Abstract
The rapid oasis expansion and urbanization that occurred in Xinjiang province (China) in the last decades have greatly modified the land surface energy balance and influenced the local circulation under the arid mountains-plain background system. In this study, we first evaluated the ALARO regional climate model coupled to the land surface scheme SURFEX at 4 km resolution using 53 national climatological stations and 5 automatic weather stations. We found that the model correctly simulates daily and hourly variation of 2 m temperature and relative humidity. A 4-day clear sky period has been chosen to study both local atmospheric circulations and their mutual interaction. Observations and simulations both show that a low-level divergence over oasis appears between 19:00 and 21:00 Beijing Time when the background mountain-plain wind system is weak. The model simulates a synergistic interaction between the oasis-desert breeze and urban-rural breeze from 16:00 until 22:00 with a maximum effect at 20:00 when the downdraft over oasis (updraft over urban) areas increases by 0.8 (0.4) Pa/s. The results show that the oasis expansion decreases the nocturnal urban heat island in the city of Urumqi by 0.8 °C, while the impact of urban expansion on the oasis cold island is negligible.
1. Introduction
Formed by the runoff from the mountains under arid climate and desert background, the oasis is a medium or small scale intrazonal landscape [1], which is the basis of human life and economic development in Central Asia. The distribution of the oasis in Central Asia is closely related to the topography which is characterized by high mountains-basin system in which the oases are established in river deltas and the deserts widely spread in the basin [2], forming a typical landscape of Mountains-Oasis-Desert within an arid mountains-desert system. The Tianshan Mountains together with the surrounding deserts in the Xinjiang province of China contain plenty of Mountains-Oasis-Desert landscapes with different spatial scales and is one of the typical mountains-desert systems in Central Asia.
The significant differences between the oases and surrounding deserts in land surface conditions, such as soil moisture conditions and vegetation type, result in great differences in heat and moisture fluxes within the convective boundary layer [3]. The intense evapotranspiration makes the near surface temperature lower and the humidity higher over oases areas than in the surrounding deserts, making the oasis as a wet-cold island called oasis cold island (OCI) effect or oasis effect [4,5]. The OCI effect, which has already been confirmed by observational and numerical simulations studies [6,7,8], is thought to have an important impact on the sustainability of oasis [9,10,11,12]. In fact, the OCI effect may generate local atmospheric circulation called oasis-desert breeze circulation (OBC) [13], with a low-level divergent flow from the oasis to the surroundings desert and a convergent flow in the upper boundary layer. The oasis-desert breeze circulation can protect the oasis in two ways: The updraft over the surrounding desert reduces low-level hot and dry air flowing from the desert to the oasis, and at the same time, the downdraft increases the atmospheric static stability that reduces the oasis evapotranspiration [10,14,15]. Moreover, the divergent flow from the oasis to the surrounding desert brings cold and wet air that helps to protect the vegetation of the desert ecosystem [16,17,18]. The oasis-desert interactions have been summarized by Li et al. [13].
The oasis effect and the corresponding oasis-desert breeze circulation are critically dependent on the background wind and synoptic forcing [5,19,20,21] and can be observed only when there is weak synoptic forcing. However, in the mountains-plain system, when the synoptic forcing is weak, mountains induce local winds called mountain-plains wind system, with mountain wind blowing from the mountains to the plain during nighttime and plain wind blowing from the plain to the mountains during the day [22]. However, in the recent literature, only Zhang et al. [18] studied the impacts of the mountains on the oasis effect by numerical simulations and found that the oasis breeze circulation is counteracted by the strong prevailing westerly wind and that the mountain-plains wind system pushes the oasis effects to the surrounding desert.
Moreover, with the development of the population, economy and technology, the oasis area in the north slope of Tianshan Mountains has increased more than 4 times since the 1950s, resulting in a significant land-use and land-cover change and intensive urbanization [23,24]. This intense land use and land cover change has altered the land surface properties, such as albedo, leaf area index and roughness length, resulting in the change of surface energy budget that may affect the oasis-desert breeze and local climate [25]. Besides, as it is widely known, the urbanization produces the urban heat island (UHI) effect, which is characterized by warmer temperatures in the city than in the surrounding rural areas and may generate the urban–rural breeze circulation (UBC) with low-level convergent flow toward the city and divergent flow in the upper boundary layer [26,27]. In the north of Tianshan Mountains both the oasis–desert breeze circulation and the urban–rural breeze circulation may interact with each other; however, to the knowledge of the authors, no previous studies explored the interaction between both circulations in the background of a mountains-plain system.
Therefore, this study aims to (1) explore the dynamic of the oasis-desert breeze circulation in the context of a mountain-plain system using both field observations and numerical model simulations, (2) study the interaction between oasis–desert breeze circulation and urban–rural breeze circulation and their synergetic interaction, and (3) examine the historical oasis expansion induced OCI effect and urbanization induced UHI effect.
2. Experiments
2.1. Study Area
The Tianshan Mountains, which is the largest mountain range in the world arid area, is located in the hinterland of Central Asia. It lies in the central part of Xinjiang province (China) and is surrounded by two deserts, Gurbantunggut desert in the north and Taklimakan desert in the south, forming several typical mountains-desert systems. The oases in the north slope of Tianshan Mountains were first developed in the groundwater overflow zone and then were extended along the rivers, where water resource was abundant [1,24].
With the rapid development of the economy and the increase of the population, the anthropization of the oasis area in the north slope of Tianshan Mountains has increased more than four times since the 1950s, resulting in a significant land use and land cover change including an intensive urbanization [23,24]. Our study area includes the oases areas and their surrounding deserts and the mountainous areas in the north slope of Tianshan Mountains (with average height about 4000 m above sea level (asl), highest point Thomuer 7439 m asl and lowest point 154 m below sea level). It is situated between 84°50′ E and 89°08′ E and 46°15′ N and 43°18′ N, with a total area of 99,792 km2 (Figure 1a). This region has a typical continental arid and semi-arid climate, with a mean annual temperature around 6 °C and an annual precipitation amount around 220 mm. In the past 50 years, the climate in this region had a warmer and wetter trend [28,29,30], which will continue under future climate change conditions [31]. Our study area contains 2 oases covering a total area of 220 × 75 km and 40 × 25 km (Figure 1c). The analyses in this study mainly focus on the first big oasis.
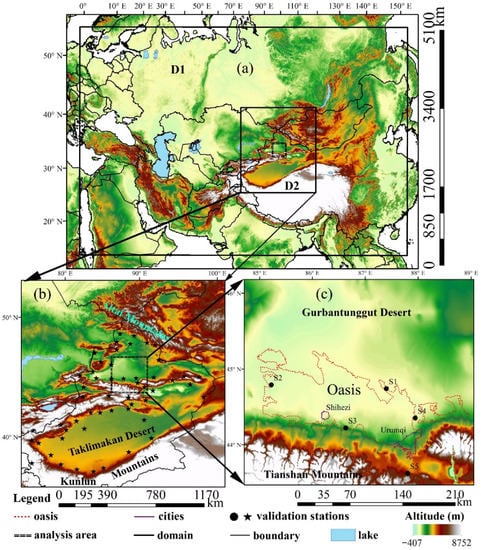
Figure 1.
The two-nested ALARO modeling domains, D1 and D2 (a), and the locations of the meteorological stations in Xinjiang province (b) and the study area (c). The shaded contour represents topography; the validation stations in (b,c) are national (climatological) and automatic weather stations, respectively. The red dotted and black lines in (c) represent the boundary of oasis and cities, respectively.
Daily observations from 53 national meteorological stations distributed over the Xinjiang province (see domain D2 in Figure 1b), are used to validate the simulation results of 2 m mean, maximum and minimum air temperature and relative humidity from the 4 km runs during the summer (June, July and August) season of 2016. Considering the availability and integrity of the observation data, another 5 automatic meteorological stations distributed in the analysis area are used to validate the hourly output during the longest clear sky period (between 9 and 12 June) in the summer of 2016 (Figure 1c). Among the 5 automatic meteorological stations, 4 stations (S1–S4) are distributed in the north, west, south and east boundaries, respectively. These 4 stations are used to detect the oasis breeze circulation. Another station (S5), which is located in the mountains, is used to detect the background mountain-plain winds.
2.2. Model Description and Configuration
The climate model ALARO-0 is the newer version (version 0) of the Aire Limitée Adaptation Dynamique Développement International (ALADIN) model that has been updated with physical parameterizations to enable simulations at 3–10 km mesh-size [32,33]. The ALADIN model, which is the limited area model version of the global scale Action de Recherche Petite Echelle Grande Echelle Integrated Forecast system (ARPEGE-IFS) [34], has been further developed with updated parameterizations for the physics part, such as the microphysics processes, and widely used in weather prediction and regional climate modelling [33,35,36,37,38,39]. ARPEGE-IFS, used both at Météo-France and ECMWF (European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts), is a global spectral model with a Gaussian grid for the gird-point calculations. The vertical discretization in ARPEGE-IFS is done according to a following-terrain pressure hybrid coordinate [33]. The ALARO-0 model has been used at the Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium for the operational numerical weather prediction applications since 2010.
The land surface parameterization, which describes the exchanges of energy and water between the soil surface, vegetation and low-level atmosphere [40,41], is a key parameterization in regional climate modelling. The Météo-France SURFace Externalisée land surface model (SURFEX) [42], which consists of the ISBA (Interactions between Soil, Biosphere and Atmosphere) [43] scheme for natural surfaces and the TEB (Town Energy Balance) [44] scheme for urban surfaces, has been implemented in the ALARO-0 model [45]. The combined ALARO-SURFEX model has shown its potential for representing the regional climate and land surface processes [38,46,47,48].
In this study, the ALARO model is driven by the global reanalysis dataset ERA-Interim produced by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts with a spatial resolution of 0.75° × 0.75° [49] at 6 h interval and run at a horizontal resolution of 50 km with 169 × 117 grid points within a domain that encompasses most of Asia (D1 in Figure 1a). The aim is to participate later to the CORDEX-CA exercise (http://www.cordex.org/domains/region-8-central-asia/). Then, the outputs were used to drive the ALARO-SURFEX model on a smaller domain nested within the outer domain (D1) at a horizontal resolution of 4 km with 500 × 500 grid points (D2 in Figure 1a,b). This inner domain (D2) covers the three Mountains that are Altai Mountains in the north, Tianshan Mountains in the central and Kunlun Mountains in the south of Xinjiang province and the north part of the Tibetan Plateau to capture the synoptic-scale features. Our main region of interest is located in the central area of the inner domain, which consists of the typical mountain-oasis-desert system in the North Slope of Tianshan Mountains (Figure 1c). Considering the facts that the physical parameterizations for ALARO used in both the 50 km and 4 km runs are identical and our analysis area that lies at the very center of the 4 km domain is very small compared to the total 4 km domain, which already eliminate a major source of mismatches between 50 and 4 km runs [50,51], we perform the downscaling from 50 to 4 km directly without an intermediate resolution domain. Hamdi et al. [35] and De Troch et al. [36] come to the same conclusion when running ALARO over western Europe with 50 and 4 km spatial resolutions finding that an intermediate domain at 10 km did not add value.
2.3. Mapping of Land Use Land Cover Types
The ECOCLIMAP dataset provides both the land cover data at 1 km horizontal resolution and its corresponding land surface parameters as input for the SURFEX land surface model [52]. In the original version of ECOCLIMAP-I/II [53], the land cover is divided into 243/573 types based on satellite observations (Figure 2a). However, the land cover data derived from AVHRR data from 1992 to 1993 failed to represent correctly the current land cover states in Xinjiang region because of the human activities and rapid expansion of the oasis (Figure 2b). Therefore, the ECOCLIMAP land cover within Xinjiang region has been updated using the independent local data generated by the Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Figure 2b).
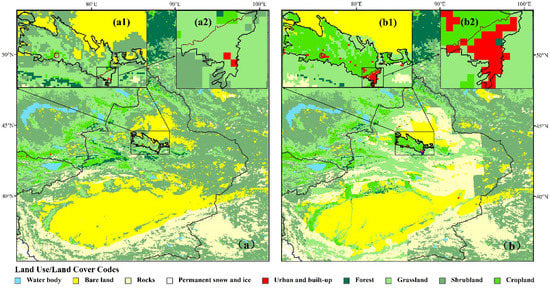
Figure 2.
The default land cover data from ECOCLIMAP (a) and the updated land cover data using the XIEG land cover database (b). The zoom-in figures (a1,b1), (a2,b2) show the land cover in oasis and Urumqi, respectively.
The implementation of the local land cover data set into ECOCLIMAP has been done in a few steps: (i) the original shape file was converted into raster file with a horizontal resolution of 20 m, (ii) the horizontal resolution of the data set was up-scaled from 20 m to 1 km (by selecting the most abundant land cover type), corresponding to the spatial resolution of ECOCLIMAP, (iii) ECOCLIMAP land covers have been then used within this study (for example oasis and cities are assigned to irrigated crops and urban and built-up covers, respectively in ECOCLIMAP; see Figure 2b) together with their corresponding physical parameters, such as albedo, leaf area index, roughness length and emissivity. For technical reasons, we updated most of the default land cover data over Xinjiang using a rectangle window which result in some sharp boundaries especially in the east part of Xinjiang (Figure 2b). However, this will have a negligible effect on our study region.
As it is clearly shown in Figure 2, the significant change between the default and the updated land cover map concerns mainly the rapid expansion of oasis and urban areas, which occurred mainly in the north and east parts within the oasis boundary. For example, in the default database, the oasis area covers only 46% of the total oases areas in the updated database, and it is concentrated mainly in the western part with small scale oases spreading near to the lower mountains in the southern part (Figure 2a). With the acceleration of industrialization and the rise of population, Urumqi, the biggest city in Xinjiang province, has experienced a rapid urbanization and expanded around three times since the beginning of 1990s (Figure 2b). Compared to Urumqi, Shihezi, a smaller city located near to the south boundary of oasis, expanded from 6.3 km2 to 52 km2.
2.4. Set-Up for Modeling-Based Sensitivity Study
In this study, 4 sensitivity simulations are conducted. The 4 simulations are performed with identical initial meteorological conditions, physical schemes and lateral boundary conditions but with different land-use types (see Table 1). In the control (CTL, New_URB) experiment, the land cover is updated, representing the current state of the land cover map in Xinjiang region, especially the oasis and urban distribution in the North Slope of Tianshan Mountains. The single-layer version of the town energy balance (TEB) scheme is then activated. In New_NoURB, the land cover is kept the same as in the CTL simulation except that the urban areas are replaced by the surrounding natural land cover type such as shrub land and grass land. In Def_NoURB, the default ECOCLIMAP land cover data are used with the urban areas replaced by surrounding land covers. Finally, in Def_URB, the default ECOCLIMAP land cover data are used except that the urban areas are updated representing the current state of urbanization and the single-layer version of the TEB scheme is then activated. The configurations of land cover for these experiments are summarized in Table 1. In each simulation, all the surface parameters (albedo, leaf area index, roughness height, building height, etc.) needed as input for the ISBA and TEB scheme are extracted from the ECOCLIMAP database. The oasis expansion effects (OASIS_Eff), urbanization effects either under default (URBAN_Eff_Def) or current state (URBAN_Eff_New) of oasis land cover and their combined effects (COMBI_Eff) can be derived from the difference of New_NoURB—Def_NoURB, Def_URB—Def_NoURB, CTL—New_NoURB and CTL—Def_NoURB, respectively (see Table 1).

Table 1.
Numerical experiments set-up.
All simulations were initialized on 1 March 2016 and a 3-month spin-up period was used before the start of the analysis on 1 June, in order to ensure model equilibrium between external forcing and internal dynamics, especially in terms of soil variables [38]. A period of 3 months was sufficient for the deep soil moisture to reach equilibrium state (not shown). More details about the downscaling configuration used in this study can be found in reference [38]. A period of 4 days from 9 to 12 June 2016 has been chosen in order to investigate the interaction between the OBC and the UBC. This period is characterized by clear sky with no precipitation, long sunshine duration and weak background winds.
With the aim of being able to represent correctly the different local circulations when running the model at high spatial resolution within the study domain, we focus only on the evaluation of the 4 km simulations.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Evaluation of ALARO-SURFEX over Xinjiang
The CTL simulation has been validated at daily scale during the summer (June, July and August) of 2016 by comparing the model outputs with 53 national meteorological stations (http://cdc.cma.gov.cn) located in the Xinjiang province (Figure 1b). The hourly validations for 2 m temperature and relative humidity of the 5 automatic meteorological stations are conducted during the 4 clear sky days (9–12 June) (Figure 1c). We use mean bias error (MBE), root mean square error (RMSE) and correlation coefficients (R2) to evaluate the overall model performance at 4 km spatial resolution.
The mean MBEs averaged over all the 53 stations are −4.12%, −1.62 °C, −3.69 °C and −0.54 °C for daily relative humidity (RH), daily 2 m mean, maximum and minimum temperature, respectively (Table 2). Thus, overall, the model simulations underestimate the daily 2 m mean, maximum and minimum temperature and relative humidity (Figure 3). As shown by the RMSE values, the error magnitude in summer maximum temperature (3.86 °C) tends to be larger than minimum temperature (1.11 °C) indicating that the correct simulation of maximum temperature is more challenging during the summer (see values for R2 in Table 2). The underestimation of the maximum temperature is mainly caused by two aspects. One aspect is the difficulties in reproducing the cloud cover correctly during the summer for regional climate model ALARO, which always gives more cloud. Another is ALARO overestimated the soil moisture in our study area, resulting in the underestimation of maximum temperature and overestimation of relative humidity. Our team is working on a new irrigation scheme in SURFEX to reproduce correctly the soil moisture. Except for these two aspects, the complex terrain in our study area may contribute to the biases to some extent. However, the cloud cover misrepresentation-induced biases in maximum temperature are the same for oasis and desert stations. Therefore, this bias in maximum temperature has little influence on OCI. For the UHI, the high intensity normally takes place during the night. Therefore, the minimum temperature is more important for UHI, which is well simulated in Figure 3c. Previous downscaling studies have shown error magnitudes comparable to or lower than those computed in previous studies [18,54].

Table 2.
Evaluation of the 4 km simulation for the summer of 2016 using the 53 stations.
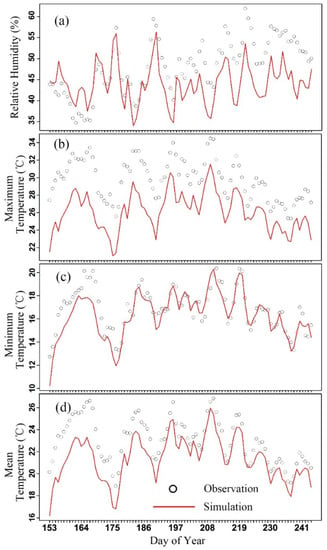
Figure 3.
Comparisons of the observed and simulated (CTL) average (a) relative humidity, (b) maximum temperature, (c) minimum temperature and (d) mean temperature over all the 53 national stations in the summer of 2016.
Figure 4 shows that the model can reproduce the dynamic of the hourly RH and 2 m temperature (T2m) very well with R2 of 0.82 and 0.93 as average over the 5 automatic weather stations. The model slightly overestimates the hourly RH while it underestimates the hourly T2m with the MBE of 0.96% and −2.35 °C for RH and T2m, respectively (Figure 4). Similar with the daily scale validation, the model reproduces minimum T2m better than the maximum T2m in the 4 clear sky days (Figure 4b).
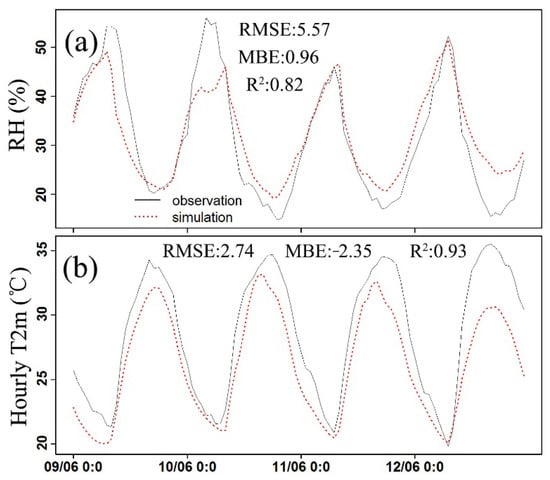
Figure 4.
Comparisons of the observed and simulated (CTL) average relative humidity (a); 2 m temperature (b) over all the 5 automatic stations in the 4 clear-sky days of 9–12 June.
From the comparison between the simulated and observed hourly wind direction and speed, the model can capture correctly the hourly variation of the wind direction an average MBE of 7.58° (Figure 5). However, the model failed to reproduce the hourly wind speed variation with an average MBE of −0.44 m s−1 (Figure 5).

Figure 5.
The hourly wind direction and wind speed validation at the 4 boundary stations during 9–12 June 2016.
3.2. The Oasis–Desert Breeze Circulation in the Context of the Mountain-Desert System
3.2.1. The Mountain-Plain Wind System
Induced by the thermal difference between mountains and basins, there are upslope winds during the day time and downslope winds (mountain wind) during the night time [22]. The station observation S5 in the mountains (see Figure 1c) and the CTL simulation present the mountain-plain wind system clearly (Figure 6a–d). At the mountain station S5, the wind direction changes from upslope winds that start around 09:00–10:00 Beijing Time (BJT) and downslope winds that start around 23:00 BJT. The CTL simulation fits very well to the observations and reproduces correctly the start of both mountain and plain circulations (Figure 6a–d). However, the simulated wind speeds are lower than the observations with an average MBE of −1.04 m s−1.
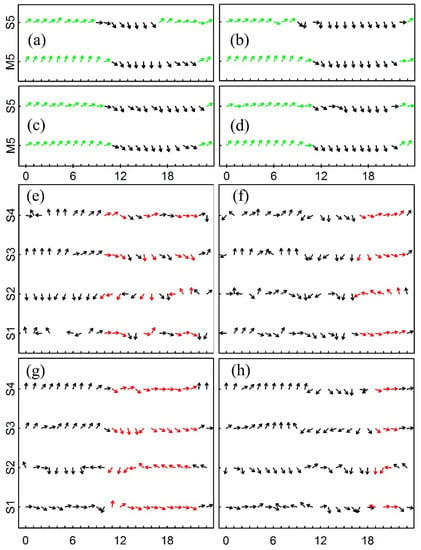
Figure 6.
The observed (S5) and simulated (M5) hourly wind direction in the mountain station and the hourly observed wind direction in the oasis boundary stations (S1–S4). (a–d,e–h) present the four days: 9, 10, 11 and 12 of June 2016; the green arrows present the mountain wind and the black arrows present the plain wind (a–d); the red arrows show the obvious period where a divergent flow is observed (e–h).
3.2.2. Oasis–Desert Breeze Circulation
We used 4 weather stations that are located at the north (S1), west (S2), south (S3) and east (S4) boundaries of the oasis area to explore the OBC (Figure 1c). According to previous studies [10,11], the oasis wet–cold island effect induces the OBC with low-level divergence and high-level convergence. So when there is strong low-level divergence occurs, the wind should blow out from the oasis area at the 4 stations simultaneously, which means that, according to the boundary direction, the wind directions should vary within 90° to 300°, 0° to 180°, 270° to 90° and 180° to 360° at the north, west, south and east boundaries, respectively.
The analysis of the observed wind directions at the oasis boundary stations indicate that the appearance time and duration of the oasis divergence are different in each day (Figure 6e–h). During the study period, the earliest appearance time of the clear divergence is at 10:00 BJT on 9 June 2016, and the latest appearance time is at 19:00 BJT on 12 June 2016; the longest duration lasts 11 h on 11 June 2016, and the shortest duration only last 3 h on 12 June 2016 (Figure 6e–h). During the 4 days, the common duration when the divergence occurs is from 19:00 to 21:00 BJT. Therefore, contrarily to previous studies [13,18], the low level divergence over oasis appears only between 19:00 and 21:00 BJT when the background mountain-plain wind system is weak during the late afternoon transition period.
3.3. Synergistic Interaction between the OBC and the UBC
3.3.1. Spatial Distribution of Temperature and Wind at the Lowest Model Level
Being the closest to the observations, the 11 June 2016 is chosen for further analysis on both oasis–desert and urban–rural breezes and their mutual interaction from the CTL simulation. Figure 7a–c presents the spatial pattern of the simulated wind speed and temperature at the lowest model level (20 m above ground level) at 09:00, 16:00 and 21:00 BJT, respectively.
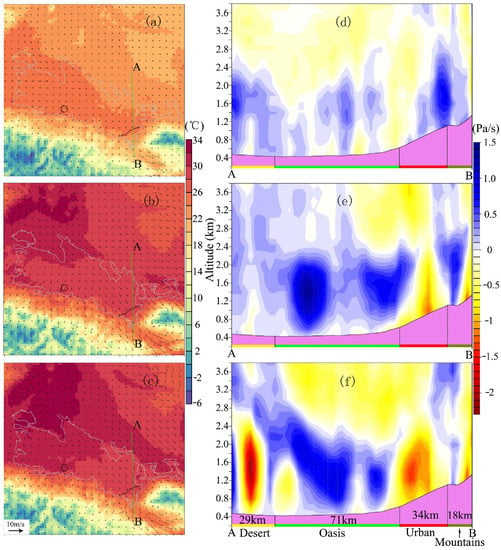
Figure 7.
The spatial patterns of the simulated wind direction (vectors) and temperature (°C, shaded contours) at the lowest model level and their corresponding vertical velocity (Pa s−1) cross section at 09:00 (a,d), 16:00 (b,e) and 21:00 (c,f) (Beijing Time, BJT) for 11 June 2016. The green line AB in (a–c) represents the location of the vertical cross section. In (d–f), the violet shaded areas at the bottom of each panel represent the terrain; along the x axis (from A to B), the yellow bar represents the extent of the desert; the green bar represents the extent of the oasis; the red bar represents the extent of the urban area; the olive green bar represents the extent of mountain areas and the number represents the width of the land use type.
At 09:00 BJT, as it is clearly shown in Figure 6c, the wind pattern is controlled by the mountain wind with no obvious OBC or UBC (Figure 6g and Figure 7a). The wind changes its direction between 10:00 and 11:00 BJT with low wind speed in the mountains (Figure 6c). From 12:00 to 18:00 BJT, the wind pattern is controlled by the plain wind (Figure 6c and Figure 7b) with a low-level divergence center in the west part of the oasis.
Different from what has been found in the previous studies [10,11,18,21], we found here that, in agreement with the observations (see Figure 6h), the significant OBC with the low level divergence occurs from 19:00 to 21:00 BJT (Figure 7c). As seen from Figure 7b, at 21:00 BJT, the wind flows out from the oasis to the surrounding desert areas through each of its boundaries and the divergence center is located near to the oasis center. During the late afternoon period where the background mountain-plain wind system is weak and in the transition period, the OBC transfers water vapor up to 32 km to the surrounding deserts (not shown), which is in agreement with the findings of Zhang et al. [18]. After 22:00 BJT, the wind direction switches to the mountain wind (Figure 6d). As the mountain wind gets strong, the OBC gets weak, and the low-level divergence disappears.
3.3.2. Vertical Velocity Cross Section
Figure 7d–f presents the corresponding vertical velocity cross sections along AB at 09:00, 16:00 and 21:00 BJT, respectively. Figure 7d shows that the vertical velocity over oasis is very weak and close to 0 Pa s−1 at 9:00 BJT, which means no signature of the OBC yet. At 16:00 BJT (Figure 7e), the updraft becomes stronger over the urban areas with mean value of −1.1 Pa s−1, which indicates the presence of the urban–rural breeze circulation in the afternoon in agreement with the literature [27]. Moreover, there is an obvious downdraft with mean value of 1.0 Pa s−1 over the north part of the oasis at the border with the desert areas. However, the oasis–desert breeze circulation has not started yet due to the strong plain wind.
At 21:00 BJT (Figure 7f), there is an updraft center over the desert with mean value of −2.0 Pa s−1, which indicates the presence of the OBC between the oases areas and the surrounding deserts [13]. It is noted that although there are clear updrafts over the urban area in the cross section of the vertical velocity, there is no convergent flows in the spatial patterns of the horizontal wind (Figure 7b,c). This could be due to the channeling effect, as it is clearly seen in Figure 7a–c, which increases the low level wind speed over the city [55,56].
The oasis–desert breeze circulation, the urban–rural breeze circulation and their synergistic interactions can be derived from the difference of the vertical velocity as it is calculated at 20:00 BJT from NoURB—Def_NoURB (Figure 8a), CTL—NoURB (Figure 8c) and CTL—Def_NoURB (Figure 8b), respectively. By comparing NoURB—Def_NoURB (Figure 8a) and CTL—Def_NoURB (Figure 8b), we can see that the downward flow (red area over oasis) is enhanced, which is induced by the existence of UBC. Similarly, by comparing CTL—Def_NoURB (Figure 8b) and CTL—NoURB (Figure 8c), we can find the upward flow (blue area) over the urban is enhanced as well, which means the existence of OBC can enhance the UBC. Therefore, it is clearly seen that both the UBC and OBC enhance each other. This synergistic interaction lasts from 16:00 until 22:00 BJT with a maximum effect at 20:00 BJT when the UBC increases the downdraft over the oasis areas by 0.8 Pa s−1 and the OBC increases the updraft over urban areas by 0.4 Pa s−1 (Figure 8).
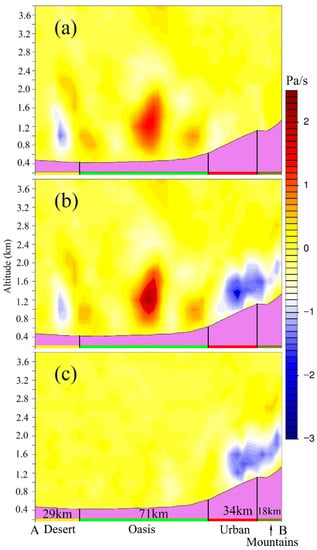
Figure 8.
The vertical cross sections of vertical velocity (Pa s−1) along AB (the green line in Figure 7a) at 20:00 BJT on the 11 June 2016 computed from: (a) NoURB—Def_NoURB, (b) CTL—Def_NoURB and (c) CTL—NoURB. The violet shaded areas at the bottom of each panel represent the terrain; along the x axis (from A to B) the yellow bar represents the extent of the desert; the green bar represents the extent of the oasis; the red bar represents the extent of the urban area; the olive bar represents the extent of mountain areas and the number represents the width of the land use type.
3.3.3. Vertical Specific Humidity Cross Section
Figure 9a–c presents the vertical specific humidity cross section. At 09:00 BJT before the oasis circulation has started, higher values of specific humidity can reach as high as 3.6 km. At lower level, the difference of the specific humidity between the oasis and desert is obvious. In the afternoon at 16:00 BJT, the oasis wet island develops as a kind of wall up to 1.2 km in the vertical with higher humidity values over oasis than in the surrounding desert area. Due to the background plain wind, the maximum wet-island effect is not found in the center of the oasis area but shifted to the border with the urban areas, with higher specific humidity values in the north part of the city of Urumqi. In the afternoon, urban areas trigger the initiation of turbulence and large eddies that increase the vertical mixing and push the wet air into high levels over the urban area. At the high atmosphere levels, the oasis is drier than the urban area [10,16].
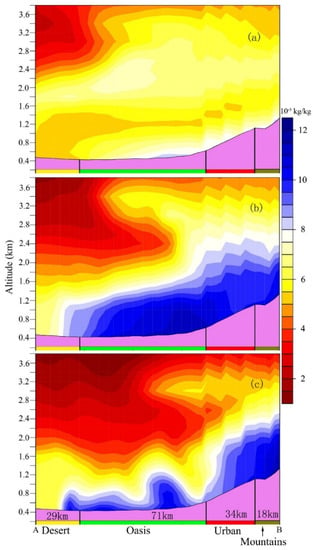
Figure 9.
The vertical cross sections of specific humidity (10−3 kg/kg) along AB (the green line in Figure 7a) at 09:00 (a), 16:00 (b) and 21:00 (c) BJT on the 11 June 2016. The violet shaded areas at the bottom of each panel represent the terrain; along the x axis (from A to B) the yellow bar represents the extent of the desert; the green bar represents the extent of the oasis; the red bar represents the extent of the urban area; the olive bar represents the extent of mountain areas and the number represents the width of the land use type.
At 21:00 BJT, the extension of the oasis wet island can reach up to 20 km into the surrounding desert (Figure 9c) while previous study shows that, even for a relatively smaller (30 × 30 km) oasis, the circulation can reach up to 40 km into the desert [10]. The absence of background winds such as the mountain/plain wind in their study region may partly explain the difference. With the development of the OBC at the interface with the surrounding desert areas, the wet atmosphere layers are closer (less than 0.8 km for values above 9.0 × 10−3 kg/kg) to the oasis areas (Figure 9c), helping to keep the wet condition of the oasis. For the desert, the OBC brings the cold and wet air into the desert, which increases the humidity of the surrounding desert and protects the desert ecosystem [13,57].
3.3.4. Surface Energy Balance
Figure 10 presents the diurnal evolution of the surface energy balance in three grid points representing the city center of Urumqi Figure 10a, the center of the oasis Figure 10b and in the desert area Figure 10c as an average for the 11 June 2016. Note that the sign convention is positive-downwards (negative flux is cooling the surface). During daytime, the radiation difference between the city center of Urumqi (Figure 10a) and both the center of the oasis areas (Figure 10b), and the desert location is positive; the urban areas gain more energy, an effect mainly controlled by the low effective urban albedo. The midday difference is typically around +36 W m−2 and +112 W m−2 between the city center of Urumqi and the center of oasis and between the city center of Urumqi and the desert location, respectively. The net radiation in the oasis is also higher (+75 W m−2) than that in the desert location, which is in agreement with previous observational studies [12,21,58,59,60]. Throughout the night, both the city center of Urumqi and the desert location lose more energy than the oasis [12,21]. Daytime sensible heat values are more than twice (2.4) as large in the desert areas as in the oasis location. The sensible heat in the desert is also higher (+14 W m−2 at midday) than that in the city center of Urumqi. The magnitude of maximum daytime sensible heat is characteristically around 41% of the maximum daytime net radiation in the desert location, 29% at the city center of Urumqi and only 14% in the oasis center.
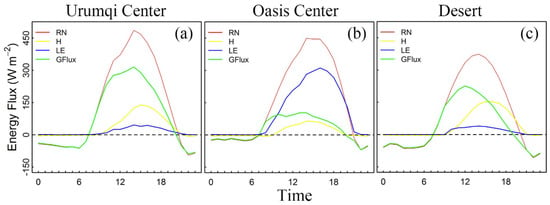
Figure 10.
The diurnal variation of the surface energy flux on the 11 June 2016 computed from the CTL simulation at Urumqi city center (a), oasis center (b) and a grid point representing the desert (c). RN: net radiation; H: sensible heat; LE: latent heat; GFlux: soil heat flux. Note that the sign convention is positive-downwards (negative flux is cooling the surface).
Daytime maximum values of soil heat flux are typically three time as large in the urban areas as in the center of oasis. Daytime maximum values of storage heat are 65%, 60% and 23% of daytime maximum net radiation at city center of Urumqi, the desert and oasis center, respectively. In the desert location peak values are reached 1–2 h before the maximum intensity of net radiation is reached. The heat stored during the day is released during the evening, which slows down urban surface cooling. The bigger contribution coming from the storage heat flux with respect to the sensible heat in the city of Urumqi is in agreement with other observational studies conducted in dry climate cities [61]. In the desert location, the storage flux is dominant in the morning while the sensible heat flux is dominant in the afternoon.
Contrarily to the urban and desert location, the latent heat flux represents the dominant contribution of the energy partitioning in the oasis center with maximum daily value representing 70% of the daytime maximum net radiation. In the center of the oasis, at 20:00 BJT, the latent heat flux exceeds the available net radiation, and the corresponding sensible heat flux is negative indicating the signature of the oasis breeze circulation [13].
3.3.5. Oasis Cold Island and Urban Heat Island Interactions
Figure 11a presents the 4-day average mean of the diurnal evolution of the maximum UHI intensity over both Urumqi (_U) and Shihezi (_S) cities. The maximum UHI intensities are extracted from 2 m temperature differences from Def_URB—Def_NoURB, CTL—NoURB and CTL—Def_NoURB within the boundaries of Urumqi and Shihezi cities. The timing of both sunrise (SR) and sunset (SS) is shown with vertical lines. It is clear that the oasis expansion decreases the nocturnal UHI for both Urumqi and Shihezi by 0.8 °C and 0.7 °C, respectively. During the daytime the oasis expansion has a neutral effect on Urumqi while for Shihezi, being within the oasis areas, the UHI decreases from 13:00 BJT with difference up to 0.6 °C during the OBC event. The combined effect of urbanization and oasis expansion has a neutral effect during the night for both cities since both effects cancel each other. However, during the day, the combined effect increases the maximum UHI in Urumqi from the early morning 09:00 BJT up to 17:00 BJT with maximum increase of 1.2 °C at 11:00 BJT.
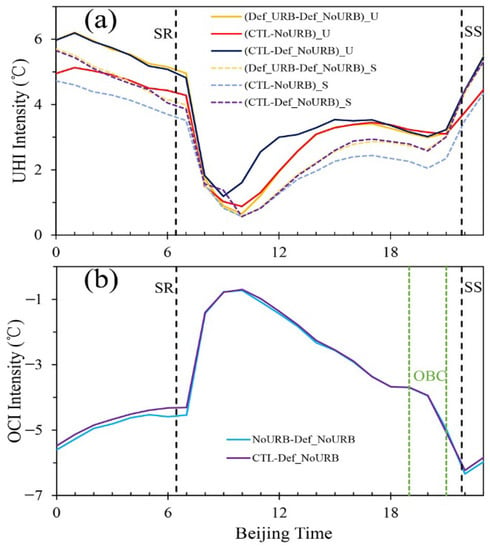
Figure 11.
The 4-day average mean of the diurnal evolution of (a) the maximum UHI intensity over both Urumqi (_U) and Shihezi (_S) cities extracted from 2 m temperature differences from Def_URB—Def_NoURB, CTL—NoURB and CTL—Def_NoURB. The timing of both sunrise (SR) and sunset (SS) is shown with vertical lines and (b) the maximum OCI intensity over the oases’ areas extracted from 2 m temperature differences between NoURB − Def_NoURB and CTL − Def_NoURB. The timing of the OBC event is shown with green vertical lines.
Figure 11b presents the 4-day average mean of the diurnal evolution of the maximum OCI intensity over the oases areas extracted from 2 m temperature differences between NoURB—Def_NoURB and CTL—Def_NoURB. The timing of the OBC event is shown with green vertical lines. It is clear that the oasis expansion decreases the near surface temperature day and night with cooling effect up to −6.3 °C during nighttime. The OCI is symmetric to the UHI with bigger values during the night than during the day, with minimum cooling effect of −0.7 °C in the early morning around 10:00 BJT. Between 10:00 and 18:00 BJT, with the increase of the afternoon evapotranspiration, the cooling effect increases at a rate of −0.4 °C h−1 while during the OBC event (19:00–21:00 BJT) the cooling rate is more than double, with value around −0.9 °C h−1. The impact of the urbanization derived from the difference between CTL—Def_NoURB and NoURB—Def_NoURB is neutral with a slight decrease of the cooling effect by 0.1 °C during the night.
4. Conclusions
In this study, the oasis breeze circulation is investigated from observations and model simulations in the context of the mountain-plains wind system in the North Slope of the Tianshan Mountains. The oasis–desert and the urban–rural breeze circulations, as well as their interactions, are investigated by using the atmospheric model ALARO coupled to the land surface model SURFEX, which is applied for the first time in arid area.
We improved the default land cover data of the ECOCLIMAP database using the land cover data that were generated by the Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography and evaluated the ALARO-SURFEX performance with 53 national meteorological stations spread in the Xinjiang province of China and 5 automatic meteorological stations in the study area. The validation results show that the model can capture the daily and hourly variation of the 2 m temperature and relative humidity in summer, although it underestimates the relative humidity and the daily 2 m temperature. This underestimation is mainly caused by two reasons. One is that the climate model ALARO gives more clouds resulting in the underestimation of daily maximum temperature. Another is that the ALARO-SURFEX model fails to reproduce the dynamic of soil water content. Besides, the complex terrain in our study area may contribute to the biases to some extent.
Firstly, we proved the existence of the oasis breeze circulation by analyzing the wind directions from four automatic stations distributed around the oasis boundary. We found that the appearance of the low-level divergence changes in the 4 clear sky days. However, the common time in the 4 days when the significant low-level divergence appears is from 19:00 to 21:00 BJT when the background mountain-plains wind system is very weak and in transition period. After 22:00 BJT, the oasis breeze is interrupted by the strong background wind. Meanwhile, we found that the mountain wind enhances the flow from oasis to desert, which would protect the vegetation in the surrounding desert by transporting much more water vapor into the desert. The model reproduces correctly the oasis–desert circulation with negative sensible heat flux and latent heat flux bigger than the net radiation at 20:00 BJT. The model simulates a synergistic interaction between oasis–desert breeze and urban–rural breeze from 16:00 BJT until 22:00 BJT with a maximum effect at 20:00 BJT when the downdraft over oasis (updraft over urban) areas increases by 0.8 (0.4) Pa s−1. Oasis expansion decreases the intensity of the nocturnal UHI for both Urumqi and Shihezi cities. During the day, the oasis expansion decreases the UHI in Shihezi while its effect is neutral in Urumqi. The combined effect of both oasis expansion and urbanization is neutral during the night for both cities; however, during the day, the UHI is bigger in Urumqi while for Shihezi the effect is neutral. Finally, the oasis cold island is symmetric to the urban heat island with bigger values during the night than during the day, and the impact of urbanization is found more during the night with a slight decrease of the oasis cooling effect. The new findings from this study enhance our understanding of the interaction between oasis and urban areas under the background of a mountain-desert system in Xinjiang.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.H., G.L. and P.C.; methodology, R.H. and P.C.; software, P.T.; validation, P.C., R.H. and H.H.; formal analysis, P.C.; investigation, P.C.; resources, R.H. and P.T.; data curation, P.C.; writing—original draft preparation, P.C.; writing—review and editing, P.C., C.L. and M.Z.; visualization, P.C. and J.W.; supervision, G.L., P.T. and P.D.M.; project administration, G.L.; funding acquisition, G.L. and R.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the International Partnership Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, grant number 131965KYSB20160004, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 41671108. Rafiq Hamdi is supported by the China Academy of Sciences President’s International Fellowship Initiative (PIFI), grant number 2018VMB0006.
Acknowledgments
We want to thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions to this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Luo, G.; Zhou, C.; Chen, X. Human-induced spatio-temporal changes of oasis through landscape pattern analysis:a case study of oasis in the Sangong Rive. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2005, 25, 2197–2205. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, G.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, W. Sustainable land-use patterns for arid lands: A case study in the northern slope areas of the Tianshan Mountains. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 510–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielke, R.A.S. Influence of the spatial distribution of vegetation and soils on the prediction of cumulus convective rainfall. Rev. Geophys. 2001, 39, 151–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bavel, C. Changes in canopy resistance to water loss from alfalfa induced by soil water depletion. J. Agric. Meteorol. 1967, 4, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, G. The microclimate character and “cold island effect” over the oasis in Hexi region. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 1987, 11, 390–396. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Ji, G.; Shen, Z.; Cheng, L.; Chen, J.; Li, S. Some achievements in scientific research during HEIFE. Plateau Meteorol. 1994, 13, 225–236. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Lu, S.; Gao, Y.; Guo, J. Simulated effects of soil moisture on oasis self-maintenance in a surrounding desert environment in Northwest China. Int. J. Clim. 2015, 35, 4116–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hintz, M.; Li, X. Evaluation of atmosphere–land interactions in an LES from the perspective of heterogeneity propagation. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 33, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lü, S. Numerical simulation of the critical scale of oasis maintenance and development in the arid regions of northwest China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 21, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.C.; Lu, S.; Chen, Y. A numerical modeling study on desert oasis self-supporting mechanisms. J. Hydrol. 2005, 312, 256–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Lü, S.; Zhang, T.; Guo, J.; Gao, Y.; Bao, Y.; Wen, L.; Luo, S.; Liu, Y. Numerical simulations of the atmospheric and land conditions over the Jinta oasis in northwestern China with satellite-derived land surface parameters. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D06114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Lu, S.; Jin, J. Integrating remote sensing data with WRF for improved simulations of oasis effects on local weather processes over an arid region in northwestern China. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, K.; Zhou, Y. Progress in the study of oasis-desert interactions. Agric. Meteorol. 2016, 230, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Gao, Y. Some new understandings of processes at the land surface in arid area from the HEIFE. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 1994, 52, 285–296. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Lu, S.; Zhang, T.; Ao, Y.; Li, S.; Bao, Y.; Wen, L.; Luo, S. Impacts of inhomogeneous landscapes in oasis interior on the oasis self-maintenance mechanism by integrating numerical model with satellite data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3729–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, R. Water vapor exchange between soil and atmosphere over a Gobi surface near an oasis in the summer. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 1917–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Lü, S.; Ao, Y. Analysis on the interaction between turbulence and secondary circulation of the surface layer at Jinta oasis in summer. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 27, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Luo, G.; Hamdi, R.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.; Maeyer, P.D.; Kurban, A. Numerical Simulations of the Impacts of Mountain on Oasis Effects in Arid Central Asia. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arritt, R.W.; Wilczak, J.M.; Young, G.S. Observations and numerical modeling of an elevated mixed layer. Mon. Weather Rev. 1992, 120, 2869–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Avissar, R. Impact of land-surface moisture variability on local shallow convective cumulus and precipitation in large-scale models. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1994, 33, 1382–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, K.; Matsuda, M.; Sato, R. Oasis effect observed at Zhangye oasis in the Hexi corridor, China. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 1997, 75, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roland, B.S. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Luo, G. Researches and progress of oasis ecology in arid areas. Arid Land Geogr. 2008, 4, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Luo, G.; Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Lv, N.; Wang, X. An analysis of oasis evolution based on land use and land cover change: A case study in the Sangong River Basin on the northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.; Hamdi, R.; Luo, G.; He, H.; Zhang, M.; Termonia, P.; De Maeyer, P. Agriculture intensification increases summer precipitation in Tianshan Mountains, China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 227, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, D.; Blake, R.; Grimm, A.; Hamdi, R.; Kim, Y.; Horton, R.; Rosenzweig, C. Urban Climate Science. In Climate Change and Cities: Second Assessment Report of the Urban Climate Change Research Network; Rosenzweig, C., Romero-Lankao, P., Mehrotra, S., Dhakal, S., Ali Ibrahim, S., Solecki, W.D., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 27–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R.; Mills, G.; Christen, A.; Voogt, J.A. Urban Climates; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hao, X.; Shen, Y. Hydrology and water resources variation and its response to regional climate change in Xinjiang. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, J. Spatial and temporal trends of climate change in Xinjiang, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Hu, Q.; Tian, H. Temperature Changes in Central Asia from 1979 to 2011 Based on Multiple Datasets. J. Clim. 2013, 27, 1143–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Liu, T.; Frankl, A.; Duan, Y.; Meng, F.; Bao, A.; Kurban, A.; De Maeyer, P. Defining spatiotemporal characteristics of climate change trends from downscaled GCMs ensembles: How climate change reacts in Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Clim. 2018, 38, 2538–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, L.; Piriou, J.-M.; Brožková, R.; Geleyn, J.-F.; Banciu, D. Cloud and precipitation parameterization in a meso-gamma-scale operational weather prediction model. Mon. Weather Rev. 2009, 137, 3960–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termonia, P.; Fischer, C.; Bazile, E.; Bouyssel, F.; Brožková, R.; Bénard, P.; Bochenek, B.; Degrauwe, D.; Derková, M.; El Khatib, R. The ALADIN System and its canonical model configurations AROME CY41T1 and ALARO CY40T1. Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubnová, R.; Hello, G.; Bénard, P.; Geleyn, J.-F. Integration of the fully elastic equations cast in the hydrostatic pressure terrain-following coordinate in the framework of the ARPEGE/Aladin NWP system. Mon. Weather Rev. 1995, 123, 515–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, R.; Van de Vyver, H.; Termonia, P. New cloud and microphysics parameterisation for use in high-resolution dynamical downscaling: Application for summer extreme temperature over Belgium. Int. J. Clim. 2012, 32, 2051–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Troch, R.; Hamdi, R.; Van de Vyver, H.; Geleyn, J.-F.; Termonia, P. Multiscale performance of the ALARO-0 model for simulating extreme summer precipitation climatology in Belgium. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 8895–8915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giot, O.; Termonia, P.; Degrauwe, D.; De Troch, R.; Caluwaerts, S.; Smet, G.; Berckmans, J.; Deckmyn, A.; De Cruz, L.; De Meutter, P. Validation of the ALARO-0 model within the EURO-CORDEX framework. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berckmans, J.; Giot, O.; Troch, R.D.; Hamdi, R.; Ceulemans, R.; Termonia, P. Reinitialised versus continuous regional climate simulations using ALARO-0 coupled to the land surface model SURFEXv5. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termonia, P.; Van Schaeybroeck, B.; De Cruz, L.; De Troch, R.; Caluwaerts, S.; Giot, O.; Hamdi, R.; Vannitsem, S.; Duchêne, F.; Willems, P.; et al. The CORDEX.be initiative as a foundation for climate services in Belgium. Clim. Serv. 2018, 11, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Mearns, L.O. Introduction to special section: Regional climate modeling revisited. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 6335–6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Corti, T.; Davin, E.L.; Hirschi, M.; Jaeger, E.B.; Lehner, I.; Orlowsky, B.; Teuling, A.J. Investigating soil moisture–climate interactions in a changing climate: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2010, 99, 125–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, V.; Le Moigne, P.; Martin, E.; Faroux, S.; Alias, A.; Alkama, R.; Belamari, S.; Barbu, A.; Boone, A.; Bouyssel, F. The SURFEXv7. 2 land and ocean surface platform for coupled or offline simulation of earth surface variables and fluxes. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 929–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noilhan, J.; Planton, S. A simple parameterization of land surface processes for meteorological models. Mon. Weather Rev. 1989, 117, 536–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, V. A physically-based scheme for the urban energy budget in atmospheric models. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2000, 94, 357–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, R.; Van de Vyver, H.; De Troch, R.; Termonia, P. Assessment of three dynamical urban climate downscaling methods: Brussels’s future urban heat island under an A1B emission scenario. Int. J. Clim. 2014, 34, 978–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, R.; Degrauwe, D.; Duerinckx, A.; Cedilnik, J.; Costa, V.; Dalkilic, T.; Essaouini, K.; Jerczynki, M.; Kocaman, F.; Kullmann, L. Evaluating the performance of SURFEXv5 as a new land surface scheme for the ALADINcy36 and ALARO-0 models. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, R.; Giot, O.; De Troch, R.; Deckmyn, A.; Termonia, P. Future climate of Brussels and Paris for the 2050s under the A1B scenario. Urban Clim. 2015, 12, 160–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, R.; Duchêne, F.; Berckmans, J.; Delcloo, A.; Vanpoucke, C.; Termonia, P. Evolution of urban heat wave intensity for the Brussels Capital Region in the ARPEGE-Climat A1B scenario. Urban Clim. 2016, 17, 176–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, D.P. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, T.T.; Peterson, R.A.; Treadon, R.E. A tutorial on lateral boundary conditions as a basic and potentially serious limitation to regional numerical weather prediction. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 2599–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, T. Lateral boundary conditions for limited area models. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 140, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, V.; Champeaux, J.-L.; Chauvin, F.; Meriguet, C.; Lacaze, R. A global database of land surface parameters at 1-km resolution in meteorological and climate models. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 1261–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faroux, S.; Kaptué Tchuenté, A.; Roujean, J.-L.; Masson, V.; Martin, E.; Moigne, P.L. ECOCLIMAP-II/Europe: A twofold database of ecosystems and surface parameters at 1 km resolution based on satellite information for use in land surface, meteorological and climate models. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 563–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, C. WRF simulation and downscaling of local climate in Central Asia: WRF SIMULATION AND DOWNSCALING IN CENTRAL ASIA. Int. J. Clim. 2017, 37, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savijärvi, H.; Liya, J. Local winds in a valley city. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2001, 100, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, J.L.F.; Pereira Filho, A.J.; Karam, H.A.; Vemado, F.; Masson, V. Effects of explicit urban-canopy representation on local circulations above a tropical mega-city. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2018, 166, 83–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Land surface process experiments and interaction study in China-from HEIFE to IMGRASS and GAME-TIBET/TIPEX. Plateau Meteorol. 1999, 18, 280–293. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto, O.; Sahashi, K.; Wang, J. Heat budget and evapotranspiration at an oasis surface surrounded by desert. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 1995, 73, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, C. Simulating Energy Balance and Hydrologic Cycle in a Desert-Oasis Transitional Zone Using RZWQM2; McGill University Libraries: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Zhao, W.; Li, S. Regional evapotranspiration rate of oasis and surrounding desert. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 3409–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cueto, R.; Jauregui, E.; Tejeda, A. Urban/rural Energy Balance Observations in a Desert City in Northern Mexico. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Urban Climate, ICUC-5, Łódź, Poland, 1–5 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).