Abstract
The range and time of the environmental effects of Asian dust are closely dependent on the pathways and the speed of dust plume movement. In this study, the occurrence and movement of two dust storms in China in May 2017 were examined by using open space- and ground-based measurement data and the backward trajectories of dust plumes. Results from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) reanalysis data showed that the dust storms were caused by the rapid coupling development of Mongolian cyclones and Asian highs. After the dust plumes arrived at the Southeastern China in the first dust event, the stable weather conditions and the Asian high slowed down the movement of the plumes, leading to the gradual diffusion of dust particles. Moreover, the Asian high in the first event and the Huabei low (a low-pressure system in North China Plain) in the second altered the movement direction of the dust plumes from southward to northward, which we denote as the “dust reverse transport (DRT)”. The DRT occurred only within the lower troposphere even though dust plumes could extended to 5–10 km in vertical direction. Statistical results of 28 spring dust events occurred in 2015–2018 showed that all these dust storms were triggered by Mongolian cyclones and/or Asian highs, and approximately 39% moved as the DRT, indicating about one third of severe spring dust storms could influence larger areas or longer time than the remained ones.
1. Introduction
Deserts in the Asian continent emit a great quantity of mineral dust (approximately 800 Tg/year) into the atmosphere annually [1,2]. The dust particles can influence the energy budget in the atmosphere not only by absorbing and scattering short- and long-wave radiation but also by modifying the optical properties and lifetime of clouds [1,3,4].
The occurrence and transport of dust storms at desert areas are dependent on the synoptic weather. Wang et al. [5] found that the regions which were affected by monsoon could have significant high frequency months of dust storms in East Asia, such as Hetao Region and Northeastern China Region. In the Gobi and desert areas of China, dust storms are often generated by developing cyclones. During its development, a cyclone, which causes a dust storm, usually generates a strong cold front and moves southeastward under the induction of the upper level jet stream, accompanied with the intensification of the dust storm [6].
The interaction between dust and other pollutants in the atmosphere during the long-range transport of the dust is one of the key processes changing physical and chemical properties of dust particles and their subsequent regional and global environmental effects [7,8]. Floating in the air, dust particles can provide sites for anthropogenic pollutants attachment, and further promotes chemical conversions, e.g. heterogeneous reactions on the surface of dust particles [9,10,11,12]. Sometimes in special circulation fields, dust particles may be transported back to the regions where they had passed by [13,14,15]. These regions suffered dust weather in a prolonged time, which deteriorated the air quality and harmed to human health [16]. In a dust backflow event occurring in Beijing in 2015, Pan et al. [14] found a continuous coating process on the surface of dust particles and Wang et al. [13] simulated that 17% of nitrate and 11% of sulfate in fine mode were produced by heterogeneous reactions and nearly all nitrate and sulfate in the coarse mode were attributed to the heterogeneous reactions. These chemical alterations may evidently change the optical and hydroscopic characteristics of dust aerosols and subsequently modify their ability acting as cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) and ice nuclei particle (INP), and influence the cloud processes consequently [13,14,17]. These processes are critical to the direct and indirect radiative forcing of dust aerosols, as well as the regional climate effects in East Asia [1,18]. Therefore, the analysis of the transport pathways of the dust will be beneficial for understanding the dust-pollutants interaction and the climate effects [16,19,20].
The North China Plain (NCP, shown in Figure 1), as one of the largest plains and the most intensively populated area in China, is frequently influenced by dust plumes originating from the Gobi desert in spring. Two severe dust events occurred from May 3 to 8 and May 11 to 14 in 2017. In this study, we focused on the effects of the synoptic weather on the occurrence and the movement of the dust plumes and the impact of transport pathways on local air quality. The spatial and temporal distributions of dust particles and the essential roles of synoptic weather in the two events are described in Section 3.1 and Section 3.2. In Section 3.3, the characteristics of the “dust reverse transport (DRT)” and the corresponding dynamic causes are investigated. Finally, we summarize the weather systems that triggered dust storms and the synoptic features that induced the DRT of 28 spring dust events from 2015 to 2018.
Figure 1.
The network of air quality monitoring stations (red dots). The region in the black rectangle represents the North China Plain (NCP).
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Air Quality Data and Synoptic Data
The air quality data publicly issued by the Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE) of the People’s Republic of China were used to study the transport processes of dust aerosols in the near-surface layer. The air quality data includes hourly mass concentrations of PM2.5 and PM10. The network of air quality monitoring stations and the geographical location of NCP are shown in Figure 1. In this study, we searched typical dust events by comparing the satellite observations with the ground-based PM10 data and figured out the suitable criterion (PM10 > 150 μg/m3 and the ratio of PM2.5 to PM10 smaller than 0.4) to determine the stations with dust plume [21]. The Cressman interpolation method [22] was used to describe the horizontal distribution of the mass concentrations of PM10.
The meteorological data from the ERA Interim reanalysis database of the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) (http://apps.ecmwf.int/datasets/data/interim-full-daily/levtype=pl/) were used to describe the synoptic weather associated with the occurrence and movement of dust storms.
2.2. Satellite Data
The Global Ozone Monitoring Experiment-2 (GOME-2) carried by the satellite MetOp-B is designed to measure the total column and profiles of atmospheric ozone and the distribution of other key atmospheric constituents with a very wide swath width of 1920 km [23]. The satellite flies at a sun-synchronous polar orbit with the altitude of about 840 km, circling the earth 14 times each day [23]. The high Absorbing Aerosol Index (AAI) in Gobi Desert region often indicates the existence of dust particles in the atmosphere. Therefore, the AAI daily images (http://www.temis.nl/airpollution/absaai/) from GOME-2 were applied to identify dust plumes that originated from Gobi desert and transported to Northern China.
The dataset of altitude-resolved measurements of the atmosphere was acquired from data of the Cloud Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations (CALIPSO) [24,25]. CALIPSO is distinctively able to provide nearly global measurements of aerosol and cloud vertical distributions with high spatial resolution [25,26], and its level 2 data provide information on the vertical distribution of clouds/aerosols, including dust aerosols, with the horizontal resolution of 5 km.
2.3. Backward Trajectories
The on-line HYbrid Single-particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) Model of NOAA was applied to calculate pathways of dust plumes (https://ready.arl.noaa.gov/HYSPLIT.php). In order to investigate the sources of dust plumes, 48-h air mass backward trajectories were computed and initialized at altitudes of 200 m and 1000 m above ground level (AGL) at the early stage of the dust events. The gridded data provided by the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) with a horizontal resolution of 1° × 1° were used in the HYSPLIT model.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Dust Transport Process in the Near-surface Layer
3.1.1. First Dust Event (3–8 May 2017)
The first dust event had three stages with two stages of dust uplifts (Stage Ι: 3–4 May 2017 and Stage ΙΙ: 5–6 May 2017), and the stage of dust diffusion (Stage ΙΙΙ: 6–8 May 2017). Figure 2a–i illustrate the synoptic weather at 1000 hPa and the distribution of surface PM10 concentration, as well as the back-trajectories of dust air masses.
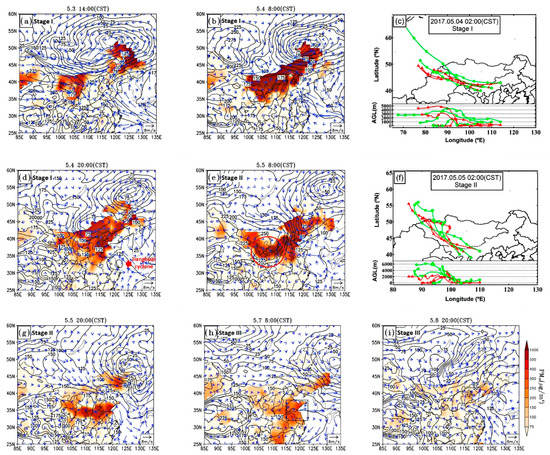
Figure 2.
The distribution of PM10 mass concentrations in the surface layer (shading, unit: μg/m3) and the synoptic features at 1000 hPa China Standard Time (CST) during the first dust event for stage I (a,b,d), stage II (e,g) and stage III (h,i). The black curves and blue vectors represent the corresponding geopotential heights (unit: gpm) with 25-gpm intervals and the wind velocity (unit: m/s). Air mass backward trajectories for 48 hours at three sites with the ending heights of 200 m (red lines) and 1000 m (green lines) above ground level (AGL) for stage I (c) and stage II (f). The area marked by the red circle in (e) means the area being affected by a new dust plume. The enclosed area by black rectangle in (h) represents the region where the phenomenon of dust reverse transport (DRT) occurred.
During the first stage, the Mongolian cyclone (52° N, 118° E) intensified quickly, leading to strong surface wind and causing the dust-uplifting (Figure 2a). At 14:00 CST (China Standard Time: GMT + 08:00) on 3 May, the strong wind (>16 m/s) area was near the boundary between China and Mongolia (Figure S1a). At the same time, the Asian cold high (47° N, 93° E) to the northwest also developed rapidly (Figure 2b). The dust storm occurred at western Inner Mongolia and moved to the east and southeast closely associated with the near-surface wind field, passing Inner Mongolia and the Loess Plateau before arriving at Northeastern China and Northern China (Figure 2b,d), which affected a vast expanse of Northern China. The PM10 concentration exceeded 1000 μg/m3 in a large region. The backward trajectories of the air masses at 02:00 CST on 4 May (Figure 2c) indicate that the dust particles came from the deserts in western Inner Mongolia and Southern Mongolia. On the night of 4 May, because a weak low-pressure system (33° N, 122° E, called the Jianghuai cyclone, labeled in Figure 2d) located at the coastal area to the East China Sea, the dust plume was blocked. Therefore, we can see a large PM10 gradient in mass concentration in the eastern edge of the dust plume.
During the second stage, the Asian cold high moved quickly southeastward, leading to the large pressure gradient between the high and low pressure areas, and stimulating a new dust plume in Northwestern China (marked by a red circle in Figure 2e). The backward trajectories at 02:00 CST on 5 May (Figure 2f) indicate further that the dust was also originated from western Inner Mongolia and Southern Mongolia. The new plume of dust moved faster than the previous one. At this stage, the Jianghuai cyclone declined, which allowed more dust to be advected southwardly (Figure 2g). In fact, similar dust plume movements were reported in previous studies that high-pressure systems carrying cold air after low-pressure systems, transported dust aerosols to lower latitude areas [27,28]. Due to the decline of the Asian high in Southern China, the pressure distribution tended to be uniform, which slowed down the movement of the dust plume, and the diffusion of dust became more significant, i.e., the Stage III (Figure 2h). On 8 May, PM10 concentration had decreased substantially and a new low-pressure system occurred in Eastern China. The nearby stronger wind from the sea made the atmospheric condition more favorable for dust diffusion (Figure 2i). During the Stage III, the movement direction of the dust plume in Eastern China changed from southward to northeastward. We call the phenomenon the “dust reverse transport (DRT)” in this study.
3.1.2. Second Dust Event (11–14 May 2017)
For the second dust event, the dust storm event was also triggered by the development of a Mongolian cyclone. On 11 May, the Mongolian cyclone developed rapidly in the southeast of Lake Baikal (53° N, 106° E, labeled in Figure 1) followed by an Asian high (Figure 3a). Under the joint effect of both the Mongolian cyclone and the Asian high, the pressure gradient in Eastern Mongolia was very large (0.7–1 equipotential line per latitude), inducing very strong wind and prompting the occurrence of the dust storm. Under the northwest wind, the dust plume moved southeastward (Figure 3a,b).
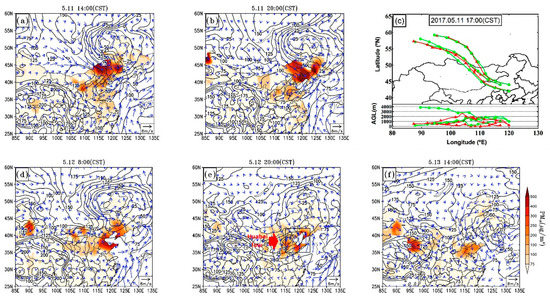
Figure 3.
The distribution of PM10 mass concentrations in the surface layer (shading, unit: μg/m3) and the synoptic features at 1000 hPa China Standard Time (CST) during the second dust event (a,b,d–f). The black curves and blue vectors represent the corresponding geopotential heights (unit: gpm) with 25-gpm intervals and the wind velocity (unit: m/s). Air mass backward trajectories for 48 h at three sites are shown in (c) with the ending heights of 200 m (red lines) and 1000 m (green lines) above ground level (AGL). The enclosed area by black rectangle in (e) represents the region where the phenomenon of dust reverse transport (DRT) occurred.
The backward trajectories (Figure 3c) at 17:00 CST on 11 May indicate that the dust plume was originated from the Gobi Desert in eastern and/or Southeastern Mongolia which was different from the first dust event. The Asian high rarely influenced the transport of the dust plume afterwards because of its rapid declining. Influenced by the north wind in the trough at the south of the Mongolian cyclone (Figure 3b), dust aerosols were transported to lower latitudes. On 12 May, dust aerosols arrived at the coastal areas of the Yellow Sea (Figure 3d). The trough at the south of the Mongolian cyclone was deepened and the low-pressure center was divided into two (Figure 3e). Dust particles were moving mainly around the southern low-pressure center (called the Huabei low in Chinese, labeled in Figure 3e) and the wind direction near the Bohai Sea changed to northward gradually. That means the movement of the dust plume also changed, which we call DRT as well. On 13 May, the Huabei low moved eastward, and dust particles left at Northern China continued to move southward by the northerlies at the rear of the low (Figure 3f).
3.2. Synoptic Weather at 500 hPa
The development of a dust storm even depends on the synoptic situation at elevated layers, especially the intensity and the location of jet streams [19,29,30]. At the beginning of the two dust events described above, the synoptic patterns at the 500-hPa level in the middle and high latitudes of East Asia were ridge-trough-ridge configurations (Figure 4a,d). As the troughs moved eastward and deepened, gales and cold air were brought to warm regions in the south, with the jet stream following behind. The troughs closed at Northeastern China afterward, becoming cold vortexes with the different timescales in each event (Figure 4b,e). After the vortexes arrived at Japanese areas, they declined gradually and became large troughs (Figure 4c,f). During the early stage of dust storms, the gradient of geopotential height near the surface was significantly large and the strong winds areas were broad, locating at the desert areas (Figure S1a–c). At the same time, the upper troposphere had also a large gradient of geopotential height. The dust transport in the near-surface layer was influenced significantly by the synoptic situation of upper layer. For instance, from 4 May to 5 May in the first dust event, guided by the rapidly moving trough at 500 hPa (Figure S1d–f), the strong wind area at 1000 hPa moved very quickly, leading to the rapid movement of the dust plume.
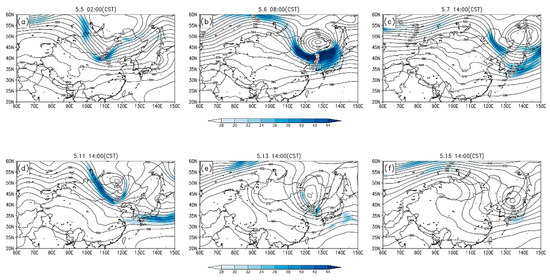
Figure 4.
Geopotential heights (black curves, unit: gpm) and jet streams (shading, unit: m/s) for the first (a–c) and second (d–e) dust events at 500 hPa.
3.3. The Verticle Distribution of Dust Particles and the Reverse Transport of Dust Plumes
The vertical structures of aerosol types observed by CALIPSO and the corresponding satellite orbits are shown in Figure 5. Dust aerosols and polluted dust aerosols were the main aerosol types in both events and were mainly distributed in the middle and lower troposphere in the range of 0–5 km (AGL), up to approximately 8~10 km somewhere. Dust plumes were always close to the surface, which is similar to the results Tan et al. [31] found.
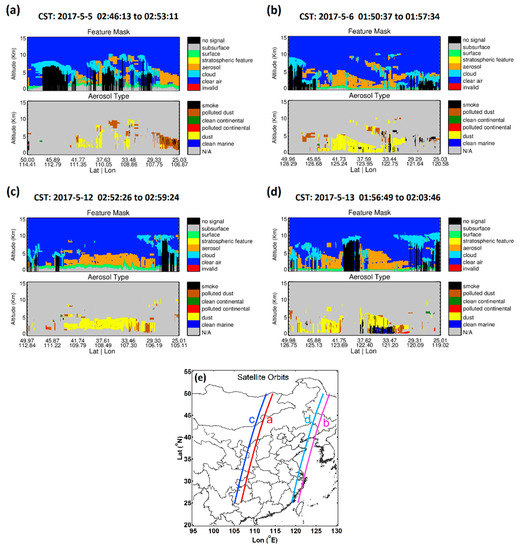
Figure 5.
The altitude-orbit cross-section of Cloud Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations (CALIPSO) observations in the first (a,b) and second dust event (c,d). The altitude refers to the height above local mean sea level. The corresponding satellite orbits are depicted in (e).
As mentioned previously, the DRT phenomena occurred in the late stage of the two dust events when the transport direction of dust plumes reversed. In order to verify the corresponding dynamic conditions, we investigated the flow field profiles (Figure 6a(ii),b(ii)) along the prevailing wind direction from location A (33.0° N, 117.3° E) to location B (36.0° N, 120.3° E) for the first dust event (the locations of A and B and the cross section are shown in Figure 6a(i),b(i) by green dots and light blue lines, respectively). At 20:00 CST on 5 May, dust plumes had arrived at the coastal zone of the Yellow Sea (Figure 6a(i)). At 08:00 CST on 6 May, a weak high was located at the Yangtze River Basin at 1000 hPa, and the southward movement of the dust plume slowed significantly (not given). As the high-pressure system continue to move eastward, the wind direction turned northward or northeastward at the dust reverse transport zone (marked by the black rectangle in Figure 2h), and the movement of the dust plumes had reversed correspondingly at 20:00 CST on 6 May (Figure 6b(i)). At location A, PM10 concentration was very high (>500 μg/m3), while was relative low at location B (<400 μg/m3). This DRT phenomenon was also confirmed by the back-trajectories (Figure S2a) and it continued in the next 30 hours (Figure S3). This is the reason why a second deterioration of air quality occurred within a short time in many cities of Shandong province (PM10 concentrations in selected sites and their locations are shown in Figure 7a,c, respectively).
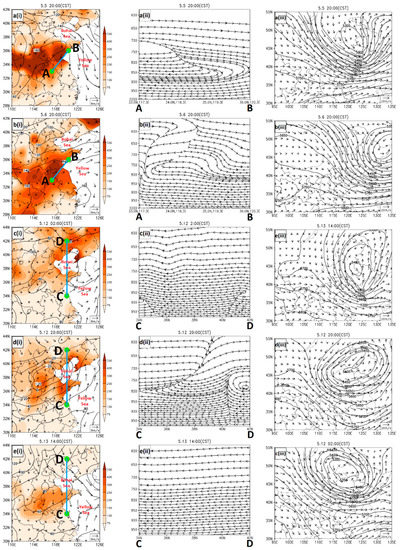
Figure 6.
The reserve transport analysis of the first (a(i)~(iii), b(i)~(iii)) and the second (c(i)~(iii), d(i)~(iii) and e(i)~(iii)) dust event in May 2017. The left column of the figures shows the same information as Figure 1. The middle column shows the streamlines along the cross section between the location A (33.0° N, 117.3° E) and B (36.0° N, 120.3° E) or between the location C (34.0° N, 120.0° E) and D (42.0° N, 120.0° E), and the right ones shows the corresponding 500-hPa synoptic features (the black curves represent the geopotential heights and the vectors stand for winds).
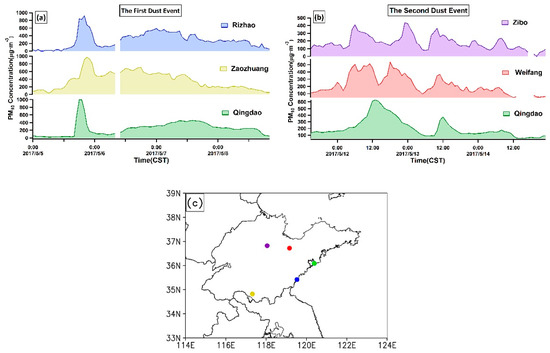
Figure 7.
The time series of PM10 mass concentrations of some stations within the dust reverse transport zone during (a) 5–8 May 2017 and (b) 11–14 May 2017. The location of these stations are shown in (c) with the same color.
We further found the synoptic weather situation in the lower troposphere was distinctively different from that in the 500-hPa layer. As shown in Figure 6a(ii),b(ii), the change of wind direction mainly occurred within the lower troposphere below 850 hPa. Therefore, although the dust would vertically reach to a very high altitude (≥5 km) at the late stage of the first dust event (Figure 5b), the DRT phenomenon occurred within the near-surface layer. The different pathways of dust particles between the lower and upper layers should be attributed to the distinct synoptic patterns. In the lower troposphere, the complex synoptic pattern caused the variable transport directions of dust plumes (Figure S2a). In contrast in the upper layer, dust aerosols could stay at a high altitude and moved straightly (Figure S2b) in the straight flow behind the trough (Figure 6a(iii),b(iii)).
In the second dust event, the DRT phenomenon occurred in the region near the Bohai Sea, especially in the central and northern Shandong Province. Similarly, we delineated the section of the flow field along the prevailing wind direction between location C (34.0° N, 120.0° E) and location D (42.0° N, 120.0° E) (Figure 6c(ii),d(ii),e(ii)) to investigate the corresponding dynamic conditions. At 02:00 CST on 12 May, the dust aerosols around Bohai Sea were transported southwardly by northerlies (Figure 6c(i)). At 14:00 CST on the same day, the mass concentration of PM10 in most areas of Shandong Province had increased substantially (Figure S4). At 20:00 CST on 12 May, southerly wind prevailed in Shandong because of the development of the Huabei low in the NCP region, resulting in the reverse of dust storm movement (Figure 6d(i)). With the eastward movement of the low, another dust reverse transport occurred accompanied with the wind shift from southerlies to northerlies in Shandong and its surrounding areas (Figure 6e(i)). This phenomenon was also supported by the back-trajectories (Figure S2c) and consequently 2 or even 3 remarkable increases of PM10 concentration were observed in many ground sites of Shandong Province (several examples are shown in Figure 7b).
Similarly, in the second dust event, the flow field demonstrates that the wind direction changed mainly in the lower troposphere below 800 hPa (Figure 6c(ii),d(ii),e(ii)) and the observations of CALIPSO showed the height of dust layers could reach a high altitude of 4 km (AGL) (Figure 5d). These facts indicate the DRT phenomenon only occurred in the lower troposphere, just like the dust air-mass back-trajectories performed (Figure S2c,d). The results should also be attributed to the distinct synoptic weather in the upper and lower layers. In the near-surface layer, the dust transport in NCP was affected by the Huabei low (Figure S2c). However, in the upper layer, dust movement was controlled by the vortex in Northeast China (Figure S2d).
3.4. Statistics of DRT in NCP
Most dust particles originating from the Gobi desert are removed quickly by gravity settling during the long-distance transport [28]. However, some severe dust storms could bring a large amount of dust particles to the remote downwind areas. If the weather condition is unfavorable for dust dispersion, dust plumes could deteriorate the air quality for a long time (>2 days). As mentioned above, both stable conditions and the distinctive synoptic weather can result in the retention of dust particles over polluted areas (e.g., the NCP region), extending the time for the mixing of dust particles and anthropogenic air pollutants in the lower troposphere. Moreover, the stable synoptic conditions could not only slow down the movement of dust aerosols but also facilitate the accumulation of anthropogenic aerosols and gaseous species. Mixing with anthropogenic pollutants, dust particles could be changed from hydrophobic to hydrophilic by the production of secondary pollutants on their surfaces, such as nitrate and sulfate [32]. In addition, mixing with anthropogenic pollutants might increase the solubility of iron and phosphorus in dust particles which are essential elements for the phytoplankton photosynthesis [33,34,35,36]. Thus, the slow-down movement and lingering of dust plumes in Eastern China might have special meaning for the marine ecosystem of the East China Sea and the Pacific Ocean [37,38]. In this study, we searched the severe spring dust events in recent 4 years to figure out the synoptic patterns resulted in this kind of dust plumes movement.
There were 28 severe spring dust events (about 79 dust days out of 368 investigated days) from 2015 to 2018 that occurred in northern and northeastern China, in which dust plumes undergone long-range transport (>1000 km). We identified these dust events by using the ground-based measurements and the criterion we referred in Section 2.1, as well as the satellite observations (CALIPSO and MetOp-B). Table 1 shows the details of the dust events, including the time of dust weather, the duration of dust weather in NCP, the weather systems triggering dust-uplifts, and whether or not the DRT and dust retention (DR) events occurred. In this study, the DR events were noted as the long-time residence (>37 h) of dust plumes at one specific area (i.e., the NCP region) without obvious movement due to the weak winds. While in DRT phenomena, the movement of dust plumes could be controlled by some distinctive mesoscale weather systems. Hence, the movement speed of dust air parcels in DRT events could be faster than the ones in DR cases obviously.

Table 1.
Statistical results of 28 spring dust cases that occurred in Northern China in spring from 2015 to 2018.
The statistical results show that about 86% and 36% dust storm occurrences were relevant to the Mongolian cyclones and Asian highs, respectively. Most dust storms (~79%) passed through the NCP region. The dust plumes of 16 events moved as the DRT or DR, in which 11 events were identified as DRT. Thus the frequency of DRT events occurrence in this study is similar to the results Wang et al. [13] calculated that dust backflow cases occurred twice per year in 2011 and 2013. We noticed that both the DRT and DR phenomena could extended the time that dust stayed over the NCP. The mean duration of dust weather in NCP is about 58 hours for the dust cases with DRT or DR phenomena, which means the dust events with DRT or DR could affect the NCP area for more than 2 days. While for the non-DRT events, the average duration is about 10 hours. And most dust cases with DRT or DR phenomena can affect the NCP region for more than 40 hours. Because dust air-mass in DRT events usually moved faster than that in DR events, it is reasonable that some DRT cases (Cases 20150328 and 20160331) were with shorter duration.
There are three different types of the DRT phenomena, which are defined as Type A, Type B and Type C (Figure 8). For Type A, dust plumes reversed from southeastward to northward or northeastward direction in the late stage of dust weather in Eastern China (Cases 20150328, 20150415, 20170417, 20170503, 20180413, and 20180522). Most of Type A DRT phenomena were caused by high-pressure systems existing to the southern or southeastern China (over the China seas sometimes) with/without the cooperation of a low-pressure system in Mongolia. It was the Asian high from the central Asia, which moved faster than the dust plumes, that altered the dust transportation. Therefore, the Type A DRT phenomena mainly occurred in the NCP region. For Type B, the wind changed from west or northwest wind to southwest wind when dust plumes were transported to Northeastern China and the adjacent areas (Cases 20150321, 20160331, 20160408, and 20170429). As a result, the NCP area was affected by the dust plume. All Type-B DRT phenomena were related to the southeastward movement of Asian highs at the east side of dust plumes. For Type C, the DRT was caused by the pull-back effect of a low-pressure system in NCP that dust plumes moved back to the place they had passed before in the convergent flow field. There was only one case of Type C DRT (Case 20170511), which is very similar to the backflow phenomenon in 2011 reported in Xu et al. [15]. From these results, we suppose that Asian highs are one of the key factors producing the DRT phenomena in NCP area.
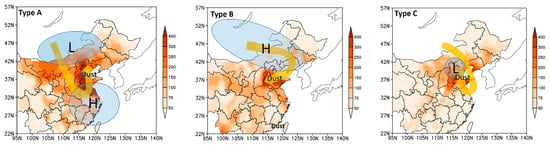
Figure 8.
Three different types of DRT. H and L stand for the high- and low-pressure system, respectively. Yellow arrows show the general dust transport pathways. The observations of PM10 mass concentrations during the Cases 20150328, 20150321, and 20170511 are used as the background for the pictures of Type A, Type B, and Type C, respectively.
4. Summary and Implication
In May 2017, two severe dust storms occurred in China from May 3 to 8 and May 11 to 14. The transport pathways of dust plumes were investigated, and the DRT phenomenon was confirmed. In the first dust event, the DRT zone was located to the north of a weak high, and the southerly flow created the DRT. In the second event, the DRT was caused by the occurrence and eastward movement of the Huabei low. With existing dust aerosols in the DRT zone, the change in wind direction led to the occurrence of two reversals of dust transport and a prolonged deterioration of air quality. In the vertical direction, dust aerosols were mainly distributed in the range from 0–5 km (AGL), up to approximately 8–10 km. However, the reverse transportation of dust merely occurred within the lower troposphere where anthropogenic aerosols and polluted gases are relatively concentrated on.
To figure out if the DRT phenomena is widespread existent in NCP areas, we investigated 28 severe dust events occurring in the springs of 2015–2018. The results show that 11 dust events, originating from the Gobi desert, moved as the DRT. Although the statistical sample size is not so large but considering the dust occurrence is decreasing [39], 28 events in latest four years should be representative. And 11 out of these 28 severe dust events have DRT phenomenon, suggesting one third of the dust events may be trapped in the highly polluted NCP. Among these DRT events, 10 of them were caused by the southeastward movement of the Asian highs that altered the circulation field, although there was an exception when the DRT was induced by the low-pressure system located in the NCP areas. The DRT and DR could all extend the residence time of dust in NCP area which are highly urban-concentrated with substantial anthropogenic emissions. The chemical composition and optical properties of dust aerosols are expected to change significantly during the DRT transport process, emphasizing the essentialness of accurate predictions of synoptic weather and the atmospheric chemical condition for evaluating the impacts of widespread dust on human health and atmospheric environment.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2073-4433/10/1/4/s1. Figure S1: (a)–(c) Synoptic maps at 1000 hPa. Geopotential heights (gpm, solid lines) are analyzed at 25-gpm intervals. Shaded areas indicate the magnitude of wind speed. (d)–(f) Geopotential heights (thin black curves, unit: gpm) and jet streams (shading, unit: m/s) at 500 hPa. The thick black curves in (d–f) stand for the troughs; Figure S2: Air mass back-trajectories for 48 hours at three sites (red, green, and blue curves) with the ending heights of (a) (c) 300 m and (b) (d) 3000 m above ground level (AGL). The interval between two adjacent markers is 6 hours; Figure S3: The flow field profiles between location A (33.0° N, 117.3° E) and B (36.0° N, 120.3° E) from 6 May 14:00 to 7 May 20:00 (CST), 2017; Figure S4: PM10 mass concentrations in the surface layer (shading, unit: μg/m3) and the synoptic pattern at 1000 hPa at 12 May 14:00 (CST). The corresponding geopotential heights (black curves, unit: gpm) are analyzed at 10-gpm intervals, and the light blue vectors stand for winds (unit: m/s).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.L. and Y.Z.; methodology, W.L.; formal analysis, W.L.; data curation, W.L.; writing—original draft preparation, W.L.; writing—review and editing, W.L., Y.Z., D.Z. and L.S.; visualization, W.L., Y.M., Y.Z. and W.W.; supervision, Y.Z., D.Z. and L.S.; funding acquisition, Y.Z., W.W., D.Z. and L.S.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 41605114, 41675146 and 41505013) and Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant Number: ZR2016DB02). D. Zhang is supported by the JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Number: JP16H02492).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to all institutions and departments who provided the data used in this research and thank the NOAA Air Resources Laboratory (ARL) for the HYSPLIT transport model.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Huang, J.P.; Wang, T.H.; Wang, W.C.; Li, Z.Q.; Yan, H.R. Climate Effects of Dust Aerosols over East Asian Arid and Semiarid Regions. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2014, 119, 11398–11416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Arimoto, R.; An, Z.S. Dust Emission from Chinese Desert Sources Linked to Variations in Atmospheric Circulation. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 1997, 102, 28041–28047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choobari, O.A.; Zawar-Reza, P.; Sturman, A. The Global Distribution of Mineral Dust and Its Impacts on the Climate System: A Review. Atmos. Res. 2014, 138, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.Y.; Winker, D.; Trepte, C. A Height Resolved Global View of Dust Aerosols from the First Year Calipso Lidar Measurements. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2008, 113, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.G.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhou, Z.J.; Shang, K.Z. Regional Characteristics of Three Kinds of Dust Storm Events in China. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.P.; Minnis, P.; Chen, B.; Huang, Z.W.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Yi, Y.H.; Ayers, J.K. Long-Range Transport and Vertical Structure of Asian Dust from Calipso and Surface Measurements During Pacdex. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2008, 113, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Z.; Iwasaka, Y. Chlorine Deposition on Dust Particles in Marine Atmosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 3613–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.B.; Zhang, D.Z.; Hayashi, M.; Ogata, H.; Ji, H.; Fujiie, W. Influences of Sulfate and Nitrate on the Hygroscopic Behaviour of Coarse Dust Particles. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, M.G.; Zhu, J.; Skorokhod, A. Model Analysis of Soil Dust Impacts on the Boundary Layer Meteorology and Air Quality over East Asia in April 2015. Atmos. Res. 2017, 187, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Cho, S.Y.; Kim, S.J. Characterization of PM2.5 Aerosols Dominated by Local Pollution and Asian Dust Observed at an Urban Site in Korea During Aerosol Characterization Experiments (Ace)-Asia Project. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2007, 57, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Du, H.H.; Chen, J.M.; Zhang, M.; Huang, X.Y.; Tan, H.B.; Kong, L.D.; Geng, F.H. Consecutive Transport of Anthropogenic Air Masses and Dust Storm Plume: Two Case Events at Shanghai, China. Atmos. Res. 2013, 127, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Z.; Zhuang, G.S.; Huang, K.; Liu, T.N.; Lin, Y.F.; Deng, C.R.; Fu, Q.Y.; Fu, J.S.; Chen, J.K.; Zhang, W.J.; et al. Evolution of Particulate Sulfate and Nitrate Along the Asian Dust Pathway: Secondary Transformation and Primary Pollutants Via Long-Range Transport. Atmos. Res. 2016, 169, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Pan, X.L.; Uno, I.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.F.; Chen, X.S.; Fu, P.Q.; Yang, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Shimizu, A.; et al. Significant Impacts of Heterogeneous Reactions on the Chemical Composition and Mixing State of Dust Particles: A Case Study During Dust Events over Northern China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 159, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.L.; Uno, I.; Wang, Z.; Nishizawa, T.; Sugimoto, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Sun, Y.L.; Fu, P.Q.; Tang, X.; et al. Real-Time Observational Evidence of Changing Asian Dust Morphology with the Mixing of Heavy Anthropogenic Pollution. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.S.; Li, Y.T.; Sun, R.W.; Dong, X.; Qiu, Q.H. Impact Characteristics of a Typical Dust Backflow Weather on the Air Quality in Beijing. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2014, 34, 297–302. [Google Scholar]
- Onishi, K.; Kurosaki, Y.; Otani, S.; Yoshida, A.; Sugimoto, N.; Kurozawa, Y. Atmospheric Transport Route Determines Components of Asian Dust and Health Effects in Japan. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 49, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archuleta, C.M.; DeMott, P.J.; Kreidenweis, S.M. Ice Nucleation by Surrogates for Atmospheric Mineral Dust and Mineral Dust/Sulfate Particles at Cirrus Temperatures. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 2617–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheesh, S.K.; Moorthy, K.K. Radiative Effects of Natural Aerosols: A Review. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 2089–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermida, L.; Merino, A.; Sanchez, J.L.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, S.; Garcia-Ortega, E.; Lopez, L. Characterization of Synoptic Patterns Causing Dust Outbreaks That Affect the Arabian Peninsula. Atmos. Res. 2018, 199, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.J.; Zhuang, G.S.; Wang, Z.F.; Sun, Y.L.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, H. Variation of Sources and Mixing Mechanism of Mineral Dust with Pollution Aerosol-Revealed by the Two Peaks of a Super Dust Storm in Beijing. Atmos. Res. 2007, 84, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.; Park, G.; Baek, J. An Effectiveness of Simultaneous Measurement of PM10, PM2.5, and PM1.0 Concentrations in Asian Dust and Haze Monitoring. J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2013, 22, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cressman, G.P. An Operational Objective Analysis System. Mon. Weather Rev. 1959, 87, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theys, N.; Campion, R.; Clarisse, L.; Brenot, H.; van Gent, J.; Dils, B.; Corradini, S.; Merucci, L.; Coheur, P.F.; Van Roozendael, M.; et al. Volcanic So2 Fluxes Derived from Satellite Data: A Survey Using Omi, Gome-2, Iasi and Modis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5945–5968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Omar, A.; Vaughan, M.; Hair, J.; Kittaka, C.; Hu, Y.X.; Powell, K.; Trepte, C.; Winker, D.; Hostetler, C.; et al. Calipso Lidar Observations of the Optical Properties of Saharan Dust: A Case Study of Long-Range Transport. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2008, 113, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Hunt, W.H.; McGill, M.J. Initial Performance Assessment of Caliop. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, I.; Yumimoto, K.; Shimizu, A.; Hara, Y.; Sugimoto, N.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Winker, D.M. 3D Structure of Asian Dust Transport Revealed by Calipso Lidar and a 4dvar Dust Model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.M.; Mashat, A.W.S. Synoptic Characteristics of Spring Dust Days over Northern Saudi Arabia. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2016, 9, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.; Chen, G.T.J.; Liu, T.H.; Lin, W.D.; Tu, J.Y. Characterizing the Transport Pathways of Asian Dust. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2008, 113, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.X.; Fang, X.M.; Kang, S.C.; Wang, H.J.; Kang, F.Q. Shifts of Dust Source Regions over Central Asia and the Tibetan Plateau: Connections with the Arctic Oscillation and the Westerly Jet. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2358–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Wenig, M.; Zhang, Z.X.; Sugimoto, N.; Larko, D.; Diehl, T. Dust Episodes in Hong Kong (South China) and Their Relationship with the Sharav and Mongolian Cyclones and Jet Streams. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2012, 5, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.C.; Shi, G.Y.; Wang, H. Long-Range Transport of Spring Dust Storms in Inner Mongolia and Impact on the China Seas. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 46, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, N.A.; Chamseddine, A. Uptake of Acid Pollutants by Mineral Dust and Their Effect on Aerosol Solubility. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 46, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, B.; Sarin, M.M.; Rengarajan, R. Atmospheric Transport of Mineral Dust from the Indo-Gangetic Plain: Temporal Variability, Acid Processing, and Iron Solubility. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2014, 15, 3226–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, A.S.; Shelley, R.U.; McElhenie, S.D.; Landing, W.M.; Hatcher, P.G. Aerosol Water Soluble Organic Matter Characteristics over the North Atlantic Ocean: Implications for Iron-Binding Ligands and Iron Solubility. Mar. Chem. 2015, 173, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furutani, H.; Meguro, A.; Iguchi, H.; Uematsu, M. Geographical Distribution and Sources of Phosphorus in Atmospheric Aerosol over the North Pacific Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Goldstein, H.L.; Reynolds, R.L.; Hu, Y.F.; Wang, X.M.; Zhu, M.Q. Phosphorus Speciation and Solubility in Aeolian Dust Deposited in the Interior American West. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2658–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.M.; Horowitz, L.W.; Levy, H.; Moxim, W.J. Impact of Air Pollution on Wet Deposition of Mineral Dust Aerosols. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Zhang, J. High Correlations between Asian Dust Events and Biological Productivity in the Western North Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Guo, L.; Fan, B.H. A New Perspective on Understanding the Reduced Spring Dust Storm Frequency in Inner Mongolia, China. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2015, 6, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).