Unveiling PM2.5 Transport Pathways: A Trajectory-Channel Model Framework for Spatiotemporally Quantitative Source Apportionment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Model Setup and Databases
2.2. Research Methods
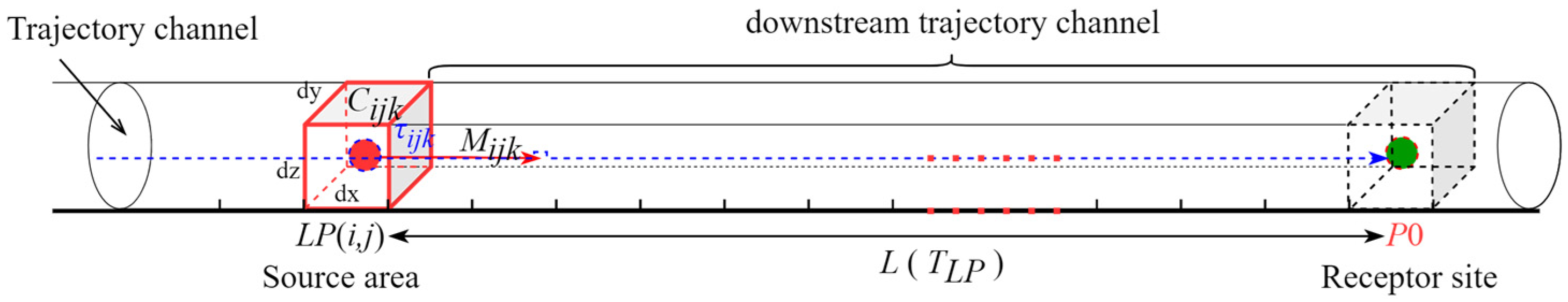
2.2.1. Trajectory-Channel Transport Model (TCTM)
2.2.2. PSCF and CWT Methods
3. Results
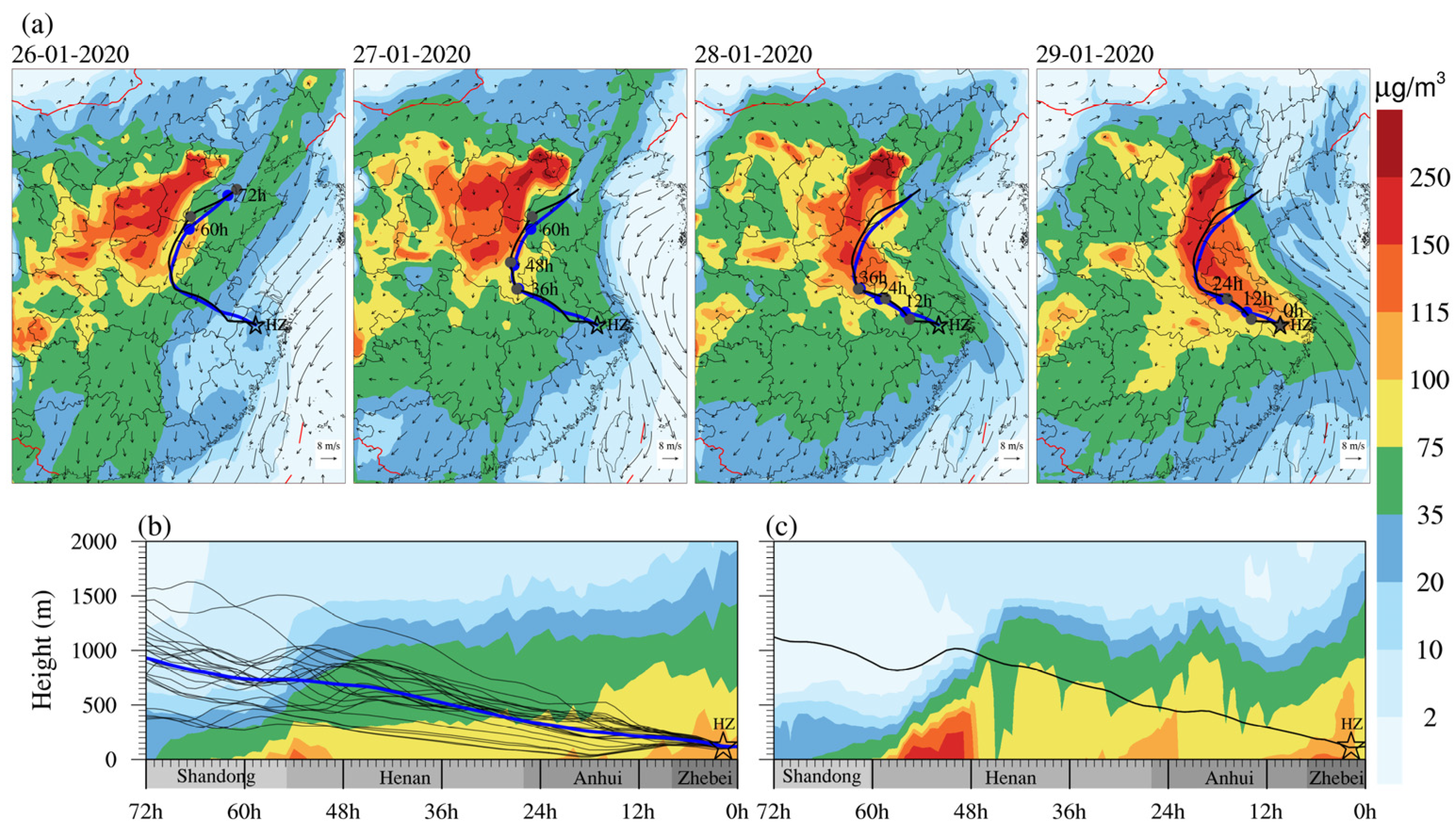
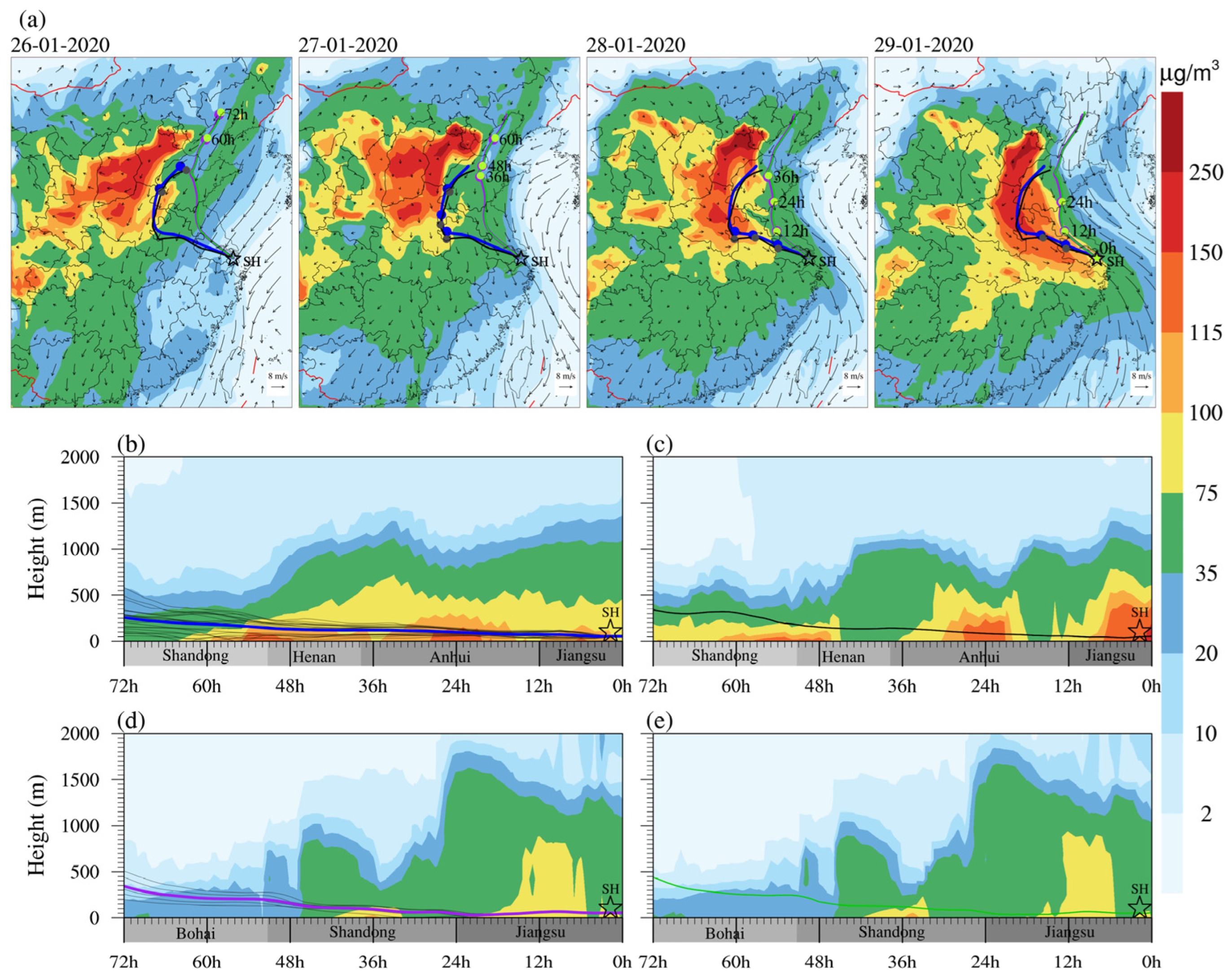
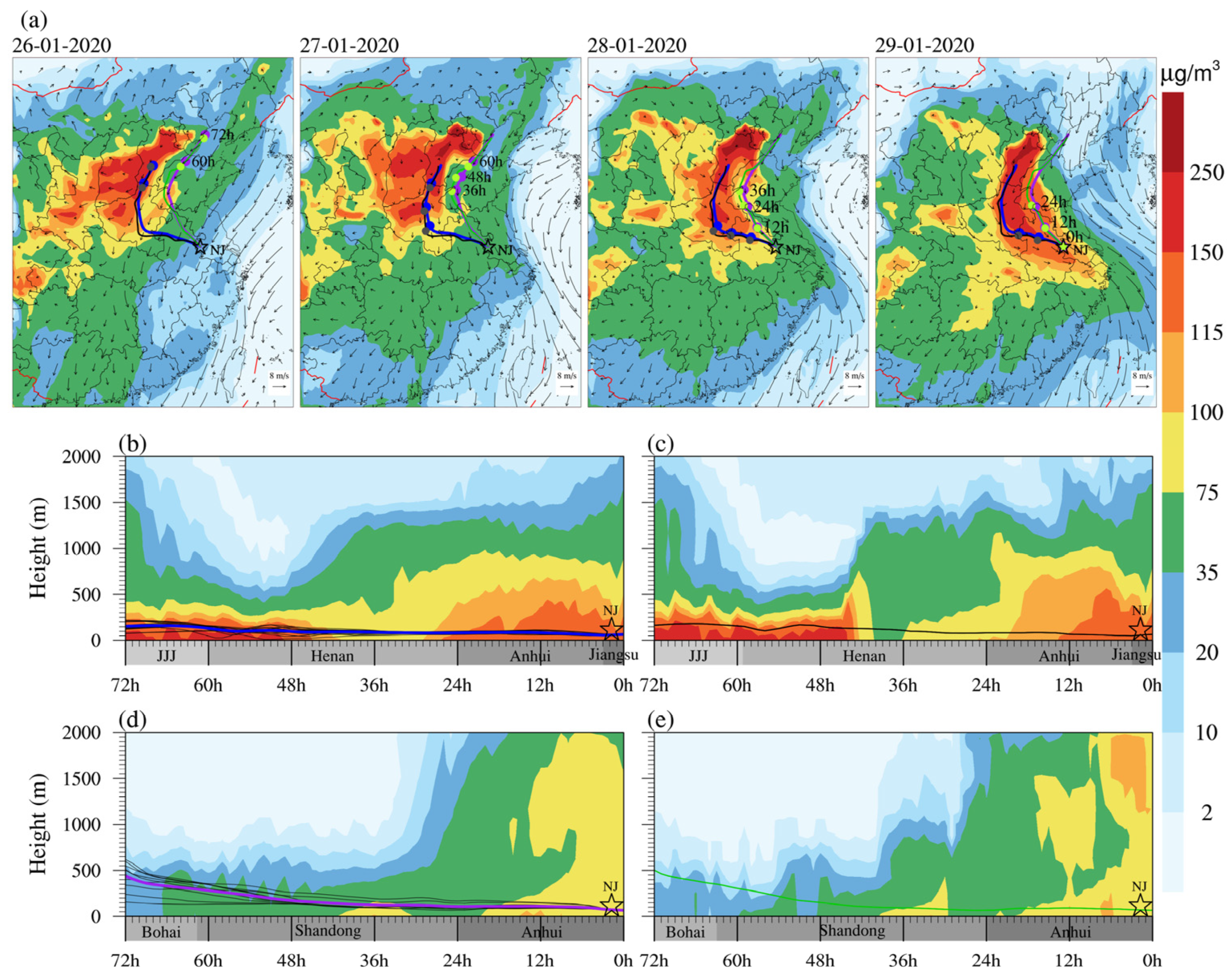
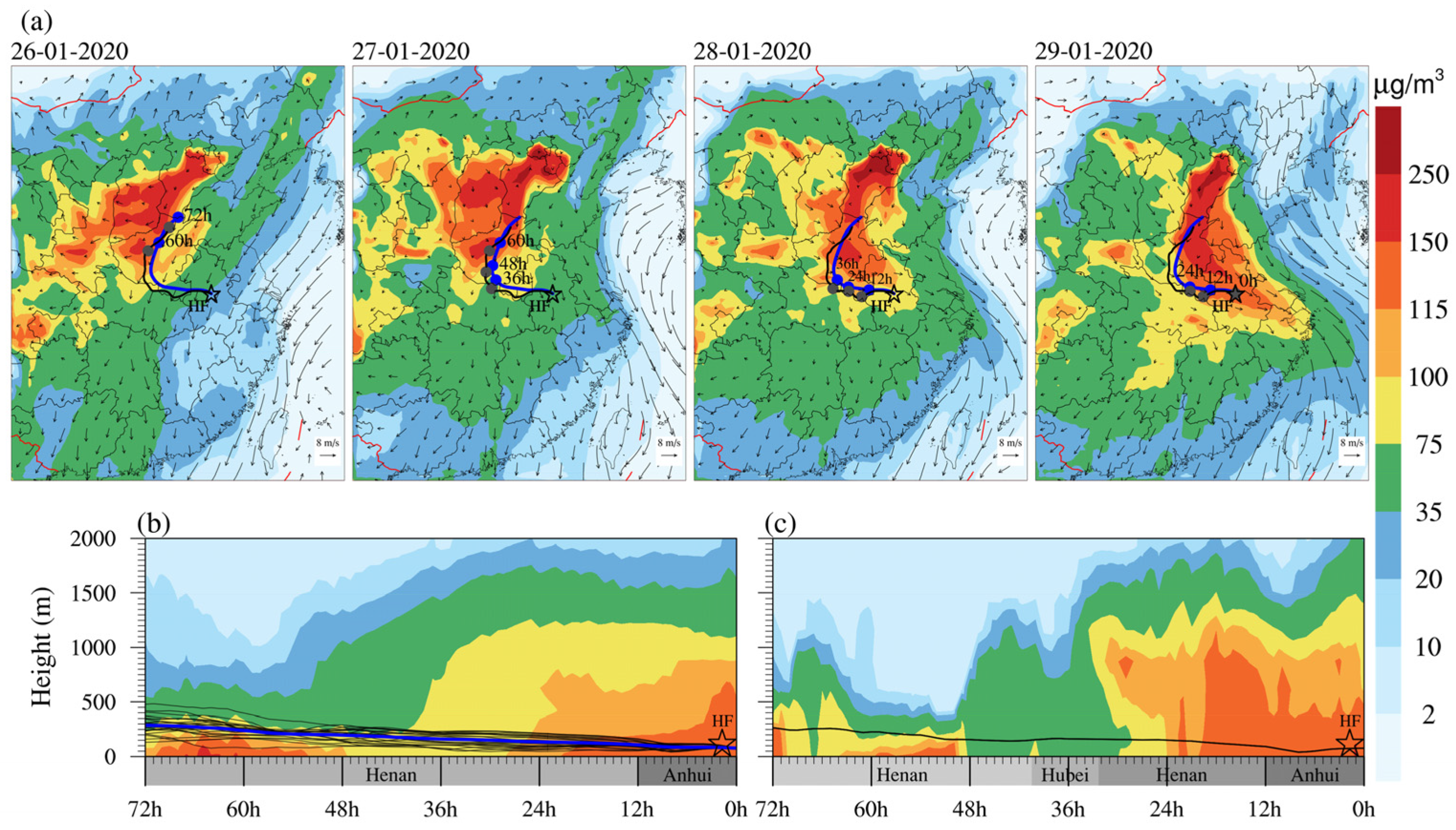
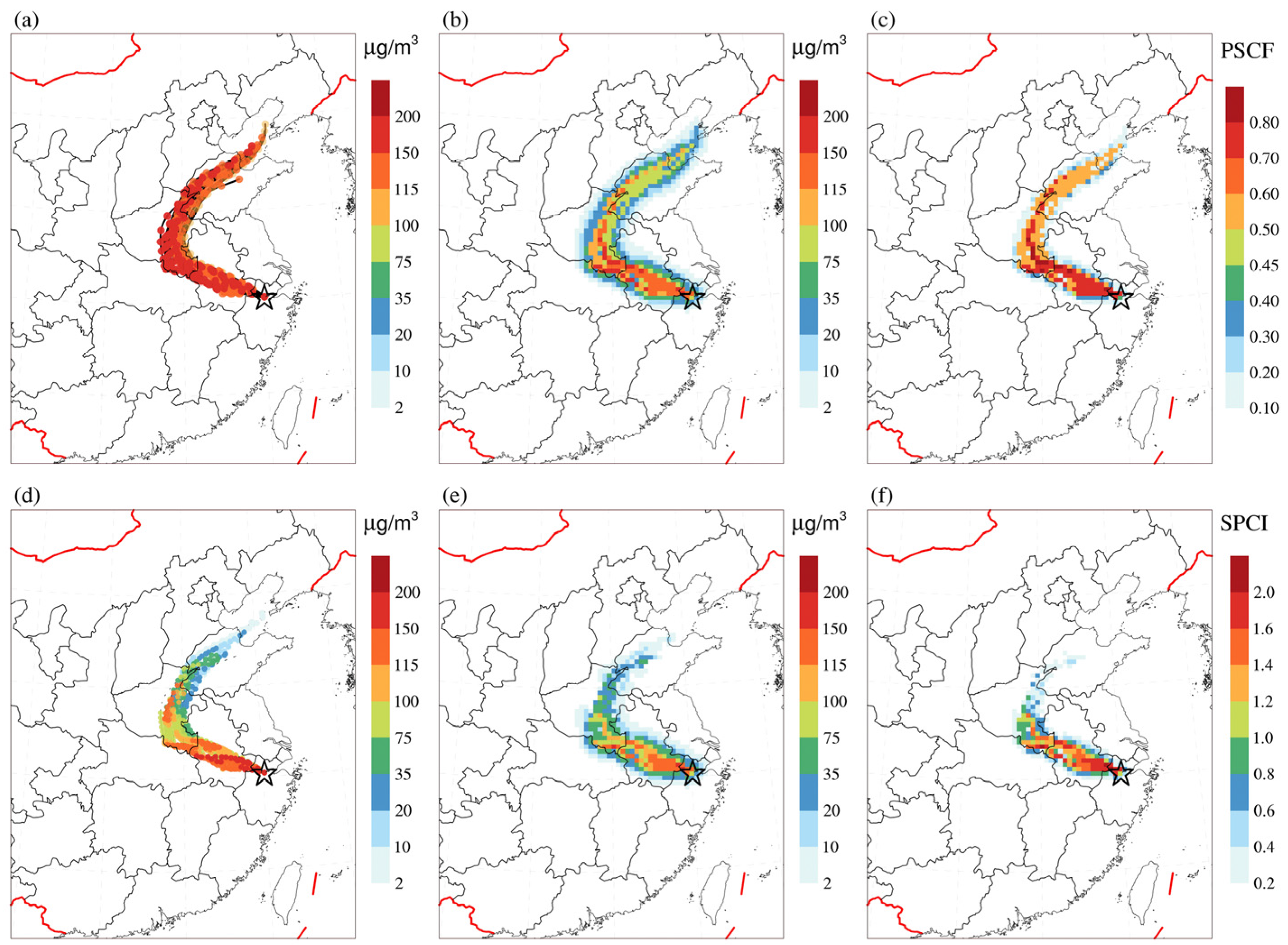
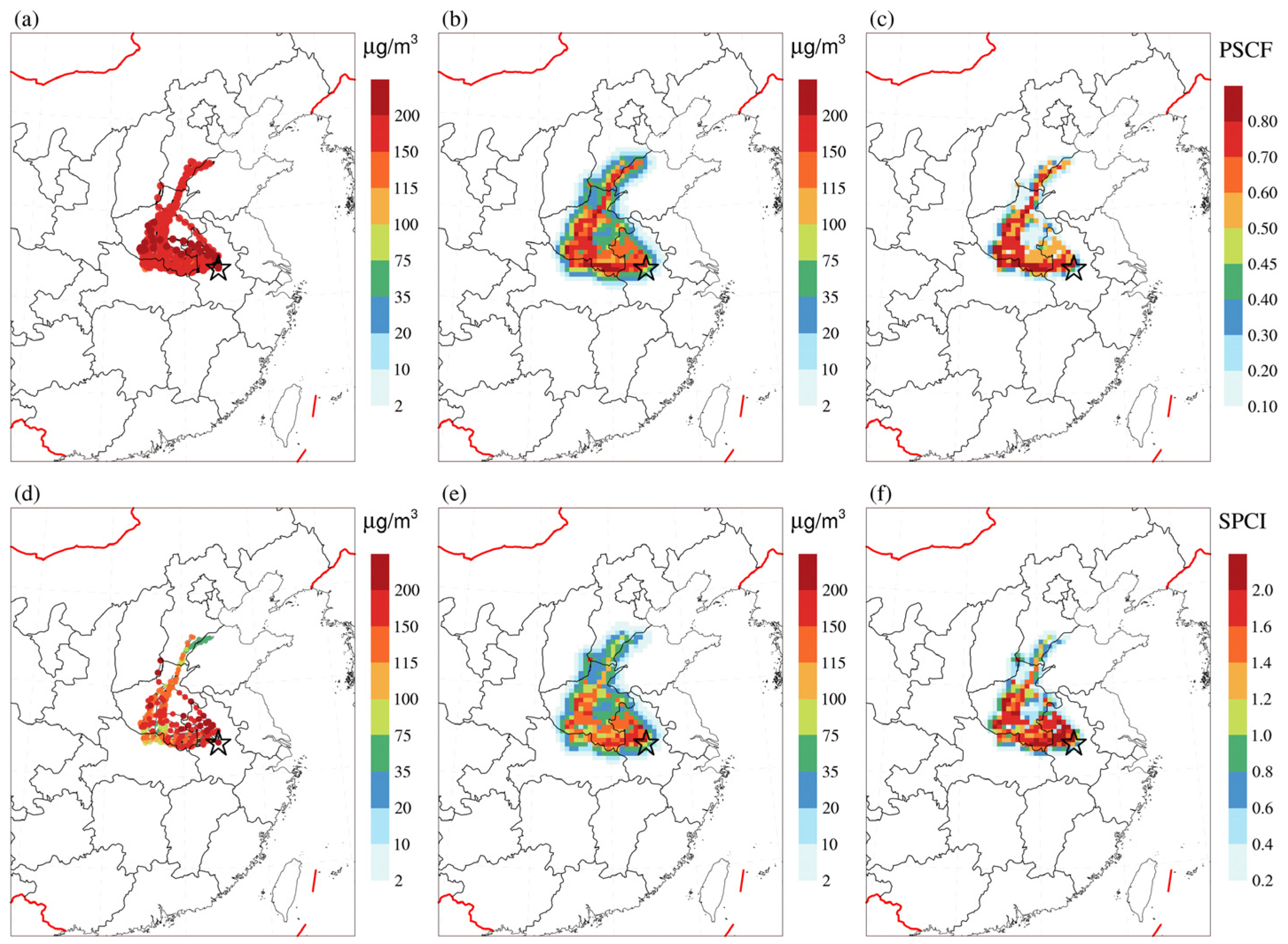
3.1. Regional Pollution Transportation Process of PM2.5
3.2. Identification Potential Sources and Transport Pathway
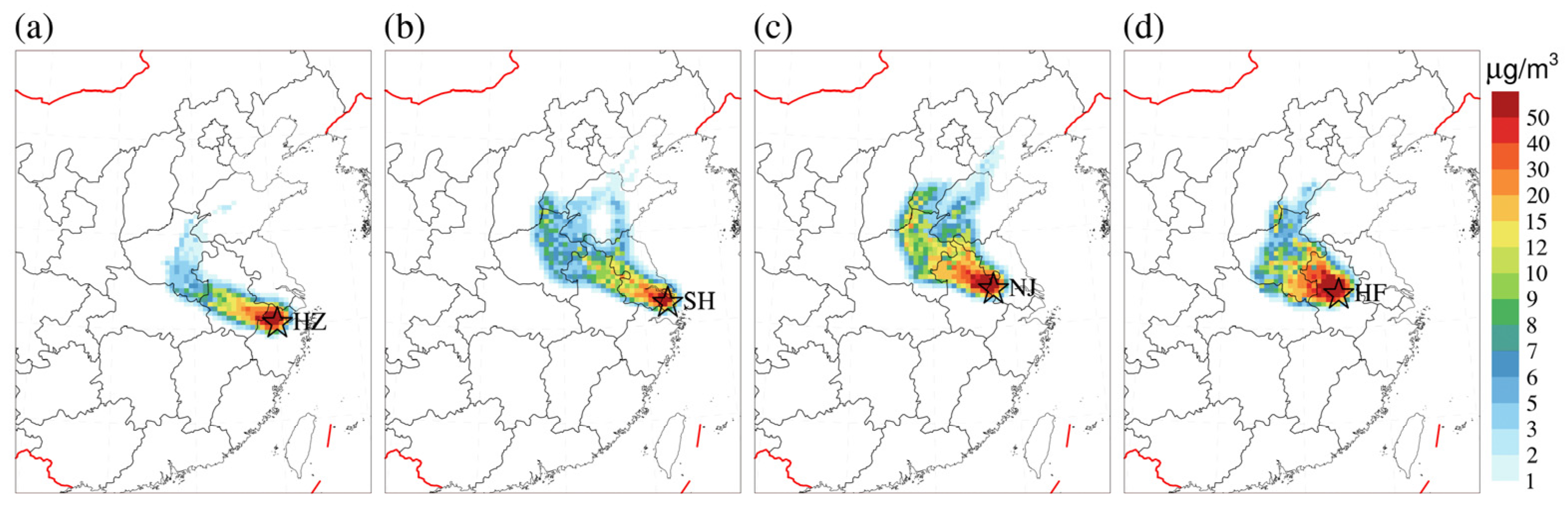
3.3. Regional Transport Contribution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Cheng, Z.; Luo, L.N.; Wang, S.X.; Wang, Y.G.; Sharma, S.; Shimadera, H.; Wang, X.L.; Bress, M.; de Miranda, R.M.; Jiang, J.K.; et al. Status and characteristics of ambient PM2.5 pollution in global megacities. Environ. Int. 2016, 89–90, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.J.; Zhao, T.L.; Liu, J.N.; Wang, H.L.; Bai, Y.Q.; Kong, S.F.; Shu, Z.Z. Regional transport patterns for heavy PM2.5 pollution driven by strong cold airflows in Twain-Hu Basin, Central China. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 269, 118847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, T.H.; Shi, Y.S.; Gilbert, K.M.; Liu, X.Y. Spatiotemporal variations of air pollutants based on ground observation and emission sources over 19 Chinese urban agglomerations during 2015–2019. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Anderson, H.R.; Frostad, J.; Estep, K.; Balakrishnan, K.; Brunekreef, B.; Dandona, L.; Dandona, R.; et al. Estimates and 25-year trends of the global burden of disease attributable to ambient air pollution: An analysis of data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2015. Lancet 2017, 389, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolker, H.R.; Reid, C.E.; Friedman, N.P.; Banich, M.T. The Association between Exposure to Fine Particulate Air Pollution and the Trajectory of Internalizing and Externalizing Behaviors during Late Childhood and Early Adolescence: Evidence from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study. Environ. Health Persp. 2024, 132, 87001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, P.K. Impacts of particulate matter pollution on plants: Implications for environmental biomonitoring. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2016, 129, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.F.; Cao, J.J.; Han, Y.M.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Du, H.Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Sun, Y.L.; Yang, W.Y.; Li, J.J.; Tang, X.; Fu, P.Q. Rapid formation of a severe regional winter haze episode over a mega-city cluster on the North China Plain. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.Q.; Yu, W.J.; Qian, Y.G.; Han, L.J.; Pickett, S.T.A.; Wang, J.; Li, W.F.; Ouyang, Z.Y. Beyond city expansion: Multi-scale environmental impacts of urban megaregion formation in China. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 9, nwab107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.P.; Wang, R.; Zhao, P. Spatial distribution and source contributions of PM2.5 concentrations in Jincheng, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.C.; Wu, Q.Z.; Zhao, R.; Cheng, H.Q.; He, H.J.; Ma, Q.; Wang, L.N.; Luo, H. New method for evaluating winter air quality: PM2.5 assessment using Community Multi-Scale Air Quality Modeling (CMAQ) in Xi’an. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 211, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.C.; Xiao, H.; Wu, Q.Z.; Wang, L.N.; Guo, Q.Y.; Cheng, H.Q.; Wang, R.R.; Tang, Z.Y. Numerical study of air pollution over a typical basin topography: Source appointment of fine particulate matter during one severe haze in the megacity Xi’an. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Zhu, B.; Gao, J.H.; Kang, H.Q.; Yang, P.; Wang, L.L.; Zhang, J.K. The source apportionment of primary PM2.5 in an aerosol pollution event over Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region using WRF-Chem, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 2966–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, L.L.; Jin, L.; Li, J.; Fu, P.Q.; Yang, W.Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.F.; Li, X.D. PM2.5 in the Yangtze River Delta, China: Chemical compositions, seasonal variations, and regional pollution events. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.; Wang, S.X.; Zhao, B.; Xing, J.; Liu, X.X.; Wei, L.; Song, Y.; Wu, W.J.; Cai, S.Y.; Zheng, H.T.; et al. Contributions of inter-city and regional transport to PM2.5 concentrations in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and its implications on regional joint air pollution control. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Tang, X.; Xu, W.S.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, H.S.; Li, J.; Wu, Q.Z.; Wang, Z.F. Application of ensemble forecast and linear regression method in improving PM10 forecast over Beijing areas. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2015, 35, 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.Y.; Hopke, P.K.; Cai, T.Q.; Fan, Z.J.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, K.N.; Zhang, Y.X. Evaluation of impact of “2 + 26′′ regional strategies on air quality improvement of different functional districts in Beijing based on a long-term field campaign. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Wang, Z.F.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X.Q.; Wang, W.; Gbauidi, A.; Gong, Y.B. Evaluation of the effect of air pollution control during the Beijing 2008 Olympic Games using Lidar data. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.J.; Wu, Y.; Huang, R.K.; Wang, J.D.; Yan, H.; Zheng, Y.L.; Hao, J.M. High-resolution simulation of link-level vehicle emissions and concentrations for air pollutants in a traffic-populated eastern Asian city. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 9965–9981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Su, J.P.; Cui, T.; Li, X.; Dong, X.; Sun, F.; Yang, Y.Y.; Tong, D.; Zheng, Y.X.; Li, Y.S.; et al. Dominant role of emission reduction in PM2.5 air quality improvement in Beijing during 2013–2017, a model-based decomposition analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 6125–6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.D.; Zhu, Y.J.; Hong, P.P. Numerical study of PM2.5 pollution in Taizhou based on Model-3/CMAQ and CAMx. Environ. Sustainable Dev. 2019, 44, 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Huang, J.P.; Hu, X.M.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y.W.; Fang, X.Z.; Luo, L.; Xiao, H.W.; Xiao, H.Y. Evaluation of WRF-Chem simulations on vertical profiles of PM2.5 with UAV observations during a haze pollution event. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 252, 118332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.Y.; Zhao, T.L.; Bai, Y.Q.; Kong, S.F.; Xiong, J.; Sun, X.Y.; Yang, Q.J.; Gu, Y.; Lu, H.C. Importance of regional PM2.5 transport and precipitation washout in heavy air pollution in the Twain-Hu Basin over Central China: Observational analysis and WRF-Chem simulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Yang, W.Y.; Hao, J.Q.; Du, H.Y. Numerical simulation study on source apportionment of PM2.5 in a heavy winter pollution event over Beijing area. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2019, 39, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, M.; Yu, M.Y.; Cai, X.H.; Du, H.Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, T.; Yan, C.Q.; Wang, X.S.; Shi, Z.B.; et al. High-time-resolution source apportionment of PM2.5 in Beijing with multiple models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 6595–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Q.; Lu, J.; Allen, P.; Livingstone, P.; Kaduwela, A.; Kleeman, M. Modeling air quality during the California Regional PM10/PM2.5 Air Quality Study (CRPAQS) using the UCD/CIT source-oriented air quality model-Part I. Base case model result. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8954–8966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Tong, J.L.; Wang, Y.F.; Chen, Y.X.; Liu, Y.L.; Zhang, X.; Ao, C.J.; Liu, H.T. Analysis of Causes and Sources of Summer Ozone Pollution in Rizhao Based on CMAQ and HYSPLIT Models. Envrion. Sci. 2023, 44, 3098–3107. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.B.; Wang, Z.F.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Xu, J.M.; Chen, H.S.; Ge, B.Z.; Zhou, G.Q.; Chang, L.Y. Development of an on-line source-tagged model for sulfate, nitrate and ammonium: A modeling study for highly polluted periods in Shanghai, China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuan, V.V.; Juana, M.D.; Roy, M.H. Review: Particle number size distributions from seven major sources and implications for source apportionment studies. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 112, 114–132. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.S.; Chien, C.J.; Tonnesen, G.S. Development of a tagged species source apportionment algorithm to characterize three-dimensional transport and transformation of precursors and secondary pollutants. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D21206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.Q.; Zhou, X.H. A review of the CAMx, CMAQ, WRF-Chem and NAQPMS models: Application, evaluation and uncertainty factors. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 343, 123183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Chen, D.S.; Cheng, S.Y.; Li, J.B.; Li, M.J.; Ren, Z.H. Identification of regional atmospheric PM10 transport pathways using HYSPLIT, MM5-CMAQ and synoptic pressure pattern analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikhovtsev, M.Y.; Molozhnikova, Y.V.; Obolkin, V.A.; Potemkin, V.L.; Lutskin, E.S.; Khodzher, T.V. Features of Temporal Variability of the Concentrations of Gaseous Trace Pollutants in the Air of the Urban and Rural Areas in the Southern Baikal Region (East Siberia, Russia). Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.P.; Liu, J.G.; Zhang, J.S.; Gui, H.Q.; Du, P.; Yu, T.Z.; Wang, J.; Lu, Y.H.; Liu, W.Q.; Cheng, Y. Identification of long-range transport pathways and potential sources of PM2.5 and PM10 in Beijing from 2014 to 2015. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 56, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.F.; Yu, J.; Cui, Y.; He, J.; Xue, P.; Cao, W.; Ying, H.M.; Gao, W.K.; Yan, Y.C.; Hu, B.; et al. Characteristics of fine particulate matter and its sources in an industrialized coastal city, Ningbo, Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Res. 2018, 203, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brereton, C.A.; Johnson, M.R. Identifying sources of fugitive emissions in industrial facilities using trajectory statistical methods. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 51, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Duan, Y.S.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.Y.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Yuan, Q.; Li, X.W.; Han, S.W.; Tong, H.J.; Huo, J.T.; et al. Measurement report: Characterisation and sources of the secondary organic carbon in a Chinese megacity over 5 years from 2016 to 2020. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 12789–12802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, F.; Anil, I.; Alagha, O. Long-range potential source contributions of episodic aerosol events to PM10 profile of a megacity. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5713–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Li, Z.L.; Cao, Y.Q.; Jiang, C.T.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.H.; Zhang, W.D.; Zhai, C.Z. Transport pathways and potential source contribution of PM2.5 pollution in Chongqing from 2015 to 2020. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2022, 42, 49–59. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.P.; Zhu, B.; Yin, Y.; Jin, L.J.; Zhang, L. Aerosol number concentration properties and potential sources areas transporting to the top of mountain Huangshan in summer. China Environ. Sci. 2014, 34, 852–861. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Kang, P.; Wang, H.L.; Qing, Q.; Ou, Y.H.; Lu, N.S.; Deng, Z.C. Analysis of Transport Pathways and Potential Sources of Atmospheric Particulate Matter in Zigong, in South of Sichuan Province. Envrion. Sci. 2020, 41, 3021–3030. [Google Scholar]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N.; Noone, K. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change. Phys. Today 1998, 51, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.K.; Holsen, T.M.; Hopke, P.K. Comparison of hybrid receptor models to locate PCB sources in Chicago. Atmos. Envirion. 2003, 37, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, I.; Zhang, L.; Blanchard, P.; Dalziel, J.; Tordon, R. Concentration-weighted trajectory approach to identifying potential sources of speciated atmospheric mercury at an urban coastal site in Nova Scotia, Canada. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 6031–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Chen, J.; Yang, H.N.; Li, R.J.; Yu, Q. Seasonal variation and potential source regions of PM2.5-bound PAHs in the megacity Beijing, China: Impact of regional transport. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.F.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, W.Y.; Tang, X.; Ge, B.Z.; Yan, P.Z.; Zhu, L.L.; Chen, X.S.; Chen, H.S.; et al. Modeling study of regional severe hazes over mid-eastern China in January 2013 and its implications on pollution prevention and control. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.F.; Xie, F.Y.; Wang, X.Q.; An, J.L.; Zhu, J. Development and Application of Nested Air Quality Prediction Modeling System. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 30, 778–790. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.D.; Chen, H.S.; Wu, Q.Z.; Wei, L.F.; Wang, Z.F.; Li, C.; Chen, D.H.; Jiang, Z.M.; Wu, W.W. Numerical study of PM2.5 regional transport over Pearl River Delta during a winter heavy haze event. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2016, 36, 2741–2751. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhuang, G.; Luo, G.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Q. Mixing of Asian mineral dust with anthropogenic pollutants over East Asia: A model case study of a super-dust storm in March 2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 7591–7607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.F.; Wang, X.; Yamaji, K.; Takigawa, M.; Kanaya, Y.; Pochanart, P.; Liu, Y.; Irie, H.; Hu, B.; et al. Impacts of aerosols on summertime tropospheric photolysis frequencies and photochemistry over Central Eastern China. Atmos. Envirion. 2011, 45, 1817–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaveri, R.A.; Peters, L.K. A new lumped structure photochemical mechanism for large-scale applications. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 30387–30415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenes, A.; Pandis, S.N.; Pilinis, C. ISORROPIA: A New Thermodynamic Equilibrium Model for Multiphase Multicomponent Inorganic Aerosols. Aquatic Geochem. 1998, 4, 123–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odum, J.R.; Jungkamp, T.P.W.; Griffin, R.J.; Flagan, R.C.; Seinfeld, J.H. The Atmospheric Aerosol-Forming Potential of Whole Gasoline Vapor. Science 1997, 276, 96–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, G.; Wang, Z.F. A global environmental atmospheric transport model (GEATM): Model description and validation. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 30, 504–518. [Google Scholar]
- Athanasopoulou, E.; Tombrou, M.; Pandis, S.N.; Russell, A.G. The role of sea-salt emissions and heterogeneous chemistry in the air quality of polluted coastal areas. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 5755–5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Gbaguidi, A.; Yan, P.Z.; Zhang, W.D.; Zhu, L.L.; Yao, X.F.; Wang, Z.F.; Chen, H. Model elucidating the sources and formation mechanisms of severe haze pollution over Northeast mega-city cluster in China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Zheng, J.; Xiao, H. Simulation Evaluation of the Contribution of Typical PM2.5 Pollution and Trans-regional Transport to Ningbo Pollution in the Yangtze River Delta. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 634–645. [Google Scholar]
- Seibert, P.; Kromp-Kolb, H.; Baltensperger, U.; Jost, D.T.; Schwikowski, M. Trajectory Analysis of High-Alpine Air Pollution Data. Air Pollut. Model. Its Appl. X 1994, 18, 595–596. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Li, Q.; Xu, J.; Li, L.; Ge, C.J.; Huang, L.; Sun, D.H.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, G.Z.; et al. Regional Air Pollution Process in Winter over the Yangtze River Delta and Its Influence on Typical Northern Cities. Envrion. Sci. 2020, 41, 1520–1534. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.M.; Wang, Y.; Guo, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.S. Characteristics, Transportation, Pathways, and Potential Sources of Air Pollution During Autumn and Winter in Taiyuan. Envrion. Sci. 2019, 40, 4801–4809. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Fang, F.X.; Liang, F.H.; Tong, L.; Xiao, H. A Comprehensive Study on Winter PM2.5 Variation in the Yangtze River Delta: Unveiling Causes and Pollution Transport Pathways. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, Y.; Zheng, J.; Fang, F.; Liang, F.; Yang, M.; Tong, L.; Xiao, H. Unveiling PM2.5 Transport Pathways: A Trajectory-Channel Model Framework for Spatiotemporally Quantitative Source Apportionment. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070883
Pan Y, Zheng J, Fang F, Liang F, Yang M, Tong L, Xiao H. Unveiling PM2.5 Transport Pathways: A Trajectory-Channel Model Framework for Spatiotemporally Quantitative Source Apportionment. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(7):883. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070883
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Yong, Jie Zheng, Fangxin Fang, Fanghui Liang, Mengrong Yang, Lei Tong, and Hang Xiao. 2025. "Unveiling PM2.5 Transport Pathways: A Trajectory-Channel Model Framework for Spatiotemporally Quantitative Source Apportionment" Atmosphere 16, no. 7: 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070883
APA StylePan, Y., Zheng, J., Fang, F., Liang, F., Yang, M., Tong, L., & Xiao, H. (2025). Unveiling PM2.5 Transport Pathways: A Trajectory-Channel Model Framework for Spatiotemporally Quantitative Source Apportionment. Atmosphere, 16(7), 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070883






