Abstract
Gas-phase chemistry has been identified as a major computational bottleneck in both the forward and adjoint modes of chemical transport models (CTMs). Although previous studies have demonstrated the potential of deep learning models to simulate and accelerate this process, few studies have examined the applicability and performance of these models in adjoint sensitivity analysis. In this study, a deep learning emulator for gas-phase chemistry is developed and trained on a diverse set of forward-mode simulations from the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) model. The emulator employs a residual neural network (ResNet) architecture referred to as FiLM-ResNet, which integrates Feature-wise Linear Modulation (FiLM) layers to explicitly account for photochemical and non-photochemical conditions. Validation within a single timestep indicates that the emulator accurately predicts concentration changes for 74% of gas-phase species with coefficient of determination (R2) exceeding 0.999. After embedding the emulator into the CTM, multi-timestep simulation over one week shows close agreement with the numerical model. For the adjoint mode, we compute the sensitivities of ozone (O3) with respect to O3, nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), hydroxyl radical (OH) and isoprene (ISOP) using automatic differentiation, with the emulator-based adjoint results achieving a maximum R2 of 0.995 in single timestep evaluations compared to the numerical adjoint sensitivities. A 24 h adjoint simulation reveals that the emulator maintains spatially consistent adjoint sensitivity distributions compared to the numerical model across most grid cells. In terms of computational efficiency, the emulator achieves speed-ups of 80×–130× in the forward mode and 45×–102× in the adjoint mode, depending on whether inference is executed on Central Processing Unit (CPU) or Graphics Processing Unit (GPU). These findings demonstrate that, once the emulator is accurately trained to reproduce forward-mode gas-phase chemistry, it can be effectively applied in adjoint sensitivity analysis. This approach offers a promising alternative approach to numerical adjoint frameworks in CTMs.
1. Introduction
CTMs provide a robust and systematic framework for simulating and quantitatively characterizing atmospheric environmental systems [1]. The forward mode of CTMs describes the spatiotemporal evolution of species concentrations, while the adjoint mode computes sensitivities of objective functions to model inputs and parameters [2,3], forming the foundation for sensitivity analysis and inverse modeling [4,5]. The computation of gas-phase chemistry is the primary time-consuming bottleneck in both the forward and adjoint modes of CTMs. The gas-phase chemistry module typically accounts for 36% to 95% of the total computational cost in forward mode simulations [6,7], largely because it involves solving large-scale and stiff systems of ordinary differential equations (ODEs) that govern gas-phase chemical kinetics. In adjoint mode, sensitivities of model outputs with respect to system states are obtained via backward integration in a time-reversed manner which requires access to intermediate model states. A checkpointing strategy stores selected states and recomputes trajectories in adjoint mode as needed, thereby increasing the computational cost. Consequently, the adjoint mode generally exhibits a computational burden 1.5 to 11 times greater than the forward mode [8,9,10].
Machine learning techniques have shown significant potential in accelerating forward-mode simulations of gas-phase chemistry. A number of studies have adopted deep learning models as efficient emulators to replace the numerical solvers used for integrating chemical kinetics [11,12,13,14,15,16]. For instance, Keller et al. [17] applied random forest regression to predict hourly concentrations of 52 pollutants from GEOS-Chem, a global 3-D model of atmospheric chemistry driven by meteorological data from NASA’s Goddard Earth Observing System (GEOS), at a 2.5° × 2° resolution. However, upon embedding the emulator into the CTM, the overall simulation became even slower than with the numerical solver. Liu et al. [18] developed a ResNet-based emulator within CMAQ to simulate hourly concentration changes of gas-phase species. In a month-long simulation, 137 out of 194 species exhibited a normalized mean bias (NMB) below 30%, along with an approximate speed-up of 10.6×. Wang et al. [19] employed ResNet in the Global Nested Air Quality Prediction Modeling System (GNAQPMS) model to simulate the concentration evolution of 47 species governed by the Carbon Bond Mechanism Z mechanism at a 0.5° × 0.5° resolution with a 20 min time step, achieving an average R2 exceeding 0.97 and a nearly 300× speed-up in offline (non-embedded) tests. Kelp et al. [20] designed an autoencoder-based neural network to predict hourly concentration changes of 12 species within the Super-Fast mechanism, enabling stable, year-long ozone simulations in GEOS-Chem via online learning.
In contrast, the application of machine learning techniques to adjoint sensitivity analysis for gas-phase chemistry remains largely underexplored and lacks systematic validation. Deep learning models are inherently differentiable and allow gradient propagation via the chain rule [21]. Sensitivities can be efficiently computed in reverse (i.e., adjoint) mode using highly optimized automatic differentiation engines supported by state-of-the-art deep learning libraries [22,23,24]. Despite this potential, only a few studies in the meteorological sciences have attempted to evaluate adjoint schemes based on deep learning models. Hatfield et al. [25] hypothesized that if a sufficiently accurate surrogate model can be constructed, its adjoint version can be readily derived with minimal effort. They demonstrated that gradients computed from the surrogate could be effectively applied in four-dimensional variational data assimilation (4D-Var) for parameterizing non-orographic gravity wave drag. Nonnenmacher et al. [26] evaluated the accuracy of emulator-derived gradients in the Lorenz-96 chaotic system and found that sensitivities obtained via automatic differentiation yielded Jacobian matrices highly consistent with those generated by the fourth-order Runge–Kutta integration method. Moreover, the errors decreased as the size of the training dataset increased, confirming that emulator-derived gradients can support accurate data assimilation and closed-loop training of physical parameterizations [27,28]. In practice, the lack of continuity in the forward-mode computations of many numerical models leads to missing or unreliable gradient information in differentiable programming. For example, in the development of the adjoint mode for CMAQ (CMAQ-ADJ) [3], although automatic differentiation tools can generate the initial adjoint code, a substantial amount of manual intervention remains necessary. Deep learning models offer a more flexible and efficient alternative for constructing adjoint systems, with the potential to significantly reduce the development and maintenance cost of adjoint models while preserving computational accuracy.
In this study, we propose a deep learning-based emulation framework to accelerate both forward and adjoint computations of the gas-phase chemistry solver in CTMs, which forms the computational core of the gas-phase chemical process. By leveraging the differentiable nature of neural networks, the emulator enables efficient gradient propagation in adjoint model. The main contributions of this work are twofold: (1) demonstrating the feasibility of replacing numerical solver with an emulator in adjoint mode, and (2) establishing a scalable pathway to significantly reduce the computational cost of adjoint sensitivity analysis. Our results confirm that emulator-derived sensitivities remain relatively accurate while delivering substantial speed-up, highlighting the potential of deep learning to advance atmospheric chemical modeling.
2. Methodology and Datasets
2.1. Chemical Model Description
The chemical model used in this study for dataset collection, baseline simulations, and emulator deployment is the CMAQ model (https://github.com/USEPA/CMAQ, accessed on 18 September 2025), an open-source CTM widely applied in air quality research, regulatory assessments, and operational forecasting [29,30], with outputs regularly evaluated against both ground monitoring networks and satellite observations to ensure accuracy and guide development [31,32]. CMAQ represents atmospheric processes through an operator-splitting framework that integrates physical transport and chemical transformation, including major processes such as advection, diffusion transport, cloud, gas-phase chemistry, and aerosol. We conducted simulations using CMAQ version 5.0, which is consistent with the forward mode of CMAQ-ADJ. The modeling domain covered all of China and parts of Southeast Asia. A total of 36 vertical layers were used, with the first layer centered at about 23 m above ground level and gradually increasing in thickness with height, up to ~18 km at the model top.
The Carbon Bond Mechanism version 5 (CB05) was employed to represent gas-phase chemistry in the simulations. CB05 provides a condensed framework that describes the inorganic chemistry of key trace gases and captures organic reactivity through a lumped species approach, in which hydrocarbons are grouped according to their structural characteristics. The mechanism includes 72 gas-phase species and 187 reactions, and the chemical system is integrated using the kinetic preprocessor (KPP) Runge–Kutta solver (https://github.com/KineticPreProcessor/KPP, accessed on 18 September 2025). Meteorological fields were generated using the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model, with boundary and initial conditions provided by the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) reanalysis dataset. Emission inputs were taken from the Multi-resolution Emission Inventory for China (MEIC), which provides detailed sectoral and spatially resolved estimates of anthropogenic emissions. To ensure reproducibility of the case study, all the simulations were initialized with clean boundary and initial conditions.
2.2. Dataset Collection
To obtain training dataset for the gas-phase chemistry emulator, we conducted simulations using CMAQ. To investigate emulator performance across different spatial scales, we designed simulations with multiple horizontal resolutions (96 km, 48 km, 24 km, and 12 km). These resolutions are commonly used in CMAQ studies [32,33], where coarse grids are suitable for capturing large-scale transport while fine grids provide more detailed regional air quality features. The horizontal resolution shapes the training data: coarse grids aid convergence with smaller volumes by capturing overall trends, while fine grids provide richer local features and stronger temporal variations that improve learning of nonlinear chemical processes at the cost of larger datasets [19]. In addition, different synchronization timesteps (4, 6, and 10 min) were employed to represent chemical processes at varying temporal resolutions. Shorter timesteps can better resolve the rapid changes of fast-reacting species, whereas longer timesteps reduce computational cost but may lead to a smoother representation of temporal variations [34]. Simulation data were extracted from January, April, July, and October of 2019 (days 1–7 of each month) to improve the representativeness and applicability of the dataset, ensuring that the training samples span a broad chemical state space across different meteorological and chemical regimes. A five-day spin-up was applied prior to each simulation. Checkpoints were set before and after the gas-phase chemistry module, and data such as species concentrations were recorded at every synchronization timestep.
Features and targets were defined from the raw simulation data to construct the dataset required for model training. Input features include the initial concentrations of chemical species, key meteorological variables (temperature, relative humidity, and pressure), photolysis rate constants, and the synchronization timestep. Given the critical role of sunlight in determining gas-phase reaction pathways, a binary condition parameter was incorporated to distinguish between photochemical and non-photochemical regimes. Target labels were defined as the concentration changes of species over a single synchronization timestep, computed as outputs minus inputs of the gas-phase chemistry module. Using concentration change as the label is advantageous because it provides a more sensitive representation of chemical evolution than post-reaction concentrations, enabling the model to better capture small-scale chemical variations. All abbreviations of chemical species are provided in Table S1, which summarizes the species from the CB05 chemical mechanism used for emulator training.
2.3. The Architecture of Deep Learning Emulator
The gas-phase chemistry emulator developed in this study employs FiLM-ResNet architecture. The adoption of a FiLM-based residual architecture is motivated by recent work demonstrating that FiLM can efficiently condition ResNet, yielding improvements in feature diversity and predictive accuracy while requiring only minimal computational overhead [35]. This provides a strong methodological foundation for employing FiLM layers to adaptively modulate chemical process representations under varying photochemical conditions. In addition, the use of a ResNet backbone is particularly well-suited for chemical process emulation because ResNet can be interpreted as discrete approximations of ODEs [36]. This close analogy ensures that the ResNet naturally aligns with the continuous-time dynamics of gas-phase chemistry, thereby making the FiLM-ResNet architecture a theoretically sound and practically effective choice for this study.
As illustrated in Figure 1, the model consists of five sequential modules: an input layer, a preprocessing layer, an input mapping layer, a residual block network, and an output layer. Inputs to the model include the initial concentrations of gas-phase chemical species, meteorological parameters, photolysis rate constants, the synchronization timestep interval, and a binary flag indicating sunlight conditions (0 for dark, 1 for light). In the preprocessing layer, a Box-Cox transformation (BCT) is applied to reduce the skewed distribution of concentration values, followed by Z-score normalization (see Figure S2 for the distributions of OH and NO2 concentrations: original data, after BCT, and after BCT followed by Z-score normalization). Photolysis rate constants and meteorological variables are scaled using Min-Max normalization, while the timestep and sunlight flag are left unprocessed. All transformed features are concatenated and passed through a fully connected layer with a nonlinear activation function, which projects the inputs into a high-dimensional latent space. This latent representation is then fed into the residual backbone network. The FiLM layer takes the binary sunlight flag as input and uses a fully connected multilayer perceptron to dynamically generate scaling factors (γ) and shifting factors (β) for each feature dimension. These modulation factors condition the residual blocks (Res-blocks), allowing the emulator to dynamically adjust its internal representations between photochemical and non-photochemical regimes [37]. The core network consists of six stacked Res-blocks. In the output layer, the model applies the inverse operations of Z-score normalization and BCT to recover the predictions in their original physical units (see Table S4 for the explicit transformation and inverse formulas). The outputs correspond to concentration changes, which are then added to the initial concentrations to compute the absolute post-reaction concentrations. This design ensures that the entire preprocessing and inverse transformation procedure is internally handled by the emulator, thereby avoiding manual data manipulation.
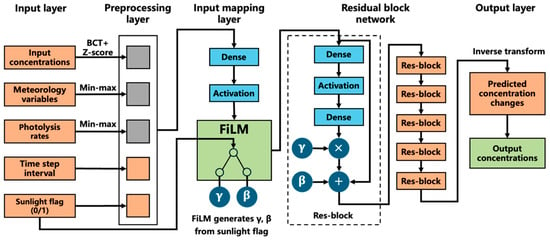
Figure 1.
Architecture of the neural network emulator. The emulator consists of five sequential submodules: input layer, preprocessing layer, input mapping layer, residual block network, and output layer. The input mapping layer incorporates a Feature-wise Linear Modulation (FiLM) module, which takes the sunlight flag as input and generates a set of scaling factors γ and shifting factors β matching the feature channel dimensions. These modulation factors are used to adjust intermediate feature representations within the subsequent residual block network, enabling prediction of species concentration changes.
2.4. Emulator Embedding Framework
To integrate our deep learning emulator into the CMAQ model, we developed an embedding framework that emphasizes portability and efficient large-scale inference. Instead of relying on Python (v3.11.8) at runtime, the trained emulator is exported using PyTorch’s static graph representation (TorchScript, PyTorch v2.5.1 with CUDA 12.4) and then compiled into a shared library through LibTorch (v2.5.1), PyTorch’s C++ backend. This shared library can be directly invoked by the Fortran-based CMAQ model via the standard iso_c_binding interface, enabling seamless coupling between the two systems. The key advantage of this framework is that it removes any Python dependencies, which is particularly important in CMAQ’s large-scale simulations where massive amounts of data must be processed efficiently. In addition, the emulator automatically applies the necessary preprocessing and inverse transformations, so that CMAQ can directly pass raw inputs and obtain the predicted post-reaction concentrations in the correct physical units (ppb) without additional manual processing (see Figure S6. Schematic diagram of the integration of the emulator in the gas-phase chemistry module in forward mode). The framework supports batched updates across the simulation domain, where multiple grid cells are processed simultaneously rather than sequentially. Emulator inference can be executed on GPUs, providing substantial speedups in large-scale simulations. Additionally, the embedding framework is fully compatible with CMAQ’s parallel architecture based on the Message Passing Interface (MPI) standard for grid-domain splitting, allowing efficient execution across distributed computing environments.
We further embedded the emulator into the gas-phase chemical module of the CMAQ model in adjoint mode using an automatic differentiation framework. The emulator can directly compute the sensitivity matrix (i.e., the Jacobian matrix), which represents the partial derivatives of species concentrations at next timestep () with respect to those at the current timestep (). Since all preprocessing and inverse transformations are embedded in the emulator architecture as differentiable operations, the outputs of FiLM-ResNet are already expressed in physical concentration units and can therefore be directly incorporated into the adjoint mode without additional reconversion. In the adjoint mode, the sensitivity of the cost function with respect to the state vector at step is represented by the adjoint variables where represents the state vector of forward concentrations at the terminal time step, which serves as the starting point for adjoint integration. The adjoint variables are recursively updated according to the chain rule. Equation (1) shows that the Jacobian matrix serves as the core operator linking forward and adjoint computations, allowing to be propagated backward to .
By leveraging the PyTorch autograd engine, the emulator automatically performs this backward propagation through its computational graph. This design avoids the need to explicitly construct high-dimensional Jacobian matrices and simultaneously replacing the core matrix–vector multiplication operation in the adjoint backward integration process (Equation (1)). The embedding framework is fully compatible with the adjoint mode of the CMAQ model (see Figure S4 for a schematic diagram), and it supports highly parallelized execution of adjoint simulations [9].
2.5. Emulator Evaluation Method
The accuracy of the emulator in forward mode was evaluated from two perspectives: single-timestep prediction and multi-timestep simulation. For the single-timestep evaluation, the emulator’s predictions were compared with those from the gas-phase chemistry solver on the test dataset. R2 was employed to assess the degree of agreement, based on either predicted concentration changes or absolute post-reaction concentrations. For the multi-timestep simulation, the emulator was integrated into the CMAQ model to replace the numerical solver in the gas-phase chemical module. At each synchronization timestep, the predicted concentrations from the emulator were passed to the subsequent aerosol module and then propagated forward, thereby enabling a continuous simulation. In this configuration, discrepancies relative to the baseline CMAQ outputs may accumulate over time. To examine the consistency and stability of the emulator, we conducted a case study using a horizontal resolution of 12 km and synchronization timestep of 4 min. The simulation period covered from 1 January to 7 January 2020, which was not included in the training dataset, allowing us to test the generalization capability of the emulator. This seven-day simulation involved 2520 successive single-timestep predictions (7 days × 24 h × 60 min/4 min), providing a rigorous evaluation of whether the emulator could remain stable throughout long-term integrations in forward mode. Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) was used to quantify prediction errors and NMB characterized the systematic bias.
For the multi-timestep validation in adjoint mode, the baseline CMAQ-ADJ model configuration followed Section S1.3 of the Supplementary Information. The emulator was integrated into the gas-phase chemical module using the automatic differentiation framework described in Section 2.4, and a 24 h adjoint run starting on 1 January 2020 was conducted with O3 specified as the receptor species. This date was chosen because the emulator exhibited the most stable performance without noticeable error accumulation during continuous simulation in forward mode regarding the results in Section 3.1, making it a suitable starting point for backward integration in the adjoint mode [26]. Emulator-derived adjoint gradients were then compared with those from the baseline CMAQ-ADJ numerical solver to evaluate their multi-timestep consistency.
To evaluate the computational efficiency of the emulator, we compared wall-clock runtimes between the standard numerical gas-phase chemical module and the emulator-integrated module in both forward and adjoint modes. For all CPU- and GPU-based experiments, 16 cores were used in parallel with MPI, and the specific hardware configurations are listed in Table S5. Two testing scenarios were considered: (1) offline mode, where the emulator was executed in a standalone PyTorch environment, and (2) integrated mode, where the emulator was embedded into CMAQ model.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Forward Accuracy Validation
The validation results demonstrate that the deep learning emulator accurately predicts concentration changes of gas-phase chemical species in a single timestep. Figure 2 presents prediction results for several species, including inorganic species (O3, NO2, NO, H2O2), radical species (HO2, C2O3, CH3O2), volatile organic compound (VOC)-related species (PAR, XYL, ISOP, TERP), as well as CO and SO2. The predicted concentration changes show strong agreement with CMAQ outputs, with R2 values exceeding 0.95 for all listed species. For species with low chemical reactivity, such as PAR and XYL, and those that are largely inactive in gas-phase chemistry, such as CO and SO2, the R2 values even exceed 0.995, demonstrating the robustness of the emulator in capturing small-scale variations in concentration. OH, a highly reactive and short-lived radical species, shows only limited dependence of its concentration tendency on initial conditions, which results in a slightly lower R2 value of 0.92. However, RMSE remains as low as 1.6 × 10−6 ppb, outperforming previous studies by Liu et al. [18] (2.8 × 10−6 ppb) and Wang et al. [19] (2.2 × 10−6 ppb), underscoring the superior precision of the FiLM-ResNet emulator. According to the summary statistics in Table S2, 60 out of 66 species achieve an R2 greater than 0.90 for single-timestep concentration change predictions, indicating robust emulator performance across most reactive species. For absolute concentration outputs, 59 species achieve an R2 above 0.99, with 74% exceeding 0.999, indicating that the neural network emulator developed in this study can simultaneously and accurately predict short-term concentration.
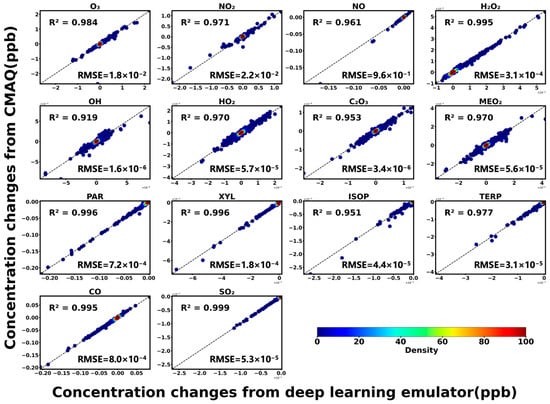
Figure 2.
Density scatter plots comparing emulator-predicted and CMAQ-simulated concentration changes for 14 species. Each panel assesses emulator performance on concentration changes. The color bar denotes point density, and the black dashed line indicates the 1:1 reference, which represents perfect agreement between emulator and CMAQ.
The emulator maintains temporal consistency without notable error accumulation over extended multi-timestep simulations, demonstrating both numerical robustness and long-term predictive stability. As shown in Figure 3, the emulator successfully reproduces the spatial distribution of surface ozone concentrations simulated by CMAQ on Days 1, 3, and 7. High consistency is observed across East Asia and other pollution-prone regions. Although localized discrepancies of up to ~20 ppb occur in certain coastal and inland areas on Day 3, these deviations do not amplify further by Day 7, reaffirming the emulator’s stability over prolonged integration periods. Figure 4 presents hourly concentration comparisons for four key species—O3, NO2, ISOP, and OH—at grid cells representing Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangzhou. The emulator reproduces the diurnal concentration profiles with high fidelity across different pollution regimes. Among the evaluated species, ozone predictions exhibit the best agreement with CMAQ outputs in Guangzhou and Beijing, with NMB values approaching zero over the seven-day simulation. The emulator also reliably captures the temporal variability of NO2 concentrations; however, a relative overestimation is observed in Shanghai on 5 January, potentially resulting from a combination of ozone overprediction and OH underprediction on that day. As one of the most chemically reactive species in the atmosphere, OH exhibits relatively larger prediction errors at the single-timestep level. Nevertheless, across multi-timestep simulations in all three cities, its NMB remains within ±5%, primarily due to the emulator’s ability to accurately replicate the diurnal cycle of radical species. Both the emulator and the numerical model return OH to near-zero concentrations during nighttime, effectively creating a natural “error-resetting” effect that mitigates the accumulation of prediction errors for highly reactive species. ISOP, a reactive VOC with two double bonds that significantly contributes to local ozone formation, is reproduced with particularly high fidelity, with R2 exceeding 0.99 across all three urban sites. Despite minor discrepancies in a few species, the emulator maintains consistently strong agreement with the CMAQ model throughout extended forward-mode simulations, while concurrently producing reliable checkpoint files for downstream gradient computations in adjoint-mode applications.
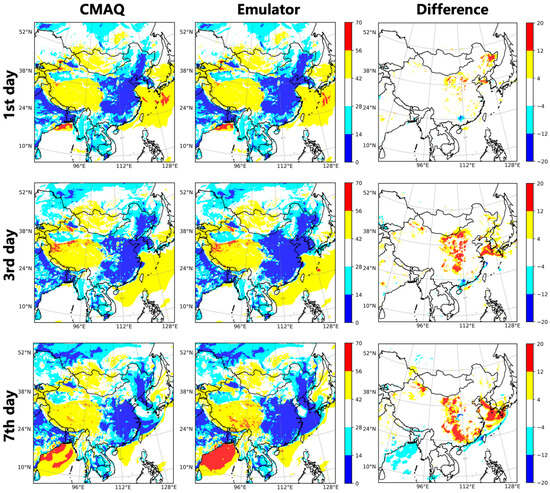
Figure 3.
Spatial distributions of ozone concentrations (ppb) on three selected simulation days, comparing predictions from the numerical model (CMAQ) and the emulator. Each row corresponds to a specific simulation day (Day 1, Day 3, and Day 7 from top to bottom). The (left) column shows CMAQ outputs, the (middle) column presents emulator-predicted concentrations, and the (right) column shows maps of the differences between emulator and CMAQ. In the difference panels, red regions indicate underestimation by the emulator relative to CMAQ, while blue regions indicate overestimation.
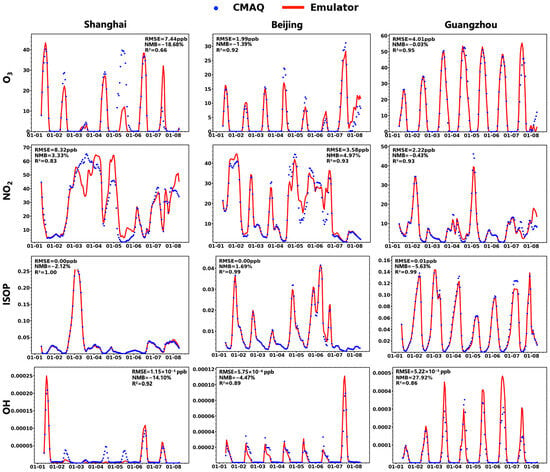
Figure 4.
Comparison of hourly time series for four air pollutants—ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), isoprene (ISOP), and hydroxyl radical (OH)—over a 7-day simulation period. Three major Chinese cities were selected for comparison: Shanghai (left), Beijing (center), and Guangzhou (right). Blue scatter points indicate outputs from the CMAQ model, and red curves show predictions from the emulator. Each subplot includes statistical evaluation metrics—root-mean-square error (RMSE), normalized mean bias (NMB), and coefficient of determination (R2).
3.2. Adjoint Accuracy Validation
The sensitivity gradients derived from the emulator closely align with those obtained from the numerical adjoint solver in the single timestep. As illustrated in Figure 5, sensitivity analysis of the receptor species O3 shows that its gradient with respect to its own initial concentration is clusters around unity, indicating that the predicted absolute concentration output of O3 is strongly governed by its initial condition. The R2 between emulator-derived and adjoint-derived self-sensitivities reaches 0.995, confirming the emulator’s capacity to accurately capture the dominant direct dependency of O3 on its initial state. Furthermore, the emulator reproduces cross-species gradients of O3 with respect to NO, NO2 and OH with R2 values exceeding 0.90, demonstrating that key chemical sensitivities can be effectively captured within the automatic differentiation framework. Nevertheless, the sensitivity estimation of O3 with respect to ISOP shows weaker alignment, with an R2 of only 0.441. This result stands in contrast to the emulator’s high predictive accuracy for ISOP concentrations in forward mode (R2 > 0.95), suggesting that certain indirect dependencies may be more susceptible to structural nuances during differentiation. This arises because automatic differentiation operates on the composite computational graph of the emulator, which does not explicitly capture the complex solver dynamics or the adaptive step-size adjustments used in numerical integrators to handle stiffness. The sensitivity of O3 with respect to ISOP can be affected by accumulated numerical artifacts or latent pathway underrepresentation. Moreover, small approximation errors in the forward trajectory may be disproportionately amplified during backpropagation, especially when interacting through stiff dynamics or nonlinear couplings. These factors may collectively contribute to the diminished sensitivity alignment observed in specific species pairs. Despite these limitations, the emulator-derived gradients are sufficiently suitable for multi-timestep simulation in adjoint mode.
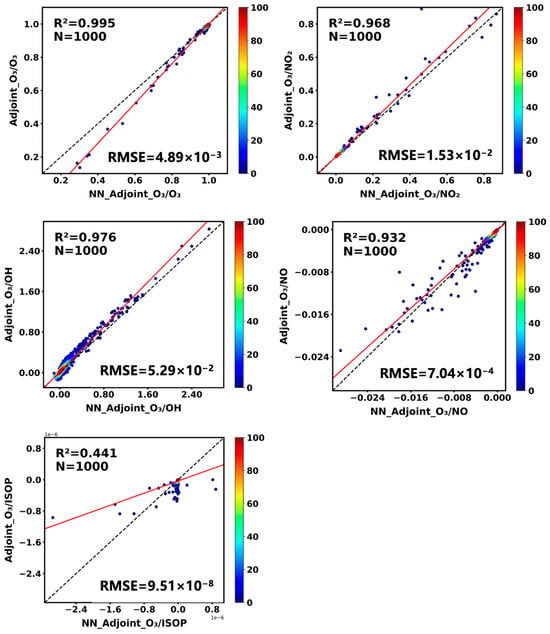
Figure 5.
Validation of single-timestep adjoint sensitivities for ozone (O3). Each subplot compares the derivative of O3 with respect to one of five species: O3, NO2 (nitrogen dioxide), OH (hydroxyl radical), NO (nitric oxide), and ISOP (isoprene). The x-axis denotes emulator-predicted gradients, and the y-axis shows reference gradients computed by the numerical adjoint solver. Color shading represents point density. The black dashed line indicates the 1:1 reference line, used as a benchmark for perfect agreement. The red solid line shows an ordinary least-squares regression fit, included as a diagnostic measure of alignment between emulator and adjoint sensitivities. Each panel reports the coefficient of determination (R2), root-mean-square error (RMSE), and the number of evaluated points.
The emulator was embedded into the gas-phase chemical module of CMAQ-ADJ to compute adjoint-mode gradients over multiple timesteps, yielding sensitivity results that remain largely consistent with those produced by the numerical adjoint model. As shown in Figure 6, following a 24 h adjoint-mode run in which O3 served as the receptor species, surface-level sensitivities of O3 with respect to five species (O3, NO2, NO, OH, and ISOP) were analyzed. For O3, NO, NO2, and OH, the spatial patterns of emulator-derived gradients exhibit strong agreement with those from CMAQ-ADJ, with most grid points aligning closely along the 1:1 line. This confirms the emulator’s suitability for adjoint sensitivity analysis in gas-phase chemistry. However, localized discrepancies are observed in southern portions of the domain, particularly in the sensitivity of O3 with respect to its own initial concentration and to NO and NO3. Sensitivities with respect to OH display slightly lower spatial consistency, consistent with the lower R2 value (0.956) observed in the single-timestep validation. OH’s sensitivity is more localized and strongly dependent on transient state variables, which makes it more susceptible to instability and gradient fluctuations during backward integration. The weakest agreement is observed for O3 sensitivities to ISOP, consistent with its poor performance in single timestep evaluations. These deviations in emulator-derived gradients during extended adjoint runs may arise from two main factors: (1) the emulator is trained solely on concentration changes and does not directly learn sensitivity structures from the chemical Jacobian, and (2) the adjoint mode relies on checkpointed concentrations recorded during the forward pass, where minor numerical discrepancies may accumulate and propagate through the backward trajectory, ultimately impacting gradient accuracy.
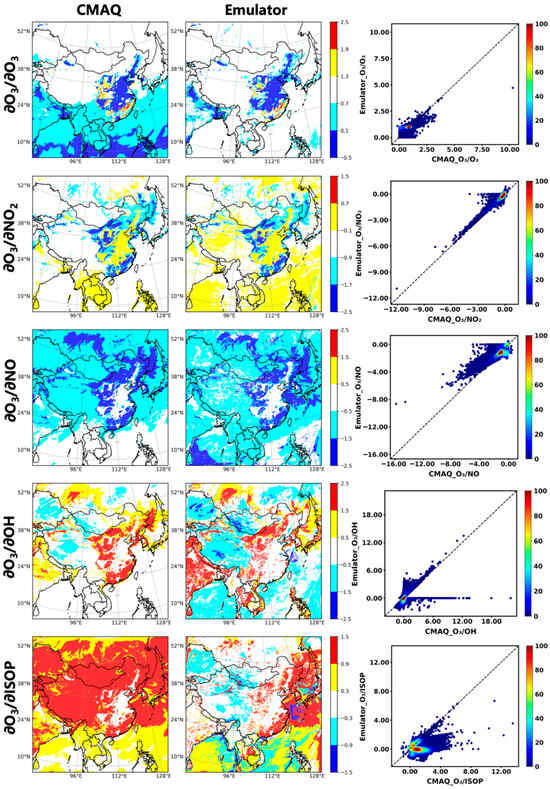
Figure 6.
Spatial distributions of ozone (O3) sensitivities with respect ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), nitric oxide (NO), hydroxyl radical (OH), and isoprene (ISOP) from a 24 h adjoint-mode simulation. For each species, the (left) column shows adjoint sensitivities from CMAQ model, the (middle) column shows emulator-derived sensitivities, and the (right) column presents scatter plot of grid-level gradients. In the scatter plots, the x-axis corresponds to CMAQ-derived gradients and the y-axis to emulator-predicted gradients, color shading indicates point density, and the black dashed line denotes the 1:1 reference line used as a benchmark for perfect agreement.
3.3. Comparison of Computational Efficiency
The emulator achieves substantial computational speed-ups compared to the numerical solvers in both forward and adjoint modes. In forward mode (Figure 7a), the gas-phase chemical module of CMAQ requires approximately 478 s to perform a full concentration update across the simulation grid using 16 CPU cores in parallel with MPI. By contrast, the emulator completes the same task in only 6 s in a Python environment, corresponding to an 80× acceleration. With GPU inference, the runtime is further reduced to 3.7 s, yielding a speed-up of nearly 130×. These offline timings reflect standalone emulator execution outside the CTM framework and highlight the computational efficiency of deep learning-based inference in accelerating chemical simulations. Once the emulator is embedded into the CMAQ system, performance is affected by inter-process communication and data exchange overheads. Manual coupling through Fortran introduces additional latency, as large volumes of data must be serialized and transferred between the Fortran environment and the Python interpreter, a process that is both error-prone and computationally expensive [38]. With the integration framework proposed in this study, the embedded emulator achieves a speed-up of approximately 2× in CPU and up to 4.6× with GPU acceleration. Notably, the concentration update routine, which is the most compute-intensive part, requires only 59 s on GPU, underscoring the emulator’s efficiency for core numerical operations. In the integrated setting, however, overhead from model initialization and memory allocation becomes non-negligible, as each inference call is triggered only once per synchronization timestep. Additionally, MPI enforces single-threaded execution within each process, preventing deep learning frameworks from fully exploiting multithreading capabilities, and leading to longer runtimes than standalone GPU inference.
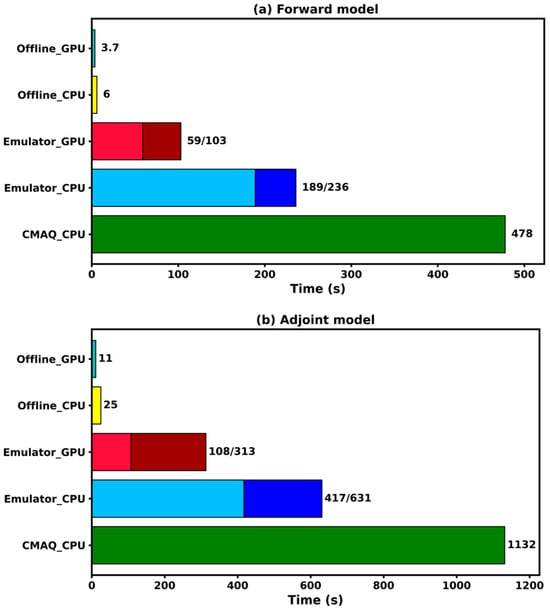
Figure 7.
Execution time of the gas-phase chemical module under five configurations in (a) forward mode and (b) adjoint mode. Configurations include “Offline_CPU”, “Offline_GPU”, “Emulator_CPU”, “Emulator_GPU”, and the CMAQ numerical model (“CMAQ_CPU”). In each bar, the light red (forward) or light blue (adjoint) segments denote the time spent directly on species concentration or adjoint variable updates by the emulator, while darker segments represent other processing overhead. Total runtime is labeled to the right of each bar, and embedded emulator configurations are additionally annotated as “direct time/total time” fractions.
In adjoint mode (Figure 7b), the neural network emulator also delivers considerable speed-ups. A single backward execution of the gas-phase chemical module in CMAQ-ADJ, corresponding to one adjoint run for gradient computation, requires approximately 1132 s. By comparison, the embedded emulator reduces this runtime to 631 s on CPU and 313 s on GPU, corresponding to speed-ups of about 1.8× and 3.6×, respectively. During the automatic differentiation backward pass, updating adjoint variables on GPU takes 108 s. Although this is longer than the 11 s reported for the offline benchmark, the performance remains competitive given the additional overhead associated with model initialization and inter-language data exchange in the embedded setting. These findings highlight the efficiency of the emulator’s Jacobian-free design for adjoint computations. The embedding framework introduced in this study offers two notable advantages. First, it enables batch-parallel adjoint inference across spatial grid points while incorporating preprocessing steps directly within the model execution pipeline, thereby improving GPU resource utilization at scale. Second, the use of the LibTorch backend facilitates low-level execution optimizations, further reducing computational cost and improving runtime consistency in high-resolution simulations.
3.4. Limitations and Outlook
Although the proposed emulator shows highly consistent concentration predictions with the CMAQ model in forward-mode gas-phase chemistry simulations, there remains room for improvement in adjoint gradient emulation. In nonlinear chemical systems, even small perturbations can be strongly amplified during reverse-mode differentiation, making the gradient path highly sensitive and prone to distortion. This issue is particularly pronounced for highly reactive, short-lived radical species. In this study, sensitivity analysis was validated only for O3, and broader evaluations with other receptor species are still required to fully assess the reliability of emulator-derived gradients. Nevertheless, the emulator-derived approach has already shown the potential to be applied in contexts such as 4D-Var data assimilation and parameterization learning, where accurate gradient information is essential [39,40].
Moreover, continuous improvements in the emulator’s forward-mode prediction of key species are expected to enhance the stability and reliability of gradients obtained via automatic differentiation [25,26]. At the same time, several challenges remain. In the current design, the training labels for the emulator are based on concentration changes. For certain highly reactive species such as OH, their simulated concentrations under nighttime non-photochemical conditions often decay rapidly to near-zero values. In the Runge–Kutta numerical algorithm used in CMAQ, such species may even appear as slightly negative during integration of stiff equations, but CMAQ automatically resets the post-reaction concentrations to the minimum physically meaningful value. While this does not affect forward-mode performance, it means that the corrected concentration-change labels used for emulator training often correspond to “no variation” samples at night. As a result, the emulator can reproduce forward concentration changes well, but its adjoint gradients become less expressive, limiting the ability to capture sensitivity structures and nonlinear dynamics in these cases.
Future research could further advance the use of emulators for gas-phase chemistry adjoint simulations along two key directions. One important step is to expand the training data coverage through more representative high-dimensional state-space sampling strategies, which would enhance the model’s generalization under extreme and provide more comprehensive dynamical constraints for stable training. Another promising direction is to incorporate gradient information directly through joint training frameworks such as the Sobolev training framework [41]. By including derivative information (e.g., Jacobian matrices or adjoint gradients) as additional supervision signals in the loss function, such approaches would allow the model to optimize both functional approximation and sensitivity consistency simultaneously. Additionally, our emulator in adjoint mode can be integrated into a 4D-Var data assimilation framework. This integration allows for the correction of simulation biases by incorporating observational constraints in future research.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we proposed and implemented a neural network emulator that can simultaneously replace both the forward and adjoint modes of the gas-phase chemistry solver in CMAQ model. The emulator is trained on large-scale CMAQ simulation data spanning multiple spatial resolutions and synchronization timesteps, and it accurately captured concentration changes in gas-phase chemistry by incorporating a sunlight-aware input mapping layer and a residual neural network. The model supported stable, continuous operation over multi-timestep simulations. We validated the accuracy of sensitivities obtained through automatic differentiation and achieve end-to-end integration of the gas-phase chemistry solver using an efficient embedding scheme based on LibTorch. Notably, this work represented the first successful demonstration of adjoint-mode acceleration using deep learning techniques. Our findings showed that the emulator yielded controllable approximation errors when O3 is used as a representative receptor species, offering a promising solution for rapid development and maintenance of the adjoint models in gas-phase chemical modules within CTMs.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos16091109/s1, Table S1. Species from the CB05 chemical mechanism used for emulator training. Species marked with an asterisk (*) are not used as inputs to the emulator, Table S2. Comparison of the emulator’s prediction performance for each species under photochemical and non-photochemical conditions. Metrics include R2 and RMSE for both post-reaction concentrations and concentration changes, photochemical samples, and non-photochemical samples, Table S3. List of Abbreviations Table S4. List of Abbreviations Table S5. System configuration and parallel settings used for the numerical, 1.2 Supplementary Figures, Figure S1. Density scatter plots comparing emulator-predicted versus CMAQ-simulated concentration changes for ten selected species under (a) lighted and (b) non-lighted conditions. The color bar indicates point density, and the black dashed line denotes the 1:1 reference. Each subplot includes RMSE and R2 metrics to quantitatively assess the emulator’s performance. Figure S2. Distributions of OH and NO2 concentrations in the training dataset: original data, after Box–Cox Transformation (BCT), and after BCT followed by Z-score normalization. Figure S3. Training and Validation Loss over Epochs. Figure S4. Schematic diagram of the integration of the emulator in the gas-phase chemistry module in adjoint mode. Figure S5. Comparison of hourly time series for four representative air pollutants at 96 km resolution. Figure S6. Schematic diagram of the integration of the emulator in the gas-phase chemistry module in forward mode. In this design, the TorchScript-based emulator substitutes only the numerical integration of gas-phase chemical reactions, while all other scientific processes in CMAQ remain unchanged. Photolysis rates (J values) are still computed by the PHOT subroutine, which relies on meteorological and cloud fields provided by WRF (including pressure, temperature, ozone profiles, cloud-top and cloud-base heights, liquid water content, and cloud fraction), thereby accounting for altitude- and cloud-dependent effects on photochemistry. Meanwhile, physical transport processes such as vertical diffusion (VDIFF), horizontal/vertical advection (HADV, ZADV), horizontal diffusion (HDIFF), and cloud processes (CLOUD) continue to be simulated by their original CMAQ modules [42].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.C.; Methodology, Y.L.; Formal analysis, Y.L.; Investigation, Y.L., M.L. and J.L.; Writing—original draft preparation, Y.L.; Writing—review and editing, Z.C. and Y.L.; Visualization, Y.L.; Supervision, Z.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2023YFC3705700), the Innovation Group Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (T2421002), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (T2122022).
Institutional Review Board Statement
No applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
No applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The CMAQ-ADJ model is described in [3], where the source code is also available for download. The code for emulator training, model embedding, and gradient validation is publicly available at: https://github.com/liuylong5/FiLM-Resnet (accessed on 18 September 2025).
Acknowledgments
We thank Jianbing Dong and Kuang Lei at NVIDIA for their assistance with the model embedding code. We are also grateful to Yuxiao Yi and Junjie Yao for their helpful suggestions on data preprocessing. Special thanks to Amir Hakami for proposing the idea of distinguishing sunlight condition in the emulator. The computations in this paper were run on the Siyuan-1 cluster supported by the Center for High Performance Computing at Shanghai Jiao Tong University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Brasseur, G.P.; Jacob, D.J. Modeling of Atmospheric Chemistry, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-1-316-54475-4. [Google Scholar]
- Henze, D.K.; Hakami, A.; Seinfeld, J.H. Development of the Adjoint of GEOS-Chem. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 2413–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Russell, M.G.; Hakami, A.; Capps, S.L.; Turner, M.D.; Henze, D.K.; Percell, P.B.; Resler, J.; Shen, H.; Russell, A.G.; et al. A Multiphase CMAQ Version 5.0 Adjoint. Geosci. Model Dev. 2020, 13, 2925–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Gong, S.; He, J.; Zhang, L.; Ke, H.; An, X. Quantification of SO2 Emission Variations and the Corresponding Prediction Improvements Made by Assimilating Ground-Based Observations. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandu, A.; Daescu, D.N.; Carmichael, G.R.; Chai, T. Adjoint Sensitivity Analysis of Regional Air Quality Models. J. Comput. Phys. 2005, 204, 222–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevedo, D.; Do, K.; Delic, G.; Rodríguez-Borbón, J.; Wong, B.M.; Ivey, C.E. GPU Implementation of a Gas-Phase Chemistry Solver in the CMAQ Chemical Transport Model. ACS EST Air 2025, 2, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Linford, J.C.; Sandu, A.; Sander, R. Chemical Mechanism Solvers in Air Quality Models. Atmosphere 2011, 2, 510–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakami, A.; Henze, D.K.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Singh, K.; Sandu, A.; Kim, S.; Byun; Li, Q. The Adjoint of CMAQ. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7807–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daescu, D.; Carmichael, G.R.; Sandu, A. Adjoint Implementation of Rosenbrock Methods Applied to Variational Data Assimilation. In Air Pollution Modeling and Its Application XIV; Gryning, S.-E., Schiermeier, F.A., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 361–369. ISBN 978-0-306-46534-5. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, T.; Feng, S.; Steward, J.; Tian, X.; Baker, D.; Baxter, M. Development of the Tangent Linear and Adjoint Models of the Global Online Chemical Transport Model MPAS-CO2 v7.3. Geosci. Model Dev. 2024, 17, 1543–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Seinfeld, J.H. A Neural Network-Assisted Euler Integrator for Stiff Kinetics in Atmospheric Chemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 4676–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Guo, L.; Zheng, Z.; Riemer, N.; Tessum, C.W. Atmospheric Chemistry Surrogate Modeling With Sparse Identification of Nonlinear Dynamics. J. Geophys. Res. Mach. Learn. Comput. 2024, 1, e2024JH000132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, S.; Jagtap, A.D.; Babaee, H.; Susi, B.T.; Karniadakis, G.E. Learning Stiff Chemical Kinetics Using Extended Deep Neural Operators. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2024, 419, 116674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelp, M.M.; Tessum, C.W.; Marshall, J.D. Orders-of-Magnitude Speedup in Atmospheric Chemistry Modeling through Neural. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-S.; Clusius, P.; Boy, M. Neural Network Emulator for Atmospheric Chemical ODE. Neural Netw. 2025, 184, 107106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelp, M.M.; Jacob, D.J.; Kutz, J.N.; Marshall, J.D.; Tessum, C.W. Toward Stable, General Machine-Learned Models of the Atmospheric Chemical System. JGR Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD032759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, C.A.; Evans, M.J. Application of Random Forest Regression to the Calculation of Gas-Phase Chemistry within the GEOS-Chem Chemistry Model V10. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 1209–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Shen, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Cheng, Y. Emulation of an Atmospheric Gas-Phase Chemistry Solver through Deep Learning: Case Study of Chinese Mainland. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, L.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Wang, Z. Deep Learning-Based Gas-Phase Chemical Kinetics Kernel Emulator: Application in a Global Air Quality Simulation Case. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 955980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelp, M.M.; Jacob, D.J.; Lin, H.; Sulprizio, M.P. An Online-Learned Neural Network Chemical Solver for Stable Long-Term Global Simulations of Atmospheric Chemistry. J. Adv. Model Earth Syst. 2022, 14, e2021MS002926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning Representations by Back-Propagating Errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, G.R.; Sandu, A.; Potra, F.A. Sensitivity Analysis for Atmospheric Chemistry Models via Automatic Differentiation. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baydin, A.G.; Pearlmutter, B.A.; Radul, A.A.; Siskind, J.M. Automatic Differentiation in Machine Learning: A Survey. arXiv 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. arXiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, S.; Chantry, M.; Dueben, P.; Lopez, P.; Geer, A.; Palmer, T. Building Tangent-Linear and Adjoint Models for Data Assimilation with Neural Networks. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2021, 13, e2021MS002521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonnenmacher, M.; Greenberg, D.S. Deep Emulators for Differentiation, Forecasting, and Parametrization in Earth Science Simulators. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2021, 13, e2021MS002554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbrecht, M.; White, A.; Bathiany, S.; Boers, N. Differentiable Programming for Earth System Modeling. Geosci. Model Dev. 2023, 16, 3123–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irrgang, C.; Boers, N.; Sonnewald, M.; Barnes, E.A.; Kadow, C.; Staneva, J.; Saynisch-Wagner, J. Will Artificial Intelligence Supersede Earth System and Climate Models? arXiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, K.W.; Napelenok, S.L.; Foley, K.M.; Pye, H.O.T.; Hogrefe, C.; Luecken, D.J.; Bash, J.O.; Roselle, S.J.; Pleim, J.E.; Foroutan, H.; et al. Description and Evaluation of the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) Modeling System Version 5.1. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 1703–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, B.; Kang, D.; Mathur, R.; Yu, S.; Schere, K. An Operational Evaluation of the Eta–CMAQ Air Quality Forecast Model. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 4894–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-Y.; Dash, U.K.; Yu, J.; Yumimoto, K.; Uno, I.; Song, C.H. Implementation of an Ensemble Kalman Filter in the Community Multiscale Air Quality Model (CMAQ Model v5.1) for Data Assimilation of Ground-Level PM2.5. Geosci. Model Dev. 2022, 15, 2773–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Jang, C.; Phillips, S.; Wang, B. Modeling Intercontinental Air Pollution Transport over the trans-Pacific Region in 2001 Using the Community Multiscale Air Quality Modeling System. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, 2008JD010807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, S.-H.; Xing, J.; Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G.; Jang, C.; Wang, W.-X.; Hao, J.-M. Understanding of Regional Air Pollution over China Using CMAQ, Part I Performance Evaluation and Seasonal Variation. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2415–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandu, A.; Verwer, J.G.; Van Loon, M.; Carmichael, G.R.; Potra, F.A.; Dabdub, D.; Seinfeld, J.H. Benchmarking Stiff Ode Solvers for Atmospheric Chemistry Problems-I. Implicit vs Explicit. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 3151–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkoglu, M.O.; Becker, A.; Gündüz, H.A.; Rezaei, M.; Bischl, B.; Daudt, R.C.; D’Aronco, S.; Wegner, J.D.; Schindler, K. FiLM-Ensemble: Probabilistic Deep Learning via Feature-Wise Linear Modulation. arXiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, E.; Strub, F.; de Vries, H.; Dumoulin, V.; Courville, A. FiLM: Visual Reasoning with a General Conditioning Layer. arXiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Ma, Z.; Yao, Y.; Xu, L.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Z. WRF–ML v1.0: A Bridge between WRF v4.3 and Machine Learning Parameterizations and Its Application to Atmospheric Radiative Transfer. Geosci. Model Dev. 2023, 16, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonavita, M.; Laloyaux, P. Machine Learning for Model Error Inference and Correction. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2020, 12, e2020MS002232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarbanel, H.D.I.; Rozdeba, P.J.; Shirman, S. Machine Learning: Deepest Learning as Statistical Data Assimilation Problems. Neural Comput. 2018, 30, 2025–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnecki, W.M.; Osindero, S.; Jaderberg, M.; Świrszcz, G.; Pascanu, R. Sobolev Training for Neural Networks. arXiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-Y.; Park, C.; Yoo, J.-W.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, H.W. Adjoint sensitivity of inland ozone to its precursors and meteorological and chemical influences. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 192, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).