Abstract
Turbidity has been one of the most typical problems in urban rivers, accompanied by eutrophication. Though the colloid is a nonnegligible factor associated with turbidity and nutrient enrichment in urban rivers, the characteristics of nitrogen enrichment and bacterial communities of colloids under different turbidity conditions of urban rivers have not been well understood. In this study, colloids of low and high molecular weights (LMW, 30 kDa–0.2 μm, and HMW, 0.2–1 μm) were separately collected from the bulk water (<1 μm) of several typical urban rivers in China. Since the colloidal concentration presented the significantly highest correlation with turbidity, colloidal characteristics were further explored under three turbidity gradients with two cutoffs of 10 and 30 NTU. Results showed that colloidal organic matter in medium and high turbidity rivers was mainly sourced from the release of endogenous plankton and the proportion of colloidal organic carbon in dissolved organic carbon increased from 33% to 38% with increased turbidity. Colloidal ammonia nitrogen in medium turbidity accounted for the highest proportion (an average of 60%) in bulk water, which could be explained by the significantly positive correlation of colloidal ester groups and ammonia nitrogen (R2 = 0.47). Bulk water, HMW, and LMW colloids presented different dominant bacterial genera and LMW colloids also contained three unique dominant filterable genera: Flavobacterium, Acinetobacter, and Limnohabitans. LMW colloidal filterable bacteria under medium and high turbidities presented the greatest potential for dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium, which might further enhance the enrichment of ammonia nitrogen in colloids. This study provides a primary understanding of the characteristics of colloids and colloidal bacterial communities in urban rivers from the perspective of turbidity and puts a new insight on the remediation of rivers under medium turbidity.
1. Introduction
In the past several decades, intense human activities have caused the widespread deterioration of rivers especially in low- to mid-income countries, which were typically characterized by increased eutrophication and turbidity [1]. The global climate changes, such as extreme drought and heat waves, extensively enhanced the deterioration in the water quality of most urban rivers via the endogenous release of pollutants from sediments or plankton [2]. Apart from the massive reduction in the exogenous input of nutrients, the improvement in the self-remediation or bio-transformation for internal organic matter and nitrogen is another effective way for the restoration of eutrophic and turbid rivers. Thus, it is important to understand the occurrence, migration, and transformation mechanisms of pollutants existing in different media, including bottom sediment, suspended particulate matter (>1 μm), aquatic colloids (1 kDa–1 μm), and true dissolved water (<1 kDa). Colloids, as the third phase between truly ‘dissolved’ and ‘particulate’, persisted widely in waters, soils, and sediments [3,4]. Due to the non-unified definition for colloids, operational definitions of 1 kDa (or 1 nm)–1 μm were more commonly utilized [5,6]. To date, most knowledge of rivers has focused on the easily-noticed suspended particulate matter or the bulk water (<1 μm) [7,8] but the related understanding of aquatic colloids has not been paid much attention in rivers.
Turbidity and eutrophication often occur jointly in most slow-flowing urban rivers [9]. Compared to the invisibility of eutrophication that cannot be evaluated visually, turbidity is a publicly focused important index of water quality for urban rivers and lakes [10]. In general, turbidity is mainly influenced by suspended particulate matter, followed by colloids [11]. In rivers with high sediment contents, the suspended particulate matter is generally considered to be the most important aquatic medium for the loading and transformation of nutrients. However, due to the sediment trapping by kinds of dams and the slow-flow deposition by extreme drought [12], the global sediment flux has declined to 49% of pre-dam conditions in the global hydrologic north [13]. Hence, the influence of suspended particulate matter on the turbidity and eutrophication of urban rivers gradually declined with the reduced flow rate and sediment contents.
Different from suspended particulate matter, colloids are much steadier and more dispersible in overlying water and can maintain prolonged transportation in rivers. Colloids are typically composed of metal oxides or hydrates, clay minerals, and colloidal organic matter (COM) [14,15]. However, since the relatively lower contents of Fe, Al, Si, Mn, and small amounts of mineral particles in river colloids [16], COM in aquatic colloids was mainly focused on in most studies. Studies indicated that COM was dominated by a refractory humus substance, which could color the water and decrease the transparency and turbidity. Hence, the abundance and composition of COM were also suggested to be potentially associated with turbidity [17]. As the predominant component of aquatic colloids, COM has been studied in lakes and oceans [11,18]. However, the concentration of colloids in urban rivers was generally much higher than those in lakes and seas. The proportion of colloidal organic carbon (COC) in dissolved organic carbon (DOC) reached 33% in the Fox River (1 kDa < colloids < 0.7 μm), 25% in the Northern Adriatic Sea (5 kDa < colloids < 0.22 μm), and 8.11–22.13% in Taihu Lake (1 kDa < colloids < 1 μm) [19,20,21]. On the one hand, located upstream of lakes and oceans, rivers can directly obtain allochthonous COM via terrestrial runoff. On the other hand, the eutrophication and slow-flow characteristics commonly cause the propagation of phytoplankton and bacterioplankton, the extracellular polymeric substances of which can overwhelmingly contribute to the autochthonous COM supply [22]. Hence, we presumed that colloids may be an important influence factor of turbidity in slow-flow urban rivers. However, the knowledge of the occurrence characteristics of colloids under different turbidity and eutrophication conditions has not been well understood.
In natural waters, colloids also play important roles in the biogeochemical cycles of various substances. Colloids act as one of the huge sinks and sources of phosphorus, nitrogen, metals, antibiotics, and so on, via adsorption and complexation [23,24,25,26]. Incubation experiments tested that colloid-adsorbed ammonia nitrogen in bulk water could reach 1.72 mg/L with the presence of sodium and the properties of colloids have a direct influence on the concentration of ammonia nitrogen in bulk water [27]. Thus, the nutrient-rich colloids could support the great growth of surrounding zooplankton via filter feeding. It is noteworthy that the components of colloids usually vary gradually in the transporting processes from rivers to lakes or seas. The variation of colloids is well-known and partially driven by the adsorption and aggregation processes [28]; what about the potential contribution from the biotransformation of colloidal microbes? A bulk of studies have focused on the composition and function of microbial communities in bulk water and suspended particulate matter [8,29] and explored the processes of nitrogen transformation through anammox, nitrification, and denitrification [30]. But there have been no answers to whether there is any microorganism colonizing in or on colloids; and if yes, how do they act on the transformation processes of nitrogen and COM?
The aims of this study were (1) to understand the occurrence characteristics of colloids and colloidal nitrogen in urban rivers under different turbidity conditions, (2) to reveal the composition and assemble mechanisms of microbial communities of colloids, and (3) to explore the nitrogen transformation characteristics of bacterial communities colonizing in colloids. In this study, low and high molecular weight (LMW, 30 kDa–0.2 μm, and HMW, 0.2–1 μm) colloids were collected from the bulk water (<1 μm) of several typical urban rivers in China and the living bacteria colonizing in colloids were measured via bacterial RNA detection.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Bulk Water and Colloids
In this study, water samples were collected from seventeen sites located at several urban rivers of Nanjing City (32°3′41.6″ N, 118°47′29.6″ E, China) in November 2022 (Figure 1). Five liters of surface water was sampled in each site and transported to the laboratory within 2 h for the subsequent collections of bulk water (<1 μm), HMW (high molecular weight, 0.2–1 μm), and LMW (low molecular weight, 30 kDa–0.2 μm) colloids separately.
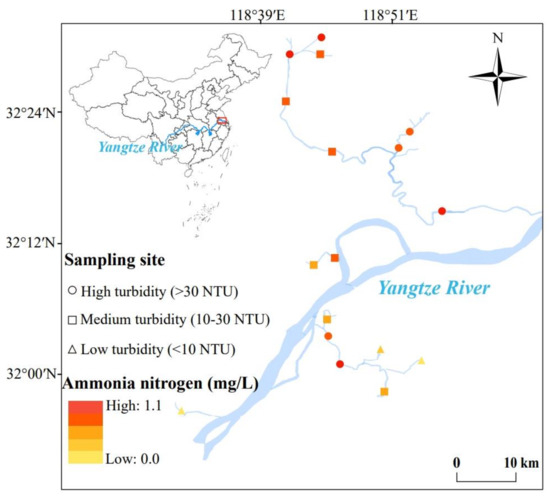
Figure 1.
Sampling sites and the turbidity conditions in rivers of this study. The sampling sites are shaped based on the turbidity gradients and are colored according to the concentration of ammonia nitrogen in water.
All cellulose acetate membranes used in the collections were pre-washed with a 10% HCl solution and rinsed with ultrapure water. Firstly, water samples were filtered through the cellulose acetate membrane with a 1 μm pore size (Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA) and the prior filtrate was defined as bulk water (<1 μm). Then, the prior filtrate was micro-filtrated through a 0.2 μm-cellulose acetate membrane and then particles (0.2–1 μm) and the secondary filtrate (<0.2 μm) were obtained. Particles were oven-dried at 105 °C for 24 h to obtain HMW colloids (0.2–1 μm) for subsequent microbial analysis. The secondary filtrate flowed through a tangential flow ultrafiltration system (TFF; Pellicon, Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA), which holds regenerated cellulose membranes with a 30 kDa molar mass cut-off to concentrate LMW colloids (30 kDa–0.2 μm) [31].
The concentration factor (cf) was crucial in the ultrafiltration process, due to the influence on the estimation of colloidal abundances [32]. In this study, an ultrafiltration permeation model was utilized to determine the cf value [32,33] and the obtained fitting curve showed that the difference in the concentrations of organic carbon in ultrafiltrate was only 4% between cf = 10 and cf = 100 (Figure S1). Therefore, 10 was selected as the cf value in this study. In addition, low cf values were also used in some other studies about river colloids [22,34]. Noticeably, the cf was fully considered in the later calculation of concentrations of COC, nitrogen, and phosphorus, with the specific calculation formula referring to the previous study [35].
2.2. Physicochemical Characterization of Bulk Water and Colloids
Seven physicochemical indices of the overlying water in each sampling site were tested in situ. Temperature, pH, oxidation–reduction potential (ORP), conductivity, and dissolved oxygen (DO) were determined using the portable multi-parameter water quality analyzer. Velocity and turbidity were measured using a portable Doppler flow meter (DPL-LS11, DAIMEIKE, Beijing, China) and a portable turbidity meter (TB100, BANTE, Shanghai, China) separately. All calculations are shown in Table S1.
The concentrations of organic carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and three-dimensional fluorescence spectra were jointly measured for bulk water and colloids. Moreover, zeta potential and functional groups were measured for the characterization of colloids. Organic carbon was measured by the Shimadzu TOC-V analyzer (TOC-VWS, SHIMADZU, Tokyo, Japan). Dissolved total phosphorus, organic phosphorus, inorganic phosphorus, dissolved total nitrogen, ammonia nitrogen, nitrate, and nitrite were measured by the flow analyzer (CLEVERCHEM Anna, DeChem-Tech, Hamburg, Germany). The zeta potential of colloids was measured by a Zeta-sizer Nano-ZS90 (Malvern, Worcestershire, UK). To quantify organic matter, the strength of colloidal functional groups was detected by Fourier Transform Infra-Red (FTIR) and calculated using the Omnic 9.2 software [36]. Fluorescence spectra of colloids and bulk water were measured using the luminescence spectrometer. Emission–excitation matrixes (EEM) were used to gain information on bulk water and colloids to characterize their fluorogenic constituents [37,38]. EEMs were generated according to the emission spectra of 200~600 nm and the excitation wavelength of 200–450 nm. Origin 2022 and MATLAB 2022 were used to obtain the diagram of components.
The fluorescence index (FI), autochthonous index (BIX), and humification index (HIX) were used to analyze the source of substances based on fluorescence spectra. Equations of the three indices are according to previous studies [39].
for excitation wavelength λex = 370 nm.
for excitation wavelength λex = 310 nm.
for excitation wavelength λex = 254 nm.
2.3. RNA Extraction and Pyrosequencing
Bacterial RNA was extracted from colloids via a RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Venlo, The Netherlands) and was reversely transcribed into DNA via TB Green Premix Ex Taq II (Takara, San Jose, CA, USA) for the following sequencing. Living bacterial community compositions were assessed by the high-throughput sequencing technology. Primers, used for amplification of the 16S rRNA gene, were the 341F (5′-CCTAYGGGRBGCASCAG-3′) and 806 R (5′-GGACTACNNGGGTATCTAAT-3′). Amplification and sequencing were accomplished by Illumina MiSeq Sequencing [40]. All sequences were checked if the length was longer than 200 bp or the quality score was >75. After quality filtration, operational taxonomic units were clustered with a 97% similarity [41]. The high-quality sequences were aligned using the SILVA database. The samples were rarefied to the same sequence depth to remove heterogeneity based on the least number of sequences for further analysis. The raw data of sequencing were deposited in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive database (PRJNA1036047).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Diversity indices were calculated by SPSS 25.0 to describe the richness and evenness of species in the community. Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) was conducted using R.4.3.2 to calculate the differences in microbial communities. The dissimilarity of microbial functions among groups was conducted via the statistical analysis of metagenomic profiles with Welch’s t-test. The relationship between microbial community and environmental factors was measured via the Mantel test with the “vegan” package in R.4.3.2. PICRUST2 and KEGG were used to predict the abundance of genes [42]. The SEM model was constructed in Amos v.22 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA).
2.5. Quantifying the Community Assembly Process
To further reveal the ecological processes of microbial communities, Stegen’s null model approach was structured and the beta nearest taxon index (βNTI) and the Bray–Curtis based RaupCrick metric (RC-bray) were calculated by using “ape”, “vegan”, and “picante” packages [43]. The model divided the community into five main ecological processes, namely heterogeneous selection, homogeneous selection, homogeneous dispersal, dispersal limitation, and ecological drift. Among them, heterogeneous selection (βNTI > 2) and homogeneous selection (βNTI < −2) were referred to as deterministic processes. Homogeneous dispersal (|βNTI| < 2 and −2 < RC-bray < −0.95), dispersal limitation (|βNTI| < 2 and 0.95 < RC-bray < 2), and ecological drift (|βNTI| < 2 and −0.95 < RC-bray < 0.95) were referred to stochastic processes.
3. Results
3.1. Occurrence Characteristics of LMW Colloids under Different Turbidity Conditions
In this study, some occurrence characteristics of LMW colloids, including the COC content, COM components, zeta potential, functional groups, and nitrogen content, were analyzed. Considering the relatively low proportion of inorganic components in aquatic colloids of rivers [16], this study mainly focused on the organic matter of aquatic colloids. In this study, the concentration of COC presented the largest correlation with turbidity, followed by total nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen. The result indicated that colloids should be one of the dominant contributors to the turbidity of slow-flowing city rivers (p < 0.05, R2 = 0.48) (Figures S2 and S3). Therefore, in order to investigate the properties of colloids under different turbidity conditions, samples were divided into three turbidity gradients, namely low turbidity (LT, <10 NTU), medium turbidity (MT, 10~30 NTU), and high turbidity (HT, >30 NTU) (Figure 1) for the following analysis of colloids in this study.
In this study, the concentration of COC was an average of 219 μmol/L, with the highest value of 251 μmol/L under the high turbidity condition (Figure 2a). Zeta potential analysis found that the zeta potential of colloids in the LT group was averagely −8.5 mV, whereas it was −10 mV in the HT group and −11 mV in the MT group (Figure 2b). In addition, the proportion of COC in DOC (<1 μm) was 33~38% (Figure 2c). Among them, the proportions of COC in DOC were 33%, 36%, and 38% under low turbidity, medium turbidity, and high turbidity conditions, respectively.
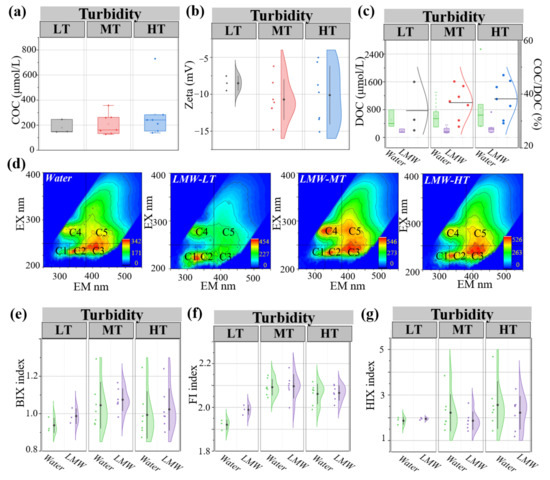
Figure 2.
Composition characteristics of LMW colloidal organic matter under different turbidity conditions. The concentration of colloidal organic carbon (a), the zeta potentials (b), and the proportion in dissolved organic carbon (c) were compared between bulk water and LMW colloids. Three-dimensional fluorescence spectra (d) were compared among bulk water and LMW colloids. FI index (e), BIX index (f), and HIX index (g) were calculated for bulk water and LMW colloids. LT, MT, and HT represent low turbidity, medium turbidity, and high turbidity, respectively. Water represents bulk water (<1 μm). LMW represents LMW colloids.
The components of COM in this study were measured using the fluorescence region intensity method (Figure 2d). The three-dimensional fluorescence spectrum was divided into five integral regions to characterize aromatic protein substances, other aromatic protein subclasses, fulvic acid-like substances, soluble microbial metabolites, and humic acid-like substances separately [44,45,46]. Compared to the low turbidity colloids, medium and high turbidity colloids presented more fulvic and humic acid-like substances, and medium turbidity colloids contained the highest soluble microbial metabolites. FI, BIX, and HIX indices were calculated to trace the source of COM (Figure 2e–g). Among them, the FI index was measured to trace the source, the BIX index was calculated to reflect the activity of biological origin, and the HIX index was used for estimating the maturity level of organic matter [39,47]. Medium turbidity colloids displayed the highest FI and BIX values (2.00 and 1.08) and the lowest HIX value (1.8), followed by the high turbidity group with values of 1.92, 1.02, and 2.25, respectively.
Colloids usually act as the sink of aquatic nitrogen and phosphorus [48]. In this study, the concentrations and proportions of colloidal nitrogen and phosphorus under different turbidity gradients were shown in Figure 3a–f. Compared to the relatively lower proportions of colloidal inorganic phosphorus and total phosphorus in bulk water phosphorus (10–20%), the proportions of ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogen both were as high as 40–60%. Specifically, medium turbid bulk water displayed the highest proportion of colloidal ammonia nitrogen (60%), followed by low (50%) and high (40%) turbid bulk water.
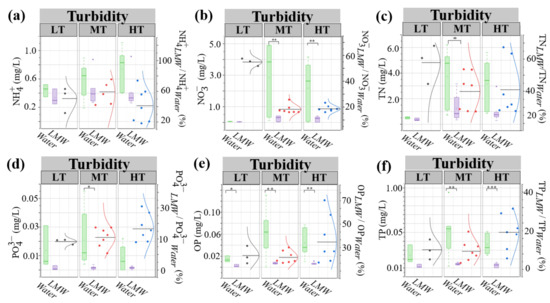
Figure 3.
Physicochemical characteristics of LMW colloids under different turbidity conditions. The concentrations of individual nitrogen and phosphorus forms in LMW colloids were displayed (a–f). Significance levels are indicated as follows: ***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01; *, and p < 0.05. LT, MT, and HT represent low turbidity, medium turbidity, and high turbidity, respectively. Water represents bulk water (<1 μm). LMW represents LMW colloids.
To understand the enrichment process of ammonia nitrogen in colloids, the functional groups of colloids were measured via infrared spectrums (Figure 4a,b). Four functional groups, surface hydroxyl (3470 cm−1, Peak A), carboxyl groups (1650 cm−1, Peak B) [49], ester groups (1406 cm−1, Peak C) [50], and carbon–carbon bonds (1136 cm−1, Peak D), were shared among colloidal samples. Among them, medium turbidity colloids contained the highest intensity of ester groups, whereas the high turbidity colloids contained the highest intensity of carbon–carbon bonds. To explore the functional groups that can absorb ammonia nitrogen, we fitted a curve between the strength of functional groups and the concentration of colloidal ammonia nitrogen. It was found that the strength of ester groups was positively correlated with colloidal ammonia nitrogen (p < 0.05, Figure 4c).
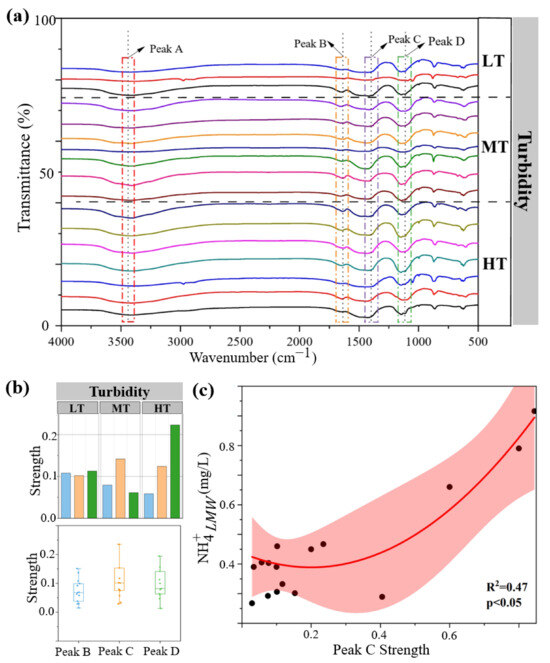
Figure 4.
Infrared spectrums of four functional groups in LMW colloids (a). The strength of three functional groups in LMW colloids was measured via infrared spectrums (b). Correlation between LMW colloidal ammonia nitrogen and functional groups (c). LT, MT, and HT represent low turbidity, medium turbidity, and high turbidity, respectively.
3.2. Composition and Function Characteristics of Active Bacterial Communities Colonized in Colloids
The living bacterial communities colonized in colloids were detected via the RNA extraction method. Shannon index showed that the bacterial diversity of all samples was highest in medium turbidity, followed by high and low turbidities in sequence (Figure 5a). Shannon and Pielou indices of bulk water and HMW colloids were similar but higher than those of LMW colloids (Figure 5b). Among the three turbidity conditions of colloids, medium turbidity colloids displayed the highest diversity, followed by high and low turbidity in sequence. NMDS analysis based on bacterial community compositions revealed that samples from bulk water and LMW colloids formed distinct clusters under three turbidities, respectively (Figure 5c–e). In particular, the lowest stress value (0.0995) was found in medium turbidity conditions. However, the samples from HMW colloids could not be clearly separated from either bulk water or LMW colloids, indicating the similarity of the bacterial community composition of HMW colloids with the other two groups.
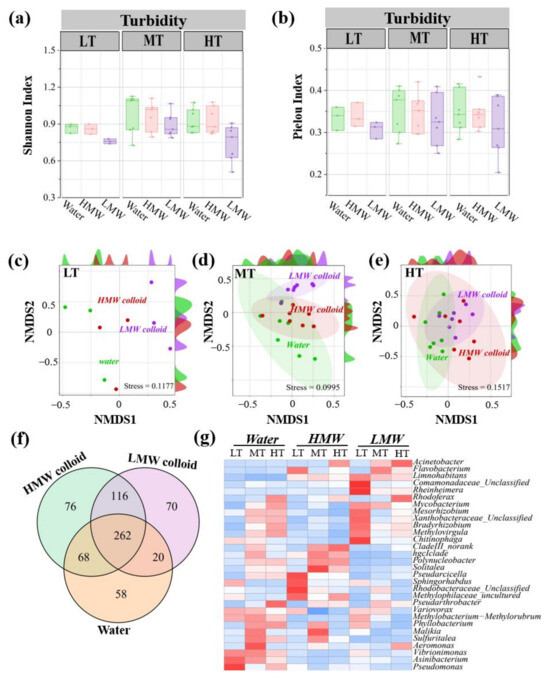
Figure 5.
Diversity and composition of bacterial communities in HMW colloid and LMW colloids under three turbidity conditions. Shannon index (a), Pielou index (b), and non–metric multidimensional scaling graphs of bacterial communities of colloids in low, medium, and high turbidity groups (c–e). Venn graph of bacterial OTUs among water, HMW, and LMW colloids. Microbial aggregation in bulk water, HMW, and LMW colloids (f). Heatmaps of the top 30 abundance bacterial genera in bulk water, HMW, and LMW colloids (g). LT, MT, and HT represent low, medium, and high turbidity, respectively. HMW and LMW represent high and low modular weight colloids, respectively. Water represents bulk water (<1 μm).
The difference in bacterial community compositions in the genus level among three habitats was further explored via Venn and heatmap methods (Figure 5f,g). For the top abundance genera, the bacterial composition of HMW colloids and bulk water was similar, while LMW colloids were far from the first two groups. Flavobacterium, Acinetobacter, Limnohabitans, Chitinophaga, Rheinheimera, Cormamonadaceae, and Rhodobacteraceae, accounted for a dominant proportion of the bacterial community from LMW colloids but existed as rare components in HMW colloids and bulk water. Though the dominant genera of LMW colloids were different under three turbidity conditions, Limnohabitans was shared by three turbidities and Flavobacterium and Acinetobacter were shared by medium and high turbidity conditions.
The βNTI and RC-bray were calculated to identify the bacterial community ecological processes of bulk water and colloids in three states based on the null model. This study found that stochastic processes dominated the bacterial community assembly of bulk water and colloids (Figure 6a). Notably, ecological drift had the greatest effect on the microbial community of bulk water and colloids. Dispersal limitation was another basic process affecting the microbial communities of bulk water and colloids. Different from bulk water, homogeneous selection was the third key influence process on the microbial communities of colloids. Compared with LMW colloids, the homogeneous selection had a greater proportion in HMW colloids.
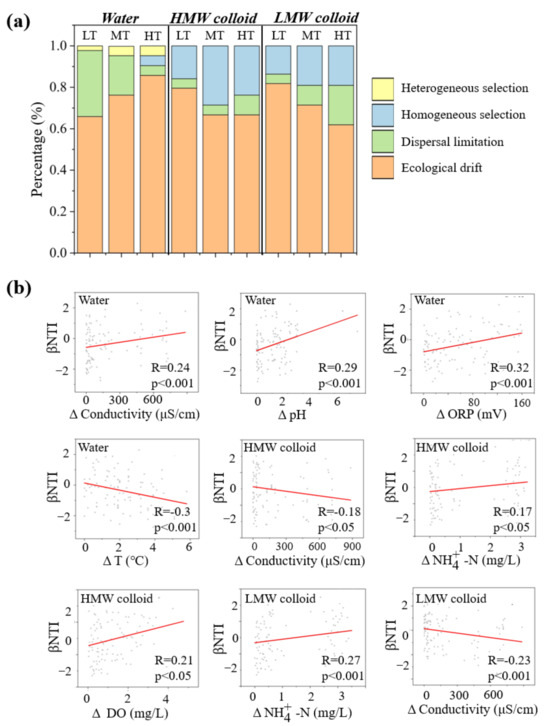
Figure 6.
Assembly mechanism of bacterial community of bulk water, HMW, and LMW colloids. The deterministic and stochastic processes were calculated based on the null model (a). Correlations between βNTI and individual environmental factors were fitted via linear regressions (b). LT, MT, and HT represent low, medium, and high turbidity, respectively. HMW and LMW represent high and low modular weight colloids, respectively. Water represents bulk water (<1 μm).
Moreover, colloids under medium turbidity showed the highest proportion of homogeneous selection, followed by high and low turbidities in sequence. To further analyze the role of environmental factors in community assembly, linear regression analysis was calculated between the bacterial βNTI value and environmental variables. In bulk water, the bacterial βNTI value was notably correlated with the changes in ORP, temperature, pH, and conductivity (p < 0.001). In colloids, the determined process was significantly correlated with the changes in DO, conductivity, and ammonia nitrogen (p < 0.001) (Figure 6b).
3.3. Characteristics of Nitrogen Transformation Function
PICRUST analysis has been used as a valuable tool for predicting the potential functional characteristics of the microbial community in different environments, such as ponds [51], tidal mudflats [52], and rivers [53]. Our results showed that microbes of colloids have significantly greater nitrogen metabolism and carbon fixation than that of bulk water (Figure 7a). Moreover, colloidal bacteria have stronger functions of degrading organic matter (Figure 7b). Nitrogen transformation processes of colloidal microbes are shown in Figure 7c. The abundances of nrfA, norC, and nirK were generally higher in colloids than those in bulk water. Compared to amoA (ammonia-oxidizing process), the abundances of nirK and norC in colloids arrived at higher levels than that in bulk water, demonstrating that colloidal bacteria have a greater denitrification potential. In addition, the high abundance of nrfA demonstrated that the process of dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA) was the major nitrogen transformation in colloidal microbes. Our results indicated should promote the enrichment of ammonia nitrogen in colloids.
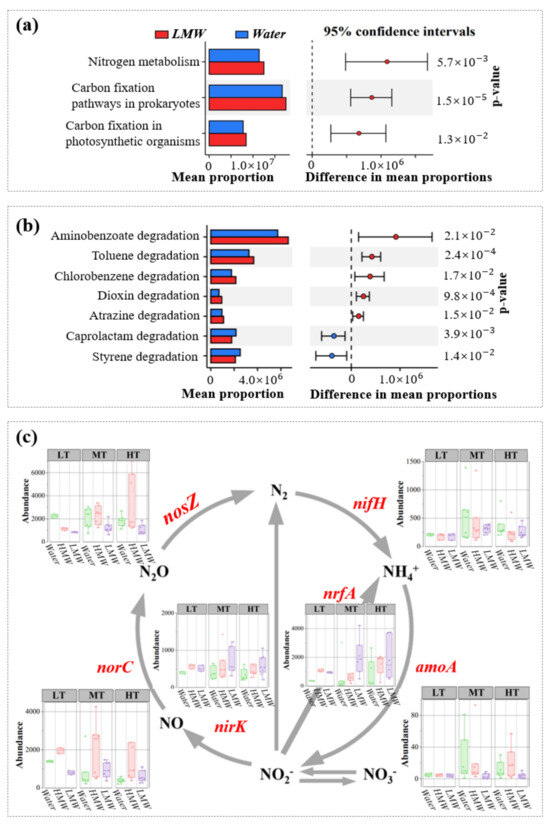
Figure 7.
Functional characteristics of bacterial communities of colloids. The difference in total metabolism functions (a) and carbon metabolism functions (b) between water and colloids were tested separately via STAMP. The abundance of genes involved in nitrogen transformation was compared among water and HMW and LMW colloids under three turbidity gradients (c). HMW and LMW represent high and low modular weight colloids, respectively. Water represents bulk water (<1 μm).
4. Discussion
4.1. Occurrence Characteristics of LMW Colloids under Different Turbidity Conditions
In this study, the concentration of COC was much higher than that in most lakes (approximately 150–170 μmol/L) and big rivers, such as Yellow River (186.8 μmol/L) and Yangtze River (197.8 μmol/L) [54]. In addition, the proportion of COC was higher than the results of COC in seawater with similar size ranges in the same season [21]. In all, the content of COC in urban rivers in this study was much higher than that reported in lakes and large rivers. The higher content of COC in urban rivers was consistent with the previous findings of higher tryptophan-like fluorescence (the main contributor of COC) in urban rivers [15]. Moreover, zeta potential analysis found that the colloids in medium and high turbidity groups presented a higher stability than that in the low turbidity group, which was consistent with the increased proportion of COC in DOC from the low to high turbidities. These results further supported the findings that the stability of colloidal particles contributed to the turbidity in the water column [11].
Our study found that medium and high turbidity colloids presented more fulvic and humic acid-like substances and medium turbidity colloids contained the highest soluble microbial metabolites. These results confirmed that the influence of colloids on turbidity partly came from the humic-like materials of colloids [55]. In addition, high BIX and FI index of colloids in medium and high turbidity groups indicated that COM in these groups primarily came from endogenous release of microbes [56] but the low turbidity colloids mainly came from both land runoff and endogenous release. These results implied that colloids in the medium and high groups could be the hotpots of microbial growth and metabolism, which might be supported by abundant nutrients. Hence, the characteristics of bacterial communities of colloids were explored subsequently.
The high proportion of colloidal ammonia nitrogen suggested that ammonia nitrogen in bulk water of urban rivers primarily existed in colloidal states. This was supported by previous observations that colloids can enrich ammonia nitrogen and act as carriers to affect their migration in groundwater [57,58]. It was noted that as the decline of the bulk ammonia nitrogen concentration in surface water from high to low turbidity, the concentration of colloidal ammonia nitrogen did not vary obviously and medium turbid water displayed the highest proportion of colloidal ammonia nitrogen (60%). The results may demonstrate the stronger stability of ammonia nitrogen in colloids, especially under medium turbidity, which may hamper the reduction and remediation process of bulk ammonia nitrogen in rivers.
Medium turbidity colloids contained the highest intensity of ester groups, which supported their highest BIX value and biodegradation from the sights of biodegradation. The high turbidity colloids contained the highest intensity of carbon–carbon bonds, which suggested the enrichment of inactive carbon in colloids under high turbidity conditions. Due to the large specific surface area, colloids contain massive adsorption sites for various contaminants. Electrostatic interactions, complexation, and ligand exchange are three possible absorption approaches of colloids [6,59]. Our findings showed that the surface of colloids mostly presented a deprotonation state with a pH of 6.5–9 across all samples (Figure S4), thus colloids with negative charges were prone to adsorb ammonia nitrogen with positive charge [60]. Ester groups of colloids can be complex with ammonia nitrogen in bulk water [61]. Moreover, Figure 4c shows that the strength of ester groups was positively correlated with colloidal ammonia nitrogen (p < 0.05). Therefore, the two mechanisms may be responsible for the enrichment of ammonia nitrogen in colloids. Furthermore, the intensity of colloidal ester groups was at maximum value under the medium turbidity condition, indicating that colloids in medium turbidity have the maximum capacity to adsorb ammonia nitrogen in bulk water from the perspective of functional groups.
4.2. Characteristics of Filterable Bacteria in Colloids
This study found that Limnohabitans, Flavobacterium, and Acinetobacter were the unique and dominant genera of LMW colloids. Limnohabitans has a prominent role in freshwater bacterioplankton communities due to high rates of substrate uptake and growth on algal-derived organic substances, which could provide an important substrate source for it [62]. Given the colloidal primary source might be algal-derived, colloids should also be an important habitat for Limnohabitans in urban rivers. In addition, it was indicated that Limnohabitans has relatively high metabolic diversity and potential for fixing CO2 [63]. Therefore, we speculated that the presence of Limnohabitans in the LMW colloids may have a great impact on the metabolism of the colloidal microbial community. Flavobacterium was associated with the degradation of complex organic compounds [64], which can be supported by the high concentrations of COC in colloids. Moreover, few previous pieces of research have found that Acinetobacter carried a number of antibiotic resistance genes in wastewater [65], which was in agreement with the colloidal adsorption of antibiotics [66]. Flavobacterium and Acinetobacter have been found to be the dominant genus for treating ammonia nitrogen in wastewater [67,68]. Then, the enriched ammonia nitrogen in colloids might be a suitable habitat for the two bacterial genera.
In this study, some active bacteria were indeed obtained in LMW colloids (30 kDa–0.2 μm), which opened a new insight into the occurrence of bacteria in colloids. According to the culturable bacteria, most bacterial size ranges from 0.22–2 μm in diameter, thus 0.22 μm-cutoff was generally used to separate bacterial cells from dissolved matter [69]. However, cultured bacteria only account for a small proportion of all the bacteria on the earth; thus, the occurrence characteristics of bacteria smaller than 0.22 μm have not been well unknown. Indeed, studies have reported the presence of bacteria smaller than 0.22 μm, for example, Wu el. reported that α- and γ-Proteobacteria were exclusively found in the 0.22 μm cell size [70]. In addition, filterable bacterial cells were active and metabolically active [71]. Wang el. found that filterable bacteria had the shape-dependent selection during the filtration process and that thin and long filterable bacteria can pass through the filter membrane, which explained the existence of Limnohabitans, Flavobacterium, and Acinetobacter in LMW colloids. We also speculated several potential reasons. On the one hand, the cell sizes of bacteria could vary temporally with the environmental conditions. Are there some environmental conditions limiting the growth of the several top-abundance genera in LMW colloids? The question needs to be further explored in the future. On the other hand, there may be some deviation in the pore size of the regenerated cellulose membranes. The obtained bacteria in LMW colloids might be very close to the threshold cutoff of 0.2 μm in this study; then, more gradients of the colloidal size among 30 kDa–0.2 μm should be further studied. In all, the occurrence of bacteria in LMW colloids needs to be studied in many more types of waters.
The results of βNTI and RC-bray found that stochastic processes dominated the community assembly of bulk water and colloids, which was similar to other studies about urban rivers in autumn [72]. Moreover, the highest proportion of ecological drift on the microbial community of bulk water and colloids was consistent with a previous finding in urban rivers [73]. In addition, colloids, as interfaces of frequent material exchange, suffered from kinds of environmental disturbance, which may also explain the relatively high contribution of ecological drift to the community of colloids. Homogeneous selection was considered to be a dominant factor in the stable state after environmental disturbance [74]. This could be supported by the stable cluster of colloidal samples based on their bacterial compositions. Compared with LMW colloids, homogeneous selection had a greater proportion in HMW colloids, similar to previous research about biofilm [75], which found that the relative importance of environmental selection increased with increasing floc size of the source sludge.
In addition, the sequence of homogeneous selection of colloids under different turbidity conditions was consistent with the components of colloids under three turbidity conditions. This result illustrated that the characteristics of autogenous organic substances in colloids might support the homogeneous selection of their colonized microbes. Linear regression analysis indicated that the enriched ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogen should participate in the homogeneous selection of their colonized microbes.
4.3. Enrichment of Ammonia Nitrogen in Colloids
Our results showed that colloidal bacteria have stronger functions of degrading organic matter, consistent with the finding that high concentrations of organic pollutants have been detected in colloids [76]. In addition, our results indicated that DNRA should promote the enrichment of ammonia nitrogen in colloids. The significant rise of nrfA in medium turbidity colloids might also correspond to the higher enrichment of ammonia nitrogen in medium turbidity.
As a whole, this study confirmed that the enrichment of colloidal ammonia nitrogen mainly came from two aspects (Figure 8). On the one hand, colloids contained large amounts of organic matter, the ester groups of which adsorbed ammonia nitrogen from surrounding water. On the other hand, the DNRA process driven by colloidal microorganisms promoted the enrichment of ammonia nitrogen under medium to high turbidity conditions. In all, the high concentrations of colloidal ammonia nitrogen were determined by the occurrence of COM and DNRA of colloidal microbes under medium or high turbidity conditions.
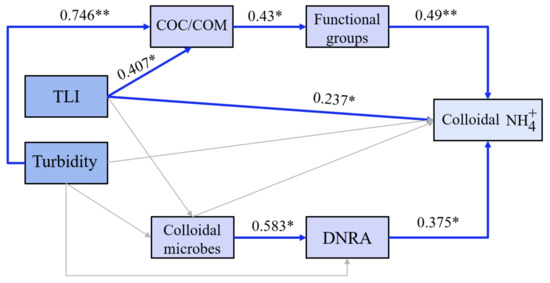
Figure 8.
Pathway diagram for the enrichment of colloidal ammonia nitrogen. The arrows indicated the correlations between variables. Among them, blue represents a significantly positive correlation; gray represents non-significance. Significance levels are indicated as follows: **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05.
In this study, it was noteworthy that the colloids in medium turbidity rivers (10~30 NTU) accounted for the highest ammonia nitrogen of bulk water (average 50%), which should be mainly enriched by two pathways. The first is the absorption by ester groups of colloids, the other is the process of dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium by bacteria colonizing on colloids. Anyway, the enrichment of ammonia nitrogen in colloids under medium turbidity conditions restrained its removal from bulk water. Therefore, the removal of colloids should be extensively considered in the remediation process of slow-flowing urban rivers. In addition, colloids should also be included as a variable in the estimation of nitrogen models for urban rivers. Besides, only two colloidal fractions of 0.2–1 μm and 30 kDa–0.2 μm were obtained but the smaller colloids of 1–30 kDa should be considered in the future, which was suggested to account for dominant COC. Our results have some limitations on the prediction of functional genes via PICRUST2; in order to further accurately explore the role of colloidal microorganisms in nitrogen transformation, quantitative research of metagenes should be combined in future research.
5. Conclusions
In this study, it was found that colloids play an important role in urban rivers because of their high contents of organic carbon (33%~38%) and ammonia nitrogen (40–60%), especially in medium turbidity, where the proportions of COC and colloidal ammonia nitrogen arrived at 36% and 60%, respectively. The concentration of colloids presented the significantly highest correlation with turbidity, suggesting that colloids were indeed one of the important components of river turbidity. There are some filterable bacteria in LMW colloids, among them, Limnohabitans, Flavobacterium, and Acinetobacter were the unique and dominant genera. There were significant differences in microbial composition and diversity between LMW-colloids and bulk water, especially in medium turbidity rivers. The stronger homogeneous selection process of colloids might explain the unique enrichment of dominant bacterial genera in colloids. Moreover, microbes of colloids presented significantly greater nitrogen metabolism and carbon fixation potentials than those of bulk water. The bacterial processes of dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium might promote the enrichment of ammonia nitrogen in colloids. We suggest that colloids and colloidal microbes should be given much more attention in future studies for the occurrence, migration, and transformation mechanisms of different pollutants in turbid rivers and lakes.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w16071024/s1, Figure S1: Fitting curve between different cfs and concentrations of organic carbon in ultrafiltrate. Figure S2: Fitting curve between concentrations of colloidal organic carbon and turbidity of river. Figure S3: Fitting curve between concentrations of colloidal organic carbon and colloidal ammonia nitrogen. Figure S4: pH of three turbidity conditions. Table S1: Physical and chemical indices of overlying water in situ.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.N. and Y.L.; Funding acquisition, Y.L.; Methodology, L.N. and R.C.; Software, R.C. and Y.C.; Validation, Y.C. and W.Z.; Visualization, Y.L., H.Z. and L.W.; Writing—original draft, R.C.; Writing—review and editing, L.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 52170158), Open project funding of key laboratory of intelligent health perception and ecological restoration of rivers and lakes (HGKFYB16), PAPD, and the Six Talent Peaks Project in Jiangsu Province (2016-JNHB-007).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhang, L.Q.; Xu, Y.J.; Li, S.Y. Riverine dissolved organic matter (DOM) as affected by urbanization gradient. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobler, C.J. Climate Change and Harmful Algal Blooms: Insights and perspective. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karathanasis, A.D.; Johnson, D.M.C. Stability and transportability of biosolid colloids through undisturbed soil monoliths. Geoderma 2006, 130, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.L.; Zhou, K. Adsorption of three selected endocrine disrupting chemicals by aquatic colloids and sediments in single and binary systems. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, M.K.; Garnier, J.M. Distribution of trace elements associated with dissolved compounds (<0.45 μm–1 nm) in freshwater using coupled (frontal cascade) ultrafiltration and chromatographic separations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.C.; Ji, L.; Kong, M.; Jiang, H.L.; Chen, J. Molecular weight-dependent adsorption fractionation of natural organic matter on ferrihydrite colloids in aquatic environment. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 363, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebka, K.; Beldowska, M.; Saniewska, D.; Korejwo, E.; Saniewski, M. Meteorological phenomenon as a key factor controlling variability of labile particulate mercury in rivers and its inflow into coastal zone of the sea. Environ. Res. 2020, 184, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.L.; Shi, M.; Wang, L.Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.L.; Niu, L.H.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, L.F. New insights into nitrogen removal potential in urban river by revealing the importance of microbial community succession on suspended particulate matter. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.Q.; Li, R.; Han, D.; Scholz, M. Response of Eutrophication Development to Variations in Nutrients and Hydrological Regime: A Case Study in the Changjiang River (Yangtze) Basin. Water 2020, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.L.; Zhou, P.C.; Pan, S.Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, L.; Niu, L.H.; Wang, L.F.; Zhang, H.J. The role of microbial communities on primary producers in aquatic ecosystems: Implications in turbidity stress resistance. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.C.; Xu, M.W.; Li, Y.N.; Liu, X.; Guo, L.D.; Jiang, H.L. Characterization, origin and aggregation behavior of colloids in eutrophic shallow lake. Water Res. 2018, 142, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudmundsson, L.; Boulange, J.; Do, H.X.; Gosling, S.N.; Grillakis, M.G.; Koutroulis, A.G.; Leonard, M.; Liu, J.G.; Schmied, H.M.; Papadimitriou, L.; et al. Globally observed trends in mean and extreme river flow attributed to climate change. Science 2021, 371, 1159–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dethier, E.N.; Renshaw, C.E.; Magilligan, F.J. Rapid changes to global river suspended sediment flux by humans. Science 2022, 376, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.K. A review on the adsorption of heavy metals by clay minerals, with special focus on the past decade. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 438–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.X.; Lead, J.R.; Baker, A. Fluorescence characterization of cross flow ultrafiltration derived freshwater colloidal and dissolved organic matter. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, K.A.; Santschi, P.H.; Leppard, G.G.; West, M.M. Characterization of organic-rich colloids from surface and ground waters at the actinide-contaminated Rocky Flats Environmental Technology Site (RFETS), Colorado, USA. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2004, 244, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilding, A.; Liu, R.X.; Zhou, J.L. Dynamic behaviour of river colloidal and dissolved organic matter through cross-flow ultrafiltration system. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 287, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.D.; Santschi, P.H. Composition and cycling of colloids in marine environments. Rev. Geophys. 1997, 35, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.C.; Houghton, E.M.; Houghton, C.J.; Guo, L.D. Variations in size and composition of colloidal organic matter in a negative freshwater estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Sun, X.; Luo, Z.; Chi, Q.; Zhu, G. Analysis of colloidal organic carbon content and its influencing factors in the waters of Taihu Lake in spring. China Environ. Sci. 2006, 26, 166–170. [Google Scholar]
- Klun, K.; Sket, P.; Falnoga, I.; Faganeli, J. Variation in Colloidal Organic Matter Composition and Aggregation in Coastal Waters (Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea). Geomicrobiol. J. 2015, 32, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolpe, B.; Guo, L.D.; Shiller, A.M.; Hassellöv, M. Size and composition of colloidal organic matter and trace elements in the Mississippi River, Pearl River and the northern Gulf of Mexico, as characterized by flow field-flow fractionation. Mar. Chem. 2010, 118, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judy, J.D.; Kirby, J.K.; Farrell, M.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Wilkinson, S.N.; Bartley, R.; Bertsch, P.M. Colloidal nitrogen is an important and highly-mobile form of nitrogen discharging into the Great Barrier Reef lagoon. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baken, S.; Moens, C.; van der Grift, B.; Smolders, E. Phosphate binding by natural iron-rich colloids in streams. Water Res. 2016, 98, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Lin, H.; Bartlett, S.L.; Houghton, E.M.; Robertson, D.M.; Guo, L.D. Partitioning and transformation of organic and inorganic phosphorus among dissolved, colloidal and particulate phases in a hypereutrophic freshwater estuary. Water Res. 2021, 196, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.J.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, T.T.; Chen, J.Y.; Wei, Q.Q.; Chen, W.F.; Zhou, Y.M.; Qi, Z.C. Colloid-mediated transport of tetracycline in saturated porous media: Comparison between ferrihydrite and montmorillonite. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Li, Y. Effects of colloids on ammonia nitrogen release under different ion conditions in natural sediments of Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 41455–41466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.C.; Guo, L.D. Molecular size-dependent abundance and composition of dissolved organic matter in river, lake and sea waters. Water Res. 2017, 117, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.L.; Wang, H.L.; Li, Y.; Lin, L.; Hui, C.Z.; Gao, Y.; Niu, L.H.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, L.F.; Wang, P.F.; et al. Bend-induced sediment redistribution regulates deterministic processes and stimulates microbial nitrogen removal in coarse sediment regions of river. Water Res. 2020, 170, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, L.; Thamdrup, B.; Trimmer, M. Coupled nitrification and N2 gas production as a cryptic process in oxic riverbeds. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guéguen, C.; Belin, C.; Dominik, J. Organic colloid separation in contrasting aquatic environments with tangential flow filtration. Water Res. 2002, 36, 1677–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Gao, L.; Guo, L.D. Seasonal Variations in Molecular Size of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter from Tile Lower Changjiang (Yangtze) River. J. Geophys. Res.-Biogeosci. 2021, 126, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belzile, C.; Guo, L.D. Optical properties of low molecular weight and colloidal organic matter: Application of the ultrafiltration permeation model to DOM absorption and fluorescence. Mar. Chem. 2006, 98, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.M.; Liu, H.J.; Qu, J.H.; Berg, M.; Qi, W.X.; Xu, W. The influence of colloids on the geochemical behavior of metals in polluted water using as an example Yongdingxin River, Tianjin, China. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.H.; Buesseler, K.O.; Ripple, P.; Andrews, J.; Belastock, R.A.; Gustafsson, O.; Moran, S.B. Evaluation of two cross-flow ultrafiltration membranes for isolating marine organic colloids. Mar. Chem. 1998, 62, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutter, M.I.; Langan, S.J.; Lumsdon, D.G.; Clark, L.M. Multi-element signatures of stream sediments and sources under moderate to low flow conditions. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix characterization of some sewage-impacted rivers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.; Inverarity, R.; Charlton, M.; Richmond, S. Detecting river pollution using fluorescence spectrophotometry: Case studies from the Ouseburn, NE England. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 124, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKnight, D.M.; Boyer, E.W.; Westerhoff, P.K.; Doran, P.T.; Kulbe, T.; Andersen, D.T. Spectrofluorometric characterization of dissolved organic matter for indication of precursor organic material and aromaticity. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. Isme J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richa, K.; Balestra, C.; Piredda, R.; Benes, V.; Borra, M.; Passarelli, A.; Margiotta, F.; Saggiomo, M.; Biffali, E.; Sanges, R.; et al. Distribution, Community Composition, and Potential Metabolic Activity of Bacterioplankton in an Urbanized Mediterranean Sea Coastal Zone. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.J.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Konopka, A.E. Estimating and mapping ecological processes influencing microbial community assembly. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Westerhoff, P.; Leenheer, J.A.; Booksh, K. Fluorescence excitation—Emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5701–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.J.; Cao, B.D.; Wang, D.S.; Ma, T.; Xia, H.; Yu, D.H. Influence of wastewater sludge treatment using combined peroxyacetic acid oxidation and inorganic coagulants re-flocculation on characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). Water Res. 2016, 88, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ifon, B.E.; Adyari, B.; Hou, L.Y.; Zhang, L.P.; Liao, X.; Peter, P.O.; Rashid, A.; Yu, C.P.; Hu, A.Y. Insight into variation and controlling factors of dissolved organic matter between urban rivers undergoing different anthropogenic influences. J. Environ. Manage. 2023, 326, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salve, P.R.; Lohkare, H.; Gobre, T.; Bodhe, G.; Krupadam, R.J.; Ramteke, D.S.; Wate, S.R. Characterization of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) in Rainwater Using Fluorescence Spectrophotometry. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 88, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.N.; Grybos, M.; Rabiet, M.; Deluchat, V. How do colloid separation and sediment storage methods affect water-mobilizable colloids and phosphorus? An insight into dam reservoir sediment. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 606, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.T.; Ge, X.; Ye, X.X.; Wang, G.Z.; Zhang, H.M.; Zhou, H.J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhao, H.J. 3D graphene/delta-MnO2 aerogels for highly efficient and reversible removal of heavy metal ions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 1970–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soong, J.L.; Calderon, F.J.; Betzen, J.; Cotrufo, M.F. Quantification and FTIR characterization of dissolved organic carbon and total dissolved nitrogen leached from litter: A comparison of methods across litter types. Plant Soil 2014, 385, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Xie, F.X.; Zhang, F.F.; Zhou, K.; Sun, H.B.; Zhao, Y.J.; Yang, Q. Analysis of bacterial community functional diversity in late-stage shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) ponds using Biolog EcoPlates and PICRUSt2. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.H.; Xie, X.D.; Li, Y.; Hu, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.L.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, L.F. Effects of nitrogen on the longitudinal and vertical patterns of the composition and potential function of bacterial and archaeal communities in the tidal mudflats. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, W.L.; Lin, L.; Wang, L.F.; Niu, L.H.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, P.F.; Wang, C. Response of bacterial community in composition and function to the various DOM at river confluences in the urban area. Water Res. 2020, 169, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.T. Colloidal organic carbon in Huanghe, Changjiang and Qiantang River. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1998, 43, 915–917. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.J.; Hur, J.; Toorman, E.A. Seasonal Variation in Flocculation Potential of River Water: Roles of the Organic Matter Pool. Water 2017, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, R.; Boyer, J.N.; Lu, X.; Maie, N.; Yang, C.; Scully, N.M.; Mock, S. Source characterization of dissolved organic matter in a subtropical mangrove-dominated estuary by fluorescence analysis. Mar. Chem. 2004, 84, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, H.; Chen, j.; Li, Y. Effect of natural colloid on ammonia nitrogen transport in different acidic and basic environment. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2014, 41, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, W.; Hai-ming, L.I.; Xiao-yu, J.I.A.; Jin-lan, W.U. Effect of Natural Colloid on Ammonia Nitrogen Transport in Water-bearing Media. Enuivon. Sci. Technol. 2009, 32, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.B.; Liu, H.J.; Zhao, X.; Jefferson, W.; Cheng, F.; Qu, J.H. Phosphate removal from water using freshly formed Fe-Mn binary oxide: Adsorption behaviors and mechanisms. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 455, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.H.; Mehlhorn, T.L.; Liang, L.Y.; McCarthy, J.F. Competitive adsorption, displacement, and transport of organic matter on iron oxide: 1. Competitive adsorption. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Schmitt, J.; Chen, Z.; Liang, L.; McCarthy, J.F. Adsorption and desorption of natural organic matter on iron oxide: Mechanisms and models. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornák, K.; Kasalicky, V.; Simek, K.; Grossart, H.P. Strain-specific consumption and transformation of alga-derived dissolved organic matter by members of the Limnohabitans-C and Polynucleobacter-B clusters of Betaproteobacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 4519–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasalicky, V.; Jezbera, J.; Hahn, M.W.; Simek, K. The Diversity of the Limnohabitans Genus, an Important Group of Freshwater Bacterioplankton, by Characterization of 35 Isolated Strains. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolton, M.; Erlacher, A.; Berg, G.; Cytryn, E. The Flavobacterium Genus in the Plant Holobiont: Ecological, Physiological, and Applicative Insights. In Microbial Models: From Environmental to Industrial Sustainability; Castro-Sowinski, S., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 189–207. [Google Scholar]
- Hubeny, J.; Korzeniewska, E.; Buta-Hubeny, M.; Zielinski, W.; Rolbiecki, D.; Harnisz, M. Characterization of carbapenem resistance in environmental samples and Acinetobacter spp. isolates from wastewater and river water in Poland. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, D.M.; Liu, X.H.; Zhao, S.N.; Cui, B.S.; Bai, J.H.; Li, Z.J. Influence of the natural colloids on the multi-phase distributions of antibiotics in the surface water from the largest lake in North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, M.F.; Zheng, K.K.; Wan, C.L.; Li, J. Promising carbon utilization for nitrogen recovery in low strength wastewater treatment: Ammonia nitrogen assimilation, protein production and microbial community structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.P.; Zhai, T.R.; Zhang, L.J.; Zhao, T.T.; Xing, Z.L.; Liu, H. Domestication and pilot-scale culture of mixed bacteria HY-1 capable of heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 384, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, P.F.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Miao, L.Z.; Yuan, Q.S.; Liu, S.; Feng, T. Do bacterioplankton respond equally to different river regulations? A quantitative study in the single-dammed Yarlung Tsangpo River and the cascade-dammed Lancang River. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.F.; Holmfeldt, K.; Hubalek, V.; Lundin, D.; Åström, M.; Bertilsson, S.; Dopson, M. Microbial metagenomes from three aquifers in the Fennoscandian shield terrestrial deep biosphere reveal metabolic partitioning among populations. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1192–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luef, B.; Frischkorn, K.R.; Wrighton, K.C.; Holman, H.Y.N.; Birarda, G.; Thomas, B.C.; Singh, A.; Williams, K.H.; Siegerist, C.E.; Tringe, S.G.; et al. Diverse uncultivated ultra-small bacterial cells in groundwater. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.X.; Adams, J.M.; Wang, L.F.; Zhang, H.J.; Chu, H.Y. More Robust Co-Occurrence Patterns and Stronger Dispersal Limitations of Bacterial Communities in Wet than Dry Seasons of Riparian Wetlands. mSystems 2023, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.; Fan, T.; Wang, S.; Yu, X.; Lu, A.; Wang, X.; Zhou, W.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, L. Seasonal changes driving shifts in microbial community assembly and species coexistence in an urban river. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini-Andreote, F.; Stegen, J.C.; van Elsas, J.D.; Salles, J.F. Disentangling mechanisms that mediate the balance between stochastic and deterministic processes in microbial succession. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1326–E1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.H.; Zhang, S.Q.; Meng, F.G. Large-sized planktonic bioaggregates possess high biofilm formation potentials: Bacterial succession and assembly in the biofilm metacommunity. Water Res. 2020, 170, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Huang, W.; Yang, J.; Ran, Y.; Chen, D.; Yang, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhan, Y. Occurrence of colloid-bound endocrine-disrupting chemicals in the Pearl River, China. China Environ. Sci. 2015, 35, 617–623. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).