Abstract
(1) Background: The relationship between air pollution and the risk of developing aphasia is still unclear. We aimed to evaluate air pollution exposure as a risk factor for developing aphasia in Taiwan. (2) Methods: This retrospective population-based cohort study used the Longitudinal Generation Tracking Database (LGTD) and the Taiwan Air Quality Monitoring Database (TAQMD). The incidence rate ratio (IRR) and adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) were calculated to examine the association between aphasia and exposure to six air pollutants: sulfur oxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen oxide (NOx), and particulate matter (PM2.5, PM10) from 2003 to 2017. (3) Results: The incidence rate ratio (IRR) of aphasia showed that individuals with high levels of SO2, CO, and NO were at a higher risk of developing aphasia. Increased exposure to airborne particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10) also increased the risk of developing aphasia. The adjusted HRs of the aphasia risk were statistically significant for all the air pollutants at higher concentrations. (4) Conclusions: Individuals exposed to ambient air pollutants have a significantly higher risk of developing aphasia. The greater the exposure to airborne particulate matter and gaseous pollutants, the more likely individuals are to develop aphasia.
1. Introduction
Air pollution has become a major threat to public health since industrialization [1]. It is the fourth leading risk factor for death (UNEP Pollution Action Note), not to mention that it continues to be one of the top contributors to the global disease burden and significantly affects people’s quality of life [2]. Air pollutants and airborne particulate matter (PM), which carry a variety of chemicals, can break the blood–brain barrier or cause inflammation in other parts of the body, eventually leading to brain damage [3,4,5,6,7]. Air pollution is unavoidable; whether the air quality index (AQI) is mild or severe, air pollutants influence human health daily [8,9].
Aphasia is an acquired language disorder commonly observed after stroke or brain injury that affects language regions in the brain [10,11]. People with aphasia often have difficulty communicating effectively with others; thus, it is considered one of the most devastating symptoms of stroke or brain injury [12,13]. Although the cause of aphasia is neurological, the contribution of environmental factors to the risk of developing aphasia remains unclear. The brain is a delicate organ highly sensitive to changes. The fact that exposure to air pollution has a deleterious influence on brain health and has been shown to increase the risk of cerebrovascular diseases raises concerns that environmental changes, such as exposure to air pollution, have a pervasive impact on neurogenic language disorders [14,15,16]. Therefore, we conducted this nationwide observational study to evaluate the association between exposure to air pollution and the risk of aphasia, based on previous studies that combined two nationwide databases: Taiwan’s National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD) and the Taiwan Air Quality Monitoring Database (TAQMD) [17,18,19,20].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
Study subjects were identified via the Longitudinal Generation Tracking Database (LGTD), which randomly extracted two million beneficiaries from Taiwan’s National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD). The NHIRD is based on the single-payer National Health Insurance (NHI) program in Taiwan, which includes registration files (e.g., the registry of medical facilities) and original medical claims data for reimbursement. Participants’ identification numbers were encrypted for privacy, but the database provided demographic information for this research. We included subjects enrolled in the NHI program after 1 January 2003. We followed them until the subjects withdrew from the program, developed aphasia, or until the end of the database at the time of data retrieval (31 December 2021). Those younger than 18 years or without related medical records were excluded from the analysis, resulting in 228,807 subjects (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Flowchart of the study design and study population selection.
2.2. Air Pollution Exposure
The air quality data were obtained from the Taiwan Air Quality Monitoring Database (TAQMD). It provides daily real-time air pollution information for 74 community-based sites monitored by the Taiwan Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) around the island. We extracted the daily concentrations of the six most common air pollutants, sulfur oxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen oxide (NOx), and particulate matter (PM2.5, PM10), for further analysis. The daily average concentration level of the six air pollutants between 2001 and 2017 was calculated, respectively. The annual concentration level for each air pollutant was divided into four levels by quartile, with Quartile 1 representing the least concentration level and Quartile 4 as the highest level: SO2 concentration (first quartile (Q1): <3.64, second quartile (Q2): 3.65–4.51, third quartile (Q3): 4.52–5.19, and fourth quartile (Q4): >5.19 ppb), CO concentration (Q1: <0.49, Q2: 0.50–0.61, Q3: 0.62–0.78, and Q4: >0.78 ppm), NO concentration (Q1: <3.89, Q2: 3.90–6.49, Q3: 6.50–10.0, and Q4: >10.0 ppb), NOx concentration (Q1: <21.7, Q2: 21.8–28.1, Q3: 28.1–37.8, and Q4: >37.8 ppb), PM2.5 concentration (Q1: <27.6, Q2: 27.7–29.1, Q3: 29.2–36.3, and Q4: >36.3 μg/m3), and PM10 concentration (Q1: <51.7, Q2: 51.8–55.1, Q3: 55.2–64.4, and Q4: >64.4 μg/m3).
Access to the LGTD and TAQMD and their use for research were approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the China Medical University and Hospital in Taiwan (CMUH109-REC2-031).
2.3. Variables of Interest
The diagnostic criteria were coded according to the International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision and 10th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM). The primary outcome variable was an aphasia diagnosis. Patients with aphasia were identified using the following medical codes: ICD-9-CM code 784.3 and ICD-10-CM code R47.01. The confounding variables included demographic factors such as sex, age, urbanization level, and comorbidities. The common comorbidities included alcohol abuse/dependence (ICD-9-CM codes 305.0 and 303; ICD-10-CM codes F101.20, F101.29, F102.20, F102.29, F102.0, F102.1, F101.0), tobacco abuse/dependence (ICD-9-CM code 305.1; ICD-10-CM codes F172.00, F172.01, F172.10, F172.11, F172.20, F172.21, F172.90, F172.91), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (ICD-9-CM codes 490–492, 494, and 496; ICD-10-CM codes J41.0, J41.1, J41.8, J42, J43.0, J43.1, J43.2, J43.8, J43.9, J44.0, J44.1, J44.9), asthma (ICD-9-CM code 493; ICD-10-CM code J45), obesity (ICD-9-CM code 278; ICD-10-CM code E66), osteoporosis (ICD-9-CM code 733; ICD-10-CM codes M80, M81, M84), and stroke (ICD-9-CM code 430-438; ICD-10-CM codes G45 G46 I60-I69).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The air quality data were first linked to the selected subjects in the LGTD based on the proximity of the monitoring sites and residential areas. The participants were then grouped based on the population density of their residential regions (i.e., urbanization level) into four groups: from the most urbanized (level 1) to the least urbanized (level 4).
Sex, urbanization level, comorbidities, and the main outcome variables are shown as numbers and percentages. Age and exposure to air pollutants are expressed as means and standard deviations. We calculated the incidence density rate of aphasia (per 1000 person-years) for different air pollutant concentrations. The incidence rate ratio (IRR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were estimated by Poisson regression. The hazard ratios (HRs) were estimated using a multivariate Cox proportional model and adjusted for confounding variables to reveal the association between air pollutants and aphasia. Data processing and statistical analyses were performed using SAS Version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). A two-tailed p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Air Pollution Exposure Information
In total, 228,807 subjects were included in this retrospective study. Of the participants, 55.5% were female. The mean age was 40.3 (±15.8) years old. Of the participants, 64.3% lived in the most urbanized area. The top three comorbidities among the sample subjects were chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (13.9%), asthma (14.1%), and osteoporosis (8.71%). The mean daily average concentration of the six air pollutants within the follow-up period was 4.62 ppb (±1.64) for SO2, 0.67 ppm (±0.29) for CO, 10.1 ppm (±10.9) for NO, 32.1 ppm (±16.8) for NOx, 31.5 μg/m3 (±7.56) for PM2.5, and 58.4 μg/m3 (±12.3) for PM10.
During the selected investigation period, 333 subjects developed aphasia. The mean follow-up time was 16.4 (±2.29) years. See Table 1 for the demographic and exposure to air pollution information.

Table 1.
Baseline demographics and exposure to air pollutants by yearly average concentration in Taiwan, 2003–2017.
3.2. Incidence Rate Ratio (IRR)
The incidence of aphasia increased with increasing levels of SO2, CO, NO, NOx, PM2.5, and PM10. The incidence rate ratios (IRRs) of aphasia for different levels of air pollutant exposure are presented in Table 2. The concentration of each air pollutant was divided into four quartiles, and the lowest concentration level (Q1) was used as the reference group. Significant IRRs of aphasia were found for subjects exposed to the highest concentration level of SO2 (IRR = 2.70, 95% CI = 2.01–3.63), NO (IRR = 1.44, 95% CI = 1.08–1.93) and CO (IRR = 2.44, 95% CI = 1.80–3.30), and for those who were exposed to higher concentration levels of NOx (Q3–Q4, IRR = 1.55–1.77), PM2.5 (Q2–Q4, IRR = 6.40–10.4) and PM10 (Q2–Q4, IRR = 5.02–7.86).

Table 2.
The risk of aphasia in patients exposed to various air pollutants stratified by quartile of the annual concentration using Poisson regression.
3.3. Adjusted Hazard Ratio (aHR)
Table 3 shows the risk of aphasia according to the concentration of different air pollutants. Significant aHR was found for subjects exposed to the highest concentration level of SO2 (aHR = 2.66, 95% CI = 1.97–3.59), NO (aHR = 1.89, 95% CI = 1.41–2.55), and CO (aHR = 3.02, 95%CI = 2.21–4.13), and for those who were exposed to the above median concentration levels (Q3–Q4) of NOx (aHR = 1.83–2.31), PM2.5 (aHR = 5.20–7.61), and PM10 (aHR = 4.41–5.99). The risk of developing aphasia increased as the concentration of air pollutants increased.

Table 3.
The risk of aphasia in patients exposed to various air pollutants stratified by quartile of the annual concentration using Cox proportional hazard regression.
Figure 2 also shows that participants exposed to higher pollution concentrations had a higher incidence of aphasia than those exposed to lower concentrations of SO2, CO, NO, NOx, PM2.5, and PM10. In all cases, the increase in the air pollution concentration level enhanced the IRR of the aphasia risk.
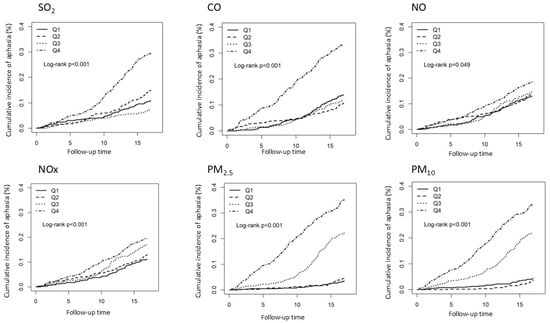
Figure 2.
Kaplan–Meier curves of the accumulative incidence rate of aphasia during the follow-up period among the different quartiles of each air pollutant.
4. Discussion
This is the first epidemiological evaluation of the risk of developing aphasia following exposure to air pollution in Taiwan. This 12-year retrospective investigation included 294,458 residents and found that individuals exposed to ambient air pollutants (SO2, CO, NO, NOx, PM2.5, and PM10) had a significantly higher risk of developing aphasia. The greater the exposure to airborne particulate matter and gaseous pollutants, typically above the median concentration, the more likely it is for people to have aphasia.
Aphasia is one of the most devastating symptoms of stroke and accounts for approximately one-third of the stroke population. A potential mediator between aphasia and air pollution is the risk of developing cerebrovascular disease. Consistent with Western investigations, a few local epidemiological studies conducted in Taiwan have shown that exposure to air pollution, such as PM2.5, PM10, NO2, SO2, and CO, correlates with hospital admissions for cerebrovascular disease, death, and degeneration in several metropolitan areas to various extents [21,22,23,24]. In their secondary analysis of the Social Environment and Biomarkers of Aging Study in Taiwan, Chuang et al. [25] examined the associations between air pollutants, blood pressure, and blood biochemistry markers among 1023 adults aged 54 and above in 2000. In the case of the one-year average exposure to air pollution, they found that increased particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5), NO2, and O3 were associated with elevated blood pressure, blood sugar (i.e., fasting glucose and hemoglobin A1c), blood lipids (i.e., total cholesterol), and inflammatory markers (i.e., neutrophils) after adjusting for lifestyle and yearly temperature. Exposure to PM10, PM2.5, and NO2 was also associated with the other inflammatory marker, interleukin 6 (IL-6). Chuang et al. supported the possible key mechanisms by which air pollutants increase the risk of cerebrovascular events [25], especially atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases, by inducing hypertension, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, or inflammation. The evidence showed that the percentage of ischemic stroke patients who experience aphasia at the time of stroke onset remains consistent at 30% [26]. Laura et al. found that 35% of adult stroke patients hospitalized in Ontario during the 2004–2005 Ontario Stroke Audit exhibited aphasia symptoms upon discharge. This corresponds to an annual incidence rate of 60 cases per 100,000 individuals [27]. Together with the current findings, our data suggest that exposure to air pollution may have a cascading effect on the risk of developing aphasia.
The current results must be interpreted cautiously when considering the relatively small cohort of patients with aphasia. There has never been a nationwide investigation into the incidence and prevalence of aphasia in Taiwan. Rough estimates were based on statistics from developed Western countries and the prevalence of stroke in Taiwan. In the present study, 0.12% of the participants in the database had aphasia. One possible reason is that not all people with aphasia were coded under the diagnosis of aphasia but under other concomitant disorders with urgent needs. However, among those with a diagnosis code for aphasia, we still found a significant tendency to develop symptoms associated with ambient air pollution. This highlights the need to pay more attention to the influence of the environment and its changes on communication disorders.
In addition, the NHIRD study has several limitations. First, surveillance bias may be influenced by urbanization and its impact on medical accessibility. This could contribute to the variations in the prevalence of aphasia between urban and rural areas. The incidence of strokes is influenced by the workload of the individual and the urban environment with a high population density [28,29]. Therefore, the regional distribution of stroke and aphasia cases and the number of healthcare facilities need to be considered. However, Taiwan’s single-payer compulsory social insurance system, which covers over 99% of residents, helps mitigate disparities in medical access by providing free healthcare [30,31]. Secondly, although indoor air pollutant levels are associated with building characteristics [32], this study did not assess the pollutant concentrations nationally. However, no evidence suggests significant variations in building characteristics across areas with different air pollution levels in Taiwan, nor has it failed to effectively block outdoor air pollutants [33,34]. Third, the NHIRD lacks data on healthy behaviors and dietary habits, and laboratory information on levels of creatinine, low-density lipoprotein particles, high-density lipoprotein particles, glucose, and homocysteine. The diagnostic criteria for alcohol abuse and dependence are based on drinking behavior and patient attitude. Additionally, previous NHIRD studies have primarily examined COPD, asthma, and tobacco abuse/dependence rather than directly assessing smoking status. Therefore, we used COPD, asthma, tobacco abuse/dependence, and alcohol abuse/dependence as proxy variables to evaluate smoking status and alcohol consumption. Nonetheless, further research is required to clarify the impact of indoor air quality. Fourth, residential location was determined based on the medical institution where the individuals sought treatment during the study period. Patients without medical records and living in areas with lower air pollution levels were excluded. This exclusion may have led to an underestimation of the aphasia risk. Finally, air pollution levels in the participants’ residential areas were estimated using data from the nearest air quality monitoring stations to clinics or hospitals. This approach may introduce bias because the measured air quality and urbanization levels may not accurately reflect the actual conditions, particularly for individuals who commute long distances between their homes and healthcare facilities. In conclusion, while we cannot establish a direct relationship between air pollution and the risk of aphasia, we can observe a correlation between them.
Our results add to environmental awareness and concerns regarding their impact on human health and highlight the need to recognize the effects of environmental changes on human language and communication. Communication disorders have drawn the least attention globally. Communication disorders affecting language, speech, and hearing are common. More than 10% of people worldwide have experienced variations in communication difficulties to some extent; however, it is often treated as a hidden disability owing to the lack of public and professional awareness or absence of obvious physical impedance in daily life [35]. There has been limited investigation into the relationship between environmental changes and communication disorders [20,36]. Recognizing the direct and indirect links between environmental changes and communicative disorders is crucial for better prevention and policymaking.
5. Conclusions
This is the first nationwide population-based cohort study of the association between air pollution and aphasia. Our results suggest that exposure to air pollution increases the risk of aphasia. In the future, more attention should be paid to the impact of environmental factors such as air pollution on communication disorders such as aphasia.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.H., P.-C.L., Y.-C.H. and K.-H.C.; methodology, C.-L.L. and K.-H.C.; software, C.-Y.C., S.C.-S.T., R.-H.C., C.-L.L. and D.-Y.C.; validation, J.H., P.-C.L., C.-Y.C., S.C.-S.T., R.-H.C., C.-L.L., D.-Y.C., C.-L.H., C.-Y.L., Y.-C.H., T.-L.H. and K.-H.C.; formal analysis, C.-L.L., T.-L.H. and K.-H.C.; investigation, J.H., P.-C.L., C.-Y.C., S.C.-S.T., R.-H.C., C.-L.L. and T.-L.H.; resources, C.-L.L. and D.-Y.C.; data curation, J.H., P.-C.L., C.-Y.C., S.C.-S.T., R.-H.C., C.-L.L., D.-Y.C., Y.-C.H., T.-L.H. and K.-H.C.; writing—original draft preparation, J.H., P.-C.L., Y.-C.H. and K.-H.C.; writing—review and editing, J.H., P.-C.L., Y.-C.H. and T.-L.H.; visualization, J.H., P.-C.L., C.-Y.C., S.C.-S.T., R.-H.C., C.-L.L., D.-Y.C., Y.-C.H. and K.-H.C.; supervision, Y.-C.H. and T.-L.H.; project administration, S.C.-S.T., R.-H.C., C.-L.L. and D.-Y.C.; funding acquisition, S.C.-S.T. and D.-Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is supported in part by the Taiwan Ministry of Health and Welfare Clinical Trial Center (MOHW113-TDU-B-212-114009), China Medical University Hospital (DMR-111-105; DMR-112-087; DMR-113-009; DMR-113-156), and Tungs’ Taichung Metroharbor Hospital (TTMHH-R1120012/R1130051/R1140020/R1140024/R140025/R140037/R1140083/R1140085).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Access to the LGTD and TAQMD and their use for research were approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the China Medical University and Hospital in Taiwan (CMUH109-REC2-031).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data were retrieved from the NHIRD published by the Taiwan National Health Insurance Bureau. Access to the database requires application to and approval by the NHIRD. The current data are not available publicly following the Personal Information Protection Act.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Health Data Science Center, China Medical University Hospital, for providing administrative, technical, and funding support. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, the decision to publish, or the preparation of the manuscript. No additional external funding was received for this study. We are thankful for the grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) of the Taiwan Government (MOST 110-2314-B-715-005, MOST 111-2314-B-715-009-MY3), intramural research grants from MacKay Medical College (MMC-RD-1091B19, MMC-RD-110-1B-P030), and MacKay Memorial Hospital (MMH-MM-10610).
Conflicts of Interest
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| LGTD | Longitudinal Generation Tracking Database |
| TAQMD | Taiwan Air Quality Monitoring Database |
| IRR | incidence rate ratio |
| aHR | hazard ratio |
| SO2 | sulfur oxide |
| CO | carbon monoxide |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| NOx | nitrogen oxide |
| PM | particulate matter |
| NHIRD | National Health Insurance Research Database |
| EPA | Environmental Protection Agency |
References
- Coccia, M. Two mechanisms for accelerated diffusion of COVID-19 outbreaks in regions with high intensity of population and polluting industrialization: The air pollution-to-human and human-to-human transmission dynamics. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, C.; Van Landschoot, L.; Vanroelen, C.; Gadeyne, S. The Public’s Perceptions of Air Pollution. What’s in a Name? Environ. Health Insights 2022, 16, 11786302221123563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shou, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, D.; Yin, H.; Shi, Y.; Chen, M.; Lu, L.; Qian, Q.; Zhao, D.; Hu, Y.; et al. Ambient PM2.5 chronic exposure leads to cognitive decline in mice: From pulmonary to neuronal inflammation. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 331, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajipour, S.; Farbood, Y.; Gharib-Naseri, M.K.; Goudarzi, G.; Rashno, M.; Maleki, H.; Bakhtiari, N.; Nesari, A.; Khoshnam, S.E.; Dianat, M.; et al. Exposure to ambient dusty particulate matter impairs spatial memory and hippocampal LTP by increasing brain inflammation and oxidative stress in rats. Life Sci. 2020, 242, 117210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwannasual, U.; Lucero, J.; McDonald, J.D.; Lund, A.K. Exposure to traffic-generated air pollutants mediates alterations in brain microvascular integrity in wildtype mice on a high-fat diet. Environ. Res. 2018, 160, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwannasual, U.; Lucero, J.; Davis, G.; McDonald, J.D.; Lund, A.K. Mixed Vehicle Emissions Induces Angiotensin II and Cerebral Microvascular Angiotensin Receptor Expression in C57Bl/6 Mice and Promotes Alterations in Integrity in a Blood-Brain Barrier Coculture Model. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 170, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, N.C.; Haghani, A.; Johnson, R.G.; Hsu, T.M.; Saffari, A.; Sioutas, C.; Kanoski, S.E.; Finch, C.E.; Morgan, T.E. Prenatal and early life exposure to air pollution induced hippocampal vascular leakage and impaired neurogenesis in association with behavioral deficits. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlmutt, L.D.; Cromar, K.R. Comparing associations of respiratory risk for the EPA Air Quality Index and health-based air quality indices. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 202, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Han, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Qian, Y. A review of current air quality indexes and improvements under the multi-contaminant air pollution exposure. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.E.; Cullen, B.; Crawford, S.; Evans, J.J. A systematic review of mood and depression measures in people with severe cognitive and communication impairments following acquired brain injury. Clin. Rehabil. 2023, 37, 679–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, M.; Newman-Norlund, R.; Bonilha, L.; Fridriksson, J.; Hickok, G.; Hillis, A.E.; den Ouden, D.-B.; Rorden, C. The Aphasia Recovery Cohort, an open-source chronic stroke repository. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelkraut, L.; López-Barroso, D.; Torres-Prioris, M.J.; Starkstein, S.E.; Jorge, R.E.; Aloisi, J.; Berthier, M.L.; Davila, G. Spectrum of neuropsychiatric symptoms in chronic post-stroke aphasia. World J. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, S.M.; Sebastian, R. Diagnosing and managing post-stroke aphasia. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2021, 21, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellani, B.; Bartington, S.; Wistow, J.; Heckels, N.; Ellison, A.; Van Tongeren, M.; Arnold, S.R.; Barbrook-Johnson, P.; Bicket, M.; Pope, F.D. Mitigating the impact of air pollution on dementia and brain health: Setting the policy agenda. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zundel, C.G.; Ryan, P.; Brokamp, C.; Heeter, A.; Huang, Y.; Strawn, J.R.; Marusak, H.A. Air pollution, depressive and anxiety disorders, and brain effects: A systematic review. Neurotoxicology 2022, 93, 272–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, B.; Barratt, B.; Batalle, D.; Gale-Grant, O.; Hughes, E.J.; Beevers, S.; Cordero-Grande, L.; Price, A.N.; Hutter, J.; Hajnal, J.V. Prenatal exposure to air pollution is associated with structural changes in the neonatal brain. Environ. Int. 2023, 174, 107921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Lin, C.L.; Hsieh, T.L.; Tsai, F.J.; Chang, K.H. Long-term exposure to air pollution and risk of Sarcopenia in adult residents of Taiwan: A nationwide retrospective cohort study. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Lin, H.J.; Tsai, S.C.; Lin, C.L.; Hsu, C.Y.; Hsieh, T.L.; Chen, C.M.; Chang, K.H. Exposure to Air Pollutants Increases the Risk of Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Taiwan Residents. Toxics 2022, 10, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.H.; Teng, C.J.; Hsu, Y.C.; Tsai, S.C.; Lin, H.J.; Hsieh, T.L.; Muo, C.H.; Hsu, C.Y.; Chou, R.H. Long-Term Exposure to Air Pollution Associates the Risk of Benign Brain Tumor: A Nationwide, Population-Based, Cohort Study in Taiwan. Toxics 2022, 10, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.C.; Hsu, Y.C.; Lai, J.N.; Chou, R.H.; Fan, H.C.; Lin, F.C.; Zhang, R.; Lin, C.L.; Chang, K.H. Long-term exposure to air pollution and the risk of developing sudden sensorineural hearing loss. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.F.; Chang, C.C.; Yang, C.Y. Relationship between hemorrhagic stroke hospitalization and exposure to fine particulate air pollution in Taipei, Taiwan. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2014, 77, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Y.; Li, C.H.; Martini, S.; Hou, W.H. Association between air pollution and risk of vascular dementia: A multipollutant analysis in Taiwan. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, D.H.; Wang, J.L.; Chuang, K.J.; Chan, C.C. Traffic-related air pollution and cardiovascular mortality in central Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1818–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.S.; Goggins, W.B.; Chiu, H.F.; Yang, C.Y. Evidence for an association between air pollution and daily stroke admissions in Kaohsiung, Taiwan. Stroke 2003, 34, 2612–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, K.J.; Yan, Y.H.; Chiu, S.Y.; Cheng, T.J. Long-term air pollution exposure and risk factors for cardiovascular diseases among the elderly in Taiwan. Occup. Environ. Med. 2011, 68, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grönberg, A.; Henriksson, I.; Stenman, M.; Lindgren, A.G. Incidence of aphasia in ischemic stroke. Neuroepidemiology 2022, 56, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, L.; Kagan, A.; Lindsay, M.P.; Fang, J.; Rowland, A.; Black, S. Incidence and Profile of Inpatient Stroke-Induced Aphasia in Ontario, Canada. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 91, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapral, M.K.; Austin, P.C.; Jeyakumar, G.; Hall, R.; Chu, A.; Khan, A.M.; Jin, A.Y.; Martin, C.; Manuel, D.; Silver, F.L. Rural-urban differences in stroke risk factors, incidence, and mortality in people with and without prior stroke: The CANHEART stroke study. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2019, 12, e004973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avan, A.; Digaleh, H.; Di Napoli, M.; Stranges, S.; Behrouz, R.; Shojaeianbabaei, G.; Amiri, A.; Tabrizi, R.; Mokhber, N.; Spence, J.D. Socioeconomic status and stroke incidence, prevalence, mortality, and worldwide burden: An ecological analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Yip, W.; Chang, H.J.; Chou, Y.J. Trends in rural and urban differentials in incidence rates for ruptured appendicitis under the National Health Insurance in Taiwan. Public Health 2006, 120, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siroux, V.; Pin, I.; Oryszczyn, M.P.; Le Moual, N.; Kauffmann, F. Relationships of active smoking to asthma and asthma severity in the EGEA study. Epidemiological study on the Genetics and Environment of Asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2000, 15, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, S.; Bekö, G. Indoor air quality in the Swedish housing stock and its dependence on building characteristics. Build. Environ. 2013, 69, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondeau, P.; Iordache, V.; Poupard, O.; Genin, D.; Allard, F. Relationship between outdoor and indoor air quality in eight French schools. Indoor Air 2005, 15, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boomhower, S.R.; Long, C.M.; Li, W.; Manidis, T.D.; Bhatia, A.; Goodman, J.E. A review and analysis of personal and ambient PM2.5 measurements: Implications for epidemiology studies. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHutchion, L.D.; Pringle, J.M.; Tran, M.N.; Ostevik, A.V.; Constantinescu, G. A survey of public awareness of dysphagia. Int. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2021, 23, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.G.; Chen, Y.H.; Yen, S.Y.; Lin, H.C.; Lin, H.C.; Chou, K.R.; Cheng, C.A. Air Pollution Exposure and the Relative Risk of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Taipei. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).