Abstract
With the operation of the world’s second-largest hydropower facility, Baihetan Hydropower Station, the risk of landslide deformation has increased. To address these potential threats, we employed Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) technology for a large-scale landslide investigation and comprehensively revealed the deformation mechanisms of landslides near the dam site. Our research indicates that the alternating geological features of soft and hard rock layers are the primary causes of landslides, especially the fracturing phenomena of vast amounts of mudstone upon contact with moisture. This leads to the reservoir’s left bank’s dip-slope being susceptible to slip and tensional failure, while the reservoir’s right bank’s reverse slope is more prone to plastic flow and tensional damage. Rapid water level changes and altered rainfall patterns are key factors that trigger landslide instability. Furthermore, we also explored the relationship between fault zones, seismic activity, and landslides, particularly noting the fully coupled state of the southern end of the Daliangshan fault zone, which might further exacerbate landslide deformation.
1. Introduction
Sustainable resource and energy management remains one of the paramount challenges of the 21st century. Hydropower projects, a source of substantial clean energy, pose a viable solution for reducing pollution and mitigating flood risks [1,2]. Southwest China, where the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau transitions into the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau and Sichuan Basin, boasts significant topographic drops and an abundance of hydropower resources, making it the primary region for current and future hydropower ventures in China [3]. Most notably, the combined installed capacity and power generation of the four cascading mega-hydropower stations on the lower Jinsha River—Wudongde, Baihetan, Xiluodu, and Xiangjiaba—double that of the Three Gorges Project, the world’s largest hydropower station. These hydropower stations are poised to become the most extensive global green energy base [4]. However, challenges persist due to the region’s inherent geophysical traits: the steep, high slopes, intense seismic activity, rapid water flows, and fluctuating water levels [5,6,7]. These factors contribute to geological disasters, such as landslides [8] and collapses [9], which in turn threaten significant human and economic losses [10]. Consequently, landslides in particular warrant further attention and mitigation strategies to ensure the safety and sustainability of these initiatives.
In addition to their direct impact, landslides in reservoir areas frequently precipitate secondary disasters [11]. For example, landslides that fall into a river can induce significant wave surges. These waves have the capacity to wreak havoc on surrounding structures, destroying buildings, facilities, agricultural lands, and roads on the opposite river bank. They can also capsize vessels or cause them to sink, thereby leading to further loss of life and property. Deciphering the intricate causal mechanisms underpinning these landslides, which are subject to an interplay of both internal and external factors, presents a considerable challenge in ongoing research [12,13]. External factors, such as drastic water level changes, intense rainfall [14,15], and powerful earthquakes [16], have been recognized as key triggers of landslides. Simultaneously, the existence of weak interlayers within the slope, which compromise stability, are crucial internal determinants [17,18]. The characteristics of the slip zone, including mineralogy [19], grain size, thickness, and structural attributes [20], shape the behavior of landslides and their potential shift from slow creep to rapid movement [21]. Considering the complexity of these determinants, landslides within reservoir regions, or slopes with potential instability, are markedly influenced by fluctuations in water storage. This disruption to the slope’s original equilibrium conditions substantially amplifies the probability of landslide occurrence [15,22]. With the recent completion of the initial water storage by the Baihetan Hydropower Station, the largest in the region and the second-largest in China, these risks have become more pronounced [23]. The water storage process may impact slope stability through several mechanisms; it can lead to a redistribution of stress within the slope, a reduction in the shear strength of the slip zone, and an increase in water levels both underground and at the surface. These factors collectively contribute to triggering landslide deformation [24,25]. Given the gravity of the situation, there is an urgent need for a comprehensive, large-scale landslide survey, particularly in the area around the dam head. This necessity is underscored by the imperative to ensure the safety and stability of the dam and surrounding regions in the face of the increasing threat of landslides.
Identifying geological hazards in vast mountainous regions is challenging [26]. Accurate slope deformation measurements are vital for landslide prevention [27]. Various detection methods exist, such as GNSS, GPS, and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) imagery [28], but they face challenges in wide-area monitoring due to costs and limited coverage, especially in cloud-prone mountainous areas [29]. These techniques often miss micro deformations [30,31,32]. InSAR technology, however, offers broad area detection and frequent monitoring, with proven benefits in landslide detection [33,34,35,36]. Yet, its application in steep areas encounters issues like terrain and atmospheric effects [37]. The small baseline subsets (SBAS) technique mitigates these effects, enhancing measurement accuracy [38]. SBAS-InSAR detects minor deformations over long periods, reducing the need for exhaustive fieldwork [39,40,41]. This efficiency is crucial for landslide risk mitigation. Early hazard detection with this technique aids in timely interventions and advances prevention systems [42,43].
In light of this, our study implemented an integrated multi-scale approach for analyzing the factors and mechanisms behind landslide deformation in the Baihetan Hydropower Station’s reservoir area. Initially, SBAS-InSAR technology was utilized to examine the landslide deformations, providing a comprehensive restoration of the surface deformation of the slopes surrounding the dam site before and after the reservoir’s impoundment. Based on this foundation, further research was conducted using UAV surveys for regional aerial photography and macroscopic–microscopic laboratory analysis of rocks. This comprehensive approach revealed the deformation mechanisms and developmental characteristics of the slopes in this region. The outcomes of this research are pivotal, offering valuable insights for landslide prevention and early warning strategies during and beyond the impoundment period of the Baihetan Reservoir. Furthermore, our findings serve as an essential reference for future efforts to identify and analyze active landslides in complex terrains.
2. Study Area and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study area is located in the lower reaches of the Jinsha River in Southwest China, covering four giant dams: Wudongde, Baihetan, Xiluodu, and Xiangjiaba (Figure 1). The research scope extends about 90 km upstream and about 20 km downstream from the Baihetan Hydropower Station. This section is the most intensely cut segment of the lower Jinsha River, with river-cutting depths mostly between 2000 and 3000 m. The predominant orientations of the mountain trends and structural lines are toward the north–south. The terrain slopes down from west to east and south to north. The altitude of the eastern bottom of the valley at the Jinsha River water surface is approximately 600 m, with a rear edge altitude of about 1450 m. The valley forms an asymmetrical “V” shape, with a steeper right bank slope exceeding 45°, while the left bank slope is gentler, with an average slope of about 20°.
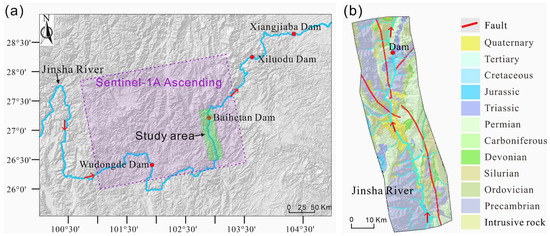
Figure 1.
(a) Distribution of hydropower stations in the lower Jinsha River and location of the study area covered by Sentinel-1A and (b) geological structure and geological ages distribution of the study area (adapted from the study by Li et al. [44]).
The geological structure of the study area belongs to the Sichuan–Yunnan structural system, located at the intersection of the northern section of the Sichuan–Yunnan trending structural zone and the eastern part of the Yunnan ‘Duo’ character structure. The main structural system of Qiaojia County consists of the north–south structural zone and the northeast-oriented structure (Yaoshan Structural Belt). Within 150 km of the study area, the main regional fault zones include the Liangshan Fault Zone, the Zemu River Fault Zone, and the Xiaojiang Fault Zone.
2.2. InSAR Data Acquisition and Processing
The SBAS technique can better suppress the impact of spatiotemporal decorrelation and extract useful information based on multiple master images. The principle of this method is to connect multiple interferometric pairs with short spatiotemporal baselines and use the spatially distributed coherence to recover displacement time series. To determine the landslide distribution affected by the first impoundment in the dam area near the Baihetan reservoir and analyze the disaster impact from January 2019 to December 2021, Senetinel-1A SAR images were acquired. The data coverage area is shown in Figure 1 and the main parameters are shown in Table 1. The precise orbital datasets of the Sentinel-1 satellite were introduced to eliminate the impact of orbital errors. A 30 m digital elevation model (DEM) was also used to eliminate the impact of the terrain phase, which was from (https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/, accessed on 18 February 2022).

Table 1.
The main parameters of the Sentinel-1 data.
Before performing interferometry on the SAR images, preprocessing involves initially importing Sentinel-1A SAR data and corresponding precise orbit data. Importing accurate orbital data helps to reduce phase errors caused by orbital inaccuracies during InSAR processing. Subsequently, the Goldstein filtering algorithm was applied to suppress phase noise. Finally, phase unwrapping was conducted using the minimum cost flow algorithm. The SBAS-InSAR inversion process was completed in two parts; the first step involved calculating the deformation of all image pairs based on a linear model and using singular value decomposition (SVD) to remove planar effects and refine orbits and perform phase unwrapping, thereby enhancing the accuracy of terrain change results. The second inversion estimates deformation rates from the first inversion and refines the corrections by filtering out atmospheric phases and using ground control points (GCPs) to further refine data corrections, ultimately obtaining deformation measurements in the time series (Figure 2).
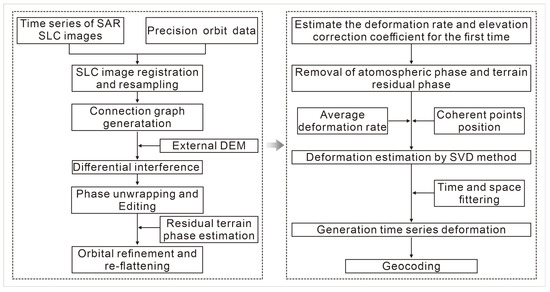
Figure 2.
Detection workflow for reservoir slope deformation based on SBAS-InSAR.
2.3. Investigation and Testing of “Prone-Slide” Layers
Utilizing a DJI Phantom 4 drone equipped with a high-precision camera, we conducted a detailed aerial survey following a pre-designed flight path over areas with landslides. This method generated orthographic images that enabled us to precisely outline the boundaries and extent of landslide regions, effectively overcoming the limitations inherent to satellite data reliance. Through an integrated analysis of these comprehensive datasets, we gained a thorough understanding of the morphology, size, and direction of numerous landslides within the reservoir area.
To delve deeper into the mechanisms behind landslide occurrence, we focused on the response of “prone-slide” layers upon contact with water. By conducting expansion experiments on representative soft rocks (such as mudstone) and hard rocks (such as sandstone), we investigated the continuous expansion characteristics of rocks under the influence of water and the pattern of moisture content changes over time. The use of scanning electron microscopy allowed us to further observe the evolution of the main rock layer structures after water immersion, deepening our understanding of how changes in rock structure can affect landslide stability. In determining the lateral constraint expansion rate of the rocks, we initially placed the pre-treated samples within a metal ring coated with Vaseline to reduce friction and simulate natural environmental conditions. Filter paper and permeable plates were placed at both ends of the sample to ensure uniform moisture conditions. Subsequently, a fixed metal load block was placed on top of the sample, and a constant pressure of 5 kPa was applied using a vertical dial gauge to simulate the actual pressure that rocks experience in geological environments.
Lateral confinement expansion rate of rocks:
where H is the height of the specimen (mm) and is the axial deformation value of the specimen with lateral confinement (mm).
Finally, by incorporating data from the comprehensive GPS network in the southeastern Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, as detailed in the work of Li et al. [45], along with recent data on regional fault zones and seismic activities, we further explore the potential influence of the regional tectonic stress field and the characteristics of crustal movements on “prone-slide” layers.
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Deformation Zones and Landslides
To address the geometric distortions between the ascending and descending orbits of Sentinel-1A, we combined the displacement results from both orbit data using a resampled grid. This method yielded a more accurate depiction of the actual surface displacements and made it easier to determine displacement rates across the study region. Additionally, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the landslide’s morphology and extent, we deployed a small UAV for precise field investigations within the landslide area.
Figure 3 depicts the deformation zones as seen in remote sensing imagery. In this visualization, red negative values signify displacements moving away from the satellite, while blue positive values indicate displacements moving toward the satellite. Throughout the reservoir impoundment period, the water level rose from 666 m to 836 m. It was during this period that six new landslides were identified, aligning with findings from earlier research [23]. We conducted a meticulous analysis of the landslides near the dam site. One significant deformation, labeled S1–4, resulted from unloading and stress readjustments due to construction excavation. This was compounded by rock damage and dynamic loading from construction blasting. As shown in Figure 3, the area displayed four major deformation zones associated with landslides. Three of these landslides were located upstream of the dam, with a maximum displacement rate of 127 mm/year, while one was situated downstream. The closeness of these landslides to the dam poses significant risks to reservoir operations, with a heightened potential for causing serious incidents [46]. As a result, it is crucial to rigorously examine the factors affecting the formation and behavior of landslides near the dam. Understanding these factors is invaluable for predicting potential deformation patterns of slopes on both banks, especially given the continued influence of reservoir water levels.
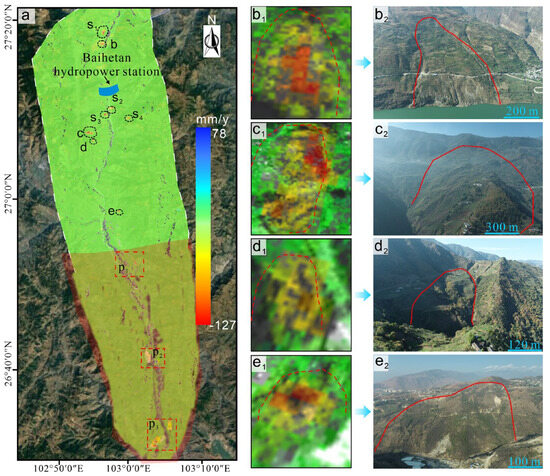
Figure 3.
(a) Deformation zones near the dam site identified by InSAR; (b1,c1,d1,e1) as landslide areas, red dashed lines indicate landslide boundaries; (b2,c2,d2,e2) further delineated by UAV-determined landslide deformation areas, red solid lines represent actual landslide boundaries. Additionally, the S1–4 region in the figure indicates a non-landslide deformation zone. The six landslides found in the P1–3 area are consistent with the results of previous studies [23].
In the reservoir region, the overall deformation characteristics of the slopes on either bank reveal a specific pattern: each rock layer forms an angle of 15° to 25° with the horizontal plane. This moderate inclination results in a lower predisposition towards slope movement, which primarily manifests as creep deformation in these areas. Yet, the geology and topography play a unique role in each bank’s landslide features and modes of failure, leading to stark differences between the left and right banks, as shown in Figure 4. On the left bank, characterized by prevalent down-dip slopes, stress tends to concentrate at the slope’s trailing edge. As the soft rock deterioration reaches a critical threshold, the overlying hard rocks begin to fracture under their self-weight and accumulated stress, culminating in a slide-tensile type failure for the down-dip slopes. In contrast, the slopes on the right bank are influenced by the weight of the rocks, causing the overlying harder rock mass to undergo tensile fracturing, disintegration, and uneven subsidence, which ultimately triggers a failure mode of plastic flow-tensile type. The stability of the slopes is significantly affected by the development of soft rock layer structural planes that align with the direction and inclination of the slopes. The stability of the slopes is significantly influenced by the structural planes of key soft rock layers, which are consistent in their orientation and inclination. Furthermore, it largely depends on the structural properties of the thick soft rock layers, particularly mudstone. The physical and chemical properties of these rocks play a crucial role in determining landslide behavior.
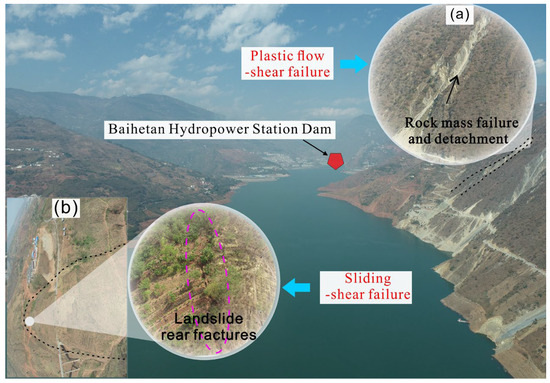
Figure 4.
Landslide failure modes on the left and right banks in the near-dam area: (a) plastic flow-tensile failure on the reverse slope and (b) sliding–tensile failure on the forward slope.
3.2. “Prone-Slide” Layer Distribution and Swelling Behavior
This study conducted a detailed investigation of the slope structures and their lithological composition near the Baihetan Hydropower Station reservoir area using UAV technology.
We discovered that the geological structure of this region primarily consists of Cretaceous and Triassic strata, characterized by an alternating pattern of soft and hard rocks, with the rock layers nearly parallel to each other. As depicted in Figure 5, which represents the typical stratigraphic features of this area, the hard rock layers are predominantly composed of well-structured thick or very thick sandstone, whereas the soft rock layers mainly consist of structurally fragmented mudstone, with some soft rock layers reaching several meters in thickness.
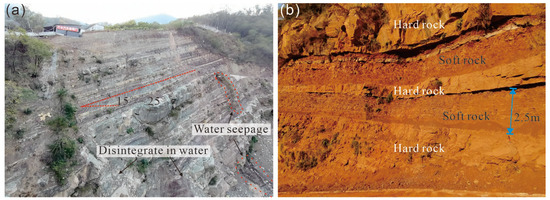
Figure 5.
The interlayered soft and hard stratigraphic structure in the study area, characterized predominantly by mudstone as the soft layers. (a) illustrates a typical example of a thin, alternating soft and hard layered structure and (b) depicts a typical example of a thick, alternating soft and hard layered structure.
Through the analysis of extensive drilling data in the area (Figure 6a), we quantified the thickness of hard and soft rocks, discovering that hard rock layers form the majority of the strata, with soft rock layers usually not exceeding 30% of the total stratum thickness. The sedimentary environment of this region is complex, with significant variation between layers and frequent and thin soft weak interlayers, leading to poor layer stability. Mudstone interlayers, in particular, see a significant deterioration in their engineering properties under the influence of external environmental factors such as engineering excavation and water infiltration, making them prone to slope instability. Accordingly, in this study, we classified the strata of the Baihetan reservoir area into Class I, Class II, and Class III based on the actual proportion of mudstone (x), where x < 15%, 15% < x < 25%, and 25% < x < 35% respectively (Figure 6b). It was found that Class III areas are widespread, and investigations indicate that landslide distributions predominantly occur within these Class III areas.
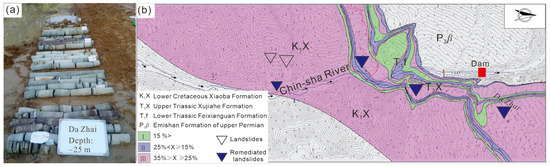
Figure 6.
Stratigraphic distribution features near the dam site: (a) partial drilling data and (b) distribution of soft rock proportion.
As presented in Figure 7, our research findings suggest that these rock types, when exposed to water, experience rapid swelling and deterioration. Mudstone, in particular, demonstrates a rapid water absorption and expansion characteristic within the first five hours, with an expansion rate exceeding 4%, and reaches a peak expansion rate of nearly 4.5% after 10 h, before showing a slow and steady expansion trend. Sandstone, on the other hand, displays the least expansion among these rocks, with an expansion rate of only about 0.1%, indicating negligible swelling when exposed to water and suggesting a more stable structure, which aligns with observations from field investigations. This swelling behavior and subsequent structural degradation are mainly controlled by the expansion of hydrophilic clay minerals within the rocks. We further noted that prolonged water exposure led to the gradual disintegration, softening, and mudification of these weak interlayers. This progression results in the weakening of the overall rock structure and a reduction in its cohesion and internal friction angle. These changes have serious implications for geological stability, significantly reducing the resistance to sliding, and establishing potential failure surfaces, or sliding zones, at the landslide’s base.
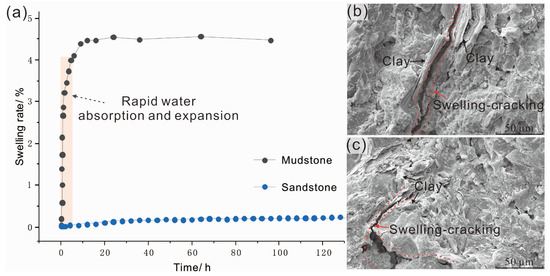
Figure 7.
Features of the expansion and deformation of typical soft and hard rocks when exposed to water under lateral confinement. (a) Expansion deformation curve and (b,c) the microstructural features of mudstone.
The stability of these soft rock layers is further compromised under the influence of external factors such as rainfall, water levels, and seismic activities. In particular, the hydropower station exacerbates this instability by raising water levels to accumulate a substantial amount of potential energy, which is then converted into green electrical energy. This process directly triggers landslides or collapses. As depicted in Figure 8, the construction of the Baihetan Dam and subsequent water impoundment led to a rapid increase in water levels, causing rapid expansion and deterioration of the water-saturated soft rock layers. Moreover, the rise in water levels resulted in the widening of the river channel and the inundation of adjacent slopes, increasing the unit weight of the rock mass. Consequently, the increased water levels amplify the gravitational force acting on potential sliding planes within the rock mass, thereby raising the likelihood of landslides.
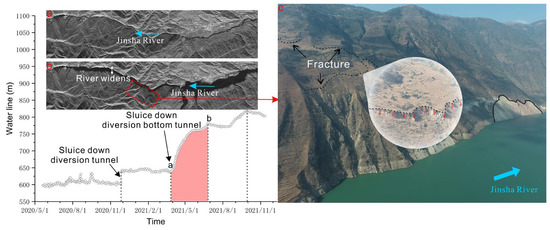
Figure 8.
Illustration of the changes in the Jinsha River channel and its impacts on the banks on both sides during the rapid rise of water levels. (a) A remote sensing image of the Jinsha River channel before water storage, (b) a remote sensing image showing the widened Jinsha River channel after rapid water storage, and (c) a depiction of the typical bank failure induced in the near-dam area during the rapid water storage period.
To conclude, the geological configuration of alternating soft and hard strata in this region predisposes the area to landslide formation. Critical triggers, including substantial rainfall during the summer and rapid increases in water levels during reservoir impoundment periods, significantly exacerbate landslide instability. Of particular significance are the pronounced effects of changes in water levels and rainfall variability on landslide occurrences. Additionally, the area’s location along the southeastern edge of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, a region known for its heightened tectonic activity, may enhance the detrimental factors contributing to landslide deformation. A pertinent example of this is the multitude of landslide events initiated by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake [47]. As a result, it becomes crucial to further investigate the influence of regional uncertainties, including faults and seismic events, on landslide development in this area. This comprehensive approach will provide a more thorough understanding of landslide dynamics, paving the way for more effective preventative strategies.
4. Discussion: Impact of Faults and Earthquakes on Landslides
To gain comprehensive insight into the enduring formation mechanism of landslide disasters, it is vital to undertake thorough research into the tectonic and seismic activities prevalent in the region. This will aid in exposing the concealed risk factors embedded within the deformation processes. Observations from GPS data, as well as plate tectonic models, denote that the southeastern periphery of the Tibetan Plateau, which encapsulates the research area, is a hotbed of tectonic activity [45,48]. This incessant orogenic activity is underscored by a complex deformation regime featuring both vertical and horizontal strain partitioning. These processes are driven by the relentless northward drift of the Indian Plate, leading to a differential southeastward compression of the Sichuan–Yunnan and Bayan Har blocks. The differential movements of these geological blocks have precipitated the formation of a sinuous, left-lateral strike-slip fault system.
In the vicinity of the reservoir, the primary faults include the Freshwater River-Xiaojian Fault and the Daliangshan Fault. Their relationship with landslides is clearly depicted in Figure 9. Over recent years, more than a hundred earthquakes, most with a magnitude lower than 3, have occurred within these regions, with focal depths predominantly between 10–20 km, mainly characterized as shallow earthquakes. Notably, the DF fault is a left-lateral strike-slip fault stretching approximately 250 km, accompanied by a vertical motion of a normal fault. Its overall trend is SN~N30°W, with the main fault plane inclining westward at a steep angle. The DF fault, as a whole, is divided into four segments from north to south: these are the Asbestos–Yuexi Fault, the Puxionghe Fault, the Butuo Fault, and the Sikai–Jiaojihe Fault. These fault segments are relatively independent and have not yet fully connected. The DF fault has remained active during the Holocene epoch, with it being associated with surface-rupturing earthquakes [48,49]. The left-lateral slip rate at the southern end of the Daliangshan Fault near the dam area of Baihetan is 4.3 ± 0.1 mm/yr, and the horizontal shortening rate is 4.2 ± 0.7 mm/yr [45]. Its locked state shows full coupling, with no evident surface slippage, but stresses in the crust continually accumulate, which might trigger earthquakes and elevate seismic risk when reaching a certain threshold. According to the records of recurrent strong earthquake behavior in the southern section of the Daliangshan Fault, its repeat interval is 1710–2460 years, and the accumulated seismic energy is equivalent to an earthquake of magnitude M~7.6 [48]. Earthquakes and active faults may trigger or accelerate phenomena such as landslides and collapses during their movement. In particular, major earthquakes may trigger regional landslide mass events, such as causing complete landslide slippage and forming landslide-dammed lakes, thus leading to a chain of disasters.
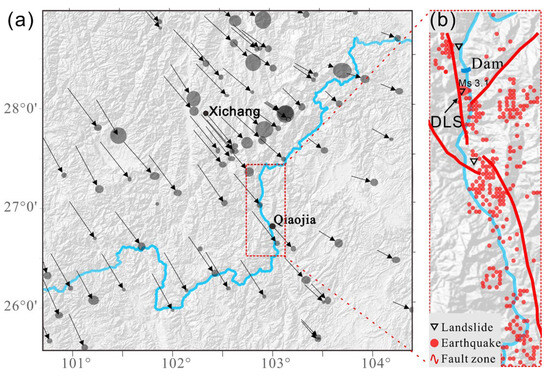
Figure 9.
Active tectonic activity near the study area: (a) GPS horizontal velocity field in the southeastern Tibetan Plateau (adapted from the study by Li et al. [45]) and (b) fault zones near the study area and earthquakes that have occurred in the past decade.
In close proximity to the southern end of the DF fault lie Landslide 1 and Landslide 2. Landslide 1, located on the left bank of the reservoir area, is the largest landslide in the study area, displaying a range of typical recent and active geomorphic features of deformation. The landslide extends approximately 1500 m in length and 600 m in width, covering a deformed area of about 9 square kilometers. As depicted in Figure 10, it exhibits a sinuous concave shape formed by cliffs sliding from the southeast, and two primary deformation zones have been observed. In Area A, numerous tension cracks can be seen, resulting in a distinct landslide fan indicative of evident sliding traces. Moreover, a fissure several hundred meters in length and several meters in width is visible, with deformation activities dating back over ten years (judged by observing the vegetation growth in the crack). In Area B, a depression formed during the landslide deformation process, multiple cracks have a deformation history surpassing 15 years, and the entire landslide’s deformation history exceeds 30 years. Not only that, but newly formed fissures of several tens of centimeters further indicate that the landslide is still active. The intricate deformation areas of the entire landslide and the unstable slope sizes suggest that there may be multiple overlapping landslide planes rather than a single one. Of particular note, under the influence of the fully coupled state at the southern end of the Daliang Mountains Fault Zone, several minor earthquakes have occurred near the landslide, including a magnitude 3.1 earthquake in 2019, with the epicenter located 15 km below the landslide.
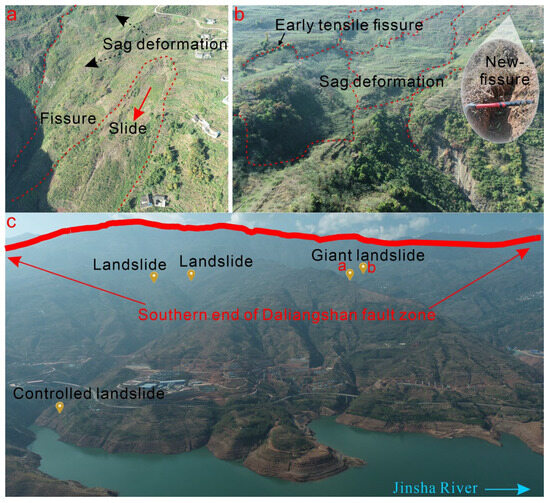
Figure 10.
(a,b) Deformation characteristics of typical landslides and (c) distribution of landslides in proximity to the dam site on the left bank.
From the evidence presented, we have discovered that this large landslide has a prolonged history of creeping deformation, making it a quintessential example of slow-moving landslides. Understanding these phenomena will aid in forecasting and identifying potential risk hazards, thereby enabling us to take necessary preventative measures to avoid or at least mitigate possible disasters that may be triggered as a result.
5. Conclusions
This article successfully identifies widespread landslide areas within the reservoir region using InSAR technology, an effective monitoring tool, which lays the groundwork for further exploration of the causes and development patterns of landslides in reservoir areas. Active landslides observed through InSAR technology indicate that interlayered geological features of soft and hard rocks are the primary driving forces behind the formation of landslides. In terms of deformation characteristics, thick mudstone and other soft rocks rapidly deteriorate and collapse upon contact with water, leading to the formation of cavities and continuous fractures. Influenced by the geological structure and topography, the dip-slope of the reservoir’s left bank is prone to slip and tensional damage, while the reverse slope of the reservoir’s right bank tends to exhibit plastic flow and tensional damage. Additionally, rapid rises in water levels and changes in rainfall patterns have been identified as key factors triggering landslide instability.
This study unveils the largest landslide in the area along with its typical active creeping deformation features, providing a vital reference for our in-depth understanding of the landslide characteristics in the region. Of particular concern are the frequent seismic history and the fully coupled state of the southern section of the Daliangshan fault zone, suggesting a potential risk of large-scale earthquakes in the area, which could accelerate the landslide deformation process.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.Z. and J.M.; Methodology, J.M.; Formal analysis, S.Z.; Data curation, S.Z. and G.F.; Writing—original draft, S.Z. and J.M.; Writing—review & editing, G.F.; Funding acquisition, J.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Guobin Fu was employed by the company Zhejiang Huadong Geotechnical Investigation & Design Institute Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Penghao, C.; Pingkuo, L.; Hua, P. Prospects of Hydropower Industry in the Yangtze River Basin: China’s Green Energy Choice. Renew. Energy 2019, 131, 1168–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu, P.A.; Asumadu-Sarkodie, S. A Review of Renewable Energy Sources, Sustainability Issues and Climate Change Mitigation. Cogent Eng. 2016, 3, 1167990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Guo, F.; Hu, J. Research on Multi-Energy Complementary Clean DC Delivery Considering Sending-End Resources and the Matching Mode of Receiving-End Peak Load Regulation. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Electronic Materials and Information Engineering, EMIE 2022, Hangzhou, China, 15–17 April 2022; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.-Z.; Chen, Z.-J.; Fan, X.-C.; Cheng, Z.-J. Hydropower Development Situation and Prospects in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yao, X.; Yao, J.; Zhou, Z.; Feng, X.; Liu, X. Analysis of Deformation Characteristics for a Reservoir Landslide before and after Impoundment by Multiple D-InSAR Observations at Jinshajiang River, China. Nat. Hazards 2019, 98, 719–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Cao, W.; Gu, J. Formation Mechanism and Movement Processes of the Aizigou Paleolandslide, Jinsha River, China. Landslides 2019, 16, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Yao, X.; Li, C.; Zhu, X. Driving Effects of Dynamic Geomorphologic Environments on Gravitational Erosion Hazards: A Case of the Baihetan Drainage Area of the Jinsha River, China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yao, X.; Yao, L.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, K.; Li, L.; Yao, C.; Gu, Z. Identifying the Mechanism of Toppling Deformation by InSAR: A Case Study in Xiluodu Reservoir, Jinsha River. Landslides 2022, 19, 2311–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, J. Impact of Upstream Reservoirs on Geomorphic Evolution in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2023, 48, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ge, S.; Yang, Q.; Ma, X. Impoundment-Associated Hydro-Mechanical Changes and Regional Seismicity Near the Xiluodu Reservoir, Southwestern China. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2020JB021590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Villanueva, V.; Allen, S.; Arora, M.; Goel, N.K.; Stoffel, M. Recent Catastrophic Landslide Lake Outburst Floods in the Himalayan Mountain Range. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2017, 41, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Peng, J.; Shi, P.; Tang, H.; Ouyang, C.; Zou, Q.; Liu, L.; Li, C.; Lei, Y. Scientific Challenges of Research on Natural Hazards and Disaster Risk. Geogr. Sustain. 2021, 2, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, P.; Handwerger, A.L.; Bièvre, G. Life and Death of Slow-Moving Landslides. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.M.; Li, C.D.; Zuo, Q.J.; Zhan, H.B.; Criss, R.E. Spatiotemporal Deformation Characteristics and Triggering Factors of Baijiabao Landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China. Geomorphology 2019, 343, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykes, A.P.; Bromhead, E.N. The Vaiont Landslide: Re-Assessment of the Evidence Leads to Rejection of the Consensus. Landslides 2018, 15, 1815–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Sun, C.; Li, X.; Ren, Y.; Xu, J.; Huang, T. Characterizing the Distribution Pattern and Geologic and Geomorphic Controls on Earthquake-Triggered Landslide Occurrence during the 2017 Ms 7.0 Jiuzhaigou Earthquake, Sichuan, China. Landslides 2021, 18, 1275–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Ling, S.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Jiang, W. Oxidation of Black Shale and Its Deterioration Mechanism in the Slip Zone of the Xujiaping Landslide in Sichuan Province, Southwestern China. Catena 2021, 200, 105139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäbitz, M.; Janssen, C.; Wenk, H.R.; Wirth, R.; Schuck, B.; Wetzel, H.U.; Meng, X.; Dresen, G. Microstructures in Landslides in Northwest China—Implications for Creeping Displacements? J. Struct. Geol. 2018, 106, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, Q.; Hu, Z. Effects of Rainwater Softening on Red Mudstone of Deep-Seated Landslide, Southwest China. Eng. Geol. 2016, 204, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauhal, T.; Zangerl, C.; Fellin, W.; Holzmann, M.; Engl, D.A.; Brandner, R.; Tropper, P.; Tessadri, R. Structure, Mineralogy and Geomechanical Properties of Shear Zones of Deep-Seated Rockslides in Metamorphic Rocks (Tyrol, Austria). Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2017, 50, 419–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, S.; Wang, G.; Dattola, G.; Crosta, G.B. Physical Mechanical Characterization of a Rockslide Shear Zone by Standard and Unconventional Tests. Landslides 2019, 16, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Huo, Z.; Peng, X.; Wang, S.; Yamasaki, S. Mechanism for the Rapid Motion of the Qianjiangping Landslide during Reactivation by the First Impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam Reservoir, China. Landslides 2008, 5, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Chen, C.; Shi, X.; Wu, M.; Feng, W.; Xu, Q.; Liang, R.; Zhuo, G.; Li, Z. Dynamic Landslides Susceptibility Evaluation in Baihetan Dam Area during Extensive Impoundment by Integrating Geological Model and InSAR Observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 116, 103157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Feng, W.; Wu, M.; Ye, Z.; Fang, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, R.; Dun, J. The Initial Impoundment of the Baihetan Reservoir Region (China) Exacerbated the Deformation of the Wangjiashan Landslide: Characteristics and Mechanism. Landslides 2022, 19, 1897–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolin, H.; Yueping, Y.; Renjiang, L.; Peng, Z.; Zhen, Q.; Yang, L.; Shulou, C.; Qiuwang, L.; Kaikai, X. Three-Dimensional Experimental Investigation on Hazard Reduction of Landslide-Generated Impulse Waves in the Baihetan Reservoir, China. Landslides 2023, 20, 2017–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sui, L.; Zhou, R.; Xun, Z.; Du, C.; Guo, X. Mountainous SAR Image Registration Using Image Simulation and an L2E Robust Estimator. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Yang, M.; Liao, M.J.E.G. Complex Surface Displacements of the Nanyu Landslide in Zhouqu, China Revealed by Multi-Platform InSAR Observations. Eng. Geol. 2023, 317, 107069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Li, Z.; Xu, Q.; Bürgmann, R.; Milledge, D.G.; Tomas, R.; Fan, X.; Zhao, C.; Liu, X.; Peng, J.J.I.G.; et al. Entering the Era of Earth Observation-Based Landslide Warning Systems: A Novel and Exciting Framework. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2020, 8, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, J.; Zhang, L.; Deng, S.; Zhang, G.; Liao, M.; Gong, J. Automatic Detection and Update of Landslide Inventory before and after Impoundments at the Lianghekou Reservoir Using Sentinel-1 InSAR. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 118, 103224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Bawden, G.W.; Kim, J.-W.; Zhao, C.; Qu, W. Mapping Ground Deformation over Houston–Galveston, Texas Using Multi-Temporal InSAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 290–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Gong, H.; Chen, B.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Gao, M.; Si, Y.; Guo, L.; Shi, M.; et al. Quantifying the Contribution of Multiple Factors to Land Subsidence in the Beijing Plain, China with Machine Learning Technology. Geomorphology 2019, 335, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Gong, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Lei, K.; Zhu, L.; Duan, L.; Zhao, X. Land Subsidence and Its Relation with Groundwater Aquifers in Beijing Plain of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Liao, M.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Tang, M.; Gong, J. Detection and Displacement Characterization of Landslides Using Multi-temporal Satellite SAR Interferometry: A Case Study of Danba County in the Dadu River Basin. Eng. Geol. 2018, 240, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Yu, Y.; Liao, M.; Gong, J.; Luo, H. Measuring Precursory Movements of the Recent Xinmo Landslide in Mao County, China with Sentinel-1 and ALOS-2 PALSAR-2 Datasets. Landslides 2018, 15, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, Z.; Zhao, C.; Kang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Du, C. Automatic Extraction of Potential Landslides by Integrating an Optical Remote Sensing Image with an InSAR-Derived Deformation Map. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Xu, W.; Ding, X.; Bürgmann, R.; Giri, S.; Liu, X. A Multi-Platform, Open-Source, and Quantitative Remote Sensing Framework for Dam-Related Hazard Investigation: Insights into the 2020 Sardoba Dam Collapse. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 111, 102849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, J.; Feng, W.; Yi, X.; Zhang, G.; Wu, M. Detection and Mapping of Active Landslides before Impoundment in the Baihetan Reservoir Area (China) based on the Time-Series InSAR Method. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A New Algorithm for Surface Deformation Monitoring Based on Small Baseline Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizzani, P.; Berardino, P.; Casu, F.; Euillades, P.; Manzo, M.; Ricciardi, G.; Zeni, G.; Lanari, R. Surface Deformation of Long Valley Caldera and Mono Basin, California, Investigated with the SBAS-InSAR Approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, W.; Li, Z. Review of the SBAS InSAR Time-Series Algorithms, Applications, and Challenges. Geod. Geodyn. 2022, 13, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Meng, X.; Jordan, C.; Novellino, A.; Dijkstra, T.; Chen, G. Investigating Slow-Moving Landslides in the Zhouqu region of China Using InSAR Time Series. Landslides 2018, 15, 1299–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dai, K.; Deng, J.; Ge, D.; Liang, R.; Li, W.; Xu, Q. Identifying Potential Landslides by Stacking-InSAR in Southwestern China and Its Performance Comparison with SBAS-InSAR. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; He, Y.; Peng, J.; Yang, C.; Kang, Y. Small-Scale Loess Landslide Monitoring with Small Baseline Subsets Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Technique—Case Study of Xingyuan Landslide, Shaanxi, China. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 026030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, C.; Yao, X.; Shao, B.; Ouyang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y. Large-Scale Landslides around the Reservoir Area of Baihetan Hydropower Station in Southwest China: Analysis of the Spatial Distribution. Nat. Hazards Res. 2022, 2, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hao, M.; Song, S.; Zhu, L.; Cui, D.; Zhuang, W.; Yang, F.; Wang, Q. Interseismic Fault Slip Deficit and Coupling Distributions on the Anninghe-Zemuhe-Daliangshan-Xiaojiang Fault Zone, Southeastern Tibetan Plateau, Based on GPS Measurements. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2021, 219, 104899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Shi, L.; Wang, R.; Tan, C.; Hu, D.; Mei, Y.; Xu, R. Zonation of the Landslide Hazards in the Forereservoir Region of the Three Gorges Project on the Yangtze River. Eng. Geol. 2001, 59, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Li, W. Post-Earthquake Landsliding and Long-Term Impacts in the Wenchuan Earthquake Area, China. Eng. Geol. 2014, 182, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; He, H.; Ikeda, Y.; Wei, Z.; Chen, C.; Xu, Y.; Shi, F.; Bi, L.; Shirahama, Y.; Okada, S.; et al. Paleoearthquake History Along the Southern Segment of the Daliangshan Fault Zone in the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Tectonics 2019, 38, 2208–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Ikeda, Y.; He, Y.; Togo, M.; Chen, J.; Chen, C.; Tajikara, M.; Echigo, T.; Okada, S. Newly-Generated Daliangshan Fault Zone—Shortcutting on the Central Section of Xianshuihe-Xiaojiang Fault System. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2008, 51, 1248–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).