Abstract
In this study, diurnal characteristics and long-term changes in extreme precipitation (PR) in the Republic of Korea (KR) are investigated. Hourly PR data from 59 ASOS stations across the country over a 50-year period (1973–2022) are used. The focus is on the summer season (June to September), during which extreme PR frequently occurs. During the period 1973–1997 (FP), both the amount and frequency of extreme PR events peak between 01 and 09 LST. In contrast, during the period 1998–2022 (LP), a notable increase in extreme PR and its frequency is observed between 04 and 12 LST, with the peak occurrence hours shifting to this time frame. An analysis of atmospheric variables related to extreme PR is conducted for the 04–12 LST time frame. Compared to all PR events during the summer season, a low-level low-pressure anomaly is found west of the KR, leading to southerly winds and positive specific humidity anomalies over the south of the KR. Relative to the FP period, both the amplitude and frequency of high water vapor content have increased during the LP period. This intensified moisture may be associated with the observed increase in extreme PR during 04–12 LST. However, no significant changes are found in the strength and frequency of the southerly wind.
1. Introduction
According to the Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) Working Group I by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), published in 2021, the global surface temperature during the first two decades of the 21st century (2001–2020) increased by 0.99 °C compared to 1850–1900. It also reported a high likelihood that global average precipitation (PR) over land has increased since 1950, with a sharper rise since 1980 [1]. Additionally, the AR6 WG1 report highlighted that, in most land regions including East Asia, the frequency and intensity of extreme heat and heavy rainfall events have increased since the 1950s. Under the ongoing warming climate, the Republic of Korea (KR) has also experienced increased frequency and intensity of extreme rainfall events, resulting in significant damage. The “109-Year Climate Change Analysis Report of Republic of Korea,” based on domestic observation data, indicated an increase in PR over the past 109 years (1912–2020), particularly due to a marked increase in the frequency of extreme PR [2]. Recently, growing attention has been directed toward the time of day when such extreme PR events occur. For example, during a four-day period from 8–11 August 2022, extreme PR events occurred in Yangpyeong (622.2 mm) and Dongjak-gu, Seoul (577.5 mm). On August 8 specifically, extreme PR exceeding 100 mm per hour occurred overnight in southern Seoul, sparking heightened public concern regarding the timing of extreme PR events [3].
Interest in the diurnal variation in PR, including the timing of extreme PR events, has been addressed in several previous studies. These studies have investigated the diurnal characteristics and long-term trends of PR in East Asia [4,5,6,7,8] and in KR [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. Among studies in KR, Jung and Suh [11] suggested that PR in KR generally showed a primary peak with large amplitude in the early morning and a secondary peak with smaller amplitude in the late afternoon. Lee and Lee [13] found that the diurnal variation in intense PR (≥10 mm hr−1) changed over time, with the frequency of such events in the latter period (1988–2014) increasing significantly in the afternoon for stations in Seoul, Incheon, Pohang, and Daegu; in the morning for Chupungnyeong and Ulsan; and in the evening for Gwangju, Yeosu, and Jeju.
Previous studies in KR have often used data from a limited number of observation stations [13,14,17,18], or those using many stations have typically relied on shorter or older observation periods [9,11]. Therefore, to produce reliable climate change information on highly variable PR and to adequately reflect recent changes, it is essential to analyze diurnal variation using long-term and widespread observation data.
This study analyzes the characteristics and long-term changes in the diurnal variation in extreme PR in KR using 50 years (1973–2022) of meteorological observation data from 59 Korea Meteorological Administration (KMA) stations. Furthermore, we examined the synoptic-scale atmospheric mechanisms that could support these long-term changes.
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Data
To analyze the diurnal variation in extreme PR in KR, this study uses hourly PR data from 59 Automated Synoptic Observing System (ASOS) stations provided by the Open MET Data Portal of the KMA for the period from 1973 to 2022. The locations of these stations are shown in Figure 1, and only those stations with hourly PR records beginning in 1973 are selected.
Figure 1.
Locations of the 59 ASOS stations used in this study.
To investigate the characteristics and mechanisms of atmospheric variables associated with extreme PR, we utilize hourly data from the ERA5 reanalysis dataset (Fifth generation ECMWF atmospheric reanalysis) provided by the Climate Data Store Portal of ECMWF for lower tropospheric variables at the 850 hPa level, including geopotential height (zg), specific humidity (hus), zonal wind (ua), and meridional wind (va) [19]. ERA5 is a state-of-the-art global atmospheric reanalysis product developed using a wide range of observational data and data assimilation techniques. It provides high-resolution outputs in both time (hourly) and space (0.25° grid) and has been widely used in East Asian climate studies [20,21,22,23,24,25]. The ERA5 data are used without any spatial regridding, both for generating spatial fields and for calculating values. Finally, to exclude the influence of typhoons, we utilize hourly typhoon center position data from the best track archive of the Regional Specialized Meteorological Center (RSMC) Tokyo.
2.2. Methodology
As extreme PR events in KR typically occur from June to September [26], this period is selected as the analysis season to accurately reflect the characteristics of such events. The study period from 1973 to 2022 is divided into two 25-year subperiods: the early period (1973–1997, FP) and the later period (1998–2022, LP), in order to investigate long-term changes in the diurnal variation in extreme PR. In this study, the analysis is conducted based on KR standard time (UTC + 9 h) (LST). To derive clear results from the hourly PR data, 3 h accumulations are calculated in 8 time frames (e.g., 01–03, 04–06 LST, etc.). Due to the frequent occurrence of zero-PR hours in PR data, only cases with PR ≥ 0.1 mm per 3 h are considered for analysis.
To analyze the diurnal variation in extreme PR, it is necessary to define extreme PR events. While some previous studies have used fixed thresholds such as the KMA heavy PR advisory criterion (60 mm per 3 h) [13,14,16], using such thresholds can lead to an overrepresentation of certain stations or a reduction in sample size. Therefore, in this study, the 95th percentile threshold is calculated individually for each station based on 3 h accumulated PR data during the FP period. Cases exceeding this threshold are defined as extreme PR events. This percentile-based approach ensures a consistent classification of extreme PR across stations and allows for a sufficient number of events. It has also been adopted in several previous studies [20,22,24,27,28,29] and in the IPCC AR6 WG1 report [1].
Using ERA5 atmospheric variables averaged over a 3 h frame, consistent with the PR data, we investigate the characteristics and changes in atmospheric variables for each time frame. Since ERA5 data use UTC-based time coordinates, the time coordinates are converted to LST before being used in the analysis. Finally, cases where typhoons approached the designated emergency zone (north of 28° N and east of 132° E) as defined by KMA are excluded to eliminate typhoon-related effects from the analysis. The analysis process used in this study is summarized in Figure 2.
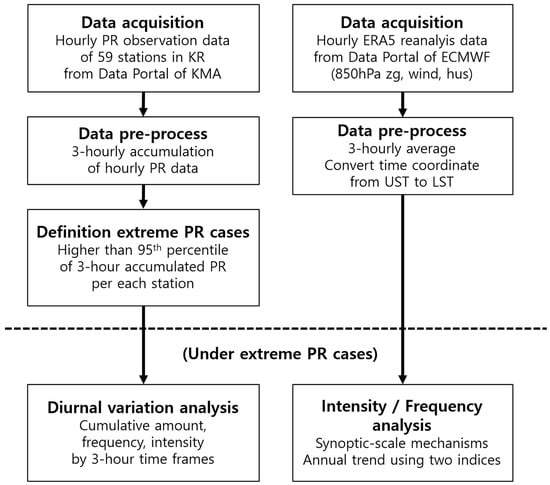
Figure 2.
The analysis process flow diagram used in this study.
3. Results
3.1. Diurnal Characteristics of Extreme PR
As noted in previous studies, extreme PR events in KR typically exhibited a pronounced primary peak in the early morning and a smaller secondary peak in the late afternoon. This distribution was affected by PR frequency rather than intensity [11,13].
To investigate this distribution, the diurnal distribution of the cumulative amount during extreme PR events in KR from June to September is analyzed, as shown in Figure 3a (blue bars) and Table 1a (FP). The diurnal distributions of extreme PR frequency and intensity are also presented in Figure 3b,c and Table 1b,c, respectively. During the FP period (1973–1997), the cumulative amount from extreme events exhibits a primary peak between 01–09 LST (816.99 mm). After 10 LST, the cumulative amounts gradually decrease, with relatively low values observed from 16 to 24 LST. This study identifies only the primary peak (01–09 LST), in contrast to previous studies that also noted a smaller secondary peak during 16–24 LST [11,13,14,17]. As highlighted in previous work, the diurnal variation in PR can exhibit regional characteristics [11,13,17]. The use of data from 59 ASOS stations in this study likely reflects overlapping regional features, and stations with noticeable secondary peaks may have been limited to only a portion of the total stations.
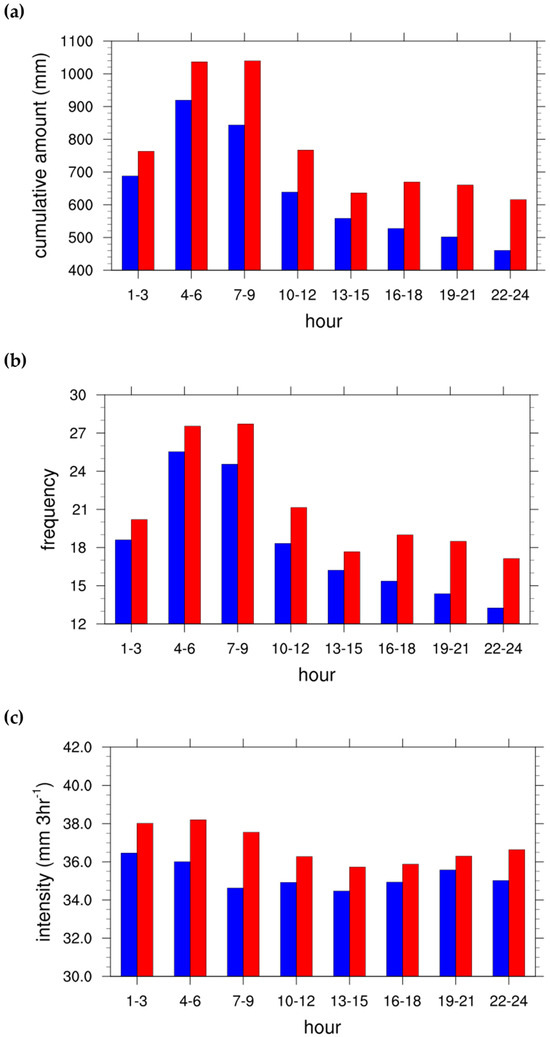
Figure 3.
Histograms of diurnal (a) cumulative amount (mm), (b) frequency, and (c) intensity (mm 3 hr−1) of extreme PR events over the KR. Statistics based on hourly PR data from 59 ASOS stations for the periods 1973–1997 (blue bars) and 1998–2022 (red bars), during June to September (JJAS). The amount and frequency are accumulated over each 25-year period.

Table 1.
Diurnal (a) cumulative amount (mm), (b) frequency, and (c) intensity (mm 3 hr−1) of extreme PR events over the KR, during the first (1973–1997, FP) and later (1998–2022, LP) periods, for the JJAS season. The amount and frequency are accumulated over each 25-year period. Anomalies are presented as both absolute and relative values. The statistical significance of anomalies is assessed using the non-parametric Kolmogorov–Smirnov two-sample test for each time frame (**: 0.01 < p-value ≤ 0.05, ***: p-value ≤ 0.01).
Next, we examine the diurnal distributions of extreme PR frequency and intensity (Figure 3b,c, Table 1b,c). The PR frequency also shows a maximum between 01 and 09 LST with 22.90 occurrences. For the PR intensity, a primary peak is seen at 35.69 mm per 3 h during 01–09 LST, and a secondary peak of 35.18 mm per 3 h during 16–24 LST. This bimodal distribution differs from the unimodal distributions seen in cumulative amount and frequency. Furthermore, the amplitude of variation in intensity is much smaller than that of the cumulative amount. The ratio between the maximum and minimum intensity is 1.057 (5.7% difference), whereas for the cumulative amount, it is 1.996 (99.6% difference). This suggests that the cumulative amount is more influenced by event frequency than intensity, consistent with findings from previous studies [9,11].
The diurnal distributions of extreme PR in the LP period (1998–2022) are presented in Figure 3 (red bars) and Table 1 (LP). Compared to the FP period, the cumulative amount from extreme events increases across all time frames. A particularly large increase occurs during 04–12 LST, with cumulative amounts rising from 800.53 mm to 947.73 mm—a difference of 147.20 mm (18.39%). Moreover, the time of peak cumulative amount shifts from 04–06 LST in the FP period to 07–09 LST in the LP period. The third-highest value also shifts to 10–12 LST.
The frequency of extreme events also increases across all time frames in the LP period (Figure 3b, Table 1b), with a notable rise from 22.80 to 25.47 occurrences (11.71%) during 04–12 LST. Similarly, the timing of the maximum shifted from 04 to 06 LST to 07–09 LST, and the third-highest occurrence time shifted to 10–12 LST.
Changes in the PR intensity are somewhat different from those in frequency (Figure 3c, Table 1c). Although intensity increases slightly in all time frames during the LP period, only the increase during 07–09 LST (8.46%) is statistically significant. This suggests that the increase in cumulative amount from 04 to 12 LST (18.39%) is more closely linked to frequency than to intensity.
We also analyze the diurnal distribution of all summer PR events (not limited to extreme cases) (Figure S1). Similarly to extreme events, the maximum values of the cumulative amount, frequency, and intensity occur in 01–09 LST during the FP period (blue bars in Figure S1). Compared to the FP period, the cumulative amount increases by 188.50 mm (8.39%) during 04–12 LST in the LP period (red bars in Figure S1). This increase is smaller than the 18.39% rise observed in extreme PR, suggesting that extreme events are more sensitive to change.
Lastly, during the 16–24 LST—where values are relatively low in the FP period—larger increases are observed in the LP period, similar to or exceeding those seen from 04 to 12 LST (Figure 3, Table 1). Specifically, the cumulative amount rises by 151.98 mm (30.60%), and the event frequency increases by 3.88 occurrences (27.08%). These results suggest that the secondary peak in the late afternoon becomes more prominent in terms of both the cumulative amount and frequency. However, the primary peak during 04–12 LST still dominates in the LP period, and therefore, the next section focuses on the characteristics and changes in atmospheric variables during that time frame.
3.2. Intensity Characteristics and Changes in Atmospheric Variables
Jin et al. [17] analyzed the mechanisms of atmospheric variables related to the diurnal variation in PR in KR using data from 502 stations, including both ASOS and Automatic Weather System (AWS) observations from 2011 to 2020. Specifically, they found that the maximum PR tended to occur during the late night to morning hours (02–10 LST, LNMP) in the western and eastern coastal regions, and during the afternoon to evening hours (14–22 LST, AEP) in the mountainous and southern coastal regions in KR. They also found that LNMP events were associated with strong synoptic-scale environments (e.g., low-pressure systems) and enhanced nocturnal southerly winds, whereas AEP events were influenced by weaker synoptic conditions and local convergence during the afternoon.
Building upon this, this study analyzes the intensity characteristics and changes in atmospheric variables at the synoptic scale during extreme PR events. Figure 4 shows the anomaly fields of atmospheric variables during extreme PR events in the FP period. These anomaly fields are calculated by subtracting the mean fields of extreme PR events from the summer climatological mean fields, focusing on lower-tropospheric geopotential height, wind, and specific humidity.
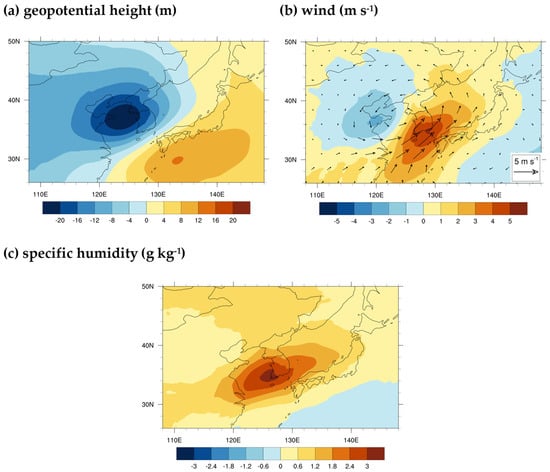
Figure 4.
Spatial anomalies of 850 hPa (a) geopotential height (m), (b) wind (m s−1), and (c) specific humidity (g kg−1) during extreme PR events over the KR, calculated for the FP period and JJAS season. Anomalies are based on summer climatologies during the FP period. Shading in the wind variable represents the meridional wind speed.
During extreme PR events, compared to the summer mean, negative geopotential height anomalies (indicative of a low-pressure system) are observed west of the KR, while positive anomalies (indicative of high pressure) appeared south of Japan (Figure 4a). As a result, strong southwesterly winds and large positive anomalies in specific humidity are induced over southern KR (Figure 4b,c). These increases in atmospheric moisture can support the occurrence of extreme PR.
Next, the spatial distributions of three key atmospheric variables during extreme PR events are presented for both the FP and LP periods in Figure 5, along with the differences between the two periods. Since the characteristic features of these variables during extreme events are already discussed (Figure 4), we focus here on changes during the 04–12 LST, when the peak amount and frequency are observed.
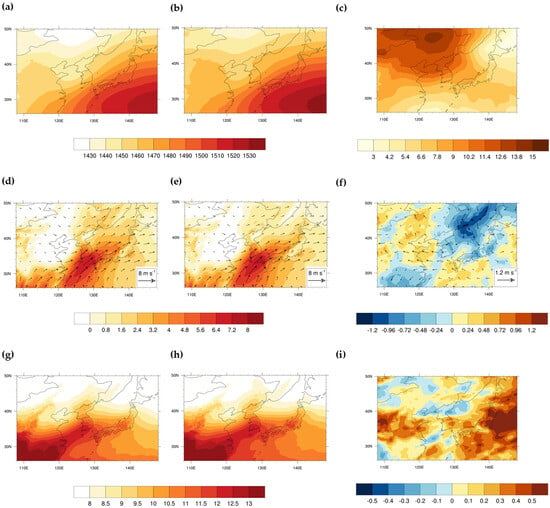
Figure 5.
Spatial distributions of 850 hPa (a–c) geopotential height (m), (d–f) wind (m s−1), and (e–i) specific humidity (g kg−1) during extreme PR events over the KR for 04–12 LST. The first and second columns show results for the FP and LP periods, respectively. The third column shows the differences between the two periods. Shading in the wind panels represents the meridional wind speed.
In the LP period, the geopotential heights generally increased across East Asia due to global warming (Figure 5c). Notably, substantial increases are seen over the continental region of northeastern China and moderate increases over the northwestern Pacific south of Japan. These patterns suggest enhanced surface warming over the continent and an expansion of the high-pressure zone over the northwestern Pacific. As a result, wind anomalies develop: northeasterly anomalies over the eastern continent (Primorsky Krai–East Sea–Korean Peninsula region), and southeasterly anomalies over the southern KR and western Japan, along the periphery of the northwestern Pacific high (Figure 5f). Although this suggests an increase in the southerly wind strength—a key dynamic variable for moisture transport—over southern KR, the anomaly magnitudes are small, implying limited impact by dynamic contributions.
Finally, the change in specific humidity between the FP and LP periods is shown in Figure 5i. Considerable increases are observed over KR, as well as in parts of China and Japan, whereas decreases are noted over North Korea and nearby areas. This indicates an enhancement in the thermodynamic conditions (i.e., atmospheric moisture) over KR, which is likely associated with the observed increases in the cumulative amount and event frequency during 04–12 LST (Figure 3, Table 1).
3.3. Frequency Characteristics and Changes in Atmospheric Variables7
As shown in the previous section (Figure 4b,c and Figure 5d,e,g,h), extreme PR events in KR are associated with southerly winds and relatively high specific humidity anomalies over southern regions of the KR, and with northerly winds and relatively low specific humidity anomalies over the northwestern regions of the Korean Peninsula. In other words, extreme PR is accompanied by pronounced differences in both dynamic and thermodynamic variables. Therefore, this section focuses on analyzing the frequency characteristics and changes in systems associated with extreme PR, using changes in the meridional wind speed at 850 hPa (va850) as a dynamic variable and specific humidity at 850 hPa (hus850) as a thermodynamic variable.
Figure 6 presents the mean fields of the meridional wind and specific humidity during extreme PR events in the FP period. Regions with strong northerly and southerly winds over northwestern and southern Korean Peninsula, respectively, are identified and highlighted in the blue and red boxes in Figure 6a. The difference in area average values between these regions (red–blue) is shown in the upper-right corner of the figure. For specific humidity (Figure 6b), regions of relatively low and high specific humidity anomalies are selected, and the difference in area average values is similarly indicated. The selected regions differ slightly depending on the variable, due to differences in the spatial structure of their fields. For the FP period, the difference in meridional wind between regions is 7.10 m s−1, and for specific humidity, it is 3.06 g kg−1. These values are adopted as thresholds to define new indices.
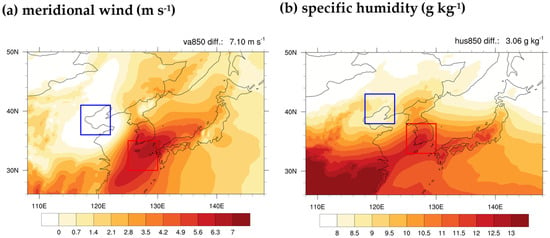
Figure 6.
Climatological spatial distributions of 850 hPa (a) meridional wind (m s−1) and (b) specific humidity (g kg−1) during extreme PR events over the KR, based on the 1973–1997 period and JJAS season. The differences between the area-averages of the southern (red) and northwestern (blue) regions of the KR are presented in the upper-right corner of each variable.
Specifically, the number of days during which these regional differences exceeded the thresholds are defined as the Extreme Southern Wind Days (ESWD) and Extreme Wet Days (EWD), representing the frequency of favorable dynamic and thermodynamic conditions, respectively, for extreme PR. The annual trends in ESWD and EWD for 04–12 LST are then analyzed (Figure 7).
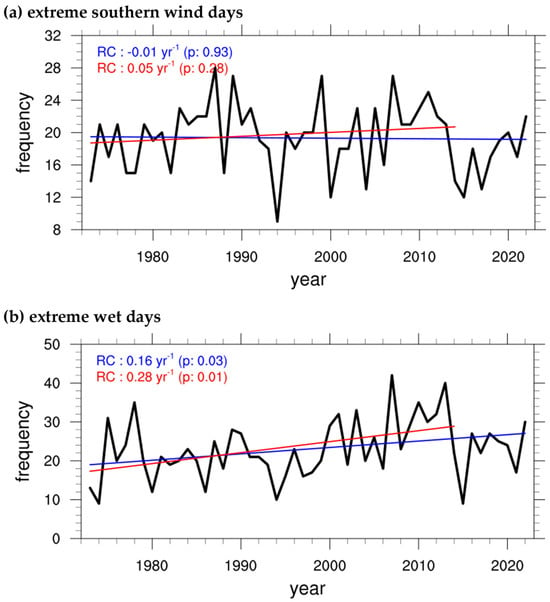
Figure 7.
Time series of annual (a) extreme southern wind days and (b) wet days associated with extreme PR events over the KR for 04–12 LST. Linear regression coefficients are shown in the upper-left corner of each panel for the period 1973–2022 (blue) and 1973–2014 (red). Significances of the linear trend are calculated by using the non-parametric Mann–Kendall test.
Both indices exhibit interannual variability, with notable drops during years with low PR, such as 1994 and 2015. Since the extremely dry conditions in 2015 could influence the trend analysis of extreme PR events, trends are also evaluated for the pre-2015 period (1973–2014) separately (red trend lines), in addition to the full period (blue lines).
For ESWD, the trend over the full period is −0.01 yr−1, indicating no significant change. Similarly, the trend for the pre-2015 period has a p-value of 0.28, showing that the frequency of favorable dynamic conditions has not changed significantly. This result is consistent with the findings on the intensity of dynamic variables presented in the previous section (Figure 5f).
In contrast, EWD shows a statistically significant increasing trend over the full period, with a rate of 0.16 yr−1 (p-value: 0.03). For the pre-2015 period, the increase is even more pronounced at 0.28 yr−1 (p-value: 0.01) (Figure 7b). This suggests that favorable thermodynamic conditions (i.e., higher water vapor) for extreme PR have become more frequent in recent decades. This trend aligns with the intensification of thermodynamic variables (Figure 5i) and is likely related to the observed increases in the cumulative amount and frequency of extreme PR events during the 04–12 LST.
4. Discussion
Extreme PR during the FP period shows a clear early morning peak, while the secondary peak in the afternoon—often noted in previous studies—is relatively small (Figure 3). However, this secondary peak becomes more evident in the LP period. As noted in earlier research, the diurnal variation in extreme PR in KR exhibited regional characteristics [11,13,17]. Specifically, coastal regions in western KR tended to peak in the early morning, while mountainous areas showed peaks in the afternoon and evening. Similarly, atmospheric mechanisms related to extreme PR may vary by region. Therefore, future studies should consider these regional characteristics when analyzing the afternoon secondary peaks and their associated atmospheric mechanisms.
Both intensity and frequency analyses for atmospheric variables show clearer changes in thermodynamic variables than in dynamic ones (Figure 5 and Figure 7). This implies that increases in extreme PR and its frequency during the 04–12 LST are largely attributable to thermodynamic variable. To quantify the contributions of different atmospheric variables to changes in PR, several previous studies have used moisture budget analysis [30,31,32,33]. In particular, the methodology of Seager et al. [34], employed by Lee et al. [31], decomposes changes in PR changes into components such as evaporation, dynamics, and thermodynamics. Applying this method in future studies could enable a more detailed understanding of the mechanisms and contributions behind changes in the diurnal variation in PR in KR.
Finally, we examine the characteristics and changes in atmospheric variables associated with extreme PR at the synoptic scale (Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7). However, several previous studies have indicated that the diurnal variation in extreme PR is influenced not only by synoptic-scale conditions but also by mesoscale atmospheric processes. Although our study demonstrates synoptic-scale features, a limitation of this study is that it does not clarify the atmospheric mechanisms responsible for the primary peak. As mentioned above, Jin et al. [17] demonstrated that the primary peak over the KR was driven by the nocturnal enhancement of low-level jets, while the secondary peak was attributed to local convergence. They further suggested that the intensification of the low-level jet was linked to boundary layer inertial oscillation. Similar mesoscale mechanisms have also been reported in China [6]. In another study, Park et al. [16] characterized extreme PR events in KR using localized mid-tropospheric (600 hPa) saturation deficit and upward mass flux. Therefore, future research should aim to investigate the long-term changes in the characteristics of extreme PR in KR by incorporating mesoscale atmospheric variables, alongside long-term observational datasets.
5. Summary and Conclusions
We analyze the characteristics and long-term changes in the diurnal variation in summer (June to September) extreme precipitation (PR) across the Republic of Korea (KR) using hourly PR observations from 59 ASOS stations (Figure 1). Extreme PR cases are defined based on the 95th percentile of 3 h accumulated PR at each station. Additionally, we examine synoptic-scale atmospheric mechanisms supporting long-term changes in extreme PR using 850 hPa geopotential height, wind, and specific humidity data from the ECMWF ERA5 reanalysis dataset.
Results show that during the first period (1973–1998, FP), the maximum cumulative amount from extreme events occurs between 01 and 09 LST (816.99 mm, Figure 3a, blue bars, Table 1a). When broken down into 3 h time frames, the 04–06 LST have the highest amount, followed by 07–09 LST and then 01–03 LST. Extreme PR frequency also peaks during 01–09 LST (22.90 occurrences), indicating a similar diurnal distribution to the cumulative amount. In contrast, the PR intensity shows two peaks—between 01 and 09 LST and 16 and 24 LST—with smaller amplitude, suggesting a different distribution and indicating that the cumulative amount distributions are more influenced by frequency than intensity.
For the later period (1998–2022, LP), the cumulative amount from extreme events increases in all time frames (Figure 3a, red bars, Table 1a). Particularly large increases occur between 04 and 12 LST. In 3 h time frames, the 04–06 LST and 07–09 LST have the highest amount, with 10–12 LST ranking third. The cumulative amount during 04–12 LST increases by 147.20 mm (18.39%) compared to the FP period, and the peak time frame shifts from 01–09 LST to 04–12 LST. Similarly, the frequency increases by 2.67 occurrences (11.71%) during the same period. The PR intensity also increases in the LP period but only shows a statistically significant rise (8.46%) during 07–09 LST (Figure 3c, Table 1c), reinforcing that frequency, not intensity, primarily contributed to the increase in extreme PR amount.
We also examine the synoptic-scale atmospheric characteristics and their long-term changes associated with extreme PR events. Compared to the summer climatology, extreme events are accompanied by a lower geopotential anomaly over the west of the KR and strong southwesterly winds and increased specific humidity over the southern KR (Figure 4). Focusing on the 04–12 LST, where extreme PR peaks, we find that in the LP period, there are changes in the dynamic variable (southerly wind strength) contributing to moisture transport over southern KR. However, the magnitude of the anomaly is small, so its impact is expected to be limited. Meanwhile, the thermodynamic variable (specific humidity) considerably decreases in North Korea and surrounding areas but increases over KR, China, and Japan.
To assess the frequency of favorable conditions for extreme PR, we define two indices based on regional differences in the meridional wind (va850) and specific humidity (hus850): Extreme Southern Wind Days (ESWD) and Extreme Wet Days (EWD) (Figure 7). While the ESWD index does not exhibit a statistically significant trend, the EWD index shows a significant upward trend across the full period (0.16 yr−1, p-value: 0.03) and an even greater increase in the pre-2015 period (0.28 yr−1, p-value: 0.01). These results suggest that thermodynamic conditions favorable to extreme PR have become more frequent.
In this study, reliable characteristics and long-term changes in the diurnal variation in summer extreme PR over KR are presented based on long-term observational data. Therefore, despite some limitations, the findings are expected to contribute not only to advancing scientific understanding but also to developing climate change adaptation strategies by central and local governments.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos16070780/s1, Figure S1: Histograms of diurnal PR statistics of all PR events over the KR.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: D.-H.K., J.-U.K. and J.S.; data acquisition: D.-H.K. and J.-U.K.; data analysis: D.-H.K., J.-U.K., J.S. and K.-O.B.; visualization: D.-H.K.; writing—original draft preparation: D.-H.K.; writing—review and editing: D.-H.K., J.-U.K., J.S., C.-Y.C., K.-O.B. and S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Korean Meteorological Administration Research and Development Program “Developing and Assessing Climate Change Scenarios” under Grant (KMA2018-00321).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not Applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The ASOS observation data can be downloaded from the Open MET Data Portal of KMA (https://data.kma.go.kr/cmmn/main.do (accessed on 20 June 2025)), and the ECMWF ERA5 data can be downloaded from the Climate Data Store Portal of ECMWF (https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/datasets/reanalysis-era5-pressure-levels?tab=overview (accessed on 20 June 2025)).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- IPCC. AR6 Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KMA. 109-Year Climate Change Analysis Report of Republic of Korea. 2021. Available online: http://www.climate.go.kr/home/bbs/view.php?code=71&bname=scenario&vcode=6511&cpage=1&vNum=43&skind=&sword=&category1=&category2= (accessed on 1 May 2025). (In Korean).
- KMA. Abnormal Climate Report. 2023. Available online: http://www.climate.go.kr/home/bbs/view.php?code=93&bname=abnormal&vcode=6609&cpage=1&vNum=16&skind=&sword=&category1=&category2= (accessed on 1 May 2025). (In Korean).
- Kanada, S.; Tsuguti, H.; Kato, T.; Fujibe, F. Diurnal Variation of Precipitation around Western Japan during the Warm Season. Sola 2014, 10, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Sha, W.; Iwasaki, T.; Wen, Z. Diurnal Cycle of a Heavy Rainfall Corridor over East Asia. Mon. Weather Rev. 2017, 145, 3365–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Luo, X.; Zhu, K.; Sun, Z.; Fei, J. The Controlling Role of Boundary Layer Inertial Oscillations in Meiyu Frontal Precipitation and Its Diurnal Cycles Over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 5090–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Chen, G.; Du, Y.; Wen, Z. Diurnal Variations of Low-Level Winds and Precipitation Response to Large-Scale Circulations during a Heavy Rainfall Event. Mon. Weather Rev. 2019, 147, 3981–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Huang, D.; Chen, J.; Zeng, J.; Liu, A. Variations and Comparisons in Hourly and Daily Precipitation Extremes over Eastern China in Recent Warming Periods. Int. J. Climatol. 2024, 44, 5192–5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, G.-H.; Kwon, H.-J. Diurnal Variation of Precipitations over south Korea and its Implication. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 1998, 34, 222–237. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, H.-S.; Lim, G.-H.; Oh, J.-H. Interpretation of the Transient Variations in the Time Series of Precipitation Amounts in Seoul, Korea. Part I: Diurnal Variation. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 2989–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.-H.; Suh, M.-S. Characteristics and Types of the Diurnal Variation of Hourly Precipitation during Rainy Season over South Korea. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 41, 533–546, (In Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.-H.; Seo, K.-H. Analysis of Diurnal and Semidiurnal Cycles of Precipitation over South Korea. Atmosphere 2008, 18, 475–483, (In Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Lee, S.H. A Long-term Trend of Hourly Summer Precipitation in South Korea. J. Clim. Res. 2016, 11, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, T.; Park, C.; Kim, G.; Cha, D.-H. Long-term Variability of Summer Heavy Rainfall in the Seoul Metropolitan Area. J. Clim. Res. 2019, 14, 209–219, (In Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, E.; Park, C.; Son, S.-W.; Roh, J.-W.; Lee, G.-W.; Lee, Y.-H. Classification of Localized Heavy Rainfall Events in South Korea. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 56, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.-K.; Chang, M.; Ho, C.-H.; Ha, K.-J.; Kim, J.; Sohn, B.-J. Two Types of Diurnal Variations in Heavy Rainfall during July over Korea. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 2201–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.-G.; Lee, H.; Baik, J.-J. Characteristics and Possible Mechanisms of Diurnal Variation of Summertime Precipitation in South Korea. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2022, 148, 551–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KMA. KMA Publications: Summer Forecast. 2022. Available online: https://data.kma.go.kr/data/publication/publicationWbList.do (accessed on 1 May 2025). (In Korean).
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-H.; Min, S.-K.; Zhang, X.; Sillmann, J.; Sandstad, M. Evaluation of the CMIP6 Multi-Model Ensemble for Climate Extreme Indices. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2020, 29, 100269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Y.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, J. Changes in the Drought Condition over Northern East Asia and the Connections with Extreme Temperature and Precipitation Indices. Glob. Planet. Change 2021, 207, 103645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-R.; Moon, M.; Yun, J.; Ha, K.-J. Trends and Spatio-Temporal Variability of Summer Mean and Extreme Precipitation across South Korea for 1973–2022. Asia-Pac. J Atmos. Sci. 2023, 59, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Yong, Y.; Hawcroft, M.K. Long-Term Trends in Atmospheric Rivers over East Asia. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 60, 643–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Huang, A.; Wu, P.; Huang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhao, D.; Yang, B.; Chen, S. Typical Synoptic Patterns Responsible for Summer Regional Hourly Extreme Precipitation Events Over the Middle and Lower Yangtze River Basin, China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL104829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-H.; Min, S.-K.; Cha, D.-H.; Byun, Y.-H.; Lott, F.C.; Stott, P.A. Attribution of the Unprecedented 2021 October Heatwave in South Korea. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2022, 103, E2923–E2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KMA. Rainy Season (Changma) Analysis Report. 2022. Available online: https://www.kma.go.kr/kma/archive/pub.jsp?field1=grp&text1=why_how#gal_cate13 (accessed on 1 May 2025). (In Korean).
- Zhang, X.; Alexander, L.; Hegerl, G.C.; Jones, P.; Tank, A.K.; Peterson, T.C.; Trewin, B.; Zwiers, F.W. Indices for Monitoring Changes in Extremes Based on Daily Temperature and Precipitation Data. WIREs Clim. Change 2011, 2, 851–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharin, V.V.; Zwiers, F.W.; Zhang, X.; Wehner, M. Changes in Temperature and Precipitation Extremes in the CMIP5 Ensemble. Clim. Change 2013, 119, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosio, A.; Mentaschi, L.; Fischer, E.M.; Wyser, K. Extreme Heat Waves under 1.5 °C and 2 °C Global Warming. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 054006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.-Y.; Shin, H.-J.; Jang, C.J.; Kim, H.-J. Projected Change in East Asian Summer Monsoon by Dynamic Downscaling: Moisture Budget Analysis. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 51, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Min, S.-K.; Fischer, E.; Shiogama, H.; Bethke, I.; Lierhammer, L.; Scinocca, J.F. Impacts of Half a Degree Additional Warming on the Asian Summer Monsoon Rainfall Characteristics. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 044033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Ha, K.-J.; Timmermann, A. Disentangling Impacts of Dynamic and Thermodynamic Components on Late Summer Rainfall Anomalies in East Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 8623–8633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Ha, K.-J.; Jeong, J.-Y. Identifying Dynamic and Thermodynamic Contributions to the Record-Breaking 2022 Summer Extreme Rainfall Events in Korea. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 60, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seager, R.; Naik, N.; Vecchi, G.A. Thermodynamic and Dynamic Mechanisms for Large-Scale Changes in the Hydrological Cycle in Response to Global Warming. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 4651–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).