Abstract
Affected by point and non-point source pollution, the Fenhe River Basin faces significant environmental challenges. This study aimed to analyze the distribution characteristics and influencing factors of antibiotics in the water and sediments of the Fenhe River Basin. Samples were collected from 23 sites within the basin, and 26 antibiotics from five different classes were detected and analyzed using high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS). The water–sediment partition coefficient (Kp) was calculated, and spatial analysis was conducted using geographic information system (GIS) technology. The results showed that 25 antibiotics were detected in the water, with concentrations ranging from 130 to 1615 ng/L, and 17 antibiotics were detected in the sediments, with concentrations ranging from 121 to 426 μg/kg. For quinolones (QNs), except for ofloxacin, all others could be calculated with overall high values of Kp ranging from 692 to 16,106 L/kg. The Kp values for QNs were generally higher in the midstream, with considerable point source pollution from industries and non-point source pollution from developed agriculture. The distribution of Kp is closely associated with risk. This study found that the Kp values of the antibiotics were influenced by various factors such as temperature, water flow, and the physicochemical properties of sediments. Correlation analysis revealed significant relationships between Kp and parameters such as river width, water depth, water quality (total nitrogen, total phosphorus, and chemical oxygen demand), and sediment pH and clay content.
1. Introduction
The widespread use of antibiotics has significantly improved quality of life by treating bacterial infections and reducing mortality rates [1]. However, it has also led to pervasive overuse, which poses serious consequences [2,3]. Large quantities of antibiotics enter aquatic environments through sewage treatment plants, surface runoff, and infiltration into groundwater [4,5,6]. Studies have shown that the rivers worldwide are generally polluted by antibiotics, with the highest concentration of 1900 ng/L [7,8]. Researchers have been investigating antibiotics in major river basins in China, such as the Yangtze, Yellow, Huaihe, Haihe, Liaohe, and Zhuhai rivers [9,10,11]. Among them, Haihe’s content was the highest, with an average value as high as 494 µg/L [12,13,14,15]. These antibiotics can persist in watersheds, affecting microbial communities and aquatic organisms [16,17]. Additionally, antibiotics can disrupt ecosystems and enter the human body through the food chain, posing risks to both ecological and human [18]. This highlights the urgent need for sustainable practices to mitigate these risks and protect ecosystems and human health.
Antibiotics in water can enter sediments through adsorption and deposition, where they bind to sediment particles and settle at the bottom [19]. When watershed conditions change, such as during storms, floods, or alterations in water flow, these sediments can resuspend and release pollutants back into surface waters, contributing to ongoing contamination [20]. The interactions between the aqueous and sediment phases play a crucial role in the persistence and stability of pollutants within the watershed, influencing how long and how widely antibiotics can affect the environment [21,22]. To better describe the dynamics of antibiotics in water and sediments, scientists use the partition coefficient (Kp). Studies have shown that the Kp of antibiotics varies greatly, with quinolones as high as 114.2–169,324 L/kg [23,24,25] and macrolides as high as 57.7–11,377 L/kg [25]. By quantifying these interactions, researchers can develop more effective strategies for managing and mitigating antibiotic contamination in aquatic environments.
The partition coefficient (Kp) provides a clearer understanding of the dynamic processes of antibiotics within watersheds, highlighting how these substances distribute between the water and sediment phases [26,27,28]. Influenced by factors such as temperature, water flow, and flow rate, the partition coefficient can exhibit significant variability, resulting in differing migration and accumulation processes [29]. Traditionally, Kp is derived from the octanol–water partition coefficient (Kow), serving as a general predictor of compound behavior [16,30]. However, in specific study areas, Kp is influenced by numerous local factors, such as sediment composition, organic matter content, and seasonal changes, often deviating substantially from ideal conditions. This variability means that Kp can differ greatly across different regions and times. Despite this, current research tends to overlook the spatiotemporal variability of Kp, which is crucial for accurately assessing the environmental impact of antibiotics [24,31]. Addressing this gap in understanding could lead to better management practices for antibiotic pollution in diverse aquatic environments.
Additionally, the partition coefficient is significantly impacted by the physicochemical parameters of sediments, such as grain size, composition, pH, metal content, organic carbon content, nutrient content, and ionic strength [23,32,33]. The physicochemical properties of antibiotics, including molecular weight, hydrophobicity, and functional groups, also play a crucial role [26,33,34]. Some researchers have established linear models of Kp with the physicochemical properties of sediments using regression equations. Others have found that Kp shows a linear relationship with logKow (octanol–water partition coefficient) and molecular weight [33]. However, these models often focus on only a subset of sediment parameters, such as pH, organic carbon, ionic strength, and grain size [35]. In reality, the distribution behavior of antibiotics is influenced not only by the physicochemical properties of sediments but also by the physicochemical factors in the water.
This study, based on measured data of antibiotics in the water and sediments of the Fenhe River Basin, investigated the distribution characteristics of antibiotics within the basin. It analyzed the spatiotemporal variability of the partition coefficient to elucidate the migration pathways and fate of antibiotics in the Fenhe River Basin. Using geographic information system (GIS) spatial analysis techniques, this study examined the spatial variability of the partition coefficient and identified the influencing factors. This study is essential for accurately studying the behavior and fate of antibiotics in basins.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Fenhe River, a primary tributary of the Yellow River, is located in the ecologically fragile region of the Loess Plateau (Figure 1). Originating in Ningwu County in northern Shanxi, it flows through 34 counties and cities across six municipalities, eventually joining the Yellow River in Hejin. The Fenhe River stretches 716 km with a watershed area of 39,741 km2. As the mother river of Shanxi, the Fenhe River not only serves as a major source of drinking water for the region but also receives substantial amounts of industrial and domestic wastewater. Research has shown that antibiotics are widely distributed throughout the Fenhe River Basin.
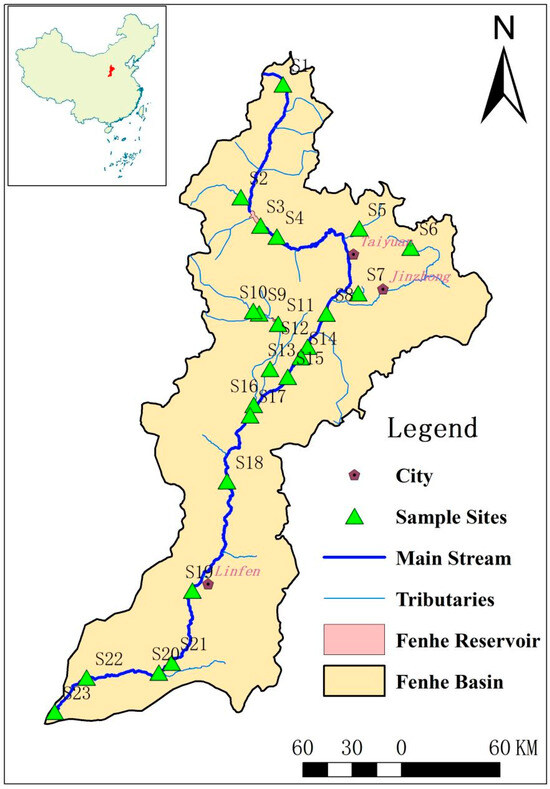
Figure 1.
Locations of the study area and sample sites.
2.2. Sample Collection and Experimental Analysis
Samples were collected from 23 sampling points in the Fenhe River Basin, including the river source, downstream of major cities, reservoirs, and densely populated livestock farming areas, the confluence with the Yellow River, and major tributaries (Figure 1). Surface water and sediment samples were gathered during the dry season (November 2019) for analysis.
Water samples were collected from the surface using a plexiglass water sampler and stored in 1 L amber glass bottles. During collection, 0.5 g of Na2-EDTA was added, and the pH was adjusted to 4.0 using 0.1 M sulfuric acid, followed by 10 mL of methanol. Sediment samples from the 0–20 cm layer were collected using a Peterson grab sampler, with approximately 1 kg placed in 1 L amber glass bottles, to which 0.5 g of Na2-EDTA was added. All samples were kept in a 4 °C sampling box and transported to the laboratory on the same day. Sediment samples were immediately transferred to a −20 °C freezer, freeze-dried, and sieved through a 2 mm mesh before being stored for analysis. Water samples were filtered through 0.45 μm glass fiber filters, concentrated using HLB solid-phase extraction cartridges, eluted with methanol, and concentrated by nitrogen blowdown with internal standards added for volume determination before analysis. Sediment samples were extracted using a high-pressure solvent extractor, with the extracts concentrated by nitrogen blowdown and internal standards added for volume determination before analysis.
The sample extracts were then analyzed by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry using an Agilent 1260-6460 Triple Quadrupole system (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA), which was tuned before detection. The dissolved oxygen concentration in each water sample was determined using an LH-D9 pen-type dissolved oxygen meter (Hangzhou Yingao Instrument Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China). The pH and temperature of the water at each sampling point were measured on-site using a PHB-4 portable pH meter (Shanghai Yidian Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). Other physicochemical parameters were measured using the methods described in the Chinese Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water (GB3838-2002) [36]. The particle composition of the sediment was determined using the weighing method.
The analytes included 26 compounds from five categories of antibiotics (ANTs): (1) sulfonamide antibiotics (SAs): sulfamethoacetamide (SAAM), sulfamethoxazole (SDZ), sulfamethoxazole (STZ), sulfamethoxazole (SPD), sulfamethoxazole (SMR), sulfamethoxazole (SX), sulfamethoxazole (SDM), sulfamethoquinoxaline (SQX), trimethoprim (TMP), and sulfamethoxazole (SMX); (2) quinolone antibiotics (QNs): enoxacin (ENO), norfloxacin (NOR), ofloxacin (OFL), ciprofloxacin (CIP), and enrofloxacin (ENRO); (3) tetracycline antibiotics (TCs): doxycycline (DOX), aureomycin (CTC), tetracycline (TC), and oxytetracycline (OTC); (4) chloramphenicol antibiotics (CAs): chloramphenicol (CHL), thiamphenicol (THI), and florfenicol (FF); (5) macrolide antibiotics (MLs): azithromycin (AZM), clarithromycin (CTM), roxithromycin (RTM), and erythromycin (ETM).
2.3. Quality Control
The fitting equations of the standard curves for the antibiotics had R2 values greater than 0.995. The detection limits for surface water ranged from 0.01 to 6.25 μg/L and for sediment from 0.01 to 7.89 μg/kg. During the detection process, intermediate points on the standard curves were rechecked, and blank, parallel, and matrix-spiked samples were included for quality control. The concentrations of blank samples were below the detection limits, and the concentration deviations of the rechecked points did not exceed 20% to verify instrument stability. The relative deviation of the parallel samples’ measurements should be less than 30%, and the recovery rates of the matrix-spiked samples should be controlled between 40% and 150%.
2.4. Partition Coefficient
The formula for the partition coefficient (Kp) is as follows:
where Kp represents the water–sediment partition coefficient (L/kg); Cs is the concentration of antibiotics in the sediment phase (µg/L); and Cw is the concentration of antibiotics in the water phase (µg/kg). During analysis, if both phases do not show detectable levels, the partition coefficient is not studied. If one phase does not show detectable levels, the concentration is considered to be half of the detection limit.
Kp = Cs/Cw
The Kp values for SMR, SX, SDM, and CTM were not calculated because these antibiotics were not detected in the surface water or sediment. The Kp values for SDZ, STZ, SPD, TMP, SMX, and FF were set to zero because these antibiotics were not detected in the sediment. Kp values for DOX and OFL were not calculated because DOX was not detected in surface water, and OFL was detected in sediment from only one sampling site.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
To better reveal the spatial distribution characteristics of the partition coefficient and explore its regional differences, GIS spatial analysis technology was further applied based on the calculation of Kp. Then, correlation analysis was further conducted to discover the influencing factors.
The spatial distribution maps were drawn using ArcGIS 10.2 (ESRI, Redlands, CA, USA). Correlation analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 22.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA), and Kolmogorov–Smirnov tests were performed to determine whether the data had normal distributions. If a dataset had a normal distribution, Pearson correlation coefficients were used to identify correlations between the Kp values and physicochemical variables. If a dataset did not have a normal distribution, Spearman correlation coefficients were used to identify correlations. Each antibiotic concentration lower than the method detection limit was replaced with zero before statistical analysis was performed. Each antibiotic concentration higher than the method detection limit but lower than the method quantification limit was replaced with a value of half of the method quantification limit before statistical analysis was performed. Antibiotics detected in <10% of the samples were not subjected to statistical analysis.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Antibiotic Concentration and Partition Coefficient
During the dry season, 25 out of 26 types of antibiotics were detected in the surface water, with the exception of sulfisoxazole. The concentration ranged from 130 to 1615 ng/L (Table 1). In the sediments, 17 types of antibiotics were detected during the dry season, with concentrations ranging from 121 to 426 μg/kg and an average of 172 μg/kg. The antibiotics that were not detected in the sediments included sulfadiazine, sulfapyridine, sulfamethazine, sulfisoxazole, sulfadimethoxine, trimethoprim, sulfamethoxazole, oxytetracycline, and clarithromycin.

Table 1.
Statistics of antibiotics in the water and sediment in the dry season.
Since the number of SAs detected in the sediments was limited, only the Kp of sulfamethazine and sulfaquinoxaline could be calculated, but their values were very high, reaching up to 3640 L/kg and 3201 L/kg, respectively. For QNs, except for ofloxacin, all others could be calculated with overall high values of Kp ranging from 692 to 16,106 L/kg. For TCs, only doxycycline did not have a calculated value, with the Kp of the others being relatively low, ranging from 17.4 to 843 L/kg. The Kp of CAs ranged from 865 to 2972 L/kg, and that of MLs ranged from 307 to 908 L/kg.
This might be because most SAs are highly hydrophilic, making it difficult for them to enter sediments [24]. Sulfaquinoxaline, however, has a higher hydrophobicity, leading to its higher Kp. Sulfamethazine, used extensively as an eye medication for conjunctivitis and keratitis and as a postoperative anti-infective drug [37], accumulates in sediments over time due to prolonged use. The higher Kp values for ofloxacin and trimethoprim could be attributed to the reduced water flow during the dry season, allowing more time for these substances to exchange into sediments, resulting in higher concentrations in the sediments. QNs contain positively charged nitrogen atoms and more ionic functional groups [38], giving them strong hydrophobicity and more ionic functional groups within the molecules [26]. Additionally, QNs in water are easily photodegraded [24,39] and thus exhibit strong adsorption properties upon entering sediments [40,41,42,43], resulting in high Kp values. The detection frequency of ofloxacin was low, but the detected concentrations were high. This could be due to ofloxacin being a third-generation quinolone antibiotic primarily used in human medicine, making it less prone to photodegradation and hydrolysis compared to other quinolone antibiotics [24]. It is more persistent in the environment [44], leading to more ofloxacin entering sediments and resulting in higher Kp values compared to other substances and regions. Compared to other areas, the overall Kp in the Fenhe River Basin was lower, possibly due to the higher sediment load in the basin, facilitating the transport of antibiotic substances, and resulting in the highest sediment concentrations downstream.
Compared to the other areas, the Kp values for QNs were generally higher [24,32,45]. This may be because the Fenhe River, as a main tributary of the Yellow River, has a high sediment content. QNs, as esterophilic compounds, are more likely to adsorb in suspended matter and then enter sediments. Their concentrations may be lower in the Fenhe River Basin than those found in other areas [25]. However, the concentration of TCs is lower than in other regions. As an animal disease prevention drug and animal feed additive, the large quantities used result in high concentrations in the water. However, since TCs are easily hydrolyzed and photolyzed after entering water, their sediment content is lower [46].
3.2. Spatial Distribution
The highest and lowest values of Kp for sulfamethazine were observed at S7 and S8, respectively (Figure 2). This might be because S7 is a concentrated discharge area, but the corresponding sediment did not allow for timely exchange, resulting in the lowest Kp. However, at the nearby S8, sulfamethazine, sulfaquinoxaline, and azithromycin all exhibited the highest Kp, likely due to their delayed effect in the water, causing higher sediment concentrations after entering the sediment despite the relatively low surface water discharge at this location. The Kp values for QNs were generally higher in the midstream, possibly because these areas are major entry points for antibiotics. The Fenhe River, located on the Loess Plateau, experiences low temperatures and low surface water flow in November. Quinolones, being lipophilic [25], more readily enter sediments, leading to higher Kp values in the midstream. Doxycycline, as a second-class broad-spectrum tetracycline antibiotic, showed minimal variation in usage across the entire basin, resulting in small differences in Kp. The overall distribution of chlortetracycline was similar to QNs, with higher values in the Xiao River (S6) and Ciyao River (S13) tributaries. As a main tetracycline antibiotic, it is extensively used in the livestock and poultry industries. MLs had the lowest Kp at S15, where there is a significant amount of farming activity. The relatively high water discharge rate and fast flow speed at this location prevented timely sediment entry, resulting in lower Kp values. Tetracycline, oxytetracycline, roxithromycin, and erythromycin exhibited relatively small differences across the entire basin.
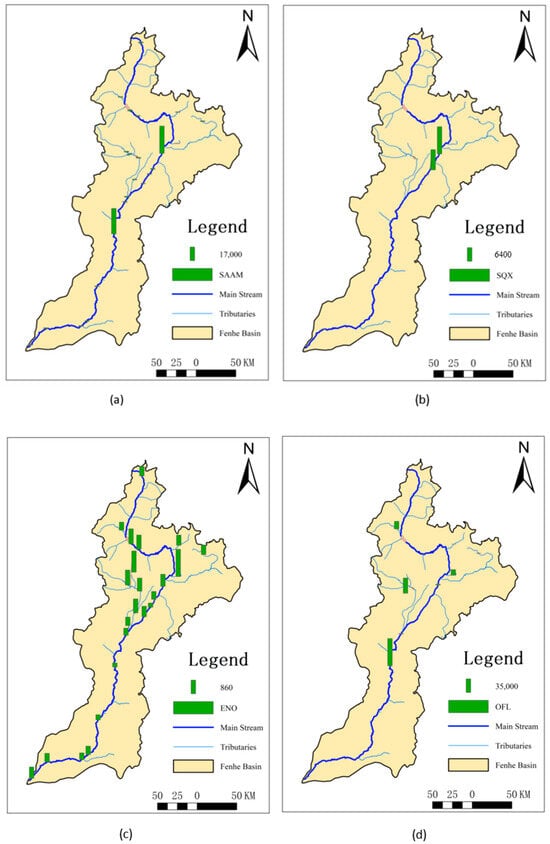
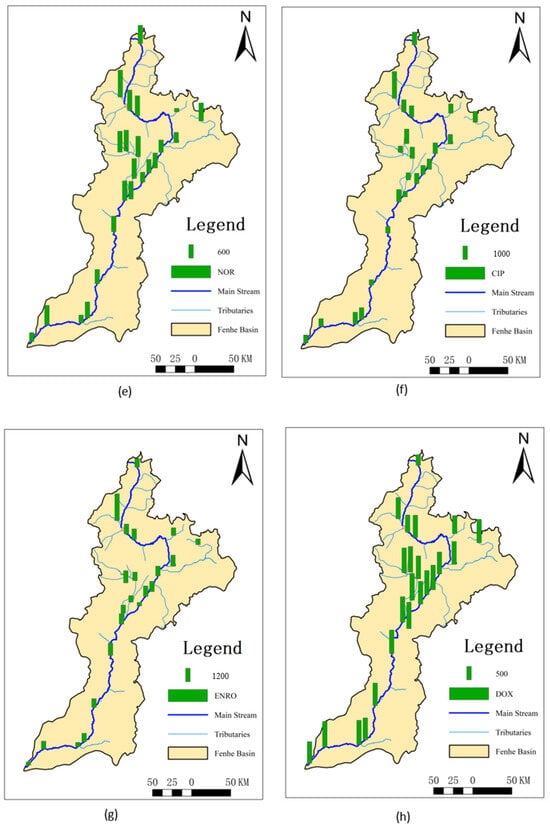
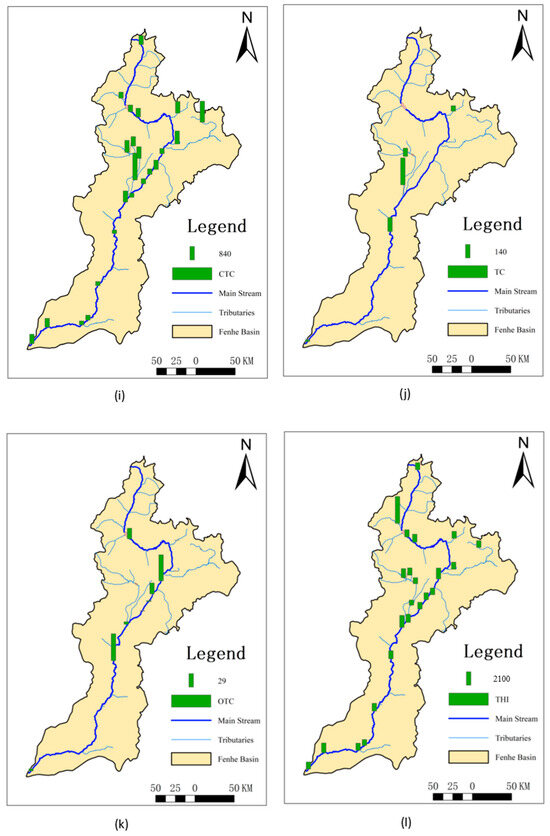
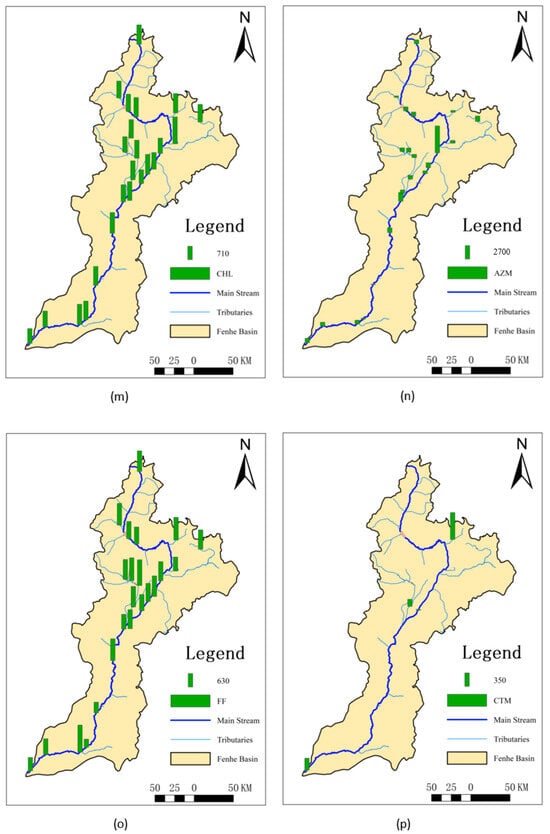
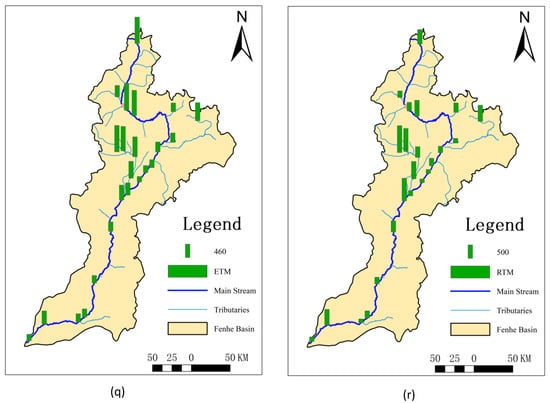
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of partitioning coefficients in the dry season of the Fenhe River.
The results showed that the Kp values for antibiotics varied greatly, ranging from 0.020 to 16,106 L/Kg. The distribution of Kp values is closely associated with risk. When the value of Kp is large, it indicates that antibiotics are prone to accumulate in sediments and cause secondary pollution as the disturbance enters the water again [47]. It will become a persistent source of pollution, bringing ongoing risks to both the environment and human health. However, the Kp value was small, meaning the substance remains in the water and is transported downstream with the water flow, resulting in an increase in antibiotic content and posing greater risks to the downstream ecology and human health [23].
3.3. Analysis of Factors Influencing the Partition Coefficient
Based on correlation analysis, Kp showed a strong correlation with river width (W), water depth (H), and water quality parameters such as total nitrogen (W-TN), total phosphorus (W-TP), chemical oxygen demand (CODcr), permanganate index (CODMn), sediment pH (S-pH), and clay content (S-NL) (Table 2). Additionally, there were strong correlations with water pH (W-pH), conductivity (W-conductivity), total organic carbon (W-TOC), ammonia nitrogen (W-NH3-N), organic matter in the sediment (S-organic matter), nitrate nitrogen in the sediment (S-NO3-N), and suspended solids content (SS).

Table 2.
Correlation analysis of the partitioning coefficients and physical–chemical indexes in the dry season.
The Kp values for enoxacin and chloramphenicol were negatively correlated with CODcr and CODMn. Both TP and TN showed a negative correlation with Kp, indicating that the concentration of nutrients in the water plays a significant role in the interaction between antibiotics in sediments and the water phase, and this influence varies by region [24]. The non-point source (NPS) pollution problem in the Fenhe River Basin was more prominent, and TP and TN were mainly of NPS [48]. The pH of the sediment is a crucial influencing factor. For instance, during the dry season, sulfamethazine, chloramphenicol, and roxithromycin exhibited strong correlations with sediment pH. This could be because pH can alter the ionic state in the sediment, with ion exchange possibly being a key factor affecting the adsorption process [49,50]. Additionally, the particle size content of sediment also affects the partition coefficient to some extent, as the grain size and composition of different types of sediments can influence their partitioning [33]. Besides the physicochemical properties of sediment and water, the surrounding environment of the sampling site also impacts the partition coefficient. For example, the Kp value for erythromycin during the dry season was positively correlated with water temperature, possibly because higher temperatures enhance the biodegradation of antibiotics [51]. Azithromycin, chloramphenicol, and florfenicol were more susceptible to hydrological conditions, showing a negative correlation with river width and depth, indicating that favorable hydrological conditions facilitate their retention in the water and subsequent migration.
The results showed that Kp is significantly influenced by the physicochemical properties of watersheds [33,52]. The interaction between surface water and sediment is crucial for the persistence and stability of antibiotics in these environments [22]. Therefore, understanding and determining the regional Kp is essential for accurately studying the behavior and fate of antibiotics in basins.
4. Conclusions
This study provided a comprehensive analysis of the distribution and influencing factors of antibiotics in the Fenhe River Basin. For QNs, except for ofloxacin, all others could be calculated with overall high values of Kp ranging from 692 to 16,106 L/kg. The Kp values for QNs were generally higher in the midstream, possibly because these areas are major entry points for antibiotics. Our findings demonstrated that, affected by point and non-point source pollution, the partition coefficients (Kp) of antibiotics were significantly affected by both the physicochemical properties of the sediment and water quality parameters. Specifically, river width, water depth, total nitrogen, total phosphorus, chemical oxygen demand, sediment pH, and clay content were all strongly correlated with Kp values. The application of GIS technology for spatial analysis revealed distinct patterns in the distribution of antibiotics across the basin. These patterns are essential for understanding the migration pathways and the ultimate fate of these contaminants. The distribution of Kp values is closely associated with risk. When the Kp value is large, it indicates that antibiotics are prone to accumulate in sediments and become a continuous source of pollution, bringing further ongoing risks to the environment and human health. However, when the Kp is small, the substance is retained in the water and is transported downstream with the water flow, bringing greater risks to the downstream ecology and human health. This study underscores the need for targeted strategies to mitigate antibiotic pollution in the Fenhe River Basin. By highlighting the key factors influencing antibiotic distribution, our research provides valuable insights that can inform effective environmental management practices and policy decisions aimed at reducing the impact of antibiotics on both ecological and human health.
Author Contributions
Methodology, J.Z.; Software, L.W.; Resources, H.Y.; Writing—original draft, J.Z.; Writing—review & editing, L.W.; Funding acquisition, H.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42377379).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the editors and anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Peng, X.; Cao, L.; Liu, Y. Spatio-temporal distribution and source identification of antibiotics in suspended matter in the Fen River Basin. Chemosphere 2023, 345, 140497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, Z.; del Torso, S.; Hadjipanayis, A.; van Esso, D.; Drabik, A.; Sharland, M. Antibiotic prescribing for upper respiratory infections: European primary paediatricians’ knowledge, attitudes and practice. Acta Paediatrica 2012, 101, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.R.; Duan, Y.P.; Zhang, Z.B.; Gao, Y.F.; Dai, C.M.; Tu, Y.J.; Gao, J. Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics pollution the Yangtze River basin, China: Emission, multimedia fate and risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Chen, B.; Nie, X.; Shi, Z.; Huang, X.; Li, X. The distribution and partitioning of common antibiotics in water and sediment of the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Guo, Z.; Hua, X. Antibiotics in water and sediments from Liao River in Jilin Province, China: Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colzani, L.; Forni, C.; Clerici, L.; Barreca, S.; Dellavedova, P. Determination of pollutants, antibiotics, and drugs in surface water in Italy as required by the third EU Water Framework Directive Watch List: Method development, validation, and assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 14791–14803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolpin, D.W.; Furlong, E.T.; Meyer, M.T.; Thurman, E.M.; Zaugg, S.D.; Barber, L.B.; Buxton, H.T. Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in US streams, 1999-2000: A national reconnaissance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ouyang, W.; Lin, C.; Wang, J.; Cui, X.; Li, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhu, W.; He, M. Occurrence, distribution, and potential ecological risks of antibiotics in a seasonal freeze-thaw basin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, Q.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Deng, S.; Yu, G. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the aquatic environment in China: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 189–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Duan, L.; Xu, T.; Hou, P.; Xu, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, H. Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Antibiotics in Urban River-Wetland-Lake Systems in Southwest China. Water 2024, 16, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ouyang, W.; Lin, C.; Wang, L.; Guo, Z.; Pei, J.; Zhang, S.; He, M.; Liu, X. Anthropogenic activities drive the distribution and ecological risk of antibiotics in a highly urbanized river basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 938, 173596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Jing, L.; Teng, Y.; Wang, J. Characterization of antibiotics in a large-scale river system of China: Occurrence pattern, spatiotemporal distribution and environmental risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, M.; Guo, C.; An, D.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, B. Distribution and ecological risk of antibiotics in a typical effluent-receiving river (Wangyang River) in north China. Chemosphere 2014, 112, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shen, L.; Qin, S.; Cui, J.; Liu, Y. Quinolones antibiotics in the Baiyangdian Lake, China: Occurrence, distribution, predicted no-effect concentrations (PNECs) and ecological risks by three methods. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wu, T.; Wang, Z.; Xu, X.; Ye, M.; Zhao, Z. Environmental characteristics of antibiotics and antibiotic-resistance genes in the Suzhou River of Shanghai, China. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedlewicz, G.; Bialk-Bielinska, A.; Borecka, M.; Winogradow, A.; Stepnowski, P.; Pazdro, K. Presence, concentrations and risk assessment of selected antibiotic residues in sediments and near-bottom waters collected from the Polish coastal zone in the southern Baltic Sea—Summary of 3 years of studies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 787–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams-Nguyen, J.; Sallach, J.B.; Bartelt-Hunt, S.; Boxall, A.B.; Durso, L.M.; McLain, J.E.; Singer, R.S.; Snow, D.D.; Zilles, J.L. Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance in Agroecosystems: State of the Science. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialk-Bielinska, A.; Stolte, S.; Arning, J.; Uebers, U.; Boeschen, A.; Stepnowski, P.; Matzke, M. Ecotoxicity evaluation of selected sulfonamides. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ouyang, W.; Lin, C.; Wang, L.; Guo, Z.; Pei, J.; Zhang, S.; He, M.; Liu, X. Effect of antibiotics, antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and extracellular antibiotic resistance genes on the fate of ARGs in marine sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 891, 164305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Liu, G.; Fu, W.; Cheng, M. Seasonal variation and sediment-water exchange of antibiotics in a shallower large lake in North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.L.; Fileman, T.W.; Evans, S.; Donkin, P.; Readman, J.W.; Mantoura, R.F.C.; Rowland, S. The partition of fluoranthene and pyrene between suspended particles and dissolved phase in the Humber Estuary: A study of the controlling factors. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 243, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskaoui, K.; Zhou, J.L. Colloids as a sink for certain pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2010, 17, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z. Distribution, residue level, sources, and phase partition of antibiotics in surface sediments from the inland river: A case study of the Xiangjiang River, south-central China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 2273–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Yan, X.; Shen, Y.; Di, M.; Wang, J. Antibiotics in surface water and sediments from Hanjiang River, Central China: Occurrence, behavior and risk assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 157, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Cheng, D.; Liu, G.; Liang, B.; Cui, B.; Bai, J. Temporal-spatial variation and partitioning prediction of antibiotics in surface water and sediments from the intertidal zones of the Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harimurti, S.; Rahayu, W.P.; Ikfini, H.; Widada, H.; Orbayinah, S.; Wibowo, A.E.; Kurnia, K.A. Partition coefficient of gamavuton-0 in different organic solvents and pH: Experimental study. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1295, 136553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.F.; Ying, G.G.; Zhao, J.L.; Tao, R.; Su, H.C.; Chen, F. Simultaneous determination of four classes of antibiotics in sediments of the Pearl Rivers using RRLC–MS/MS. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3424–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.J.; Ying, G.G.; Zhao, J.L.; Yang, J.F.; Wang, L.; Yang, B.; Liu, S. Trends in the occurrence of human and veterinary antibiotics in the sediments of the Yellow River, Hai River and Liao River in northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chu, K.; Hua, Z.; Li, Q.; Lu, Y.; Ye, F.; Dong, Y.; Li, X. Dynamics of antibiotic resistance genes in the sediments of a water-diversion lake and its human exposure risk behaviour. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 929, 172563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Luo, Y. Occurrence, distribution, and ecological-health risks of selected antibiotics in coastal waters along the coastline of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Meng, W.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, C. Occurrence, distribution and bioaccumulation of antibiotics in the Liao River Basin in China. Environ. Sci.-Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, L.; Jin, M.; Yang, X.; Wu, Q.L. Trends in the occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in shallow lakes in the lower-middle reaches of the Yangtze River basin, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 183, 109511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Zhou, J.L. Occurrence and behavior of antibiotics in water and sediments from the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreca, S.; Forni, C.; Colzani, L.; Clerici, L.; Daverio, D.; Dellavedova, P. Study on the Stability of Antibiotics, Pesticides and Drugs in Water by Using a Straightforward Procedure Applying HPLC-Mass Spectrometric Determination for Analytical Purposes. Separations 2021, 8, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertpaitoonpan, W.; Ong, S.K.; Moorman, T.B. Effect of organic carbon and pH on soil sorption of sulfamethazine. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB3838-2002[S/OL]; Chinese Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2002. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ (accessed on 25 August 2024).
- Leibold, A.M.; Suie, T. Invitro effects of sulfacetamide on ocular strains of bacteria. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1958, 45, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, H. Adsorption behavior of antibiotic in soil environment: A critical review. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. Chin. 2015, 9, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doorslaer, X.; Dewulf, J.; Van Langenhove, H.; Demeestere, K. Fluoroquinolone antibiotics: An emerging class of environmental micropollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 500–501, 250–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolls, J. Sorption of Veterinary Pharmaceuticals in Soils: A Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 3397–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Shi, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y. Occurrence, distribution and bioaccumulation of antibiotics in the Haihe River in China. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ju, Z.; Su, Z.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Song, Y.; Wen, D.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, J. The antibiotic resistance and risk heterogeneity between urban and rural rivers in a pharmaceutical industry dominated city in China: The importance of social-economic factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Shi, Y.; Gao, L.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y. Occurrence of antibiotics in water, sediments, aquatic plants, and animals from Baiyangdian Lake in North China. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Li, N.; Zheng, H.; Lin, H. Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in river water in Hong Kong. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 125, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, D.; Xie, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, S.; Cui, B.; Bai, J. Occurrence and Partitioning of Antibiotics in the Water Column and Bottom Sediments from the Intertidal Zone in the Bohai Bay, China. Wetlands 2016, 36, S167–S179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, A.K.; Meyer, M.T.; Boxall, A.B.A. A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 725–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Duan, S.; Hu, X.; Xu, W.; Xu, Y.; Wen, G.; Cao, Y. Spatiotemporal dynamics, bioaccumulation, and critical influencing factors of antibiotics in tilapia aquaculture: A study on source identification and environmental fate within typical farming systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 477, 135328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Dang, D.; Liu, Y.; Peng, X.; Liu, R. Dynamic Water Environment Capacity Assessment Based on Control Unit Coupled with SWAT Model and Differential Evolution Algorithm. Water 2023, 15, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, X.; Wu, W.; Zhao, X. Occurrence, seasonal variation and risk assessment of antibiotics in the reservoirs in North China. Chemosphere 2014, 111, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassman, S.A.; Lee, L.S. Sorption of three tetracyclines by several soils: Assessing the role of pH and cation exchange. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7452–7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamek, E.; Baran, W.; Sobczak, A. Assessment of the biodegradability of selected sulfa drugs in two polluted rivers in Poland: Effects of seasonal variations, accidental contamination, turbidity and salinity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 313, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siamionau, A.V.; Egorov, V.V. Determination of Single-Ion Partition Coefficients between Water and Plasticized PVC Membrane Using Equilibrium-Based Techniques. Membranes 2022, 12, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).