Altering Brain Amyloidosis by Intra-Lingual and Extra-Nasal Exposure of Aβ Aggregates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
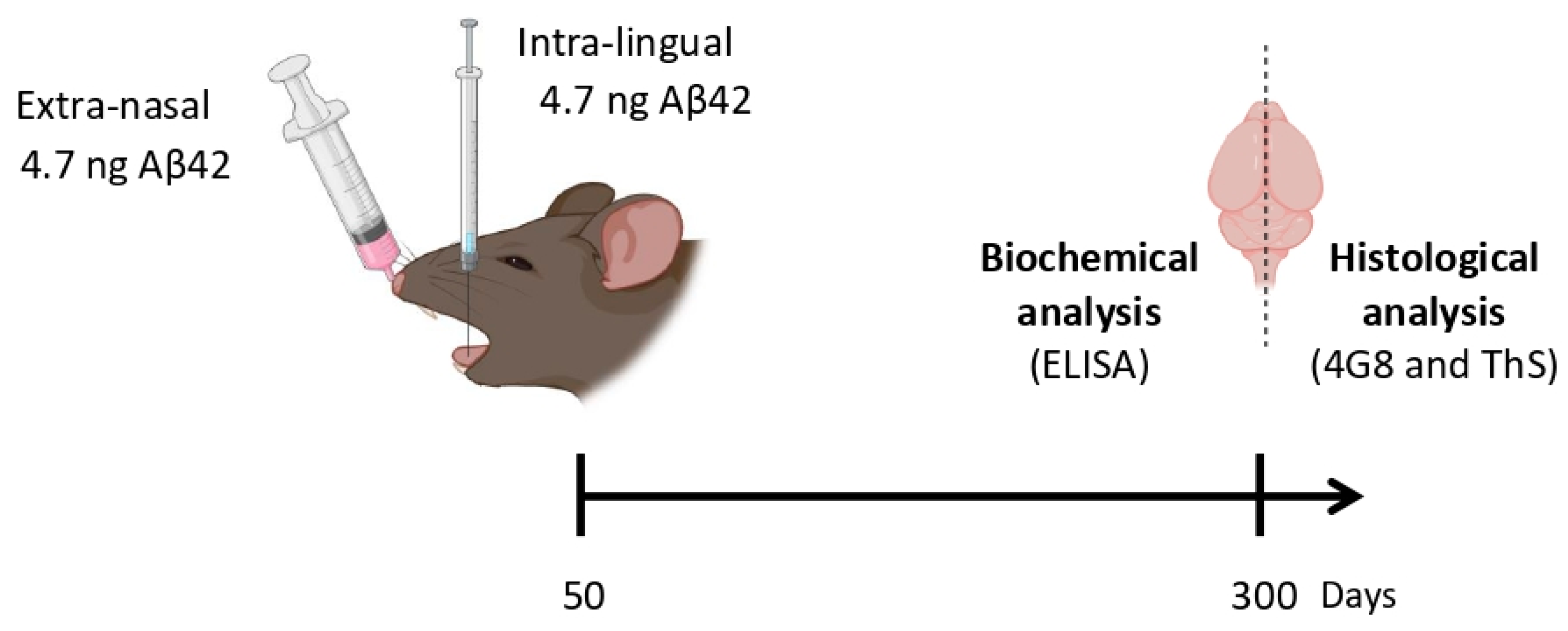
2.1. Mouse Model
2.2. Inoculum
2.3. Intra-Cerebral Injections
2.4. Intra-Lingual Injections
2.5. Extra-Nasal Administration
2.6. Untreated Animals
2.7. Aβ Immunofluorescence and Thioflavin-S (ThS) Staining
2.8. Image Analysis
2.9. Attack Rate
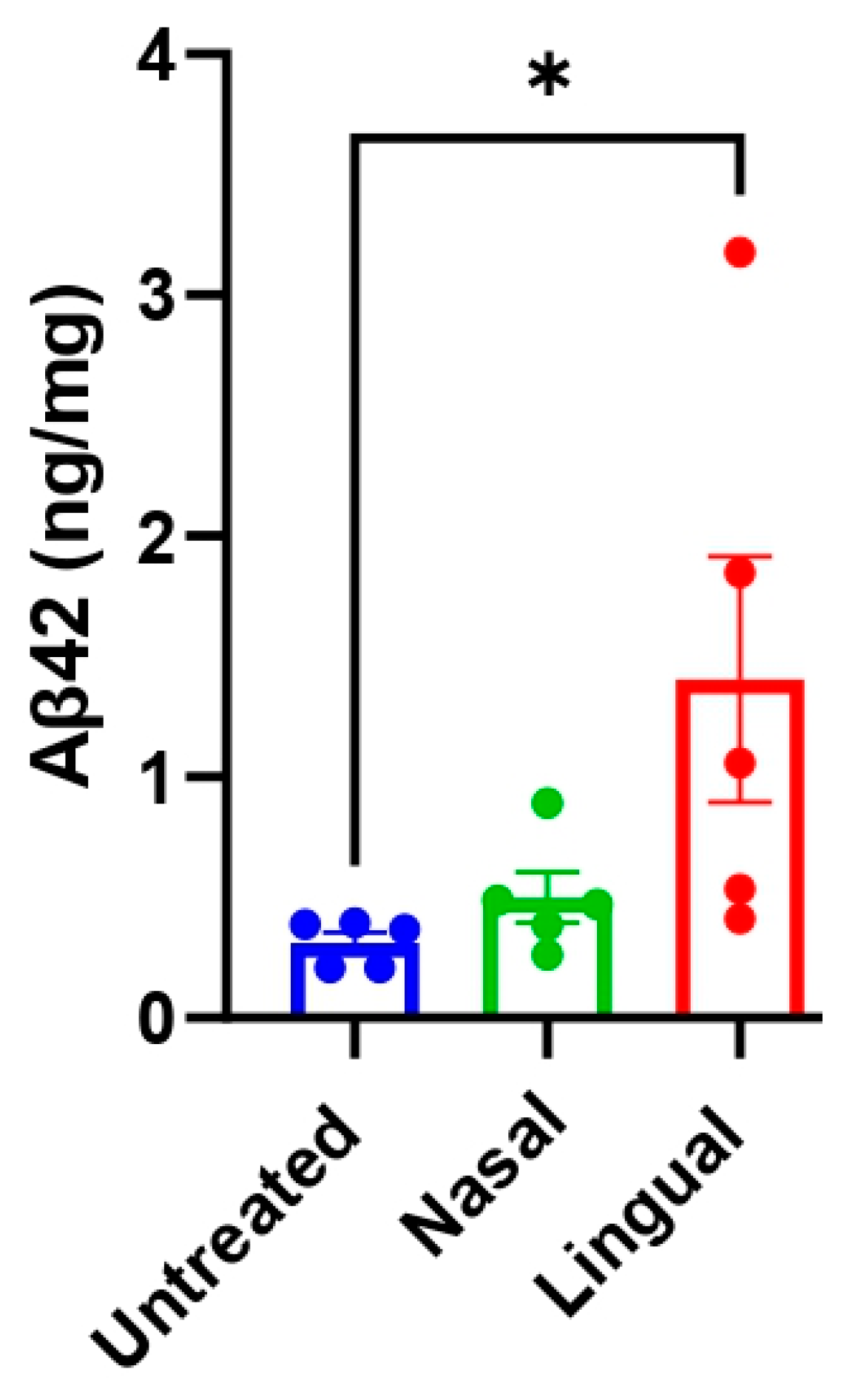
2.10. Insoluble Aβ42 Quantification by ELISA
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
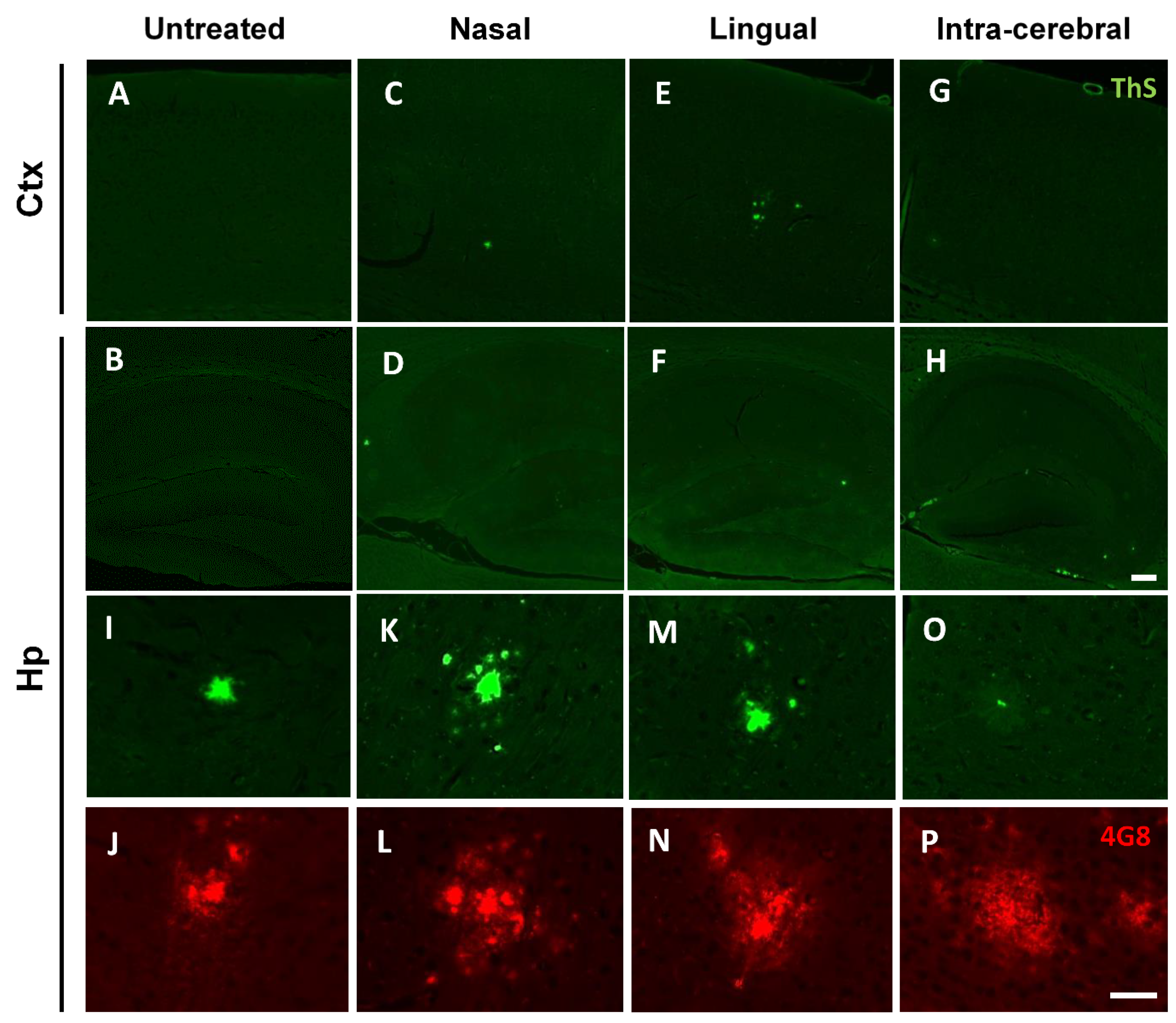
3.1. Acceleration of Brain Aβ Deposition after Intra-lingual Administration of an Aβ-Laden Brain Extract
3.2. Abundant Deposition of Cerebral Nasal-Seeded Aβ in the Olfactory Bulb of Treated Mice
3.3. Nasal- and Lingual-Administered Seeds Induce Fibrillar Aβ Deposits in the Brain of Injected Animals
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knopman, D.S.; Amieva, H.; Petersen, R.C.; Chételat, G.; Holtzman, D.M.; Hyman, B.T.; Nixon, R.A.; Jones, D.T. Alzheimer Disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2021, 7, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querfurth, H.W.; Laferla, F.M. Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 28, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twohig, D.; Nielsen, H.M. α-Synuclein in the Pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.A.; Higgins, G.A. Alzheimer’s Disease: The Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis. Science 1992, 256, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selkoe, D.J.; Hardy, J. The Amyloid Hypothesis of Alzheimer’s Disease at 25 Years. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampel, H.; Hardy, J.; Blennow, K.; Chen, C.; Perry, G.; Kim, S.H.; Villemagne, V.L.; Aisen, P.; Vendruscolo, M.; Iwatsubo, T.; et al. The Amyloid-β Pathway in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 5481–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowsky, J.L.; Fadale, D.J.; Anderson, J.; Xu, G.M.; Gonzales, V.; Jenkins, N.A.; Copeland, N.G.; Lee, M.K.; Younkin, L.H.; Wagner, S.L.; et al. Mutant Presenilins Specifically Elevate the Levels of the 42 Residue β-Amyloid Peptide in Vivo: Evidence for Augmentation of a 42-Specific γ Secretase. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, H.; Cole, S.L.; Logan, S.; Maus, E.; Shao, P.; Craft, J.; Guillozet-Bongaarts, A.; Ohno, M.; Disterhoft, J.; Van Eldik, L.; et al. Intraneuronal Beta-Amyloid Aggregates, Neurodegeneration, and Neuron Loss in Transgenic Mice with Five Familial Alzheimer’s Disease Mutations: Potential Factors in Amyloid Plaque Formation. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 10129–10140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, K.; Chapman, P.; Nilsen, S.; Eckman, C.; Harigaya, Y.; Younkin, S.; Yang, F.; Cole, G. Correlative Memory Deficits, Abeta Elevation, and Amyloid Plaques in Transgenic Mice. Science 1996, 274, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, R.; Bravo-Alegria, J.; Duran-Aniotz, C.; Soto, C. Titration of Biologically Active Amyloid-β Seeds in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, M.D.; Lipinski, W.J.; Callahan, M.J.; Bian, F.; Durham, R.A.; Schwarz, R.D.; Roher, A.E.; Walker, L.C. Evidence for Seeding of β-Amyloid by Intracerebral Infusion of Alzheimer Brain Extracts in β-Amyloid Precursor Protein-Transgenic Mice. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 3606–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, R.; Bravo-Alegria, J.; Moreno-Gonzalez, I.; Duran-Aniotz, C.; Gamez, N.; Edwards, G.; Soto, C. Transmission of Cerebral Amyloid Pathology by Peripheral Administration of Misfolded Aβ Aggregates. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 5690–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer-Luehmann, M.; Coomaraswamy, J.; Bolmont, T.; Kaeser, S.; Schaefer, C.; Kilger, E.; Neuenschwander, A.; Abramowski, D.; Frey, P.; Jaton, A.L.; et al. Exogenous Induction of Cerebral Beta-Amyloidogenesis Is Governed by Agent and Host. Science 2006, 313, 1781–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, L.C.; Schelle, J.; Jucker, M. The Prion-Like Properties of Amyloid-β Assemblies: Implications for Alzheimer’s Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a024398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusiner, S.B. Prions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13363–13383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collinge, J. Prion Diseases of Humans and Animals: Their Causes and Molecular Basis. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 519–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguzzi, A.; Sigurdson, C.; Heikenwaelder, M. Molecular Mechanisms of Prion Pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2008, 3, 11–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, R.; Callegari, K.; Soto, C. Prion-like Features of Misfolded Aβ and Tau Aggregates. Virus Res. 2015, 207, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, C. Transmissible Proteins: Expanding the Prion Heresy. Cell 2012, 149, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, D.J.; Abrams, J.Y.; Schonberger, L.B.; Leschek, E.W.; Mills, J.L.; Lee, V.M.Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Evaluation of Potential Infectivity of Alzheimer and Parkinson Disease Proteins in Recipients of Cadaver-Derived Human Growth Hormone. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaunmuktane, Z.; Mead, S.; Ellis, M.; Wadsworth, J.D.F.; Nicoll, A.J.; Kenny, J.; Launchbury, F.; Linehan, J.; Richard-Loendt, A.; Walker, A.S.; et al. Evidence for Human Transmission of Amyloid-β Pathology and Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy. Nature 2015, 525, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purro, S.A.; Farrow, M.A.; Linehan, J.; Nazari, T.; Thomas, D.X.; Chen, Z.; Mengel, D.; Saito, T.; Saido, T.; Rudge, P.; et al. Transmission of Amyloid-β Protein Pathology from Cadaveric Pituitary Growth Hormone. Nature 2018, 564, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamaguchi, T.; Taniguchi, Y.; Sakai, K.; Kitamoto, T.; Takao, M.; Murayama, S.; Iwasaki, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Shimizu, H.; Kakita, A.; et al. Significant Association of Cadaveric Dura Mater Grafting with Subpial Aβ Deposition and Meningeal Amyloid Angiopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 132, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Gutierrez, R.; Morales, R. The Prion-like Phenomenon in Alzheimer’s Disease: Evidence of Pathology Transmission in Humans. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1009004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartz, J.C.; Kincaid, A.E.; Bessen, R.A. Rapid Prion Neuroinvasion Following Tongue Infection. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kincaid, A.E.; Bartz, J.C. The Nasal Cavity Is a Route for Prion Infection in Hamsters. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 4482–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duran-Aniotz, C.; Morales, R.; Moreno-Gonzalez, I.; Hu, P.P.; Fedynyshyn, J.; Soto, C. Aggregate-Depleted Brain Fails to Induce Abeta Deposition in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshy, S.M.; Kincaid, A.E.; Bartz, J.C. Transport of Prions in the Peripheral Nervous System: Pathways, Cell Types, and Mechanisms. Viruses 2022, 14, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisele, Y.S.; Fritschi, S.K.; Hamaguchi, T.; Obermüller, U.; Füger, P.; Skodras, A.; Schäfer, C.; Odenthal, J.; Heikenwalder, M.; Staufenbiel, M.; et al. Multiple Factors Contribute to the Peripheral Induction of Cerebral β-Amyloidosis. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 10264–10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasoff-Conway, J.M.; Carare, R.O.; Osorio, R.S.; Glodzik, L.; Butler, T.; Fieremans, E.; Axel, L.; Rusinek, H.; Nicholson, C.; Zlokovic, B.V.; et al. Clearance Systems in the Brain-Implications for Alzheimer Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMattos, R.B.; Bales, K.R.; Cummins, D.J.; Dodart, J.C.; Paul, S.M.; Holtzman, D.M. Peripheral Anti-A Beta Antibody Alters CNS and Plasma A Beta Clearance and Decreases Brain A Beta Burden in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8850–8855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza, F.; Greenberg, S.M.; Savoiardo, M.; Gardinetti, M.; Chiapparini, L.; Raicher, I.; Nitrini, R.; Sakaguchi, H.; Brioschi, M.; Billo, G.; et al. Anti-Amyloid β Autoantibodies in Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy-Related Inflammation: Implications for Amyloid-Modifying Therapies. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 73, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, K.; Senda, T.; Hata, R.; Kuroda, M.; Hasegawa, M.; Kato, M.; Abe, M.; Kawaguchi, K.; Nakai, S.; Hiki, Y.; et al. Patients That Have Undergone Hemodialysis Exhibit Lower Amyloid Deposition in the Brain: Evidence Supporting a Therapeutic Strategy for Alzheimer’s Disease by Removal of Blood Amyloid. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 51, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhuang, Z.Q.; He, C.Y.; Pan, Q.G.; Tang, M.Z.; Hu, X.L.; Shen, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.R.; Chen, S.H.; et al. Physiological Clearance of Amyloid-Beta by the Kidney and Its Therapeutic Potential for Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 6074–6082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roher, A.E.; Esh, C.L.; Kokjohn, T.A.; Castaño, E.M.; Van Vickle, G.D.; Kalback, W.M.; Patton, R.L.; Luehrs, D.C.; Daugs, I.D.; Kuo, Y.; et al. Amyloid Beta Peptides in Human Plasma and Tissues and Their Significance for Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2009, 5, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, X.L.; Xiang, Y.; Jin, W.S.; Wang, J.; Shen, L.L.; Huang, Z.L.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.H.; Zeng, F.; Liu, J.H.; et al. Blood-Derived Amyloid-β Protein Induces Alzheimer’s Disease Pathologies. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 1948–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlokovic, B.V.; Ghiso, J.; Mackic, J.B.; Mccomb, J.G.; Weiss, M.H.; Frangione, B. Blood-Brain Barrier Transport of Circulating Alzheimer′s Amyloid β. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 197, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackic, J.B.; Bading, J.; Ghiso, J.; Walker, L.; Wisniewski, T.; Frangione, B.; Zlokovic, B.V. Circulating Amyloid-β Peptide Crosses the Blood–Brain Barrier in Aged Monkeys and Contributes to Alzheimer’s Disease Lesions. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2002, 38, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawuenyega, K.G.; Sigurdson, W.; Ovod, V.; Munsell, L.; Kasten, T.; Morris, J.C.; Yarasheski, K.E.; Bateman, R.J. Decreased Clearance of CNS β-Amyloid in Alzheimer’s Disease. Science 2010, 330, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.R.; Wang, Q.H.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y.H.; Yao, X.Q.; Zeng, F.; Li, J.; Zhou, F.Y.; Wang, L.; Yan, J.C.; et al. Associations Between Hepatic Functions and Plasma Amyloid-Beta Levels-Implications for the Capacity of Liver in Peripheral Amyloid-Beta Clearance. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 2338–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, L.D.; Ahumada, P.; Cabrera, D.; Arab, J.P. Liver Dysfunction as a Novel Player in Alzheimer’s Progression: Looking Outside the Brain. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risacher, S.L.; Fandos, N.; Romero, J.; Sherriff, I.; Pesini, P.; Saykin, A.J.; Apostolova, L.G. Plasma Amyloid Beta Levels Are Associated with Cerebral Amyloid and Tau Deposition. Alzheimer’s Dement. Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2019, 11, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giampietri, L.; Belli, E.; Beatino, M.F.; Giannoni, S.; Palermo, G.; Campese, N.; Tognoni, G.; Siciliano, G.; Ceravolo, R.; De Luca, C.; et al. Fluid Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Disorders: Toward Integrative Diagnostic Frameworks and Tailored Treatments. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janelidze, S.; Teunissen, C.E.; Zetterberg, H.; Allué, J.A.; Sarasa, L.; Eichenlaub, U.; Bittner, T.; Ovod, V.; Verberk, I.M.W.; Toba, K.; et al. Head-to-Head Comparison of 8 Plasma Amyloid-β 42/40 Assays in Alzheimer Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.C.; Kim, S.J.; Hong, S.; Kim, Y.S. Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease Utilizing Amyloid and Tau as Fluid Biomarkers. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, D.L.; Adlard, P.; Peden, A.H.; Lowrie, S.; Le Grice, M.; Burns, K.; Jackson, R.J.; Yull, H.; Keogh, M.J.; Wei, W.; et al. Amyloid-β Accumulation in the CNS in Human Growth Hormone Recipients in the UK. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 134, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, H.L.; Lemere, C.A.; Maron, R.; Spooner, E.T.; Grenfell, T.J.; Mori, C.; Issazadeh, S.; Hancock, W.W.; Selkoe, D.J. Nasal Administration of Amyloid-β Peptide Decreases Cerebral Amyloid Burden in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2000, 48, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, A.W.; Núñez, G.; Quinteiro, P.S.; Salazar, I.; Chamero, P. Anatomy, Histochemistry, and Immunohistochemistry of the Olfactory Subsystems in Mice. Front. Neuroanat. 2014, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarmolinsky, D.A.; Zuker, C.S.; Ryba, N.J.P. Common Sense about Taste: From Mammals to Insects. Cell 2009, 139, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Games, D.; Adams, D.; Alessandrini, R.; Barbour, R.; Borthelette, P.; Blackwell, C.; Carr, T.; Clemens, J.; Donaldson, T.; Gillespie, F.; et al. Alzheimer-Type Neuropathology in Transgenic Mice Overexpressing V717F Beta-Amyloid Precursor Protein. Nature 1995, 373, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, H.H.C.; Ingelsson, M.; Watts, J.C. The Existence of Aβ Strains and Their Potential for Driving Phenotypic Heterogeneity in Alzheimer’s Disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 142, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Soto, C.; Morales, R. Peripherally Administrated Prions Reach the Brain at Sub-Infectious Quantities in Experimental Hamsters. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urayama, A.; Morales, R.; Niehoff, M.L.; Banks, W.A.; Soto, C. Initial Fate of Prions upon Peripheral Infection: Half-life, Distribution, Clearance, and Tissue Uptake. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 2792–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burwinkel, M.; Lutzenberger, M.; Heppner, F.L.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.; Baier, M. Intravenous Injection of Beta-Amyloid Seeds Promotes Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy (CAA). Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

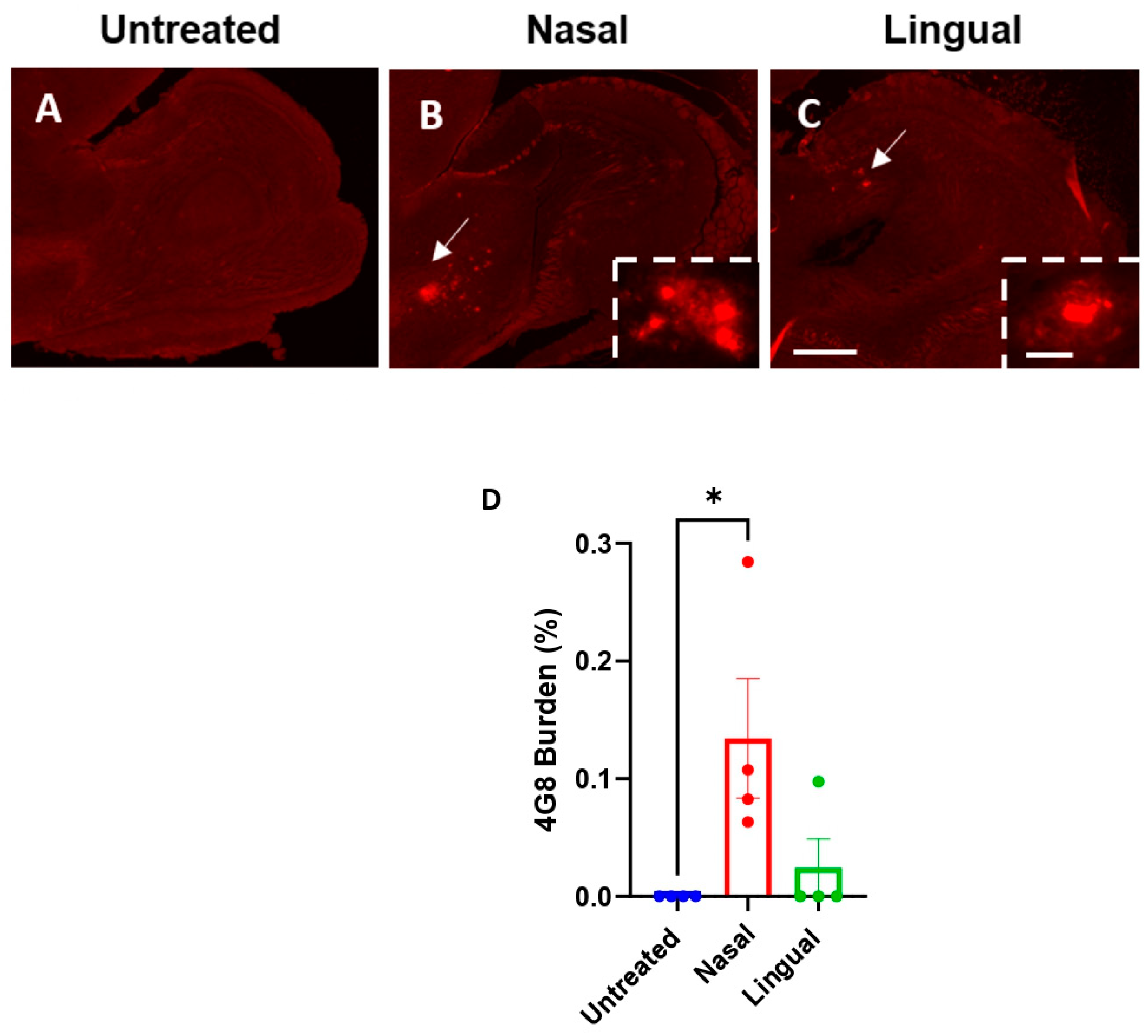

| Group | n | Attack Rate | 4G8 Burden Mean ± SD | Fold | p Value (Compared to Non-Treated) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | 5 | 3/5 | 0.0977 ± 0.055 | 8.42 | 0.0769 |
| Lingual | 5 | 5/5 | 0.1157± 0.0745 | 9.95 | 0.0339 |
| Untreated | 4 | - | 0.0116 ± 0.016 | 1 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gamez, N.; Bravo-Alegria, J.; Huang, Y.; Perez-Urrutia, N.; Dongarwar, D.; Soto, C.; Morales, R. Altering Brain Amyloidosis by Intra-Lingual and Extra-Nasal Exposure of Aβ Aggregates. Cells 2022, 11, 3442. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11213442
Gamez N, Bravo-Alegria J, Huang Y, Perez-Urrutia N, Dongarwar D, Soto C, Morales R. Altering Brain Amyloidosis by Intra-Lingual and Extra-Nasal Exposure of Aβ Aggregates. Cells. 2022; 11(21):3442. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11213442
Chicago/Turabian StyleGamez, Nazaret, Javiera Bravo-Alegria, Yumeng Huang, Nelson Perez-Urrutia, Deepa Dongarwar, Claudio Soto, and Rodrigo Morales. 2022. "Altering Brain Amyloidosis by Intra-Lingual and Extra-Nasal Exposure of Aβ Aggregates" Cells 11, no. 21: 3442. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11213442
APA StyleGamez, N., Bravo-Alegria, J., Huang, Y., Perez-Urrutia, N., Dongarwar, D., Soto, C., & Morales, R. (2022). Altering Brain Amyloidosis by Intra-Lingual and Extra-Nasal Exposure of Aβ Aggregates. Cells, 11(21), 3442. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11213442






