Abstract
Climate change, marked by decreasing rainfall and increasing extreme events, represents a major challenge for water resources, particularly in semi-arid regions. To estimate aquifer recharge, it is essential to assess the fraction of precipitation contributing to groundwater recharge and to implement a water balance model. However, the limited number of rainfall stations has led researchers to rely on satellite and reanalysis rainfall products. The accuracy of these datasets is essential for reliable hydrological modeling. In this study, we evaluated five rainfall products—CHIRPS, ERA5_Ag, CFSR, GPM, and PERSIANN-CDR—by comparing them to ground measurements from gauging stations in the central Haouz region of Marrakech. The evaluation was conducted at three temporal scales: daily, monthly, and annual. Statistical metrics, including RMSE, MAE, NSE, Bias, and Pearson correlation, as well as classification metrics (accuracy, F1 score, recall, precision, and Cohen’s Kappa), and wavelet analysis, were applied to assess the accuracy of the products. The results identified ERA5_Ag and GPM as the most accurate products in capturing rainfall events. Nevertheless, ERA5_Ag showed a high bias. After applying the quantile mapping method to correct the bias, the product exhibited greater accuracy. The corrected datasets from these two products will be used to estimate recharge over the last 30 years, contributing to the development of a hydrogeological model for groundwater dynamics.
1. Introduction
The intercomparison of satellite products and climate precipitation models with measured data from weather stations is a discipline that has been carried out by many researchers around the world in order to validate the contribution of remote sensing and improve the quality of data from both satellites and climate models. In the 1990s, intercomparison studies of precipitation products [1,2,3,4,5] revealed an improvement of accuracy in the estimation of precipitation (satellites and climate models), with the aim of enhancing and developing the algorithms of climate models. Studies comparing satellite products with measured data have already been initiated in Africa, demonstrating perfect agreement between them [6,7,8]. The main objective of this comparison lies in the fact that the limited number of meteorological stations makes the spatialization of precipitation over large areas less effective. This spatialization process is essential for generating raster datasets used as inputs for hydrological models and climate index calculations [9,10,11,12,13,14]. It has to be noted that each data source has its own performance level in providing climate variables, depending on the primary data used. These may come from direct satellite observations [15,16] or from algorithms based on multi-source satellite data interpretation [17,18,19]. The climate context of the study area can affect the performance of these data sources. For instance, a satellite product may perform well in a temperate climate but be less reliable in an arid region. Several studies have explored these discrepancies; for example, refs. [20,21,22] examined that satellite-based products tend to be more accurate in tropical regions but less precise in arid, mountainous, or highly variable precipitation zones. Similarly, studies of [23,24,25] indicate that satellite products often struggle to estimate precipitation accurately in mountainous regions due to complex orographic effects. Likewise, in arid and semi-arid regions, reanalysis products such as ERA5 and MERRA-2 tend to underestimate precipitation, as they have difficulty in capturing local and sporadic events. The selected product from this study must perform well across three key evaluation tests. The first test involves statistical comparison metrics, including Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE), Bias, and Pearson correlation. The second test applies classification metrics and wavelet analysis to assess the products’ ability to capture precipitation variability. The best performing product will be selected for use in estimating diffuse recharge and building a water balance model of the study area, which is the aim of the next article.
2. Study Area
The area of interest in this study is an alluvial plain, bordered to the south by the High Atlas mountains, to the north by the Jbilettes, to the west by Oued N’Fis and to the east by Oued Rhdate. Figure 1 shows its geographical location, which is situated between 31° and 32° north latitude and 7° and 9° west longitude.
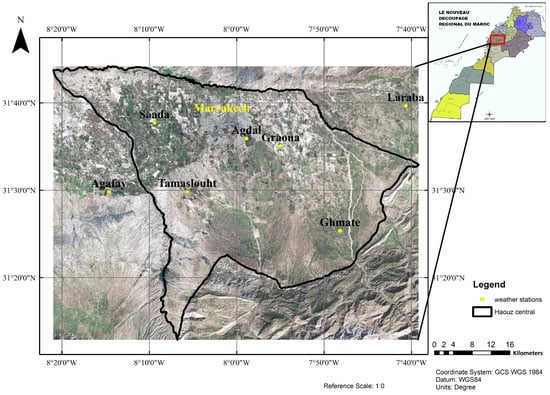
Figure 1.
Geographical location of the study area and the distribution of meteorological stations across the region.
The Haouz plain is generally dry, due to high average temperatures (reaching 40 °C) and intense evaporation. The four months from June to September constitute the dry season, with around 10 mm of precipitation per month. While precipitation is distributed throughout the year, most of it falls between October and May, varying between 25 and 65 mm per month. The annual precipitation ranges from 220 to 800 mm, with an average of approximately 415 mm, based on data from 1973 to 2009 (September to August). The region has a semi-arid continental climate.
3. Materials and Methods
The comparison is based on analysis at the pixel-point scale, relatively linked to the location of the meteorological measurement stations. The latter are irregularly distributed in the region, adding their limited number and the mismatch between the launch dates of each station, showing a well-defined contrast, ranging from 2003 to 2019, with a gap of 16 years, which complicates the analyses. The raw precipitation data from gauged stations have a 30 min time step, requiring transformation to a daily, monthly and annual time scale. The transformation is the sum of the values recorded at a time step of 30 min. The satellite data have a daily, monthly and annual time step, enabling statistical intercomparison analyses. For satellite data extraction, we adopt the proximity criterion, selecting the pixel value that coincides with or is closest to the geographical position of the weather station. Statistical tests are conducted over different time period from each station to another, due to their different commencement dates. Multiscale tests are applied while considering the variability and magnitude of the time scales (daily, monthly and annual). The range of data chosen for comparison tests has no gaps in the recordings, making the analyses more reliable and representative.
3.1. Characteristics of Rainfall Products and Gauged Stations
Each meteorological station is presented by its geographical coordinates, altitude, date of first start-up, parameters measured, and frequency of measurement; see Table 1. The present study took five automatic measuring stations belonging to LMI TREMA [26], which are well distributed geographically across the study area. Given the proximity of the Graoua and Agdal stations, we chose to use data from the Agdal station, which offers better data quality. Similarly, for the Laraba and Saada stations, we selected Laraba because of its longer measurement period than Saada. Thus, the weather stations selected provide representative, spatially well-distributed data that are sufficient for intercomparison studies.

Table 1.
Characteristics of gauged stations in the central Haouz plain.
For satellite and reanalysis products, the value is assigned to the pixel corresponding to the spatial location of the measuring station. Satellite data cover several spatial and temporal scales; Table 2 lists the characteristics of each satellite and reanalysis product used for precipitation estimates. In order to address the potential temporal lag between satellite products and station data, we examined time shifts ranging from 1 to 3 days. We identified the presence of this lag by analyzing the timestamps of both datasets. To quantify the effect of this lag, we applied a time shift to the satellite data and calculated the correlation with the station data for each shift. The correlation was computed for different time lags (from −3 to +3 days), with the data shifted forward and backward to capture any potential delay in satellite observations. The results were then analyzed to determine how the lag influences the temporal correlation. By accounting for this temporal shift, we ensured a more accurate representation of the relationship between the satellite and station data in the study. This analysis was realized as part of the preprocessing step before applying the assessment. Following this, we prepared a dataset for further analysis.

Table 2.
Characteristics of rainfall products used in this study.
3.2. Statistical Metrics
Assessing the robustness of satellite and reanalyzed precipitation products by comparing them with meteorological stations measurements is an approach adopted by several authors [27,28,29,30,31,32,33]. Statistical measures are used to evaluate satellite and reanalysis datasets by analyzing estimation errors in relation to gauged station measurements. The principal metrics employed to assess the performance of satellite and reanalysis products in estimating precipitation are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Statistical metrics used to assess rainfall products.
The root-mean-square (RMSE) metric is used to assess the dispersion between measured and estimated values and provides an overview of the ability of models (in our case, satellites and reanalysis products) to provide estimates of variables that are closer to in situ measurements. Several studies have employed this parameter to assess model outputs and quantify the differences between simulated and observed data [34,35,36,37].
The Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE) is a metric used to evaluate and compare model performance [38,39,40,41]. It compares the error of model predictions to the variability in observed data. While similar to R2, NSE is different in key ways: it can range from to 1 [42], whereas R2 ranges from 0 to 1. Unlike R2, which only shows how much variance is explained by the model, NSE also penalizes models that are biased or consistently differ from observed values. In some cases, the NSE can show a negative value when comparing rainfall products with gauged station data. This indicates that the rainfall product performs worse than using the mean of the observed station data as a predictor, suggesting that the product fails to accurately represent rainfall patterns or significantly deviates from gauged stations data. This happens because the NSE compares the squared differences between the observed data and the rainfall product data; if they are far off, the squared differences will be large, resulting in a negative value for NSE.
The Mean Absolute Error (MAE) measures the average magnitude of the errors between predicted and observed values [43,44]. It is calculated as the average of the absolute differences between these values, regardless of the direction of the errors (i.e., whether they are positive or negative). The mathematical expression is presented in Table 3.
Systematic errors and deviations in measurements or estimations are quantified by Bias. The output of a model is biased when it differs from the actual values. A high Bias indicates the model’s weakness in capturing the complexity of the data, while a low Bias indicates that the model provides fewer errors and that the outputs are closely matched to the real data. The relationship between Bias and variance must be taken into account when validating a model, as the balance between these two parameters is essential if the model is to be accurate and reliable. In general, a low Bias produces accurate outputs, while a low variance provides consistent outputs. The value of Bias ranges between the infinite interval (, ), with a value of 0 indicating complete agreement between measured and estimated values.
The Pearson R correlation index, commonly used by researchers in many fields [18,45,46,47,48,49,50], is a statistical measure that quantifies the linear relationship between two variables and assesses the degree of interdependence between them. This index is used to assess the linear fit of precipitation between satellite products and weather stations. Pearson’s R coefficient is the product of dividing the covariance of the two variables by the product of their standard deviations. The value of R lies within the interval −1 and 1. Values below 0 indicate that the relationship between the variables is negative; i.e., if variable X increases, variable Y decreases, and vice versa. An R coefficient of zero indicates that there is no linear relationship between the two variables. In terms of interpretation, a correlation does not indicate causality but rather signifies a concrete statistical relationship. For example, a hidden common factor may influence both variables, creating the causal relationship.
3.3. Classification Metrics and Wavelet Analysis
The intercomparison of satellite and reanalyzed products is improved by the application of other statistical measures, such as classification metrics. The detailed visualization of each product’s performance is explored through the confusion matrix. By definition, this matrix is a table showing the true and false predictions for each class. The calculation of classification metrics depends on this matrix. For a binary classification problem (rainy day or dry day), the shape of the matrix is shown in Table 4. The classification threshold is an important criterion that should be defined when calculating the matrix. This threshold defines the minimum amount of precipitation from which such a day is considered as rainy; for the case of the present study, we have defined a threshold of 1 mm, by which all days with precipitation greater than or equal to 1 mm are classified as a rainy day, while days less than 1 are classified as dry days.

Table 4.
Confusion matrix forme.
Classification metrics are derived from the confusion matrix. Accuracy is one of the classification metrics, measuring the percentage of agreement between observed and estimated data, which is aimed to assess the overall reliability of the products. Precision indicates the proportion of days estimated as rainy that were actually rainy according to the measuring stations. Recall measures the product’s ability to detect all the rainy days recorded by the weather stations. The F1-Score metric is an average between recall and precision and is useful for evaluating the overall performance of products. Cohen’s Kappa metric evaluates products by measuring the agreement between estimates and actual values. Table 5 below shows the formulas for calculating these metrics.

Table 5.
Classification metrics used in this study.
Wavelet analysis provides a significant additional value in the study. This approach makes it possible to examine rainfall variations on different time scales. By analyzing the wavelet spectrum of each series, we can identify the dominant periods of observed and estimated precipitation and see the rainfall event capture performance of each product. The process of applying this method is described as follows. The first step concerns data preprocessing, which is crucial for ensuring the reliability of the results, and the preparation of data series so that the comparison series must cover the same period and have the same temporal resolution (daily, monthly or annual). The second step involves the application of wavelet transforms. We chose the continuous wavelet transform (CWT) to analyze the temporal signals; as opposed to the Fourier method, the CWT decomposes the signal into fixed frequencies, enabling us to analyze the variability of precipitation as a function of frequency and time, thus generating a temporal spectrogram showing the differences in precipitation between stations and satellite products and reanalyzing them.
The mathematical expression of CWT (1) is written as follows:
where : wavelet coefficients associated with scale a and time position b, and
is the Mother wavelet function (2).
The complex Morlet wavelet was selected for the reason that it is better adapted to climatic series. Scales from 1 to 50, on the other hand, enable precipitation cycles to be analyzed at different temporal resolutions. The wavelet parameters used are listed in Table 6 below.

Table 6.
Wavelet parameters used for precipitation data analysis.
3.4. Application of Quantile Mapping for Bias Correction
The product selected is often biased, which means that the direct use of the raw precipitation series may have a negative effect on the hydrological modeling results. The quantile mapping method is used to correct bias in the product’s precipitation series. This method adjusts the distribution of product data to match a reference series (measuring stations) [51,52,53,54]. This technique works by constructing cumulative distribution functions (CDFs) for both datasets (satellite/reanalysis products and weather station data). It then identifies equivalent quantiles in the biased distribution, establishing a correspondence with observations. In concrete terms, each value in the biased data is adjusted according to this correspondence and replaced by a value closer to the observed data. The mathematical expression of the CDF function is given by Formula (3) below:
with representing the biased data, their empirical CDF, and the CDF of the observed data, gives the quantile of the biased data, and adjusts this quantile to the observed data.
All data processing, calculations and visualizations in this study were performed exclusively using Python 13.10.10 libraries and custom-developed scripts.
4. Results
Plots of the precipitation values measured and those from satellites and reanalysis products give an idea of the variability of the data in relation to the gauged measurements from the stations. The data show a cyclical trend, providing information on dry and wet periods [55]. There are also peaks distributed irregularly over time, which indicate periods of thunderstorms recorded at the stations [56,57]. We can already observe that precipitation values are both overestimated and underestimated by products. This variability must be quantified by applying the statistical metrics already mentioned. The accuracy of satellite products and climate models depends on the study’s objective, especially for precipitation. For applications like flood modeling, high temporal precision and minimal errors are crucial to ensure reliable hydrological calculations [9]. On the other hand, studies focusing on aquifer recharge from rainfall generally operate on an annual time scale. The range of precipitation data provided by the products is 20 years long, which is practically large enough to assess their performance.
4.1. Application of Statistical Continuous Metric for Raw Data (Daily, Monthly, and Annual)
At the daily scale, mean absolute errors show similar values from one product to another, with a mean value of 0.85. The CHIRPS product shows the highest mean of the five stations (MAE = 1.6), while CFSR and GPM show minimal values compared to the other products (0.77 and 0.76). As for RMSE, CHIRPS shows the highest values in all five products (RMSE = 6), while ERA5_Ag shows the lowest (RMSE = 2.5). The other products are evenly distributed. The Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE), on the other hand, shows negative trends in several products, while the CHIRPS product still shows significant negative values in all stations and the ERA5_Ag product shows positive values in all stations, with the exception of the Agdal station, which has a negative value; see Figure 2.
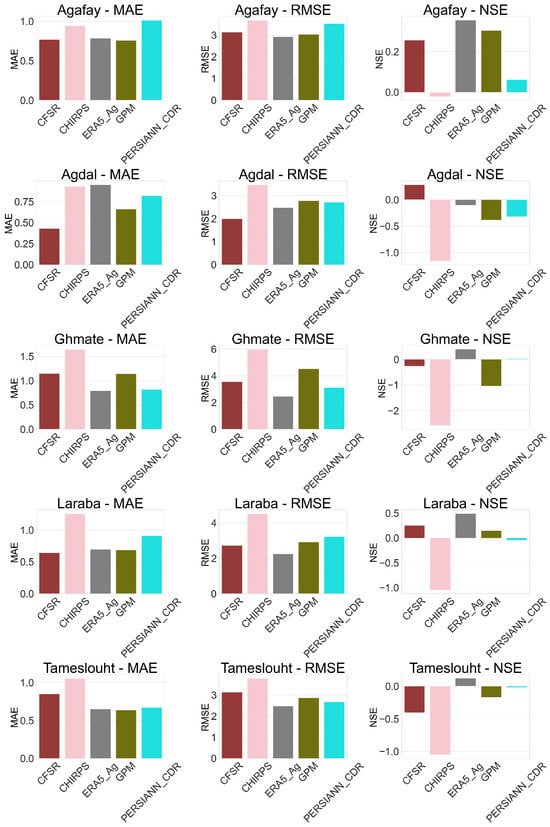
Figure 2.
Statistical metrics of the weather stations compared to rainfall products in the study area—daily time steps.
On a monthly scale, MAE shows different values from one product to another, with an average value deviation of 17 between the observed and estimated values, the product CHIRPS still shows the highest value of the five stations (MAE = 30) while PERSIANN_CDR and GPM show minimal values compared to the other products (10 and 13). As for RMSE, CHIRPS and ERA5_AG show the highest values across all five products (RMSE = 32 and 28, respectively), while the other products are contrasted from station to station, with PERSIANN_CDR showing the lowest values (RMSE = 15 at the Tameslouht station). Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE) values contrasted strongly between products, with CHIRPS showing negative trends at all stations except Agafay, while PERSIANN_CDR showed positive values at all stations. The other products show alternating negative and positive values across different stations; see Figure 3.
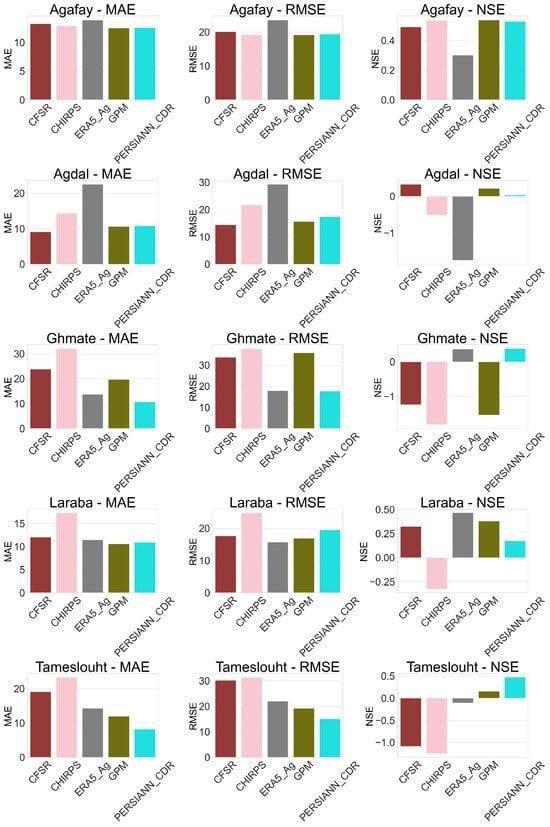
Figure 3.
Statistical metrics of the weather stations compared to rainfall products in the study area—monthly time steps.
As for the annual scale, the highest calculated MAE value is that of the ERA5_Ag product (MAE = 260 at the Agdal station), while the CHIRPS product has the lowest average of the five stations (MAE = 36 at the Agdal station), with the other products fluctuating between them. In terms of RMSE, ERA5_Ag has the highest value of the five products (RMSE = 260 at the Agdal station); the other products contrast from one station to another, with CHIRPS showing the lowest values (RMSE = 42 at the Ghmate station). On the other hand, the Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE) shows highly contrasted values, with the best performance recorded at the Laraba station, where the CHIRPS product showed a value of 0.65. Values close to 0 are expressed by the PERSIANN_CDR product, with negative values of CFSR product at the Ghmate and Tameslouht stations (−48 and −5 respectively), and other minimum negative values at the Agdal station; see Figure 4.
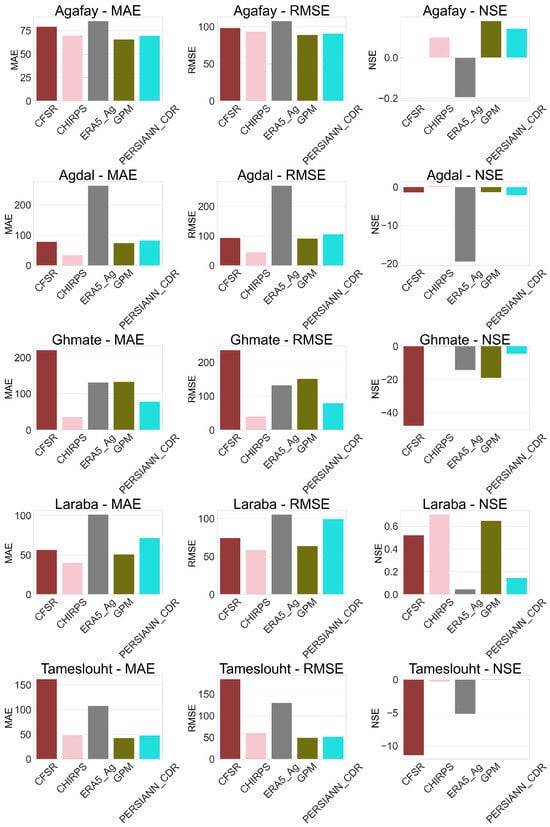
Figure 4.
Statistical metrics of the weather stations compared to rainfall products in the study area—annual time steps.
4.2. Evaluation of Bias in Rainfall Products
Bias, which measures trends in the over- or underestimation of precipitation products, is an essential complement to statistical metrics. It can be used to detect directional errors, which provides an additional perspective on product performance. On a daily scale, the observed bias values are quite low, ranging from 0.2 to 0.8. While this may suggest that the data are perfect, this is not the case. This apparent precision is explained by the high prevalence of zero values in the precipitation series, a typical feature of semi-arid climates, and by the low amounts of precipitation recorded, which influence the structure of the data. However, for a more comprehensive assessment, it is necessary to analyze the bias at broader temporal scales, such as monthly and annual. Table 7 shows the bias values for each station, for both monthly and annual time scales.

Table 7.
Precipitation bias analysis.
The analysis of variability in precipitation at different stations reveals distinct trends among the products studied. In general, some products show a marked underestimation (negative bias), while others overestimate observed precipitation (positive bias). At Agafay, the CFSR, CHIRPS, and GPM products systematically underestimate precipitation, although the difference with observations remains moderate. In contrast, ERA5_Ag shows a marked overestimation, while PERSIANN_CDR has a more moderate negative bias. At Agdal, CFSR underestimates precipitation, while CHIRPS slightly overestimates it. The ERA5_Ag, GPM, and PERSIANN_CDR products show a trend of overestimation, with ERA5_Ag having the highest bias, indicating a notable overestimation. In Ghmate, all products except PERSIANN_CDR show a tendency to overestimate, in particular CFSR and CHIRPS, which have very high biases. In Laraba, CFSR and PERSIANN_CDR underestimate precipitation, but with relatively small biases. Inversely, CHIRPS, ERA5_Ag, and GPM overestimate precipitation, with ERA5_Ag showing the largest discrepancy. At Tameslouht, CFSR, CHIRPS, ERA5_Ag, and GPM overestimate precipitation, and CFSR shows the highest bias. GPM shows a more moderate positive bias, while PER-SIANN_CDR shows a slight underestimation.
4.3. Correlation Analysis of Rainfall Product Performance
As a complement to the statistical tests already conducted in the present study, correlation analysis identifies the best-performing products by quantifying the strength and direction of the linear relationship between the two data sets (measured and observed) and provides an understanding of their spatio-temporal behavior. Table 8 below illustrates the correlation values between gauged stations and the rainfall products.

Table 8.
Correlation coefficients of precipitation products with ground-based stations across three time steps: daily, monthly, and annual.
The rainfall products evaluated show varied performance according to station and time scale (daily, monthly, annual). The CFSR product shows variable performance from moderate to stable correlations on the daily and monthly scales (e.g., 0.58 to 0.73 at Agafay), with a clear improvement on the annual scale for some stations, reaching 0.93 at Ghmate and 0.83 at Laraba. However, at Tameslouht, low results were observed, with a daily correlation of −0.74. For CHIRPS, daily correlations are generally low (often below 0.4) but improve considerably at monthly (0.75 at Agafay) and annual (0.74 at Agdal, 0.98 at Laraba) scales. At Ghmate, performances are inconsistent, with negative correlations at the monthly scale. ERA5_Ag is the most robust product, displaying high and stable correlations at all scales, including the annual scale (0.99 at Ghmate and 0.97 at Laraba). However, at Tameslouht, a notable exception occurs, with an annual correlation falling to −0.98. The GPM product shows great variability; while its performance is moderate on the daily and monthly scales (0.57 to 0.78 at Agdal), it shows strong variability on the annual scale, with a correlation of 0.95 at Tameslouht versus −0.64 at Ghmate. Lastly, PERSIANN_CDR shows generally low correlations on a daily basis (0.25 to 0.38) but a notable improvement on a monthly (0.74 at Agafay) and annual (0.92 at Ghmate and 0.76 at Agdal) scales. Graphical illustrations of the correlation are shown in Figure 5 below.
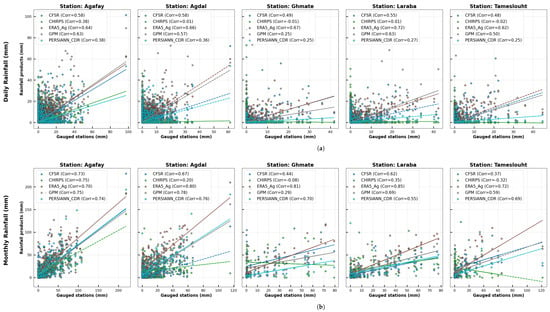
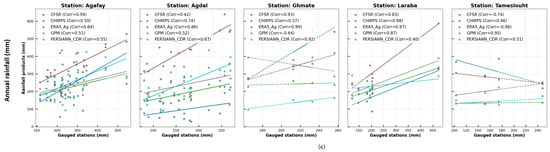
Figure 5.
Pearson correlation of precipitation products with ground-based stations across three time steps: daily, monthly, and annual. (a) Daily, (b) monthly, (c) annual.
4.4. Wavelet Approach to Temporal and Extreme Event Analysis
The evaluation of rainfall products is enhanced by the integration of advanced analyses, i.e., wavelet analysis and classification metrics. The combination of these two approaches provides a better understanding of the product’s weaknesses, refining adjustments, and optimizing their use for hydrological applications. Although CHIRPS shows better correlations on an annual scale at some stations, its daily performance remains poor. Wavelet analysis can target these differences, splitting time series into different frequency scales and identifying disparities in the representation of temporal variations. On the other hand, despite the reliability of the ERA5_Ag product, it presents high biases in some stations, such as Agdal. Classification metrics highlight if these biases relate to specific event types, such as the inability of this product to capture heavy precipitation (extreme events). The reliability of a product lies in the fact that it is accurate at three time scales (daily, monthly, or annual) and that it is capable of representing extreme events that are essential for hydrological applications. It is clear that these two approaches are complementary: wavelet analysis gives a global view of performance across the three time scales, while classification metrics provide a targeted assessment of specific events (the ability to detect intense rainfall).
4.4.1. Visualization of the Continuous Wavelet Transform (CWT)
A first perception reveals that, according to the interpretation of the power spectrum of all products, we observe on each product some peaks at specific frequencies with variable positions and amplitudes. These peaks reflect the periodicity of precipitation. The aim of this study is to analyze the correspondence between these peaks with those of the gauged stations. The scalogram shows the evolution of periodicity over time, intense colors indicate high signal strength at a given frequency at a given time. The scalogram of the measuring station can be compared with that of the precipitation products to see if they reproduce the same temporal variations of the stations. As for the global power spectrum, it assesses the similarity between product data and stations, directly comparing the power distribution between different products. Identical curves indicate a better correspondence in terms of frequency, while differences show discrepancies in the total variance of the products. Interpreting the results of the wavelet analysis involves assessing the graphical conformity of the weather station parameters with the precipitation products shown in Figure 6.
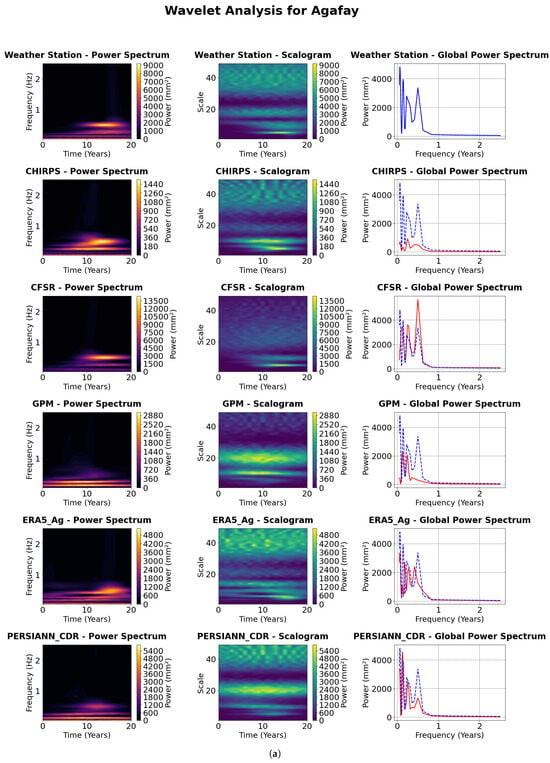
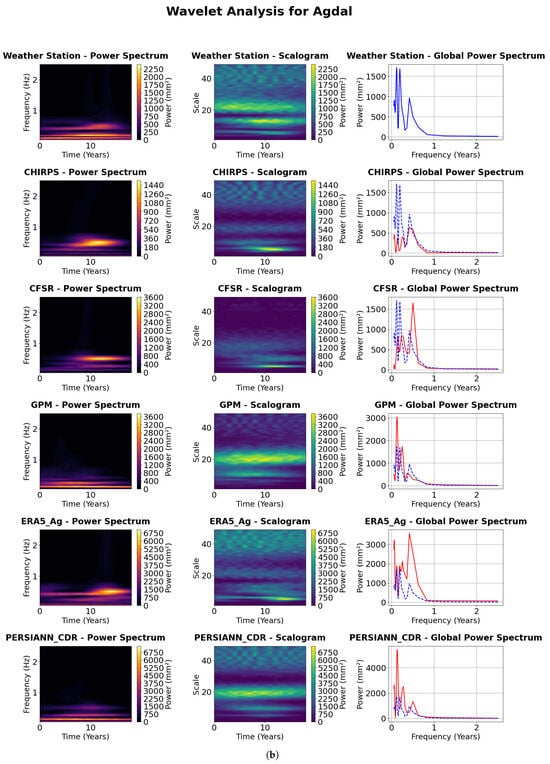
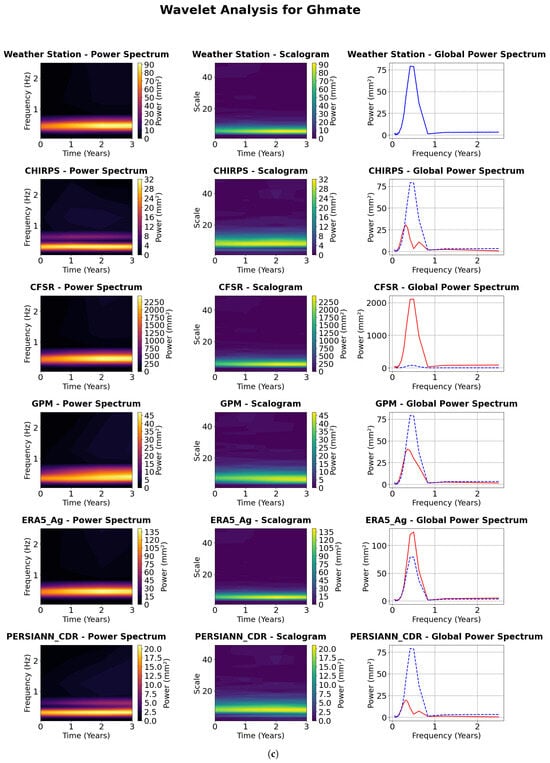
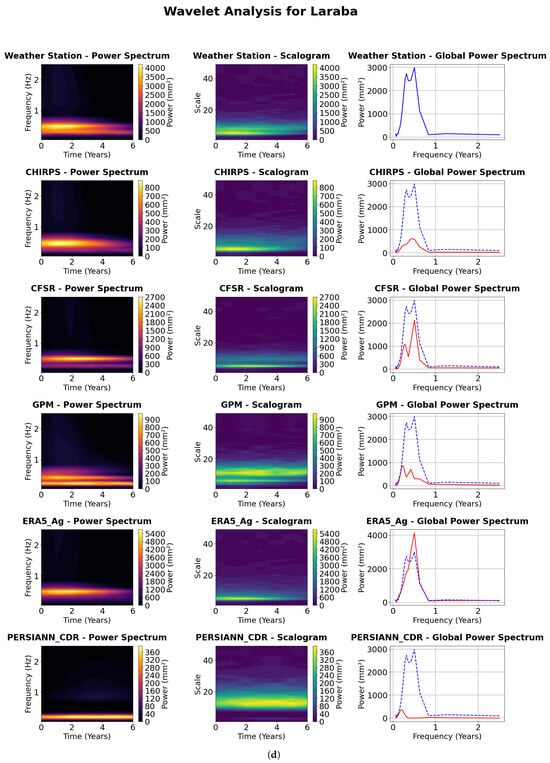
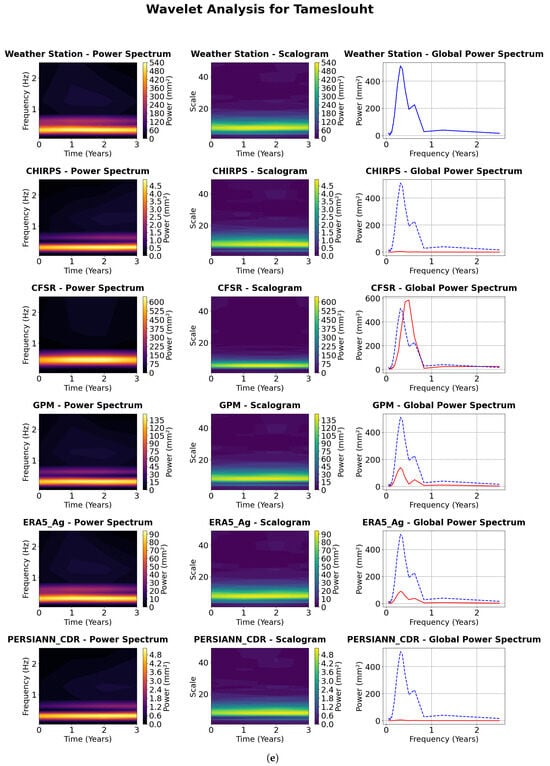
Figure 6.
Wavelet power spectrum and scalograms—annual time scale at five gauged stations. The red line refers to the global power spectrum of products, whereas the dashed blue line refers to the one of gauged stations. (a) Agafay station, (b) Agdal station, (c) Ghmate station, (d) Laraba station, (e) Tameslouht station.
4.4.2. Power Spectrum Analysis
The analysis of Agdal’s weather station data reveals a pronounced and persistent annual cycle over the 20 year period, with a relatively stable semiannual component. Enhanced spectral power at lower frequencies, indicative of longer-term variability, is primarily concentrated in the earlier portion of the time series. CHIRPS, GPM, and PERSIANN_CDR exhibit a well-defined annual cycle across the full period, with GPM additionally displaying a more coherent and pronounced semiannual signal relative to CHIRPS and PERSIANN_CDR. Intermittent and weaker high-frequency components are also detected. CFSR and ERA5_Ag consistently capture both annual and semiannual cycles throughout the record. Notably, ERA5_Ag demonstrates increasing power at lower frequencies during the latter half of the series, suggesting the emergence of longer-term climatic variability. In contrast, CFSR displays a more temporally uniform distribution of low-frequency power. For the Agdal station, weather station data indicate a robust and persistent annual cycle throughout the 20 year period, with a fairly stable semiannual component and intermittent power at lower frequencies. CHIRPS, GPM, and PERSIANN_CDR also highlight a dominant and stable annual cycle. GPM continues to show a clearer and more consistent semi-annual signal, while PERSIANN_CDR reveals some presence of lower frequency power, especially during the mid to later years of the record. CFSR and ERA5_Ag exhibit strong and stable annual and semiannual cycles. ERA5_Ag, in particular, displays more pronounced and variable power in the lower frequency bands, suggesting shifts in multi-year climatic patterns. CFSR also reflects relatively consistent power at longer time scales. At Ghmate, the 3-year weather station dataset reveals a pronounced band of high power centered on the annual cycle. CHIRPS, GPM, and PERSIANN_CDR show consistently strong power at the annual frequency across the same period. ERA5_Ag and CFSR similarly reflect a clear and coherent annual cycle. The semi-annual component is present and relatively stable over this shorter period, with CFSR also indicating some dispersed power at lower frequencies. Data from the Laraba weather station highlight a strong and consistent annual cycle over the 6-year period. The semiannual cycle is also visible and relatively stable, while lower frequency power appears intermittently. CHIRPS, GPM, and PERSIANN_CDR confirm the presence of a dominant and stable annual cycle. GPM and PERSIANN_CDR exhibit a more consistent semiannual band than CHIRPS. CFSR and ERA5_Ag) display robust annual and semiannual cycles, with noticeable power at lower frequencies throughout the 6-year period, indicating detectable multi-year variability even over this relatively short timescale. At Tameslouht, the weather station data reveal a strong and persistent annual cycle across the 3-year period, with a noticeable semiannual component also present. CHIRPS, GPM, and PERSIANN_CDR consistently capture the annual cycle across all products. CFSR and ERA5_Ag exhibit clear annual signals, with the semi-annual cycle also appearing relatively stable and coherent during the 3-year observation window.
4.4.3. Scalogram Analysis
The intensity of the colors represents the strength of the signal, with warm red being interpreted as the period of maximum variation. At the Agafay station, we can see areas of high signal strength (warm colors) that seem to correspond temporally to certain variations. The CHIRPS, GPM, ERA5_Ag and PERSIANN_CDR products captured these temporal variations, while the CFSR product was unable to capture them. At the Agdal station, three zones of varying power were observed, with two zones located at low frequency with high power, followed by a zone of moderate power at high frequency. The GPM and PERSIANN_CDR products captured these variations well, while CHIRPS and ERA5_Ag captured the low-frequency variation with the exact amplitude but were unable to capture the high-frequency zones. On the other hand, the CFSR product shows a weaker visual match with the station, with lower intensity and less pronounced patterns. For the Ghmate station, the CFSR and ERA5_Ag scalograms show zones of high power (warm colors) that correspond in time to the variations observed in the station’s scalogram, especially at low frequencies (large scales). This suggests a good ability to reproduce long-term temporal variations, whereas the CHIRPS, GPM and PERSIANN_CDR scalograms show less visual correspondence with that of the station, with an overall intensity more pronounced than that of the station. For the Laraba station, the CFSR and ERA5_Ag scalograms show zones of high power that correspond to the variations observed at the measuring station. The CHIRPS product also captures these variations, but at low power. The GPM and PERSIANN_CDR products show patterns of intensity different from those at the measurement station. Lastly, the Tameslouht station shows an area of high power at low frequency, corresponding to temporal variations in precipitation. While the CHIRPS, GPM, ERA5_Ag and PERSIANN_CDR products capture these long-term variations well, we also note that the CFSR product shows a weak correspondence with that of the station, marked by lower intensity and less pronounced patterns in Figure 6.
4.4.4. Global Power Spectrum Analysis
The global power spectrum corresponds to the average power spectrum over the entire period, offering a direct comparison of dominant frequencies between the products and the station. At the Agafay station, four peaks between 0.1 and 0.5 Hz confirm the previous observations. The CHIRPS product plot illustrates the peaks with an amplitude totally different from that of the station (minor peaks), while the CFSR product shows a perfect match, capturing the low-frequency peak but expressing a weakness in capturing high-frequency variations. The ERA5_Ag and PERSIANN_CDR products showed a strong match to station variations (tending to capture both high and low frequency variations well). The GPM product expressed a medium match, as it presented only two low-frequency peaks, while it failed to capture high-frequency variations. For the Agdal station, the GPM, ERA5_Ag, and PERSIANN_CDR products perfectly captured temporal variations at both low and high frequencies, with a difference in power between them. The CHIRPS and CFSR products capture all the variations, but with a high power contrast (CHIRPS minimizes power and CFSR maximizes power at high frequencies and minimizes it at low frequencies). As for the Ghmate station, a dominant peak is observed around frequency 0.5 Hz, ERA5_Ag and GPM reproduce the peak well with a slight difference in power, while CHIRPS and PERSIANN_CDR show two low-power peaks distributed between 0.1 and 0.5 Hz, while CFSR increases the peak. For the Laraba station, we observe two confused peaks spread between the frequencies 0.3 and 0.5; the CFSR and ERA5_Ag products reproduce these two peaks well. We also find that GPM and CHIRPS show peaks with a poor match with the station; the PERSIANN_CDR product expresses a poor match with the station (peak very much reduced at 0.1 Hz). Moving at the Tameslouht station, the relative peaks are confused (the first is at 0.3 Hz, the second is at 0.6 HZ). It can be noted that the CFSR product reproduces a peak at the average frequency of the two station’s peaks with the same power, which is validated by previous observations. The GPM and ERA5_Ag products reproduce the same peaks but with different powers (they minorize the peaks); on the other hand, the CHIRPS product was unable to generate any peaks, showing a stable line of power 0.
4.5. Analysis of Classification Metrics
The evaluation of the rainfall products compared with meteorological station data showed significant disparities in terms of the detection of dry and rainy days. An analysis of the confusion matrix, shown in Figure 7, for the different stations and products shows that at the Agafay station, the ERA5_Ag product detects rainy days well, with an overestimation of precipitation. A good balance is shown by the CHIRPS product, with some rainy days missed. For the Agdal station, the GPM product detects rainy days better, with moderate errors, while ERA5_Ag overestimates precipitation. For the Ghmate, Laraba and Tameslouht stations, the ERA5_Ag product offers better results. The PERSIANN_CDR product generates more false precipitation.
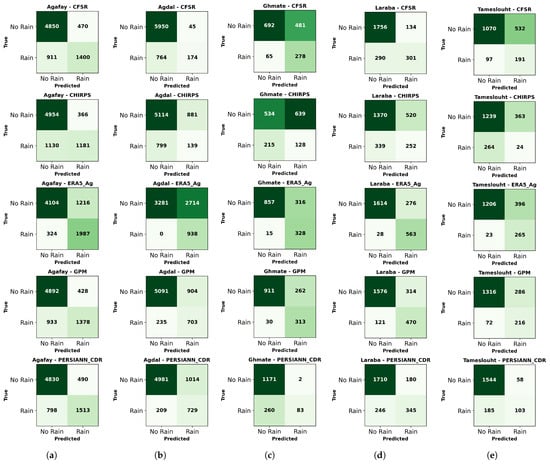
Figure 7.
Confusion matrix for different products and stations; dark green indicates a high value, whereas light green indicates a low value. The overall structure of the confusion matrix is as follows: True Negatives (TN): “No Rain” correctly predicted (top left). False Positives (FP): “Rain” wrongly predicted (top right). False Negatives (FN): “No Rain” wrongly predicted (bottom left). True Positives (TP): “Rain” correctly predicted (bottom right): (a) Agafay station, (b) Agdal station, (c) Ghmate station, (d) Laraba station, (e) Tameslouht.
The classification metrics offer a complementary perspective to the previous analyses and provide a better understanding of the strengths and limitations of each product. The set of metrics deployed is used to assess the products’ ability to detect rainfall events and distinguish between all rainy days. This analysis focuses solely on daily precipitation, as the threshold for declaring a rainy day is set at 1 mm. A transformation of the database is therefore necessary to facilitate the calculations. Figure 8 below shows the histograms of each metric for each station.
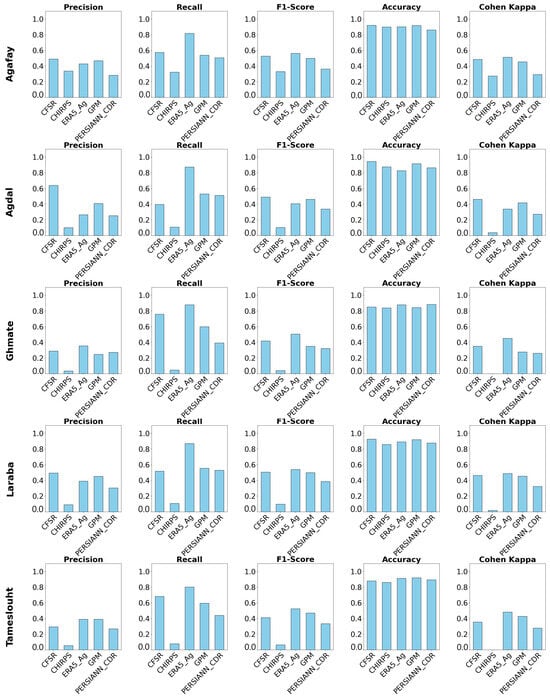
Figure 8.
Performance comparison of precipitation products based on several evaluation metrics.
The analysis of the performance of precipitation products (GPM, CFSR, ERA5_Ag, CHIRPS and PERSIANN_CDR) at five stations (Agafay, Agdal, Ghmate, Laraba and Tameslouht) reveals significant differences. ERA5_Ag stands out as the most reliable, demonstrating impressive recall (up to 0.85) and high F1 scores (up to 0.6), supported by robust Cohen’s Kappa coefficients (up to 0.55). GPM and CFSR follow close behind, with solid performances, notably in terms of accuracy and F1 score, although they do not outperform ERA5_Ag. On the other hand, PERSIANN_CDR and especially CHIRPS show weak results, even negative in some cases. As a complement to assess the performance of these products, particularly in contexts where the classes are unbalanced, such as the detection of rainy days from dry days, which are more frequent, we use the precision–recall curve to show the trade-off between precision and recall for the chosen threshold. Curves that maintain high precision over a wide recall range reflect the product’s ability to detect rainy days, while a sharp drop in precision as recall increases reflects the product’s weakness in generating many false positives as it tries to capture more rainy days. Figure 9 provides a good illustration of the precision–recall curves applied to all products. The analysis of the letters reveals notable differences. Overall, ERA5_Ag consistently demonstrates the most reliable performance, with PR curves approaching the ideal top-right corner in all stations. This indicates that ERA5_Ag effectively detects rainfall events while minimizing false alarms, confirming its robustness across varying climatic and topographic conditions. GPM also shows relatively good performance, achieving high recall values but with slightly reduced precision, suggesting a tendency to overpredict rainfall events. In contrast, CHIRPS and PERSIANN_CDR exhibit weak classification capabilities, characterized by low precision and recall, particularly in challenging stations like Agdal and Ghmate. These products frequently misclassify events, likely due to limitations in spatial or temporal resolution. CFSR displays the least consistent behavior, with significant variation across stations and overall poor discrimination between rain and no-rain events. Despite minor fluctuations from one station to another.
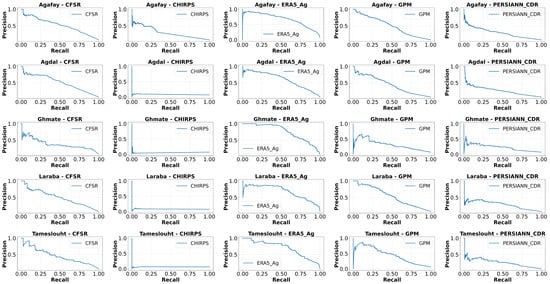
Figure 9.
Precision–recall curve for different satellite and reanalysis products.
In summary, wavelet analysis completes the evaluation of rainfall products in order to select an effective one for deployment in hydrological studies in the study area. This evaluation was carried out on two scales: firstly, analysis of the products’ ability to capture the signal, and secondly, identification of the presence or absence of seasonal and interannual variability. It can be seen that all products show good capture of the dominant seasonal signal (annual frequency), although differences are observed in intensity and variability. The CHIRPS and ERA5_Ag products reproduce interannual variations corresponding to specific climatic events. PERSIANN_CDR and GPM products are also found to frequently underestimate precipitation. The biases noted in CFSR and PERSIANN_CDR and the underestimation of intense events by CHIRPS limit their direct use in hydrological studies. ERA5_Ag and GPM are therefore recommended for their reliability. However, to improve their efficiency, it is recommended that all significant biases must be corrected.
4.6. Application of Bias Correction
We observed that although the products track local rainfall patterns well, their rainfall amounts do not match the measured data. To overcome this problem, we use the quantile mapping technique to correct biases and generate a final corrected dataset. An assessment of the effectiveness of the correction is carried out by calculating the bias and other statistical measures after correction. It is important to note that this correction is applied to two products that appear to be the most effective in the study area: ERA5_Ag and GPM. The temporal evolution of the bias provides valuable information on the performance of a product in reproducing precipitation comparable to that measured by stations. Analysis of raw data often reveals significant variations, reflecting systematic errors attributable to a variety of causes, such as extreme weather events or seasonal variations poorly captured by the model (or satellite). Graphs comparing the evolution of raw and corrected data enable us to assess the quality of the adjustments applied to correct bias. In particular, we can observe a significant reduction in variations at many stations, with a better match between the corrected precipitation peaks and those recorded by the stations. The correction was performed on daily time-step data, followed by a transformation of the corrected data to monthly and annual scales for a more global analysis. Figure 10 shows graphs of the evolution of the bias on a monthly and annual scale respectively. At the daily scale, the graphs appear more condensed due to the large number of days in the database. For this reason, the monthly and annual scales are preferred in the illustrations, offering a clearer, more legible view of variations and peaks in bias.
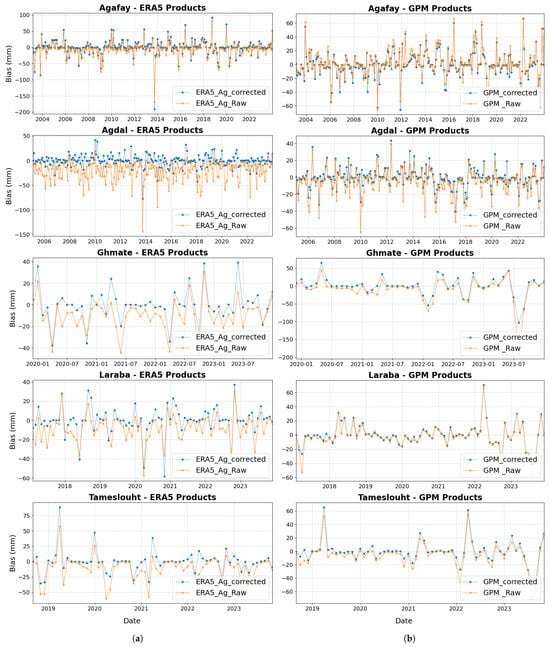
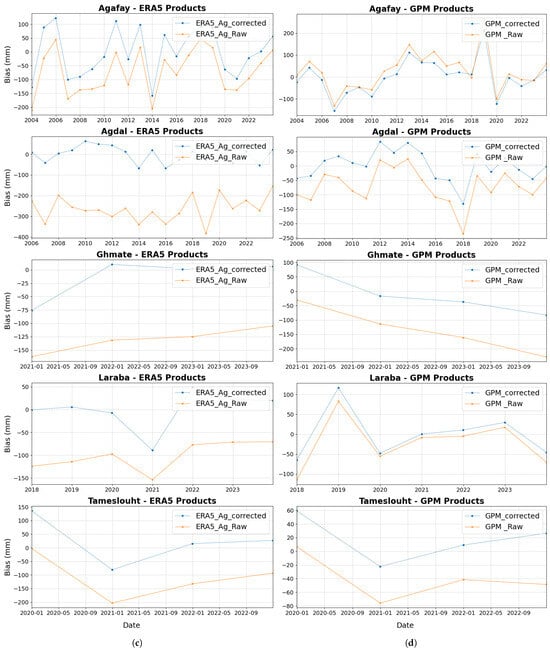
Figure 10.
Graphical illustration of the Bias evolution of raw and corrected data of rainfall products (ERA5_Ag and GPM); blue dashed lines indicate corrected data, and yellow lines indicate raw data. (a) ERA5_Ag monthly scale, (b) GPM monthly scale, (c) ERA5_Ag Annual scale, (d) GPM Annual scale.
The correlation between corrected, raw, and measurement station data is illustrated in Figure 11. There is a marked improvement in correlation at several stations for both products, while maintaining the same general trends, with strong correlations already present in the initial data. The most significant observation is that the GPM product shows a tendency to improve correlation at many stations. Although this improvement remains moderate, it reflects better data quality after correction. In contrast, the ERA5_Ag product shows no significant change in correlations, reflecting the intrinsic quality of the raw data, which already correlate well with observations. However, bias correction remains essential before any direct exploitation of the data.
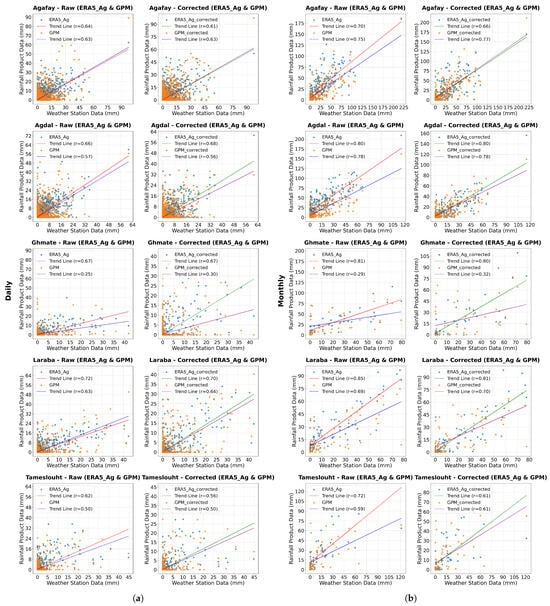
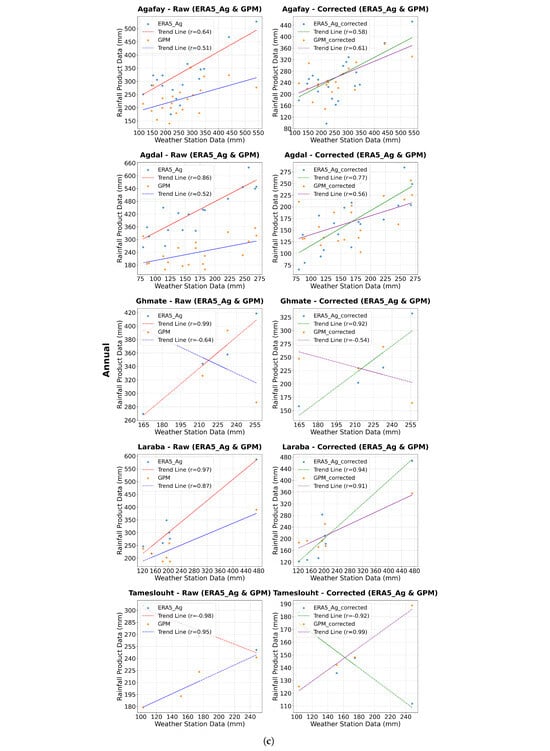
Figure 11.
Correlation graphs of precipitation data from rainfall products (ERA5_Ag and GPM) and weather station data at different time scales (daily, monthly and annual). (a) Daily scale. (b) Monthly scale. (c) Annual scale.
The plots in Figure 12 show the comparison of cumulative distribution functions (CDF) of precipitation for raw (uncorrected) and corrected data, between weather stations and ERA5_Ag, GPM products. Discrepancies between the curves indicate differences in precipitation estimates between the different products. Looking at the raw (uncorrected) data, we can clearly see that the curves of the two products (ERA5_Ag and GPM) are offset from that of the station, which confirms the significant bias of the products. After bias correction, the graphs show curves very close to those of the stations, indicating the improved accuracy of the products after correction.
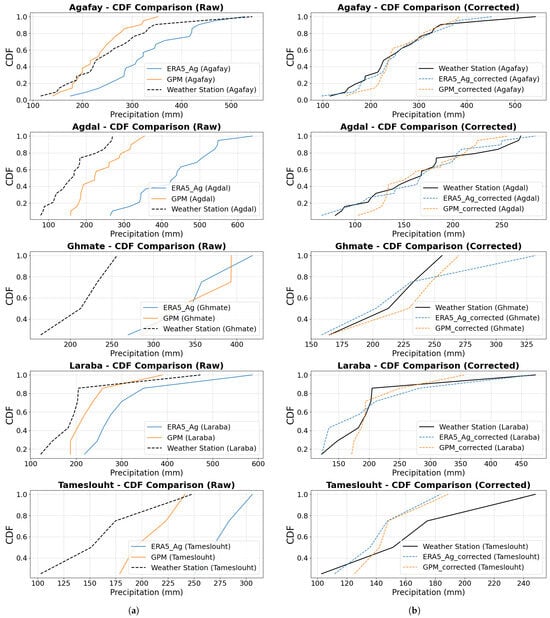
Figure 12.
CDF comparison of weather station data and rainfall products (ERA5_Ag and GPM) before correction and after correction. (a) Raw data. (b) Corrected data.
Precipitation time plots for all measurement stations, as well as for the ERA5_Ag and GPM products, are shown in Figure 13. Both products perform remarkably well after correction, with rainfall event peaks precisely aligned with those observed at the measurement stations, confirming the effectiveness of the correction applied. Furthermore, they better capture the temporal variability of precipitation, making them well qualified for integration into hydrological models, enabling results to be reliably exploited.
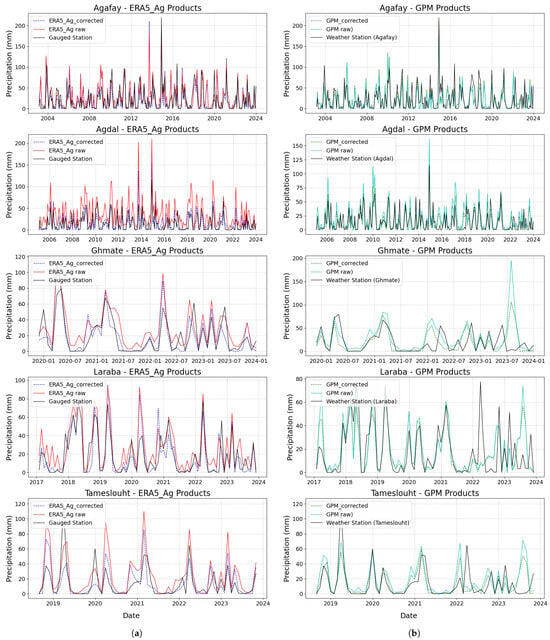
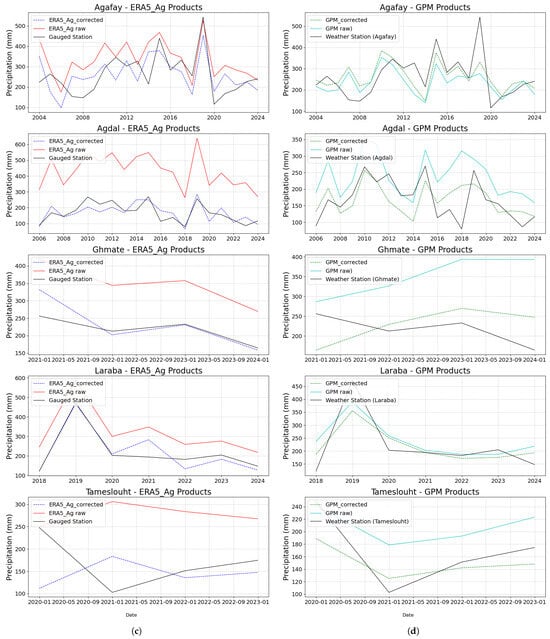
Figure 13.
Temporal evolution of precipitation: Comparison of corrected ERA5_Ag and GPM products with measurement stations, the black line represents the weather station, the dashed lines represent the corrected products (blue for ERA5_Ag and green for GPM), the red line corresponds to the raw ERA5_Ag product, and the light blue line corresponds to the raw GPM product: (a) monthly scale for ERA5_Ag, (b) annual scale for GPM, (c) annual scale for ERA5_Ag, (d) annual scale for GPM.
5. Discussion
In a context of climate change, the use of longer time series of climate variables, of which rainfall is a part, is becoming essential. The challenge resides in the quality of the data provided by the products, which in turn requires a revolution in the development of new satellite data processing algorithms. In the present study, the results of the statistical metrics show considerable variability in the performance of the different products, depending on the time scale. We find that the CHIRPS and ERA5_Ag products seem the most contrasted, with CHIRPS showing a tendency to underestimate precipitation and ERA5_Ag to overestimate it. The PERSIANN_CDR and GPM products show relatively stable performance [58,59,60,61] but are not always the most accurate. The CFSR product, while showing low errors on the daily scale, performs less well on the monthly and annual scales. Similar results have been revealed by other researchers, with refs. [62,63,64] finding that PERSIANN failed to capture precipitation variability, which was expressed by diminished performance when applying a hydrological model, and [6] found that PERSIANN_CDR tended to underestimate precipitation at most stations. He also mentioned that ERA5 tends to overestimate precipitation and CHIRPS to generate good precipitation variability; on the other hand, ref. [65] found that ERA5 provided good hydrological simulation results very close to observations in North America. The same results are found by [6] in a comparison study of reanalyzed precipitation products. On the other hand, ref. [66] mentioned that CHIRPS overestimates precipitation on a monthly scale. Thus, from these investigations, we can already observe that each product expresses its performance in a specific spatio-temporal context. In the local context, studies have been carried out in the study area, with the aim of using and comparing precipitation from satellite products and reanalysis climate models with measurements from weather stations [67,68,69,70]. The evaluation of PERSIANN-CCS-CDR, ERA5 was carried out by [68] with the aim of assessing drought in the Tensift basin, of which the central Haouz is a part, and revealed that both products correlate well with station measurements, as well as finding that PERSIANN-CCS-CDR performs well in calculating drought indices. The study by [70] also showed that PERSIANN-CDR and ERA5 are among the most accurate products for providing precipitation data. On the other hand, the study by [71] evaluating the performance of eight hydrological models applied to 30 basins in Morocco found that ERA5 performed well, followed by CHIRPS and PERSIANN-CDR. Similarly, the GPM-IMERG product is widely deployed by researchers in Morocco and in the surrounding study area [51,57,59,72], and its efficiency is practically confirmed by all these authors. In this study, we evaluated all five products, and after evaluation, we selected two that appear to be the best in the semi-arid context: ERA5_Ag and GPM. Statistical metrics alone are not enough to judge a product’s effectiveness. For this reason, we have applied classification metrics combined with the wavelet method [73,74,75,76]. However, bias correction remains an indispensable criterion prior to direct exploitation of the data [77]. The study by [62] showed that bias correction plays an important role in improving the quality of precipitation data, with bias reduction ranging from −1% to −72%. Another study [78] showed that detection models for seasonal precipitation indices improved after Bias correction, while ref. [79] revealed that the estimation of hourly precipitation was significantly improved by using machine learning methods for Bias correction. In Morocco, refs. [51,80] have shown the importance of bias correction and its influence on hydrological model outputs. However, contrary to some studies, which observed a good estimation of CHIRPS in the study area [55,81], our results suggest that the area of interest plays a role in the choice of product. The last two studies dealt with the Tensift basin as a totality, whereas in the present study, we investigated a small portion of this basin with well-distributed measuring stations. Thus, the difference in results can be justified by the spatial resolution of the products, as well as by the ability of the product itself to capture precipitation variations in a small area. The implications of these results are particularly significant for hydrological studies and those focused on modeling groundwater recharge under changing climatic conditions. Understanding the classification performance of different rainfall products helps improve the accuracy of recharge estimations, which are highly sensitive to precipitation inputs. By capturing the temporal variability of rainfall in the study area, these findings contribute to a better projection of future precipitation patterns. Moreover, integrating this information with machine learning tools offers a powerful approach for estimating the future dynamics of groundwater recharge. Given the similarities in climatic and hydrological conditions across many semi-arid regions, these insights are not only locally relevant but also may be transferable to comparable basins. To test the broader applicability of our findings, we plan to extend and validate this analysis in the Ouarzazate basin, which is a region with climatic characteristics close to those of our current study area. However, the study area should be equipped with additional gauging stations, notably in the western and eastern Haouz, in order to provide better coverage of the plain and bring greater benefits when using modeling techniques. Future studies should explore [1] the estimation of recharge based on water balance, taking into account climate change, in order to better understand the future behavior of the groundwater.
6. Conclusions
The intercomparison of the five rainfall products (CHIRPS, ERA5_Ag, GPM, CFSR, and PERSIANN_CDR) with the precipitation measurement enabled us to select products that appear to be the best in performance. The other products may express their performance in another region; this does not indicate the weakness of the products but rather the choice of a suitable product for the study area. This study revealed the stability of the CFSR and PERSIANN_CDR products, although their accuracy is not always optimal. In contrast, the CHIRPS product showed variability in performance, with contrasting results. These results are consistent with other research, which highlights the differences in performance of these products according to spatio-temporal contexts. The performance evaluation of these products identified ERA5_Ag and GPM as the most suitable for the study area, with recommendations for their use in hydrological studies, in particular to model groundwater recharge under a climate change scenario. In addition, the integration of bias correction techniques involving the use of machine learning must be undertaken in order to improve the quality of precipitation data and optimize its use in hydrological models. However, to ensure more reliable results, the network of measuring stations needs to be extended, particularly in the western and eastern Haouz, to cover a larger part of the Tensift basin. As a result, further studies need to be carried out on water balance formulations, taking climate change into account, in order to better understand the impacts on groundwater recharge in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.C. and N.-E.L.; methodology, A.C.; formal analysis, A.C.; investigation, A.C., N.-E.L. and H.I.; writing—original draft preparation, A.C. and N.-E.L.; writing—review and editing, A.C., N.-E.L., L.Z., H.I. and M.I.; visualization, A.C., N.-E.L. and L.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to the International mixte Laboratory “LMI TREMA” for providing us with meteorological data from stations in the study area. We also thank the staff of the I-Maroc (“Artificial Intelligence/Applied Mathematics, Health/Environment: Simulation for Decision Support”), part of the RD MULTITHÉMATIQUE—APRD2020 program, which is funded by the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research (DESRS) and the OCP Foundation (FOCP), for their technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Barrett, E. The Estimation of Monthly Rainfall from Satellite Data. Mon. Weather Rev. 1970, 98, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, E.; Martin, D. The Use of Satellite Data in Rainfall Monitoring; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Ebert, E.; Manton, M.; Arkin, P.; Allam, R.; Holpin, G.; Gruber, A. Results from the GPCP Algorithm Intercomparison Program (AIP). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 2875–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, E.E.; Manton, M.J. Performance of Satellite Rainfall Estimation Algorithms during TOGA COARE. J. Atmos. Sci. 1998, 55, 1537–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Arkin, P. Global Precipitation: A 17-Year Monthly Analysis Based on Gauge Observations, Satellite Estimates, and Numerical Model Outputs. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 2539–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maphugwi, M.; Blamey, R.; Reason, C. Rainfall Characteristics over the Congo Air Boundary Region in Southern Africa: A Comparison of Station and Gridded Rainfall Products. Atmos. Res. 2024, 311, 107718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, R.; Chambon, P.; Jobard, I.; Kirstetter, P.; Gosset, M.; Bergès, J.C. Comparing Satellite and Surface Rainfall Products over West Africa at Meteorologically Relevant Scales during the AMMA Campaign Using Error Estimates. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 715–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romilly, T.; Gebremichael, M. Evaluation of Satellite Rainfall Estimates over Ethiopian River Basins. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaddor, I.; Achab, M.; Hafidi Alaoui, A. Hydrological Simulation (Rainfall-Runoff) of Kalaya Watershed (Tangier, Morocco) Using Geo-Spatial Tools. JOWSET J. Water Sci. Environ. Technol. 2016, 1, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Qadem, A.; Sébastien, L.; Zohair, Q. Contribution to the hydroclimatic study of a semi-arid mountain basin: The case of the Zloul watershed (pleated Middle Atlas). In Proceedings of the CES’19, Béni Mellal, Morocco, 8–11 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lek, S.; Dimopoulos, I.; Derraz, M.; El Ghachtoul, Y. Rainfall-Runoff Modelling Using Artificial Neural Networks. J. Water Sci. 1996, 9, 319–331. [Google Scholar]
- Soufiane, T. Modeling of Hydrology and Erosion in the Oued Beht Watershed (Northwest Morocco). Master’s Thesis, University Ibn Tofail, Kenitra, Morocco, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Satish Kumar, K.; AnandRaj, P.; Sreelatha, K.; Bisht, D.S.; Sridhar, V. Monthly and Seasonal Drought Characterization Using GRACE-Based Groundwater Drought Index and Its Link to Teleconnections across South Indian River Basins. Climate 2021, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, V.; Anderson, K.A. Human-induced modifications to land surface fluxes and their implications on water management under past and future climate change conditions. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 234–235, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashouri, H.; Hsu, K.L.; Sorooshian, S.; Braithwaite, D.; Knapp, K.; Cecil, D.; Nelson, B.; Prat, O. PERSIANN-CDR: Daily Precipitation Climate Data Record from Multisatellite Observations for Hydrological and Climate Studies. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A.; et al. The Climate Hazards Infrared Precipitation with Stations—A New Environmental Record for Monitoring Extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horanyi, A.; Munoz Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.; Stocker, E.; Bolvin, D.; Nelkin, E.; Tan, J. GPM IMERG Final Precipitation L3 Half Hourly 0.1 Degree x 0.1 Degree, Version V06B. 2019. Available online: https://oneclimate.acdguide.cloud.edu.au/records/ex70x-h1j79 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Pan, H.L.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Kistler, R.; Woollen, J.; Behringer, D.; et al. The NCEP Climate Forecast System Reanalysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 1015–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.T.; Mohammed, S.A.; Hamouda, M.A.; Mohamed, M.M. Impact of Topography and Rainfall Intensity on the Accuracy of IMERG Precipitation Estimates in an Arid Region. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AghaKouchak, A.; Behrangi, A.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.-l.; Amitai, E. Evaluation of Satellite-Retrieved Extreme Precipitation Rates across the Central United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D02115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setti, S.; Maheswaran, R.; Sridhar, V.; Barik, K.K.; Merz, B.; Agarwal, A. Inter-Comparison of Gauge-Based Gridded Data, Reanalysis and Satellite Precipitation Product with an Emphasis on Hydrological Modeling. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharnouki, I.; Aouissi, J.; Benabdallah, S.; Tramblay, Y. Assessing the Variability of Satellite and Reanalysis Rainfall Products Over a Semi-Arid Catchment in Tunisia. Acta Geophys. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.P.; Kumbhar-Patkar, V.; Das, S.; Deshpande, M.; Dhoka, K. Comparison of TRMM Multi-Satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) Estimation with Ground-Based Precipitation Data over Maharashtra, India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 5539–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darand, M.; Amanollahi, J.; Zandkarimi, S. Evaluation of the Performance of TRMM Multi-Satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) Estimation over Iran. Atmos. Res. 2017, 190, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarlan, L.; Khabba, S.; Er Raki, S.; Le Page, M.; Hanich, L.; Fakir, Y.; Merlin, O.; Mangiarotti, S.; Gascoin, S.; Ezzahar, J.; et al. Remote Sensing of Water Resources in Semi-Arid Mediterranean Areas: The Joint International Laboratory TREMA. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 4879–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, E.; Haile, A.; Tian, Y.; Joyce, R. Evaluation of the High-Resolution CMORPH Satellite Rainfall Product Using Dense Rain Gauge Observations and Radar-Based Estimates. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 1784–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, E.; Janowiak, J.; Kidd, C. Comparison of Near-Real-Time Precipitation Estimates from Satellite Observations and Numerical Models. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.C.; Roan, J. Retrievals for the Rainfall Rate over Land Using Special Sensor Microwave Imager Data during Tropical Cyclones: Comparisons of Scattering Index, Regression, and Support Vector Regression. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapiano, M.; Arkin, P. An Intercomparison and Validation of High-Resolution Satellite Precipitation Estimates with 3-Hourly Gauge Data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Ueno, K.; Nakamura, K. Comparison of Satellite Precipitation Products with Rain Gauge Data for the Khumb Region, Nepal Himalayas. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2011, 89, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerakachen, W.; Raksapatcharawong, M.; Seto, S. Performance Evaluation of Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) Products over the Chaophraya River Basin, Thailand. Hydrol. Res. Lett. 2014, 8, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palharini, R.; Vila, D.; Rodrigues, D.; Palharini, R.; Mattos, E.; Pedra, G. Assessment of Extreme Rainfall Estimates from Satellite-Based: Regional Analysis. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 23, 100603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Heap, A. A Review of Comparative Studies of Spatial Interpolation Methods in Environmental Sciences: Performance and Impact Factors. Ecol. Inform. 2011, 6, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, S.; Bao, A.; Hu, J.; Gebregiorgis, A.; Xue, X.; Zhang, X. Inter-Comparison of High-Resolution Satellite Precipitation Products over Central Asia. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 7181–7211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geelani, S.; Abbas, S.; Umar, M.; Usman, M.; Yousfani, I. Validation of Satellite-Based Gridded Rainfall Products with Station Data over Major Cities in Punjab. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Technol. 2024, 6, 305–318. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuzuki, K.; Nakamura, S.; Tebakari, T.; Yoshimi, K. Proposal of a New Rainfall Product Using Modified Weather Radar Data Published by the Thai Meteorological Department and Its Application: A Case Study in Thailand. Hydrol. Res. Lett. 2025, 19, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinkus, G.; Mazzilli, N.; Jourde, H.; Wunsch, A.; Liesch, T.; Ravbar, N.; Chen, Z.; Goldscheider, N. When best is the enemy of good—Critical evaluation of performance criteria in hydrological models. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 27, 2397–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, L.; Sawada, Y. A signal-processing-based interpretation of the Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 27, 1827–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpalatha, R.; Perrin, C.; Le Moine, N.; Andreassian, V. A review of efficiency criteria suitable for evaluating low-flow simulations. J. Hydrol. 2012, 420, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todini, E.; Biondi, D. Calibration, parameter estimation, uncertainty, data assimilation, sensitivity analysis, and validation. In Handbook of Applied Hydrology; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 22-1–22-19. [Google Scholar]
- Wehbe, Y.; Ghebreyesus, D.; Temimi, M.; Milewski, A.; Mandous, A. Assessment of the consistency among global precipitation products over the United Arab Emirates. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 12, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.; Matsuura, K. On the use of dimensioned measures of error to evaluate the performance of spatial interpolators. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2006, 20, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.; Matsuura, K. Advantages of the mean absolute error (MAE) over the root mean square error (RMSE) in assessing average model performance. Clim. Res. 2005, 30, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AghaKouchak, A.; Farahmand, A.; Melton, F.S.; Teixeira, J.; Anderson, M.C.; Wardlow, B.D.; Hain, C.R. Remote Sensing of Drought: Progress, Challenges and Opportunities. Rev. Geophys. 2015, 53, 452–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Vergopolan, N.; Pan, M.; Levizzani, V.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Weedon, G.P.; Brocca, L.; Pappenberger, F.; Huffman, G.J.; Wood, E.F. Global-Scale Evaluation of 22 Precipitation Datasets Using Gauge Observations and Hydrological Modeling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 6201–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, T.; Draxler, R.R. Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) or Mean Absolute Error (MAE)?—Arguments Against Avoiding RMSE in the Literature. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-Global, Multiyear, Combined-Sensor Precipitation Estimates at Fine Scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Duc, P.; Nguyen, H.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Phan Van, T.; Pham Thanh, H. Application of Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Network for Seasonal Prediction of Monthly Rainfall across Vietnam. Earth Sci. Inform. 2024, 17, 3925–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiker, W.; Tan, G.; Alriah, M.; Elameen, A. Evaluation and Correction Analysis of the Regional Rainfall Simulation by CMIP6 over Sudan. Geogr. Pannonica 2024, 28, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkirane, M.; Amazirh, A.; Laftouhi, N.E.; Khabba, S.; Chehbouni, A. Assessment of GPM Satellite Precipitation Performance after Bias Correction, for Hydrological Modeling in a Semi-Arid Watershed (High Atlas Mountain, Morocco). Atmosphere 2023, 14, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.F.; Wang, G.; Silander, J.; Wilson, A.M.; Allen, J.M.; Horton, R.; Anyah, R. Statistical Downscaling and Bias Correction of Climate Model Outputs for Climate Change Impact Assessment in the U.S. Northeast. Glob. Planet. Change 2013, 100, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panofsky, H.; Brier, G. Some Applications of Statistics to Meteorology; Pennsylvania State University Press: University Park, PA, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Themebl, M.; Gobiet, A.; Leuprecht, A. Empirical-Statistical Downscaling and Error Correction of Daily Precipitation from Regional Climate Models. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 1530–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elair, C.; Rkha Chaham, K.; Hadri, A. Assessment of Drought Variability in the Marrakech-Safi Region (Morocco) at Different Time Scales Using GIS and Remote Sensing. Water Supply 2023, 23, 4592–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaida, J.; Witam, O.; Ibnoussina, M.; Delmaki, A.; Benkirane, M. Contribution of Remote Sensing and GIS to Analysis of the Risk of Flooding in the Zat Basin (High Atlas-Morocco). Nat. Hazards 2021, 108, 1835–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouaba, M.; El Khalki, E.; Saidi, M.; Alam, J. Estimation of Flood Discharge in Ungauged Basin Using GPM-IMERG Satellite-Based Precipitation Dataset in a Moroccan Arid Zone. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 6, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eini, M.; Rahmati, A.; Piniewski, M. Hydrological Application and Accuracy Evaluation of PERSIANN Satellite-Based Precipitation Estimates over a Humid Continental Climate Catchment. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 41, 101109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachdane, M.; El Khalki, E.; Saidi, M.; Tramblay, Y. Evaluation of GPM IMERG Products and ERA5 Reanalysis for Flood Modeling in a Semi-Arid Watershed. In Proceedings of the IAHS-AISH Scientific Assembly 2022, Montpellier, France, 29 May–3 June 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tian, J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Duan, Z. Hydrologic Evaluation of TRMM and GPM IMERG Satellite-Based Precipitation in a Humid Basin of China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Xuan, W.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.-P. Evaluation and Hydrological Application of Precipitation Estimates Derived from PERSIANN-CDR, TRMM 3B42V7, and NCEP-CFSR over Humid Regions in China. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 3061–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abera, W.; Brocca, L.; Rigon, R. Comparative Evaluation of Different Satellite Rainfall Estimation Products and Bias Correction in the Upper Blue Nile (UBN) Basin. Atmos. Res. 2016, 178–179, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremicael, T.; Deitch, M.; Gancel, H.; Croteau, A.; Haile, G.; Beyene, A.; Kumar, L. Satellite-Based Rainfall Estimates Evaluation Using a Parsimonious Hydrological Model in the Complex Climate and Topography of the Nile River Catchments. Atmos. Res. 2022, 266, 105939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.; Li, L.; Jun, K. Evaluation of Multi-Satellite Precipitation Products for Streamflow Simulations: A Case Study for the Han River Basin in the Korean Peninsula, East Asia. Water 2018, 10, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarek, M.; Brissette, F.; Arsenault, R. Evaluation of the ERA5 Reanalysis as a Potential Reference Dataset for Hydrological Modelling over North America. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 2527–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo, F.; Barbosa, H.; Penaloza Murillo, M.; Moreno, M.; Farias, A. Intercomparison of Improved Satellite Rainfall Estimation with CHIRPS Gridded Product and Rain Gauge Data over Venezuela. Atmosfera 2016, 29, 323–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khalki, E.; Tramblay, Y.; Saidi, M.; Ahmed, M.; Chehbouni, A. Hydrological Assessment of Different Satellite Precipitation Products in Semi-Arid Basins in Morocco. Front. Water 2023, 5, 1243251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najmi, A.; Igmoullan, B.; Namous, M.; El Bouazzaoui, I.; Ait Brahim, Y.; El Khalki, E.; Saidi, M. Evaluation of PERSIANN-CCS-CDR, ERA5, and SM2RAIN-ASCAT Rainfall Products for Rainfall and Drought Assessment in a Semi-Arid Watershed, Morocco. J. Water Clim. Change 2023, 14, 1569–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Alaoui El Fels, A.; Saidi, M.E.; Alam, M.J.B. Rainfall Frequency Analysis Using Assessed and Corrected Satellite Precipitation Products in Moroccan Arid Areas. The Case of Tensift Watershed. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 6, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, W.; Epule, T.; Chehbouni, A.; El Khalki, E. Assessment of Satellite Precipitation Products during Extreme Events in a Semiarid Region. In Proceedings of the EMS Annual Meeting 2023, Bratislava, Slovakia, 4–8 September 2023; p. EMS2023-122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffar, O.; Hadri, A.; El Khalki, E.; Ait Naceur, K.; Saidi, M.; Tramblay, Y.; Chehbouni, A. Assessment of Hydrological Model Performance in Morocco in Relation to Model Structure and Catchment Characteristics. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 54, 101899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saouabe, T.; Ait Naceur, K.; El Khalki, E.; Hadri, A.; Saidi, M. GPM-IMERG Product: A New Way to Assess the Climate Change Impact on Water Resources in a Moroccan Semi-Arid Basin. J. Water Clim. Change 2022, 13, 2559–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilly, J.M. Element Analysis: A Wavelet-Based Method for Analysing Time-Localized Events in Noisy Time Series. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2017, 473, 20160776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobach, H.; Tropea, C.; Cordier, L.; Bonnet, J.; Delville, J.; Lewalle, J.; Farge, M.; Schneider, K.; Adrian, R. Review of Some Fundamentals of Data Processing. In Springer Handbook of Experimental Fluid Mechanics; Tropea, C., Yarin, A., Foss, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2007; pp. 1337–1398. [Google Scholar]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A Practical Guide to Wavelet Analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamrane, Z.; Turki, I.; Laignel, B.; Mahe, G.; Laftouhi, N.E. Characterization of the Interannual Variability of Precipitation and Streamflow in Tensift and Ksob Basins (Morocco) and Links with the NAO. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, V.; Jaksa, W.T.A.; Fang, B.; Lakshmi, V.; Hubbard, K.G.; Jin, X. Evaluating Bias-Corrected AMSR-E Soil Moisture using in situ Observations and Model Estimates. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12, vzj2013.05.0093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiah, W.; Johnson, R.; Muthoni, F.; Mengistu, G.; Amekudzi, L.; Kwabena, O.; Kizito, F. Bias Correction and Spatial Disaggregation of Satellite-Based Data for the Detection of Rainfall Seasonality Indices. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, D.; Kumar, D.; Amarjyothi, K.; Saha, U. Bias Correction of Satellite Precipitation Estimates Using Mumbai-MESONET Observations: A Random Forest Approach. Atmos. Res. 2025, 315, 107858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bouazzaoui, I.; Ait Brahim, Y.; Amazirh, A.; Bougadir, B. Projections of Future Droughts in Morocco: Key Insights from Bias-Corrected Med-CORDEX Simulations in the Haouz Region. Earth Syst. Environ. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habitou, N.; Morabbi, A.; Ouazar, D.; Bouziane, A.; Hasnaoui, M.D.; Sabri, H. CHIRPS Precipitation Open Data for Drought Monitoring: Application to the Tensift Basin, Morocco. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 034526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).