Abstract
The fine particles around a mining area are easy to transport under the climatic and hydrological actions such as rainfall, that causes the change in the permeability of accumulated slag and increases the hazard probability of slag debris flow. In this study, eight experiments were designed to discuss the influence of fine particle migration on the permeability characteristics and clogging of slag accumulation in different graded particles and different dry densities. The results of experiments with coarse slags of five different particle sizes show that the ratio ranging from four to six in the coarse slag size and fine size caused a significant clogging phenomenon. It is confirmed that the shape of the particles is one of the factors affecting the clogging of coarse soil besides the coarse and fine particle size, and the clogging assessment criterion for slag and the corresponding clogging patterns based on the slag shape characteristics are given. And through three kinds of different dry density-graded slag, three clogging experiments were completed to verify the clogging standard and clogging particle size. The experimental results show that the clogging particle size obtained by the clogging criteria can effectively reduce the permeability of slag accumulation, and it is considered that the equivalent particle size and particle shape characteristics are the main factors affecting the clogging performance of accumulation, while the dry density of deposits has no significant influence on it.
1. Introduction
Waste slag is accompanied by the exploitation of mineral resources. With the continuous development of mineral resources, the accumulation rate of waste slag is much higher than that of natural sources [1]. At present, the waste slag in mining areas is mainly deposited on both sides of gullies or around river channels [2], forming the potential for a typical geologically and environmentally dangerous body with unstable deposits, that can easily induce slope instability, slag debris flow, river channel outbursts and blockages and other disasters [3]. The source of slag accumulation is different from that of generally accumulated soil and natural debris flow. It is characterized by low fine particle content, a large particle size slag-pile forming a skeleton structure and strong permeability [4,5,6]. However, in the investigation of the slag-type debris flow that broke out in Haochayu of Xiaoqinling Gold Mine on July 23, 2010, it was found that the source area of the gully was rich in residual slope deposits. With the passage of time, fine residual slope deposits on both sides of the gully slope were added, the content of fine particles increased, the water retention capacity increased and the probability of debris flow outbreak increased [7]. Xue investigated the slag deposits in the Sigou mining area and the Yindongliang mining area in Fengxian County on the west side of the Qinling Mountains. It was found that the particle composition of the slag deposits increased with the increase in exposure time. The fine particle composition of the source particles increased significantly, the stability of the deposits deteriorated and the possibility of a debris flow outbreak increased [8].
The migration and accumulation of fine particles will cause the instability of the accumulation body [9,10], and that will be accelerated by clogging which is caused by fine particles blocking or being deposited through infiltration and seepage [11,12,13]. Meyer and Wells’ study suggested that the fine particles from hillside supply and the coarse particles present in the channel were critical for the initiation of debris flows [14]. Reid, M.E. pointed out that the fine particle source played an important role in the generation of pore pressure and the movement of source deposit during rainfall [15]. Coe, J.A. particularly emphasized that the transport of debris material resulting from runoff erosion was a significant factor in the formation and initiation of debris flows [16]. Therefore, a large number of physical and numerical models have been used to analyze the effects of water flow triggering and fine particle migration on the stability of slag deposits. The results of laboratory model testing showed that when the fine particle content reached about 28%, the slag debris flow can occur under weak climatic–hydrological conditions [17]; it was also observed in a similar model that the collapse of an accumulation body made it easy to produce slide–blockage–collapse-type debris flows at this level of fine particle content, and required the minimum amount of water [7,18]. The process of particle migration and deposition was established using a numerical model, and the instability failure and possible harm of the accumulation body were analyzed and calculated [19,20,21,22,23]. In order to determine the influence mechanism of fine particle migration, deposition and clogging more effectively on the instability of the accumulation slope, Wang et al. [24], through the method of model testing, found that fine particles would migrate with rainwater, block the fine pores and reduce the permeability of soil, eventually leading to failure or collapse. Subsequently, in their study of the preparation and initiation process of debris flows and the role of fine particles, Wang, Z.-B. and other scholars [11] elaborated on how fine particles migrate and block, thereby reducing soil permeability, ultimately exacerbating slope instability or triggering debris flow disasters. However, it has been found that not all sizes of fine particles can induce clogging and instability in loose accumulations. In earlier studies, particles smaller than 2 mm forming a turbid liquid were considered as the slurry part of debris flow [25,26]. Then, Cui et al. [27,28] defined 1 mm as the critical value of fine and coarse particles in debris flow, that means that the slurry formed by the appropriate fine particle size has a more significant capacity to transport the large particles during debris flow [29]. It can be seen that the decrease in the permeability of the accumulation body was the direct manifestation of clogging, that can aggravate or induce the instability of the accumulation body, and it can be reflected by the reduction in porosity and the increase in fine particle content.
Especially in noncohesive coarse soil with large particle sizes, the fine particle content determines whether these soils are a permeability failure or not [30]. And in the study of the permeability failure, it was also specified that the composition of particles and the soil compaction are clearly the main factors affecting the permeability deformation of noncohesive soil [31]. Similar experimental results have also been proposed by Ma [32] for coarse soil in dam foundation, Reddi L.N et al. [33] in soil filters and a number of scholars in stormwater treatment media [34,35,36]. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the slag particle size and dry density as variable factors in the research of the permeability stability of slag accumulation. However, few experiments, especially considering the influence of fine particle migration on the permeability characteristics of soil accumulation, like basic physical properties such as particle size or gradation and relative compaction, have been able to directly reveal the hydraulic properties’ variation in soil accumulation.
In this study, we performed clogging experiments of slag with five different particle sizes and three different dry densities using a self-designed apparatus. By analyzing the experimental data, the dominant fine particle size causing clogging and its discriminant method, as well as the clogging assessment criterion based on the correction factor for slag accumulation were determined, which provide a scientific reference for future research on the formation process of slag debris flows.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Characteristics
The raw samples from Shaanxi Fengxian lead-zinc mining area, China (Figure 1a), were gray-black block-like material (Figure 1b,d) and the main mineral composition was quartz and calcite and included a small amount of sphalerite and other metal minerals. The particle shape of the experimental slag was mainly angular, and the roundness was poor, as shown in Figure 1. The particle density of slag was approximately 2.91, the dry density was between 1.6 g/cm3 and 2.0 g/cm3, the permeability coefficient was large at about 5 × 10−3 m/s–10 × 10−3 m/s.
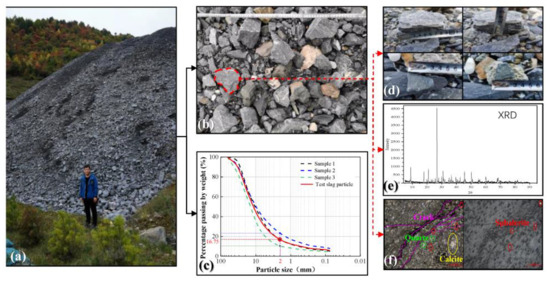
Figure 1.
Slag characterizations of study area: (a) slag accumulation area and selected samples area; (b) characteristics of slag particles; (c) particle size distribution curve of experimental slag sample; (d) slag particle shape; (e) main mineral composition of slag; (f) mineral composition and fracture distribution under stereomicroscope.
Particle sizes larger than 64 mm were found to exhibit a poor clogging performance in a series of research studies for coarse soil and dam foundation soil [19,32]. So, 3 typical slag accumulation particles removing particles size larger than 64 mm in the study area were selected (Figure 1c), and the raw samples were treated by combining an equal substitution method and a similar gradation method. The particle size distribution curve of the experimental slag sample is shown by the solid red line in Figure 1c.
2.2. Experimental Design and Apparatus
The particle size of the slag in the study area was basically coarse, mainly gravel and pebble, and the particle size of accumulated slag particles larger than 2 mm accounted for nearly 80% (Figure 1c). To assess the impact of slag particle size and slag accumulation density on clogging, model experiments in 5 different coarse slag particle sizes and 3 different dry densities of graded distribution slag were set up; the particle size distributions of all the materials were in accordance with the Udden–Wentworth scale [37,38]. The solid red line in Figure 1c shows the particle size distribution of the slag and Table 1 lists the scheme and parameters for the 8 experiments.

Table 1.
Summary of the scheme of the 8 experiments.
The slag accumulation was similar to a slope or dam body, and the seepage was mainly horizontal. In addition, the flow formed by a single precipitation in the basin did not change much, which was manifested as the infiltration process of a constant flow rate rather than that of a constant head. Therefore, a special infiltration–clogging experimental setup with constant inflow for coarse particle was built, as shown in Figure 2. It included a water supply tank and fine particle storage, monitoring equipment, a transverse cylindrical sample column and a sediment tank. In order to simulate the constant inflow, the constant flow pump was used to supply continuous water to the sample column during operation. The fine particle storage was only 8 cm away from the sample column, to ensure that the fine particles were unsinkable under the action of inflow. In the seepage and infiltration-clogging study of coarse soil, the suggestion was that the ratio of the sample column diameter to the soil media particle diameter was more than 5. So, in order to suit the maximum particle size of 64 mm in this study, the sample column was 600 mm in length with a 100 mm buffer zone on both sides, 378 mm in diameter and made of Plexiglas. Figure 2 shows a schematic and photograph of the setup.
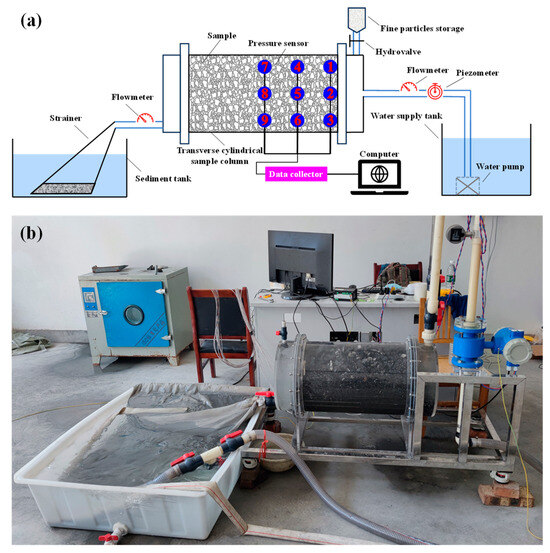
Figure 2.
Infiltration-clogging experimental setup: (a) schematic diagram, and 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 was the sensor number; (b) photograph.
In addition, the fine particle size feeding into the sample column was referred to the size of clogging particles in the coarse soil clogging behavior [39], shown in Table 1.
2.3. Experimental Procedure and Data Analysis
Before the experiments started, as a first step, the slags should be fully compacted layer by layer; and then after one layer of slag media was fully saturated, the air bubbles in the slag media ought to be released. In the process of adding slag media in layers, the sensors were buried in the specified position according to Figure 2a. Next, the infiltration-clogging experimental setup was checked for leakage and then the experiments started at a constant inflow. In the experiments, the hydraulic gradient and average velocity were monitored with time, and the fine particles could be fed in slowly and uniformly after the two monitors were stable. Finally, when the measurements were relatively stable again, the experiment was finished.
In this study, the slag materials were separated into two types, coarse slag and graded distribution slag, shown in Table 1. Due to the flow velocity, the coarse slag materials were very high and not stable during the experiment, but the flow velocity in the graded distribution slag was relatively stable. So, the permeability was characterized by hydraulic gradient and flow velocity for coarse slag, and hydraulic conductivities for graded distribution slag, respectively.
Except for the monitoring data, after the experiments, the lost fine particles were collected and the samples in column were sieved by layers to identify the clogging.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Determination of the Fine Particle Size Resulting in Clogging for Coarse Slags
The variation in hydraulic gradient and flow velocity of five groups of coarse slag with different particle sizes over time is shown in Figure 3. Under the condition of constant inflow, the variation in velocity over time presented a slow fluctuation during the experimental process, and the hydraulic gradient increased obviously after the addition of some fine particles, such as feeding fine particles sized 4–8mm to the coarse slag sized 32–64 mm, fine particles sized 2–4 mm to the coarse slag sized 16–32 mm, fine particles sized 1–2 mm to the coarse slag sized 8–16 mm, fine particles sized 0.5–1 mm to the coarse slag sized 4–8 mm, and fine particles sized 0.25–0.5 mm to the coarse slag sized 2–4 mm.
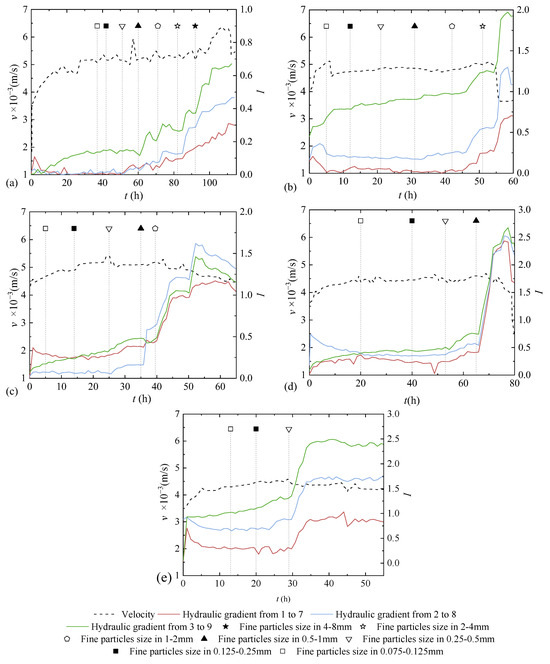
Figure 3.
The variation in hydraulic gradient and flow velocity of 5 groups of coarse slag with different particle sizes over time: (a) coarse slag particles sized 32–64 mm; (b) coarse slag particles sized 16–32 mm; (c) coarse slag particles sized 8–16 mm; (d) coarse slag particles sized 4–8 mm; (e) coarse slag particles sized 2–4 mm.
In addition to the changes in flow velocity and hydraulic gradient over time, after each experiment, the profile and longitudinal distribution diagram along the column direction of fine particle sediments or clogging were obtained, as shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5. It showed that the phenomenon of clogging and sediments of fine particles observed from the outer wall of the column (Figure 4a and Figure 5a) was basically consistent with the similar phenomenon of the sieve analysis profile (Figure 4c and Figure 5c), such as for the experiment of coarse slag sized 32–64 mm (Figure 4), fine particles sized 0.063–0.125 mm and 0.125–0.25 mm deposited at the end of the column, fine particles sized 0.25–0.5 mm, 0.5–1 mm, and 1–2 mm were distributed throughout the whole column, and fine particles sized 2–4 mm and 4–8 mm were mainly deposited in the front section of the column. In addition, the experimental samples were divided into six to eight layers along the water flow direction for sieve analysis after each experiment, then the position and mass of sediments or clogging, and the lossing mass were recorded, as shown in Figure 6. The sum of clogging percentage, sediment percentage and loss percentage ranging from 96 to 99% were attributed to measurement errors; these were within the ranges reported in the coarse soil clogging research [37]. And, the different fine particle distribution after sieving showed the same as that of fine particles clogging along the column and sieve analysis profile (Figure 4b and Figure 5b). It can also be seen that fine particles of different sizes were clogging in different positions of the column from the sieve analysis results, and combined with the change in hydraulic gradient, only certain sizes of fine particles could cause more significant clogging behavior, such as fine particles sized 4–8mm, 2–4 mm, 1–2 mm,0.5–1 mm, and 0.25–0.5 mm, respectively, and for coarse slag sized 32–64 mm, 16–32 mm, 8–16 mm, 4–8 mm, and 2–4 mm, respectively. According to the experiments of seepage clogging of coarse soil on dam foundations, Li [39] gave the clogging patterns of gravel grain and its discrimination criterion including surface clogging (De/de ≤ 4), surface-internal clogging (4 < De/de ≤ 16), internal partial pore blockage (16 < De/de ≤ 29) and unclogging (De/de > 29), where De/de was the ratio of equivalent size of coarse particles and fine particles, and the equivalent size was calculated by the particle geometric average: De = (Dmax·Dmin)0.5. Compared with the clogging results of coarse soil and coarse slag, the feeding fine particles with a ratio ranging from 4 to 6 in the coarse slag size and fine size caused a significant hydraulic gradient uplift, which was deposited in the front column of 0–10cm, conforming to the clogging criteria. And it could be seen that this clogging pattern criteria was applicable to both gravel and egg-type slag particles.
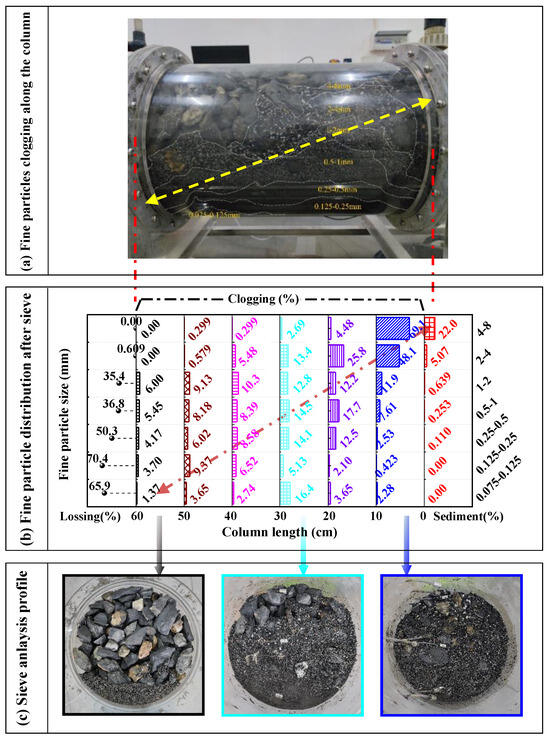
Figure 4.
The images and mass percentage of clogging particles along the sample column length for coarse slag particles sized 32–64 mm.
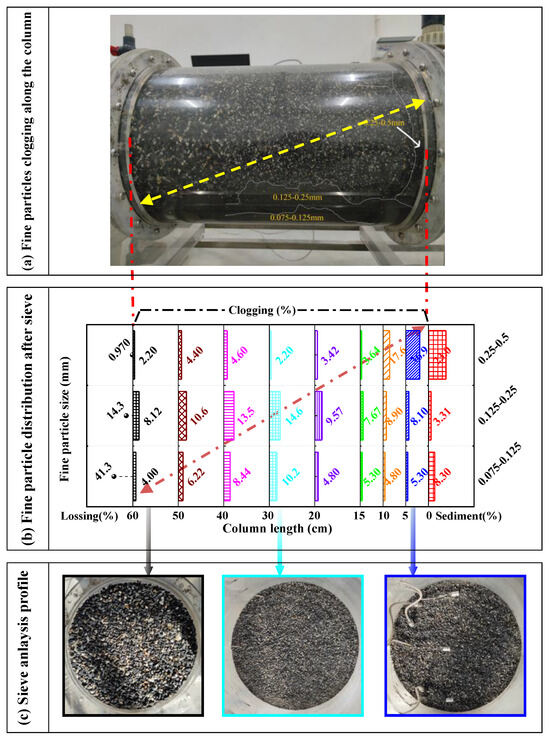
Figure 5.
The images and mass percentage of clogging particles along the sample column length for coarse slag particles sized 2–4 mm.
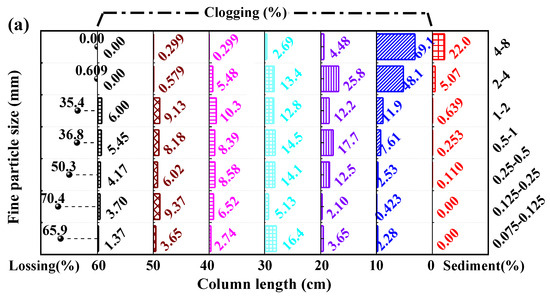
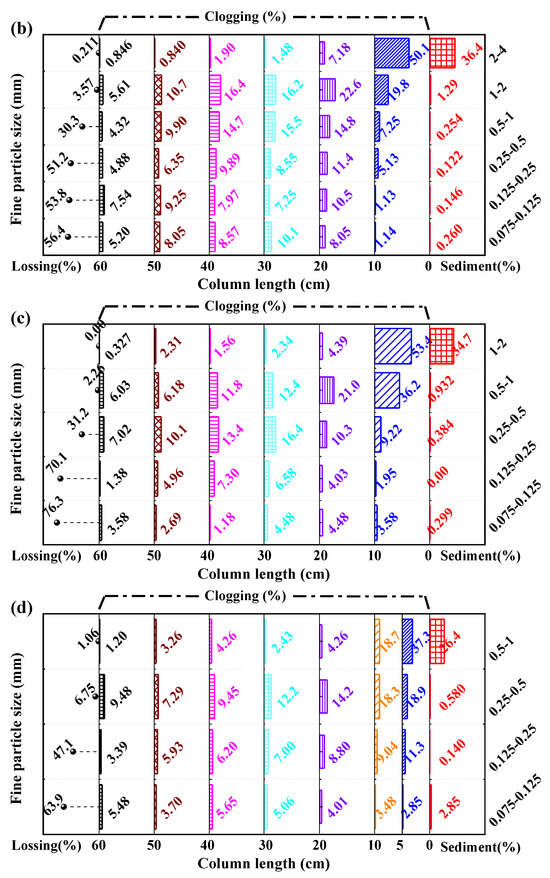
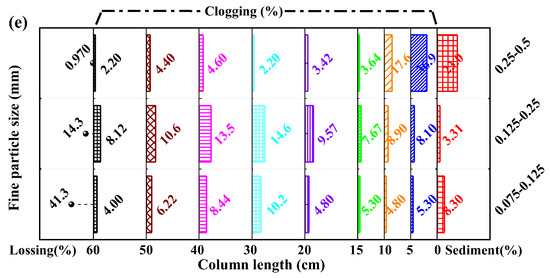
Figure 6.
The mass percentage of clogging particles along the sample column length by sieve analysis: (a) coarse slag particles sized 32–64 mm; (b) coarse slag particles sized 16–32 mm; (c) coarse slag particles sized 8–16 mm; (d) coarse slag particles sized 4–8 mm; (e) coarse slag particles sized 2–4 mm.
3.2. Clogging Assessment Criterion Based on Different Methods for Coarse Slag and Relevant Parameter Modification
In Figure 3, we found that some fine particles entering the sample column can cause the hydraulic gradient rising, but the rising was slightly slow; and a high level of loss of these fine particles was also found in the sediment tank (Figure 6), such as the variation in hydraulic gradient (Figure 3a) and loss percentage (Figure 4b) for fine particles sized 0.5–1 mm or 1–2 mm feeding into the column with coarse slag particles sized 32–64 mm. Combined with the description of the coarse soil clogging phenomenon, these fine particles may cause internal partial pore blockage, but according to the clogging pattern criteria in the study of seepage clogging of coarse soil on dam foundations above, it was judged to be unclogging. Meanwhile, when determining different clogging patterns in the study of coarse soil clogging [38], the mass percentage clogging in 75% of a certain layer was defined as demarcation. However, coarse slag clogging studies show fine particles mass clogging or sediments along the column cannot meet the 75% standard.
Therefore, based on the criterion of a coarse soil clogging pattern, combined with the variation in hydraulic gradient (Figure 3) and calculating the mass percentage of fine particles along the column (shown in Table 2) of the coarse slag, the clogging assessment criterion for coarse slags based on the ratio of coarse particles and fine particles is given: ① surface clogging pattern (SC), 4 < De/de ≤ 16, mass percentage of fine particle sediment on surface less than 50% and greater than 20%, and mass percentage of fine particles clogging in the front section of the column from 0 to 10 cm more than 50%, and the hydraulic gradient rising up significantly; ② internal partial pore blockage pattern (PB), 16 < De/de ≤ 32, mass percentage of fine particles clogging in the front section of the column from 0 to 10 cm less than 50% and mass percentage of fine particles clogging along the whole column more than 80%, and the hydraulic gradient rising up slightly slower than surface clogging; ③ sediment or losing pattern, De/de > 32, and according to the mass percentage of sediment in the column and losing outside, sediment or loss pattern can be divided into two sub-patterns: ③(a) fine particle sediment (FS), 32 < De/de < 64, mass percentage of fine particles clogging along the whole column greater than 50% and loss greater than 30%, and the hydraulic gradient rising up slowly or no obvious change; ③(b) unclogging (UC), De/de > 64, mass percentage of fine particles lost from the column by more than 50%, and mass percentage of fine particle sediment on the surface and clogging in the front section of the column from 0 to 10 cm less than 20%, and the hydraulic gradient almost unchanging, as shown in Table 3.

Table 2.
Mass percentage of feeding particle size in coarse slag media (%) and clogging patterns.

Table 3.
Clogging patterns evaluated by clogging assessment criterion with different correction factor for coarse soil and coarse slag.
In summary of the above experimental results, the critical limit of the mass percentage was 20% or 50% for coarse slag instead of 75%, different from the coarse soil clogging of the dam foundation. Moreover, except for the clogging phenomenon of the surface clogging pattern, other phenomena of the clogging patterns (hydraulic gradient change and mass percentage of clogging accumulation) were not significant in the coarse slag clogging experiments. The reason for this may be related to the pore characteristics formed by the accumulation of two different particles. Therefore, the effective aperture of particles was used to describe the clogging behavior of coarse slag, and the effective aperture [39] is calculated as follows:
where Dea denotes the effective aperture of the soil; n is the porosity of the soil; De denotes the equivalent size of the soil particles; and ɑ1 is a particle shape correction factor equal to the ratio of the soil particle surface area and sphere surface area in the same volume for ideal sand: ɑ1 = 1.5–1.9.
In Table 3, in bold font, the classification of clogging patterns and clogging assessment criterion for coarse soil are shown, calculated by the effective aperture. The calculation results show that the relationship between the coarse slag size and clogging particle size cannot satisfy the above criterion; the reason was the value range of the particle shape correction factor ɑ1 in Formula (1) was not applicable to coarse slag. In fact, the value of ɑ1 from 1.5 to 1.9 is only applicable to sandy soil [40], but the value of ɑ1 was suitable in the study of coarse soil clogging, because the pebble and gravel of coarse grains belong to the river sedimentary soil, and the shape was roundness. But the experimental samples were coarse slag, that had not undergone long-term weathering and denudation, possessing sharp edges and poor roundness, as shown in Figure 7.

Figure 7.
Images of shape differences between experiment samples of coarse slag and coarse soil.
It was considered that the shape of coarse slag affected the pore characteristics, and further affected the types of clogging patterns and clogging mass. Three typical slag particle sizes of 2–4 mm, 4–8 mm, and 8–16 mm, respectively, were selected as samples for analysis, and the shape difference of the slag samples was analyzed by particle shape quantification parameter index (including geometric shape parameters, shape coefficient, ff, the ratio of length and width, Rcd), shown in Table 4. Among the three types of quantitative indexes, the geometric parameters and the shape coefficient were about 1–2.3 times and 1.3 times that of the conventional parameters; additionally, the amount of coarse slag in three different particle sizes, the ratio of length and width ranged in 1–2, were more than 90% of the total sample. Therefore, the particle shape correction factor should be corrected to double ɑ1, that means the particle shape correction factor for the coarse slags β1 =2·ɑ1.

Table 4.
Particle shape quantification parameter index of three typical particle sizes of coarse slag.
Then, the effective aperture of particles was expressed as follows:
where β1 is a particle shape correction factor for coarse and angular grain particles; and β1 = 2ɑ1 or β1 = 3–4. Dea′ denotes the effective aperture of the coarse slag in a particle shape correction factor of β1, mm.
Then, based on calculation by the effective aperture as shown in Formula (2), the clogging assessment criterion suitable for the slag was obtained, as shown in Table 3 (bold font).
3.3. Prediction and Verification of the Clogging Particle Size of Graded Distribution Slags
3.3.1. Some Explanations Based on the Clogging Experiments of Graded Distribution Slags
In the study of the permeability characteristics of coarse soil with wide gradation size, it is found that the particle gradation and void ratios are the key factors determining the hydraulic conductivity of the coarse soil [41]. In the study of the seepage control of noncohesive soil, the graded distribution soil is simplified to a uniform soil with equivalent particle size, and the effective aperture and hydraulic conductivity are determined [30]. In the study of the clogging process of coarse soil, it was found that the equivalent particle size dominated the pore characteristics and clogging particle size, and D15, D17, D20, and D25 were taken as the equivalent particle size of graded soil, in the calculation of the clogging particle size. In addition, Liu Jie et al. [30] found that the calculated hydraulic conductivity was too small for non-uniform soil of an earth–rock dam when D20 was the equivalent particle size, but it will not happen when the equivalent particle size is D22. Therefore, D15, D17, D20, D22, and D25 were considered as the equivalent particle size of the graded distribution slag in the experiments for calculation.
In addition, the void ratio was also an important factor affecting its permeability and clogging characteristics, that was determined by the soil particle density Gs and dry density ρd. Therefore, graded distribution slag in three different dry density values was selected as materials to explain the effect of the void ratio on the clogging through experiments.
3.3.2. Experimental Verification of Graded Distribution Slags Clogging
Based on the clogging assessment criterion of slags calculated by effective aperture (Formula (2)), the effective aperture of graded distribution slags calculated by 5 different equivalent particle sizes was obtained. And combined with clogging assessment criterion based on calculation by the effective aperture with particle shape correction factor in Table 3, the calculated feeding particle size was got shown in Table 5. Except for the feeding particle size calculated by D15 is too small, the feeding particle size calculated by D17, D20, D22 and D25 was in 0.125–0.5 mm.

Table 5.
The feeding particle size calculated by clogging assessment criterion based on the effective aperture for the dry density of graded distribution slag.
The graded distribution slag clogging experiment results in three different dry densities which are shown in Figure 8. After feeding a particle size of 0.125–0.25 mm and 0.25 mm to 0.5 mm, the hydraulic conductivities of graded distribution slag reduced significantly, more than 1 order of magnitude, and in particular, the reduction range was more than 80% of the initial stable hydraulic conductivity after feeding the fine particles size of 0.25–0.5 mm. Moreover, the hydraulic conductivity from sensor 3 to sensor 9 in the dry density of 1.9×103 kg/m3 decreased by nearly 2 orders of magnitude, more significantly. In fact, the performance of effective clogging can reduce hydraulic conductivity by 1–2 orders of magnitude in the soil [32], that can significantly block the amount of incoming water, increasing the risk of disasters such as outburst for the accumulation [12,42,43].
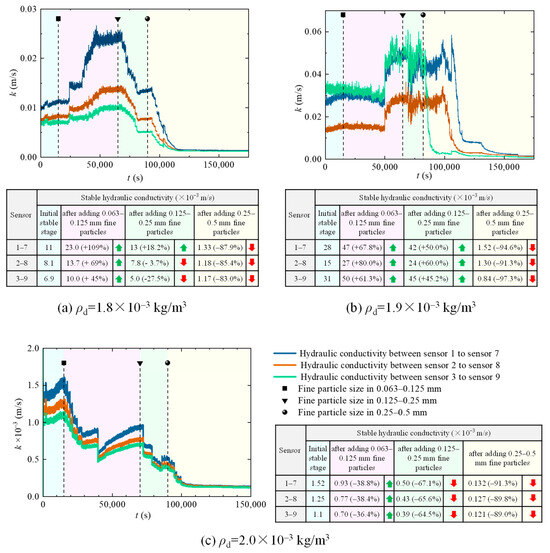
Figure 8.
The range of variation in the hydraulic conductivity after feeding fine particles in experiments process.  denoted hydraulic conductivity increased,
denoted hydraulic conductivity increased,  denoted hydraulic conductivity reduced.
denoted hydraulic conductivity reduced.
 denoted hydraulic conductivity increased,
denoted hydraulic conductivity increased,  denoted hydraulic conductivity reduced.
denoted hydraulic conductivity reduced.
Comparing the hydraulic conductivities of three kinds of dry density-graded distribution slag before and after clogging, first of all, the greater the dry density of the slags, the lower the stable hydraulic conductivity, shown both in the hydraulic conductivities in the initial and after clogging. Secondly, the slags with dry density in 1.8 × 103 kg/m3 and 1.9 × 103 kg/m3 showed increasing in hydraulic conductivity after feeding fine particles, and significantly in dry density with 1.8 × 103 kg/m3, but no such phenomenon appeared in dry density with 2.0 × 103 kg/m3. The reason for the increase might be related to the seepage failure in graded distribution slag, nothing with the fine particle feeding, and the similar phenomenon had also been found in the clogging experiments using coarse soil [32]. Furthermore, the phenomenon of clogging is different from the permeability affected by soil dry density, and its influencing factors have no relationship with the dry density of the soil, where the stable hydraulic conductivities with three different dry densities of slag after clogging are shown in Figure 8. The experiment results showed that the most obvious decrease degree of hydraulic conductivity of the experiments for three different dry densities slags were the slag with a dry density in 1.9 × 103 kg/m3, with the hydraulic conductivities in three different group sensors all reduced by more than 90%, and among them, the permeability of sensor 3 to sensor 9 decreased by 2 orders of magnitude. Finally, although the significant degree of clogging was slightly different, the clogging particle size of 0.25–0.5 mm, calculated by the effective aperture with particle shape correction factor and judged by the clogging assessment criterion for coarse slag, could effectively reduce the permeability of slag and achieve the expected clogging effect.
4. Summary and Conclusions
In fact, the inflow, and the material properties and physical characteristics of slag, largely affected the slag accumulation stability [44,45,46], in particular, in landslide dams and mine waste accumulations [12,42,47,48]. From an engineering and geological perspective, the material composition of landslide dams characterized by a mixture of unconsolidated soil and rocks in a naturally unstable state, with a wide range of grain size distributions, was very similar to the characteristics of slag accumulation, and several studies have pointed out that seepage characteristics in landslide dams is occasionally one of the main factors governing the failure of landslide dams [13,49,50,51,52,53]. Even seepage erosion caused by the permeability changes in and failure mode of landside dams has been confirmed [49,50]. Notably, research on the continuous increase in fine particles in the accumulation that changes the permeability is lacking in the literature. However, it has been proved that as the content of the fine particles in the accumulation continue to increase, that changed the grain composition of the accumulation materials leading to changes in their permeability, finally undermining the long-term stability and longevity of the landslide dams [49,54]. As a result, this paper represents an attempt to investigate the change in the permeability of slag accumulation from the perspective of fine particle migration on clogging, so as to provide a basis for the influence of fine particle migration and clogging on the slag debris flow formation.
The slag in the study area was mainly gravel and pebble, and the permeability was high after forming the accumulation. It was found that particle size, dry density (indirectly affects porosity), and particle shape were generally considered to be typical factors affecting the permeability of coarse soil [36]. Their effects on permeability for the slags were also found in this study. The experimental results showed that the larger the slag particle size, the smaller the hydraulic gradient value under the same inflow condition, as shown in Figure 3; the more compacted the graded distribution slag was, the lower the hydraulic conductivity was, as shown in Figure 8. On synthesizing the factors influencing the soil permeability and slag clogging experimental results, the particle size, compactness of accumulation and particle shape characteristics were determined as the main factors affecting the permeability of the slag. It was precisely because of the high permeability of slag accumulation that the hydraulic gradient and hydraulic conductivity easily showed significant changes after the fine particle clogging at a constant flow velocity. Consistent with the results of the coarse soil clogging test, the ratio of coarse and feeding particle size of 4/6 can cause a significant clogging effect, and this ratio was applicable to the clogging behavior of coarse soil and slag of both gravel and pebble.
In addition to the fine particle size resulting in clogging as summarized in the experimental results, clogging assessment criteria based on calculation by the effective aperture can also be used to distinguish the clogging patterns and calculate the clogging particle size in the study of coarse soil clogging behavior. However, different from the clogging of coarse soil, poor roundness, sharp edges, and some with lath shaped or long columns were found to be the main morphological features of slag (Figure 7). The above calculated particle shape correction factor of effective aperture was not applicable to slag particles. Three typical particle shape quantitative parameters were used to analyze the difference in slag particle shapes. Compared with the conventional parameters, the values of the three parameters were twice that, as shown in Table 3. And this multiplicity of changes was basically consistent with the simulation results of the permeability of irregular particles by Garcia et al. (the hydraulic conductivity of spherical particles was nearly two times higher than that of irregular particles). Therefore, clogging patterns (surface sediment, surface–internal clogging, internal partial pore blockage, sediment or loss) and clogging assessment criterion based on calculation by the effective aperture with particle shape correction factor were obtained. And it was also determined that the coarse slag clogging phenomenon and degree were related to the fine particle size, particle size and particle shape of slag.
However, in sediments, especially in accumulation of graded distribution particles with different dry densities, the pore characteristics of the accumulation may change and affect the permeability stability of the accumulation [55]. But, no considerable difference was observed in the clogging of graded distribution slag due to a different dry density in our experiments. It was also found that the change in dry density had a significant effect on the permeability, but not on the clogging effect. This evidence demonstrated that the clogging was most closely related to the effective aperture of particles, that was related to the equivalent particle size and the porosity of the graded distribution soil, and slag shape, nothing to do with the dry density of the graded distribution soil. In conclusion, the particle size or equivalent particle size and the particle shape characteristics were determined as the main factors affecting the accumulation clogging performance, while the dry density of accumulation had no significant influence on it.
Author Contributions
All the authors have made significant contributions to the writing and revision of this article. Among them, S.L.: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, methodology, funding acquisition, writing—original draft; J.C.: investigation, project administration, validation, visualization, writing—review and editing; J.M.: conceptualization, investigation, visualization, writing—original draft; H.L.: investigation, project administration, validation; H.G.: investigation, resources, writing—original draft; Y.Q.: validation, writing—review and editing; F.H.: validation; Y.J.: validation; S.L. was the person responsible for this article; J.M., S.L. and H.G. were the corresponding authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41907255, 41602359, 42177155) and the Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (No. 2017JQ4019).
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Hao Li was employed by Kunming Engineering Corporation limited. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Valenta, R.K.; Lèbre, É.; Antonio, C. Decarbonisation to drive dramatic increase in mining waste-Options for reduction. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 190, 106859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.-H.; Cui, Y.-F.; Peng, J.-B. Erosion and transport mechanisms of mine waste along gullies. J. Mt. Sci. 2019, 16, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhou, K.-L.; Jin, W.; Ma, N.; Zeng, C. Hazard characteristics and causes of the “7.22” 2021 debris flow in Shenshuicao gully, Qilian Mountains, NW China. Landslides 2023, 20, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-X. Research on the Development Law and Initiation Mechanism of Mine Slag Debris. Master’s Thesis, North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, Zheng Zhou, China, May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.-H.; Zhuang, J.-Q.; Li, Y.-Z.; Zhang, L.-Y. Model Test on Sediment Discharge Rate of Debris Flow Induced by Mine Waste. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2017, 34, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.-S.; Fan, W.; Xiong, W.; Yan, F.-R. Development Features and Risk of Inducing Slag Debris Flow at Daxicha Gully. Eng. Geol. 2009, 17, 415–420. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.-N.; Chen, H.-Q.; Yang, M.; Ke, H.-L.; Zhang, J.-H.; Liu, R.-P.; Qiao, G. Controlling role of particle sizes of mining waste residues in the initiation of mine debris flow: A case study of the Xiaoqinling gold mining area. Geol. Bull. China 2015, 34, 1993–2000. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, X.-C. Development Law and Environmental Effect of Typical Mine Debris Flow in West Qinling Mountains; Shaanxi Science and Technology Press: Xi’an, China, 2010; pp. 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, J.-Q.; Cui, P.; Hu, K.-H.; Chen, X.-Q. Fine Particle Size Moving and It’s Effective on Debris Flow Initiation. Mt. Res. Dev. 2015, 33, 713–720. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.-F.; Zhou, X.-J.; Guo, C.-X. Experimental study on the moving characteristics of fine grains in wide grading uncon-solidated soil under heavy rainfall. J. Mt. Sci.-Engl. 2017, 14, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-B.; Mai, T.-K.; Qi, C. Effect of Fine of Soil in the Process of Debris Flow Preparation and Initiation. J. Eng. Geol. Guilin China 2017, 25, 357–364. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.-H.; Liu, B.-X.; Peng, J.-B.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Zhuang, J.-Q.; Huang, W.-L.; Leng, Y.-Q.; Duan, Z. Experimental study on the longitudinal evolution of the overtopping breaching of noncohesive landslide dams. Eng. Geol. 2021, 288, 106–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.-H.; Peng, J.-B.; Jiang, C.; Guo, W.-L. A Preliminary Study of the Failure Modes and Process of Landslide Dams Due to Upstream Flow. Water 2019, 11, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, G.A.; Well, S.G. Fire-Related Sedimentation Events on Alluvial Fans, Yellowstone National Park, U.S.A. J. Sedi.-Ment. Res. 1997, 67, 776–791. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, M.E.; Brien, D.L.; Lahusen, R.; Roering, J.; Fuente, J.D.L.; Ellen, S.D. Debris-flow initiation from large, slow-moving landslides. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Debris-Flow Hazards Mitigation: Mechanics, Prediction, and Assessment, Davos, Switzerland, 10–12 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Coe, J.A.; Kinner, D.A.; Godt, J.W. Initiation Conditions for Debris Flows Generated by Runoff at Chalk Cliffs, Central Colorado. Geomorphology 2008, 96, 270–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.-B. Experiment of Initiation Mechanism of Mine Debris Flow. Master’s Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.-N.; Cao, Y.-B.; Zhang, J.-H.; Chen, H.-Q.; Yang, M.; Wang, X.-W. Research on Starting of Mine Debris Flow Based on Artificial Simulation Experiment in Xiaoqinling Gold Ore Area. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2009, 28, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.-B.; Wang, C.-M.; Wang, G.-C.; Ma, J.-Q. Infiltration clogging test and simulation by PFC3D for loose dam foundation. Shuili Xuebao 2012, 43, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, P.; Zhang, L.-M.; Chen, H.-X.; Fan, R.-L. EDDA 2.0: Integrated simulation of debris flow initiation and dynamics considering two initiation mechanisms. Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 2841–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Che, H.-X. Hazard assessment of a catastrophic mine waste debris flow of Hou Gully, Shimian, China. Eng. Geol. 2020, 275, 105733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Cui, Y.-F. Combining seismic signal dynamic inversion and numerical modeling improves landslide process re-construction. Earth Surf. Dyn. 2022, 10, 1233–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-D.; Du, D.-W.; Man, T.; Ge, Z.; Huppert, H.E. Particle clogging mechanisms in hyporheic exchange with coupled lattice Boltzmann discrete element simulations. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 013312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-B.; Li, K.; Wang, R.; Hu, M.-J. Impact of fine particle content on mode and scale of slope instability of debris flow. Adv. Sci. Technol. Water Resour. 2016, 36, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Z.; Zhang, S. A preliminary analysis of the characteristics of debris flow. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on River Sedimentation; Chinese Society for Hydraulic Engineering: Beijing, China, 1980; pp. 225–226. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, X.-J. Effect of Fine Grain and Debris Flow Slurry Bodies on Debris Flow Motion. Mt. Res. 1991, 9, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, P. Studies on condition and mechanism of debris flow initiation by means of experiment. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1992, 37, 759–763. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Tang, H.; Hu, K.-H.; Jens, M.T.; Wei, F.-Q. Deriving debris-flow dynamics from real-time impact-force measure-ments. J. Geophys. Res.-Earth 2023, 128, e2022JF006715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T. Debris Flow: Mechanics, Prediction and Countermeasures, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis: Leiden, the Netherlands; London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. Seepage Control of Earth-Rock Dams Theoretical Basis; Engineering Experiences and Lessons; China Water & Power Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 30–45. [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi, K.; Peck, R.B.; Mesri, G. Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice, 3rd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1996; p. 592. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.-Q.; Zhao, X.-J.; Li, S.-B.; Peng, H.; Xiao, L.-L.; Ma, D.-H.; Zhang, X.-S. Exploring the clogging process in coarse soil deposits in a dam Foundation. B Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddi, L.N.; Xiao, M.; Hajra, M.G.; Lee, I.M. Physical clogging of soil filters under constant flow rate versus constant head. Can. Geotech. J. 2005, 42, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandra, H.S.; McCarthy, D.; Fletcher, T.D.; Deletic, A. Assessment of clogging phenomena in granular flter media used for stormwater treatment. J. Hydrol. 2014, 512, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatt, B.E.; Fletcher, T.D.; Deletic, A. Hydraulic and pollutant removal performance of fine media stormwater filtration systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 7, 2535–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-J.; Du, X.-Q.; Yang, Y.-S.; Ye, X.-Y. Surface clogging process modeling of suspended solids during urban storm-water aquifer recharge. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 1418–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.-W. Different soil classifications in domestie geoteehnieal standards. In Proceedings of the 2nd National Conference on Engineering Safety and Protection, Beijing, China, 20–22 August 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.-Q.; Peng, H.; Li, S.-B.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, X.-S.; Ma, D.-H. Exploring the Occurrence of Clogging in Highly Permeable Coarse Soils of Dam Foundations. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 3, 8868052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-B.; Wang, C.-M.; Wang, G.-C.; Ma, J.-Q. Clogging types distinguishing of coarse-grained soil and determination of optimal range of clogging grain size. Shuili Xuebao 2013, 44, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar]
- Mintz, D.M.; Schubert, S.A.; Hui, Y.-J.; Ma, H.-M. Hydraulics on Granular Materials; Water Conservancy Press: Beijing, China, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Rao, Y.-K.; Ni, Q. Effects of gradation and void ratio on the coefficient of permeability of coarse-grained soil. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2019, 46, 108–116. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Li, Y.; Gou, H.-X.; Asch, T.; Gao, X.; Zheng, Y.-S.; Xin, C.-L. Hydraulic properties of co-seismic landslide deposits around the Wenchuan earthquake epicentre: Large-scale column experiments. Eng. Geol. 2021, 287, 106102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-D.; Huang, T.-W.; Wu, Y.-J. Soil drainage clogging mechanism under vacuum preloading: A review. Transp. Geotech. 2024, 45, 101178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T.; Ikeda, A.; Nagayama, T.; Mizuyama, T. Hydraulic model tests for propagation of flow and sediment in floods due to breaking of a natural landslide dam during a mountainous torrent. Int. J. Sediment. Res. 2018, 33, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.-S.; Tang, C.; Chen, Z.-H.; Wang, S.-Y.; Yang, T. A calculation method for predicting the runout volume of dam-break and non-dam-break debris flows in the Wenchuan earthquake area. Geomorphology 2019, 327, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.-S.; Zhou, W.; Yang, C.-L.; Hu, G.-S.; Gao, Y.-C.; Han, D. The processes and mechanism of failure and debris flow initiation for gravel soil with different clay content. Geomorphology 2010, 121, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.-H.; Peng, J.-B.; Jiang, C.; Guo, W.-L. Formation conditions of landslide dams triggered by incision of mine waste accumulations. J. Mt. Sci.-Engl. 2019, 16, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Li, Y.; Fan, Y.; Xiong, M.-Z.; Luo, H.; Mcsaveney, M.; Zheng, Y.-S. Flow amplification from cascading landslide dam failures: Insights from flume experiments. Eng. Geol. 2022, 297, 106483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.-H.; Peng, J.-B.; Liu, B.-X.; Jiang, C.; Guo, J. Influence of textural properties on the failure mode and process of landslide dams. Eng. Geol. 2020, 271, 105613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, S.-F. Formation mechanisms and prediction models of debris flow due to natural dam failures. J. Sediment Res. 1993, 4, 42–57. [Google Scholar]
- Awal, R.; Nakagawa, H.; Kawaike, K.; Baba, Y.; Zhang, H.; Kawaike, K. Experimental study on prediction of failure mode of landslide dams. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion, Tokyo, Japan, 5–7 November 2008; pp. 655–660. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Cao, S.-Y.; Yang, K.-J.; Li, W.-P. Experimental study of breach process of landslide dams by overtopping and its initiation mechanisms. J. Hydrodyn. 2015, 27, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.-G.; Wei, Y.-W.; Wu, L.; Lei, Y. Experimental investigation of failure modes and breaching characteristics of natural dams. Geomat. Nat. Haz. Risk 2018, 9, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermini, L.; Casagl, N. Prediction of the behavior of landslide dams using a geo-morphological dimensionless index. Earth Surf. Proc. Land 2003, 28, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrashk, M.; Chang, S.-C.; Deng, Y.-B. On active and inactive voids and a compression model for granular soils. Eng. Geol. 2017, 222, 156–167. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).