Abstract
The Eastern Kunlun Fault (EKF) is situated in an area with a history of significant seismic events, yet it has witnessed a dearth of major earthquakes in recent years. This study conducted a detailed analysis of the hydrogeochemical characteristics of the springs in the EKF and their temporal variation, aiming to address the gaps in the research on the hydrogeochemistry in the region and to investigate the changes in water chemistry during the seismogenic process. In this study, the main elements, trace elements, hydrogen isotopes, oxygen isotopes, and strontium isotopes of 23 springs in the EKF were analyzed. The results indicated that the groundwater recharge in the eastern part of the Eastern Kunlun Fault Zone mainly originates from atmospheric precipitation, as supported by its isotopic characteristics. The spring water is immature, showing weak water–rock interactions. A hydrochemical analysis classified the springs into 11 main types, reflecting varying degrees of water–rock interaction. Based on measurements using quartz geothermometers, the estimated geothermal reservoir temperatures ranged from 39.6 to 120.3 °C, with circulation depths of 1.3 to 3.8 km. By means of regularly monitoring three selected springs, this study also explored the relationship between earthquakes and hot spring chemical variations. Finally, a conceptual model of hydrogeochemistry was proposed to describe the groundwater circulation in the study area.
1. Introduction
Springs are a window to deep crustal changes [1]. A seismically active fault provides upwelling conduits for fluids in active tectonic settings [1,2,3]. The distribution and properties of the fault systems significantly control the depth and geochemical composition of the circulating fluid [4,5,6]. Furthermore, stress accumulation, changes in stress state, and variations in thermal dynamic conditions can alter the balance of water–rock systems [7]. In recent years, the research has increasingly focused on investigating the connection between hydrogeochemistry and seismic activity [8,9,10,11]. For example, before and after the 2019 Benevento earthquake in Italy, anomalies in water chemistry were observed, including increased dissolved CO2 levels, a decreased pH, and abnormal concentrations of major ions (Ca2+, Na+, HCO3−, etc.), which returned to their typical concentrations after the seismic activity [12]. Similarly, before the 1995 Galicia earthquake in Spain, the concentration of Cl− in the water doubled [13]. Moreover, some trace elements such as Pb, B, etc., may also show changes prior to earthquakes [14].
The Eastern Kunlun Fault (EKF), situated in the northern part of the Tibetan Plateau, has been highly active in the late Quaternary and has experienced six earthquakes of magnitudes ranging from 7 to 8 in its history [14]. During a period of regular monitoring, three earthquakes occurred near the EKF: the Maerkang MS 6.0 earthquake, the Gande MS 4.7 earthquake, and the Maduo MS 5.0 earthquake. Notably, the Maqin and Maqu sections within the EKF are considered seismic gap regions with a high population density, posing potential threats to the safety of life and property in this area [15,16,17,18]. However, the previous research on the Eastern Kunlun Fault Zone (EKF) has predominantly focused on its geological and tectonic aspects, rock formation, ore deposit geology, and geochemical characteristics. In the field of hydrogeochemistry, research on the characteristics of the chemical components of the water and their long-term evolution mechanisms in the eastern part of the EKF region is limited.
Examining the hydrological and geochemical changes that take place alongside seismic events can enhance our understanding of the relationship between fluid geochemistry and seismic activity. This knowledge can aid in monitoring the water chemistry composition in highly seismically active areas and in identifying earthquake activity [19,20]. The objective of this study was to explore the Eastern Kunlun Fault Zone’s hydrogeochemical characteristics to fill the significant gap in the hydrogeochemical background data, with a focus on analyzing the hydrogeochemical composition of springs of varying temperatures within the fault zone and their changes before and after earthquakes to reveal the intrinsic connection between seismic activity and changes in groundwater chemistry.
2. Geological Setting
The EKF, stretching approximately 500 km, acts as the boundary between the Bayankhara crustal blocks and the Kunlun Qaidam Basin in the northern region of the Tibetan Plateau (see Figure 1). The study area exhibits various structural features, including the Jungong fault, the intersection zone of the Xigongzhou Fault, the uplift of the A’nyêmaqên Mountains, and the Maqu area’s intersection with the Minjiang Fault. Additionally, the Huya Fault forms a horsetail-shaped contraction structure. Within the research area, geomorphic features like the Xigongzhou and Mohatang basins, the Min Mountain uplift, and single-faulted basins (the Maqin and Maqu basins) have led to stress accumulation in the EKF’s mid-eastern section [21]. The fault itself has a dip angle ranging from 60° to 80° and strikes predominantly at 280°–310°, with a southwestward dip. The EKF’s eastern section is a large strike-slip fault consisting of three main segments, namely Maqu, Maqin, and Tuosuohu, from east to west. The Tuosuohu segment is situated to the west of the A’nyêmaqên Mountains and exhibits a sinistral slip rate of 4.0–10.9 mm/a (millimeters per year) [21,22,23]. Its strike direction is between 280° and 290°. The Maqin segment extends over an approximate distance of 110 km, exhibiting a northwest–southeast orientation. It begins in the Yangkao gully, passes through Dongqinggou, Rirang, Dawutan, and Dawumuchang, and ends in eastern Kendingna. Since the late Pleistocene, its slip rate has been estimated at 6.0–12.5 mm/a [21,22,23,24]. The Maqu segment extends for 110 km with a dip angle ranging from 60° to 75°, striking at 280°–305°. It originates from Mohatang, traverses through Awancang Fault, Halawen, Tangdi, and Keshengtuoluo, and terminates in the south of Maqu County. Its sliding rate gradually increases from east to west [15].
The mid-eastern part of the EKF has experienced several significant earthquakes according to historical records. Over the past century, the Tuosuohu segment has been struck by three major earthquakes, with the most recent being the Tuosuohu MS 7.5 earthquake in 1937. The recurrence period for earthquakes in this segment is estimated to have been 630 ± 130 years over the last 2000 years [21,25]. In the Maqin sector, there have been seven major earthquakes in the past 10,000 years, with the most recent occurring in 534 BC. The recurrence interval for earthquakes in Maqin has been approximately 600 ± 100 years in the past 2000 years [21,26,27]. Compared to the Maqin and Tuosuohu sections, the seismic activity in the Maqu region is notably diminished, with the most recent earthquake having occurred approximately 1055 years ago. The recurrence interval for earthquakes in Maqu is estimated to be 1000 years [28]. The temporal and spatial sequences of earthquakes in the three sections (Maqin, Maqu, and Tuosuohu) suggest an interaction between them. Co-seismic dislocations in the southeast section generate stress–strain loading on the adjacent sections, leading to the triggering or acceleration of other earthquakes. The time since the most recent earthquakes in the Maqin and Maqu sections is approaching or has exceeded the recurrence time for each segment. Furthermore, the stress on the Maqin and Maqu sections was amplified by the 2008 Wenchuan MS 8.0 earthquake. Consequently, the middle of the EKF presents a higher earthquake risk [15].
The research area falls within a transition zone that exhibits characteristics of both arid and semi-arid climates, accompanied by cold alpine conditions [29]. The yearly mean temperature hovers around −3.7 °C to −7.7 °C [30], and the annual precipitation amounts to ~250 mm, concentrated mainly in the summer. The region experiences high evaporation rates and a dry climate. Its surface water sources include atmospheric precipitation, glacial meltwater, and lakes [30,31]. Its topography slopes downward from the higher northeast to the lower southwest. Previous studies have indicated that the lithology near the fault zone primarily consists of Carboniferous Limestone and Indo-Chinese epoch porphyritic biotite granite, along with Permian, Triassic, and Cretaceous feldspar–quartz sandstone [32]. The extensive exposure of intrusive rocks such as granite is related to magmatic activity dating back to the Permian and Triassic periods.
The magmatic history of the central–Eastern Kunlun Fault Zone spans the period from the Paleozoic to the Cenozoic. In the Paleozoic to Early Mesozoic, magmatism was possibly linked to island arc formation and oceanic spreading, intensifying with the closure of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean. The Mesozoic was marked by significant intrusions, especially of granites and metallic minerals during the Triassic to Jurassic periods, driven by the India–Eurasia interaction. The Late Mesozoic to Cenozoic saw a continued uplift of the Tibetan Plateau, with magmatic activities related to crustal stretching and mantle upwelling. The uplift of granite to the surface has, to some extent, increased the geothermal gradient in the study area [33,34]. Recent magmatic activities and geothermal phenomena in the Quaternary, especially the Holocene, suggest ongoing sub-crustal processes [35,36].
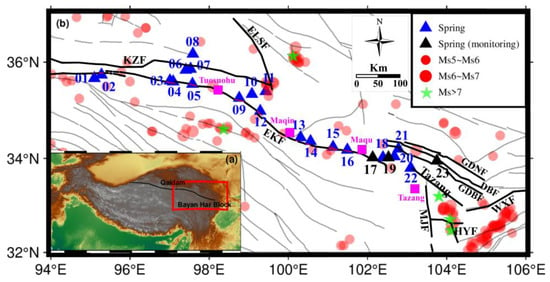
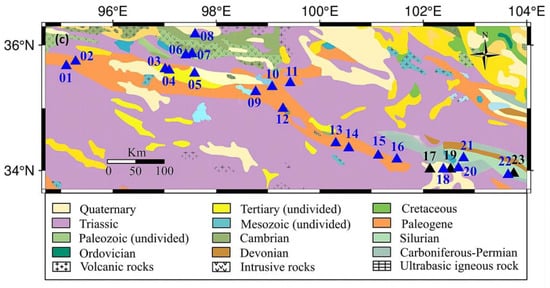
Figure 1.
(a) Macro-regional map [37]. (b) Active structure map with locations of sampling sites in the mid-eastern part of the Kunlun Mountain Fault. KZF: Kunzhong Fault; EKF: Eastern Kunlun Fault; ELSF: Eelashan Fault; JGF: Jungong Fault; HYF: Huya Fault; MJF: Minjiang Fault; WXF: Weixi Fault; GDNF: Guanggaishan–Dieshannanmi Fault; GDBF: Guanggaishan–Dieshanbeimi Fault; circle: earthquake; black square frame: sampling area; triangles: sampling sites [38]; pink square: names of the sections of the EKF. (c) Geological map with sampling sites of the study area (black line): the sites indicated with blue triangles were sampled once, while the black triangles represent the long-term monitored springs with a sampling frequency of 3 days.
In the Eastern Kunlun Fault Zone, intense tectonic movements have led to the development of fractures and enhanced fissure connectivity. The primary and secondary fault systems in the eastern part of the EKF significantly influence the groundwater dynamics. Additionally, the tectonic activity and the thermal properties of intrusive rocks may contribute to the formation of hydrothermal systems, where geothermal fluids are heated in deeper geological settings and then ascend to shallower strata or the surface through fracture systems.
3. Sampling and Methods
A total of 23 springs along the EKF were sampled for groundwater analysis from May to July 2021 (see Figure 1). Two methods, a census and detailed surveys, were employed for the sample analysis. In the detailed survey stage, three springs were selected for regular monitoring, with water samples collected every three days for geochemical analysis. A total of 609 water samples were collected, with 587 obtained from the three regularly monitored springs.
During sampling, the sampler wore rubber gloves and rinsed a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottle (50 mL) three times with spring water. The bottle was fully immersed in the spring water and tightly sealed to prevent air entry during collection. We also recorded the weather conditions, sampling time, odor, location, and exposed lithology. Finally, the samples were promptly transported to the laboratory, preserved in 50 mL PET containers, and stored at 4 °C.
In this study, various parameters were analyzed, including conductivity, pH, dissolved oxygen, cationic concentration (Na+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, etc.), anion concentration (NO3–, SO42–, Br–, CO32–, HCO3–, etc.), isotopes (hydrogen, oxygen, and strontium), and other indicators. The pH and electrical conductivity were measured on site using a multiparameter probe, while the water temperature was recorded using a digital thermometer with an accuracy of 0.1 °C during the sampling process. The HCO3− and CO32− contents were determined using chemical titration using a ZDJ–100 potentiometric titrator with a solution of 1% phenolphthalein, 0.1% methyl orange, and 0.05 mol/L HCl (place 5 mL of water sample in a beaker and add two drops of phenolphthalein. If the solution does not change color, add another two drops of methyl orange. Then, using a 1 mL dropper, add hydrochloric acid until the solution becomes colorless. The amount of hydrochloric acid used represents the concentration of carbon dioxide. If the solution changes color after adding two drops of phenolphthalein, add hydrochloric acid using a 1 mL dropper until the solution becomes colorless. Then, add two drops of methyl orange and record the concentration of carbonate dioxide). For cation (Ca2+, K+, Mg2+, and Na+) and anion (Cl−, NO3−, CO32−, HCO3−, Br−, and SO42−) determination, the water samples were diluted tenfold and transferred into 2 mL PET bottles. The concentrations were measured using a Dionex ICS-900 ion chromatograph and an AS 40 automatic sampler at the Key Laboratory of Earthquake Prediction of the China Earthquake Administration. The reproducibility of the measurements was within ±2%, and the detection limit was 0.01 mg/L [20]. The reliability of the data was evaluated using ion balance (ib) equations.
Trace elements (Ag, Al, Ba, Be, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Li, Mn, B, Mo, Ni, Pb, Sb, Sn, Sr, Th, Ti, Tl, U, V, Zn) were analyzed at the Test Center of the Research Institute of Uranium Geology using an Element XR ICP-MS (Thermo Fisher, Bremen, Germany). Quality control was performed using multi-element standard solutions (IV-ICPMS 71A, IV-ICP-MS 71B, and IV-ICP-MS 71D, Inorganic Ventures), with the analytical errors for the trace elements being less than 10%. The SiO2 concentration was obtained by multiplying the measured silicon concentration using the 5300 DV Inductively Coupled Plasma Emission Spectrometer by a factor of 2.13. The hydrogen and oxygen isotopes were analyzed at the Earthquake Forecasting Key Lab of the China Earthquake Administration using a Finnigan MAT 253 mass spectrometer and the TC/EA method. V-SMOW was used as the standard, and the analytical accuracy was within −1‰ to 1‰ for δD and −0.2‰ to 0.2‰ for δ18O. Additionally, the Sr isotope analysis was conducted using a Phoenix Thermal Ionization Mass Spectrometer, with an error of 2σ.
4. Results
Table 1 presents the concentrations of the major elements, while Table 2 provides the concentrations of the trace elements. The ion balance equations indicated that the measurement error for the ions was less than 5%, confirming the usefulness of the data [39,40].

Table 1.
The composition of spring water ions, hydrochemistry type, and 87Sr/86Sr ratios. (Water temperature was measured using a digital thermometer with a precision of 0.1 °C during sample collection).

Table 2.
Trace elements in spring water samples.
Based on Table 1, the temperatures of the springs ranged from 2.2 °C to 60.4 °C, with the majority being cool springs. Among these, 18 were cold springs, with their temperatures ranging from 2.2 °C to 22.2 °C (an average of 9.3 °C), significantly higher than the local average temperature of −3.7 °C. Additionally, there were two low-temperature springs (25.9–28 °C, average of 26.95 °C) and three medium-temperature springs (44.2–60.4 °C, average of 51.2° C). The highest recorded temperature was 60.4 °C at spring EKF 11. It is speculated that the variation in temperature is primarily attributed to differences in the circulation depth and the mixing of the springs with other water bodies to some extent during their ascent [41].
Table 1 also displays the significant variation in the electric conductivity and TDS (total dissolved solids). The electric conductivity ranged from 349.8 to 4577 µS/cm. The lowest conductivity was recorded at EKF 14, while the highest conductivity was observed at EKF 9, which was 13 times higher than the lowest value. The TDS values ranged from 332.12 to 3753.51 mg/L. Interestingly, the eastern springs in the study area exhibited lower TDS and electric conductivity values. Their pH values ranged from 7.34 to 8.60, with an average value of 8, indicating the alkaline nature of these springs.
Regarding the analysis of the chemical element concentrations, a Piper plot was created, as shown in subsequent sections. From Table 1, it is evident that the main cations were Ca2+, Na+, and Mg2+, and the main anion was HCO3−. However, notable levels of SO42− and CO32− were also observed in some springs. In addition to the major elements, Table 2 summarizes the results of the trace element analysis. It is evident from Table 2 that elements such as B, Sr, and Li exhibited significantly higher concentrations compared to other trace elements. Furthermore, the water samples contained various minor elements, as observed in the analysis.
The isotopes’ characteristics are illustrated in Table 1. The stable hydrogen isotopic ratios (δD) of the water samples ranged from −107.3‰ to −67.2‰, while the stable oxygen isotopic ratios (δ18O) ranged from −14.4‰ to −6.9‰. Additionally, the 87Sr/86Sr ratio ranged from 0.707827 to 0.713388.
5. Discussion
5.1. Major Elements
A Piper diagram was constructed (Figure 2) to determine the water chemistry types for each sampling point, and these are recorded in Table 1. This analysis revealed 11 distinct water chemistry types in the study area: Na-Mg-HCO3-Cl, Mg-SO4-HCO3, Na-Cl, Na-HCO3, Ca-Na-HCO3, Na-Ca-Cl-HCO3, Na-Cl-SO4, Na-SO4, Na-Mg-Cl, Ca-Mg-HCO3, and Ca-HCO3. In the Tuosuohu area, the predominant ions were Na+, Ca2+, Cl−, and HCO3−, and in the Maqin, Maqu, and Tazang sections, the dominant ions were Mg2+, Ca2+, and HCO3−. Ca-HCO3-type water, characteristic of leached water in sedimentary rock areas, was primarily concentrated in the Maqin, Maqu, and Tazang sections. This can be attributed to the abundance of limestone in these areas. Limestone is composed of carbonate rocks, including calcite and dolomite, which are rich in CaCO3 and MgCO3. As groundwater flows through limestone, it dissolves the Ca2+, Mg2+, and HCO3− present in the rocks.
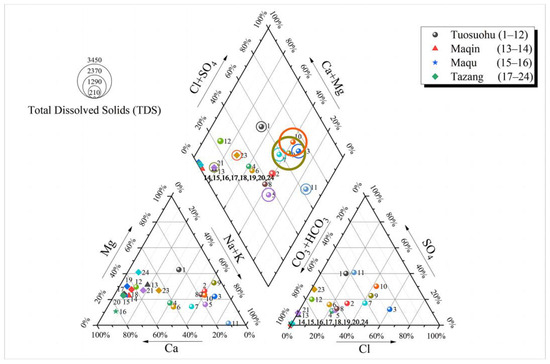
Figure 2.
Piper diagram.
The Ca/Mg values in the research region ranged from 0.25 to 12.67, with an average of 3.71. A Ca/Mg value greater than 1 indicates the high solubility of groundwater in limestone. The Na/K values in the Tuosuohu segment ranged from 8.85 to 52.86, with an average of 29.66, while the Na/Ca values in the same segment ranged from 0.65 to 8.81, with an average of 2.99. In the Maqin, Maqu, and Tazang segments, the Na/K values ranged from 2.87 to 14.84, with an average of 6.707, and the Na/Ca ratios varied between 0.05 and 0.42, with an average of 0.13. The relatively low values of Na/K and Na/Ca, with higher values in the northwestern mountainous area compared to the southeastern section, may suggest that the spring water originates from a descent spring fed by an aquifer in front of a mountain in the Maqin, Maqu, and Tazang regions [42]. The diversity in the level of total ionic salinity (TIS) was noticeable in the spring samples, as evident from the correlation plot of SO42− + HCO3− vs. Cl− (see Figure 3). The majority of the spring waters analyzed had TIS values below 30 meq/kg. The comprehensive analysis of the major elements indicated that the springs possess complex water compositions (see Table 1).
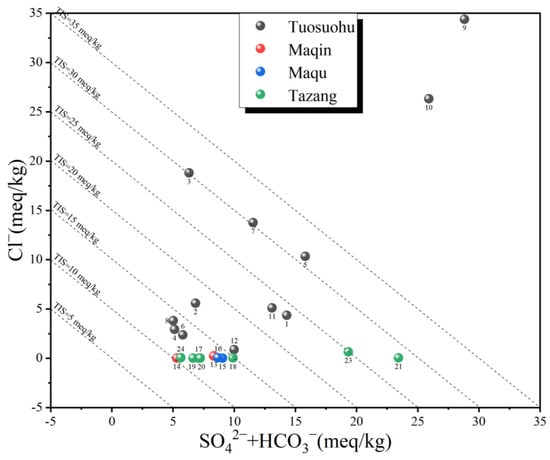
Figure 3.
This correlation plot illustrates the relationship between SO42− + HCO3− and Cl− in the springs of the EKF while also displaying isolines of total ionic salinity (TIS) for reference.
To assess the balance of water–rock reactions, a Na–K–Mg triangle diagram was employed (see Figure 4) [43]. In this study, all the samples were located along the Mg1/2 endmember, indicating an insufficient reaction between the groundwater and the surrounding rock. This observation supports the hypothesis that the fracture connectivity is strong and the water circulation speed is fast, leading to insufficient water–rock reactions and the mixing of the thermal groundwater with cold water during its ascent. Hot spring No. 11 is closer to partially balanced water, which can be attributed to its location near the fault intersection zone (ELSF and KZF), where the fault is deeper, resulting in a longer water–rock reaction time and a higher dissolution of rock components into the water.
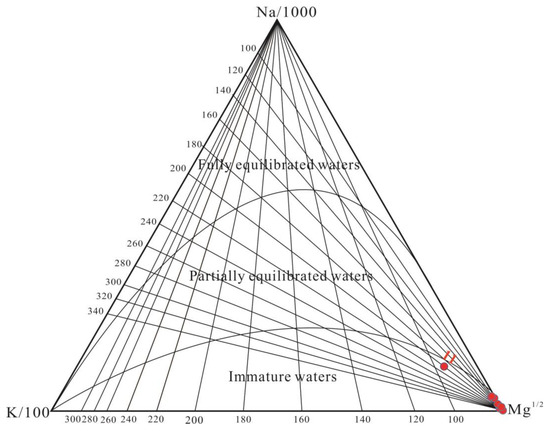
Figure 4.
Na–K–Mg triangle diagram.
The mineral saturation index (SI) of the thermal springs provides insights into the thermodynamic behavior of minerals and the equilibrium process between the water and rock. This index helps to predict the mineral types deposited during water circulation. Typically, an SI value ranging from 0 to 0.2 indicates that a mineral is in an equilibrium state. A positive SI value indicates supersaturation, while a negative SI value suggests the continued dissolution of the mineral. In this study, the mineral saturation index (SI) was determined using PHREEQC software 2.12.5 (see Figure 5). It is evident that all of the spring water samples exhibited supersaturation (SI > 0) with respect to hematite and goethite. This indicates that these minerals are abundant in the water and continuously precipitate as hot water rises. On the other hand, gibbsite and fluorite exhibited equilibrium conditions (SI ≈ 0). Most of the other minerals were in an unsaturated state (SI < 0). This can be attributed to the low mineral content, the short reaction time between the water and rock, and the inherent characteristics of the minerals themselves. The saturation index with respect to hausmannite and pyrolusite showed significant variation among the spring water samples, reflecting differences in the distribution characteristics of the surrounding rocks to some extent.
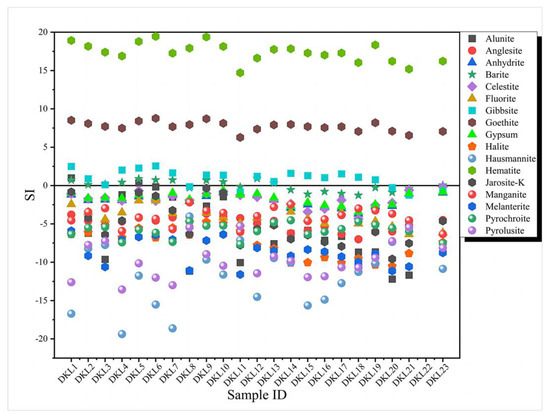
Figure 5.
The saturation indexes of springs along the EKF zone at the outflow temperature.
5.2. Trace Elements
Trace element content is generally influenced by lithology, water alkalinity, and human activities. It may also function as a gauge for assessing the extent of water–rock interaction. Different elements have different implications. In our study, we measured 26 trace elements, including Be, Ag, Cd, Al, Ba, Fe, Co, Cr, Cu, Li, Mo, Mn, Pb, Ni, Sr, Sb, Sn, Th, Ti, Tl, U, V, B, and Zn (see Table 2). It was evident that the content of the same element may vary significantly across different springs. To quantitatively evaluate the trace elements, we employed the enrichment factor (EF). The EF is an important index that quantifies the degree of enrichment of elements. Higher EF values indicate higher degrees of enrichment. The formula for EF calculation is as follows:
where Cr represents the content of a selected reference element (Al), Ci represents the content of a specific element in the sample, w represents the concentration of elements in the water sample, and r represents the concentration of elements in the rocks in the study area [44,45].
Figure 6 shows that most of the trace elements had enrichment factor (EF) values less than 1, indicating insufficient water–rock interaction, which aligns with the Na–K–Mg triangle diagram. However, the EF values for Fe, Sr, Li, and B were relatively higher compared to the other elements. The EF values for Fe were all greater than 1, which can be attributed to its mobility in water and the presence of ultramafic rocks in the research region [46]. This discovery aligns with the saturation index. Sr is prone to enrichment in alkaline solutions, and its migration is closely linked to Ca. The EF value for Sr in the Tazang segment was greater than 1. Since the Tazang segment is predominantly composed of carbonate lithology, containing high levels of Ca2+, and the pH of springs in the area is weakly alkaline, this favors the enrichment of Sr [47]. Li exhibits high chemical reactivity and a strong migration ability, making it more prone to enrichment in springs, which indicates deep fluid upwelling [48,49]. The solubility of B in groundwater rises as the depth and pressure increase [50]. In the study area, volcanic rocks, sedimentary rocks like sulfates, and sandstones may contain B. When underground water flows through underground volcanic and intrusive rocks, the heating effects (including radioactive isotope heating and residual heat after the formation of volcanic and intrusive rocks) may promote the dissolution of B into the groundwater [51]. The B content in groundwater is influenced by factors such as water temperature, flow velocity, and the path through which the water flows within the rock layers. Therefore, the B content shows variability among different springs [52,53,54]. In Figure 6, the highest EF values for Li and B were observed in the Tazang segment, gradually decreasing from the Tazang segment to the Tuosuohu segment. This suggests that the depth of fracture cutting is greater in the southeast compared to the northwest. Additionally, we observed that most of the other trace elements exhibited higher enrichment in the Tazang, Maqu, and Maqin sections, which can be attributed to the deep circulation of the southeast fault and longer water–rock reaction times.
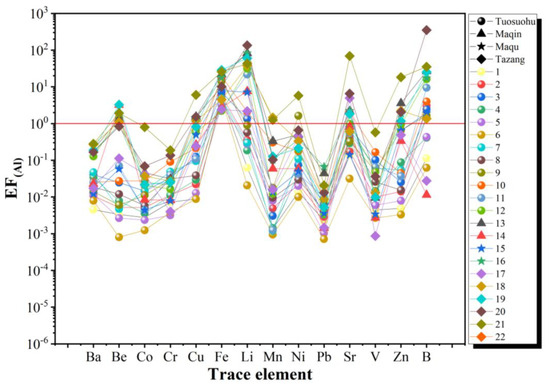
Figure 6.
Trace element distribution enrichment coefficient normalized to Al in the spring water.
5.3. Water Origin and δD, δ18O
Multiple studies have demonstrated that hydrogen and oxygen isotope values exhibit significant differences in various water sources, such as geothermal water, atmospheric precipitation, and magmatic water. This characteristic allows for the determination of the source of geothermal water [55]. From Figure 2, it can be observed that the springs in the region are primarily concentrated around the atmospheric precipitation line, suggesting that their origin is linked to atmospheric precipitation. The local atmospheric precipitation line is located in the bottom-right part of the precipitation line because the Eastern Kunlun region is different from the ocean and has a dry climate. Much of the atmospheric precipitation results from local water vapor evaporation. During evaporation, the proportion of heavy isotopes increases, resulting in an elevated hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratio [56].
Figure 7 depicts the relationship between δD and δ18O and illustrates higher isotopic values in the west compared to in the east. Among all the samples, it is noteworthy that springs No. 3, 5, 8, 9, and 11 exhibited an obvious positive δ18O drift. Existing research by Pang et al., 2016, and Li et al., 2018, indicates that a positive δ18O shift suggests intensive water–rock interactions [56,57]. These five springs are located near or at fault zones, where the fault cutting is deep, and the duration of water–rock interactions is prolonged. The occurrence of this phenomenon can be attributed to the strong reactions between the water and rock, resulting in the continuous enrichment of δ18O isotopes into the spring water upon contact with the rock [57,58,59]. Springs No. 1, 7, and 23, situated to the left of the atmospheric precipitation line, displayed a negative δ18O shift, which can be attributed to a blend of diverse water sources. Springs No. 1 and 7 are situated near a snow-capped mountain and may incorporate a significant amount of snowmelt water. Spring No. 23 is located near a fault zone, potentially being replenished by the deep water within the fault zone [60].
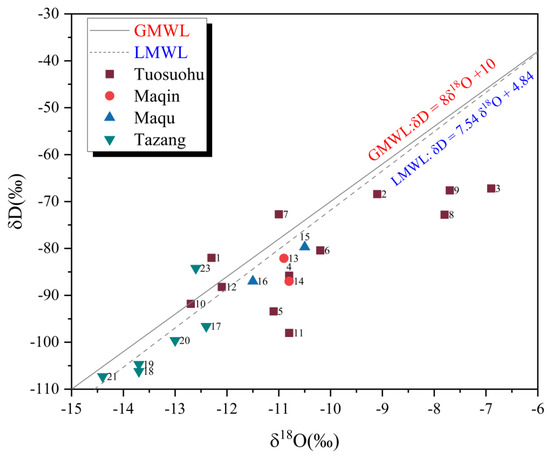
Figure 7.
Graph of the relationship between δD and δ18O. GMWL: δD = 8δ18O + 10 [61]; LMWL: δD = 7.54 δ18O + 4.84 [62].
5.4. Sr Isotope
The 87Sr isotope can be obtained from the β-decay of 87Rb. It is commonly found in minerals that are rich in calcium and potassium [63]. By analyzing the chemical makeup of spring water (Table 1), it was observed that Ca2+ and Mg2+ are widely present in the region, suggesting the significant presence of Sr. Previous research by Shand (2009) showed that 87Sr/86Sr does not participate in hydration reactions and has high mobility [42].
By exploiting the characteristics of Sr, we could use both the Sr concentrations and the 87Sr/86Sr ratios to determine the source of various chemical components in the water samples and identify whether or not the groundwater was mixed. To facilitate this analysis, we created a diagram that depicts the correlation between the Sr concentrations and the 87Sr/86Sr ratios (Figure 8). In this study, we observed that the 87Sr/86Sr ratio in the water samples primarily ranged from 0.708 to 0.716. This range can be attributed to the widespread distribution of carbonates, silicates, and surface waters in the study area. The formation of this phenomenon is closely related to the deep circulation process of atmospheric precipitation in the local thermal fluid system, during which water interacts with strontium-rich crustal rocks.
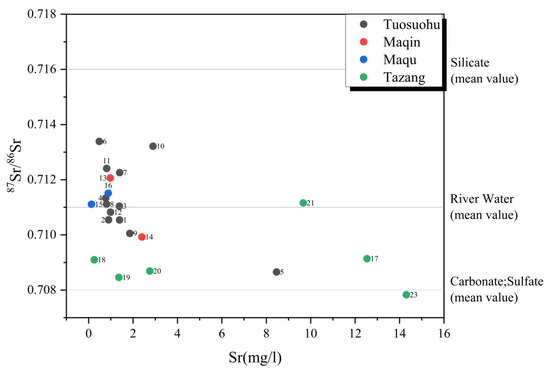
Figure 8.
Relationship between the Sr concentration and 87Sr/86Sr ratio.
Springs No. 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 12, 15, 16, and 21, near rivers and sinkholes and belonging to the Quaternary system, are characterized as descending springs with potential replenishment from the surrounding shallow waters. Therefore, they are situated close to the river water depicted on the map. On the other hand, the Tuosuohu, Maqin, and Maqu sections contain high amounts of silicates and low amounts of carbonates. As a result, in the remaining hot springs, such as those in Tuosuohu and Maqin, the 87Sr/86Sr ratios predominantly ranged between 0.711 (river water) and 0.716 (silicate), as observed in the springs numbered 6, 7, 10, 11, and 13. Notably, the Sr concentration of the Tazang water samples was concentrated between 0.708 and 0.711. The highest Sr concentration was observed in the Tazang section, which can be attributed to the groundwater flowing through a significant amount of limestone in that area. Additionally, the presence of multiple faults, such as the GDNF and the GDBF, in this section increases the contact area between the groundwater and the rock.
5.5. Reservoir Temperature and Circulation Depth
Considering the geological background and the temperature and hydrochemical composition of the springs, it is hypothesized that the highlands in the northwest might be the main groundwater recharge area. This region receives atmospheric precipitation and a small amount of meltwater recharge. During infiltration, the decay of the radioactive isotopes in the granite, the residual heat from magmatic activities since the Permian, active magmatic heat, and the frictional heat from tectonic movements might heat the groundwater through thermal conduction. This water is discharged at the surface in the lower terrain of the southeast in the form of springs with varying temperatures and through artificial extraction. Due to the steep slopes in areas like Maqin and Maqu, the relatively low Na/K and Na/Ca ratios might indicate that the cold springs in these areas are fed by shallow recharge from descending springs. In the flatter terrain of the Tazang section, there might still be some ascending springs with deeper circulation and higher temperatures.
The reservoir temperature of water can be predicted based on the chemical composition of the water samples. There are two main types of geochemical geothermometers: SiO2 geothermometers and cation geothermometers. The choice of geothermometer depends on the specific conditions. SiO2 geothermometers are typically employed in groundwater environments where the water–rock interactions are incomplete. To utilize SiO2 geothermometers effectively, it is necessary to ensure that the water temperature is ≥25 °C, the SiO2 concentration is ≥11 mg/L, and the calculated thermal storage temperature exceeds the spring water temperature [64]. Therefore, considering that the hot spring waters are not all fully equilibrated on the Na-K-Mg triangle diagram (see Figure 4), using the SiO2 geothermometer equation can provide a more accurate assessment of the reservoir temperatures:
where CSiO2 represents the concentration of SiO2 in the water [65].
The results of the reservoir temperature calculations are presented in Table 3. In the research region, the classification of most of the spring waters as cold spring waters is primarily attributed to the mixing of the springs with other water bodies during their ascent, which is also a significant factor contributing to incomplete water–rock reactions [66]. Among all the spring samples, only hot springs No. 11, 20, 21, and 23 met the requirements for using SiO2 geothermometers, with appropriate SiO2 concentrations. However, upon observing the data, we found that despite having an SiO2 concentration lower than 11 mg/L, spring No. 8’s concentration was close to 11 mg/L, still indicating its significance in calculating the reservoir temperature in this region. Therefore, to accurately assess the reservoir temperature in this area, we chose to consider the calculated results from hot springs No. 8, 11, 20, 21, and 23, determined using a SiO2 geothermometer, as representative of the reservoir temperature in this locality.

Table 3.
Heat storage temperatures of the fluids calculated using quartz geothermometers along the mid-eastern part of the Eastern Kunlun Fault.
Analysis of the thermal storage temperatures calculated using SiO2 geothermometers provided insights into quantitative calculation of the groundwater circulation depth. A more accurate estimation of the groundwater circulation depth could be achieved by utilizing the thermal storage temperatures obtained from the SiO2 thermometers for the hot springs numbered 8, 11, 20, 21, and 23 (see Table 4). The calculation formula for groundwater circulation depth is as follows:
where Z indicates the groundwater circulation depth, Z0 indicates the isothermal layer depth, T indicates the reservoir temperature (°C), T0 stands for the temperature of the isothermal layer (°C), and Tgrad indicates the geothermal gradient (°C/km).

Table 4.
Depths of origin estimated according to reservoir temperatures for geothermal waters in the EKF.
Existing articles on the Eastern Kunlun Fault Zone have conducted limited research on the geothermal parameters within our study area. However, as the Eastern Kunlun Fault Zone serves as the boundary of the Qaidam Basin, its eastern topography and geological lithology bear similarities to our research area and are contiguous with it. Therefore, we have chosen to approximate the geothermal gradient within our study area by utilizing a geothermal gradient of 3.1 °C per 100 m, derived from the eastern part of the Qaidam Basin, to represent this parameter [67]. In the research region, we assume that the annual average temperature (T0) in our study area is −3.7 °C. The thickness of the isothermal layer (Z0) refers to the depth at which the range of ground temperature variation is nearly zero. At this depth, the influence of sunlight exposure and seasonal changes is minimal, and the ground temperature remains constant throughout the year. Since Mount Gongga is also located in the eastern part of the Tibetan Plateau, its topographic elevation and temperature are similar to those in the Eastern Kunlun Fault Zone. Therefore, we used the isothermal layer thickness of 30 m from this region as an approximate value for the isothermal layer thickness in our study area [20,68].
5.6. Temporal Variation Characteristics of Springs and Response to Earthquakes
The occurrence of earthquakes has a profound impact on the stress–strain condition of fault zones, consequently affecting the characteristics of aquifers. Typically, an enlarged water–rock reaction surface, the mixing of diverse water bodies, and the release of deep geothermal fluids are associated with an increase in the porosity of fault zones [3]. The influence of earthquakes on the stress–strain state can be categorized into two types: static action and dynamic action. Static action primarily influences fault activity, while dynamic action is mainly manifested through the impact of seismic waves on aquifers. This indicates that an earthquake’s process of development involves the accumulation of stress, followed by a sudden stress release, leading to alterations in the ion concentration prior to and after the event [10,69].
It is acknowledged that intra-annual seasonality and regional precipitation patterns can impact ion concentration variations. While our study did not measure seasonal changes, precipitation, spring water discharge, and temperature data during the sampling period, we supplemented our analysis with data from three springs regularly monitored from 30 June 2021 to 17 June 2023. During this extended period, we observed that in times of minor or no seismic activity, the ion concentrations fluctuated only around the mean value. This pattern suggests that while there may be some degree of influence from seasonal variations and precipitation on ion concentrations, these factors have a minimal impact on anomalies associated with seismic activity, to the extent that their effects can be considered negligible for the purposes of our study. Hence, our findings support the premise that monitoring ion concentration changes could potentially aid in earthquake prediction.
Na+, Cl−, SO42−, Ca2+, HCO3−, K+, and F+ have been identified as sensitive indicators of earthquakes [12,20,70,71,72]. However, Ca2+ and HCO3− are prone to precipitation, K+ can be easily adsorbed by soil, and the F− concentration is below the detection limit. Thus, only Na+, Cl−, and SO42− were used to monitor earthquakes in this study.
Regular monitoring of the major anions and cations was conducted at the Maqu (EKF 17), Maixi (EKF 19), and Jiulongxia (EKF 23) springs every three days. The monitoring period for the Maqu spring (EKF 17) was 30 June 2021–21 October 2023. The monitoring period for the Maixi spring (EKF 19) was 21 June 2021–30 September 2023. The monitoring period for the Jiulongxia spring (EKF 23) was 16 August 2021–17 June 2023. To assess outliers in the ion concentrations, standard deviation (σ) was used. The mean (μ) ± double standard deviation (2σ) were employed as the upper and lower bounds for positive and negative exceptions, respectively. The monitoring results are presented in Figure 9. It is worth noting that many studies have shown that earthquakes with an MS ≤ 4 have a relatively minor impact on ion concentrations [73]. For earthquakes above a magnitude of 4 within a 400 km radius of the regularly monitored springs, please refer to Table S1 (https://data.earthquake.cn/datashare/report.shtml?PAGEID=earthquake_zhengshi), accessed on 1 October 2023.
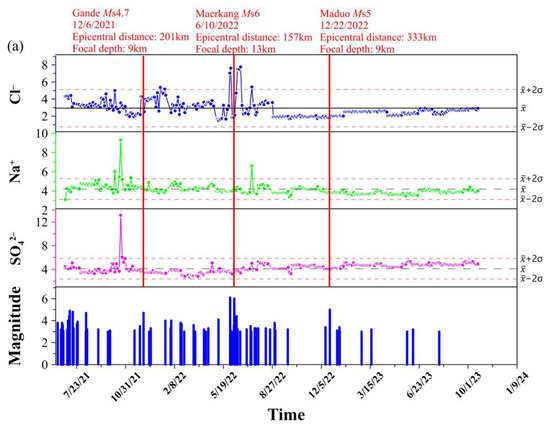
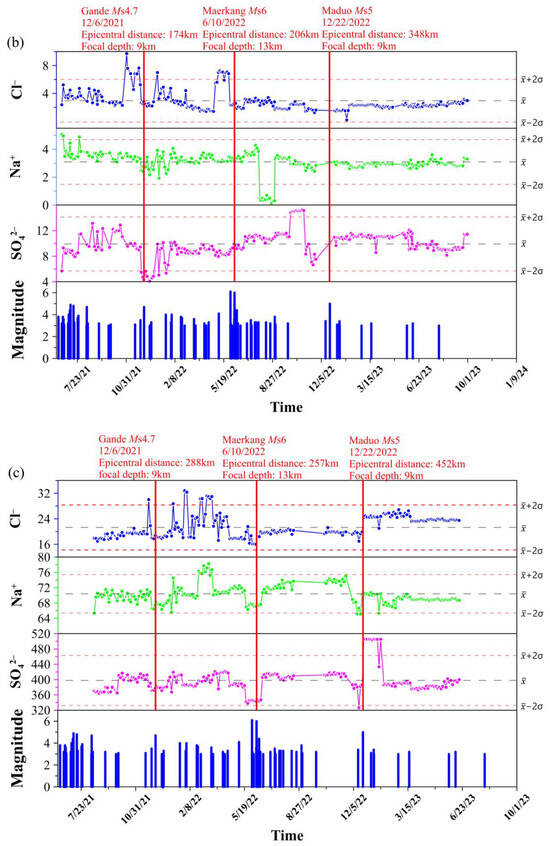
Figure 9.
Temporal variations in the concentration of Cl−, Na+, and SO42− related to earthquakes. (a) The Maqu spring (EKF 17); (b) the Maixi spring (EKF 19); and (c) the Jiulongxia spring (EKF 23).
This paper analyzes three regional earthquakes that occurred during the monitoring period in the Eastern Kunlun Fault region: the Gande MS 4.7 earthquake on 6 December 2021, the Maerkang MS 6.0 earthquake on 10 June 2022, and the Maduo MS 5.0 earthquake on 22 December 2022 (see Figure 10). These earthquakes were characterized by shallow hypocenters, significant magnitudes, and their proximity to the regularly monitored springs.
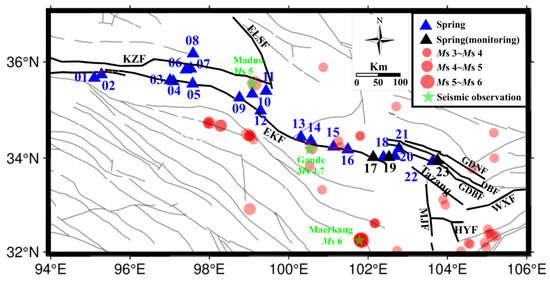
Figure 10.
Distribution of earthquakes with a magnitude of 3 or above within a 400 km radius of the regularly monitored springs during the monitoring period.
With regard to the three regional earthquakes, despite the Gande earthquake having the smallest magnitude, it was preceded by chemical changes in all three monitored springs. At the Maixi spring and the Jiulongxia spring, a decrease in their SO42− concentrations was also observed. Finally, the EKF 23 spring displayed also a decrease in its Na+ concentration. It is noteworthy that although some of the reported variations are small in magnitude, they interrupted a trend and persisted after the earthquake.
Before the occurrence of the Maerkang earthquake, there were again notable increases in the Cl− concentration at the three regularly monitored springs and a decrease in Na+ and SO42− at the EKF 23 spring. The concentration of Cl− at the Maqu regularly monitored spring, located the closest to the area of the Maerkang earthquake, increased by nearly 1.7 times. It is important to note that Cl− is an indicator of deep fluid upwelling and is less influenced by the mixing of shallow cold water. This observation aligns with previous studies, such as of the 1995 Galicia earthquake in Spain, where the concentration of Cl− in well water nearly doubled [13]. Similarly, during the Koyna MS 5.1 earthquake on 5 March 2005, the well water around the Koyna and Warna reservoirs in India doubled in its Cl− concentration, tripled in its SO42− concentration, and increased sevenfold in its F− concentration, while its δ18O values showed a decreasing trend [74]. Additionally, Zhou et al. reported a significant upward trend in the SO42− and Cl− concentrations before the Yangbi MS 6.4 earthquake [3]. These observations suggest that at fault depths, pressure promotes the movement of fluids from the deep rock medium along the fault to the aquifer. This process leads to water mixing and hydrogeochemical changes, disrupting the original system’s equilibrium [75].
The Maduo earthquake (Ms = 5) was the closest to the Maqu regularly monitored spring, yet the fluctuations in Na+, Cl−, and SO42− at Maqu were relatively small. This may have been due to the Maqu spring being located outside the tectonic system where the earthquake occurred. At the same time, no clear anomalies were recorded at the Maixi spring, while the Jiulongxia regularly monitored spring only showed anomalies after the earthquake occurred. This difference may still be related to the distance from the epicenter. From Figure 10, we can clearly see that the distance from the seismic source to Jiulongxia was relatively far, so the stress accumulation before the earthquake was not effectively transmitted to the Jiulongxia regularly monitored spring. After the earthquake, dynamic stress was effectively transmitted to the monitoring spring. At the same time, we found that compared to other earthquakes, the changes in the water’s chemical composition caused by the Maduo earthquake were relatively small. This is mainly because the magnitude of this earthquake was relatively small, and the earthquake and the regularly monitored spring were not entirely located within the same fault system. The response of the water’s chemical composition to earthquakes is influenced by various factors, including the distance from the epicenter, the magnitude of the earthquake, the tectonic position, and the type of earthquake. In addition, the anisotropic characteristics exhibited by the stress generated by the earthquake during the transmission process are also some of the important influencing factors.
5.7. The Hydrogeochemical Circulation Model of Springs in the Mid-Eastern Part of the EKF
Understanding the source and movement of groundwater in seismically active regions is crucial for investing hydrogeochemical indicators in the central and eastern EKF [74]. The EKF exhibits well-developed fractures, which facilitate the infiltration of different water bodies and the upwelling of deep fluids. In this section, we introduce a conceptual model of the hydrogeochemistry in the EKF, integrating its hydrogeochemical features, spring circulation depth, and reservoir temperature (see Figure 11).
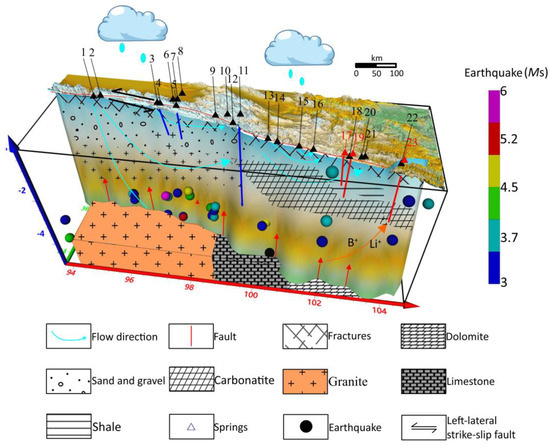
Figure 11.
The conceptual model of hydrogeochemistry along the EKF. The numbers “1–23” represent the sampling numbers of the springs. Circles of different colors represent earthquake magnitudes of varying sizes.
The analysis of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes indicates a significant evaporative effect in the EKF, with atmospheric precipitation being the primary source of replenishment for the springs near the fault zone. Some springs, such as EKF 1 and EKF 7, may mix with snowmelt water from nearby snow mountains, while EKF 23 may be replenished by the deep water within the fault zone. Springs like EKF 3, EKF 5, EKF 8, EKF 9, and EKF 11 exhibit deeper groundwater circulation and longer water–rock reaction times. Atmospheric precipitation converges at the surface and infiltrates along the fracture zones as groundwater recharge, with the circulation depths ranging from 1.29 to 3.83 km. The southeastern section shows a higher enrichment of B and Li, with a greater circulation depth of the spring water compared to the northwestern section. The EKF 11 hot spring, situated at the intersection of two fault zones, exhibits the deepest groundwater circulation, reaching a depth of 3.83 km. During this deep underground circulation, the groundwater undergoes constant heating due to the water–rock interaction. The temperature range of heat storage varies from 39.64 °C to 120.83 °C, with the main heat sources being magmatic heat, granite radiation heat, and sliding friction heat within the fault zone [76]. In terms of the heat sources within the study area, the radioactive decay within the exposed granite may release heat over time, contributing to the overall geothermal budget of the region. This decay process impacts the thermal state of the groundwater as it percolates through granite-rich strata, thereby affecting the temperature of the springs in these terrains [33,34]. Additionally, the ongoing uplift of the Tibetan Plateau and the movement of the Indian Plate ensure that the Eastern Kunlun Fault Zone is still sliding at a certain rate. The frictional heat generated by this shear movement serves as another significant geothermal contributor, which can directly elevate the temperatures of the groundwater circulating near the fault zones, leading to higher spring temperatures in these areas. The heat produced by magmatic activities is an essential source for the deep thermal environment. The residual heat from magmatic activities since the Paleozoic era, along with potential ongoing magmatic activities, transfers from the magma to the surrounding rock and then to the groundwater through conduction, affecting the higher temperature ranges of the springs [35,36]. It is important to note that due to the scarcity of hydrogeological data in this region and the absence of measurements such as flow rate, velocity, temperature variations, and drilling data in our study, we can only roughly estimate the potential heat sources for the overall spring waters in the Eastern Kunlun Fault Zone. This limitation prevents a detailed analysis of the primary heat source for each individual spring. Based on the generally low air temperatures of the springs and the predominance of immature waters in the EKF, we speculate that the influence of current magmatic activity in this area is minimal. Alternatively, the thicker crust beneath the EKF suggests that magmatic activities may occur at greater depths, thereby exerting a lesser impact on the springs. Under specific temperature and pressure conditions, water reacts with surrounding rocks such as carbonate, gypsum, etc.
There are 11 distinct types of water chemistry in the region, primarily determined according to the composition of the surrounding rocks. These include Na-Mg-HCO3-Cl, Mg-SO4-HCO3, Na-Cl, Na-HCO3, Na-Ca-Cl-HCO3, Ca-Na-HCO3, Na-Cl-SO4, Na-Mg-Cl, Na-SO4, Ca-HCO3, and Ca-Mg-HCO3. In the Tuosuohu area, the main ions present are Na2+, Ca2+, HCO3−, and Cl−, with a significant distribution of sandstones. In the Maqin, Maqu, and Tazang regions, the main ions are Mg2+, Ca2+, and HCO3−, with a prominent presence of granites and carbonates. The water samples from the area are considered immature. In regions with a greater circulation depth, the faults are weakened due to hydrostatic pressure and water–rock reactions, leading to the frequent occurrence of smaller earthquakes in Tuosuohu and Tazang. The Maqin–Maqu section near Tazang serves as a transitional area with geothermal anomalies, indicating the possibility of significant earthquakes in this region.
The hot water in the fault water channel circulates upwards due to the pressure difference. During this ascent, the EKF 3, EKF 8, EKF 15, and EKF 21 springs mix with surface water to varying degrees. As the hot water rises, significant quantities of hematite minerals and goethite minerals precipitate. The northwestern mountainous area is notably higher than the southeastern section. The spring water in the Maqin, Maqu, and Tazang regions may originate from a descent spring fed by an aquifer located in front of a mountain.
Ultimately, the groundwater surfaces as springs. Before and after the Maduo MS 5.0 earthquake, the Maerkang MS 6.0 earthquake, and the Gande MS 4.7 earthquake, there were anomalies in the water chemistry observed at three regularly monitored springs in Maqin, Maixi, and Jiulongxia. Underground fluid serves as an effective indicator of earthquake preparation and occurrence, contributing to the establishment of a conceptual model of hydrogeochemistry.
6. Conclusions
This research aimed to fill the knowledge gap regarding the hydrogeochemical characteristics of the springs along the east–central section of the Eastern Kunlun Fault Zone, with a particular focus on understanding the implications of these characteristics for earthquake prediction and monitoring. The study’s primary objective was to examine the interplay between hydrogeochemistry and seismic activity within this seismically active region.
The methodology involved sampling 23 springs across the EKF from May to July 2021, employing both census and detailed survey techniques. This approach enabled the collection of 609 water samples, with the subsequent laboratory analysis focusing on a range of parameters, including the major and trace element concentrations, isotope ratios, and mineral saturation indexes. The study’s key setting was its focus on an area known for its seismic activity and complex geological structure, making it an ideal location for examining the connections between groundwater geochemistry and earthquakes.
The research findings highlight several critical points:
- The springs’ water chemistry indicates their primary origin is atmospheric precipitation, with significant evaporative effects observed.
- The isotopic analysis revealed a decreasing concentration of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes from west to east, suggesting variations in evaporation and water–rock interactions across the fault zone.
- The study identified 11 distinct water chemistry types, reflecting the diverse lithology of the region.
- The reservoir temperatures of the springs, ranging from 39.64 °C to 120.83 °C, along with their varied circulation depths (1.29 to 3.83 km), underscore the complex interaction between geothermal activity and groundwater movement in the EKF.
- Notably, the hydrogeochemical changes observed before and after seismic events such as the Gande and Maerkang earthquakes suggest the potential to use groundwater chemistry as an indicator for earthquake prediction.
The study’s limitations include its relatively short duration and its focus on a specific segment of the EKF. These factors may restrict the generalizability of the findings and underscore the need for longer-term and broader geographic studies to fully understand the hydrogeochemical dynamics of the fault zone. Despite these limitations, the research significantly contributes to our understanding of the interplay between hydrogeochemistry and seismic activity in the EKF. In conclusion, this research not only advances our knowledge of the hydrogeochemical characteristics of the springs in the EKF but also underscores the importance of integrating hydrogeochemical analysis into earthquake prediction strategies.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w16091215/s1. Table S1: Detailed records of earthquakes above magnitude 4 within 400 km of the Maqu, Meixi, and Jiulongxia continuous monitoring stations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.L., X.Z. (Xiaocheng Zhou) and J.J.; methodology, C.L. and X.Z. (Xiaocheng Zhou); software, C.L. and X.Z. (Xiaoyi Zhu); validation, C.L., X.Z. (Xiaocheng Zhou) and J.J.; formal analysis J.L. (Jingchao Li)., J.L. (Jing Li) and X.Z. (Xiaocheng Zhou); investigation, J.W., G.X., J.L. (Jiang Li) and S.C.; data curation, C.L., G.X. and S.C.; writing—original draft preparation, C.L., X.Z. (Xiaocheng Zhou) and J.J.; writing—review and editing, C.L. and X.Z. (Xiaocheng Zhou); visualization, C.L.; supervision, X.Z. (Xiaocheng Zhou); project administration, C.L., X.Z. (Xiaocheng Zhou) and J.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was funded by the National Key Research and Development Project (2023YFC3012005, 2022YFC2204301, 2018YFE0109700, 2019YFC1509203), the Central Public Interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (CEAIEF2022030200, CEAIEF2022030205, CEAIEF20220507, CEAIEF20230602, CEAIEF20230503), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41673106, 42073063, 4193000170, U2039207), the Open Foundation of the United Laboratory of High-Pressure Physics and Earthquake Science (2022HPPES05), IGCP Project 724, and the Science and Technology Innovation Program for Postgraduate students in IDP subsidized by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (CXZZSS2023186).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors without undue reservation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chiodini, G.; Cardellini, C.; Di Luccio, F.; Selva, J.; Frondini, F.; Caliro, S.; Rosiello, A.; Beddini, G.; Ventura, G. Correlation between tectonic CO2 Earth degassing and seismicity is revealed by a 10-year record in the Apennines, Italy. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanikawa, W.; Sakaguchi, M.; Tadai, O.; Hirose, T. Influence of fault slip rate on shear-induced permeability. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2010, 115, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.L.; Zhou, X.C.; Su, H.J.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.L.; Ouyang, S.P.; Yan, Y.C.; Bai, R.L. Hydrochemical Characteristics of Earthquake-Related Thermal Springs along the Weixi-Qiaohou Fault, Southeast Tibet Plateau. Water 2022, 14, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, B.E.; Newell, D.L.; Jessup, M.J.; Grambling, T.A.; Shaw, C.A. Structural Controls on Crustal Fluid Circulation and Hot Spring Geochemistry above a Flat-Slab Subduction Zone, Peru. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2020, 21, e2020GC008919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Pang, Z.H.; Liao, D.W.; Zhou, X.C. Fluid geochemistry and its implications on the role of deep faults in the genesis of high temperature systems in the eastern edge of the Qinghai Tibet Plateau. Appl. Geochem. 2021, 131, 105036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowell, R.P. A fault-driven circulation model for the Lost City Hydrothermal Field. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2703–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yan, G.; Ma, Y.; Scheuermann, A. Measurement of In-Situ Flow Rate in Borehole by Heat Pulse Flowmeter: Field-Case Study and Reflection. Geosciences 2023, 13, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Y.; Liu, C.L.; Zhao, Y.J.; Wang, L.C. Chemical and isotopic characteristics and origin of spring waters in the Lanping-Simao Basin, Yunnan, Southwestern China. Chem. Der Erde-Geochem. 2015, 75, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.C.; Yan, Y.C.; Fang, W.Y.; Wang, W.L.; Shi, H.Y.; Li, P.F. Short-Term Seismic Precursor Anomalies of Hydrogen Concentration in Luojishan Hot Spring Bubbling Gas, Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 8, 586279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.C.; Liu, L.; Chen, Z.; Cui, Y.J.; Du, J.G. Gas geochemistry of the hot spring in the Litang fault zone, Southeast Tibetan Plateau. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 79, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, A.; Andren, M.; Kristmannsdottir, H.; Stockmann, G.; Morth, C.M.; Sveinbjornsdottir, A.; Jonsson, S.; Sturkell, E.; Gudorunardottir, H.R.; Hjartarson, H.; et al. Changes in groundwater chemistry before two consecutive earthquakes in Iceland. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, F.; Barberio, M.D. Hydrogeochemical changes before and during the 2019 Benevento seismic swarm in central-southern Italy. J. Hydrol. 2022, 604, 127250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, N.M.; Hernandez, P.A.; Igarashi, G.; Trujillo, I.; Nakai, S.; Sumino, H.; Wakita, H. Searching and detecting earthquake geochemical precursors in CO2-rich groundwaters from Galicia, Spain. Geochem. J. 2008, 42, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.; Franchini, S.; Barberio, M.D.; Billi, A.; Boschetti, T.; Giansante, L.; Gori, F.; Jonsson, S.; Petitta, M.; Skelton, A.; et al. Changes in groundwater trace element concentrations before seismic and volcanic activities in Iceland during 2010–2018. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, B.; Xiong, X.; Wang, R.; Zheng, Y.; Yadav, R.B.S. Stress evolution and seismic hazard on the Maqin-Maqu segment of East Kunlun Fault zone from co-, post- and interseismic stress changes. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 200, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Ji, L.; Liu, C. Interseismic slip rate and locking along the Maqin–Maqu Segment of the East Kunlun Fault, Northern Tibetan Plateau, based on Sentinel-1 images. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2021, 211, 104703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Ren, J.W.; Chen, C.Y.; Fu, J.D.; Yang, P.X.; Xiong, R.W.; Hu, C.Z. The Late Pleistocene activity of the eastern part of east Kunlun fault zone and its tectonic significance. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.S.; ShI, W.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Yang, N.; Zhang, C.S.; Zhang, H.P. Characteristics of the activity of the Maqu segment of the East Kunlun active fault belt and its eastward extension. Geol. Bull. China 2005, 24, 30–35. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.B.; Zhou, X.C.; He, M.; Liang, J.L.; Li, J.C.; Dong, J.Y.; Tian, J.; Yan, Y.C.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.L.; et al. Earthquakes evoked by lower crustal flow: Evidence from hot spring geochemistry in Lijiang-Xiaojinhe fault. J. Hydrol. 2023, 619, 129334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.C.; Zhou, X.C.; Liao, L.X.; Tian, J.; Li, Y.; Shi, Z.M.; Liu, F.L.; Ouyang, S.P. Hydrogeochemical Characteristic of Geothermal Water and Precursory Anomalies along the Xianshuihe Fault Zone, Southwestern China. Water 2022, 14, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seismologic Bureau of Qinghai Province, the Institute of Crustal Dynamics of China Earthquake. Eastern Kunlun Active Fault Zone; Seismological Press: Beijing, China, 1999. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Lin, A.; Sun, G.; Zheng, J. Surface Ruptures Associated with the 1937 M 7.5 Tuosuo Lake and the 1963 M 7.0 Alake Lake Earthquakes and the Paleoseismicity along the Tuosuo Lake Segment of the Kunlun Fault, Northern Tibet. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2007, 97, 474–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerome, V.D.W.; Paul, T.; Frederick, J.R.; Anne-Sophie, M.; Bertrand, M.; Yves, G.; Robert, C.F.; Marc, W.C.; Zhao, G.G.; Xu, Z. Uniform psotglacial slip-rate along the central 600 km of the Kunlun Fault (Tibet), from 26Al, 10Be, and 14C dating of riser offsets, and climatic origin of the regional morphology. Geophys. J. Int. 2002, 148, 356–388. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; He, Q.; Zhao, G. Holocene slip rate along the eastern segment of the Kunlun fault. Seismol. Geol. 2004, 26, 676–687. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.X. Eastern Kunlun Active Fault Zone and Its Seismic Activity. Earth Res. China 1996, 12, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.-f.; He, Q.-l.; Zhao, G.-g. Paleo-earthquake studies on the eastern section of the Kunlun fault. Acta Seismol. Sin. 2005, 18, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X. The Long-Trem Faulting Behavior of the Eastern Segment (Maqin-Maqu) of the East Kunlun Faults Since Ther Late Quaternary. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Geology of China Earthquake Administration, Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, A.M.; Guo, J.M. Nonuniform Slip Rate and Millennial Recurrence Interval of Large Earthquakes along the Eastern Segment of the Kunlun Fault, Northern Tibet. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2008, 98, 2866–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.N.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Huang, C.C.; Wang, N.L.; Qiu, H.J.; Wang, H.Y.; Xiao, Q.L.; Chen, D.; Lin, X.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Late Pleistocene-Holocene aeolian loess-paleosol sections in the Yellow River source area on the northeast Tibetan Plateau: Chronostratigraphy, sediment provenance, and implications for paleoclimate reconstruction. Catena 2022, 208, 105777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Sun, M.; Che, Y.; Yao, X.; Zhang, M.; Niu, S. Micrometeorological Analysis and Glacier Ablation Simulation in East Kunlun. Water 2023, 15, 3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Q.; Dong, H.L.; Yang, X.D.; Herzschuh, U.; Zhang, E.L.; Stuut, J.B.W.; Wang, Y.B. Late Holocene forcing of the Asian winter and summer monsoon as evidenced by proxy records from the northern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 280, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Second Regional Geological Survey Team of Qinghai Province, The Institute of Crustal Dynamics of China Earthquake. Report on Regional Geological Survey of the People’s Republic of China, Guoluo Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture and Youyun Community Assemblage with Scale 1:200,000, Geological Part; The Second Regional Geological Survey Team of Qinghai Province, The Institute of Crustal Dynamics of China Earthquake: Qinghai, China, 1986; pp. 210–221. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jing, G.Z.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.Q.; He, J.J.; Zhang, L.B.; Wang, F.L.; Liu, Y.; Shi, W.J.; Tan, J. Middle-LateTriassic regional-scale magmatic-hydrothermal metallogenic system in the eastern segment of the East Kunlun. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2023, 42, 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, M.; Wang, H.; Li, B.; Feng, C.; Dick, J.M.; Li, J.; Kong, H.; Zhao, Z. Geodynamic Setting and Cu-Ni Potential of Late Permian Xiwanggou Mafic-Ultramafic Rocks, East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, NW China. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 666967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, G.; Luo, Y.; Hu, S.; Xu, Q.; Billi, A. Geothermal Accumulation Constrained by the Tectonic Transformation in the Gonghe Basin, Northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Lithosphere 2022, 2022, 3936881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.W.; Zhao, W.J.; Wu, Z.H.; Shi, D.N.; Song, Y.; Deng, S.G. East Kunlun Orogeny’s uplift uncovered by deep reflection seismic data in indepth iv. Chin. J. Geophys. 2016, 59, 3211–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozer, B.; Sandwell, D.T.; Smith, W.H.F.; Olson, C.; Beale, J.R.; Wessel, P. Global Bathymetry and Topography at 15 Arc Sec: SRTM15+. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 1847–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.Y. Builing to the active tectonic database of china. Seismol. Geol. 2008, 30, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woith, H.; Wang, R.J.; Maiwald, U.; Pekdeger, A.; Zschau, J. On the origin of geochemical anomalies in groundwaters induced by the Adana 1998 earthquake. Chem. Geol. 2013, 339, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, X.; Du, J.; Xie, C.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Yi, L.; Liu, H.; Cui, Y. Hydrochemical characteristics of hot spring waters in the Kangding district related to the Lushan MS = 7.0 earthquake in Sichuan, China. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhou, X.C.; Li, Y.; He, M.; Li, J.C.; Dong, J.N.; Tian, J.; Li, K.Y.; Yan, Y.C.; Ouyang, S.P.; et al. Hydrogeochemical and Isotopic Characteristics of the Hot Springs in the Litang Fault Zone, Southeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Water 2022, 14, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shand, P.; Darbyshire, D.P.F.; Love, A.J.; Edmunds, W.M. Sr isotopes in natural waters: Applications to source characterisation and water–rock interaction in contrasting landscapes. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, A.; Ghoreyshinia, S.; Mehrabi, B.; Delavari, M. Rare earth elements geochemistry in springs from Taftan geothermal area SE Iran. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2015, 304, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giggenbach, W.F. Geothermal solute equilibria. Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicators. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 2749–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Zhang, S.Q.; Zhang, P.F.; Peng, Y. On the Lithogeochemical Features of the Upper Triassic Sequence Strata in West Sichuan. Sichuan J. Geol. 2005, 25, 198–201. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.J. Geologic Features, Provenance Nature and Tectonic Signigicance of Hongshuichuan Formation Located in the Southern Slope of the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt (Eastern Part). Master’s Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.S.; Shi, R.D.; Wu, C.L.; Wang, X.B.; Robinson, P.T. Dur’ngoi Ophiolite in East Kunlun, Northeast Tibetan Plateau: Evidence for Paleo-Tethyan Suture in Northwest China. J. Earth Sci. 2009, 20, 303–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.F.; Franks, S.G.; Aagaard, P. Origin and migration of brines from Paleozoic strata in Central Tarim, China: Constraints from 87Sr/86Sr, dD, d18O and water chemistry. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 1269–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Zhou, X.C.; He, M.; Li, J.C.; Dong, J.Y.; Tian, J.; Yan, Y.C.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.Y.; Li, Y. Hydrogeochemical origin and circulation of spring waters along the Karakorum fault, Western Tibetan Plateau: Implications for interaction between hydrosphere and lithosphere. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 1021550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.G.; Zheng, M.P.; Zhang, X.F.; Wu, Q.; Liu, X.F.; Ren, J.H.; Chen, S.S. Geothermal-type Lithium Resources in Southern Xizang, China. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2021, 95, 860–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberio, M.D.; Gori, F.; Barbieri, M.; Billi, A.; Caracausi, A.; De Luca, G.; Franchini, S.; Petitta, M.; Doglioni, C. New observations in Central Italy of groundwater responses to the worldwide seismicity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, N.K.; Harijoko, A.; Itoi, R.; Unoki, Y. Water geochemistry and soil gas survey at Ungaran geothermal field, central Java, Indonesia. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2012, 229, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.P.; Cui, H.Q.; Liu, W.P.; Chen, X.X.; Li, Z.H. An analysis of the evolution trend and influencing factors of the groundwater flow field in the Sanjiang Plain. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2021, 48, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düşünür-Doğan, D.; Üner, S. Numerical simulation of groundwater flow and temperature distribution in Aegean Coast of Turkey. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 128, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlesak, D.W.; Torregrossa, A.M.; Ehleringer, J.R.; Dearing, M.D.; Passey, B.H.; Cerling, T.E. Turnover of oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in the body water, CO2, hair, and enamel of a small mammal. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Y.; Wu, J.L.; Shen, B.B.; Zeng, H.; Li, Y.H. Water Chemistry and Stable Isotopes of Different Water Types in Tajikistan. Environ. Process. Int. J. 2018, 5, S127–S137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.H.; Kong, Y.L.; Li, J.; Tian, J. An isotopic geoindicator in the hydrological cycle. In Proceedings of the 15th Water–rock Interaction International Symposium (WRI), Evora, Portugal, 16–21 October 2016; pp. 534–537. [Google Scholar]
- Giggenbach, W.F. Isotopic shifts in waters from geothermal and volcanic systems along convergent plate boundaries and their origin. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 1992, 113, 495–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Yu, J.; Su, Y.; Xie, J.; Jia, X.; Hu, Y. δ18O shifts of geothermal waters in the central of Weihe Basin, NW China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2009, 59, 995–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson, L.; Skelton, A.; Graham, C.; Morth, C.M. The timescale and mechanisms of fault sealing and water–rock interaction after an earthquake. Geofluids 2007, 7, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic Variations in Meteoric Waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.; Yao, T.; Yang, X.; Joswiak, D.R. Implications of variations in δ18O and δD in precipitation at Madoi in the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Quat. Int. 2013, 313–314, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfried, W.E.; Chen, X.; Chan, L.H. Trace element mobility and lithium isotope exchange during hydrothermal alteration of seafloor weathered basalt: An experimental study at 350 degrees C, 500 bars. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnorsson, S. Chemical-equilibria in icelandic geothermal systems—Implications for chemical geothermometry investigations. Geothermics. 1983, 12, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, R.O.; Rowe, J.J. The deposition of silica in hot springs. Bull. Volcanol. 1966, 29, 585–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Y.; Zhang, J.; Tang, X.C.; Tian, J.; Wang, Y.C.; Guo, Q. The deep geothermal structure of high-temperature hydrothermal activity region in western Sichuan Plateau: A geophysical study. Chin. J. Geophys.-Chin. Ed. 2018, 61, 2926–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Zou, K.; Guo, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, F.; Zhu, J.; Duan, L.; Yang, G. Geothermal regime and implications for basin resource exploration in the Qaidam Basin, northern Tibetan Plateau. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2022, 239, 105400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, L.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Y.; Shi, D.; Liu, Y. Temporal variations in stable isotopes and synchronous earthquake-related changes in hot springs. J. Hydrol. 2021, 599, 126–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andren, M.; Stockmann, G.; Skelton, A.; Sturkell, E.; Morth, C.M.; Gudrunardottir, H.R.; Keller, N.S.; Odling, N.; Dahren, B.; Broman, C.; et al. Coupling between mineral reactions, chemical changes in groundwater, and earthquakes in Iceland. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2016, 121, 2315–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, A.; Liljedahl-Claesson, L.; Wasteby, N.; Andren, M.; Stockmann, G.; Sturkell, E.; Morth, C.M.; Stefansson, A.; Tollefsen, E.; Siegmund, H.; et al. Hydrochemical Changes Before and After Earthquakes Based on Long-Term Measurements of Multiple Parameters at Two Sites in Northern IcelandA Review. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid Earth 2019, 124, 2702–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toutain, J.P.; Munoz, M.; Poitrasson, F.; Lienard, A.C. Springwater chloride ion anomaly prior to a ML = 5.2 Pyrenean earthquake. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1997, 149, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.Y.; Zhou, X.C.; Zhang, Y.X.; He, M.; Tian, J.; Shen, J.F.; Li, Y.; Qiu, G.L.; Du, F.; Zhang, X.M.; et al. Hydrogeochemical Study of Hot Springs along the Tingri-Nyima Rift: Relationship between Fluids and Earthquakes. Water 2023, 15, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.V.; Nagabhushanam, P.; Sukhija, B.S. Earthquake (M 5.1) induced hydrogeochemical and δ18O changes: Validation of aquifer breaching-mixing model in Koyna, India. Geophys. J. Int. 2011, 184, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuseppe, E.; Massimo, C.; Fedora, Q. Seismogeochemical algorithms for earthquake prediction: An overview. Ann. Geophys. 1997, 40, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli, G.; Tamburello, G. Geological and Geophysical Factors Constraining the Occurrence of Earthquake Precursors in Geofluids: A Review and Reinterpretation. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.H.; Luo, J.; Cheng, Y.Z.; Duan, Z.F.; Tian, J.; Kong, Y.L.; Li, Y.M.; Hu, S.B.; Wang, J.Y. Evaluation of geological conditions for the development of deep geothermal energy in China. Earth Sci. Front. 2020, 27, 134–151. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).