Study on the Typical Environmental Factors in the Middle Part of Zhoushan Fishery Based on HY-1C/D and Other Multi-Source Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Method
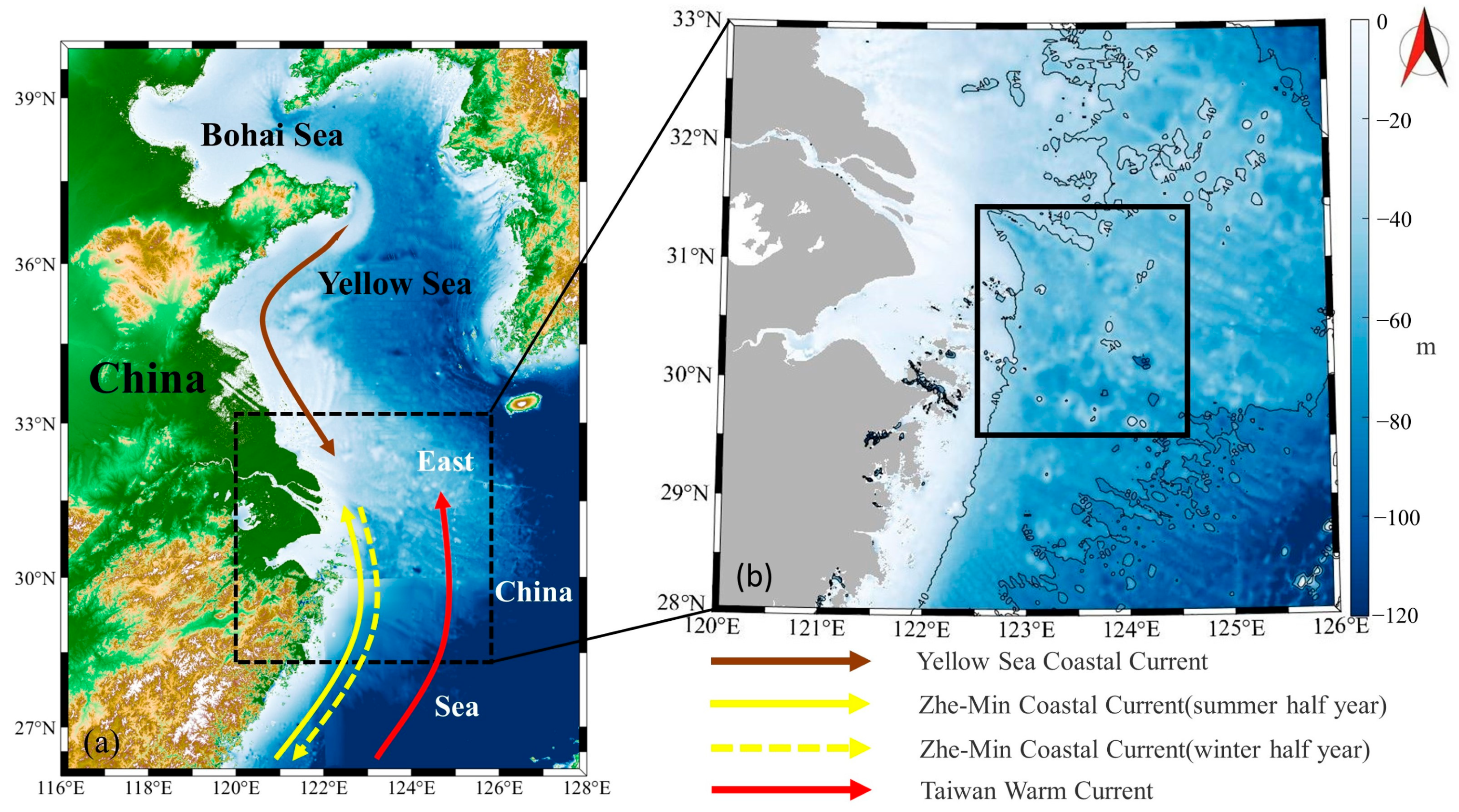
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Satellite Data
2.3. In Situ Data and Process
2.4. Temperature, Wind, Salinity, Current, and Chl-a Concentration Data
2.5. Data Processing
3. Results
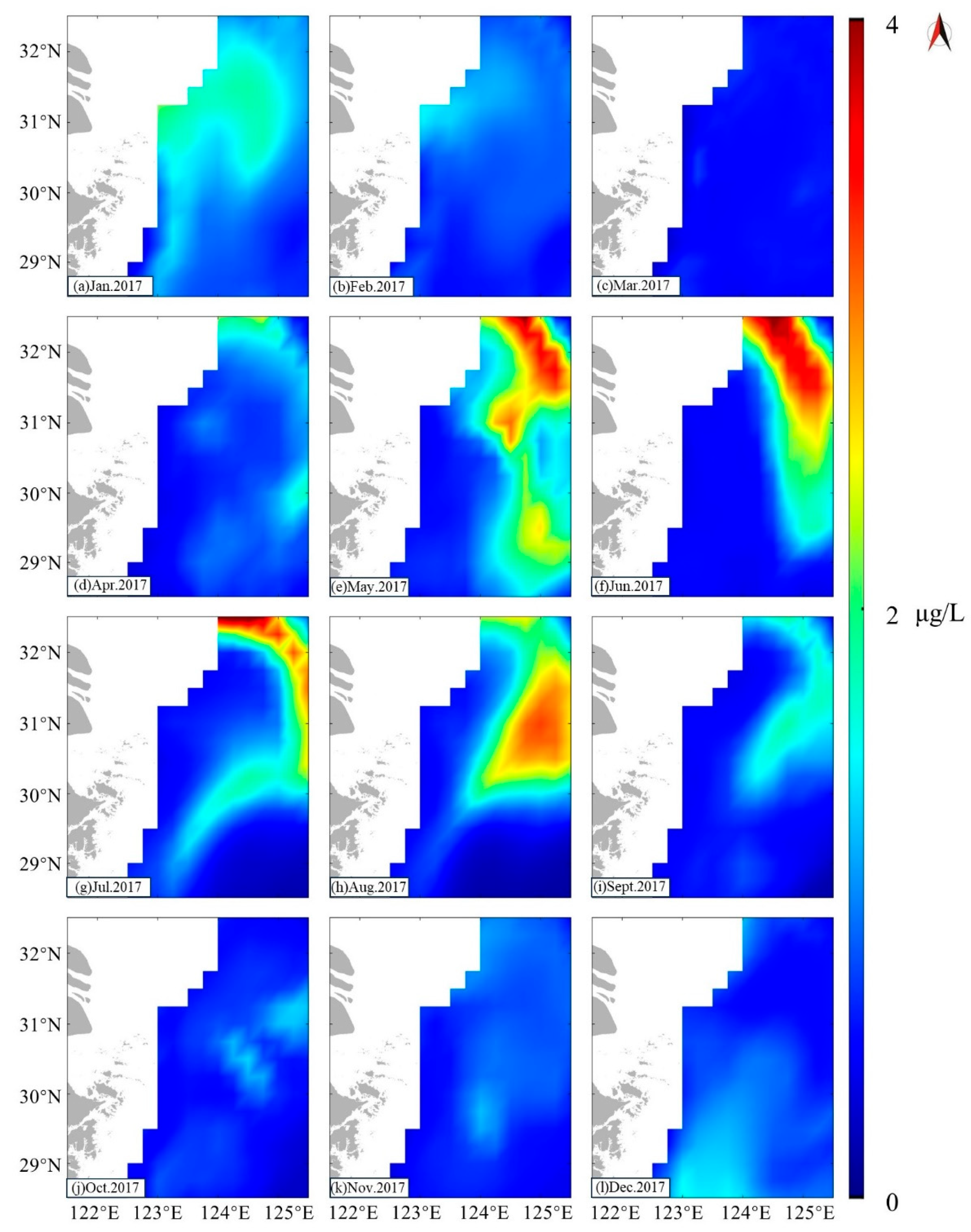
3.1. Chl-α Concentration in Study Area
3.2. Distribution of Monthly Mean OPP
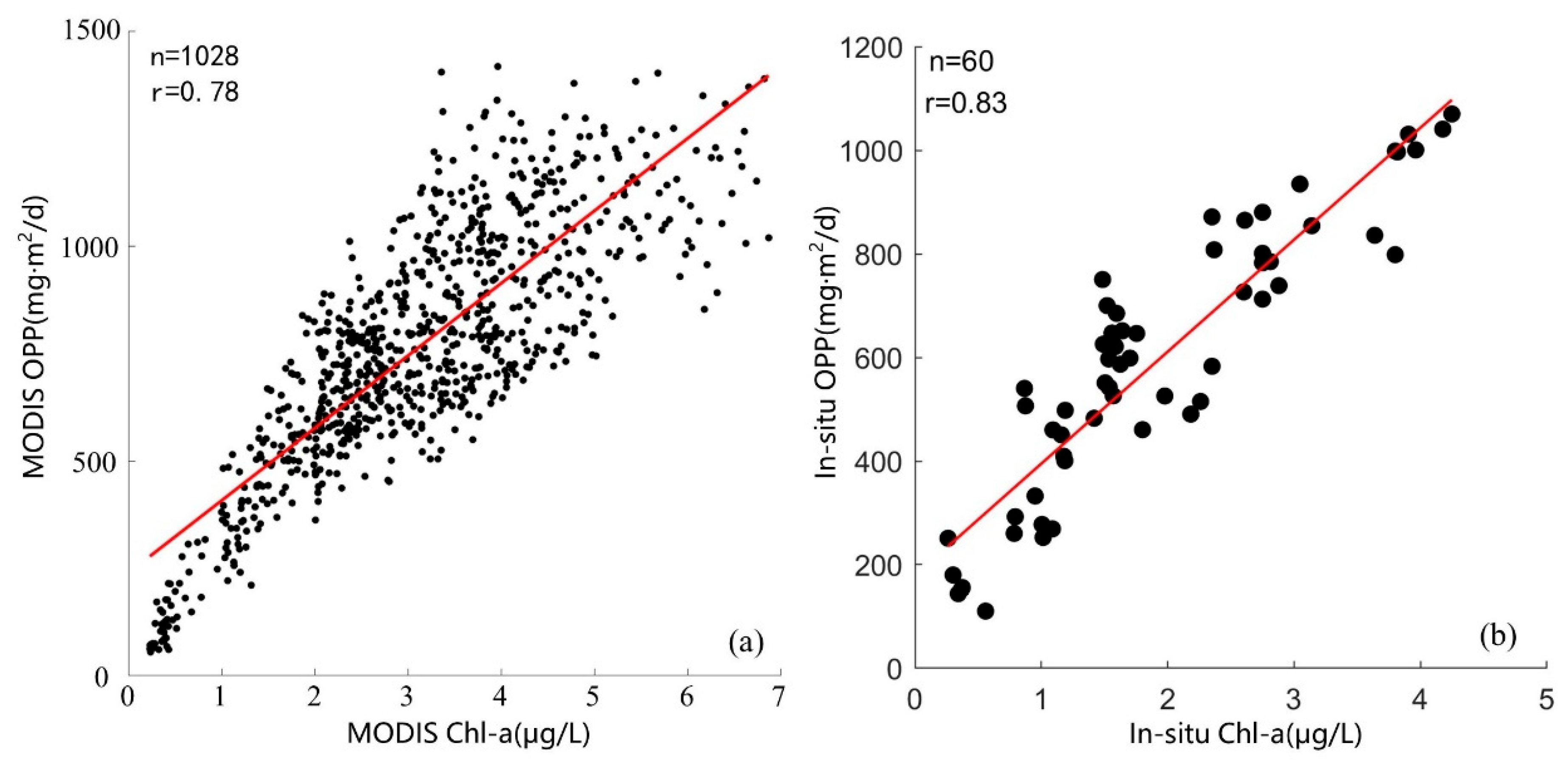
3.3. The Relationship between Chl-α Concentration and OPP
3.4. Establishment of OPP Inverse Model
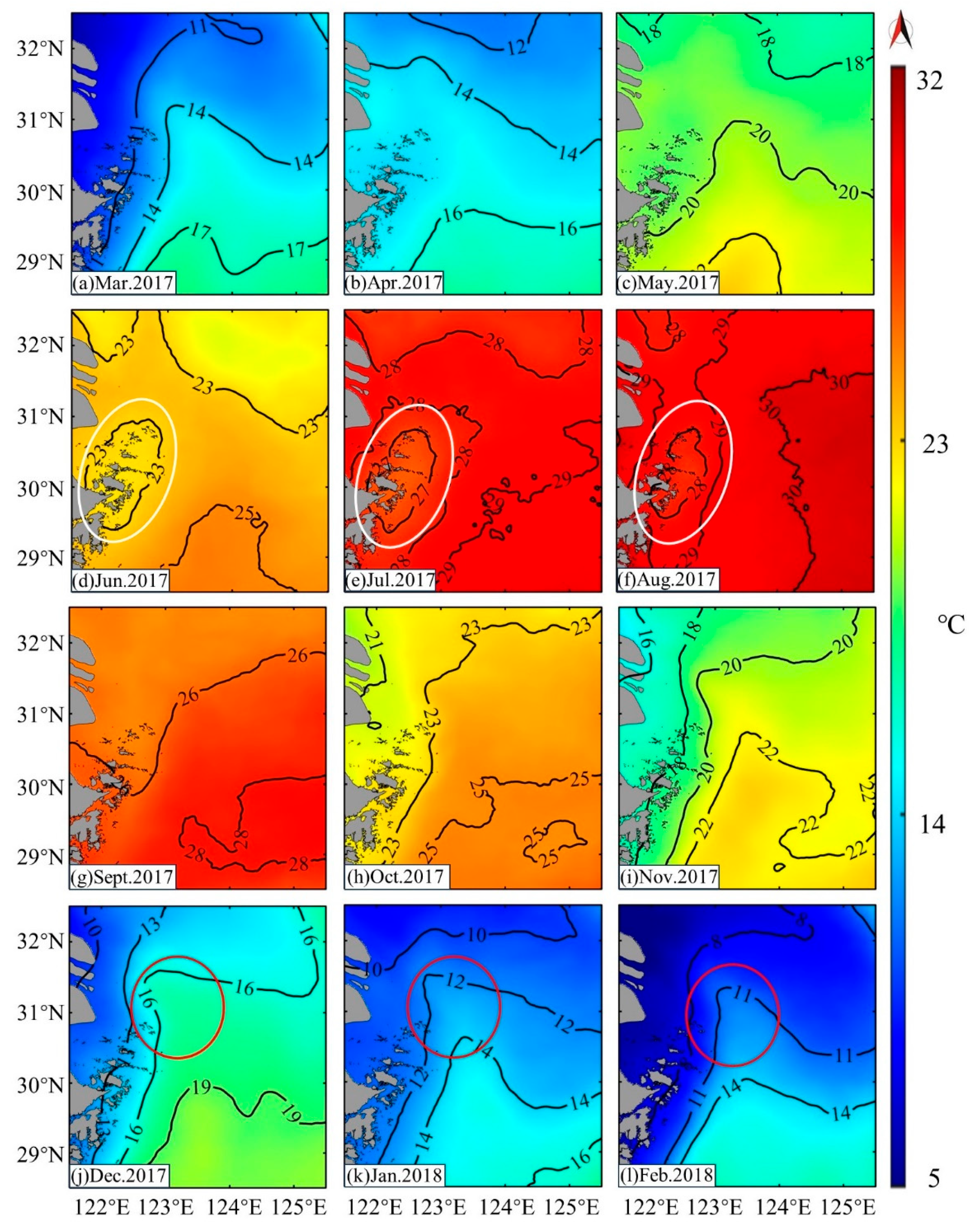
3.5. Temperature in Study Area
3.6. Hydrological Factors and Salinity
4. Discussion
4.1. Factors Contributing to the Formation of Zhoushan Fishery
4.1.1. Temperature
4.1.2. Chl-α and OPP
4.1.3. Current and Wind
4.1.4. Other Factors
4.1.5. Relationships between Different Environmental Factors
4.2. Advantages of the Model
4.3. Suggestions for the Protection and Development of Zhoushan Fishery
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, L.; Tang, R.; Yan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, J.; Yu, M. The Spatial-Temporal Consistency of Chlorophyll-a and Fishery Resources in the Water of the Zhoushan Archipelago Revealed by High Resolution Remote Sensing. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1022375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassot, E.; Bonhommeau, S.; Dulvy, N.K.; Mélin, F.; Watson, R.; Gascuel, D.; Le Pape, O. Global Marine Primary Production Constrains Fisheries Catches. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boltaña, S.; Sanhueza, N.; Aguilar, A.; Gallardo-Escarate, C.; Arriagada, G.; Valdes, J.A.; Soto, D.; Quiñones, R.A. Influences of Thermal Environment on Fish Growth. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 6814–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bœuf, G.; Payan, P. How Should Salinity Influence Fish Growth? Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2001, 130, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J.; Yicheng, W.; Renfeng, M.A. Change Conalysis of Chlorophyll Concentration in the East China Sea and Its Response to Seawater Temperature. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2020, 6, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Gong, F. Satellite remote sensing of chlorophyll a concentration in the north Pacific Fisher. Shuichan Xuebao 2005, 29, 270–274. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Wu, Y. Relation between chlorophyl II and SST fronts of the North Pacific and the distribution of squid fishing grounds. Fish. Inf. Strategy 2016, 31, 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Gaol, J.L.; Pasaribu, B.; Manurung, D.; Endriani, R. The Fluctuation of Chlorophyll-A Concentration Derived from Satellite Imagery and Catch of Oily Sardine (Sardinella Lemuru0) in Bali Strait. Int. J. Remote Sens. Earth Sci. (IJReSES) 2010, 1, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhu, W.; Zhu, H. Distribution of juvenile anchovy Japonicus and its relationship with environmental factors along the coast of Zhejiang. J. Fish. Sci. China 2021, 28, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Chen, X. Study on the Relationship between Catch of Mackerel and Environmental Factors in the East China Sea in Summer. J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Wang, X.; Li, S. Effects of Intensity and Environment Factors on Marine Primary Productivity. J. Xiamen Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 1989, 28, 423–426. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Kong, D.; Ma, L. The Influence for the Ocean Primary Yield-Power (Chlorofucine) with the Change of Inorganic Nitrogen and Reactive Phosphate in the Bohai Ocean Gulf. Environ. Monit. Chin. 2004, 20, 52–54. [Google Scholar]
- Morin, A.; Lamoureux, W.; Busnarda, J. Empirical Models Predicting Primary Productivity from Chlorophyll a and Water Temperature for Stream Periphyton and Lake and Ocean Phytoplankton. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 1999, 18, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Mao, F.; Jin, P.; Cheng, Q. Spatial-Temporal Variations of Chlorophyll-a in Qiandao Lake Using GF1_WFV Data. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 4580–4588. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Hong, Y.; Lu, F. A Study on the Correlation between the Marine Primary Productivity of Pearl River Estuary and Human Activities. Sci.-Tech Innov. Product. 2019, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wenjiang, G.; Xinjun, C.; Feng, G.; Gang, L. Study on the Dynamics of Biomass of Chub Mackerel Based on Ocean Net Primary Production in Southern East China Sea. Haiyang Xuebao 2013, 35, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Xinjun, C.; Qian, Y. Relationship between Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Neon Flying Squid Ommastrephes Bartramii and Net Primary Production in the Northwest Pacific Ocean. Haiyang Xuebao 2016, 38, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Murawski, S.A. Climate Change and Marine Fish Distributions: Forecasting from Historical Analogy. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1993, 122, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediodia, H.J.P. Effects of Sea Surface Temperature on Tuna Catch: Evidence from Countries in the Eastern Pacific Ocean. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 209, 105657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B. A study on the relationship between the distribution of fishing ground of Chilean Jack mackerel (Trachrus murphyi) and marine environment based on the fishery. In Proceedings of the Fishery Science and Technology Innovation and Development Mode Change–2011 Chinese Fisheries Society Annual Meeting Paper Abstract Collection, Xiamen, China, 15 November 2011; p. 592. [Google Scholar]
- Putri, A.R.S.; Zainuddin, M.; Musbir, M.; Mustapha, M.A.; Hidayat, R.; Putri, R.S. Impact of Increasing Sea Surface Temperature on Skipjack Tuna Habitat in the Flores Sea, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 763, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Zhou, S.; Cui, X.; Wang, D.; Shen, X. The Application Research and development of Satellite Remote Sensing for Marine Fisheries. J. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 21, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, H.; Zhao, T.; Chen, L.; Lin, S. Test of the Ocean Color Radiant Models in SeaWiFS Data. Mar. Environ. Sci. 1999, 18, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Jianqiang, L.; Xiaomin, Y.; Qingjun, S.; Jing, D.; Bin, Z. Products of HY-1C/D Ocean Color Satellites and Their Typical Applications. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2023, 27, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, C.; Mu, B.; Liu, R.-J.; Ding, J.; Zhang, M.-W.; Xiao, Y.-F.; Liang, X.-J.; Chen, X.-Y. Atmospheric Correction Algorithm for HY-1C CZI over Turbid Waters. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 90, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Guo, C. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Primary Productivity of the Yellow Sea Using HY-1B Satellite Data. Mod. Surv. Mapp. 2017, 40, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, R.; Cai, L.; Yan, X.; Ye, X.; Xu, Y.; Yin, J. Study of the Response of Environmental Factors of the Coastal Area in Zhoushan Fishery to Typhoon In-Fa Based on Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yu, Y.; Liu, C. Studies on the Situation of Pollution and Countermeasures of Control of the Oceanic Environment in Zhoushan Fishing Ground—The Largest Fishing Ground in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1991, 23, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Lu, J. Present Utilization Situation of Main Fishery Resources in Zhoushan Fishing Ground. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 14, 569–572. [Google Scholar]
- Qi-long, Z.; Fan, W.; Wei-hong, Z.; Xiao-hui, T. Seasonal Characteristics in the Water Masses in Zhoushan Fishing Ground and Adjacent Region. Haiyang Xuebao 2007, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yongdong, Z.; Haiwei, J.; Rijin, J. The Category Composition and Abundance Distributions of Ichthyoplankton along the North-Central Coast of Zhejiang Province in Spring and Summer. J. Fish. China 2011, 35, 881–889. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Yu, M.; Yan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, S. HY-1C/D Reveals the Chlorophyll-a Concentration Distribution Details in the Intensive Islands’ Waters and Its Consistency with the Distribution of Fish Spawning Ground. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y. Temporal and Spatial Dynamics of Phytoplankton Primary Production in Lake Taihu Derived from MODIS Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johan, F.; Jafri, M.Z.; Lim, H.S.; Wan Maznah, W.O. Laboratory Measurement: Chlorophyll-a Concentration Measurement with Acetone Method Using Spectrophotometer. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management, Selangor, Malaysia, 9–12 December 2014; pp. 744–748. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, U.T. Primary Production in Saline Lakes. In Proceedings of the Salt Lakes; Williams, W.D., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1981; pp. 47–57. [Google Scholar]
- Le Traon, P.Y.; Reppucci, A.; Alvarez Fanjul, E.; Aouf, L.; Behrens, A.; Belmonte, M.; Bentamy, A.; Bertino, L.; Brando, V.E.; Kreiner, M.B.; et al. From Observation to Information and Users: The Copernicus Marine Service Perspective. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madec, G.; Bourdallé-Badie, R.; Bouttier, P.-A.; Bricaud, C.; Bruciaferri, D.; Calvert, D.; Chanut, J.; Clementi, E.; Coward, A.; Delrosso, D.; et al. NEMO Ocean Engine. 2017. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/3248739 (accessed on 20 April 2024).
- Wang, H.; You, Z.; Guo, H.; Zhang, W.; Xu, P.; Ren, K. Quality Assessment of Sea Surface Salinity from Multiple Ocean Reanalysis Products. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.A.; Smedstad, O.M. Variational Data Assimilation for the Global Ocean. In Data Assimilation for Atmospheric, Oceanic and Hydrologic Applications (Volume II); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 303–343. ISBN 978-3-642-35088-7. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H. Preliminarily Comparative Study on the Applicability of ERA5 and ERA5-Land Ground Wind Speed Data over China’s Land Region. Clim. Environ. Res. 2024, 29, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Dong, L.; Yan, R.; Zhang, X.; Guo, C.; Liang, S.; Tu, J.; Feng, X.; Wang, X. Evaluation of Near-Surface Wind Speed Climatology and Long-Term Trend over China’s Mainland Region Based on ERA5 Reanalysis. Clim. Environ. Res. 2021, 26, 299–311. [Google Scholar]
- Xueping, W. Geometric Rectification and Effect Analysis of Remote Sensing Image. Comput. Appl. Softw. 2008, 25, 102–105. [Google Scholar]
- Zhengqing, G.; Zhigao, Y.; Xianfeng, W. Relative Radiometric Calibration and Radiometric Calibration Site. Remote Sens. Aer. Photogr. 2009, 4, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Zhou, M.; Liu, J.; Tang, D.; Zuo, J. HY-1C Observations of the Impacts of Islands on Suspended Sediment Distribution in Zhoushan Coastal Waters, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, X.; Ding, J.; Bai, Y.; Wang, D.; Gong, F.; Li, T. The Inversion of HY-1C-COCTS Ocean Color Remote Sensing Products from High-Latitude Seas. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrenfeld, M.J.; Falkowski, P.G. Photosynthetic Rates Derived from Satellite-Based Chlorophyll Concentration. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameda, T.; Ishizaka, J. Size-Fractionated Primary Production Estimated by a Two-Phytoplankton Community Model Applicable to Ocean Color Remote Sensing. J. Oceanogr. 2005, 61, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Chen, C.; Sun, Z.; Tang, S.; Song, X.; Yang, C.; Tian, L.; Liu, F. Estimation of the Primary Productivity in Pearl River Estuary Using MODIS Data. Estuaries Coasts 2015, 38, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D. Progress and Prospect of Remote Sensing on Phytoplankton Primary Productivity Estimation. Remote Sens. Inf. 2017, 32, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Ning, P.; Zheng, J. Species Composition and Quantitative Distribution of Fish in the Zhoushan Fishing Ground and Its Adjacent Waters. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. /Hai Yang Yu Hu Chao 2010, 41, 410–417. [Google Scholar]
- Klemas, V. Fisheries Applications of Remote Sensing: An Overview. Fish. Res. 2013, 148, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurel, B.J.; Copeman, L.A.; Spencer, M.; Iseri, P. Temperature-Dependent Growth as a Function of Size and Age in Juvenile Arctic Cod (Boreogadus Saida). ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2017, 74, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, F. Climatological Analysis of Water Masses in Zhoushan Fishing Ground and Adjacent Region. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2004, 35, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, X.; Jin, X. Diversity of Fish Community Structure in the Spring-Time Offshore Waters at the Yangtze River Estuary. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2011, 42, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Jian-sheng, L.; Fen, H.; Li-ping, Y. Study on the Rational Utilization of Pampus Argenteus Resources in the East China Sea Region. J. Nat. Resour. 2014, 29, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, W.; Chen, X.; Li, G. Influence of Sea Surface Temperature and La Niña Event on Temporal and Spatial Fluctuation of Chub Mackerel (Scomber Japonicus) Stock in the East China Sea. J. Shanghai Ocean. Univ. 2011, 20, 102–107. [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo, K.R.; Worthen, D.; Schnell, A.; Lizotte, M.P. Primary Production in Southern Ocean Waters. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1998, 103, 15587–15600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, M.L.; Knauer, G.A.; Karl, D.M.; Martin, J.H. Primary Production, New Production and Vertical Flux in the Eastern Pacific Ocean. Nature 1987, 325, 803–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polovina, J.J.; Howell, E.; Kobayashi, D.R.; Seki, M.P. The Transition Zone Chlorophyll Front, a Dynamic Global Feature Defining Migration and Forage Habitat for Marine Resources. Prog. Oceanogr. 2001, 49, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oglesby, R.T. Relationships of Fish Yield to Lake Phytoplankton Standing Crop, Production, and Morphoedaphic Factors. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 1977, 34, 2271–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifullah, A.S.M.; Kamal, A.H.M.; Idris, M.H.; Rajaee, A.H.; Bhuiyan, M.K.A. Phytoplankton in Tropical Mangrove Estuaries: Role and Interdependency. For. Sci. Technol. 2016, 12, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Jin, J.; Zhang, X.; Lu, X.; Wang, Y. Spatial-Temporal Variations of Chlorophyll-a in the Adjacent Sea Area of the Yangtze River Estuary Influenced by Yangtze River Discharge. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 5420–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, G.-C.; Wen, Y.-H.; Wang, B.-W.; Liu, G.-J. Seasonal Variation of Chlorophyll a Concentration, Primary Production and Environmental Conditions in the Subtropical East China Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2003, 50, 1219–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druon, J.-N.; Fromentin, J.-M.; Aulanier, F.; Heikkonen, J. Potential Feeding and Spawning Habitats of Atlantic Bluefin Tuna in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 439, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S. Reviews on the Biology and Culture of Silver Pomfret, Pampus Argenteus (Euphrasen, 1788). Int. J. Aquat. Biol. 2020, 8, 228–245. [Google Scholar]
- Trombetta, T.; Vidussi, F.; Mas, S.; Parin, D.; Simier, M.; Mostajir, B. Water Temperature Drives Phytoplankton Blooms in Coastal Waters. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, B.; Huang, B.; Wang, J.; Zheng, J.; Ning, P.; Yu, C. Analysis on Community Structure of Zooplankton in Zhoushan Fishing Ground and Its Adjacent Area in Summer. Zool. Res. 2010, 31, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shou, L.; Huang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Gao, A.; Liao, Y.; Chen, Q. Seasonal Changes of Macrobenthos Distribution and Diversity in Zhoushan Sea Area. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2009, 12, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Yin, W.; Feng, J.; Liu, Y.; Wong, K.; Tsou, J.Y.; Zhang, Y. Satellite-Based Analysis of Surface Upwelling in the Sea Adjacent to Zhoushan Islands in China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiansheng, L.I.; Fen, H.U.; Nan, L.I.N. Ecological Distribution of Fish Larvae and Juveniles in the Yangtze River Estuary and Its Adjacent Waters in Spring. South China Fish. Sci. 2015, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Halvorsen, K.T.; Sørdalen, T.K.; Larsen, T.; Browman, H.I.; Rafoss, T.; Albretsen, J.; Skiftesvik, A.B. Mind the Depth: The Vertical Dimension of a Small-Scale Coastal Fishery Shapes Selection on Species, Size, and Sex in Wrasses. Mar. Coast. Fish. 2020, 12, 404–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labropoulou, M.; Papaconstantinou, C. Community Structure and Diversity of Demersal Fish Assemblages: The Role of Fishery. Sci. Mar. 2004, 68, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhao, X.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, K.; Chen, Z. Relationship Between Multi-Factors and Short-Term Changes in Fishery Resources. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 693950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhurst, A.R.; Glen Harrison, W. The Biological Pump: Profiles of Plankton Production and Consumption in the Upper Ocean. Prog. Oceanogr. 1989, 22, 47–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beland, K.F.; Jordan, R.M.; Meister, A.L. Water Depth and Velocity Preferences of Spawning Atlantic Salmon in Maine Rivers. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1982, 2, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, X.; Qiao, F.; Xia, C.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, Y. Upwelling off Yangtze River Estuary in Summer. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, X. A Review on Impact of Salinity on Patterns of Fish Ecophysiology. Stud. Mar. Sin. 2002, 44, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, F.; Peng, S.; Sun, P.; Shi, Z. Effects of Low Salinity on Antioxidant Enzymes Activities in Kidney and Muscle of Juvenile Silver Pomfret Pampus Argenteus. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, S. Atlas of the Main Economic Species, Three Fields, One Corridor, and Protected Areas in the East China Sea Region; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, C.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Tsou, J.; Jiang, T.; Liang, X.S. Evaluating the Impact of Sea Surface Temperature (SST) on Spatial Distribution of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in the East China Sea. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 68, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohrenz, S.E.; Wiesenburg, D.A.; DePalma, I.P.; Johnson, K.S.; Gustafson, D.E. Interrelationships among Primary Production, Chlorophyll, and Environmental Conditions in Frontal Regions of the Western Mediterranean Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part A Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1988, 35, 793–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedland, K.D.; Stock, C.; Drinkwater, K.F.; Link, J.S.; Leaf, R.T.; Shank, B.V.; Rose, J.M.; Pilskaln, C.H.; Fogarty, M.J. Pathways between Primary Production and Fisheries Yields of Large Marine Ecosystems. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e28945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazier, J. Seasonal Variability of Temperature and Salinity in the Labrador Current. J. Mar. Res. 1982, 40, 341–356. [Google Scholar]
- Emery, W.J.; Dewar, J.S. Mean Temperature-Salinity, Salinity-Depth and Temperature-Depth Curves for the North Atlantic and the North Pacific. Prog. Oceanogr. 1982, 11, 219–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.F.; Brown, J.H. Patterns of Diversity, Depth Range and Body Size among Pelagic Fishes along a Gradient of Depth. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2002, 11, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Sensor | Band | Spectral Range/μm | Spatial Resolution/m |
|---|---|---|---|
| CZI | Band1 (Blue) | 0.421–0.500 | 50 |
| Band2 (Green) | 0.517–0.598 | ||
| Band3 (Red) | 0.608–0.690 | ||
| Band4 (NIR) | 0.761–0.891 |
| Number | Function | Fitting Model | R2 | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model1 | polynomial | y = 296.57x − 87.21 | 0.8249 | 115.95 |
| Model2 | polynomial | y = 42.59x2 + 133.7x + 29.63 | 0.8367 | 108.02 |
| Model3 | polynomial | y = 60.66 + 55.9x + 91.3x2 − 8.24x3 | 0.8377 | 107.65 |
| Model4 | Exponential | y = 0.77e(4.44x) | 0.7689 | 159.69 |
| Model5 | logarithmic | y = 323.24ln(x) + 292.00 | 0.5627 | 182.10 |
| Model6 | logarithmic | y = 190.8ln(2.41x) + 155.6 | 0.4932 | 209.79 |
| Model7 | power | y = 0.9698x5.39 | 0.8018 | 144.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Cai, L.; Yu, M.; Tang, R. Study on the Typical Environmental Factors in the Middle Part of Zhoushan Fishery Based on HY-1C/D and Other Multi-Source Data. Water 2024, 16, 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101387
Zhang X, Cai L, Yu M, Tang R. Study on the Typical Environmental Factors in the Middle Part of Zhoushan Fishery Based on HY-1C/D and Other Multi-Source Data. Water. 2024; 16(10):1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101387
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xinkai, Lina Cai, Menghan Yu, and Rong Tang. 2024. "Study on the Typical Environmental Factors in the Middle Part of Zhoushan Fishery Based on HY-1C/D and Other Multi-Source Data" Water 16, no. 10: 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101387
APA StyleZhang, X., Cai, L., Yu, M., & Tang, R. (2024). Study on the Typical Environmental Factors in the Middle Part of Zhoushan Fishery Based on HY-1C/D and Other Multi-Source Data. Water, 16(10), 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101387






