Abstract
This study investigates the dynamics and sources of atmospheric mercury in Qinhuangdao (QHD), a coastal urban area significantly impacted by both marine and terrestrial sources. Sampling of gaseous elemental mercury (GEM), fine particle-bound mercury (PBM2.5), and coarse particle-bound mercury (PBM2.5–10) was conducted from September 2022 to August 2023. The annual mean concentrations of GEM, PBM2.5, and PBM2.5–10 were 2.66, 1.01, and 0.73 ng m−3, respectively, with PBM levels among the highest reported for coastal cities in eastern China. GEM displayed a pronounced midday peak (12:00–14:00) with correlations to temperature (R2 = 0.25–0.65) and a significant winter association with SO2 (R2 = 0.52), suggesting the combined influence of surface re-emission and coal combustion. Seasonal variations in the GEM/CO ratio (spring: 7.12; winter: 2.62) further reflected the shift between natural and combustion-related sources. PBM2.5 exhibited elevated concentrations (1.0–1.4 ng m−3) under westerly winds (~3 m s−1), indicating inputs from traffic, shipping, and light industries, while PBM2.5–10 (0.5–1.1 μg m−3) was strongly linked to coal-handling activities at QHD port and soil resuspension. Backward trajectory analysis showed continental air masses dominated in winter (53–100%) and maritime air masses in summer (30–50%), whereas high Hg/Na ratios in PM2.5 (3.22 × 10−4) and PM2.5–10 (2.17 × 10−4), far exceeding typical marine aerosol values (10−7–10−5), indicated negligible marine contributions to PBM. These findings provide new insights into the processes driving mercury pollution in coastal urban environments and highlight the critical role of port-related activities in regional mercury management.
1. Introduction
Mercury (Hg) is a persistent and toxic pollutant with significant environmental and health impacts. The chemistry of atmospheric mercury is quite complex [1]. According to the residence times and migration abilities, atmospheric Hg exists predominantly in three species: gaseous elemental mercury (GEM, ), gaseous oxidized Hg (GOM), and particle-bound mercury (PBM, ) [2]. GEM, which usually constitutes over 90% of atmospheric mercury, is relatively stable and has a prolonged atmospheric lifetime, facilitating its long-range transport [3,4]. Conversely, PBM, although less prevalent, exhibits higher reactivity and greater water solubility, making it more prone to deposition by rain and washout, and thus a significant contributor to local environmental impacts [5,6].
Atmospheric Hg emissions originate from both anthropogenic and natural sources. According to the UN Environment Programme 2018 (GMA 2018) [7], East and Southeast Asia represent one of the principle sources of global anthropogenic mercury emissions, accounting for approximately 49% of the worldwide total. Pacyna et al. (2016) [8] identified fossil fuel combustion—particularly coal burning in power plants (industrial and residential boilers) as a dominant anthropogenic source, alongside artisanal and small-scale gold mining. These two activities contribute approximately 37% and 25% of global anthropogenic Hg emissions, respectively. Notably, countries such as China and India play a leading role in these emissions, reflecting the intense industrial activity and high dependence on coal-based energy in these regions.
In contrast, within natural sources, the oceans and seas are both significant sources and sinks of mercury (Hg), playing a crucial role in the global Hg cycle [9,10]. According to Pacyna et al. (2016) [8], oceanic evasion driven by solar radiation and biological processes is the largest natural emission pathway, contributing approximately 36% of global mercury emissions. However, Amos et al. (2013) [11] highlighted that mercury emissions from the ocean constitute a critical component of the global Hg cycle, not only due to their substantial magnitude but also because they involve the re-emission of legacy anthropogenic mercury. Their global biogeochemical model demonstrated that surface ocean Hg emissions, primarily driven by photoreduction and biological processes, significantly contribute to present-day atmospheric mercury, with a considerable portion originating from re-emitted historical anthropogenic sources.
Coastal regions are critical for atmospheric mercury research due to the intersection of terrestrial and marine origins, coupled with complex physical, chemical processes, and variable environmental conditions. Wang et al. (2016) [12] observed that PBM2.5 concentrations in the offshore area were higher than those in the open sea. Qin et al. (2019) [3] reported that in a coastal suburban site in eastern China, GEM concentrations were jointly affected by anthropogenic emissions, including shipping (nearly 20% of total GEM sources) and natural surface re-emissions, while photochemical oxidation enhanced GOM formation under high-ozone and -temperature conditions.
The complexity of mercury behavior in coastal environments has been increasingly elucidated through a combination of observational and modeling studies over the past decades. Early investigations highlighted the influence of long-range transport and regional anthropogenic emissions on coastal mercury levels [13]. Subsequent research advanced the understanding of gas-particle partitioning dynamics [14] and the distribution and sources of speciated atmospheric mercury, including GEM, reactive gaseous mercury (RGM), and PBM [15,16]. More recent studies have emphasized the role of mesoscale meteorological processes, particularly sea–land breeze circulations in modulating mercury concentrations near coastlines [17]. Furthermore, the inter-annual variability in mercury levels is closely linked to variations in anthropogenic emissions, meteorological conditions, and the dynamics of regional air mass transport [18].
These findings underscore the complex and distinctive dynamics of mercury cycling in coastal environments, reflecting recent advances in our understanding of Hg chemistry and its global and regional transport. Nevertheless, observational data on the size distributions of PBM and their controlling environmental drivers remain scarce, particularly for PBM in the fine (PM2.5) and coarse (PM10) fractions. Moreover, the potential influence of intensive port activities has rarely been considered in previous studies. To address these gaps, this study presents year-round measurements of GEM, PBM2.5, and PBM10 in QHD, a representative northern coastal city. By integrating chemical observations with meteorological and source-related analyses, this work aims to elucidate the mechanisms governing the temporal variability of mercury across particle size ranges and to identify the key environmental factors shaping its behavior in a marine–urban transitional setting.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
Qinhuangdao (QHD) is located in northern Hebei Province, with a population of approximately 3.1 million. It is one of the largest coal shipping ports in northern China and lies close to the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei metropolitan area. The city is simultaneously affected by industrial activities, port-related operations, vehicular traffic, and marine meteorological processes, making it a representative site for investigating coastal urban mercury pollution. The sampling site for this study was located on the rooftop of the library at Hebei Normal University of Science & Technology in QHD, approximately 1 km from the coastline and about 40 m above ground level (Figure 1). A recent study investigating the dynamics of water-soluble inorganic ions used a neighboring rooftop site about 100 m away within the same campus, under highly similar environmental conditions. Both sites are similarly affected by local urban, industrial, port, and marine influences. That work identified several potential local emission sources relevant for atmospheric mercury, including a coal-fired power plant located approximately 4.5 km to the northwest, major port operations (QHD port, 1~10 km east), as well as residential heating, vehicular traffic, and shipping emissions. Thus, the environmental context and source characteristics around the current mercury sampling site are well represented by the findings of Lyu et al. (2025) [19].
Figure 1.
Map of the sampling site.
Sampling was conducted from 15 September 2022, to 30 August 2023. However, due to the temporary closure of the building as COVID-19 restrictions (7 October–29 December 2022), no samples were collected in this interval. Therefore, two main sampling periods were completed: 15 September–6 October 2022, and 30 December 2022–30 August 2023. During these intervals, tourism in QHD was completely suspended, leading to substantially decreased local anthropogenic emissions. However, the port operations were not significantly affected, as the port was relatively isolated from the surrounding areas. As social and economic activities resumed in 2023, sampling could proceed more regularly, although some gaps still occurred due to uncontrollable factors. Both tourism and port activities can strongly influence local air quality, as increased tourist flows and port throughput elevate traffic, shipping, and cargo-related emissions. Days with a 24 h average PM2.5 concentration exceeding 75 μg/m3 were classified as haze days in accordance with the National Ambient Air Quality Standards of China (NAAQS, MEP 2012); a total of 227 samples were divided into non-haze (216) and haze (11) days.
PBM Samples were collected using two medium-volume air samplers (Juchuang Group Co., Ltd., Qingdao, Shandong, China) equipped with and inlets at a flow rate of 100 L/min for 24 h (8:00–8:00). Quartz fiber filters (90 mm, Whatman QM-A) were baked at 500 °C for six hours before use. After sampling, the filters were sealed in aluminum foil and stored at −20 °C until analysis.
2.2. Sample Analysis
2.2.1. Particle-Bound Mercury (PBM, )
PBM was analyzed using a Zeeman Cold Vapor Atomic Absorption Mercury Analyzer (RA-915+ and PYRO-915+, LUMEX, Mission, BC, Canada). The instrument detection limit (IDL) was 0.2 pg Hg per measurement. The method detection limit (MDL) was calculated as the mean of field and laboratory blanks plus three times the standard deviation, yielding an MDL of 46 pg per filter. Each filter was cut in half under normal conditions. One-half was used to determine Hg; if abnormal results or uncontrollable issues occurred, the remaining half was analyzed as a backup. Calibration was performed with certified mercury standards (GBW07402, National Research Center for Certified Reference Materials, Beijing, China) [20] at multiple concentrations. The method’s accuracy and recovery were verified by spiking blank filters with known amounts of mercury, yielding recoveries between 88% and 107%. Certified reference materials (CRMs) were analyzed every ten samples, with measured recoveries ranging from 92% to 105%. Replicate analyses (n = 10) showed a relative standard deviation of less than 8%. No significant contamination was detected in any of the blank samples.
2.2.2. Gaseous Elemental Mercury (GEM, )
GEM was directly analyzed using a Zeeman Cold Vapor Atomic Absorption Mercury Analyzer (RA-915+, LUMEX, Canada), which responds solely to the mercury element in its zero-valent state. At the inlet of the analyzer, a fiber filter was used to absorb particles from the air. A multi-path cell with an effective length of about 10 m is used to enhance the sensitivity of analysis, and the detection limit for gaseous elemental mercury (reported as an hourly average value) is 0.22 ng/m3. The analyzer operates in TEST mode to verify performance and ensure accurate measurements. For QA/QC, the instrument was calibrated regularly using zero and span gases generated by a mercury evaporator (HXG-2050, BeiJingHuaXinAnKe Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China), which provides both zero and span Hg gas for calibration. Following span calibration, zero gas was injected twice to ensure a clean system and to confirm measurement precision.
2.2.3. Routine Monitoring Data of Conventional Pollutants
All meteorological parameters (temperature, relative humidity, wind speed, and wind direction) and conventional air pollutant concentrations (, , , , , CO) used in this study were obtained from the QHD National Ambient Air Quality Monitoring Station, which is located approximately 500 m due north of the mercury sampling site. The station and sampling site share highly similar environmental conditions, and the short distance with unobstructed terrain ensures comparability of the meteorological and pollutant measurements. The monitoring station operates under the technical standards of the Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China (e.g., HJ 193-2017; HJ 618-2011), using reference-grade automated analyzers: and were measured by β-ray attenuation, SO2 by ultraviolet fluorescence. NO was measured directly by chemiluminescence with O3, whereas NOx was determined using a molybdenum converter that reduces NO2 to NO. The NO2 concentrations were then calculated as the difference between NOx and NO. O3 by ultraviolet photometry, and CO by non-dispersive infrared absorption. All instruments are regularly calibrated and maintained according to national QA/QC protocols, and the data undergo rigorous validation before public release.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Meteorological Influence and Pollutant Concentrations
Figure 2 presents the temporal variations in key meteorological parameters during the sampling period, including ambient temperature (T), relative humidity (RH), wind direction (WD), and wind speed (WS). The average T and RH were 10.8 °C (ranging from −14.8 °C to 30.8 °C) and 62% (ranging from 5% to 99%). Both parameters exhibited significant diurnal and seasonal fluctuations. The average WS is 2.24 m/s, with a range from 1.99 m/s in Winter to 2.71 m/s in Spring.
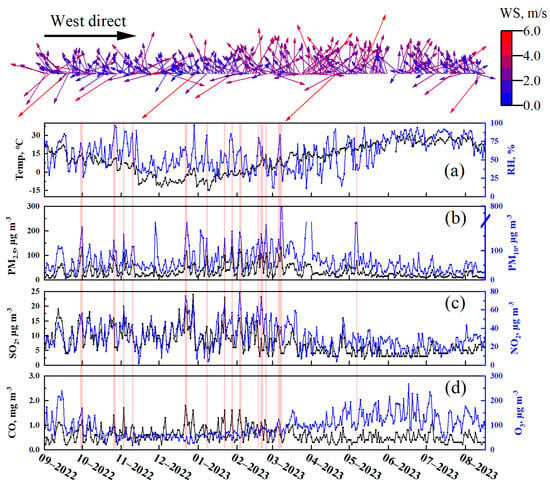
Figure 2.
Temporal variations in meteorological conditions and concentrations of conventional pollutants. Wind direction (WD) and wind speed (WS) are shown at the top of the figure, followed by (a) Ambient temperature (T) and relative humidity (RH); (b) PM2.5 and PM10; (c) SO2 and NO2, (d) CO and O3. The red lines indicate the haze days.
During the sampling period, the average conventional air pollutants were as follows: (31.4 μg/m3), (71.2 μg/m3), (7.55 μg/m3), (30.6 μg/m3), CO (0.59 mg/m3) and (95.7 μg/m3). According to the National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) of China (GB3095-2012) [21], the annual average limits for and are 35 μg m−3 and 70 μg m−3, respectively. Thus, the observed concentration of remained below the national standard, whereas slightly exceeded the threshold, suggesting a relatively greater contribution from coarse particles.
In addition, the average concentration of , CO was highest in winter compared to the other three seasons, reaching 10.4 μg/m3, 36.6 μg/m3, and 0.75 mg/m3, respectively. Although SO2 peaked in winter, its overall level was relatively low compared with historical records, reflecting the effectiveness of stringent emission control measures, a trend also observed in other Chinese cities [22]. Seasonally, the lowest concentration of and CO was observed in summer (22.7 μg/m3 and 0.46 mg/m3, respectively), and a similar pattern was observed in Beijing and Shanghai [22]. These trends were probably associated with enhanced atmospheric dispersion and stronger photochemical processes in summer [22,23]. Furthermore, the intensified photochemical activity during summer led to the highest concentration, consistent with previous findings [24].
3.2. The Variation in Concentrations of PBM and GEM
The temporal distribution of PBM and GEM is shown in Figure 3. The average concentration of GEM in QHD was 2.66 ng·m−3, and was comparable to values reported in other coastal urban areas of eastern China (Table 1), such as 3.26 ng·m−3 in Ningbo [16], 3.93 ng·m−3 in Xiamen [18], and 2.77–4.19 ng·m−3 in suburban Shanghai [14,25], but significantly lower than that observed in heavily industrialized inland cities like 9.72 ng ·m−3 in Guiyang [26].
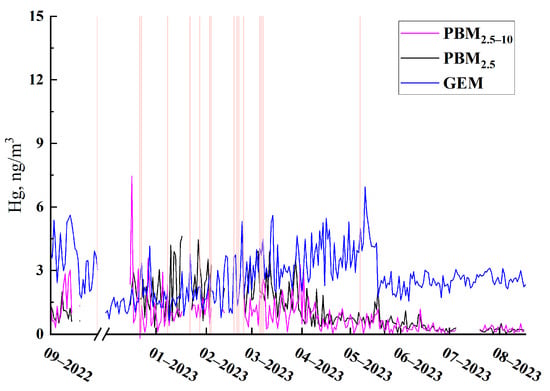
Figure 3.
Temporal variations in Hg concentrations: , and GEM (gaseous Hg) (with red line indicating the haze days).
In contrast, PBM2.5 and PBM2.5–10 levels in QHD were 1.01 ng·m−3 and 0.73 ng·m−3, respectively, and are substantially elevated compared to values reported for most suburban and remote locations (Table 1). Previous studies have shown that the PBM level in urban areas, particularly in China and South Asia, is generally elevated compared to the remote areas, with peak average values at urban sites reaching up to 1.18 ng m−3 [27]. As shown in Table 1, suburban sites in Shanghai reported significantly lower PBM levels, ranging from 0.02 to 0.20 ng·m−3 [25,28,29], as did Lulin atmospheric background station in Taiwan (0.005 ng·m−3) [30] and the remote mountain-top station site (0.0194 ng·m−3) [25,28,31].
These comparisons suggest that PBM levels in QHD rank among the highest ever reported for coastal urban sites in eastern China, likely indicating the presence of additional, site-specific sources of PBM along the QHD coast, beyond the atmospheric processes previously reported.

Table 1.
Statistics of PBM and GEM concentrations from global measurements data.
Table 1.
Statistics of PBM and GEM concentrations from global measurements data.
| Location | Type | Time | GEM (ng m−3) | PBM (pg m−3) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qinhuangdao, China | Urban | September 2022–August 2023 | 2.66 ± 1.08 | : 1.01 ± 0.77 ng m−3 : 1.74 ± 1.20 ng m−3 | This study |
| Xiamen, China | Urban | January 2020 July 2020 | 3.93 1.56 | [18] | |
| Ningbo, China | Urban | July 2013–January 2014 | 3.26 ± 1.63 | 659 ± 931 | [16] |
| Shanghai, China | Suburban | June 2015–May 2016 | 2.77 | 60.8 | [3] |
| Shanghai, China | Suburban | 1 June–31 December 2014 | 4.19 ± 9.13 | 197 ± 877 | [25] |
| Shanghai, China | Suburban | March 2014–February 2017 | 2.12 ± 0.94 | 21.81 ± 30.46 | [28] |
| Shanghai, China | Rural | 2018 | 2.01 ± 0.92 | 50.2 ± 67.2 | [14] |
| Beijing, China | Urban | September 2015–July 2016 | 4.70 ± 3.35 | 85.1 ± 95.3 | [32] |
| Guiyang, China | Urban | August to December 2009 | 9.72 ± 10.2 | 368 ± 276 | [26] |
| Xiamen, China | Urban | March 2012–February 2013 | 3.50 ± 1.61 | 174 ± 280 | [33] |
| Ningbo, China | Urban | 2015–2017 | 2.6 ± 1.0 | 316 ± 377 | [34] |
| Chongming, China | Suburban | 2012–2015 | 2.65 ± 1.73 | 21.5 ± 25.4 | [29] |
| Taiwan, China | Remote | January 2014–December 2016 | 1.54 ± 0.34 | 5.0 ± 12.0 | [30] |
| Qinghai, China | Remote | September 2007–September 2008 | 1.98 ± 0.98 | 19.4 ± 18.0 | [31] |
| Seoul, Korea | Urban | February 2005–Februry 2006 | 23.9 ± 19.6 | [35] | |
| Fukuoka, Japan | Urban | June 2012–May 2013 | 2.33 ± 0.49 | 10 ± 11 | [36] |
| Chicago, USA | Urban | 2007 | 2.5 ± 1.5 | 17 ± 87 | [37] |
| Reno, USA | Suburban | 2007–2009 | 2.0 ± 0.7 | 18 ± 22 | [38] |
| Mt.Pic du Midi, France | Remote | November 2011–November 2012 | 1.86 ± 0.27 | 14.0 ± 10.0 | [39] |
3.3. Diurnal GEM in Urban Coast
GEM is chemically stable in the atmosphere with a lifetime of several months to a year, and its concentrations are influenced heavily by a combination of local sources, surface exchange, boundary layer processes, combustion-related sources, and long-range transport [40]. Previous studies have classified GEM diurnal cycles into two types: daytime-controlled and nighttime-controlled patterns [41]. And the meteorological factors, particularly temperature and boundary layer dynamics, play critical roles in shaping both seasonal and diurnal variations in GEM [42].
In this study, GEM exhibited a consistent daytime-controlled pattern across all four seasons (Figure 4). Concentrations peaked at noon, with maxima persisting for several hours in summer, coinciding with the highest temperatures. Similar unimodal patterns have been reported in New York, Toronto, Jeju Island, and coastal Chinese cities such as Qingdao, Ningbo, and Xiamen, where solar radiation and temperature were identified as dominant controls [40,43,44]. Previous studies on mercury fluxes from soil have also demonstrated that solar radiation and temperature are the main drivers of surface emission [45].
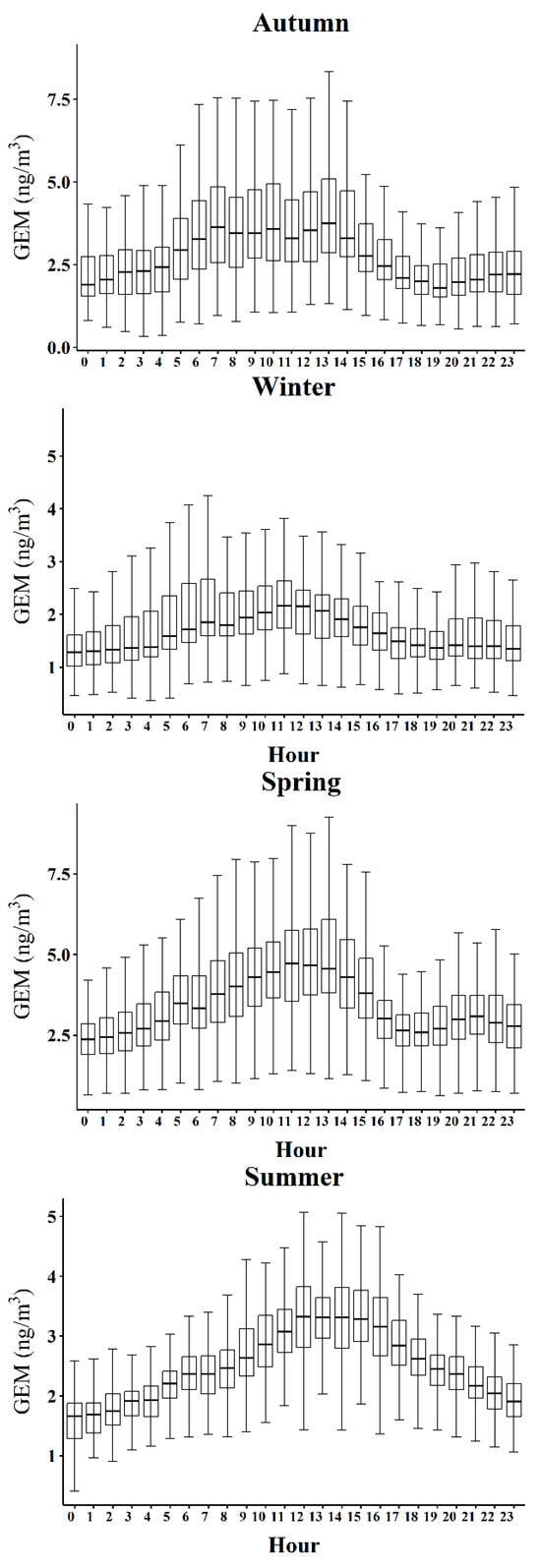
Figure 4.
Diurnal variation in GEM (gaseous Hg) levels across seasons: the middle line represents the median, the box edges represent the 25th and 75th percentiles, and the upper and lower whiskers represent the maximum value within Q3 + 1.5 × IQR and the minimum value within Q1 − 1.5 × IQR, respectively. (IQR: interquartile range).
In QHD, GEM concentrations consistently peaked between 12:00 and 14:00 in all four seasons, with the midday enhancement lasting up to four hours in summer (Figure 4). The correlation between GEM and temperature, however, exhibited pronounced seasonal differences, with regression coefficients ranging from R2 = 0.25 in summer to R2 = 0.65 in autumn. This pattern is in line with the results of Chong et al. (2020) [42], strongly suggesting that temperature-dependent surface re-emission is a major contributor to GEM variability. Although absolute temperatures are highest in summer, the deeper boundary layer, stronger vertical mixing, and enhanced photooxidation processes dilute near-surface GEM, weakening the correlation. By contrast, the relatively dry and sunny conditions and the shallower boundary layer in autumn favor both re-emission and accumulation of GEM, resulting in the strongest GEM–temperature relationship.
Boundary layer and circulation dynamics further influence the observed diurnal variations. Shallow nocturnal boundary layers can trap Hg species, while stronger daytime mixing dilutes concentrations [46]. However, the coastal setting of QHD highlights the additional role of sea–land breeze circulation and marine boundary layer (MBL) processes. During summer, strong sea breezes and shallow MBLs may enhance marine re-emission, whereas in winter, a more stable MBL suppresses vertical mixing and favors accumulation of continental emissions [2,9,47]. These processes help explain the rapid decline of GEM concentrations after midday, despite its long atmospheric lifetime.
Anthropogenic activities also contribute to the observed patterns. Vehicle emissions are a detectable but relatively minor source, as indicated by a weak morning enhancement around 07:00 in autumn and winter, likely linked to traffic [3]. Previous tunnel studies demonstrated that the gasoline-powered vehicles can release a substantial amount of mercury to the atmosphere [48]. Consistent with this, studies in Ningbo and Xiamen reported bimodal diurnal GEM patterns coinciding with rush hours (6–8 a.m. and 4–6 p.m.), which were attributed primarily to traffic emissions [16,33].
However, emissions inventories suggest that vehicular mercury emissions are small compared with coal combustion [49,50,51]. In winter, GEM levels were significantly associated with SO2 (R2 = 0.52), reflecting the influence of combustion sources. A coal-fired power plant is located approximately 4.5 km north of the site, but given the widespread adoption of advanced flue-gas cleaning technologies in the past decade, its direct mercury contribution is probably limited. Instead, regional coal combustion for residential heating and smaller industrial sources appear more important.
3.4. Multiple Regression Analysis of Meteorological and Pollutant Effects on Mercury
Multiple linear regression analyses were conducted on , and GEM to evaluate the effects of meteorological factors and pollutant emissions on mercury concentrations.
The multiple linear regression models for GEM, PBM2.5, and PBM2.5–10 were established after removing multicollinearity factors based on variance inflation factors (VIF). The models for GEM, PBM2.5, and PBM2.5–10 explained 61.3%, 50.2%, and 77.6% of the variance, respectively (R2 = 0.613, 0.502, 0.776; adjusted R2 = 0.602, 0.481, 0.744) (Table 2). All three regressions were highly significant (GEM: F = 52.7; PBM2.5: F = 23.22; PBM2.5–10: F = 38.76; all p < 0.001), and residual standard errors were 0.381, 0.447, and 0.736 ng m−3 for GEM, PBM2.5, and PBM2.5–10, respectively. For GEM and PBM2.5, residuals were well distributed with no evident violations of linear-model assumptions, and the PBM2.5–10 model showed no signs of overfitting.

Table 2.
Results of multiple linear regression models for and GEM with meteorological parameters (TEMP, RH, WS, and PRES) and conventional pollutants (PM2.5, SO2, CO, NO2 and O3): including F-test results (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, ns: not significant).
To better identify the dominant factors, standardized regression coefficients (β) were derived from the multiple linear regression model (Table 1). Temperature (T) was the most influential factor, but its effects differed markedly among species. For GEM, T showed a strong positive association (β = +0.715), indicating enhanced concentrations through surface re-emission. By contrast, PBM2.5 exhibited a pronounced negative response (β = −0.597, p < 0.001), suggesting enhanced volatilization or desorption at higher temperatures, while PBM2.5–10 showed only a weak negative influence. In addition to chemical conversion of GEM to GOM followed by partitioning into particles via atmospheric oxidants (e.g., Cl, Br, BrO, I, and OH) [15,52,53], previous studies have shown that PBM may also form via the physical adsorption of GEM onto particle surfaces, a process strongly affected by ambient temperature [54]. Furthermore, field observations in Qingdao indicated that elemental carbon and organic matter, due to their porous structures and adsorption capacities, could promote the conversion of GEM to particulate mercury [42,55]. Taken together, these results suggest that both oxidation–partitioning and physical adsorption pathways contribute to PBM variability, with their relative importance modulated by meteorological conditions and particle composition.
SO2, widely recognized as a key tracer of coal combustion, is indirectly indicative of anthropogenic mercury emissions, particularly from coal combustion sources, identified as the dominant source of atmospheric mercury in China [49]. It has been reported that the GEM, GOM, and PBM2.5 approximately accounted for 53%, 37% and 10% of the total Hg emissions in coal-fired power plants [56]. Recent studies indicate that GEM is the dominant species in coal-fired power plant emissions, while the proportion of GOM is much lower than 25% [57]. In the present study, SO2 exhibited a medium positive association with GEM (β = +0.431), probably reflecting contributions from combustion sources [18]. In contrast, SO2 showed a weak negative relationship with PBM2.5 (β = −0.238, p < 0.01), but a weak positive association with PBM2.5–10 (β = +0.270, p < 0.001), indicating that its influence on mercury speciation may vary with particle size and may involve complex photochemical and physicochemical transformation pathways.
Previous studies have indicated that GOM can be reduced back to GEM by SO2 in both the gas and aqueous phases, thereby weakening the secondary formation of PBM [33,58,59]. This reduction pathway may explain why SO2 exhibits a weak or even negative correlation with PBM2.5, and the suppression of GOM production in the atmospheric photochemical pathway by SO2. In contrast, the relationship between SO2 and PBM2.5–10 appears to be more complex. To date, detailed chemical mechanisms describing Hg transformations within coarse particles have not been well established. Thus, the weak positive β value for PBM2.5–10 with SO2 may be primarily influenced by different primary emissions rather than secondary processes [59].
WS had minimal influence on GEM and PBM2.5, but was the dominant factor for PBM2.5–10 (β = +0.540, p < 0.01), indicating enhanced resuspension and transport of coarse particle-bound mercury from local sources. RH exerted negative effects on GEM, PBM2.5, and PBM2.5–10, possibly due to enhanced deposition or suppressed volatilization.
Other variables showed weaker and less consistent effects. CO was weakly negative for GEM (β = −0.223) but nonsignificant for PBM2.5 and PBM2.5–10, probably indicating that the combustion sources contribute to varying mercury species. O3 and NO2 had weak positive associations with GEM, negligible impact on PBM2.5, and no significant influence on PBM2.5–10. PRES had minimal effects in all models.
3.5. PBM Variation with Wind Speed and Wind Direction
Previous studies have demonstrated that atmospheric mercury concentrations are influenced by multiple factors, including combustion emissions, industrial activities, atmospheric chemical reactions, physical transport processes, and meteorological conditions [30,60,61,62]. However, the abnormally high concentrations of PBM observed in this study exceed the typical levels reported in similar environments and cannot be fully explained by these conventional factors. Hence, polar plot analysis was used to identify the potential sources, and the results are presented in Figure 5. While SO2 and NO2 appear to have predominantly local sources, the Hg species are more associated with longer-range emissions, although with very different source regions.
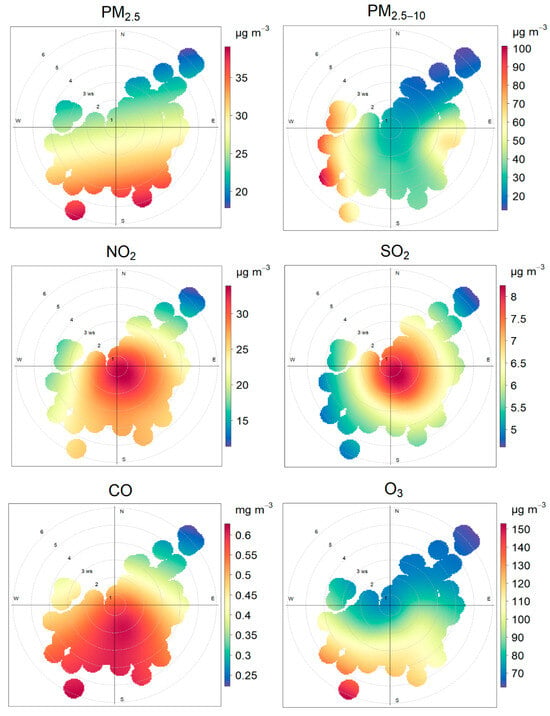
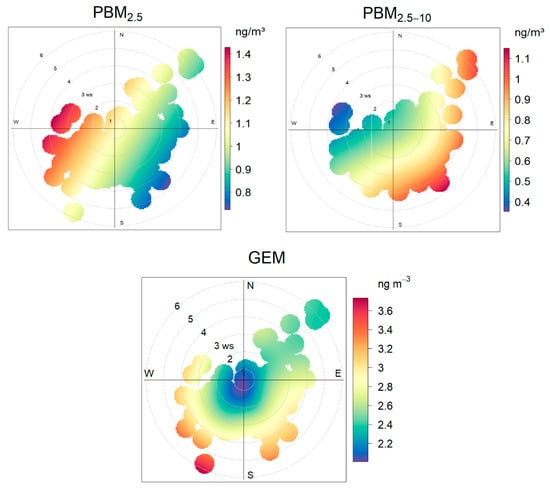
Figure 5.
Polar plot analysis of common pollutants ( and GEM.
The polar plot analysis revealed that PM2.5, NOx;, and CO exhibited similarly elevated concentrations under southerly wind conditions, likely attributable to emissions from vehicles and ships along the eastern to western coast. In addition, when the prevailing winds were from the west, the sampling site was affected by coarse particles, leading to higher PM2.5–10 concentrations. These coarse particles were probably associated with nearby construction activities, exposed soil surfaces, farmland, and road dust.
However, the polar plot patterns of PBM2.5 and PBM2.5–10 differed markedly from each other, suggesting that mercury sources at the sampling site are more complex. High PBM2.5 concentrations (1.0–1.4 ng m−3) were observed under westerly winds (approximately 3 m s−1) (Figure 6). Previous studies have shown that mobile combustion is an important source of atmospheric mercury [49,63], and Nie et al. (2020) [17] further suggested that heavy-duty traffic and recreational activities, such as motorboats and sailboats near seaside resorts, can increase ambient Hg concentrations. Nevertheless, emissions from heavy fuel oil combustion by ships and from heavy-duty road vehicles along the southwestern coast are unlikely to fully explain the high PBM2.5 levels observed in this study [19,49]. Another potential source should also be considered: the western and northwestern sectors of the site, which belong to the Economic and Technological Development Zone and host multiple light industrial and manufacturing facilities. Although direct evidence of substantial mercury emissions from these facilities is lacking, contributions from fine particulate-bound mercury cannot be excluded.
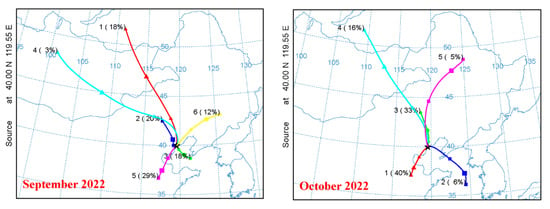
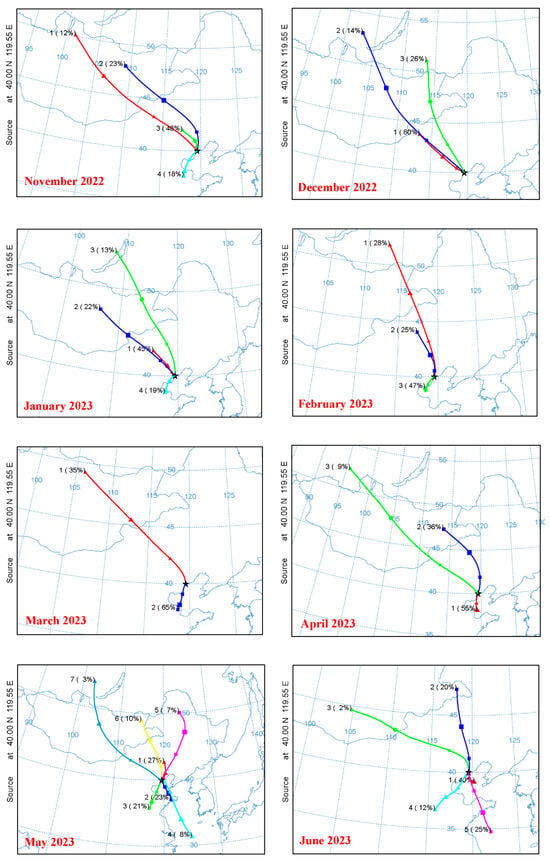
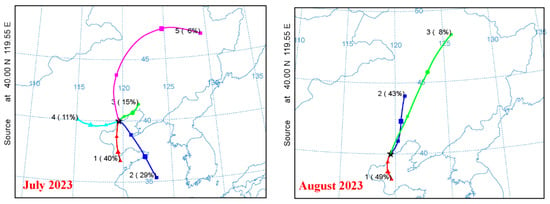
Figure 6.
Illustrates the monthly composite of air mass back trajectories from September 2022 to August 2023, with each trajectory simulated for a total run time of 48 h. These trajectories were calculated at an elevation of 50 m above ground level utilizing the HYSPLIT (Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory) model.
For coarse particle-bound mercury (PBM2.5–10), concentrations ranging from 0.5 to 1.1 μg/m3 were observed under westerly, southerly, and easterly winds (Figure 5). Unlike fine particles, PBM2.5–10 is less affected by combustion emissions or atmospheric photochemical transformations and is more strongly linked to the resuspension of primary particles. The sampling site is located approximately 1 km north of QHD port, which extends ~10 km eastward along the coastline and is the largest coal import–export terminal in northern China. Intensive coal handling, storage, and transshipment activities at the port are likely to release Hg-enriched coarse particles, and the spatial consistency between PBM2.5–10 enhancements and prevailing wind directions supports the port’s dominant contribution.
Coal itself contains markedly higher Hg levels (0.02–1.35 mg/kg, average 0.2–0.3 mg/kg) than biomass (71 μg/kg) or limestone (42 μg/kg) [49,64,65,66], reinforcing the role of coal-related activities in coarse PBM emissions. In addition, resuspended soils may represent another important source, given that background Hg levels in uncontaminated soils typically range from 12.3 to 96 μg/kg, while highly contaminated sites can reach 236–856 μg/kg [67,68,69,70,71,72,73]. These findings suggest that both coal-related processes at the port and soil resuspension substantially affect PBM2.5–10 levels in this coastal urban region and warrant further source-specific investigations and regulatory attention.
GEM concentrations exhibited a pronounced increase under strong westerly, southerly, and eastly winds, strongly suggesting influences from marine boundary layer dynamics or long-range atmospheric transport [2,12,74]. In contrast, the polar plots for NO2, SO2, and CO indicate strong local influences, with elevated concentrations slightly southeast of the sampling site. While small on-campus sources such as canteens and faculty dining halls exist, their contribution is likely negligible. More substantial sources are located between the campus and the port. A major east–west arterial road, which crosses QHD and carries heavy traffic, passes directly south of the sampling site and represents an important local source. In addition, a traditional-style commercial food street, approximately 1.5 km in length, attracts an average of 50,000–60,000 visitors per day, with peak activity between 17:00 and 21:00.
In addition, numerous vessels are typically anchored 1–2 nautical miles offshore while awaiting entry into the port for loading and unloading, and their substantial emissions during running represent another source of air pollution. Port activities more broadly are also recognized as important contributors to gaseous pollutants. For example, Weiss-Penzias et al. (2013) [75] reported elevated GEM, CO, NO2, and SO2 concentrations in port areas along the U.S. Pacific coast, with GEM reaching up to ~7 ng m−3 in the Port of Long Beach. These enhancements were attributed to stationary emissions in the port area and to ship plumes, with an estimated emission factor of 0.05 ± 0.01 mg GEM per kg of fuel burned for cargo ships. Such findings highlight the strong impact of port and shipping activities on local air quality.
The patterns of NO2 and SO2 further indicated that the coal-fired power plant located to the north was not the main contributor to GEM during the study period. Elevated CO concentrations observed under strong southerly winds likely reflect the advection process rather than local combustion. Backward trajectory analysis (Figure 6) showed that air mass transported by south eastly winds occurred frequently throughout the year, carrying pollutants along the coast from the Tangshan (TS), a major industrial city located approximately 160 km southeast of QHD. TS is well known for its extensive iron, steel, and cement production, which represent significant regional sources of atmospheric mercury.
3.6. The Ratios of GEM/CO
Combustion of fossil fuels and biomass was the most important source of local GEM and CO. Given the relatively stable and long lifetime, CO is often used as a tracer for human combustion emissions. Similarly, GEM is also stable with residence time in the atmosphere, and thus GEM/CO is commonly used to infer GEM sources and estimate mercury emission [40].
The GEM/CO ratio displayed distinct seasonal variability, with the highest values in spring (7.12 pg/m3·ppb−1) and summer (6.20 pg/m3·ppb−1), followed by autumn (5.93 pg/m3·ppb−1), and the lowest in winter (2.62 pg/m3·ppb−1). This pattern reflects enhanced surface mercury re-emissions under warm conditions and suppression under colder ones [76,77]. The low winter ratios are further linked to increased CO emissions from coal combustion during the heating season, when the average GEM/CO ratio (3.57 pg/m3·ppb−1) was far below that in the non-heating period (6.93 pg/m3·ppb−1, p < 0.001) [78,79]. These results are consistent with regulatory measures (GB13223-2011) [80] and a gradual energy shift toward natural gas, which has reduced mercury emissions from power plants [64].
Wind direction had little effect on the GEM/CO ratio, with northerly and southerly values (5.83 pg/m3·ppb−1 vs. 5.37 pg/m3·ppb−1, p > 0.05) showing no significant difference. Although northerly winds typically bring polluted inland air [13] and southerly winds cleaner marine air [36], both directions appeared to be affected by similar transport processes. Back-trajectory analysis in QHD during a dust event suggested that the air masses traveled along mixed land–sea pathways before reaching the sampling site, which may have reduced the expected contrast between northerly and southerly winds [81].
Pollution episodes exerted a stronger influence, with the GEM/CO ratio significantly lower on haze days (3.66 pg/m3·ppb−1) than on non-haze days (5.58 pg/m3·ppb−1, p < 0.01). Elevated CO from fossil fuel combustion, particularly vehicles and heating, diluted the ratio [82], whereas higher values on non-haze days indicate stronger relative contributions from natural surface re-emissions [40,51]. Overall, these findings demonstrate that GEM/CO variability is shaped primarily by seasonal meteorology and combustion intensity, while wind direction plays a secondary role, and haze episodes further amplify the impact of anthropogenic emissions.
3.7. Air Mass Origins and Maritime Influence on Mercury Dynamics
Backward air mass trajectory analysis is widely used to trace the origins and transport pathways of air masses arriving at the sampling site. In this study, the HYSPLIT model was applied to cluster 48 h back-trajectories during the sampling periods in QHD.
The results revealed clear seasonal differences in air mass origins and transport patterns, reflecting the varying influence of continental and maritime air masses (Figure 6). Specifically, continental air masses were dominated by long-range transport from northern regions (53–100% in winter) and short-range transport from the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei area, with stronger contributions in autumn and winter.
Maritime air masses are predominantly of medium to short-range origin. One type originates from the southern Bohai Sea or the Shandong Peninsula, crosses the Bohai Sea, passes over the coastal heavy industrial cities in the northern Bohai region, and reaches QHD carrying high concentrations of pollutants. Another type comprises seasonal air masses originating from the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea, which pass over the Shandong Peninsula before crossing the Bohai Sea to arrive in QHD. These maritime air masses exhibit pronounced seasonality; for example, in summer (June–August), those from the Yellow Sea account for approximately 30%, while those from the southern Bohai Sea can reach nearly 50%, reflecting the strong influence of the summer monsoon on air mass transport.
The Hg/Na ratios were used to evaluate the potential contribution of marine aerosols to mercury concentrations, the characteristic Hg/Na ratio of marine aerosols reported in the literature is to (dimensionless mass ratio, g/g) [83,84], while that of seawater is approximately (dimensionless mass ratio, g/g) [85]. The average Hg/Na mass ratio was in and in , strongly suggested that marine aerosol contributes minimally to PBM concentrations. The elevated Hg/Na ratios coincide with the polar plots results, which further support the hypothesis that anthropogenic sources significantly influence PBM distributions.
Furthermore, the elevated GEM concentrations under southerly winds underscore the influence of marine air mass interactions. The elevated GEM concentrations under high-speed southerly winds further underscore the importance of MBL dynamics (Figure 5), and the evasion of dissolved gaseous mercury (DGM) from ocean surfaces represents another potential contributing factor [2,74].
4. Conclusions
This study provided a comprehensive investigation of atmospheric mercury dynamics in QHD, a coastal urban region of North China influenced by complex land–sea interactions. The annual mean concentrations of GEM, PBM2.5, and PBM2.5–10 were 2.66, 1.01, and 0.73 ng m−3, respectively. Compared with other coastal sites in eastern China, PBM levels in QHD were among the highest, highlighting the significance of local emissions in addition to regional background contributions.
GEM exhibited a pronounced diurnal cycle, consistently peaking between 12:00 and 14:00, with the midday enhancement persisting for up to four hours in summer. Strong correlations with temperature (R2 = 0.25–0.65) underscored the importance of surface re-emission, while significant associations with SO2 in winter (R2 = 0.52) indicated the influence of coal combustion. Seasonal variations in GEM/CO ratios, ranging from 7.12 pg/m3 · ppb−1 in spring to 2.62 pg/m3 · ppb−1 in winter, further distinguished the dominance of natural re-emission under warm conditions and combustion-related inputs during the heating season. Elevated GEM concentrations under southerly winds also suggested the additional role of marine boundary layer processes in modulating coastal mercury levels.
For particulate mercury, distinct size-dependent patterns were observed. PBM2.5 exhibited enhanced concentrations of 1.0–1.4 ng m−3 under westerly winds (~3 m s−1), reflecting contributions from traffic, shipping, and nearby light industries. In contrast, PBM2.5–10 concentrations of 0.5–1.1 μg m−3 were strongly linked to coal-handling operations at QHD port and to soil resuspension, confirming the dominant role of port-related processes in coarse particle-bound mercury pollution. These findings indicate that fine and coarse PBM are influenced by distinct sources and mechanisms, with fine PBM more associated with combustion and industrial activities, and coarse PBM largely determined by mechanical disturbances of Hg-rich materials.
Air mass analysis further demonstrated the dual influence of continental and maritime pathways. Continental air masses, originating from the north and the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, accounted for 53–100% of transport in winter and were closely tied to elevated mercury levels. By contrast, maritime air masses contributed 30–50% in summer, reflecting monsoonal influence. However, the average Hg/Na ratios in PM2.5 (3.22 × 10−4, dimensionless mass ratio, g/g) and PM2.5–10 (2.17 × 10−4, dimensionless mass ratio, g/g) were far above the characteristic range of marine aerosols (10−7–10−5, dimensionless mass ratio, g/g), confirming that marine sources contributed negligibly to PBM. Instead, anthropogenic emissions and terrestrial resuspension dominated particulate mercury levels, while GEM was more sensitive to both surface re-emission and atmospheric circulation patterns.
In summary, atmospheric mercury pollution in QHD is primarily governed by the interplay of temperature-driven re-emission, coal combustion, marine boundary layer influence, port coal-handling activities, and regional transport. Among these, port-related processes emerge as a critical source of coarse PBM, while GEM reflects both natural re-emission and anthropogenic combustion inputs. These results underscore the importance of controlling coal-related emissions and port operations to mitigate mercury pollution in coastal urban regions, providing valuable insights for regional air quality management and policy implementation under the Minamata Convention.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.Z.; Methodology, R.L., Y.M. and L.Z.; Software, Y.M., J.C. and Y.W.; Validation, L.X., Y.M. and J.C.; Formal analysis, L.X., X.W., J.C. and L.Z.; Investigation, R.L., L.X., X.W., Y.M. and L.Z.; Resources, Y.M. and J.C.; Data curation, R.L., L.X., X.W., Y.M., J.C., L.Z. and Y.W.; Writing—original draft, R.L. and Y.W.; Writing—review & editing, R.L. and R.M.H.; Visualization, R.L., X.W., Y.M. and J.C.; Supervision, R.L., Y.M., J.C., L.Z. and R.M.H.; Project administration, R.L. and L.Z.; Funding acquisition, R.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Hebei Natural Science Foundation (B2022407001).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Lumex Instruments & Technology (Tianjin) Co., Ltd. for their valuable technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
Dr. Jie Cheng and Ms. Liqiu Zhou are employees of Lumex Instruments & Technology (TianJin). The paper reflects the views of the scientists and not the company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Schroeder, W.H.; Munthe, J. Atmospheric mercury—An overview. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Yang, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Xiao, C.; Liang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yin, Y.; Hu, L.; Shi, J.; et al. New evidence for atmospheric mercury transformations in the marine boundary layer from stable mercury isotopes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 9713–9723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Yu, G.; Zhao, N.; Lin, Y.; Fu, Q.; Wang, D.; Xie, Z.; Deng, C.; et al. Characteristics of atmospheric mercury in a suburban area of east China: Sources, formation mechanisms, and regional transport. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 5923–5940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Vogt, R.; Larssen, T. Environmental mercury in China: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 2431–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Cheng, I.; Zhang, L. Current understanding of the driving mechanisms for spatiotemporal variations of atmospheric speciated mercury: A review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 12897–12924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrist, D.; Kirk, J.L.; Zhang, L.; Sunderland, E.M.; Jiskra, M.; Selin, N.E. A review of global environmental mercury processes in response to human and natural perturbations: Changes of emissions, climate, and land use. Ambio 2018, 47, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Mercury Assessment 2018; UN Environment Programme, Chemicals and Health Branch: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Pacyna, J.M.; Travnikov, O.; De Simone, F.; Hedgecock, I.M.; Sundseth, K.; Pacyna, E.G.; Steenhuisen, F.; Pirrone, N.; Munthe, J.; Kindbom, K. Current and future levels of mercury atmospheric pollution on a global scale. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 12495–12511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprovieri, F.; Pirrone, N.; Ebinghaus, R.; Kock, H.; Dommergue, A. A review of worldwide atmospheric mercury measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 8245–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soerensen, A.L.; Jacob, D.J.; Streets, D.G.; Witt, M.L.I.; Ebinghaus, R.; Mason, R.P.; Andersson, M.; Sunderland, E.M. Multi-decadal decline of mercury in the North Atlantic atmosphere explained by changing subsurface seawater concentrations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, H.M.; Jacob, D.J.; Streets, D.G.; Sunderland, E.M. Legacy impacts of all-time anthropogenic emissions on the global mercury cycle. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2013, 27, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ci, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Guo, J. Speciated atmospheric mercury in the marine boundary layer of the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 131, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ci, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Niu, Z. Atmospheric gaseous elemental mercury (GEM) over a coastal/rural site downwind of East China: Temporal variation and long-range transport. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2480–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Qin, X.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Liu, C.; Fu, M.; Wang, X.; Huo, J.; Duan, Y.; Fu, Q.; et al. Atmospheric mercury in a developed region of eastern China: Interannual variation and gas-particle partitioning. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Dou, H.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Hao, J. Characteristics and Sources of Speciated Atmospheric Mercury at a Coastal Site in the East China Sea Region. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 2913–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Chen, J.; Deng, J.; Tong, L.; Xu, L.; Niu, Z.; Yin, L.; Chen, Y.; Hong, Z. Pattern of atmospheric mercury speciation during episodes of elevated PM2.5 levels in a coastal city in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Mao, H.; Li, P.; Li, T.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhen, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Total gaseous mercury in a coastal city (Qingdao, China): Influence of sea-land breeze and regional transport. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 235, 117633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L.; Hong, Y.; Li, M.; Fan, X.; Yin, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, C.; Chen, G.; et al. Measurement report: Atmospheric mercury in a coastal city of Southeast China—Inter-annual variations and influencing factors. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 11187–11202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, R.; Mu, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, X.; Ma, Y.; Harrison, R.M. Dynamics of water-soluble inorganic ions in Qinhuangdao: Particle size association and influences of environmental conditions. Urban Climate 2025, 61, 102390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBW07402; Soil Composition Analysis Standards. National Research Center for Certified Reference Materials: Beijing, China. Available online: https://www.ncrm.org.cn/English/CRM/pdf/GBW07404_20160301_135930536_1704880.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2025).
- GB3095-2012; National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) of China. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Sun, W.; Shao, M.; Granier, C.; Liu, Y.; Ye, C.S.; Zheng, J.Y. Long-Term Trends of Anthropogenic SO, NO, CO, and NMVOCs Emissions in China. Earth’s Future 2018, 6, 1112–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, S.; Yin, K.; Zhao, Z.; Ying, N.; Fan, J. Network approach reveals the spatiotemporal influence of traffic on air pollution under COVID-19. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2022, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.; Brimblecombe, P.; Lam, Y.F.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Ozone pollution in China: A review of concentrations, meteorological influences, chemical precursors, and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Duan, Y.; Cheng, N.; Xiu, G. Atmospheric mercury speciation in Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Feng, X.; Qiu, G.; Shang, L.; Zhang, H. Speciated atmospheric mercury and its potential source in Guiyang, China. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4205–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fu, X.; Wang, X.; Feng, X. Measurements and Distribution of Atmospheric Particulate-Bound Mercury: A Review. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 103, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Wang, S.; Wu, Q.; Tang, Y.; Wen, M. Measuring and Regression Modeling of Gas–Particle Partitioning of Atmospheric Oxidized Mercury at a Coastal Site in Shanghai. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lyman, S.; Mao, H.; Lin, C.J.; Gay, D.A.; Wang, S.; Sexauer Gustin, M.; Feng, X.; Wania, F. A synthesis of research needs for improving the understanding of atmospheric mercury cycling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 9133–9144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.S.P.; Sheu, G.-R.; Chang, S.-C.; Lin, N.-H. Effects of temperature and relative humidity on the partitioning of atmospheric oxidized mercury at a high-altitude mountain background site in Taiwan. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 261, 118572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.W.; Feng, X.; Liang, P.; Deliger; Zhang, H.; Ji, J.; Liu, P. Temporal trend and sources of speciated atmospheric mercury at Waliguan GAW station, Northwestern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 1951–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X. Concentrations and gas-particle partitioning of atmospheric reactive mercury at an urban site in Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Niu, Z.; Tong, L.; Yin, L.; Chen, Y. Characteristics and sources of atmospheric mercury speciation in a coastal city, Xiamen, China. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, G.; Hong, Y.; Xiao, H.; Chen, J. Gas-particle partitioning of atmospheric reactive mercury and its contribution to particle bound mercury in a coastal city of the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 239, 117744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Han, Y.-J.; Holsen, T.M.; Yi, S.-M. Characteristics of atmospheric speciated mercury concentrations (TGM, Hg(II) and Hg(p)) in Seoul, Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 3267–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marumoto, K.; Hayashi, M.; Takami, A. Atmospheric mercury concentrations at two sites in the Kyushu Islands, Japan, and evidence of long-range transport from East Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 117, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratz, L.E.; Keeler, G.J.; Marsik, F.J.; Barres, J.A.; Dvonch, J.T. Atmospheric transport of speciated mercury across southern Lake Michigan: Influence from emission sources in the Chicago/Gary urban area. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 448, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, S.N.; Gustin, M.S. Determinants of atmospheric mercury concentrations in Reno, Nevada, U.S.A. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 408, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Marusczak, N.; Heimbürger, L.E.; Sauvage, B.; Gheusi, F.; Prestbo, E.M.; Sonke, J.E. Atmospheric mercury speciation dynamics at the high-altitude Pic du Midi Observatory, southern France. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 5623–5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, W. Pollution characteristics and source difference of gaseous elemental mercury between haze and non-haze days in winter. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, T.; Ueno, T.; Fu, F. Sequential variation of atmospheric mercury in Tokai-mura, seaside area of eastern central Japan. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zeng, Y. Variation characteristics and source differences of gaseous elemental mercury over four seasons in Qingdao: Influence of weather processes. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 222, 117118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, M.S.; Song, X.; Lu, J.Y.; Feng, X. Atmospheric gaseous elemental mercury in downtown Toronto. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 4016–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-D.; Huang, J.; Mondal, S.; Holsen, T.M. Variation in concentrations of three mercury (Hg) forms at a rural and a suburban site in New York State. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 448, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Wang, S.; Qiu, G.; Hou, Y.; Tang, S. Total gaseous mercury emissions from soil in Guiyang, Guizhou, China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Dollard, G.J.; Pepler, S. Gas-phase mercury in the atmosphere of the United Kingdom. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiskra, M.; Wiederhold, J.G.; Skyllberg, U.; Kronberg, R.-M.; Hajdas, I.; Kretzschmar, R. Mercury Deposition and Re-emission Pathways in Boreal Forest Soils Investigated with Hg Isotope Signatures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7188–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, M.S.; Lewis, C.W.; Stevens, R.K.; Keeler, G.J.; Dvonch, J.T.; Tremblay, R.T. Ft. McHenry tunnel study: Source profiles and mercury emissions from diesel and gasoline powered vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 8711–8724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y.; Duan, L.; Wu, Q.; Wang, F.; Yang, M.; Yang, H.; Hao, J.; et al. Updated Emission Inventories for Speciated Atmospheric Mercury from Anthropogenic Sources in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 3185–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacyna, E.G.; Pacyna, J.M.; Steenhuisen, F.; Wilson, S. Global anthropogenic mercury emission inventory for 2000. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 4048–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirrone, N.; Cinnirella, S.; Feng, X.; Finkelman, R.B.; Friedli, H.R.; Leaner, J.; Mason, R.; Mukherjee, A.B.; Stracher, G.B.; Streets, D.G.; et al. Global mercury emissions to the atmosphere from anthropogenic and natural sources. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5951–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-J.; Pongprueksa, P.; Lindberg, S.E.; Pehkonen, S.O.; Byun, D.; Jang, C. Scientific uncertainties in atmospheric mercury models I: Model science evaluation. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 2911–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subir, M.; Ariya, P.A.; Dastoor, A.P. A review of uncertainties in atmospheric modeling of mercury chemistry I. Uncertainties in existing kinetic parameters—Fundamental limitations and the importance of heterogeneous chemistry. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5664–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, M.; Marumoto, K. Formation of atmospheric particulate mercury in the Tokyo metropolitan area. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Duan, Y.; Han, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, J.; Wang, W. Particulate mercury in ambient air in Shanghai, China: Size-specific distribution, gas–particle partitioning, and association with carbonaceous composition. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacyna, E.G.; Pacyna, J.M. Global Emission of Mercury from Anthropogenic Sources in 1995. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2002, 137, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigelt, A.; Slemr, F.; Ebinghaus, R.; Pirrone, N.; Bieser, J.; Bödewadt, J.; Esposito, G.; van Velthoven, P.F.J. Mercury emissions of a coal-fired power plant in Germany. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 13653–13668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. Two years measurement of speciated atmospheric mercury in a typical area of the north coast of China: Sources, temporal variations, and influence of regional and long-range transport. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 228, 117235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, D.; Chen, W. Mercury concentration and isotopic composition on different atmospheric particles (PM10 and PM2. 5) in the subtropical coastal suburb of Xiamen Bay, Southern China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 261, 118604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Cheng, N.; Xiu, G.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y. Characteristics and source appointment of atmospheric particulate mercury over East China Sea: Implication on the deposition of atmospheric particulate mercury in marine environment. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Zhang, L.; Huang, C. Measurements of size-fractionated concentration and bulk dry deposition of atmospheric particulate bound mercury. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, X.; Yuan, X.; Zeng, G.; León, T.; Liang, J.; Chen, G.; Yuan, X. Characteristics of Particulate Pollution (PM2.5 and PM10) and Their Spacescale-Dependent Relationships with Meteorological Elements in China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, T.G. Mercury emissions from automobiles using gasoline, diesel, and LPG. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 7547–7552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. Control of mercury emissions from stationary coal combustion sources in China: Current status and recommendations. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedli, H.R.; Radke, L.F.; Lu, J.Y. Mercury in smoke from biomass fires. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 3223–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thy, P.; Jenkins, B.M. Mercury in Biomass Feedstock and Combustion Residuals. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 209, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Luo, T.-C.; Zhang, B.-R.; Zhang, H.-F.; Han, Y.-w.; Zhao, Z.-D.; Hu, Y.-K. Chemical composition of the continental crust as revealed by studies in East China. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 1959–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S. Composition of the continental crust. In The Crust; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 3, pp. 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, D.M.; Dostal, J.; Keays, R.R. Additional estimates of continental surface Precambrian shield composition in Canada. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1976, 40, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R. Abundance of chemical elements in the continental crust: A new table. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1964, 28, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Lehmann, B.; Deng, C.; Luo, A.; Zhang, X.; Moynier, F.; Yin, R. Mercury abundance and isotopic composition in granitic rocks: Implications for Hg cycling in the upper continental crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2023, 361, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans Wedepohl, K. The composition of the continental crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1217–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleku, D.L.; Lazareva, O.; Pichler, T. Mercury in groundwater—Source, transport and remediation. Appl. Geochem. 2024, 170, 106060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Feng, X.; Zhang, G.; Xu, W.; Li, X.; Yao, H.; Liang, P.; Li, J.; Sommar, J.; Yin, R.; et al. Mercury in the marine boundary layer and seawater of the South China Sea: Concentrations, sea/air flux, and implication for land outflow. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss-Penzias, P.S.; Williams, E.J.; Lerner, B.M.; Bates, T.S.; Gaston, C.; Prather, K.; Vlasenko, A.; Li, S.M. Shipboard measurements of gaseous elemental mercury along the coast of Central and Southern California. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lindberg, S.E. Processes influencing the emission of mercury from soils: A conceptual model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 21889–21896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Tang, S.; Shang, L.; Yan, H.; Sommar, J.; Lindqvist, O. Total gaseous mercury in the atmosphere of Guiyang, PR China. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 304, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.W.; Zhang, H.; Lin, C.J.; Feng, X.B.; Zhou, L.X.; Fang, S.X. Correlation slopes of GEM/CO, GEM/CO2, and GEM/CH4 and estimated mercury emissions in China, South Asia, the Indochinese Peninsula, and Central Asia derived from observations in northwestern and southwestern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1013–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, T.; Talbot, R.; Mao, H.; Hall, C.B.; Yang, X.; Fu, C.; Zhuang, B.; Li, S.; Han, Y.; et al. Characteristics of atmospheric Total Gaseous Mercury (TGM) observed in urban Nanjing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 12103–12118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB13223-2011; Emission Standard of Air Pollutants for Thermal Power Plants. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Wang, W.; Zhou, H.; Lyu, R.; Li, W.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, X.; Shao, L. Chemical evaluation of aerosol particles in an intense Asian dust storm in a coastal city: Direct vs. reverse transport stages. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 155, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Balasubramanian, R.; Zhu, Q.; Behera, S.N.; Bo, D.; Huang, X.; Xie, H.; Cheng, J. Characteristics of atmospheric particulate mercury in size-fractionated particles during haze days in Shanghai. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 131, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.P.; Fitzgerald, W.F. The distribution and biogeochemical cycling of mercury in the equatorial Pacific Ocean. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1993, 40, 1897–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.E.; Sommar, J.; Gårdfeldt, K.; Jutterström, S. Air–sea exchange of volatile mercury in the North Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Chem. 2011, 125, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, G.-R.; Lin, N.-H. Mercury in cloud water collected on Mt. Bamboo in northern Taiwan during the northeast monsoon season. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4454–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).