Abstract
Climate change and intensified human activity have altered the landscape pattern of nature reserves and are expected to induce persistent changes in habitat quality. Using GIS technology and landscape ecological theories, we quantitatively analyzed landscape fragmentation characteristics and the driving factors for the interior and peripheries of the Qinling–Daba Mountains nature reserves during 2010–2017. Using spatial principal component analysis, landscape pattern indices, and Geodetector, we evaluated the habitat quality status of different nature reserve types in different regions and the impacts of human disturbance on these areas. The results are as follows: (1) Most national nature reserves in the Qinling–Daba Mountains were moderately or highly fragmented during 2010–2017, and the fragmentation degree of a few reserves exhibited a decreasing trend. (2) The fragmentation degree of landscape patches from the core areas to the experimental areas of the inner nature reserves showed a trend of being low in the middle and high in the surrounding area; the level of landscape fragmentation gradually decreased from the edge of 1 km (M-1) to 5 km (M-5). (3) There was spatial differentiation in the intensity of landscape fragmentation among the nature reserves; human activity intensity, land-use degree, elevation, slope gradient, and topographic relief were the factors influencing the spatial differentiation of landscape fragmentation, and the contribution of anthropogenic factors was significantly greater than that of natural factors. Human activities, such as the construction of network infrastructures, irrational partition management, expansion of agricultural and industrial production activities, were the main reasons for the spatial differentiation of landscape fragmentation in the nature reserves. These results can provide significant scientific support for ecological restoration in the nature reserves and contribute to the coordinated development between socio-economic system and ecological environment in the exceedingly impoverished areas.
1. Introduction
Landscape fragmentation is an intrinsic driver of habitat quality deterioration and a major cause of ecosystem degradation and biodiversity reduction [,]. The reduced patch size, increased habitat isolation, greater edge distances, and lower connectivity caused by this fragmentation leads to changes in interactions among ecosystem components and alters species’ growth environments. The effects of landscape fragmentation on habitats are continuous, detrimental, and unpredictable. The process and effects of landscape fragmentation can be identified by the reactions of many organisms [,]. When habitats are highly exposed to anthropogenic activity, their structures and function exhibit long-term changes [], which is of great significance for research on the spatial structure and characteristics of landscape fragmentation under different land-use scenarios and their impact on habitat quality.
Nature reserves have been regarded as an important tool for protecting habitat integrity and species diversity. The landscape integrity and ecological benefits of reserves play an essential role in maintaining the human–land relationship []. Although systematic research on the effectiveness of nature reserves is still in its infancy, the effectiveness and suitability of the range of nature reserves remain to be explored, as only 20–50% of global nature reserves are effectively managed []. The landscape ecosystems of nature reserves bordering densely populated areas have undergone significant changes, thus affecting the balance of ecosystem diversity; landscape fragmentation is the main cause of these changes []. Effective and precise conservation is a critical method for avoiding biodiversity loss and maintaining ecosystem balance []. In the face of potential threats due to the presence of multiple internal and external environmental factors, the timeliness of the scope of nature reserves and the sustainability of the related policy and regulations requires substantial research support, especially in developing areas where coordinated development and ecological protection are the top priorities. In recent years, the number of nature reserves in China has increased rapidly, but conservation benefits have not improved []. Therefore, it is necessary to study the fragmentation of landscape in typical national nature reserves in depth.
Island biogeography theory is fundamental for studying the ecological succession pattern of landscapes and has been widely used by domestic and international scholars in the research of habitat fragmentation and landscape renovation [,]. Landscape-based habitat quality evaluation is mainly applied to regions, such as small watersheds, mountains, plateaus, and cities [,,], with relatively broad research areas. The study of terrestrial surface landscapes and habitat fragmentation based on land cover is currently mainstream. Land cover change can directly affect species’ habitats and the ecosystem’s functions and services [], leading to significant alterations in the ecological linkage between habitat quality and land-use intensity [,]. In addition, the loss, degradation, and fragmentation of natural habitats caused by land-use change are the dominant anthropogenic drivers of biodiversity change []. Studies have shown that 70% of remaining forests are located within 1 km of forest edges, 50% of forest fragments are within 500 m of the forest edges, 20% of the remaining forests are located within 100 m from the edges, and most remaining forest patches are less than 10 hm2 in size []. This edge effect of vegetation primarily reflects the degree of landscape fragmentation within the ecosystem, the effects of which are persistent [,,,]. Therefore, investigating landscape fragmentation and its effects on habitat status based on land cover was the focus of this study. We selected ten national nature reserves of different types in China’s north–south transitional zone and the Qinling–Daba Mountains as the research objects because this area is relatively sensitive to changes in the surrounding ecological environment. Based on land use and land cover data, we explored the variation characteristics of habitat fragmentation in different landscapes and their spatial differentiation using landscape patch indices and the spatial principal component analysis method. Then, we investigated the critical drivers of fragmentation using Geodetector. This study aimed to provide a reference for the precise management of nature reserves in China’s north–south transitional zone affected by climate change and anthropogenic activities. Moreover, by revealing the habitat quality status and landscape ecological patterns of the nature reserves in the Qinling–Daba Mountains, we can provide theoretical support for these nature reserves’ sustainable development and ecosystem optimization.
2. Study Area and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
The Qinling–Daba Mountains are located between 30°–36° N and 101°–114° E, spanning Sichuan, Gansu, Shaanxi, Chongqing, Hubei, and Henan provinces. This region has a width of approximately 300 km from north to south and a length of approximately 1000 km from east to west, with a total area of around 300,000 km2 and an altitude range of 13–5528 m (Figure 1). The Qinling–Daba Mountains sit in the transitional region from the northern subtropical zone to the warm temperate zone, serving as an essential ecogeographical transition zone and a natural dividing line of climate in China. Within this transition zone, the topography varies significantly, and its natural geographical location has led to complex horizontal and vertical distribution patterns of vegetation coverage. The northern slope of the Qinling Mountains is mainly covered by warm–temperate deciduous broadleaved forests, while evergreen–deciduous, broadleaved mixed forests cover the southern slope. The northern slope of the Daba Mountain is connected with the southern slope of the Qinling Mountain, and the vegetation types on these slopes are similar. The southern slope of the Daba Mountains is covered by subtropical evergreen broadleaved forests. The regional vegetation and temperature change with altitude, showing obvious vertical zonality [,]. The Qinling–Daba Mountains are one of the 17 vital Biodiversity Ecological function zones identified in the National Major Function Zone Planning of China. The region has a large population with a scattered distribution, and the mountainous area between the Qinling and Daba Mountains is economically under-developed and has prominent problems with poverty, making it an important concentrated contiguous special hardship area in China. Effective management by local governments has led to the integrated development of land resources, but the partition management mode has made the natural habitat more fragmented. By the end of 2015, there were 26 national nature reserves in the Qinling–Daba Mountains, with a total area of approximately 1.47 × 104 km2 accounting for 5% of the entire land area of the Qinling–Daba Mountains, and 43 local nature reserves with a total area of 1.09 × 104 km2 accounting for 3.6% of the land area, which is lower than the global average (12%). In this study, we selected ten national nature reserves according to the division of land-use types and their indicative levels in the north–south transitional zone [,] as shown in Figure 1.
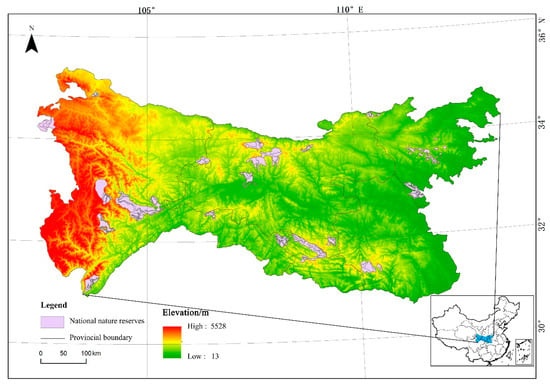
Figure 1.
Distribution of national nature reserves in the Qinling–Daba Mountains.
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
The 2010 and 2017 land-use type data used in this study were obtained from the Globeland30 data set developed and improved by the National Geomatics Center of China (http://ngcc.sbsm.gov.cn/ngcc/) (accessed on 20 September 2020) for the National High-Tech Research and Development Program (863 Program), with a spatial resolution of 30 m. Supported by ArcGIS 10.3 software, we preprocessed the data by cropping, mosaicking, and resampling and reclassified the land-use types into nine categories including agricultural land, grassland, forest, shrubland, wetland, water area, land for facilities, bare land, and snowfield, according to the land-use/cover type classification standards of the Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (RESDC), Chinese Academy of Science (http://www.resdc.cn/) (accessed on 16 September 2020). Then, we verified the distribution pattern of these land-use types with reference to the 1 km land-use data set from the RESDC website. Information from the nature reserves was obtained from the functional zoning maps provided on the website of the Ministry of Environmental Protection of China (http://www.zhb.gov.cn/stbh/zrbhq/) (28 July 2020), and the nature reserves’ boundaries in the maps were vectorized to obtain layers for the whole study area.
DEM data were derived from the NASA_SRTM data set with a 30 m spatial resolution. The elevation and slope gradient information were first extracted using ArcGIS, and the topographic relief of the entire Qinling–Daba Mountains was obtained by the mean change-point analysis method. Referring to the other region extraction method applied to the study area [], we classified the topographic relief of the Qinling–Daba Mountains into six levels: flat ground (<30 m), terrace (30–70 m), hills (70–200 m), low-relief mountains (200–500 m), medium-relief mountains (500–1000 m), and high-relief mountains (>1000 m) [].
2.3. Study Methods
2.3.1. Construction of a Composite Landscape Fragmentation Indicator
To investigate the overall landscape fragmentation pattern of the selected ten nature reserves in the Qinling–Daba Mountains, in this study, we calculated the landscape indices using the Patch metric module in FRAGSTATS 4.2 software to analyze the landscape fragmentation with the comparative method quantitatively. Considering the local situation of the Qinling–Daba Mountains, we selected the patch area (PA), patch shape index (PSI), fractal dimension index (FRAC), contagion index (CONTIG), and Euclidean nearest neighbor distance (ENN) to characterize the degree of landscape fragmentation in different regions [,]. The algorithm and ecological significance of each landscape index are explained in related literature []. Because the information of landscape fragmentation reflected by the selected landscape patch indices may exhibit overlap, we used the principal component analysis method to reorganize the selected indices into a set of independent synthetic variables. By characterizing the degree of regional landscape fragmentation using this method, redundancy can be avoided. These synthetic variables were then used as the analysis variables of the Geodetector to explore the influencing factors. The results of the principal component analysis are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Results of principal component analysis of landscape indices.
The formula for a composite indicator of landscape fragmentation is as follows:
where Zi represents the degree of landscape fragmentation; i denotes the nature reserve type in the study area; PCn represents the principal component scores of n indices; PA, PSI, FRAC, CONTIG, and ENN represent the patch area index, patch shape index, patch fractal dimension index, contagion index, and Euclidean nearest neighbor distance, respectively.
The path metrics and Class metrics modules in the FRAGSTS 4.2 software were used to calculate the landscape indices of different nature reserve types in the Qinling–Daba Mountains in 2017 with the aim of generating synthetic variables to characterize the degree of fragmentation. The results are shown in Figure 2. To investigate the spatial differentiation pattern of landscape fragmentation from the core to the edges of each nature reserve, we selected the functional partitions of the nature reserve and a 5 km buffer zone on its periphery as the research objects, which are (from inside to outside): the interior (core area, buffer area, and experimental area) and edge areas of 1–5 km (M-1, M-2, M-3, M-4, and M-5). The edge areas were divided according to the Euclidean distance of 1–5 km from the boundary to the core area, respectively, and the landscape fragmentation of the nature reserve was studied on this basis.
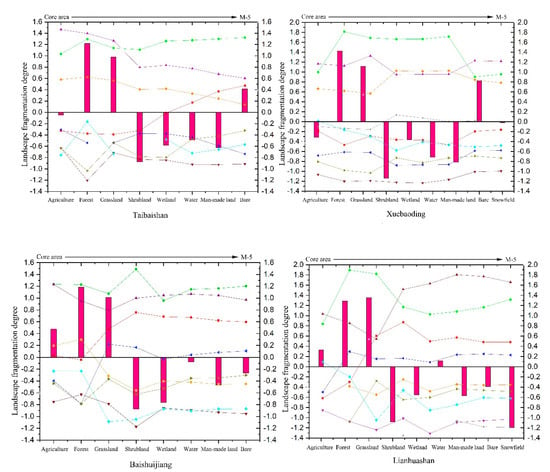
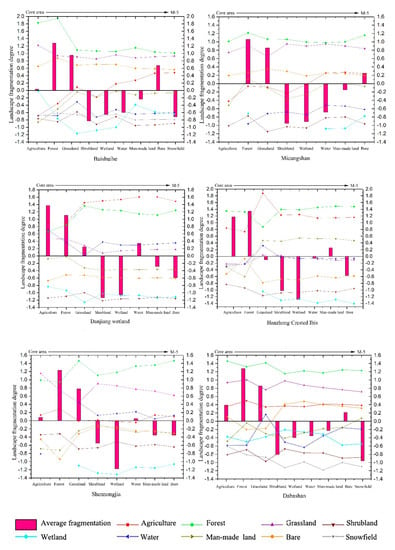
Figure 2.
Fragmentation of core–edge landscapes in Qinling–Daba Mountains nature reserves.
2.3.2. Determination of Factors Influencing Landscape Fragmentation
Factor detection and interactive detection methods in the Geodetector model were employed to investigate the relationship between landscape fragmentation in the Qinling–Daba Mountains nature reserves and its driving factors to quantitatively analyze the factors influencing regional landscape fragmentation []. First, the explanatory variables were constructed with the ArcGIS platform, and 2000 random points were created to extract the synthetic variables of landscape fragmentation, topographic relief, land-use type, human activity intensity, elevation, and slope gradient. Then, these explanatory variables were discretized into categorical variables, and the natural breakpoint method and land-use classification criteria were applied for partitioning. The basis of Geodetector is that if an independent variable had a significant effect on a dependent variable, then the spatial distribution of these two variables should be similar []. The model is as follows:
where q is the spatial heterogeneity of each indicator, and q ∈ [0,1]; W is the sample size of all indicators in the study area; α2i is the variance of sub-regional indicators; i = 1, 2, …, n, i denotes the partition of each indicator, and n represents the number of all partitions. The magnitude of q reflects the degree of spatial heterogeneity of each nature reserve in the Qinling–Daba Mountains. The larger the q value, the higher the spatial heterogeneity, and the greater the influence of partitioning factors on the spatial distribution of regional landscape fragmentation. The smaller the q value, the stronger the randomness of spatial distribution. Specifically, q = 0 indicates that the landscape fragmentation in the study area is absent of spatial heterogeneity, and q = 1 means that the indicators have perfect spatial heterogeneity.
In this study, topographic relief, elevation, slope gradient, land-use degree, and human activity intensity were chosen as the explanatory variables reflecting the landscape fragmentation. The factor detection method can reveal the extent to which each driving factor explains the spatial variation of the dependent variable in the Qinling–Daba Mountains nature reserves []. Interactive detection allows us to explore whether the interaction among multiple driving factors has increased or decreased the explanatory power of synthetic variables on the dependent variables in the nature reserve [].
Based on the results of principal component analysis for landscape patch indices, we extracted synthetic variables to characterize the degree of landscape fragmentation and chose the Hanzhong Crested Ibis nature reserve, which has a large KMO and cumulative variance contribution rate, as the research object to explore the influencing factors of landscape fragmentation in the nature reserves. The synthetic variables were input into the Geodetector for the analysis. In the partitioning process, which was conducted simultaneously, topographic relief classification was performed following the specified criteria, but the other driving factors were subjected to the systematic classification method of ArcGIS and the natural breakpoint method.
2.3.3. Quantitative Indices of Human Activity Intensity
To characterize the impact of regional human activity intensity on the degree of landscape fragmentation, we took the artificial land surface as the basic feature and used the intensity of land surface development and utilization and the level of human disturbance as the quantitative standard for human activity intensity considering the land-use intensity data from ten national nature reserves in the Qinling–Daba Mountains. Based on the regional land-use/cover variation data, we estimated the quantitative disturbance intensity of each nature reserve as the intensity of human activities []. The quantitative model of human activity intensity can be calculated by the following equations:
where HMI is the intensity of human activities in a nature reserve; SCV is the converted equivalent area of impervious surface; S is the total area of the region; SVi is the area of the land-use/cover type i; Gi is the conversion coefficient for the impervious surface equivalent of the land-use/cover type i; n is the number of land-use/cover types in the region. SCV is a quantization unit that compares the degrees of influence of different human activity modes on surface land use and their reflections in each land-use type. Gi is the index weight of each land-use type and surface vegetation characteristic in response to human activities. It is converted into a conversion coefficient for the artificial impervious surface equivalent according to human activity intensity.
For land-use/cover types with different impact degrees, the variation characteristics of the surface’s natural attributes can serve as a basis for determining Gi values. With reference to the relevant study of Xu, Y., et al. [], the conversion coefficients were determined by considering the conservation objectives of different nature reserves. The results are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Conversion coefficients of impervious surface equivalents for different land-use types.
3. Analysis of Results
3.1. Variation Characteristics of Landscape Fragmentation in Different Types of Nature Reserves
The variations in landscape fragmentation in the studied nature reserves in the Qinling–Daba Mountains from 2010 to 2017 show that landscape fragmentation had an overall decreasing trend. The degree of landscape fragmentation declined in seven nature reserves and increased in the remaining three reserves. From the results of landscape indices presented in Table 3, we can see that the PA and CONTIG of the Baishuijiang, Dabashan, Xuebaoding, and Lianhuashan nature reserves had an obviously decreasing trend from 2010 to 2017, indicating that the landscape patch areas in these nature reserves were becoming smaller, and the patches were gradually dispersed. Moreover, the increasing trend in FRAC suggests that the regional landscape patch structure tended to be complicated, and the degree of landscape fragmentation exhibited a rising trend. The PA and CONTIG indices of the Shennongjia and Micangshan nature reserves also had a downward trend, indicating that the area of the patches in these regions shrank and the degree of spatial aggregation decreased; the PSI and FRAC indices slightly increased, showing that the shape of the landscape patches developed from regular to irregular, and the degree of landscape fragmentation in these regions had a slight rise. The variation trends of PA, FRAC, and CONTIG of the Baishuihe nature reserve were consistent with those of Shennongjia and Micangshan, with larger magnitudes. Their ENN index increased, indicating that the patches became more dispersed and poorly connected, and the regional landscapes were increasingly fragmented. The Danjiang Wetland and Hanzhong Crested Ibis nature reserves had significant changes in CONTIG and ENN, and their variation trends were consistent; their PSI index decreased, indicating that the degree of landscape fragmentation in these two regions improved from 2010. Similarly, the Taibaishan nature reserve also had gradual improvement in its landscape fragmentation degree. Its PA and FRAC values increased, and there were more large patches which had shapes that became more regular.

Table 3.
Landscape type index of each nature reserve in the Qinling–Daba Mountains.
The synthetic variables of the landscape indices of the Qinling–Daba Mountains nature reserves from 2010 to 2017 show that most nature reserves were significantly fragmented (Figure 3). The degree of fragmentation varied among the different types of nature reserves. Its order from high to low in 2010 was Baishuihe > Xuebaoding > Lianhuashan > Danjiang Wetland > Micangshan > Hanzhong Crested Ibis > Shennongjia > Taibaishan > Dabashan > Baishuijiang, and Baishuihe and Xuebaoding exhibited more severe landscape fragmentation than the other nature reserves. In 2017, the greatest to least fragmentation was observed as follows: Danjiang Wetland > Lianhuashan > Baishuihe > Hanzhong Crested Ibis > Micangshan > Shennongjia > Taibaishan > Xuebaoding > Baishuijiang > Dabashan. The landscape fragmentation was particularly significant in Danjiang Wetland and Baishuihe, and the fragmentation degree was the lowest in Dabashan. After 2010, the degree of fragmentation decreased in Taibaishan, Danjiang Wetland, and Hanzhong Crested Ibis in the order of Danjiang Wetland > Hanzhong Crested Ibis > Taibaishan. The fragmentation in their different types of landscapes was improved to a certain extent. In summary, the overall landscape fragmentation in the Qinling–Daba Mountains nature reserves became more severe during the seven years, but the fragmentation in some nature reserves was mitigated.
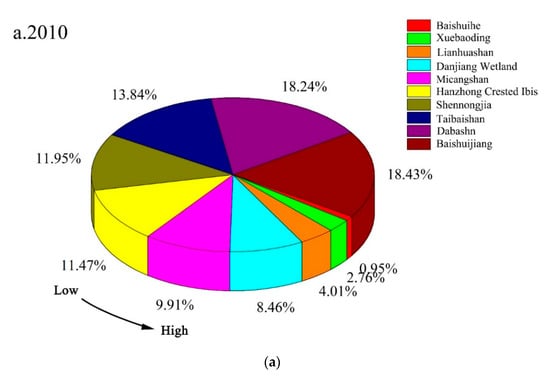
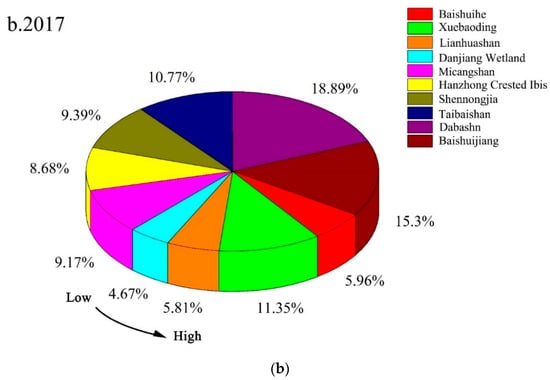
Figure 3.
Proportion of the comprehensive variable scores of the landscape patch index in 2010 (a) and 2017 (b).
The spatial distribution of landscape fragmentation in major nature reserves in the Qinling–Daba Mountains is demonstrated in Figure 4. In 2010, the highly fragmented areas of the Baishuijiang nature reserve were mainly concentrated in its northwest, southwest, and some marginal areas in the northeast; in 2017, the range of the highly fragmented regions remained the same, but the degree of fragmentation became higher, and the fragmentation gradually spread to the core area. The spatial distribution pattern of fragmentation in the Dabashan nature reserve during 2010–2017 was not apparent. Sporadic fragmentation mainly occurred in the north and southwest and was rarely distributed in the central area; the broken topography made the landscape more isolated and fragmented. The moderately and highly fragmented regions in Shennongjia were dispersed in its interior, and the fragmentation degree of the edges was relatively low. In 2010, the landscape of the Micangshan nature reserve was dominated by low to moderate fragmentation, and the highly fragmented regions were scattered in the central and western areas; by 2017, fragmentation became more severe at the edges of the entire nature reserve and had spread to the interior. The distribution of landscape fragmentation in Micangshan is closely related to topography and rivers. The dramatic topographic relief and convergence of river tributaries have created diverse landscapes. In 2010, the highly fragmented regions in the Xuebaoding nature reserve were concentrated in its western, northern, and southern border areas; by 2017, the fragmented regions had gradually developed to the central area with an increased number of patches, forming a continuous belt. The landscape fragmentation in the Baishuihe nature reserve is particularly significant. Baishuihe exhibited the most serious landscape fragmentation in the watershed. In 2017, the moderately and highly fragmented regions were concentrated in its edges, and the mildly fragmented regions were alternated with moderately to highly fragmented regions in its central area. In the Lianhuashan nature reserve, the moderately and highly fragmented regions were distributed from the southern periphery to its edges. The fragmentation at its northern borders was more serious than in its southern area, and the fragmented regions gradually expanded from the edges to the interior of the nature reserve. In comparison, the Taibaishan, Danjiang Wetland and Hanzhong Crested Ibis nature reserves were the focus of national environmental policies [], and human disturbance was gradually reduced in these regions. From 2010 to 2017, the degree of fragmentation gradually decreased in the entire region, and most of this area was dominated by medium to high fragmentation, with the highly fragmented regions concentrated at the edges. In summary, from the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of landscape fragmentation in the ten nature reserves in the study area from 2010 to 2017, we can find that the fragmentation degree had an upward trend in most nature reserves. Moreover, the moderately and highly fragmented regions were concentrated at the edges, and the fragmentation degree was reduced in only a few nature reserves. The highly fragmented nature reserves were all subjected to different levels of disturbance in their interior. The anthropogenic disturbance was relatively significant, and the fragmentation tended to develop from the edges to the core areas.
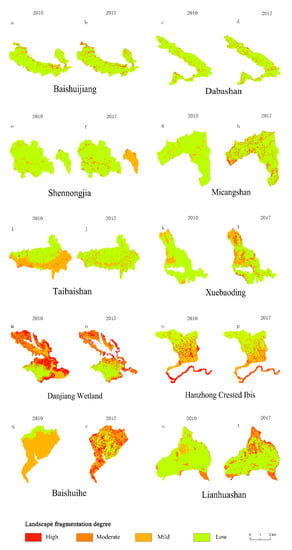
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution of landscape fragmentation in different types of nature reserves.
3.2. Core–Edge Spatial Differentiation of Landscape Fragmentation among Nature Reserve Types
3.2.1. Analysis of Landscape Fragmentation in the Interior of the Nature Reserves
The kappa coefficient was 0.83, and the classification results were applied to the entire study area. Most nature reserves in the study area exhibited a high degree of landscape fragmentation in their interior, with significant differences in spatial distribution. The fragmentation degree mainly decreased from the core area to the experimental area. According to Figure 2 and Figure 4, the fragmentation was the most severe in the Danjiang Wetland nature reserve, with an overall fragmentation score of less than 1.5 for the entire nature reserve. The average scores for shrubland and wetland were much lower than 0, the scores for grasslands, wetland, and water areas gradually decreased from the core area to the experimental area, and the general fragmentation level was high. Changes in the fragmentation degree of the internal functional areas were the most drastic in the Lianhuashan nature reserve, where the average fragmentation degree was the highest for shrubland, wetland, and snowfield landscapes, and the average scores for shrubland and snowfield were lower than 0.8. The fragmentation variations in the landscape patches of the internal forest and water areas were relatively large. From the core area to the experimental area, the fragmentation degree increased first and then decreased, and the spatial differentiation of landscape fragmentation was evident in the three main functional areas. The variations of the fragmentation curves of the Baishuihe nature reserves were generally consistent with few fluctuations. The fragmentation levels of the forest and shrubland patches in the core area were higher than the average values of 1.28 and 0.95, indicating a low degree of fragmentation. However, the fragmentation degree of the forest and wetland significantly increased in the experimental area, showing a prominent edge effect. The Hanzhong Crested Ibis nature reserve had dramatic changes from the buffer area to the experimental area. The fragmentation degree showed a downward trend in the forest, bare land, and shrubland. The fragmentation of the shrubland patches was the most severe, and the fragmentation levels of the agricultural land and man-made facility patches rose rapidly in the experimental area. The overall fragmentation of patches in the Micangshan nature reserve first decreased and then increased, with relatively significant variations observed in the patches of shrubland and man-made facilities. The fragmentation degree of shrubland, wetland, and water area landscapes was below –0.6, and the overall fragmentation was significant. The variations of landscape fragmentation in the Shennongjia nature reserve were also drastic, especially for the forest, grassland, and bare land, and the magnitude of the changes was between 0.4 and 0.6. The fragmentation degree of the wetland patches was generally high, with intense human activities on their peripheries. The landscape fragmentation characteristics and variations of the interior of the Taibaishan and Xuebaoding nature reserves were generally consistent. The fragmentation degree of shrubland was significantly higher than that of other types of patches, but the overall fragmentation magnitude of Xuebaoding tended to level off. The Baishuijiang and Dabashan nature reserves had a relatively low fragmentation degree, and the landscape fragmentation in these two regions was the most prominent in shrubland and snowfield, respectively. The overall score of the water area patches had great variations, and the fragmentation level of the internal man-made facility patches decreased first and then increased. The comparison of the nature reserves revealed that although the matrix landscapes were generally forest and grassland, the number of matrix patches increased while the core area was reduced. The matrix at the edges of most nature reserves became more fragmented, and a trend in habitat loss emerged. Some of the agricultural land patches of protected areas appear in the core area and even have a tendency to expand towards the core area, and the expansion of construction land also follows this pattern. The region is mostly a concentration of poor people, and the pattern of cultivation is rougher, and the negative impact of the management model accelerates the trend in landscape fragmentation within the protected areas. These findings indicate that ecological protection is essential in the Qinling–Daba Mountains. Some landscape ecological types that urgently require conservation are not protected. On the contrary, their area is shrinking under the disturbance of intense human activities, and the landscapes have been further fragmented.
3.2.2. Analysis of Landscape Fragmentation at the Edges of Nature Reserves
Variations in the landscape fragmentation on the peripheries of the nature reserves were relatively minimal across the study area, excluding those around M-1, and the fragmentation level of the landscape patches around M-1 was relatively high. The magnitude of landscape fragmentation variations on the peripheries of the Baishuijiang, Xuebaoding, and Lianhuashan nature reserves was also relatively high. Specifically, the forest patches around Xuebaoding had the most prominent variation magnitude of 0.8. The fragmentation degree of forest patches gradually increased from M-1 to M-5, while the variation trends of grassland, water areas, and shrubland were the opposite. All landscape types between M-1 and M-2 of Baishuijiang and Lianhuashan had the most remarkable variations (0.55). Particularly, the cross impacts between agricultural land and vegetation landscapes were significant, and the patches of major habitats were unstable. The greatest landscape fragmentation variations on the peripheries of the Shennongjia and Hanzhong Crested Ibis nature reserves were observed in M-1 (0.67), and as the distance from the nature reserves increased, the variation curves flattened. For the Taibaishan, Micangshan, and Baishuihe nature reserves, the fluctuations in the variation curves were mildest within M-5, but the agricultural land and man-made facilities exhibited significant variations. The degree of landscape fragmentation in this area gradually decreased, the patches were concentrated, and the anthropogenic disturbance was greater than natural disturbances. The fragmentation fluctuations of the forest, grassland, and wetland landscapes on the periphery of the Taibaishan nature reserve were lower than other areas, and the level gradually increased from M-5 to the boundary of the nature reserve, which was considered to be closely related to human activity at the edge of this area. Landscape fragmentation at the edges was more obvious than at the interior, where the landscape matrix gradually loses its dominance, biological habitats undergo potential migration, and external patches gradually replenish the missing habitats, causing the destruction of the original habitats, leading to fragmentation in terms of biological processes and, more importantly, the addition of external human factors dominates this fragmentation process.
In summary, the degree of landscape fragmentation in the interior and exterior of all nature reserves in the study area differed significantly. The most significant differences occurred at the edges of the nature reserves and their peripheries, and the fragmentation degree of the core areas rose under the impact of the edge areas. With the increasing severity and breadth of human impact, anthropogenic directional selection has led to the clustered distribution of agricultural land and man-made facility land patches. These land-use types are interspersed among natural habitats, increasing the degree of landscape fragmentation. Changes to landscape patches, forest, grassland, shrubland, and wetland areas were generally reduced, especially in the core areas of nature reserves and at the edges, while that of agricultural land and man-made facility areas demonstrated increasing trends. For different types of landscapes, the area of some anthropogenic landscapes is expanding, and the patches were distributed in a contiguous region, with a decreased degree of fragmentation. Particularly, the area of agricultural land was expanding, and the old and new farmlands were overlapping and complementing each other, forming a contiguous area, making agricultural land the dominant landscape type in certain regions. Internal landscape habitat processes and external environmental changes provide the conditions for landscape fragmentation in protected areas. Agricultural production activities and zoning management of protected areas continually partition essential ecological landscapes, resulting in the fragmentation of native forests, grassland, shrubland, and wetland. These landscape patches exhibited a mosaic distribution pattern. The dominance of these landscapes is gradually decreasing, and their fragmentation degree is rising. Thus, species have to migrate due to the shrinking habitats, and biodiversity is reduced.
3.3. Analysis of Influencing Factors
The detection results for the driving factors in the Hanzhong Crested Ibis nature reserve are listed in Table 4. It is shown that the q-statistics of land-use type and human activity intensity were 0.478 and 0.384, respectively, both indicating significant spatial differentiation and high influence strength; the explanatory power of slope factor on regional landscape fragmentation was 0.254, with the least influence. The strength of the influencing factors on landscape fragmentation in the nature reserve ranks in the following order: land-use intensity > human activity intensity > elevation > topographic relief > slope gradient. All influencing factors passed the significance test. Although the overall intensity of human activity in nature reserves exhibited a decreasing trend during 2010–2017 (Figure 5), the explanatory power of human disturbance factors on landscape fragmentation was still more dominant than that of natural factors. The results reveal that the gradual reduction of the natural vegetation area of the forest and grasses was accompanied by an increase in the amount of built-up land and population in the area that had affected the spatial differentiation of the landscape pattern. Therefore, lowering the intensity of human activity within and around nature reserves is crucial for protecting ecological landscape patterns and reducing landscape fragmentation.

Table 4.
Factor detection results.
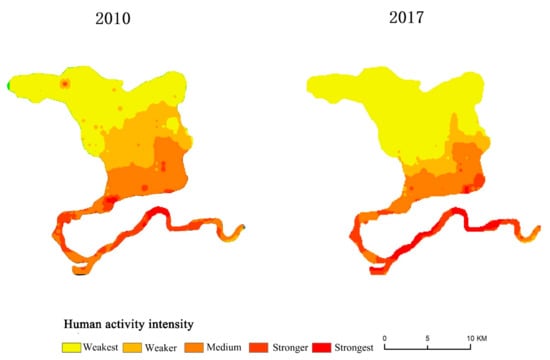
Figure 5.
Intensity of human activities in the Hanzhong Crested Ibis nature reserve.
Table 5 shows that the combination of any two factors had a more significant impact on the degree of landscape fragmentation in the nature reserve than any individual factor, and the factors with relative significant influence exhibited a relatively significant effect of double-factor enhancement. In terms of the interaction degree of the influencing factors of fragmentation, the order of their explanatory power is as follows: human activity intensity ∩ land-use type > topographic relief ∩ land-use type > elevation or slope gradient ∩ land-use type > elevation ∩ human activity intensity > topographic relief or slope gradient ∩ human activity intensity > topographic relief or slope gradient ∩ elevation > topographic relief ∩ slope gradient. Moreover, the explanatory power of the interaction of any two factors is greater than that of a single factor. Therefore, it can be seen that the effect of a single natural factor on landscape fragmentation is limited, but after interacting with an anthropogenic factor, the influence can become more prominent. This means that the synthetic effect of anthropogenic factors had a more significant impact, which is crucial for explaining the landscape fragmentation in nature reserves.

Table 5.
Interactive detection results.
4. Conclusions and Discussion
4.1. Conclusions
In this study, we took ten typical national nature reserves within the Qinling–Daba Mountains as research objects to explore the degree of landscape fragmentation and its influencing factors in the Qinling–Daba Mountains from 2010 to 2017. The results are as follows.
The landscape pattern of most nature reserves in the Qinling–Daba Mountains exhibited a trend of increasing fragmentation, although the degree of landscape fragmentation in some of the evaluated nature reserves was decreasing. From 2010 to 2017, the landscape fragmentation level was the highest in the Danjiang Wetland and Baishuihe nature reserves, and Dabashan had the lowest degree of fragmentation. The fragmentation degree in the Taibaishan, Danjiang Wetland, and Hanzhong Crested Ibis nature reserves gradually decreased, and the habitat conditions improved.
The degree of landscape fragmentation from the core areas to the experimental areas in the interior of the Qinling–Daba Mountains nature reserves was low in the middle and high in the surrounding areas. The level of landscape fragmentation gradually decreased from the edge of 1 km (M-1) to 5 km (M-5). Human activities were relatively intense around the edges at 1 km (M-1), and the degree of landscape fragmentation in these areas was found to be high. The spatial distribution of fragmented landscape patches in the nature reserves were differentiated. The high-value areas appeared in the regions with intense human activities, and the low-value areas were located in the regions with mild topographic relief.
The land-use degree, human activity intensity, elevation, slope gradient, and topographic relief significantly affected the spatial differentiation of landscape fragmentation in the Qinling–Daba Mountains nature reserves, and anthropogenic activities play a leading role. Human disturbance was the main cause of the fragmentation of ecological landscapes in the Qinling–Daba Mountains nature reserves. In particular, the construction of network infrastructures, irrational partition management, and expansion of agricultural and industrial production activities are the three most important factors that lead to the fragmentation of landscapes in nature reserves.
4.2. Discussion
The global climate is undergoing unprecedented changes. The distribution of species diversity is restricted by the changing climate and is sensitive to climate change’s effects. The impact of climate change on the functional structure of landscape ecosystems will be a major cause of biodiversity loss in the future []. Many studies on the influence of climate change on habitat status and biodiversity have revealed the significant effect of climate change on the reduced suitability and spatial distribution of nature reserves. Climate change also has considerable potential impacts on habitat quality [,,]. In this study, we analyzed the landscape fragmentation in nature reserves from the aspects of topographic and anthropogenic influencing factors, not involving the effects of climate variables on the suitability of nature reserves. The Qinling–Daba Mountains are a climatic transition zone. It may be necessary to explore the impact of climate change on habitat fragmentation in nature reserves in further studies to elucidate climate change-induced variations in the ecological landscape patterns in the Qinling–Daba Mountains.
In addition, since most nature reserves are small, with varying shapes and distribution scales, the use of low-resolution data may lead to the mismatch of spatial scales, thus affecting the accuracy of the findings presented herein. Therefore, it is necessary to reveal the landscape fragmentation of each nature reserve from the entire region of the Qinling–Daba Mountains. The present study’s results also indicate that the interiors of some nature reserves are still affected by human activities, especially the nature reserves which have peripheries that are densely populated and highly urbanized. The influence of anthropogenic factors on landscape fragmentation in nature reserves is greater than that of natural factors, basically in agreement with Zhang, J.Q., et al. [].
The expansion of rural development may damage nearby nature reserves. Human activities inside nature reserves are becoming increasingly frequent, mainly including the networking of tourist facilities and transportation infrastructure, illegal deforestation and land clearing, inappropriate production methods, and destructive living habits (Figure 6). Various types of anthropogenic disturbances are combined, jointly leading to significant edge effects in nature reserves, basically in agreement with Jin, C.P., et al. [].

Figure 6.
Field research photos of the Qinling–Daba Mountains nature reserves.
Human activities are more intense within 1 km of the peripheral area. The expansion of agricultural economic development has made land-use types more differentiated and landscape patterns more complex and fragmented. There are a large number of poor populations in the region, and slow economic development hinders the transformation and upgrading of the management model of nature reserves. Excessive intervention by policy measures and unreasonable zoning management measures have accelerated the trend of landscape fragmentation in nature reserves []. From the perspective of sustainable development, strict protection measures suitable for the local area should be formulated to properly control the human activities in the national nature reserves and precisely manage the ecological and environmental problems in these areas.
Landscape fragmentation is often accompanied by widespread habitat fragmentation, whereas the effects of habitat fragmentation are two-sided. Although it can cause habitat loss through species migration lag [] and extinction debt [], it also strengthens the functional linkage among species habitats, brings positive edge effects, decreases population competition, and enhances landscape complementarity []. Habitat restoration is most effective when carried out by natural mechanisms, but anthropogenic conservation measures can also improve the overall habitat quality. Therefore, although the impacts of habitat fragmentation within the landscapes are negative in some specific cases, these impacts cannot be treated as the same in all contexts. The results of these impacts must be analyzed in detail with species distribution models, such as ecological niches, to provide theoretical support for the effectiveness of nature reserves based on biodiversity and eco-environmental quality.
At present, nature reserves are established to conserve internal biodiversity and protect the natural environment. Conservation means have also been increasing in recent years. For example, through the reconstruction of specific habitats and corridors, the connectivity among the fragments increases, and the negative effects of fragmentation are thus mitigated []. However, the habitats within nature reserves are simultaneously affected by natural factors and human activities. It is impossible to assess the rationality of the nature reserve design based on available technical tools, and the time lag of nature reserves cannot be evaluated []. Distinguishing between the contribution of natural and anthropogenic disturbances is the key to judging the suitability of nature reserves. This can help develop conservation policies flexibly, thereby contributing to the sustainable development of nature reserves. In this study, we used land-use data to analyze habitat fragmentation among different landscape types. Our work was limited in that we were neither able to study habitat quality nor evaluate the suitability of the studied reserves. As climate change and human activity continue to impact global ecosystems, the spatial changes in nature reserves ought, with time and the functional partitioning from core to edge, to warrant deeper investigation []. Different types of nature reserves have different protection objects and roles, and research on habitats should be specific in its focus to yield suitably detailed findings. Multi-dimensional and multi-perspective exploration of internal habitat statuses will be a key approach for future research.
Field photos taken in 2020 showing the trend in landscape fragmentation in the inner and marginal areas of the Qinling–Daba Mountains nature reserves:
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.Z., H.Y. and Y.Z.; methodology, Y.Z. and H.Y.; software, Y.Z. and H.Y.; validation, L.Z., Y.Z. and C.M.; formal analysis, Y.Z.; investigation, Y.Z. and H.Y.; resources, L.Z. and C.M.; data curation, H.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z. and H.Y.; writing—review and editing, Y.Z., H.Y., L.Z. and C.M.; supervision, L.Z. and C.M.; project administration, L.Z. and C.M.; funding acquisition, L.Z. and C.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 41430637, and the Special Investigation of Basic Science and Technology Resources, grant number 2017FY100902. The National Natural Science Foundation of China is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC), and the Special Investigation of Basic Science and Technology Resources is funded by Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research (CAS).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are particularly grateful to Baiping Zhang, researcher and PhD supervisor of the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, who presides over the “Comprehensive Scientific Investigation of China’s North–South Transition Zone” project. As members of the research group for the project (funding number 2017FY100902), we thank Quantong Chen, Pingping Zhang, and Qingdong Dong for their contributions during field trips and raw data collection. The authors are also very grateful to the editors and reviewers for their comments and suggestions on improving this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ding, L.; Xu, G.; Lu, J.; Zhang, D.; Fang, B. Landscape fragmentation and its effect on biodiversity. J. Jiangsu For. Sci. Technol. 2005, 32, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, M.J.; Banks, S.C.; Driscoll, D.A.; Hicks, A.J.; Melbourne, B.A.; Davies, K.F. Short- and long-term effects of habitat fragmentation differ but are predicted by response to the matrix. Ecology 2017, 98, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, N.M.; Brudvig, L.A.; Clobert, J.; Davies, K.F.; Gonzalez, A.; Holt, R.D.; Lovejoy, T.E.; Sexton, J.O.; Austin, M.P.; Collins, C.D.; et al. Habitat fragmentation and its lasting impact on Earth’s ecosystems. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindenmaver, D.; Fischer, J. Habitat fragmentation and landscape change: An ecological and conservation synthesis. Austral Ecol. 2010, 32, 477–478. [Google Scholar]
- Geldmann, J.; Barnes, M.; Coad, L.; Craigie, I.D.; Hockings, M.; Burgess, N.D. Effectiveness of terrestrial protected areas in reducing biodiversity and habitat loss. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 161, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.; Dudley, N.; Segan, D.B.; Hockings, M. The performance and potential of protected areas. Nature 2014, 515, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Jiang, P.; Zhao, H.; Fan, J. Fragmentation process of wetlands landscape in the middle reaches of the Heihe River and its driving forces analysis. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 4436–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pressey, B.; Mccauley, D.J.; Morgan, L.; Possingham, H.P. A to–do list for the world’s parks. Nature 2014, 515, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, J.; Gao, F. Study on ecosystem service values in national nature conservation areas in Guangdong Province from 2000 to 2010. Res. Environ. Sci. 2014, 27, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar]
- Langlois, L.A.; Drohan, P.J.; Brittingham, M.C. Linear infrastructure drives habitat conversion and forest fragmentation associated with Marcellus shale gas development in a forested landscape. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, C.D.; Holt, R.D.; Foster, B.L. Patch size effects on plant species decline in an experimentally fragmented landscape. Ecology 2009, 90, 2577–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreiraa, M.; Fonsecabc, C.; Vergílioc, M.; Caladod, H.; Gile, A. Spatial assessment of habitat conservation status in a Macaronesian island based on the InVEST model: A case study of Pico Island (Azores, Portugal). Land Use Policy 2018, 78, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Gong, J.; Li, J. Spatiotemporal change of habitat quality in ecologically sensitive areas of eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: A case study of the Hehuang Valley, Qinghai Province. Resour. Sci. 2020, 42, 991–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, K.; Zhao, Q.; Wen, M.; Hua, L.; Lin, T.; Shi, L. Assessment of landscape pattern effect and ecosystem service of island urban forest. Remote. Sens. Land Resour. 2014, 26, 128–133. [Google Scholar]
- Cerrillo, R.M.N.; Vieira, D.J.E.; Ochoa-Gaona, S.; De Jong, B.H.J.; Delgado-Serrano, M.D.M. Land cover changes and fragmentation in mountain neotropical ecosystems of Oaxaca, Mexico under community forest management. J. For. Res. 2019, 30, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cao, Q.; Shi, S.; Huang, X.; Lu, Z. Spatio-temporal variability of habitat quality in Beijing–Tianjin–Heibei Area based on land use change. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 26, 3457–3466. [Google Scholar]
- May, F.; Rosenbaum, B.; Schurr, F.M.; Chase, J.M. The geometry of habitat fragmentation: Effects of species distribution patterns on extinction risk due to habitat conversion. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 2775–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, M.; Lefebvre, V.; Peres, C.; Banks-Leite, C.; Wearn, O.; Marsh, C.; Butchart, S.H.M.; Arroyo-Rodríguez, V.; Barlow, J.; Cerezo, A.; et al. Creation of forest edges has a global impact on forest vertebrates. Nature 2017, 551, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, M.; Lefebvre, V.; Gardner, T.A.; Arroyo-Rodriguez, V.; Baeten, L.; Banks-Leite, C.; Barlow, J.; Betts, M.G.; Brunet, J.; Cerezo, A.; et al. Supporting information for “BIOFRAG—A new database for analyzing biodiversity responses to forest fragmentation”. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 4, 1524–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barlow, J.; Lennox, G.D.; Ferreira, J.; Berenguer, E.; Lees, A.C.; Nally, R.M.; Thomson, J.R.; Ferraz, S.F.d.; Louzada, J.; Oliveira, V.H.F.; et al. Anthropogenic disturbance in tropical forests can double biodiversity loss from deforestation. Nature 2016, 535, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosa, I.M.D.; Smith, M.J.; Wearn, O.R.; Purvis, D.; Ewers, R.M. The environmental legacy of modern tropical deforestation. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 2161–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Zhou, C.; Chen, S. The geo-info-spectrum of montane altitudinal belts in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2003, 58, 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Ren, Z.; Li, J. Study on the ecological value of soil conservation of vegetation in the Qinling-Daba Mountains. Arid. Zone Res. 2006, 1, 144–148. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, D.; Qin, Y. Geographical expression and quantitative exploration of the China’s north-south transitional zone. Geogr. Res. 2021, 40, 1857–1869. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, L.; Yao, Y.; Cui, Y.; Liu, J. Spectra structures of altitudinal belts and their significance for determining the boundary between warm temperate and subtropical zones in the Qinling-Daba Mountains. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 889–901. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L. Relief amplitude based on county units in west Henan Mountain area and its correlation with distribution of population and economic activities. Areal Res. Dev. 2019, 38, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Tan, F.; Zhou, L. Analysis on the influence of landscape fragmentation on species diversity. J. Green Sci. Technol. 2018, 24, 158–161. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, S.; An, N.; Yin, Y.; Wang, J.; Qiu, Y. Landscape pattern in Da’an City of Jilin Province based on landscape indices and local spatial autocorrelation analysis. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 1860–1871. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J. Landscape Ecology: Pattern, Process, Scale and Hierarchy; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Gong, J.; Qi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J. Assessment of ecosystem food production and its spatiotemporal heterogeneity in the Bailong River Watershed, Gansu. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Tang, Q. Human activity intensity of land surface: Concept, method and application in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1349–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Duan, W.; Ding, H.; Feng, Y.; Wen, Y. Preference analysis of household ecological compensation in Crested Ibis protected area in Hanzhong, Shaanxi based on choice experiments. Resour. Sci. 2017, 39, 1792–1800. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, H.M.; Leadley, P.W.; Proençarob, V.; Scharlemann, A.P.W.; Fernandez-Manjarrés, J.F.; Araújo, M.B.; Balvanera, P.; Biggs, R.; Cheung, W.W.L.; Chini, L.; et al. Scenarios for global biodiversity in the 21st century. Science 2010, 330, 1496–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Staudinger, M.D.; Carter, S.L.; Cross, M.S.; Dubois, N.; Duffy, J.E.; Enquist, C.; Griffis, R.; Hellmann, J.J.; Lawler, J.J.; O’Leary, J.; et al. Biodiversity in a changing climate: A synthesis of current and projected trends in the US. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2013, 11, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgine, M.; Jetz, W. The effect of range changes on the functional turnover, structure and diversity of bird assemblages under future climate scenarios. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 2917–2928. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, M.B.; Alagador, D.; Cabeza, M.; Nogués-Bravo, D.; Thuiller, W. Climate change threatens European conservation areas. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Gong, J.; Liu, D.Q. Dynamics and driving factors of landscape fragmentation based on Geodetector in the Bailongjiang watershed of Gansu Province. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2018, 38, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, C.P.; Wang, C.; Wen, R.H.; Hou, P. Analysis of land cover change in Danjiang Wetland National Nature Reserve and its inner and outer areas from 2000 to 2015. Environ. Monit. Early Warn. 2019, 11, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.W. Study on the status quo and management measures of ecotourism in Taibai Mountain Nature Reserve. J. Green Sci. Technol. 2020, 21, 214–217. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, S.T.; Sax, D.F. Balancing biodiversity in a changing environment: Extinction debt, immigration credit and species turnover. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; May, R.M.; Lehman, C.L.; Nowak, M.A. Habitat destruction and the extinction debt. Nature 1994, 371, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damschen, E.I.; Drudvig, L.A. Landscape connectivity strengthens local–regional richness relationships in successional plant communities. Ecology 2012, 93, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, P.; Huang, L.; Xiao, T.; Wang, J. Dynamic changes of habitats in China’s typical nature reserves on spatial and temporal scales. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobrowski, S.Z.; Littlefield, C.E.; Lyons, D.S.; Hollenberg, C.; Carroll, C.; Parks, S.A.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Hegewisch, K.; Gage, J. Protected-area targets could be undermined by climate change-driven shifts in ecoregions and biomes. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).