attributes were assessed and categorized into four quadrants of importance–performance characteristics, wherein cultural environmental resources show relatively high performance but built environmental resources need further actions to improve their value perception and interpretation among the public. This research demonstrated that the digital footprints of social media users as a participatory tool can work well in terms of data accessibility, value identification, and public representation, advancing the theoretical framework of Chinese industrial heritage management and global practices.
1. Introduction
Current international heritage management is moving beyond a static material-based approach into a more dynamic people-centered process, wherein heritage is considered to be an important resource integrated into sustainable urban development [1,2]. To achieve such a goal, the UNESCO Recommendation on the Historic Urban Landscape (hereafter, the HUL Recommendation) has identified public participation as a pivotal tool for implementing the HUL Recommendation in heritage protection and management [3]. Urban heritage is then understood and managed through a landscape-based perspective with the attributes, values, and interests associated with the public identified [4].
Among various types of urban heritage, industrial heritage is often neglected more although it carries rich historical information reflecting industrial manufacturing, construction technology, material innovation, and social needs at different industrial development stages in history [5,6]. International policies for industrial heritage protection, including The Dublin Principles (2011) [7] and the Taipei Declaration on Asian Industrial Heritage (2012) [8], recognize industrial heritage as an emerging type of urban heritage. These international policies recommend that industrial heritage management approaches cannot simply adopt a static or isolated perspective of “frozen” heritage properties but need to take into consideration heritage function, time, and cultural continuation integrated into current post-industrial social needs and future city visions [9]. However, current industrial heritage protection often results in a heated discussion about the adaptive reuse of building materials and structures, but lacks sufficient consideration of socio-cultural needs and values [6,10]. Tangible heritage manifestations and characteristics can be adaptively maintained and preserved while related intangible manifestations also need to be associated with local communities and daily activities to enhance symbolic meanings and place significance. The management approach of industrial heritage needs to be furthered by including reciprocity and mutuality among the public in the sustainable evolvement of both tangible and intangible cultural heritage manifestations and place identity. Therefore, the historic urban landscape of industrial heritage (hereafter, industrial heritage landscape) could adopt an operational approach to more inclusively managing industrial heritage protection and adaptive reuse [10]. The identification, assessment, and planning of industrial heritage landscape attributes and values have become technical steps for local heritage managers and professionals [11].
Having identified public participation as an implementation tool, international heritage researchers and professionals have explored the methodologies of public participation in various global top-down and bottom-up contexts. Within the various contexts of public participation, collection and solicitation of community needs are necessary, but this process often encounters the barriers of limited samples, significant time requirement, and high financial cost [12]. Along with the development of smart cities, smart technologies and tools in the Web 3.0 era are providing more digital participatory platforms and opportunities for the public to address their spatial experiences and perceptions, contributing to the decision-making of urban policy formulation [13,14]. Social media is being used to collect multivocal narratives, and its user-generated content as a digital footprint reflects heritage attributes, importance, and performance through textual comments, photo sharing, and location sharing [15,16]. A concept of digital footprints from social media users has been noticed in the urban planning field to advance heritage tourism management, from which users’ locations, active paths, activities, spatial experiences, and value perceptions can be well identified [16,17]. Therefore, social media users’ digital footprints can enable academic studies and heritage practices to present a variety of interests, encounters, and cross-dialogues among different heritage communities, with the potential to be a participatory tool in heritage identification and assessment [18].
This study tested the use of digital footprints of social media users as a public participatory tool to identify and assess industrial heritage landscapes, targeting Liangdancheng in China as an empirical case. The digital footprints include user-shared textual comments, images, and locations on social media, which have been processed (1) through content analysis (CA) of the public’s spatial perceptions to identify industrial heritage landscape attributes, and (2) through importance-performance analysis (IPA) of the public’s spatial experiences to propose integrated management recommendations and planning actions. The Liangdancheng industrial heritage landscape in the Sichuan Province of China (Figure 1) was built during a Chinese special history period of “Sanxian” Industrial Construction (literally Chinese Third-Front Construction Movement) between the 1960s and 1980s, and it was inscribed on the Chinese National Industrial Heritage List in 2018. The “Sanxian” Industrial Construction involved science and technology manufacturing industries, the industrial economy, and transportation infrastructure development [19]. At that time, Sichuan Province was selected as one of the key areas due to its outstanding industry-based foundation and rich raw material resources [19,20]. Nowadays, the Sanxian industrial heritage in Sichuan not only retains industrial physical remains, but also intangible landscape attributes such as manufacturing techniques, spirits, and significant symbols [20]. This research demonstrated that the use of digital footprints of social media users as a public participatory tool can work well in terms of data accessibility, value identification, and public representation, furthering the management approach of industrial heritage from a static “historic artefact” to a dynamic “urban landscape”, for the improvement in Chinese heritage management practices and international theories.
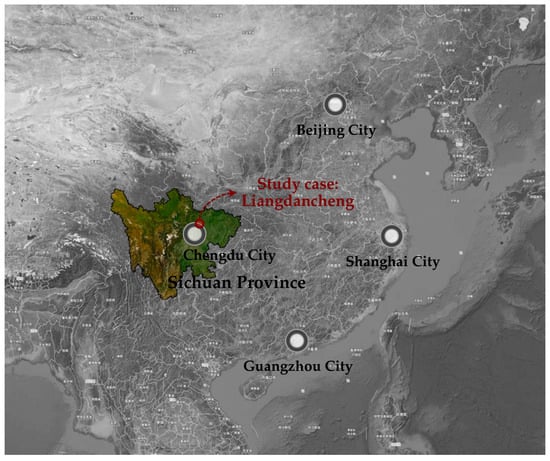
Figure 1.
The location of Liangdancheng in Sichuan Province, China.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Industrial Heritage Landscapes and Public Participation
Industrial heritage is part of the development process of the world’s industrialization and is a significant symbol of industrial civilization. In general, industrial heritage involves the attributes of machinery, transport, mining, and lighting, and it also has intangible cultural expressions of values such as history, science, technology and aesthetics [21]. With the changing concept of heritage protection, based on the HUL Recommendation, urban heritage institutions and city managers are increasingly emphasizing the holistic and sustainable management of industrial heritage as dynamic large-scale and multilayered historic urban landscapes [4]. Furthermore, the concept of the industrial heritage landscape encompasses not only the tangible attributes of historic buildings, roads, parks, machinery, and equipment, but also intangible expressions including industrial culture, symbolic significance, and people’s lives and stories [21]. As mentioned in the Nizhny Tagil Charter, consultation with the public on the management of industrial heritage needs to be ensured to identify heritage-attributed values, and through extensive public participation, to incorporate the combined views of the public, experts, scholars, and government officials into the comprehensive framework of sustainable urban development [22]. Therefore, the identification of the attributes and value of the industrial heritage landscape has been a priority for its management process. In this process, people’s interests are included in the management scheme of the industrial heritage landscape, wherein public participation is often seen as an effective way to understand the local context [23,24].
Public participation is necessarily conducted within heritage management’s whole process of identification, programing, and execution steps [25]. Promoting the public’s participation can help experts and governments better understand local conditions and people’s needs; if management plans deviate from local expectations, civil protests could happen [12]. In addition, to improve the credit of participatory activities, the methods and platforms also need experts and governments to pay enough attention. For example, community leaders, experts, and elites can always grant more power but “ordinary voices” are weak in public meetings. However, with the development of digital technologies, “ordinary voices” can have more channels and platforms to be heard much more clearly, such as social media, digital maps, and hotlines [12,26]. In the case study of this research, the Sanxian industrial heritage landscape witnessed the movement of the Chinese national development of the science and technology industries between the 1960s and the 1980s from birth to decline, reflecting the lifestyle, tradition, and cultural activities of local communities [27]. For the Sanxian industrial heritage, the significance of public participation has been widely recognized by scholars [28]. Increasingly, scholars are concerned about the expressions of the Sanxian industrial heritage landscape in contemporary society from the perspective of the public’s spatial perceptions and experiences [27]. A people-centered participatory management approach is needed to identify the characteristics of the associated values and attributes [27,28].
2.2. Digital Footprint
With the development of the Internet and smart technologies, many people are using words and pictures to express their spatial experiences and preference for urban heritage, with the help of social media such as Twitter, Flickr, and Weibo [29]. These massive amounts of unstructured data are known as digital footprints because this type of user-generated content records the public’s place experiences, spatial behaviours, emotional tendencies, etc. [16]. These big data also encompass important historical information such as monuments, traditional activities, and historic site locations [29,30]. Hence, the digital footprint is often used to assess the spatial quality of cultural heritage properties and expand the channels and platforms of public participation [29]. For example, Van der Hoeven used qualitative content analysis of social media activities to reveal the diverse layers of heritage values attributed to Dutch cities’ urban landscapes [30]. In addition, interdisciplinary analysis methods such as affective computing and deep learning have been applied to social media data analysis to improve computational accuracy and efficiency [14,31]. Kumar et al. used a convolutional neural network to identify heritage risks in social media images [31].
Thus, in the context of heritage management, digital footprints highlight the connection between public interests and heritage sites [29]. Through user-generated content on social media as public participatory platforms, the priority and interests of the public (social media users) in the heritage protection and adaptive reuse processes could be further identified and enhanced. Social media are accessible to any community group who is concerned about the heritage, and the platforms are open to various voices [30]. In line with this, the whole management process of industrial heritage protection, including identification, programming, and execution, needs methodological improvement and related analytical techniques in the engagement of digital footprints as a public participation tool. Advanced techniques of online data mining and quantitative value assessment could also be furthered and included in the steps of the tool’s implementation. Therefore, whether digital footprints can support public participation in collecting community interests for industrial heritage management is still up for debate [26]. Accordingly, this study addressed this concern by processing user-generated data from social media as an innovative tool for community participation, based on the case of the Liangdancheng industrial heritage landscape in China.
3. Methodology
3.1. Case Overview
The industrial heritage landscape of Liangdancheng in China’s Sichuan Province, which was the former location of the National Academy of Engineering Physics Research, was selected as the case study. It was included in the Chinese National Industrial Heritage List in 2018 and has 167 industrial buildings built in the 1960s, including an information center, a public auditorium, and some celebrities’ former residences. From the landscape-based perspective, the tangible heritage of Liangdancheng can be represented by architectural constructions and structures, historic sites, and artifacts, as shown in Figure 2a. These remaining tangible attributes are associated with the intangible value attributes of industrial production technology, collective memory, events, and the spirit of Chinese “Sanxian” Industrial Construction. The intangible heritage can also be represented in collective events, memories, place identity, and cultural and creative products. As indicated in Figure 2b, Langdancheng has the Jingying Gate at the entrance, with the reception hall on the right and a pathway leading to the main attractions within the park on the left, including the Golden Hall, Wang Ganchang’s former residence, Deng Jiaxian’s former residence, and the History Museum. The area extending from Bei Lin (group of monumental stones) to the southeast encompasses the Education Hall and former air-raid shelter, while on the southwest side of the park lies the Study Centre, primarily dedicated to conducting education- themed training activities.

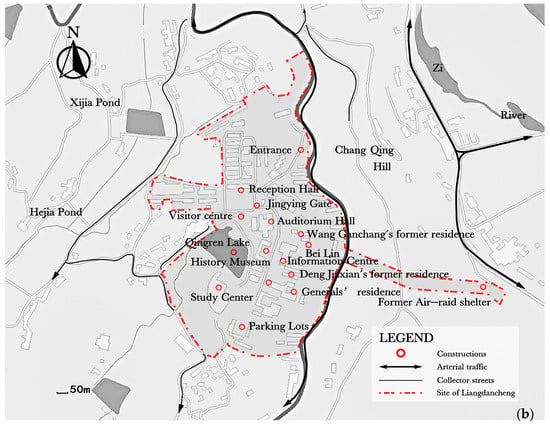
Figure 2.
(a) An aerial view of current Liangdancheng (source: https://tuchong.com/23602951/95372905/, accessed on 18 May 2024); (b) cartography of significant landscape features and the precise location of Liangdancheng.
Construction at Liangdancheng finished in 1965; the research institute the moved into the site in 1969 but functionally stopped in 1992, as Figure 3 shows. Around 2010, the local government undertook actions for the protection and exhibition of Liangdancheng’s industrial heritage while focusing more on buildings’ structures, artifacts, and historic exhibits. In 2013, the ownership of Liangdancheng transferred from the government to a real estate company for tourism development. Consequently, the tourism industry and commercial activities experienced rapid growth, causing damage to historic buildings and cultural traditions associated with the local industrial landscape. The identification and integrated protection of both local tangible and intangible heritage attributes to enhance the sense and significance of place have remained limited with the Liangdancheng industrial heritage landscape. Therefore, the selection of Liangdancheng in this study not only has a representative meaning in terms of the theoretical aspect but also has profound significance in practice.
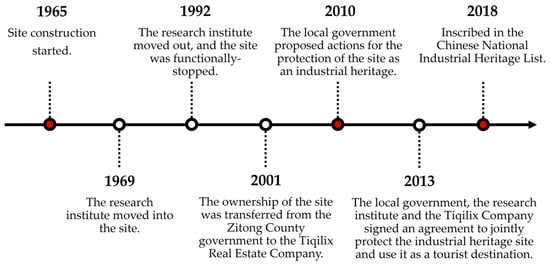
Figure 3.
The history and developmental timeline of Liangdancheng.
3.2. Data Collection and Preliminary Cleansing
Users’ textual comments and images shared on social media platforms, Ctrip, Meituan, and Weibo were used as data sources of public participation in this research, but some other social media platforms that contain significant amounts of marketing promotion information or tour advertisements are excluded. Ctrip and Meituan are the largest online platforms in China for sharing the travelling experiences of both national and local visitors, while Weibo is the most widely used platform by the public. All three platforms contain massive quantities of textual comments, photo sharing, and other user-generated content related to the Liangdancheng industrial heritage landscape. All user-generated content reflects Liangdancheng industrial heritage’s attributes, importance, and performance through the public’s spatial perceptions and experiences.
The final dataset identified 19,361 words of textual comments and 618 images between 16 October 2015 and 27 October 2022. Then, the dataset was subjected to a preliminary cleansing process, as follows: (1) removed governmental/official promotional texts and images; (2) deleted online “robotic” unrelated texts and images; and (3) unified the consistency of names, for example, using “902 Site” instead of the full name “China Academy of Engineering Physics”. Finally, a total of 15,676 words of valid textual comments and 606 valid images (Table 1) were collected for the next step of data analysis.

Table 1.
Summary of user-generated content acquisition and the profiles of social media.
3.3. Data Analysis Methods
3.3.1. Content Analysis for Landscape Attribute Identification
This research employed the method of content analysis (CA) to process and analyze the collected data, developing a three-level coding system to count attributes’ frequencies for the landscape identification of Liangdancheng’s industrial heritage. Based on the HUL Recommendation, the three primary aspects of built, cultural, and natural environmental resources were identified as the first-level codes. The second-level codes were open codes built on third-level codes that were the attributes’ names directly mentioned in either textual comments or shared images. For example, built environmental resources (first-level codes) included architectural constructions, structures, and sites, as well as historical artefacts (second-level codes), and related third-level landscape attributes were identified to include celebrities’ former residences, museums, historic buildings, the Auditorium Hall, etc.
For the identification of landscape attributes, the ROST Content Mining 12 (ROST CM 12) digital tool was selected to process textual comments and NVivo 12 was used to facilitate the manual analysis of images. The specific steps were as follows: (1) researchers independently reviewed the textual comments and images for initial coding work, including the steps of extracting keywords of landscape attributes from the textual comments and collected images, unifying keywords’ representation consistency, and establishing a table of keywords; (2) textual comments were imported into ROST CM 12 and images were imported into the NVivo 12 platform for the counting of keywords; and (3) high-frequency keywords were identified, and related landscape attributes and their importance were also collected.
3.3.2. Importance–Performance Analysis
The paper used the Importance–Performance Analysis (IPA) method to assess the public’s perception and spatial experiences of the landscape attributes of Liangdancheng’s industrial heritage. Initially proposed by Martilla and James, this method has been well applied in various domains such as tourist satisfaction, spatial experiences, and local competitiveness evaluation, for urban policy-making and decision-making at a local level [32]. In the data analysis process, the frequency of each landscape attribute was regarded as its “importance” while its “performance” was identified through the Likert five-point scale in Table 2. Assigned values of 5, 4, 3, 2, and 1 expressed very satisfied, satisfied, neutral, not satisfied, and very unsatisfied, respectively, and the value identification was proven by multiple researchers.

Table 2.
Likert five-point scale for the performance of landscape attributes.
A formula for weighted average score calculation was developed for both first-level and second-level codes:
In (1), Ei represents the score obtained from the public spatial experiences of first-level and second-level codes. Xij denotes the performance score of landscape attributes coded at the second and third levels, while the frequency assigned to spatial experiences for these attributes is denoted by Wij.
With the two dimensions of importance and performance, Liangdancheng’s landscape attributes were distributed into four quadrants: Quadrant I—“Keep up the Goodwork (Maintain Excellence)” (high importance and high performance); Quadrant II—“Potential Overkill” (low importance but high performance); Quadrant III—“Low Priority” (low importance and low performance); and Quadrant IV—“Focus Here” (high importance but low performance). Specifically, landscape attributes in Quadrant I—“Keep up the goodwork” showed a high degree of significance and outstanding community values while also demonstrating good protection with good implementation of adaptive reuse. Quadrant II—“Potential Overkill”, despite the low level of significance, exhibited high performance and favorable public perception of landscape attributes; thus, maintaining the status quo is recommended. For those attributes situated in Quadrant III—“Low priority”, characterized by both low significance and poor performance, further exploration would be necessary to identify potential opportunities for protection and reuse within optimization strategies. Lastly, landscape attributes positioned in Quadrant IV—“Focus Here” showed high significance but inadequate performance levels, requiring focused efforts towards optimization.
4. Results
4.1. Landscape Attributes’ Identification
Based on the user-generated content on social media, Table 3 presents the identified landscape attributes of the Liangdancheng industrial heritage. Among the three first-level codes, built environmental resources maintain the highest keyword frequency at 1000 times, natural environmental resources have the lowest keyword frequency at 288 times, and cultural environmental resources are perceived 702 times. In general, the built environment is perceived as the most essential part of the Liangdancheng industrial heritage landscape while its natural environment is the least important of all.

Table 3.
Attribute identification of the Liangdancheng industrial heritage landscape.
4.1.1. Built Environmental Resources
In descending order, the frequencies of Liangdancheng landscape attributes related to built environmental resources are 688 times, historic artifacts; 300 times, architectural constructions and structures; and 12 times, sites. This indicates that the perceived value of Liangdancheng among the public is not only focused on architectural constructions and materials, but also on display contents, including celebrity sculptures and stone-engraved slogans. However, the perception of the overall characteristics of the road system is relatively weak. Specifically, in terms of the aspect of historic artifacts, high frequencies are associated with pictures (181 times) and red bricks (124 times). Celebrity sculptures (77 times), stone-engraved slogans (55 times), and gatepost couplets (45 times) are also notable landscape attributes with relatively high frequencies, but other attributes’ frequencies are below 22. The landscape attributes of historic artifacts with featured themes or serial pictures show stronger perceived value, compared to single historical objects such as typewriters, tanks, and phonographs. For example, despite their limited number, celebrity sculptures, stone-engraved slogans, and gatepost couplets possess a strong perceived value of the landscape. Furthermore, some attributes that have a large quantity but are difficult to understand cannot be well perceived with their values, such as scientific research artifacts and video exhibits. Therefore, the quantity, quality, and understandability of historic artifacts as exhibition contents can directly influence people’s value perception, contributing to landscape attributes’ identification.
Regarding architectural constructions and structures, Deng Jiaxian’s former residence and the Jingying Gate (the main entrance) are mentioned 53 and 52 times, respectively, while other landscape attributes such as the History Museum and the Golden Hall are mentioned fewer than 22 times. Deng Jiaxian’s former residence and the Jingying Gate are landmarks of Liangdancheng and representative landscape attributes, so their values are perceived most. Furthermore, although Wang Ganchang’s former residence (n = 7) and Li Yingjie’s former residence (n = 3) shared common architectural styles, materials, and historical background with Deng Jiaxian’s, the number of times they are addressed in users’ footprints is significantly different. This shows that attributes of architectural constructions and structures with better publicity can well present landscape values and be strongly perceived. Regarding the landscape attributes of sites, roads are addressed 11 times and the courtyard is mentioned only 1 time, indicating the characteristics of the masterplan and overall road planning in Liangdancheng cannot be easily perceived as the spatial logic of “courtyard-street-site”.
4.1.2. Cultural Environmental Resources
Liangdancheng’s cultural environmental resources contain people (n = 343), events (n = 250), spirits (n = 95), and cultural creative products (n = 14), and the landscape attributes of events and people are strongly perceived by the public. Events involve historical and current events, while people include historical figures and (current) tourists. Specifically, in the historical events, the frequency of “two-bomb” history is the highest (n = 133 times), but every other event is only addressed fewer than 52 times. Patriotic education is the highest among current events, which is mentioned also 52 times. Regarding historical figures, Deng Jiaxian and the “two-bomb” heroes have relatively high frequencies, of 59 and 49, respectively. Mass tourists (n = 76) and parents & children (n = 65) are addressed significantly more than family tourists (n = 5). However, some anonymous/ordinary scientists’ stories and science education are also not addressed much, with frequencies of no more than 19. Among spirits and cultural creative products, only “Sanxian” spirit and its dedication have the strongest value perception, and their frequencies are 42 and 29, respectively. Some landscape attributes without explanation or promotion, such as endeavor, bomb souvenirs, cartridge souvenirs, and fridge magnets, are rarely addressed in users’ footprints, so they are hardly identified as core attributes of Liangdancheng. The spirits of endeavor, scientific research, and pioneering have yet to achieve a good effect on public perception and education. Cultural creative products could be the landscape attributes of persistent public education through the track of propagandizing, explanation, commemoration, and memory. Therefore, regarding cultural environmental resources, landscape attributes are not only concerned with historical figures, events, and group activities, but also identified with current people, events, and cultural creative products relying on the cultural significance of spatial experiences.
4.1.3. Natural Environmental Resources
Besides built and cultural environmental resources, collected digital footprints indicate that the public can also perceive the values of Liangdancheng through its landscape attributes of geographical and surrounding characteristics. Plants are mentioned 277 times, while the frequencies of water systems and topography are 6 and 5, respectively. More specifically, natural environment and flowers & plants have a relatively high frequency at 163 and 74. The results indicate that the overall plan of Liangdancheng (parks and natural scenery) has yet to be perceived well as a natural landscape attribute.
4.1.4. Mapping the Landscape Attributes of the Liangdancheng Industrial Heritage
In this research, the recognition outcomes of the three types of landscape attributes were overlaid onto the map of Liangdancheng, with text size and color indicating public perception frequency (Figure 4). This spatial distribution map reveals that attributes with higher importance are concentrated in the central area of Liangdancheng, along peripheral road systems, and in scattered corners. More specifically, areas with frequent public perception and high importance include Jingying Gate and Deng Jiaxian’s former residence at the center of Liangdancheng. Attributes such as red bricks, pictures, models, and celebrity sculptures hold the highest significance for the public due to their iconic entranceways or typical buildings within Liangdancheng. Architectural materials, historical pictures, and celebrity sculptures are regarded as useful in understanding the history behind the industrial heritage landscape.
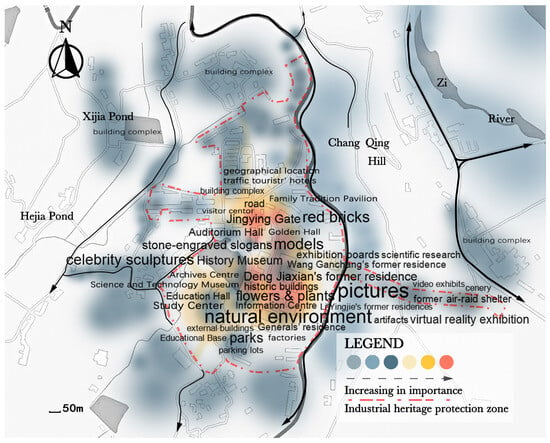
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution map of landscape attributes and their relative significance.
The high-importance buildings in Liangdancheng include the History Museum and the Auditorium Hall, which are characterized by landscape attributes with strong public spatial experiences such as stone-engraved slogans, trucks, “two-bomb” achievements, and endeavors. These attributes indicate that after gaining initial knowledge about “two-bomb” history, the public pays attention to preserving historical information and inheriting spirits. On the other hand, landscape attributes with a lower frequency of public perception and lesser importance can be found in the education hall, the Information Center, and the Study Center scattered throughout Liangdancheng. These areas feature video exhibits, commemorative coins, science education exhibits related to national defense development, and cultural activities. Therefore, this indicates that industrial heritage landscapes in Liangdancheng encompass built, cultural, and natural environmental resources while possessing multilayered tangible and intangible attributes. This demonstrates their overall characteristics of value correlation and spatial dependence.
4.2. Landscape Attributes Identification
4.2.1. The Importance–Performance Score of Liangdancheng Landscape Attributes
Based on mining the public’s spatial experiences within user-generated content, the performance of the Liangdancheng industrial heritage landscape attributes was assessed, and their importance was scored based on the attributes’ identification frequency. The mean and weighted average were processed to obtain the performance score, as Table 4 shows. Overall, Liangdancheng received a performance score of 3.77 (out of 5), indicating that most people are satisfied with their spatial experiences while visiting Liangdancheng; however, further optimization of protection and reuse strategies is necessary to improve the overall spatial quality of the Liangdancheng industrial heritage landscape.

Table 4.
Performance evaluation of the Liangdancheng industrial heritage landscape.
More specifically, regarding first-level codes, the built environmental resources score 3.40 (out of 5), that score of cultural environmental resources is 3.82, and the score of natural elements is 4.11. These scores suggest that the positive interpretation of the public’s spatial experience is more influenced by cultural environmental resources such as Sanxian spirits and events, as well as the natural environmental resources of various plants. Nonetheless, built environmental resources scored lowest among the three first-level codes; further work is needed in the people–spatial experience performance system of identifying and interpreting the values and attributes of the Liangdancheng industrial heritage landscape. Regarding second-level codes’ performance, spirits and plants are the highest, scoring 4.28 and 4.13, respectively. Additionally, architectural constructions and structures, sites, events, and people also have a relatively high performance. However, the lowest performed attribute is the surrounding rivers, scoring 2 (out of 5), as well as cultural creative products and topography, which only score 3. Interestingly, these three types of attributes’ weights are relatively low, with the numbers 0.04, 0.01, and 0.09, respectively. On the contrary, the landscape attributes of plants, architectural constructions and structures, and events are perceived most and then identified as having the highest importance, with weights of 0.87, 0.61, and 0.47, respectively.
4.2.2. IPA Analysis Results
In this research, importance–performance analysis (IPA) was conducted for each landscape attribute, and four quadrants of two-dimensional space were established based on the importance and performance values. The four quadrants are represented as Quadrant I—“Maintain Excellence”, Quadrant II—“Potential Overkill”, Quadrant III—“Low Priority”, and Quadrant IV—“Focus Here”. The results of the IPA analysis are presented in Figure 5. The overall results in Figure 5a show that the built environmental resources are mainly located in Quadrant III—“Low Priority” and Quadrant IV—“Focus Here”, while the cultural environmental resources are mainly in Quadrant I—“Maintain Excellence” and Quadrant II—“Potential Overkill”. However, Quadrants I and III both exhibit a scattered distribution of the natural environmental resources in Liangdancheng. Therefore, despite their high value and low importance, the overall performance of landscape attributes related to built environmental resources is weak, indicating a need for better planning regarding heritage protection and reuse. Regarding cultural environmental resources, the importance of the attributes varies in value perception but their performance, in general, is relatively high. Regarding natural environmental resources, the higher importance of the attributes is aligned with better performance, so lower importance leads to little performance satisfaction among the public. Therefore, it is necessary to enhance the performance of built environmental resources, further clarify the importance of cultural environmental resources, and maintain the protection state of natural environmental resources in terms of both the importance and performance perceived by the public, to improve the spatial quality of the Liangdancheng industrial heritage landscape. Table 5 shows several representative examples of Liangdancheng landscape attributes in each IPA quadrant.
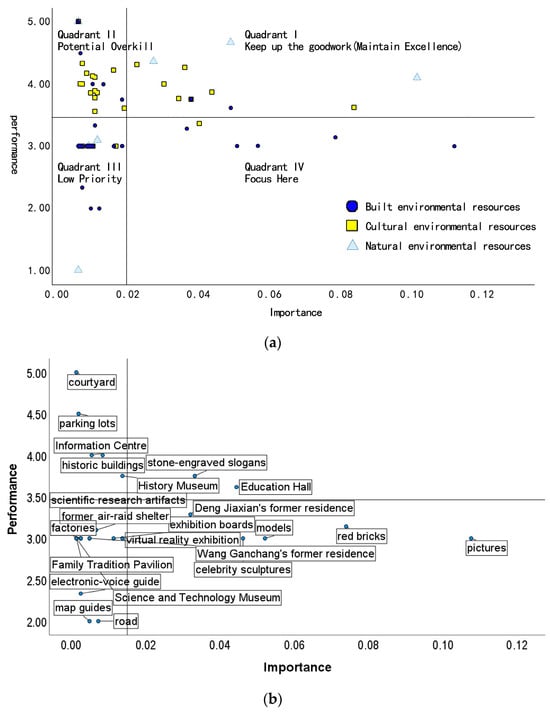
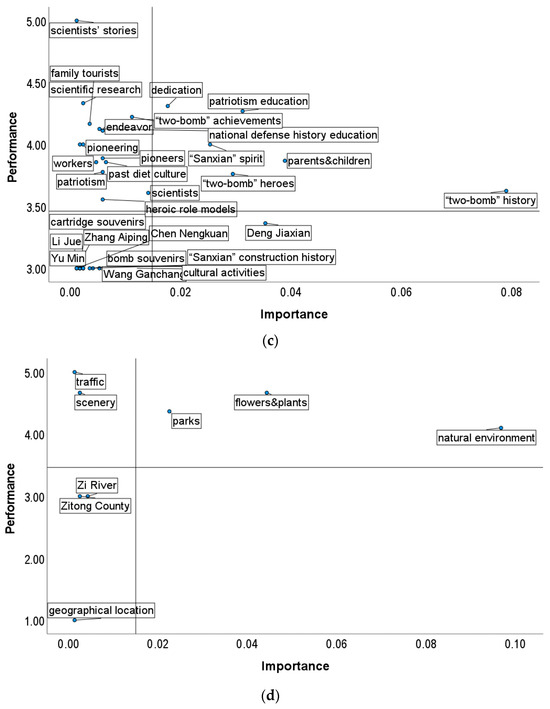
Figure 5.
(a) IPA analysis results of the Liangdancheng landscape attributes; (b) IPA analysis results of built environmental resources; (c) IPA analysis results of culture environmental resources; (d) IPA analysis results of natural environmental resources.

Table 5.
Examples of Liangdancheng landscape attributes in each IPA quadrant.
In the IPA analysis of the built environmental resources (Figure 5b), Quadrant I—“Maintain Excellence” includes stone-engraved slogans and the education hall; Quadrant II—“Potential Overkill” includes the courtyard, the history museum, and the information center. Quadrant III—“Low Priority” contains the largest number of landscape attributes, such as Deng Jiaxian’s former residence, models, red bricks, and celebrity sculptures. Quadrant IV—“Focus Here” includes landscape attributes such as Li Yingjie’s former residence, exhibition boards, and electronic-voice guide. The results show that built environmental attributes are perceived most by the public, in which the architectural constructions and structures attributes are manifested with the highest importance, but their performance is still insufficient. Among the architectural constructions and structures attributes, the education hall and Deng Jiaxian’s former residence are of strong importance; the education hall is located in Quadrant I—“Maintain Excellence”, whereas Deng Jiaxian’s former residence is in Quadrant IV—“Focus Here”. Within such a situation, both of the attributes are of high importance but their performance manifestations are significantly different, so targeted actions need to be taken to maintain their importance perception and improve people’s appreciation towards Deng Jiaxian’s former residence. Used as public reading and learning materials, historic artifacts such as models, pictures, exhibition boards, and electronic-voice guides vary in degrees of importance. Their distribution lies within Quadrant III—“Low Priority” and Quadrant IV—“Focus Here”, indicating inadequate support for guiding facilities in building theme museums and related interpretation materials. This research also reveals that the importance of buildings and the performance of display materials are tightly associated. Red bricks, pictures, and celebrity sculptures aligned with Deng Jiaxian’s former residence and Jingying Gate are located in the same quadrant. Therefore, it could be a possible way to improve the perceived quality of Liangdancheng’s built environment resources by advancing the sense of experience, visibility, and readability for exhibitions’ presentation.
In the IPA analysis of cultural environmental resources (Figure 5c), the landscape attributes in Quadrant I—“Maintain Excellence” include parents and children, “two-bomb” heroes, Sanxian spirit, patriotic education, and dedication (in Chinese, fengxian jingshen). The attributes in Quadrant II—“Potential Overkill” are family tourists, endeavor, science education, and past diet culture. Quadrant III—“Low Priority” includes the historical figure Zhang Aiping and local cultural activities. Quadrant IV—“Focus Here” only includes the scientist Deng Jiaxian. Scientists and scientists’ stories have good performance but a weak public perception of importance. Furthermore, other historical figures (but not as famous among the public), such as Yu Min and Li Jue, are associated with low perceived frequency and poor interpretation quality. This indicates that historical figures, especially scientists, can deeply influence the improvement in people’s spatial experiences. However, because of insufficient knowledge and background information about the figure, it is hard for the public to perceive related landscape attributes and values, highlighting the need to strengthen the introduction and publicity of Sanxian historic people through multiple platforms. In terms of landscape attributes in cultural events (both historical and contemporary), the great history of “Two Bombs” has better importance and performance perception when compared to national defense history and education and “Sanxian” construction history. In addition, cultural creative products such as stamps and souvenirs are in Quadrant III—“Low Priority”, indicating that the public considers these landscape attributes to be unimportant, and their quality of performance is also not good enough; to some extent, the public does not show much care about these attributes’ value interpretations.
In Figure 5d, regarding the IPA analysis of natural environmental resources, Quadrant I—“Maintain Excellence” includes flowers, plants, parks, and the general natural environment. Quadrant II—“Potential Overkill” includes traffic and scenery, while Quadrant III—“Low Priority” encompasses Zitong County, Zi River, and geographical location. More specifically, flowers, plants, and the general natural environment are easy to perceive and can easily produce positive spatial experiences for the public. However, people’s perception of Zi River and Zitong County is weak and presents a poor performance. These findings reveal that although green environments composed of plants and flowers in parks meet high public expectations, there is limited will to improve the structure of “big” natural attributes, geographic characteristics, and traffic systems, to advance the performance of natural landscape attributes in Liangdancheng.
5. Discussion
Identified as a crucial tool for heritage management worldwide, public participation can provide a scientific basis for decision-making in various technical steps such as identifying landscape attributes, assessing potential values, and formulating/implementing management plans [25]. However, in practice, public participation always requires significant manpower and material resources, and often faces challenges related to the breadth and depth of data collection, such as limited samples, inaccurate information feedback, and delayed effectiveness [18]. Along with changes in information technology, digital footprints have bridged the gap created by difficult access to public-generated data. The spontaneous social media content posted and shared by heritage visitors and users brings together key information on heritage values, people’s behavior, visitor feedback, and spatial characteristics, without the “push” from experts or governments in open community meetings [18,26,33]. Thus, these data truly reflect the public’s choice preferences and deep-rooted behavior patterns.
The inclusion of public participation is necessary to identify local resources, values, and needs, as well as to reconcile conflicts between the public, experts, and governments in plan implementation. Through the analysis of digital footprints as a participatory tool, people’s interests can be well identified and then support value assessment processes. This research analyzed digital footprints from social media platforms’ public textual comments and image sharing to reveal the attributes and expressions of industrial heritage landscapes in Liangdancheng. We present the technical path of digital footprints from data collection to analysis for future decision-making in Figure 6. However, in practice, this tool, with its three steps, also needs to be the supplemented by the collection of ideas from experts, governments, and real estate companies. Specifically, this research found that visitors do not know local history well, meaning they cannot perceive and value some cultural attributes enough, such as the importance of the formal residences of Wang Ganchang and Zhang Aiping. Within such a situation, experts need to play a better role in educating the public and conducting the participatory process. For example, in each step, the government can organize a public discussion meeting based on the analysis results of the digital footprints conducted by professionals or experts. In this meeting, the discussion would not just focus on the negotiation between different groups’ benefits, but also on researching digital footprints’ analytical results and how to truly integrate the public’s voices, to improve decision-making and plan-implementation processes.
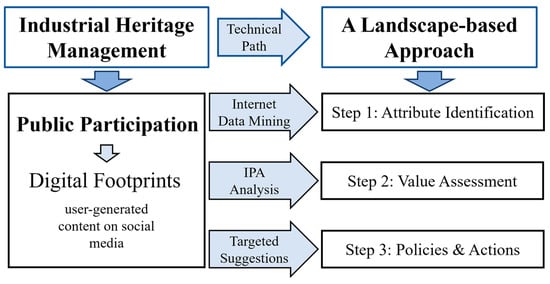
Figure 6.
Technical path of processing digital footprints to include public participation in a landscape-based management approach.
With regard to traditional approaches to the protection of industrial heritage, a material-based process for immovable cultural relics is often implemented, with the objective of focusing on the protection of historic constructions, buildings, and monuments [1]. In the absence of the consideration of the needs and interests of the public, it is difficult for industrial heritage sites to achieve long-term vitality or be integrated into current urban development activities [6,10]. This research has positive implications for establishing an efficient public participation platform and mechanism. Through the path in Figure 6, the attributes and values of the industrial heritage landscape are identified through the analysis of public spatial perceptions and experiences, while excavating tangible and intangible multilayer landscape attributes such as topography, architectural constructions and structures, events, and spirits.
Hence, the data of digital footprints on social media carry valuable information about diverse group perspectives and their interests; large-scale industrial heritage sites have multilayer landscape attributes of built, cultural, and natural environmental resources, requiring the holistic and dynamic process of a landscape-based approach for decision-making. In addition to tangible heritage, this research revealed that the public’s view of the Liangdancheng industrial heritage landscape also encompasses intangible heritage attributes, such as the Sanxain spirit, historical activities, and current cultural creativity. Therefore, from the perspective of a landscape-based approach, this digital public participation tool can be effective in practice, to help identify value attributes (built, cultural, and natural) and bridge the gap between heritage protection and local development. The landscape-based approach can reveal and maintain the connections between different heritage value attributes, and this holistic approach promotes cultural continuity in time and space and strengthens the link between industrial heritage in the past and the present.
6. Conclusions
This study tested the use of people’s digital footprints on social media as a public participatory tool for identifying and assessing industrial heritage landscape attributes and values, taking Liangdancheng in China as a case study. By applying the method of CA (content analysis) in the process of data mining, an approach was developed in this research to identify the attributes of the industrial heritage landscape from ten categories within built, cultural, and natural environmental resources. For example, built environmental landscape resources were identified to include the landscape attributes of architectural constructions and structures, parks, and sites, as well as historic artifacts. Cultural environmental landscape resources include people (historical figures, scientists, and tourists), events (festivals and activities), spirits (patriotism and Sanxian spirit), and cultural creative products. Therefore, the identification of industrial heritage attributes and values from a broader landscape-based perspective can move beyond a material-centered approach to include both tangible and intangible characteristics, wherein user-generated content is collected to reflect the public’s spatial experiences and value perceptions.
Moreover, to target the needs and interests of the public, this research conducted IPA (importance–performance analysis) to assess the landscape attributes’ importance and performance in presenting people’s spatial experiences in Liangdancheng. Based on the assessment, landscape attributes were categorized into four quadrants: (1) maintain excellence, (2) potential overkill, (3) low priority, and (4) focus here. There were 27 landscape attributes in Quadrant III—“Low Priority”, while Quadrant IV—“Focus Here” only has 6 attributes. For example, in Quadrant IV, the attributes of Deng Jiaxian’s former residence, sculptures, red bricks, pictures, and the historic figure of Deng Jiaxian are of importance but have poor performance. Therefore, further protection and planning actions of the local industrial heritage landscape are needed to maintain these attributes’ value perception and significance among the public, but also to better enhance the public’s understanding and experience. Through the collection and assessment of digital footprints as a public participation method, this paper can provide effective technological support established via social media platforms for the integrated management of industrial heritage landscapes.
In summary, this study showed that digital footprints on social media can be used as an effective participatory tool to solicit the public’s needs and interests, incorporating the protection of the industrial heritage landscape into its long-term integrated planning framework for sustainable adaptive reuse. Nonetheless, in practice, more stakeholders’ interests and social roles need to be further organized, to ensure management plans are “authorized” and “public-included”. Additionally, the developed methodology can contribute to a more inclusive and dynamic landscape-based heritage management approach, wherein the public’s ideas are well considered by experts and governments. Regarding future research, further studies are encouraged to advance data mining technologies (artificial intelligence, machine learning, etc.) for analyzing digital footprints on social media and explore a value-oriented process of engaging multiple stakeholder groups, including the public, governments, experts, and enterprises.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L.; Investigation, Q.D.; Methodology, J.L., Q.D. and Y.S.; Software, J.P. and Q.D.; Supervision, J.L., F.F. and Y.S.; Visualization, J.P.; Writing—original draft, J.L. and J.P.; Writing—review and editing, J.L., F.F. and Y.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by MOE (Ministry of Education in China) Project of Humanities and Social Sciences, grant number 23YJC760055; Cultural and Museum Project of Sichuan Provincial Cultural Heritage Administration in China, grant number SCWW2023B09; Chengdu Philosophy and Social Science Planning Project in China, grant number 2022CZ011.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all project funders, journal editors, and the anonymous reviewers for their comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Poulios, I. Discussing Strategy in Heritage Conservation: Living Heritage Approach as an Example of Strategic Innovation. J. Cult. Herit. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 4, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bastawissi, I.Y.; Raslan, R.; Mohsen, H.; Zeayter, H. Conservation of Beirut’s Urban Heritage Values Through the Historic Urban Landscape Approach. Urban Plan. 2022, 7, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/conventiontext/ (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Rey-Pérez, J.; Pereira Roders, A. Historic Urban Landscape: A Systematic Review, Eight Years after the Adoption of the HUL Approach. J. Cult. Herit. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 233–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cenci, J.; Becue, V.; Koutra, S. The Overview of the Conservation and Renewal of the Industrial Belgian Heritage as a Vector for Cultural Regeneration. Information 2021, 12, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, C.; Wang, L.; Rao, F. Typology, Preservation, and Regeneration of the Post-1949 Industrial Heritage in China: A Case Study of Shanghai. Land 2022, 11, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICOMOS; TICCIH. Joint ICOMOS—TICCIH Principles for the Conservation of Industrial Heritage Sites, Structures, Areas and Landscapes. Available online: https://ticcih.org/about/about-ticcih/dublin-principles/ (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- TICCIH. Taipei Declaration for Asian Industrial Heritage. Available online: https://ticcih.org/about/charter/taipei-declaration-for-asian-industrial-heritage/ (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- Iqbal, N.; Akbar, S.H.; Van Cleempoel, K. Identification of Industrial Heritage and a Theoretical Framework for an Industrial Heritage Inventory System in Pakistan. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.K. Industrial and Cultural Heritage of the Ma On Shan Iron Mine Landscape and the Making of Industrious Hong Kong. Asia Pac. Viewp. 2022, 63, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba Dorado, M.I. Design of a Transdisciplinary Methodology for the Identification and Characterisation of Industrial Landscapes. Heritage 2022, 5, 3881–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Pereira Roders, A.; Van Wesemael, P. Community Participation in Cultural Heritage Management: A Systematic Literature Review Comparing Chinese and International Practices. Cities 2020, 96, 102476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwardhi, D.; Trisyanti, S.W.; Virtriana, R.; Syamsu, A.A.; Jannati, S.; Halim, R.S. Heritage Smart City Mapping, Planning and Land Administration (Hestya). ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, N.; Nourian, P.; Luo, R.; Pereira Roders, A. Heri-Graphs: A Dataset Creation Framework for Multi-Modal Machine Learning on Graphs of Heritage Values and Attributes with Social Media. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardin, F.; Calabrese, F.; Fiore, F.D.; Ratti, C.; Blat, J. Digital Footprinting: Uncovering Tourists with User-Generated Content. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2008, 7, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Olmedo, M.H.; Moya-Gómez, B.; García-Palomares, J.C.; Gutiérrez, J. Tourists’ Digital Footprint in Cities: Comparing Big Data Sources. Tour. Manag. 2018, 66, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, E.; Zambrano-Verratti, J.; Kleinhans, R. Web-Based Participatory Mapping in Informal Settlements: The Slums of Caracas, Venezuela. Habitat Int. 2019, 94, 102038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginzarly, M.; Pereira Roders, A.; Teller, J. Mapping Historic Urban Landscape Values through Social Media. J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zou, B. Industrialization from Scratch: The “Construction of Third Front” and Local Economic Development in China’s Hinterland. J. Dev. Econ. 2021, 152, 102698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Xiang, M. Study on Planning Layout and Spatial Form of the Third-Line Construction in North Sichuan—Taking Four Cities in Northern Sichuan as Examples. J. Soc. Sci. 2023, 11, 325–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pozo, P.B.; González, P.A. Industrial Heritage and Place Identity in Spain: From Monuments to Landscapes. Geogr. Rev. 2012, 102, 446–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TICCIH. The Nizhny Tagil Charter for the Industrial Heritage. Available online: https://ticcih.org/about/charter/ (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Landorf, C. A Framework for Sustainable Heritage Management: A Study of UK Industrial Heritage Sites. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2009, 15, 494–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oevermann, H.; Degenkolb, J.; Dießler, A.; Karge, S.; Peltz, U. Participation in the Reuse of Industrial Heritage Sites: The Case of Oberschöneweide, Berlin. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2016, 22, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Pereira Roders, A.; Van Wesemael, P. Imagine the Old Town of Lijiang: Contextualising Community Participation for Urban Heritage Management in China. Habitat Int. 2021, 108, 102321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroughi, M.; De Andrade, B.; Pereira Roders, A. Capturing Public Voices: The Role of Social Media in Heritage Management. Habitat Int. 2023, 142, 102934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xiang, M. Research Hotspots and Prospects of Third-Tier Construction Industrial Heritage. World J. Eng. Technol. 2022, 10, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.H.; Zhang, H. Progress and Prospects in Industrial Heritage Reconstruction and Reuse Research during the Past Five Years: Review and Outlook. Land 2022, 11, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Lu, Y.; Martin, J. A Review of the Role of Social Media for the Cultural Heritage Sustainability. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Hoeven, A. Historic Urban Landscapes on Social Media: The Contributions of Online Narrative Practices to Urban Heritage Conservation. City Cult. Soc. 2019, 17, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Ofli, F.; Imran, M.; Castillo, C. Detection of Disaster-Affected Cultural Heritage Sites from Social Media Images Using Deep Learning Techniques. J. Comput. Cult. Herit. 2020, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martilla, J.A.; James, J.C. Importance-Performance Analysis. J. Mark. 1977, 41, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroughi, M.; Andrade, B.; Roders, A.P. Capturing Experts’ Knowledge in Heritage Planning Enhanced by AI: A Case Study of Windcatchers in Yazd, Iran. J. Cult. Herit. 2024, 67, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).