Abstract
Colored wheat lines, which feature elevated anthocyanin content and associated traits, represent valuable genetic resources for enhancing the plant’s nutritional and aesthetic properties. This genome-wide association study (GWAS) utilized a set of radiation-induced mutant lines to identify genetic loci linked to agricultural and biochemical traits. The GWAS models Fixed and Random Model Circulating Probability Unification, and the Bayesian-information and Linkage-Disequilibrium Iteratively Nested Keyway were employed to increase the reliability of marker–trait associations (MTAs). In total, 35 significant MTAs were identified, and seven single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were commonly detected by both models. To explore candidate genes, a ± 1.5-Mb window around each significant SNP was analyzed according to the estimated linkage disequilibrium decay, revealing 635 genes. Among these, several genes were annotated as transcription factors and enzymes associated with flavonoid biosynthesis and modification, including MYB, WD-repeat proteins, and UDP-glycosyltransferases. Expression profiling and RT-qPCR further supported the functional relevance of selected SNP–gene pairs, particularly for anthocyanin accumulation and seed color variation. In summary, the integration of GWAS, gene annotation, and expression data could provide valuable insights into the genetic basis of complex traits in wheat, providing data for future molecular studies and marker-assisted breeding of colored wheat mutant cultivars.
1. Introduction
Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) provides a significant portion of calories and protein to the global population. Since its domestication approximately 10,000 years ago, wheat has played a key role in global food security because of its wide adaptability, broad cultivation range, and nutritional value. Wheat contributes approximately 20% of the total dietary calories and protein consumed globally [1]. Colored wheat has recently attracted interest as a potential food source with enhanced nutritional quality. Colored wheat lines are rich in natural antioxidants, including anthocyanins and polyphenols, which are associated with health-promoting properties. In addition to their nutritional benefits, the pigments in colored wheat might provide natural alternatives to synthetic food colorants, meeting the growing consumer demand for functional and visually distinctive food products [2]. Given its nutritional and functional potential, colored wheat has also emerged as a promising genetic material for mutation breeding. Its rich accumulation of natural pigments, particularly anthocyanins and other phenolic compounds, both contributes to antioxidant activity and offers a unique biochemical background for evaluating mutagen-induced phenotypic changes. In particular, the diverse pigmentation and associated biochemical profiles of colored wheat provide an excellent platform for investigating the effects of induced mutations and identifying novel traits related to pigment biosynthesis, nutritional quality, and stress responses [3,4,5].
Mutation breeding is a well-established approach in crop improvement in which genetic variations are introduced to generate novel traits [6]. This approach is particularly effective for broadening the genetic base of cultivated plants, especially in elite cultivars with limited diversity. Among various mutagenic agents, gamma radiation has been widely utilized in plant breeding as a physical mutagen because of its capacity to generate stable and heritable genetic mutations without the incorporation of foreign DNA [7]. Gamma radiation-induced mutagenesis has facilitated the rapid development of cultivars with enhanced agronomic traits, including improved nutritional profiles, abiotic stress tolerance, and resistance to pests and diseases [8]. Additionally, the safety and regulatory acceptance of mutation breeding are well established. As of early 2022, more than 3365 officially released mutant varieties derived from more than 240 plant species, primarily food crops and ornamental plants, have been developed globally [9]. In particular, gamma radiation has been successfully applied to cereal crops such as rice, wheat, and barley to generate genetic diversity and select for beneficial phenotypes. Sao et al. [10] demonstrated the effectiveness of gamma radiation (300 Gy) including in early flowering, reducing plant height, and increasing yield potential in mutant lines derived from three traditional rice landraces. Similarly, the gamma-irradiated wheat mutant Fu4185 exhibited enlarged seed size, along with stable quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for thousand-kernel weight [11]. In barley, low doses of gamma radiation (5–10 Gy) were found to enhance growth, yield traits, and antioxidant activity while simultaneously inducing dose-dependent changes in photosynthetic pigments, protein profiles, and key metabolic constituents [12]. These findings highlight the broad applicability of gamma radiation for inducing beneficial agronomic traits such as increased yield and early flowering and enhancing physiological and biochemical characteristics related to plant metabolism and stress adaptation across diverse cereal crops.
Genetic research in wheat has historically been hindered by the complexity of its large (approximately 17 Gb) allohexaploid genome. Early efforts to decode the genome relied on chromosome-specific BAC-based assemblies, such as the physical map and sequence of chromosome 3B [13]. The release of the IWGSC RefSeq v1.0, the first fully annotated reference genome for hexaploid wheat, provided a comprehensive foundation for genomic analysis and gene discovery [14]. Subsequent improvements, including RefSeq v2.0 and v2.1, enhanced the accuracy and contiguity of genome assemblies through the integration of long-read sequencing and Hi-C scaffolding [15,16]. The development of high-quality wheat reference genomes has facilitated advanced genetic analysis, particularly genome-wide association studies (GWASs). In recent decades, high-density single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) genotyping arrays, such as the Illumina Wheat 90K SNP array, have significantly enhanced the resolution and efficiency of GWASs in wheat. These platforms have enabled the rapid and accurate genotyping of large populations, permitting the precise identification of genetic variants linked to important agronomic, physiological, and quality-related traits. The availability of dense marker data has also facilitated the integration of GWAS results into marker-assisted breeding programs. Thus, GWAS has become a key approach for dissecting complex traits and accelerating genetic improvement in wheat.
Thus, we performed a GWAS to identify loci associated with key agronomic and biochemical traits in 48 lines of colored wheat, including 47 M7 mutant lines and one wild-type parental line, developed through gamma radiation-induced mutagenesis. A radiation dose of 200 Gy was applied to induce mutations in the parental line, which resulted in diverse pigmentation and phenotypic variation. This study aimed to explore the genetic basis of these traits and identify potential markers that can be utilized for future functional studies and breeding applications. These lines, characterized by diverse pigmentation and phenotypic variation, were evaluated for seed color parameters, antioxidant activity, anthocyanin content, and agronomic traits.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
A colored wheat line with deep-purple grains used as the initial material for gamma radiation-induced mutagenesis, which was performed at the Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute by exposing 200 g of colored wheat seeds to cobalt−60 gamma radiation. Irradiation was delivered using a 150-TBq capacity source (Nordion, Ottawa, ON, Canada) at 25 Gy/h, resulting in a final dose of 200 Gy. Following irradiation, the treated seeds were sown in a designated radiation breeding field. In the M1 generation, individual plants exhibiting distinct morphological changes were selected and harvested. Successive generations were advanced through single spike selection to stabilize heritable traits. For the M2–M7 generations, mutant lines exhibiting diverse phenotypic variation, including differences in plant architecture, spike morphology, grain coloration, and days to heading (HDs), were systematically screened. For this study, 47 M7 mutant lines derived from gamma-ray irradiation, along with the wild-type parental line, were evaluated under field conditions to assess phenotypic diversity and key agronomic traits. Field evaluations of agronomic traits were conducted over two consecutive growing seasons (2021–2022 and 2022–2023) at the radiation breeding field of the Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (Jeongeup-si, Jeollabuk-do, Republic of Korea) to assess the yield potential and field adaptability of selected mutant lines based on key agronomic parameters relevant to wheat improvement. Each line was planted in two biological replicates, and each replicate plot consisted of five rows. The plots were arranged sequentially by line number without formal randomization, and the same layout was maintained across both growing seasons to ensure consistency. For trait measurements, the middle three rows of each plot were harvested and used for agronomic and biochemical analyses. HDs were recorded when more than 50% of the spikes had emerged in a given line. Plant height (PH) was measured from the soil surface to the base of the spike, excluding the awns. Spike length (SL) was calculated as the distance from the base of the first spikelet to the terminal spikelet, with awns omitted from the measurement. Thousand-grain weight (TGW) was calculated by measuring the total weight of 100 manually counted seeds from each mutant line. The number of kernels per spike was assessed by manually counting the grains from randomly selected main spikes. These agronomic traits were later employed in association analysis with genome-wide SNP genotyping data generated using the wheat 90K iSelect SNP array (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) to identify potential trait-linked loci.
2.2. Seed Color Determination
Seed color parameters were assessed using a Lab-model colorimeter (Colormate, Scinco, Seoul, Republic of Korea), which provided Hunter L* (lightness), a* (red–green), and b* (yellow–blue) values. The device was calibrated prior to use for standard white and black tiles under a D65 light source. For measurement, seeds from each sample were placed in individual containers to ensure consistent positioning. Color data were acquired using ColorMaster software (version 2017; Scinco, Seoul, Republic of Korea), and the final values of L*, a*, and b* were used to characterize the visual pigmentation of each mutant line.
2.3. Quantification of Total Anthocyanin Content
The total anthocyanin concentration in wheat grains was measured using a spectrophotometric method adapted from a previously reported protocol [17], with minor modifications. Briefly, 0.5 g of homogenized seed tissue were extracted with 10 mL of acidified methanol solution (methanol containing 1% HCl, w/v), followed by incubation at 4 °C for 24 h to enhance pigment solubilization. After incubation, the mixture was centrifuged at 16,000× g for 20 min. The resulting supernatant was carefully filtered using a 0.2 μm syringe filter to remove any particulates prior to analysis. Absorbance was measured at 530 and 657 nm using a UV–Vis spectrophotometer (Evolution 260 Bio, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). To correct for background absorbance from chlorophyll degradation products and other interfering compounds, anthocyanin content was calculated using the following equation: Q = (A530 − 0.25 × A657) × M−1, where Q is the total anthocyanin content; A530 and A657 are the absorbance values at 530 and 657 nm, respectively; and M represents the sample weight (g) of the homogenized tissue.
2.4. Preparation of Seed Extracts
Wheat seed samples (approximately 1 g per each line) were milled into a find powder using a mechanical homogenizer. The powder material was extracted with 10 mL of 80% methanol via sonication in an ultrasonic water bath at 25 °C for 30 min to facilitate the release of bioactive compounds. Following extraction, the mixtures were clarified by filtration through 0.45 µm syringe filters to remove insoluble residues. The resulting filtrates were aliquoted and stored at −20 °C until further analysis. These seed extracts were subsequently utilized to evaluate antioxidant capacity, total phenolic content, and flavonoid concentrations.
2.4.1. Determination of Antioxidant Capacity
The ABTS assay followed a previously reported method [18]. Totals of 7mM ABTS and 2.45 mM potassium persulfate were incubated in the dark at room temperature for 12 h to generate ABTS radicals. The solution was diluted with 80% methanol to an absorbance of 0.7 at 734 nm. Then, 10 µL of extract was mixed with 190 µL of ABTS solution and incubated for 6 min, and the absorbance was recorded at 734 nm.
For the DPPH radical-scavenging assay, 0.2 mL of the extract was combined with 3.8 mL of DPPH solution, as described previously [19]. The solution was incubated at ambient temperature for 30 min in the dark, after which absorbance was measured at 517 nm using a UV–Vis spectrophotometer.
For both ABTS and DPPH assays, the radical-scavenging activity was calculated as:
where A_control represents the absorbance of the blank (ABTS+ without sample), and A_sample represents the absorbance in the presence of the extract.
[(A_control − A_sample)/A_control] × 100
For the FRAP assay, a commercial kit (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was used in accordance with the supplier’s protocol. The assay was performed at 37 °C, and absorbance at 595 nm was measured in the kinetic mode over 60 min using a plate reader (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). The results were expressed as millimolar concentrations of ferrous ion equivalents, as determined using a standard calibration curve.
TAC was measured using a commercial kit (MAK187, Sigma-Aldrich) that quantifies Cu2+ reduction. For this assay, 10 µL of the extract were mixed with 10 µL of 50× diluted Cu2+ reagent and incubated for 90 min in the dark at room temperature. The absorbance was measured at 570 nm, and antioxidant activity was expressed in Trolox equivalents using a standard curve prepared according to the kit instructions (MAK187, Sigma-Aldrich).
2.4.2. Quantification of Total Phenolic Content
Total phenolics were analyzed using a phenolic compound assay kit (MAK365, Sigma-Aldrich) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Each reaction contained 40 µL of extract (adjusted to 100 µL with distilled water), 20 µL of PC probe, and 80 µL of assay buffer. After a 10 min incubation at room temperature with gentle agitation, absorbance was measured at 480 nm using a Bio-Rad spectrophotometer in the end-point mode. The phenolic content was determined using a catechin standard curve prepared according to the manufacturer’s instructions provided with the phenolic compound assay kit (MAK365, Sigma-Aldrich).
2.4.3. Determination of Flavonoid Content
The flavonoid concentration was assessed using a plant flavonoid colorimetric assay kit (Elabscience, Houston, TX, USA). Wheat seeds (0.02 g) were homogenized and extracted in 60% ethanol at 60 °C for 2 h. After centrifugation, the supernatant was used for the assay. The assay mixture was prepared as instructed by the manufacturer, and absorbance was measured at 510 nm. Flavonoid content was calculated using a standard curve based on the optical density of known concentrations.
2.5. Genotyping and SNP Calling
For genotyping, leaf tissues were collected from individual plants representing each M7 mutant line and immediately stored at −80 °C until DNA extraction. Genomic DNA was isolated from a single plant per line using the cetyltrimethylammonium bromide method following a protocol adapted from the USDA genotyping manual. DNA samples were submitted to the USDA-ARS Small Grains Genotyping Laboratory (Fargo, ND, USA) for genotyping using the iSelect 90K SNP array. SNP allele clustering and genotype calling were conducted using the GenomeStudio Polyploid Genotyping Module v2.0 (https://support.illumina.com/downloads/genomestudio-2-0.html; accessed on 12 June 2024). Quality-control filtering was applied by removing SNP markers with minor allele frequency (MAF) < 0.05, call frequency < 0.95, and genotype calling rate < 0.90. In addition, 3182 SNPs lacking chromosome position information were excluded from further analysis. In total, 19,695 high-confidence SNPs were retained and used for population structure analysis and GWAS. Genotypes with missing data were imputed using BEAGLE v4.1 under default parameters to ensure a complete genotype matrix for downstream analyses.
2.6. Population Structure and Linkage Disequilibrium (LD)
To evaluate the genetic structure of the population, model-based clustering was conducted using STRUCTURE v2.3.4 (https://web.stanford.edu/group/pritchardlab/structure_software/release_versions/v2.3.4/html/structure.html) with a burn-in of 10,000 iterations, followed by 100,000 Markov Chain Monte Carlo repetitions for each run. The number of clusters (K) tested ranged from 1 to 10, with three independent replicates performed per K. The optimal K value was inferred using the ΔK method implemented in Structure Harvester. To further explore the genetic relationships among individuals, principal component analysis (PCA) was performed using Python 3.9 (https://www.python.org/downloads/release/python-390/) based on the SNP genotype matrix obtained from the imputed VCF file. Genotype data were processed using the scikit-allel package, in which the number of alternative alleles per site was extracted and transposed to form a genotype matrix. PCA was conducted using the scikit-learn implementation, and the top three principal components (PC1, PC2, and PC3) were used to visualize the population structure in three-dimensional space. Individuals were colored according to their group assignment as determined by the STRUCTURE Q-matrix (K = 2), with group labels corresponding to the highest membership coefficient per individual. The 3D PCA plot was generated using Matplotlib (https://matplotlib.org/, v3.7.2, accessed on 30 May 2025) and saved at high resolution for publication.
2.7. Correlations of Agronomic and Biochemical Traits with GWAS Data
Phenotypic evaluations were conducted over two consecutive growing seasons (2021–2022 and 2022–2023). For each trait, best linear unbiased predictions (BLUPs) were estimated using the lme4 package in R (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). A linear mixed model was fitted with genotype, year, replication, and genotype-by-year interaction as random effects. The resulting BLUPs were used for both correlation analysis and GWAS. To explore the relationships among traits, pairwise Pearson’s correlation coefficients were calculated on the basis of the BLUP-estimated values. The correlation matrix was visualized using the PerformanceAnalytics R package [20]. GWAS was performed using the GAPIT R package (version 3.0) to identify loci associated with agronomic and biochemical traits. Two models were applied: Fixed and Random Model Circulating Probability Unification (FarmCPU) and Bayesian-information and Linkage-Disequilibrium Iteratively Nested Keyway (BLINK). In total, 19,906 high-quality SNP markers were used for association analysis after filtering. Missing phenotypic values were predicted from the fitted model to create a complete dataset for GWAS. Manhattan plots were generated to visualize the chromosomal distribution of significant marker–trait associations (MTAs), whereas Q–Q plots were used to evaluate the distribution of observed versus expected p-values. A fixed significance threshold of −log10(p) ≥ 4.0 was used to detect marker–trait associations.
2.8. Gene Expression Analysis
RT-qPCR was performed using Bio-Rad CFX Opus 96 (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) and TB Green premix EX Taq II (Takara, Tokyo, Japan). RT-qPCR primers for the indicated genes were designed using an oligonucleotide properties calculator. Each PCR mixture (20 µL) contained 10 µL of 2× TB Green premix EX Taq II, 1 µL of first-strand cDNA, and gene-specific primers. The reactions were performed using the following protocol: 30 s of denaturation at 95 °C, followed by 40 cycles of PCR amplification at 95 °C for 10 s and 65 °C for 30 s. The primers are presented in Supplementary Table S1.
3. Results
3.1. Phenotypic Evaluations and Trait Correlation Analysis
The representative morphological diversity among the 48 colored wheat lines, including 47 M7 mutants and one wild-type parental line, is presented in Figure 1. Figure 1 presents the field phenotypes of each line at two developmental stages, maturity stage and harvest stage, demonstrating evident differences in plant morphology, senescence patterns, seed coloration, and spike architecture. Figure 1 display the corresponding grain and spike morphology, respectively, highlighting substantial variation in grain shape, pigmentation, and spike compactness. These images collectively reflect the phenotypic diversity induced by gamma-ray mutagenesis. Each of the 48 lines, comprising 47 M7 mutant lines and one wild-type parental line, was evaluated for several agronomic and biochemical traits, including TGW, PH, SL, TAC, phenolic compound content, flavonoid levels, anthocyanin concentrations, and colorimetric parameters (L*, a*, b*). The distribution of trait values presented in Figure 2 illustrates considerable phenotypic variability across the mutant lines.
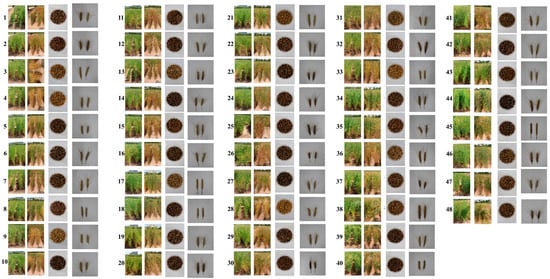
Figure 1.
Representative phenotypes of selected M7 colored wheat mutant lines. From left to right: representative morphologies of selected M7 mutant lines at two developmental stages—maturity and harvest—highlighting differences in PH, senescence, and overall plant architecture; grain images showing variation in seed size, shape, and coloration among lines; and spike morphologies demonstrating diversity in SL and compactness.
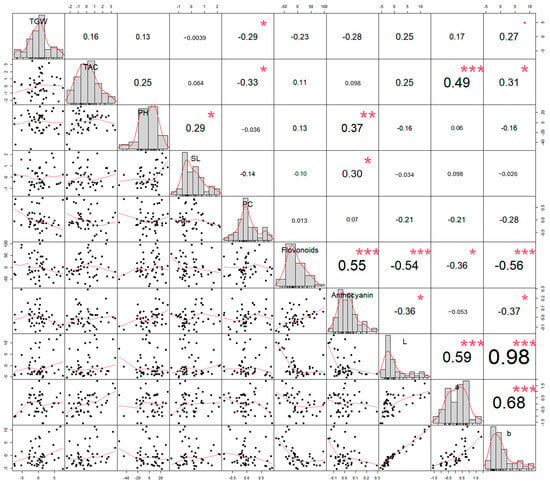
Figure 2.
Distribution and correlation analysis of agronomic, biochemical, and colorimetric traits. Trait distributions and pairwise associations were analyzed for 48 colored wheat lines (47 M7 mutants and 1 wild-type), including TGW, TAC, PH, SL, phenolic compound content, flavonoid content, anthocyanin concentration, and colorimetric values (L*, a*, b*). Pairwise Pearson’s correlation matrix presenting scatterplots in the lower triangle, correlation coefficients in the upper triangle, and density distributions along the diagonal. Asterisks indicate statistical significance: *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, and * p < 0.05.
To explore the relationships among agronomic, biochemical, and colorimetric traits, pairwise Pearson’s correlation coefficients were calculated. The distribution of each trait and their pairwise associations are visually represented through a scatterplot matrix in Figure 2.
Several trait pairs exhibited significant correlations at the p < 0.001 level. TAC exhibited a significant positive correlation with a* (r = 0.49), suggesting that lines with greater antioxidant potential also tend to exhibit more intense red pigmentation. Flavonoid content was positively correlated with the anthocyanin concentration (r = 0.55), reflecting their shared roles as major classes of polyphenolic pigments. In addition, flavonoid content was negatively correlated with both L* (r = −0.54) and b* (r = −0.56), indicating that higher flavonoid accumulation is associated with darker and less yellow seed coloration. Colorimetric parameters also demonstrated strong intercorrelations. Specifically, L* had a strong positive correlation with a* (r = 0.59) and an extremely strong correlation with b* (r = 0.98), suggesting that lightness is closely tied to both red and yellow hue components.
3.2. Marker Distribution, Population Structure, and LD Decay
Of the 81,587 SNP markers present on the wheat 90K iSelect SNP array, 22,877 high-quality SNP markers were retained after removing those with MAF < 0.05 and missing data > 10%. Among these, 19,695 markers were successfully anchored to chromosomal positions and utilized for downstream analyses including GWAS and LD estimation (Supplementary Table S2). The 19,695 mapped SNPs were distributed across the A (12,132 SNPs), B (6,326 SNPs), and D subgenomes (1237 SNPs; Supplementary Table S3). The highest marker density was observed on chromosome 2A (2398 SNPs), followed by chromosomes 1A (2366 SNPs) and 3A (1520 SNPs). Conversely, the lowest numbers of markers were found on chromosomes 5D (99 SNPs) and 4D (106 SNPs), reflecting lower representation in subgenome D.
Population structure analysis revealed clear genetic clustering among the 48 wheat lines, comprising 47 M7 mutant lines and one wild-type parental line. As presented in Figure 3A, PCA based on SNP genotypes separated the lines into two major clusters along the first three principal components, suggesting substantial genetic divergence between the groups. This pattern was further supported by STRUCTURE analysis (Figure 3B), which assigned individuals into two distinct subpopulations. Consistently, the ΔK method based on STRUCTURE output identified K = 2 as the most likely number of genetic clusters (Figure 3C), confirming the existence of two major subpopulations in the mutant groups. Genome-wide LD was estimated using pairwise r2 values among the 19,695 SNPs. As illustrated in Figure 3D, LD decreased progressively with increasing physical distance between marker pairs. The LD decay distance, defined as the physical distance at which the r2 value decreases to half of its maximum, was approximately 1.5 Mb.
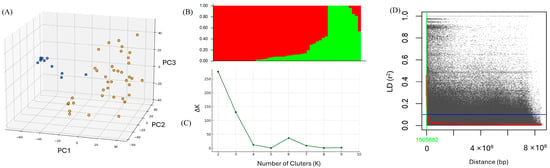
Figure 3.
Genotype structure and genome-wide LD decay analysis. (A) PCA of 48 genotypes based on SNP data illustrates the genetic relationships among individuals, with two distinct clusters observed. (B) Population structure analysis inferred by STRUCTURE software (K = 2) reveals two subpopulations within the genotypes, represented by red and green clusters. (C) ΔK plot generated by the Evanno method identified K = 2 as the optimal number of clusters, supporting the presence of two major genetic groups. (D) Genome-wide LD decay plot depicting the relationship between physical distance and LD (r2). The red curve indicates the nonlinear fit of LD decay, and the point at which LD decays to half its maximum is marked in green (approximately 1.5 Mb).
3.3. GWAS
Several significant MTAs were identified across the wheat genome for four traits (anthocyanin content, L*, SL, and TGW) using BLINK and FarmCPU (Figure 4). In the BLINK model (Figure 4A), MTAs exceeding the threshold of –log10(p) > 4 were identified for all four traits. Notably, strong signals were observed for SL and TGW, with several SNPs reaching high significance on chromosomes 1A, 2B, 3B, and 6A. The Q–Q plots associated with BLINK revealed moderate genomic inflation, with deviations from the expected line indicating the presence of true associations. By contrast, the FarmCPU model (Figure 4B) yielded a greater number of significant MTAs across traits, although the magnitude of –log10(p) values was generally comparable to that of BLINK. FarmCPU appeared to detect more dispersed associations across multiple chromosomes, especially for anthocyanin. The corresponding Q–Q plots highlighted tighter adherence to the expected distribution in the lower range, indicating better control of false positives while still capturing true associations. Overall, the use of both models provided complementary insights into the genetic basis of trait variation, and SNPs with –log10(p) > 4 were retained for downstream functional annotation and candidate gene analysis. In total, 35 significant MTAs were selected using the threshold (Table 1). Among these, 13 MTAs were detected by the BLINK model, 22 MTAs were detected by the FarmCPU model, and 7 SNPs were commonly identified by both models, indicating the robustness of these associations. Notably, several markers such as BS00026777_51 (1A), BS00109911_51 (7A), and RAC875_c8714_653 (7A) were associated with multiple traits or identified across both models, highlighting their potential pleiotropic effects or consistent signals across analytical methods. The anthocyanin trait exhibited the largest number of significant associations, particularly under the FarmCPU model, with many MTAs concentrated on chromosomes 2A and 2B. Several markers (e.g., BobWhite_c5633_59, BobWhite_rep_c66057_98, IAAV3697) shared identical or nearly identical chromosomal positions, suggesting that they represent the same locus or tightly linked regions. The MAFs of these SNPs ranged 0.052–0.468, and the estimated effects varied in both magnitude and direction, reflecting the diverse genetic contributions to each trait. Additionally, the Holm–Bonferroni-adjusted p-value provided further support for the reliability of associations by incorporating trait heritability estimates, serving as candidates for downstream functional annotation and gene discovery.
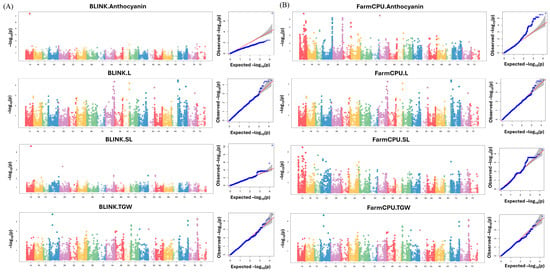
Figure 4.
(A) Manhattan and Q–Q plots of GWAS for four phenotypic traits (anthocyanin, L*, SL, and TGW) using the BLINK model. (B) Corresponding plots generated using the FarmCPU model. Manhattan plots display the –log10(p) values for MTAs across 21 wheat chromosomes (1A–7D), whereas the Q–Q plots compare the observed versus expected p-values to assess model fit. A significance threshold of –log10(p) > 4 was applied to identify MTAs.

Table 1.
Significant MTAs detected through GWAS using the BLINK and FarmCPU algorithms.
3.4. Genotypic Effects of Significant SNPs on Trait Variation
To gain deeper insights into the genomic context of the significant MTAs, a comprehensive gene annotation was conducted using the IWGSC Wheat RefSeq v2.1 reference genome. Considering the estimated LD decay distance of approximately 1.5 Mb, all genes located within ±1.5 Mb of each significant SNP were selected. This search resulted in the identification of 635 genes surrounding the MTA regions (Supplementary Table S4).
Based on the functional annotation of these genes, several SNPs with putative associations to phenotypic traits were prioritized, as presented in Figure 5. Five SNP markers (BS00026777_51, BobWhite_c5633_59, Kukri_c49784_86, Kukri_c9898_1766, and RAC875_c38916_66) were selected because of their strong and consistent associations with anthocyanin content across two consecutive growing seasons (Figure 5). BobWhite_c5633_59 and Kukri_c49784_86 were positioned near TraesCS4A02G047900 (a MYB transcription factor) and TraesCS2A02G591500 (a WD repeat-containing protein), respectively, both of which are putatively involved in the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. For instance, wheat lines with the GG genotype at BobWhite_c5633_59 and the CC genotype at Kukri_c49784_86 exhibited significantly higher anthocyanin levels than other genotypes, along with visibly darker seed coloration. RT-qPCR further supported these findings, revealing significantly elevated expression of TraesCS4A02G047900 and TraesCS2A02G591500 in high-anthocyanin genotypes, consistent with the observed pigmentation phenotype.
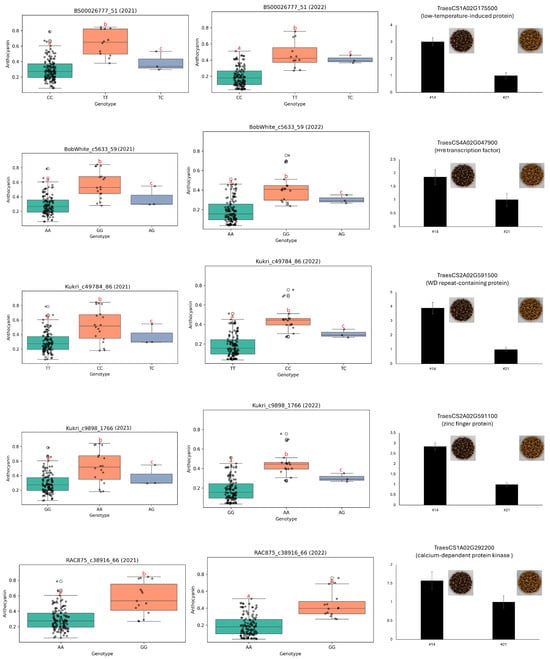
Figure 5.
Genotypic effects of significant SNPs on anthocyanin content and expression of nearby candidate genes. Boxplots presenting differences in anthocyanin content among genotypes at five SNP loci (BS00026777_51, BobWhite_c5633_59, Kukri_c49784_86, Kukri_c9898_1766, and RAC875_c38916_66) across two growing seasons (2021 and 2022). Line #14 exhibits high anthocyanin content in seed, while line #21 exhibits low content. Bar graphs show RT-qPCR results for candidate genes located near each SNP, along with representative seed color images corresponding to contrasting genotypes. Candidate genes include those encoding low-temperature-induced proteins, WD repeat-containing proteins, calcium-dependent protein kinases, transcription factors, and zinc finger proteins. Statistical significance for boxplots was assessed using one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan’s multiple range test (p < 0.05). RT-qPCR was performed in triplicate, and error bars represent standard errors. Different lowercase letters a, b and c indicate correlation between three columns. The symbol that resembles letter “T” in the picture is the error bar.
Two additional SNP markers, namely BS00109911_51 and RAC875_c8714_653, were selected because of their consistent association with seed brightness (L* value) across two consecutive years (Figure 6). BS00109911_51 displayed significant genotypic differences in L* values, with the AA genotype associated with lower brightness and the GG genotype linked to higher values. This phenotypic variation was further supported by expression analysis of the nearby candidate gene TraesCS7A02G002600, which encodes a UDP-glycosyltransferase putatively involved in anthocyanin modification and stabilization. Notably, this gene exhibited higher expression in lines with darker seeds. Similarly, RAC875_c8714_653 was associated with L* variation, with the AA genotype consistently linked to brighter seed color. The nearby gene TraesCS7A02G003600 encodes homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase, an enzyme potentially involved in pigment degradation or modification. Differential expression of this gene was observed between genotypes, with higher expression in lines exhibiting lighter seed coloration.
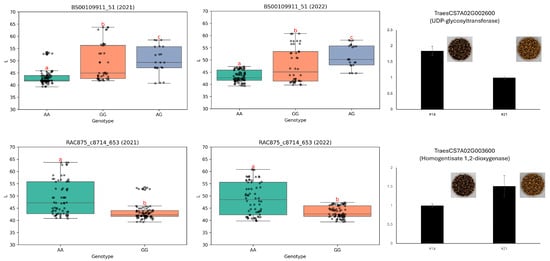
Figure 6.
Genotypic effects of significant SNPs on seed lightness (L*) and associated gene expression. Boxplots illustrating seed lightness (L*) variation among genotypes at SNP loci BS00109911_51 and RAC875_c8714_653 across two growing seasons (2021 and 2022). RT-qPCR analysis was conducted to examine the expression of nearby candidate genes, and representative seed phenotype images are provided. Identified candidate genes include UDP-glycosyltransferases and homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenases. Statistical analysis was conducted using one-way ANOVA and Duncan’s multiple range test (p < 0.05). Gene expression values represent the mean of three biological replicates, and error bars indicate standard errors. Different lowercase letters a, b and c indicate correlation between three columns. The symbol that resembles letter “T” in the picture is the error bar.
IEx_c5759_663 had a consistent association with SL across both years (Figure 7). The AA genotype was associated with significantly longer spikes than the GG genotype, with the AG genotype displaying intermediate values. This phenotypic trend was further supported by expression analysis of nearby candidate genes. TraesCS1A02G191700, encoding an abscisic acid receptor PYR1, and TraesCS1A02G192700, encoding a replication factor C subunit, both had higher expression in lines with longer spikes.
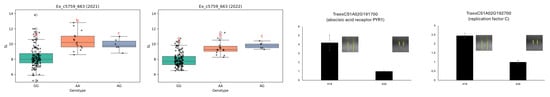
Figure 7.
SNP-associated variation in spike length (SL) and expression of candidate genes. Boxplots displaying variation in spike length (SL) across genotypes at SNP marker Ex_c5759_663 in the 2021 and 2022 growing seasons. Line #19 exhibits a long spike, whereas line #26 displays a short spike. Seed morphology images for each genotype are shown alongside bar graphs representing the expression levels of nearby genes, including those encoding an abscisic acid receptor (PYR1) and replication factor C. Statistical differences among genotypes were determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan’s multiple range test (p < 0.05). RT-qPCR was performed using three biological replicates, and error bars represent standard errors. Different lowercase letters a, b and c indicate correlation between three columns. The symbol that resembles letter “T” in the picture is the error bar.
4. Discussion
Gamma-ray gamma radiation-induced mutagenesis remains a powerful and versatile tool in crop improvement, particularly for generating broad genetic variation in a non-transgenic manner. Recent studies have highlighted the capacity of this technique to introduce diverse types of mutations, including SNPs, small insertions and deletions, and larger chromosomal rearrangements across various crop species, thereby facilitating the discovery of novel beneficial alleles [21,22]. These literature-based features are consistent with our observations, as the M7 colored wheat mutants in this study showed substantial phenotypic variation in plant morphology, pigmentation, and spike architecture.
In this study, we observed significant and robust correlations between biochemical and colorimetric traits in the M7 mutant wheat lines. Lines with higher antioxidant levels exhibited stronger red pigmentation. These findings are consistent with previous reports in pigmented wheat. For example, Sun et al. [23] reported that purple wheat grains exhibited significantly higher levels of total polyphenols, flavonoids, and antioxidant activity than white wheat, primarily because of elevated concentrations of anthocyanin compounds. In addition, colored wheat lines with purple, blue, and black pigmentation featured significantly higher anthocyanin content and antioxidant activity, which was attributed to their superior antioxidative and anti-inflammatory potential [24]. Flavonoid content and anthocyanin concentration, as co-regulated products of the phenylpropanoid pathway, tend to accumulate together in pigmented cereals. In barley, coordinated expression of flavonoid and anthocyanin biosynthetic genes has been observed during grain development [25]. Likewise, in purple wheat, key structural genes such as TaCHS and TaANS displayed strong correlations with anthocyanin levels across developmental stages [26]. Our results also revealed negative correlations between flavonoid content and both L* and b*, suggesting that higher flavonoid accumulation was associated with darker and less yellow seed coloration in the M7 mutants. This is supported by studies finding that seed coat flavonoids, including flavanols and proanthocyanidins, are principal contributors to reddish-brown pigmentation in wheat grains, and highly pigmented cereal lines often exhibit both high flavonoid content and reduced lightness/color brightness [27]. L* had a strong positive correlation with b*, indicating coordinated expression of brightness in seed coloration. L* was positively correlated with b*, indicating coordinated expression of brightness in seed coloration. Similar trends have been reported in blackish-purple rice, in which cyanidin 3-glucoside content exhibited significant positive correlations with L* and b*, suggesting that anthocyanin accumulation can influence lightness and yellowness in grain appearance [28].
In our study, the distribution and quality of SNP markers across the wheat genome reflect key insights into the underlying genomic architecture of the M7 mutant lines. Consistent with previous reports [29], the A and B subgenomes were more densely represented, whereas the D subgenome was sparsely covered, particularly on chromosomes 5D and 4D, a common limitation caused by its lower diversity and representation in genotyping platforms. Population structure analysis revealed clear genetic differentiation among the 48 wheat lines. PCA separated the lines into two major clusters, indicating significant genomic divergence likely induced by mutagenesis or selection. This finding was corroborated by STRUCTURE analysis, which visually confirmed subpopulation assignments, and further validated by the ΔK method identifying K = 2 as the most probable number of genetic groups. The clear separation into two genetic clusters based on our PCA and STRUCTURE analyses indicates substantial genetic heterogeneity within the M7 mutant population. This heterogeneity should be considered in downstream association studies to reduce the risk of false-positive signals due to population stratification, as emphasized in previous studies [30]. Our genome-wide linkage disequilibrium (LD) analysis revealed a typical decay pattern, with r2 declining as physical distance increased. The LD decay distance in our panel was approximately 1.5 Mb. This is agreement with previous reports, where LD decay varied depending on germplasm type from as short as 0.29 Mb in genetically diverse panels [31], to intermediate ranges of 1.5–3.0 Mb [32] and up to 10–32 Mb in Mexican bread wheat landraces [33], reflecting differences in genetic diversity and selection history. This finding suggests moderate historical recombination in the studied mutant population.
Thirty-five significant MTAs were identified across four traits using BLINK and FarmCPU. Notably, several markers were associated with multiple traits or identified across models, suggesting potential pleiotropic effects or stable QTL regions. Notably, anthocyanin content exhibited the highest number of associations, particularly on chromosomes 2A and 2B, under the FarmCPU model. This chromosomal distribution aligns with previous reports that identified anthocyanin biosynthetic genes, such as F3H and ANS, on chromosomes 2A and 2B [34,35]. These genes have been shown to play central roles in pigmentation control in wheat. While our study did not directly test these genes, the co-localization of significant SNPs in these regions suggests they may underlie some of the observed associations. Additionally, some SNPs shared nearly identical chromosomal positions, possibly representing the same locus. These findings highlight important candidate regions and markers for further functional validation and marker-assisted selection in wheat breeding.
To elucidate the genetic basis underlying trait variation, significant SNPs identified through GWAS were further investigated via genomic annotation and expression analysis. Based on our LD decay analysis (Figure 3D), where r2 declined to half of its maximum at approximately 1.5 Mb, candidate genes were selected within ± 1.5 Mb of each significant MTA. This interval was considered appropriate for identifying putative functional genes in linkage with associated loci, particularly given the broad genetic variation introduced by gamma-ray mutagenesis. A moderately flexible region was adopted to avoid omitting relevant genes, in line with the exploratory objectives of the study. In total, 635 genes were identified within these regions, providing a broad yet targeted genomic context for candidate gene discovery. Among the associations, several SNPs related to anthocyanin content were located near genes involved in flavonoid biosynthesis, particularly TraesCS4A02G047900 and TraesCS2A02G591500. These regulatory components, which encode a MYB transcription factor and a WD repeat-containing protein, respectively, form part of the MYB–bHLH–WD40 complex, a key transcriptional module driving anthocyanin accumulation in many plants, as previously described [36]. In this study, the strong expression of these genes in genotypes with higher anthocyanin levels, as confirmed by RT-qPCR, reinforced their potential functional role. Similarly, SNPs associated with seed brightness (L*) were found near TraesCS7A02G002600 encoding UDP-glycosyltransferase, which participates in anthocyanin modification and stabilization [37]. The differential expression patterns between bright and dark seed lines support the involvement of this gene in pigmentation traits. Homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase, encoded by the candidate gene TraesCS7A02G003600, might participate in pigment catabolism, aligning with its higher expression in light-colored genotypes. This gene shares homology with the soybean gene homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase, known to participate in the degradation of homogentisate, a precursor of tocopherol and brown pigments. In soybean, previous studies have shown that loss-of-function mutations in this pathway result in the accumulation of brown pigments in seeds, suggesting a role in regulating pigment intensity [38]. Concerning SL, Ex_c5759_663 was consistently associated with phenotypic variation and located near TraesCS1A02G191700 and TraesCS1A02G192700, encoding the abscisic acid receptor PYR1 and a replication factor C subunit, respectively. ABA signaling components such as PYR1 and replication factor C subunits might regulate spike elongation, potentially through coordinated roles in growth regulation, DNA replication, and cell-cycle progression [39,40].
In this study, a significance threshold of −log10(p) ≥ 4.0 was applied to identify marker–trait associations. While GAPIT provides Bonferroni correction, it was not applied in this study to avoid excessive false negatives. This is because Bonferroni is often considered overly conservative in exploratory GWAS, particularly when the sample size is relatively small [41]. Instead, a fixed threshold was selected to enable more flexible detection of SNPs associated with phenotypic variation. This decision reflects the exploratory nature of this study, which aimed to assess radiation-induced genetic diversity and uncover novel alleles in mutant wheat lines. Similar thresholds have also been used in recent GWASs employing multi-locus models such as FarmCPU and BLINK [42,43].
Although most traits measured in this study, including seed color and agronomic traits, are likely quantitative in nature, making it difficult to fully validate specific associations solely based on the expression of a few nearby genes, the identification of 635 genes within the ±1.5-Mb regions surrounding significant SNPs provides a valuable genomic resource. These candidate genes might represent starting points for future molecular and functional studies aiming to dissect the genetic basis of complex traits. Although the relatively small population size (48 lines) may have limited the statistical power of GWAS and increased the possibility of false negatives, this limitation is inherent in studies involving mutagenized populations derived from a single genetic background. Nevertheless, the present work serves as a foundational step in utilizing radiation-induced variation to uncover novel alleles related to pigmentation and plant architecture in colored wheat. Further studies using larger and more genetically diverse populations may help to confirm and refine these preliminary associations. Overall, the integration of GWAS, genomic proximity, and gene expression profiling highlighted several biologically plausible genes that might contribute to phenotypic variation in wheat. Moreover, this study underscores the importance of utilizing radiation-induced mutant populations as a powerful approach to broaden phenotypic diversity and uncover novel alleles for breeding purposes.
5. Conclusions
This study utilized an integrative genome-wide association approach to explore the genetic basis of seed pigmentation and major agronomic traits in colored wheat lines. Using BLINK and FarmCPU models, 35 significant MTAs were identified, seven of which were consistently detected across both models, indicating their potential robustness. Gene annotation within ±1.5 Mb of significant SNPs identified 635 nearby genes, with several candidates involved in pigment biosynthesis and modification pathways. Although expression analyses of selected candidate genes supported some genotype–phenotype relationships, most of the traits examined are quantitative in nature; therefore, they are influenced by complex genetic networks beyond single-gene effects. Nonetheless, the integration of association signals, genomic proximity, and transcript abundance helped highlight biologically meaningful candidate genes. These findings offer a foundational resource for future functional studies and could assist in the marker-assisted selection of colored wheat varieties. Furthermore, this research supports the utility of radiation-induced mutant populations in expanding phenotypic diversity and accelerating the discovery of beneficial alleles in wheat improvement.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy15081933/s1, Supplementary Table S1: List of primers used in this study; Supplementary Table S2: Detailed SNP information for the 19,696 markers used in downstream analysis, including SNP IDs, chromosomal positions, and genotypes (haplotypes) across 48 M7 mutant wheat lines; Supplementary Table S3: Summary of SNP markers retained after quality filtering (MAF ≥ 0.05, missing data ≤ 10%) and their chromosomal distribution across the A, B, and D subgenomes in the wheat 90K iSelect array; Supplementary Table S4: List of 635 genes located within ± 1.5 Mb of significant SNPs identified from GWAS, based on the IWGSC Wheat RefSeq v2.1 genome annotation.
Author Contributions
M.J.H.: Conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, validation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. C.S.K.: Formal analysis, data curation, investigation, methodology. D.Y.K.: Supervision, conceptualization, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the research program of the Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (Project No. 523420–25).
Data Availability Statement
All data relevant to this study are included within the article and its Supplementary Files.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BLINK | Bayesian-information and Linkage-Disequilibrium Iteratively Nested Keyway |
| BLUP | Best linear unbiased predictions |
| CC | Creative Commons |
| FarmCPU | Fixed and Random Model Circulating Probability Unification |
| FRAP | Ferric reducing antioxidant power |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association study |
| IWGSC | International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium |
| LD | Linkage disequilibrium |
| MAF | Minor allele frequency |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| PH | Plant height |
| QTL | Quantitative trait loci |
| SL | Spike length |
| SNP | Single-nucleotide polymorphism |
| TGW | Thousand-grain weight |
References
- Loskutov, I.G.; Khlestkina, E.K. Wheat, barley, and oat breeding for health benefit components in grain. Plants 2021, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padhy, A.K.; Kaur, P.; Singh, S.; Kashyap, L.; Sharma, A. Colored wheat and derived products: Key to global nutritional security. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 1894–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Nam, B.M.; Ahn, J.W.; Kwon, S.J.; Seo, Y.W.; Kim, J.B. Characterization of novel mutants of hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) with various depths of purple grain color and antioxidant capacity. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Beta, T. Comparison of antioxidant activities of different colored wheat grains and analysis of phenolic compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 9235–9241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Yadav, M.; Tiwari, A.; Ali, U.; Krishania, M.; Bala, M.; Mridula, D.; Sharma, P.; Goudar, G.; Roy, J.K.; et al. A comparative study of colored wheat lines across laboratories for validation of their phytochemicals and antioxidant activity. J. Cereal Sci. 2023, 112, 103719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, G.H.; Kalpande, H.V.; Sargar, P.R.; Deshmukh, S.S.; Patil, S.A. Mutation breeding in crop improvement. In Elements of Plant Breeding; Iterative International Publishers: Chikmagalur, India, 2024; pp. 74–87. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Kong, F.; Sun, K.; Wang, T.; Guo, T. From classical radiation to modern radiation: Past, present, and future of radiation mutation breeding. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 768071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Datta, P.S. Gamma irradiation to improve plant vigour, grain development, and yield attributes of wheat. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2010, 79, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Kumar, S.S. Mutation Breeding: A Tool for Crop Improvement and Agricultural Sustainability. RCA Issue Brief 2025, 2, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sao, R.; Sahu, P.K.; Patel, R.S.; Das, B.K.; Jankuloski, L.; Sharma, D. Genetic improvement in plant architecture, maturity duration and agronomic traits of three traditional rice landraces through gamma ray-based induced mutagenesis. Plants 2022, 11, 3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Chai, L.; Chen, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhai, H.; Zhao, A.; Peng, H.; Yao, Y.; You, M.; Sun, Q.; et al. Identification and characterization of a high kernel weight mutant induced by gamma radiation in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Genet. 2015, 16, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.A. Influence of radio-grain priming on growth, antioxidant capacity, and yield of barley plants. Biotechnol. Rep. 2022, 34, e00724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choulet, F.; Alberti, A.; Theil, S.; Glover, N.; Barbe, V.; Daron, J.; Pingault, L.; Sourdille, P.; Couloux, A.; Paux, E.; et al. Structural and functional partitioning of bread wheat chromosome 3b. Science 2014, 345, 1249721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium (IWGSC); Appels, R.; Eversole, K.; Stein, N.; Feuillet, C.; Keller, B.; Rogers, J.; Pozniak, C.J.; Choulet, F.; Distelfeld, A. Shifting the limits in wheat research and breeding using a fully annotated reference genome. Science 2018, 361, eaar7191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walkowiak, S.; Gao, L.; Monat, C.; Haberer, G.; Kassa, M.T.; Brinton, J.; Ramirez-Gonzalez, R.H.; Kolodziej, M.C.; Delorean, E.; Thambugala, D.; et al. Multiple wheat genomes reveal global variation in modern breeding. Nature 2020, 588, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, Y.; Kang, L.; Yin, C.; Bi, A.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Xu, J.; et al. Population genomics unravels the Holocene history of bread wheat and its relatives. Nat. Plants 2023, 9, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mita, S.; Murano, N.; Akaike, M.; Nakamura, K. Mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana with pleiotropic effects on the expression of the gene for β-amylase and on the accumulation of anthocyanin that are inducible by sugars. Plant J. 1997, 11, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.G.; Carl, P.; Boudt, K.; Bennett, R.; Ulrich, J.; Zivot, E.; Cornilly, D.; Hung, E.; Lestel, M.; Balkissoon, K. Package ‘PerformanceAnalytics’. R Team Coop. 2018, pp. 13–14. Available online: https://github.com/braverock/PerformanceAnalytics (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Bharat, R.A.; Prathmesh, S.P.; Sarsu, F.; Suprasanna, P. Induced mutagenesis using gamma rays: Biological features and applications in crop improvement. OBM Genet. 2024, 8, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhan, X.; Liu, L.; Feng, F.; Guo, Z.; Wang, D.; Chen, H. Biological effects of gamma-ray radiation on tulip (Tulipa gesneriana L.). PeerJ 2022, 10, e12792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, N.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, B.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, G.; Ye, L. Comparative metabolic analysis and antioxidant properties of purple and white wheat grains: Implications for developing functional wheat varieties. Food Qual. Saf. 2024, 8, fyad060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Chunduri, V.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, R.; Khare, P.; Kondepudi, K.K.; Bishnoi, M.; Garg, M. Anthocyanin bio-fortified colored wheat: Nutritional and functional characterization. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Abbas, H.M.K.; Zhan, C.; Huang, Y.; Huang, S.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Luo, J.; Zeng, X. Integrative metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses reveal the mechanisms of Tibetan hulless barley grain coloration. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1038625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ji, G.; Xu, Z.; Feng, B.; Zhou, Q.; Fan, X.; Wang, T. Metabolomics and transcriptomics provide insights into anthocyanin biosynthesis in the developing grains of purple wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 11171–11184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Hou, H.; Ma, X.; Sun, S.; Wang, H.; Kong, L. Metabolomics and gene expression analysis reveal the accumulation patterns of phenylpropanoids and flavonoids in different colored-grain wheats (Triticum aestivum L.). Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, T.H.; Kwon, S.W.; Ryu, S.N.; Koh, H.J. Correlation analysis between grain color and cyanidin-3-glucoside content of rice grain in segregate population. Plant Breed. Biotechol. 2015, 3, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wong, D.; Forrest, K.; Allen, A.; Chao, S.; Huang, B.E.; Maccaferri, M.; Salvi, S.; Milner, S.G.; Cattivelli, L.; et al. Characterization of polyploid wheat genomic diversity using a high-density 90,000 single nucleotide polymorphism array. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2014, 12, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, A.L.; Patterson, N.J.; Plenge, R.M.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Shadick, N.A.; Reich, D. Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Habib, M.; Ahmed, Z.; Sadia, B.; Bernardo, A.; Amand, P.S.; Bai, G.; Ghori, N.; Khan, A.I.; Awan, F.S.; et al. Genotyping-by-sequencing based molecular genetic diversity of Pakistani bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) accessions. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 772517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrov, V.; Kartseva, T.; Alqudah, A.M.; Kocheva, K.; Tasheva, K.; Börner, A.; Misheva, S. Genetic diversity, linkage disequilibrium and population structure of Bulgarian bread wheat assessed by genome-wide distributed SNP markers: From old germplasm to semi-dwarf cultivars. Plants 2021, 10, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikram, P.; Sehgal, D.; Sharma, A.; Bhavani, S.; Gupta, P.; Randhawa, M.; Pardo, N.; Basandra, D.; Srivastava, P.; Singh, S.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis of Mexican bread wheat landraces for resistance to yellow and stem rust. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Dong, Y.X.; Tang, X.Z.; Tu, T.L.; Zhao, B.; Sui, N.; Fu, D.L.; Zhang, X.S. Comparative transcriptome analysis revealing the effect of light on anthocyanin biosynthesis in purple grains of wheat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 3465–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Jiao, B.; Zhao, P.; Xu, T.; Gu, S.; Huo, C.; Pang, J.; Zhou, S. Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis of anthocyanin metabolism in wheat pericarp. BMC Genom. Data 2025, 26, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Dubos, C.; Lepiniec, L. Transcriptional control of flavonoid biosynthesis by MYB–bHLH–WDR complexes. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, D.; Lim, E.K.; Poppenberger, B.; Vaistij, F.E. Glycosyltransferases of lipophilic small molecules. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 567–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, M.G.; Cahoon, R.E.; Nguyen, H.T.; Cui, Y.; Sato, S.; Nguyen, C.T.; Phoka, N.; Clark, K.M.; Liang, Y.; Forrester, J.; et al. Identification of homogentisate dioxygenase as a target for vitamin E biofortification in oilseeds. Plant Physiol. 2016, 172, 1506–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidler, J.; Graska, J.; Gietler, M.; Nykiel, M.; Prabucka, B.; Rybarczyk-Płońska, A.; Muszyńska, E.; Morkunas, I.; Labudda, M. PYR/PYL/RCAR receptors play a vital role in the abscisic-acid-dependent responses of plants to external or internal stimuli. Cells 2022, 11, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, T.; Ishibashi, T.; Kimura, S.; Tanaka, H.; Hashimoto, J.; Sakaguchi, K. Characterization of all the subunits of replication factor C from a higher plant, rice (Oryza sativa L.), and their relation to development. Plant Mol. Biol. 2003, 53, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffari, A.; Silver, M.J.; Zavattari, P.; Moi, L.; Columbano, A.; Meaburn, E.L.; Dudbridge, F. Estimation of a significance threshold for epigenome-wide association studies. Genet. Epidemiol. 2018, 42, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Yang, T.; He, F.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, X.; Wang, C.; Kang, J. A genome-wide association study reveals novel loci and candidate genes associated with plant height variation in Medicago sativa. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, A.; Feyissa, T.; Maccaferri, M.; Sciara, G.; Tuberosa, R.; Ammar, K.; Abeyo, B. Genome-wide association analysis unveils novel QTLs for seminal root system architecture traits in Ethiopian durum wheat. BMC Genomics 2021, 22, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).