Study on the Microbial Mechanism of Bacillus subtilis in Improving Drought Tolerance and Cotton Yield in Arid Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
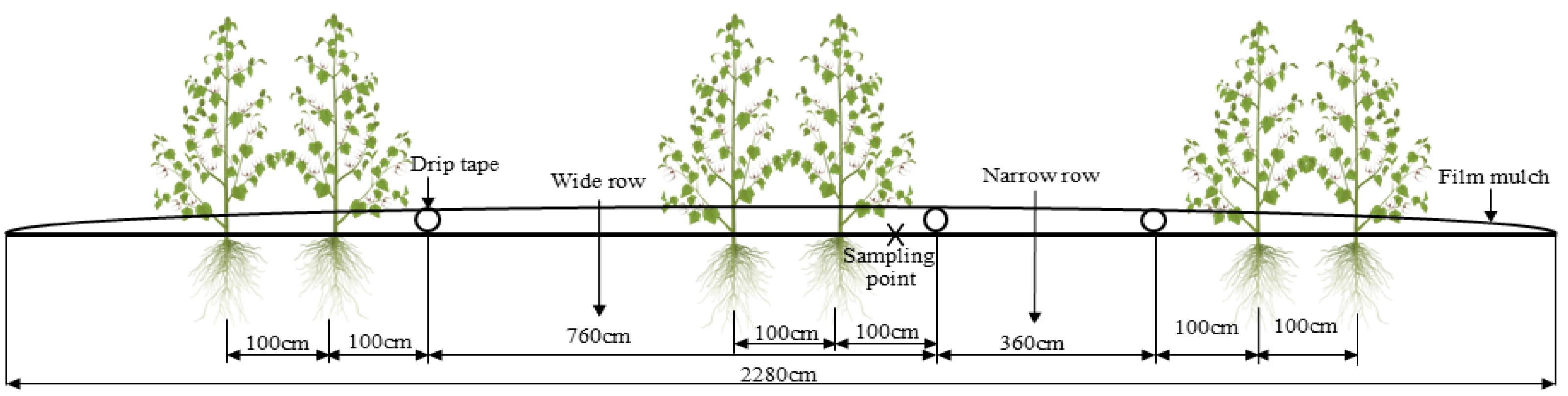
2.1. Field Test
2.2. Soil and Plant Sampling
2.3. The Method for DNA Extraction, PCR Conditions, and the Platform/Technique Used for Sequencing
2.3.1. The Method for DNA Extraction
2.3.2. PCR Amplification and Homogenization Treatment
2.3.3. Construction and Sequencing of Sequencing Library
2.4. Soil Chemistry and Enzyme Analysis
2.4.1. Analysis of Soil Indicators
2.4.2. Determination of Soil Enzyme
2.4.3. Determination of Malondialdehyde and SPAD Value
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cotton Yield
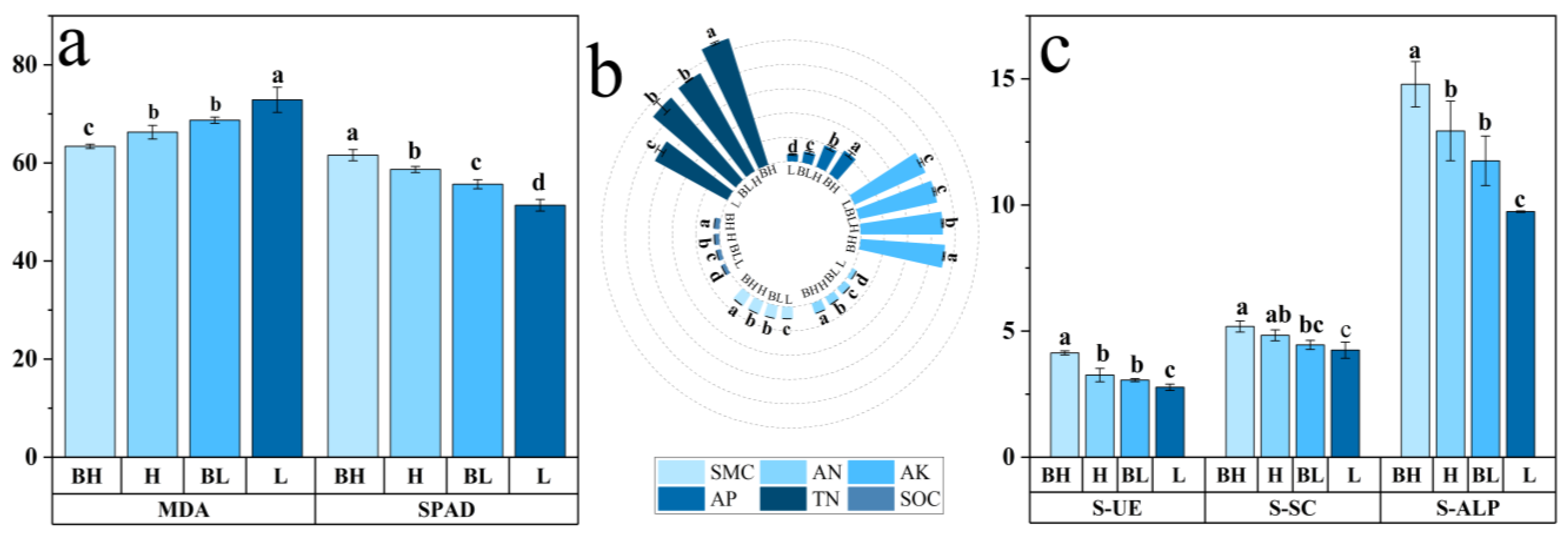
3.2. Physicochemical Properties of Rhizosphere Soil
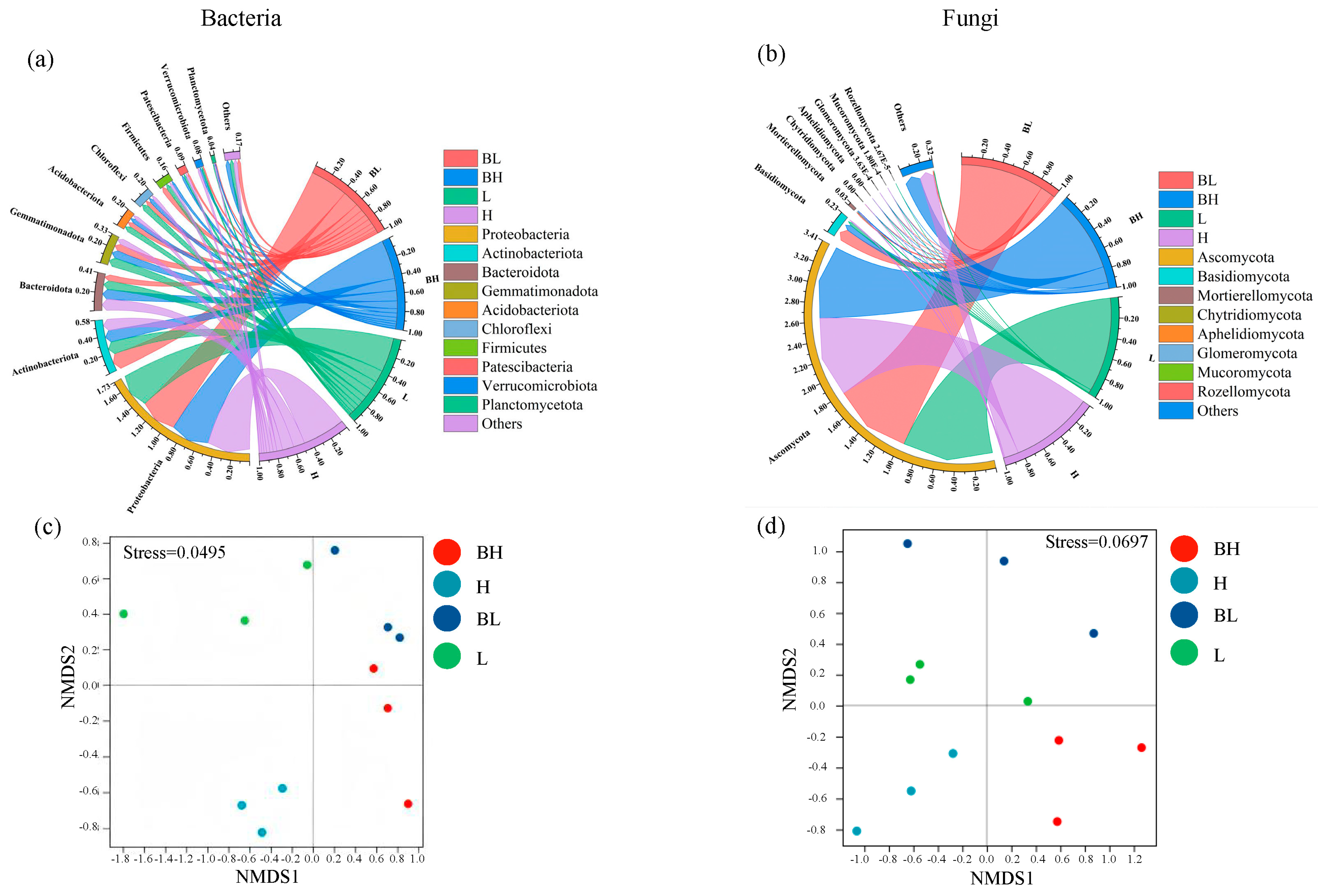
3.3. Changes in Soil Microbial Community
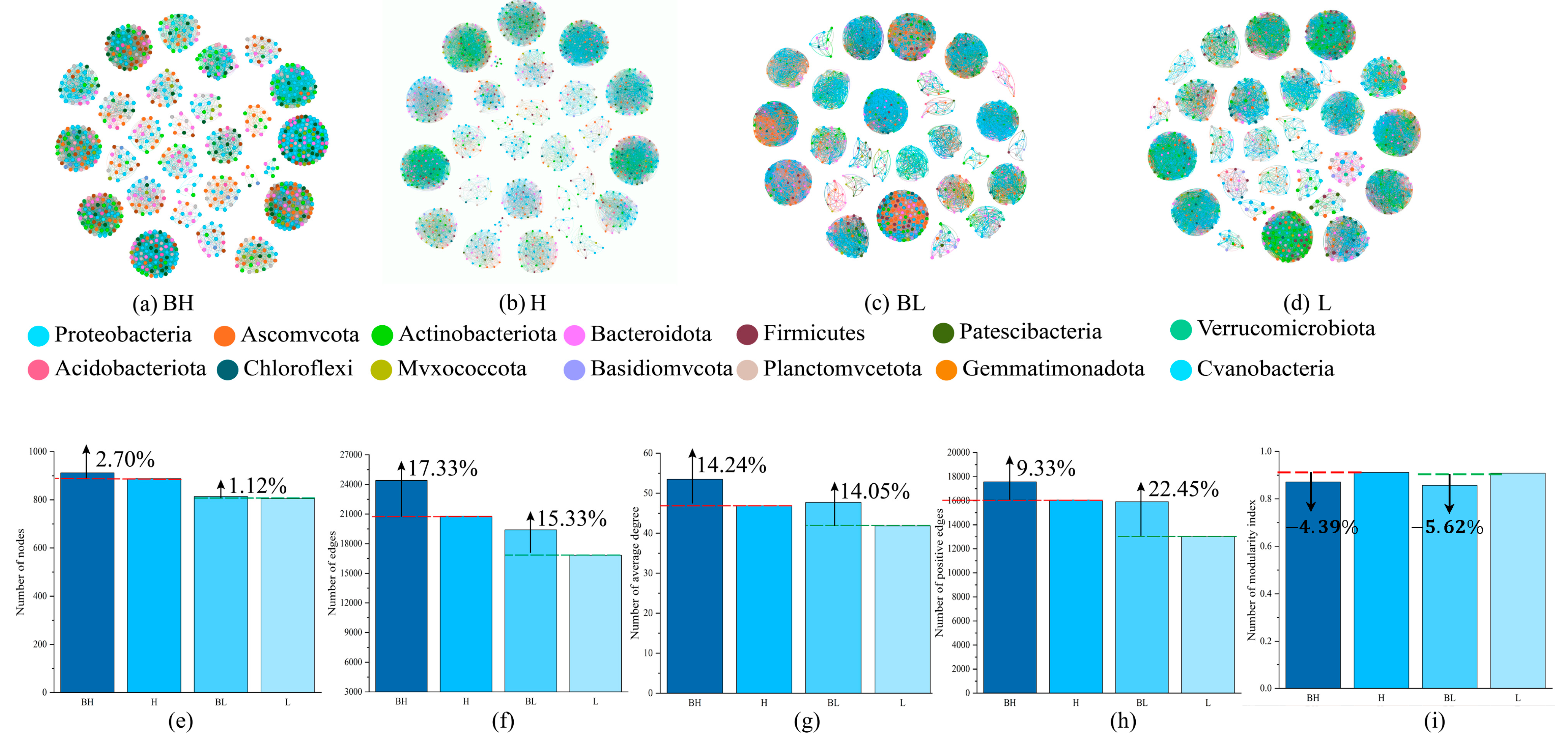
3.4. Soil Microbial Synbiotic Network
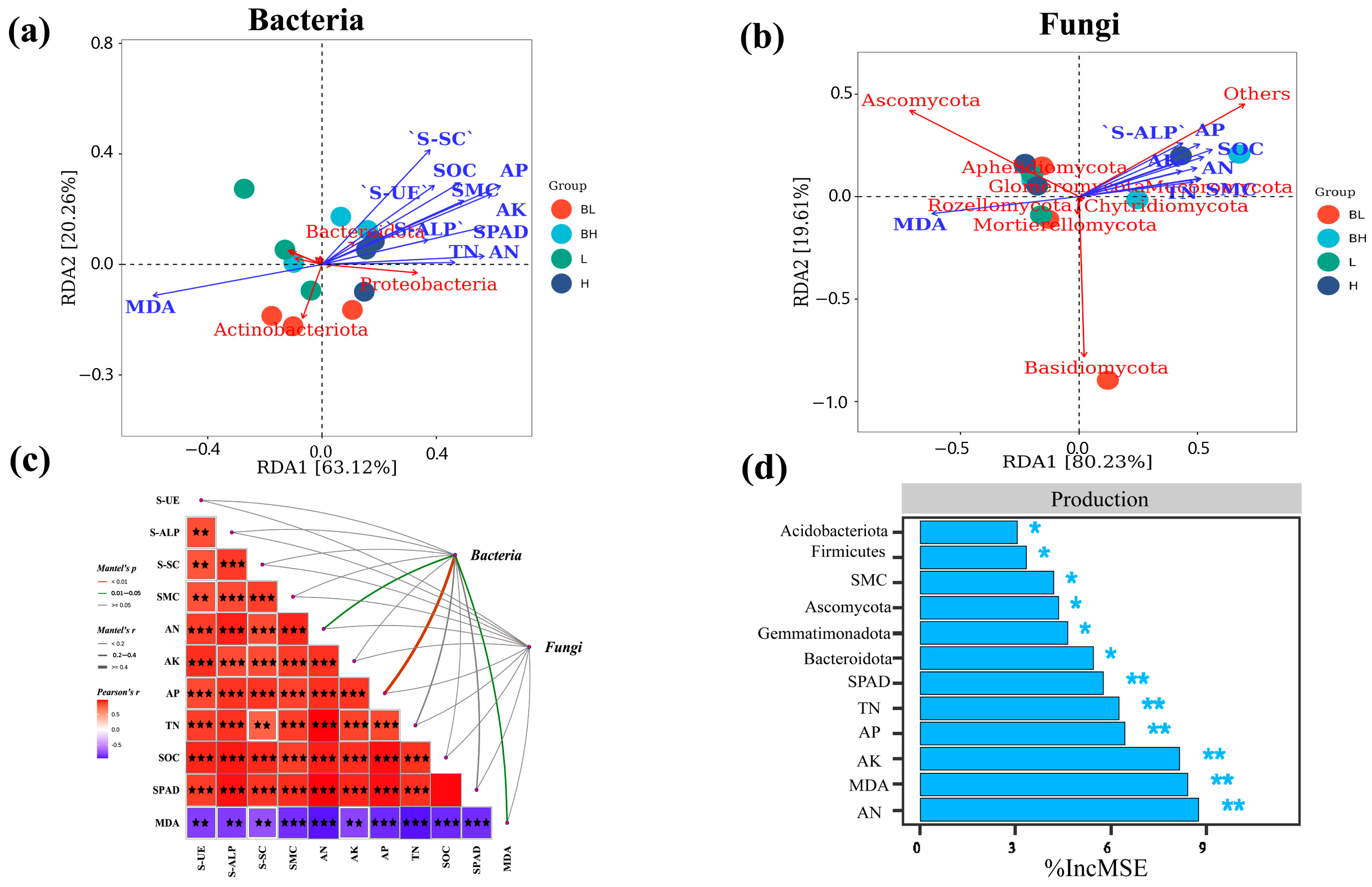
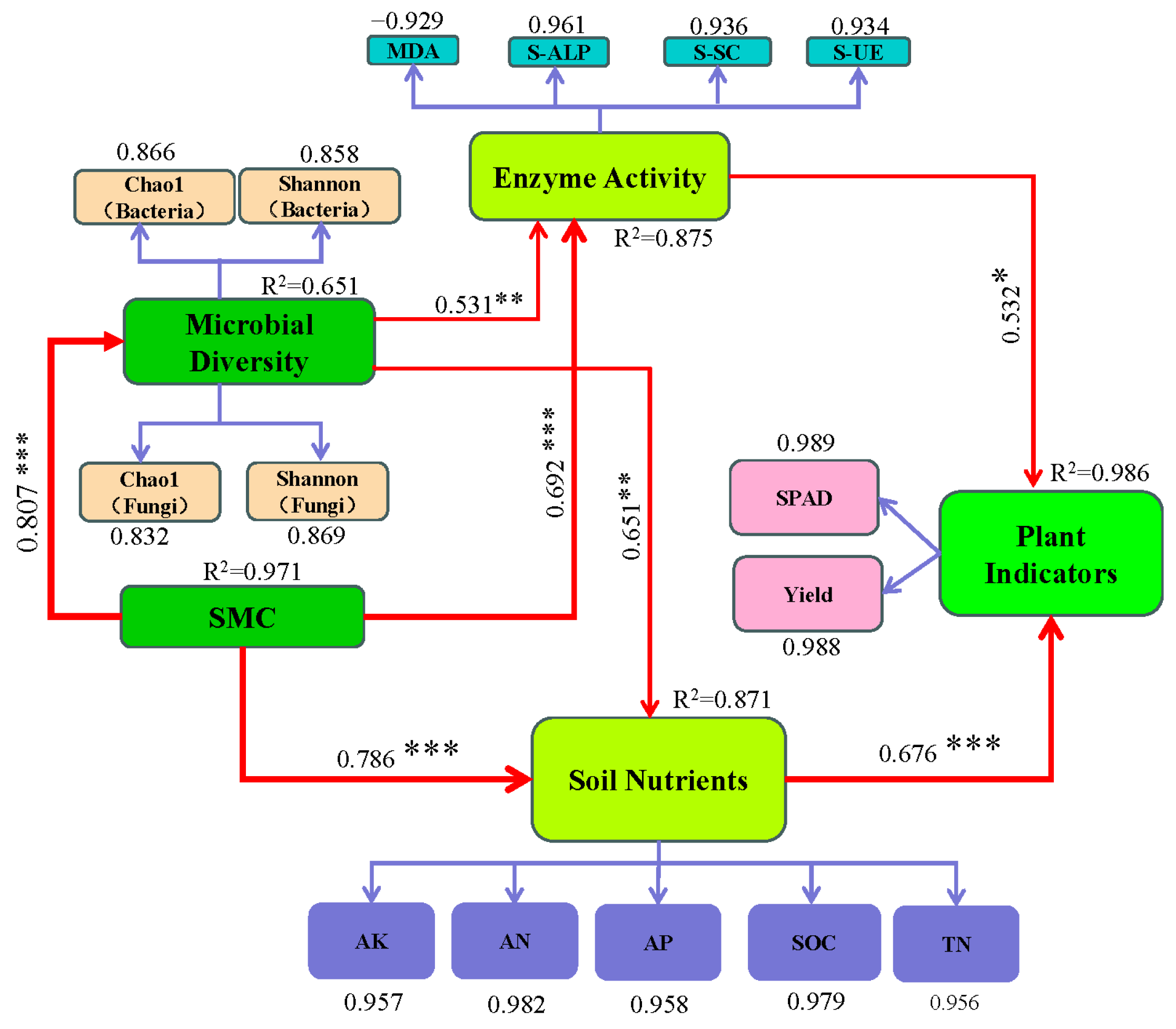
3.5. The Relationship Between Soil Microbial Community and Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of B. subtilis on Cotton Yield and Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
4.2. Responses of Cotton Rhizosphere Microbial Community to B. subtilis
4.3. B. subtilis Mainly Affects Soil Quality and Crop Yield by Changing Microbial Communities
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xia, J.; Chen, J.; She, D.X. Impacts and countermeasures of extreme drought in the Yangtze River Basin in 2022. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2022, 53, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, J.I.; Martin, E.R.; Basara, J.B.; Furtado, J.C.; Otkin, J.A.; Lowman, L.E.L.; Hunt, E.D.; Mishra, V.; Xiao, X. Global Projections of Flash Drought Show Increased Risk in a Warming Climate. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Hu, J.; Zhou, C.Y.; La, B. Progress on the Mechanism of Interaction between Saline Plants and Inter-rooted Soil Microorganisms under Saline Stress. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2024, 55, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.M.; Wang, A.H. Interannual Variability and Key Influencing Factors of Drought in China over the Past 120 Years. Clim. Environ. Res. 2024, 29, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.N.; Liu, X.H.; Zeng, X.M.; Jia, R.X. Research progress from individual plant physiological response to ecological model prediction under drought stress. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 10042–10053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, I.; Aleem, S.; Junaid, J.A.; Ali, Z.; Aleem, M.; Shahzad, R.; Farooq, J.; Khan, M.I.; Arshad, W.; Ellahi, F. Multiomics approaches to explore drought tolerance in cotton. J. Cotton Res. 2024, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, D.K.; Impa, S.M.; McCallister, D.; Patil, G.B.; Abidi, N.; Ritchie, G.; Jaconis, S.Y.; Jagadish, K.S.V. High day and night temperatures impact on cotton yield and quality—Current status and future research direction. J. Cotton Res. 2023, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.M.; Chattha, W.S.; Khan, A.I.; Zafar, S.; Subhan, M.; Saleem, H.; Ali, A.; Ijaz, A.; Anwar, Z.; Qiao, F.; et al. Drought and Heat Stress on Cotton Genotypes Suggested Agro-Physiological and Biochemical Features for Climate Resilience. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1265700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Khan, A.A.; Cheema, H.M.N.; Khan, S.H.; Iqbal, Z. Cotton germplasm characterization for drought tolerance based on morpho-physiological and fiber quality parameters. SABRAO J. Breed. Genet. 2023, 55, 1079–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Sun, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X. Drought coping strategies in cotton: Increased crop per drop. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; He, H.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, J.; Jiao, G.; Xiang, C.; Wang, C.; et al. AtZAT10/STZ1 Improves Drought Tolerance and Increases Fiber Yield in Cotton. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1464828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.; Yu, S.; Zhang, F.; Ma, T.; Ding, J.; Chen, K.; Chen, X.; Dai, Y. Effects of Soil Water Regulation on the Cotton Yield, Fiber Quality and Soil Salt Accumulation under Mulched Drip Irrigation in Southern Xinjiang, China. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asargew, M.F.; Masutomi, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Aono, M. Water Stress Changes the Relationship between Photosynthesis and Stomatal Conductance. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, F.; Mi, N.; Ming, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, B. Responses of dry matter accumulation and partitioning to drought and subsequent rewatering at different growth stages of maize in Northeast China. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1110727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejnák, V.; Tatar, Ö.; Atasoy, G.D.; Martinková, J.; Çelen, A.E.; Hnilička, F.; Skalický, M. Growth and Photosynthesis of Upland and Pima Cotton: Response to Drought and Heat Stress. Plant Soil Environ. 2015, 61, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Gan, Q.; Liu, R.; Xu, H. Impact of Drought on Soil Microbial Biomass and Extracellular Enzyme Activity. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1221288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Gao, P.; Zuo, L.; Duan, L.; Cang, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, X.; Zhang, L. Soil Quality Evaluation for Cotton Fields in Arid Region Based on Graph Convolution Network. Land 2023, 12, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoso, M.A.; Wagan, S.; Alam, I.; Hussain, A.; Ali, Q.; Saha, S.; Poudel, T.R.; Manghwar, H.; Liu, F. Impact of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) on Plant Nutrition and Root Characteristics: Current Perspective. Plant Stress 2024, 11, 100341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xiao, C.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, T.; Xu, K.; Chen, J.; Lin, Z.; Chen, J.; Tian, S.; Lu, L. Inoculation of Multi-Metal-Resistant Bacillus sp. to a Hyperaccumulator Plant Sedum Alfredii for Facilitating Phytoextraction of Heavy Metals from Contaminated Soil. Chemosphere 2024, 366, 143464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igiehon, B.C.; Babalola, O.O.; Hassen, A.I. Rhizosphere Competence and Applications of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria in Food Production—A Review. Sci. Afr. 2024, 23, e02081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Liu, H.; Gong, P.; Li, P.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, M.; Meng, Q.; Ye, F.; Yin, W. Study of the Mechanism by Which Bacillus subtilis Improves the Soil Bacterial Community Environment in Severely Saline-Alkali Cotton Fields. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 178000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wu, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X. Biochar Combined with Bacillus subtilis SL-44 as an Eco-Friendly Strategy to Improve Soil Fertility, Reduce Fusarium Wilt, and Promote Radish Growth. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 251, 114509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ning, S.; Lin, S.; Hu, X.; Song, Z. Application of Magnetized Ionized Water and Bacillus subtilis Improved Saline Soil Quality and Cotton Productivity. Plants 2024, 13, 2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashem, A.; Tabassum, B.; Fathi Abd_Allah, E. Bacillus subtilis: A Plant-Growth Promoting Rhizobacterium That Also Impacts Biotic Stress. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahapatra, S.; Yadav, R.; Ramakrishna, W. Bacillus subtilis Impact on Plant Growth, Soil Health and Environment: Dr Jekyll and Mr. Hyde. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 3543–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.; Yu, M.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Yin, D.; Zuo, S.; Ren, J. Microbial Organic Fertilizer Improved the Physicochemical Properties and Bacterial Communities of Degraded Soil in the North China Plain. Sustainability 2024, 16, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Gu, L.; Bao, L.; Zhang, S.; Wei, Y.; Bai, Z.; Zhuang, G.; Zhuang, X. Application of Biofertilizer Containing Bacillus subtilis Reduced the Nitrogen Loss in Agricultural Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 107911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Islam, S.; Husain, F.M.; Yadav, V.K.; Park, H.-K.; Yadav, K.K.; Bagatharia, S.; Joshi, M.; Jeon, B.-H.; Patel, A. Bacillus subtilis ER-08, a multifunctional plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium, promotes the growth of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) plants under salt and drought stress. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1208743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zeng, Q.; Han, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xu, H. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on Cucumber Seedling Growth and Photosynthetic System under Different Potassium Ion Levels. Biology 2024, 13, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Zhou, B.; Ren, P.; Chen, X.; Zhou, D.; Yao, S.; Fan, D.; Chen, X. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on Cotton Physiology and Growth under Water and Salt Stress. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 303, 109038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Y.; Yi, Y.; Wang, H.; Wei, B.; Zeng, L. Two Bacillus spp. Strains Improve the Structure and Diversity of the Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Community of Lilium brownii var viridulum. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mageshwaran, V.; Gupta, R.; Singh, S.; Sahu, P.K.; Singh, U.B.; Chakdar, H.; Bagul, S.Y.; Paul, S.; Singh, H.V. Endophytic Bacillus subtilis Antagonize Soil-Borne Fungal Pathogens and Suppress Wilt Complex Disease in Chickpea Plants (Cicer arietinum L.). Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 994847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miljaković, D.; Marinković, J.; Balešević-Tubić, S. The Significance of Bacillus spp. in Disease Suppression and Growth Promotion of Field and Vegetable Crops. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Dou, X.; Liao, D.; Li, K.; An, C.; Li, G.; Dong, Z. Microbial Fertilizers Improve Soil Quality and Crop Yield in Coastal Saline Soils by Regulating Soil Bacterial and Fungal Community Structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 949, 175127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Min, K.; Liu, T.; Li, C.; Xu, J.; Hu, F.; Li, H. The Potential Role of Fertilizer-Derived Exogenous Bacteria on Soil Bacterial Community Assemblage and Network Formation. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishisaka, C.S.; Ventura, J.P.; Bais, H.P.; Mendes, R. Role of Bacillus subtilis Exopolymeric Genes in Modulating Rhizosphere Microbiome Assembly. Environ. Microbiome 2024, 19, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daunoras, J.; Kačergius, A.; Gudiukaitė, R. Role of Soil Microbiota Enzymes in Soil Health and Activity Changes Depending on Climate Change and the Type of Soil Ecosystem. Biology 2024, 13, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, Y.H.; Ganie, M.A.; Shah, T.I.; Bangroo, S.A.; Mir, S.A.; Shah, A.M.; Wani, F.J.; Qin, A.; Rahman, S.U. Soil Microbial and Enzyme Activities in Different Land Use Systems of the Northwestern Himalayas. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, T.M.; Acosta-Martínez, V.; Calderón, F.; Jackson, L.E. Soil Enzyme Activities, Microbial Communities, and Carbon and Nitrogen Availability in Organic Agroecosystems across an Intensively-Managed Agricultural Landscape. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, B.; Bai, Y.; Guo, S.; He, Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Zhai, J.; Cao, H. Effect of Irrigation Water Salinity on Soil Characteristics and Microbial Communities in Cotton Fields in Southern Xinjiang, China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Zhou, B.; Duan, M.; Cao, T.; Wen, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, M.; Cheng, W.; Zhu, H.; et al. Combination of Biochar and Trichoderma harzianum Can Improve the Phytoremediation Efficiency of Brassica juncea and the Rhizosphere Micro-Ecology in Cadmium and Arsenic Contaminated Soil. Plants 2023, 12, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Mu, W. Irrigation with Ionized Brackish Water Affects Cotton Yield and Water Use Efficiency. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 175, 114244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xiong, W.; Qi, J.; Pan, H.; Chen, S.; Peng, Z.; Gao, H.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Wei, G.; et al. Trophic Interrelationships Drive the Biogeography of Protistan Community in Agricultural Ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 163, 108445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Xie, P.; Yang, S.; Niu, G.; Liu, X.; Ding, Z.; Xue, C.; Liu, Y.-X.; Shen, Q.; Yuan, J. ggClusterNet: An R package for microbiome network analysis and modularity-based multiple network layouts. iMeta 2023, 1, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Ge, L.; Zhao, R.; Peng, C.; Zhou, X.; Li, P.; Liu, Z.; Song, H.; Tang, J.; Zhang, C.; et al. Phenolic Compounds Weaken the Impact of Drought on Soil Enzyme Activity in Global Wetlands. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1372866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schärer, M.-L.; Fuchslueger, L.; Canarini, A.; Richter, A.; Lüscher, A.; Kahmen, A. Post-Drought Organic Carbon Mineralization Leads to High Productivity and Nutrient Uptake Efficiency of Perennial Grassland after Rewetting. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 204, 109744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Z.; Ahmad, M.; Raza, M.A.; Hilger, T.; Rasche, F. Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacillus sp. Modulate Soil Exoenzyme Activities and Improve Wheat Growth. Microb. Ecol. 2024, 87, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Chen, J.Y.; Cao, X.; Meng, L.Q.; Liu, Z.T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Yu, D.S. Research Progress and Application of Phosphate-Solubilizing Microorganisms in Soils. HJAS 2022, 12, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.H.; Li, J.X.; Chen, G.; Wang, T.; Chi, X.Y.; Qi, P.S. Phosphate Solubilizing Microorganisms and Application Progress in Saline-alkaline Soil. Soils 2021, 53, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Cheng, H.; Liang, X.M.; Chen, Y.L.; Wu, S.W.; Hu, C.X. Research progress of acidified soil amelioration and carbon sequestration. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 7871–7884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, V.; Condón, S.; Gayán, E. Impact of Sporulation Temperature on Germination of Bacillus subtilis Spores under Optimal and Adverse Environmental Conditions. Food Res. Int. 2024, 182, 114064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Qin, Z.; Wu, J.; Wang, Q.; Yin, Y. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on Carbon Components and Microbial Functional Metabolism during Cow Manure–Straw Composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 303, 122868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogsa, I.; Bellich, B.; Blaznik, M.; Lagatolla, C.; Ravenscroft, N.; Rizzo, R.; Stopar, D.; Cescutti, P. Bacillus subtilis EpsA-O: A Novel Exopolysaccharide Structure Acting as an Efficient Adhesive in Biofilms. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniz, F.; Zheng, W.; Bais, H.; Jin, Y. Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria Mediate Soil Hydro-Physical Properties: An Investigation with Bacillus subtilis and Its Mutants. Vadose Zone J. 2023, 22, e20274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.L.; Zhou, B.B.; Chen, X.P.; Liang, C.F. Mechanisms of Bacillus subtilis in modulating soil microenvironment and enhancing cotton yield. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2025, 41, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, O.-G.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.-S.; Keum, H.L.; Lee, K.-C.; Sul, W.J.; Lee, J.-H. Bacillus subtilis Strain GOT9 Confers Enhanced Tolerance to Drought and Salt Stresses in Arabidopsis Thaliana and Brassica Campestris. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.; Hou, X.; Liang, X. Response Mechanisms of Plants Under Saline-Alkali Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 667458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslennikova, D.; Lastochkina, O. Contribution of Ascorbate and Glutathione in Endobacteria Bacillus subtilis-Mediated Drought Tolerance in Two Triticum aestivum L. Genotypes Contrasting in Drought Sensitivity. Plants 2021, 10, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastochkina, O.; Yuldashev, R.; Avalbaev, A.; Allagulova, C.; Veselova, S. The Contribution of Hormonal Changes to the Protective Effect of Endophytic Bacterium Bacillus subtilis on Two Wheat Genotypes with Contrasting Drought Sensitivities under Osmotic Stress. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buqori, D.M.A.I.; Sugiharto, B.; Suherman Siswoyo, T.A.; Hariyono, K. Mitigating drought stress by application of drought-tolerant Bacillus spp. enhanced root architecture, growth, antioxidant and photosynthetic genes expression in sugarcane. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Zhou, B.; Bi, Y.; Chen, X.; Yao, S.; Yang, X. Bacillus subtilis Can Promote Cotton Phenotype, Yield, Nutrient Uptake and Water Use Efficiency under Drought Stress by Optimizing Rhizosphere Microbial Community in Arid Area. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 227, 120784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Hussain, A.; Iqbal, A.; Shah, F.; Wu, W.; Cai, H. Microbial Utilization to Nurture Robust Agroecosystems for Food Security. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, P.; Khobra, R.; Sundha, P.; Chandra, A.; Sharma, R.K.; Singh, G.P. Bacillus subtilis Strain BS87 as a Biocontrol Agent against Spot Blotch Disease: Effect on Growth, Nutrient Status, and Antioxidant Enzymes in Wheat. Acta Physiol. Plant 2024, 46, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Gong, X.; Dang, K.; Li, J.; Yang, P.; Gao, X.; Deng, X.; Feng, B. Linkages between Nutrient Ratio and the Microbial Community in Rhizosphere Soil Following Fertilizer Management. Environ. Res. 2020, 184, 109261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Pioppi, A.; Kiesewalter, H.T.; Strube, M.L.; Kovács, Á.T. Disentangling the factors defining Bacillus subtilis group species abundance in natural soils. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 26, e16693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Li, Z.J.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Tang, S.C.; Huang, D.; Luo, H.B. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on structure and metabolism of microbial community under a multi-bacteria co-fermentation system. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 39, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Chu, H.; Zhang, B.; Wei, X.; Chen, W.; Wei, G. Linking soil fungi to bacterial community assembly in arid ecosystems. iMeta 2022, 1, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.J.; Wang, J.J.; Wei, M.; Pang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, S.W.; Huang, Z.Y. Bacillus velezensis FH-1 promotes rice seedlings growth by regulating specific spatiotemporal soil microbiome. Microbiol. China 2024, 51, 2381–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiyam, D.; Dubey, A.; Malla, M.A.; Kumar, A. Lipopeptides from Bacillus: Unveiling biotechnological prospects—Sources, properties, and diverse applications. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2024, 55, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.S.; Liu, J.N.; Hu, L.C.; Wen, R.Z.; Zhou, G.Y. Analysis of Volatile Compounds from Bacillus subtilis Y13 and Its Antimicrobial Activity. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2019, 35, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Xiao, J.; Gao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, B.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced salt tolerance in Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. via Bacillus subtilis inoculation alters microbial community. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 3, e0381223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N.; Li, S.; He, L.; Feng, Y.; Saeed, M.; Ma, Y.; Ni, Z.; Zhu, D.; Chen, H. High-Throughput Screening and Identification of Lignin Peroxidase Based on Spore Surface Display of Bacillus subtilis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2025, 105, 2179–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Long, T.; Jiang, Z.; Mu, W.; Su, M.; Ni, L.; Ji, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, K.; Zhan, R.; et al. Comparison of Lignin Degradation and Flavor Compound Formation in Roasted Tobacco by Two Bacillus subtilis Strains. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1538773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemzadeh, Z.; Parhizkar, M.; Mirmohammadmeygooni, S.; Shabanpour, M.; Chalmers, G. Forest Soil Inoculation with Bacillus subtilus Reduces Soil Detachment Rate to Mitigate Rill Erosion. Rhizosphere 2023, 26, 100707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, Y. The Function of Root Exudates in the Root Colonization by Beneficial Soil Rhizobacteria. Biology 2024, 13, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.S.; Gaonkar, V.V.; Mukadam, H.M.; Gaikwad, S.V.; Shinde, S.S.; Gaonkar, V.V.; Mukadam, H.M.; Gaikwad, S.V. Bacillus subtilis: A Biological Marvel in the Domain of Agriculture and Environmental Science. In Bacillus subtilis—Functionalities and One Health Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.Q.; Zhao, W.S.; Su, Z.H.; Dong, L.H.; Guo, Q.G.; Ma, P. Effect of Bacillus subtilis NCD-2 on the Growth of Tomato and the Microbial Community Structure of Rhizosphere Soil Under Salt Stress. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2021, 54, 4573–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.R.; Xing, D.X.; Xiao, Y.; Liao, S.T.; Zou, Y.X.; Liu, F.; Li, E.N.; Zhou, D.L.; Yang, Q. Rhizosphere colonization of Bacillus subtilis biocontrol strain SEM-9 and the effect on microbial diversity in rhizosphere soil. J. South China Agric. Univ. 2022, 43, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xu, Z.; Xie, J.; Hesselberg-Thomsen, V.; Tan, T.; Zheng, D.; Strube, M.L.; Dragoš, A.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, R.; et al. Bacillus velezensis Stimulates Resident Rhizosphere Pseudomonas Stutzeri for Plant Health through Metabolic Interactions. ISME J. 2022, 16, 774–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Gong, T.; Wang, J.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhen, J.; Ning, M.; Yue, D.; Du, Z.; Chen, G. Effects of Compound Microbial Fertilizer on Soil Characteristics and Yield of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 20, 2740–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.P.; Chen, Z.; Yang, H. Effects of biocontrol agents on fungi community diversity and structure in rhizosphere soil of continuous cropping celery. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2024, 2, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Ma, X.; Wang, W.; Xu, C.; Xiang, X.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Tran, L.-S.P.; Zhang, B. Ameliorating Drought Resistance in Arabidopsis and Alfalfa under Water Deficit Conditions through Inoculation with Bacillus tequilensis G128 and B. Velezensis G138 Derived from an Arid Environment. Plant Stress 2025, 15, 100727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.R.; Yu, T.; Chen, P.; Li, X.Y. Research advances on the antimicrobial effect of bacteriostatic substances from Bacillus spp. Chin. J. Antibiot. 2024, 49, 481–489. [Google Scholar]
- Caballero, P.; Macías-Benítez, S.; Moya, A.; Rodríguez-Morgado, B.; Martín, L.; Tejada, M.; Castaño, A.; Parrado Rubio, J. Biochemical and Microbiological Soil Effects of a Biostimulant Based on Bacillus licheniformis-Fermented Sludge. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, S.; Qiang, R.; Lu, E.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Q. Response of Soil Microbial Community Structure to Phosphate Fertilizer Reduction and Combinations of Microbial Fertilizer. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 899727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Sierra, N.D.; Posada, L.F.; Santa-María, G.; Romero-Tabarez, M.; Villegas-Escobar, V.; Álvarez, J.C. Bacillus subtilis EA-CB0575 genome reveals clues for plant growth promotion and potential for sustainable agriculture. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2020, 20, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Zeng, M.B.; Li, Q.R.; Jia, Q.Y.; Liu, X.L.; Hou, Y.Y.; Fan, C.M.; Chen, Y.H.; et al. Advances in several important antimicrobial lipopeptids from Bacillus spp. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 1768–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.-M.; Bu, L.-Y.; Chen, W.-F.; An, D.-R.; Wei, G.-H.; Wang, H.-L. Effect of High-volume Straw Returning and Applying Bacillus on Bacterial Community and Fertility of Desertification Soil. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 5176–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.P.; Xue, Z.Q.; Yang, Z.Y.; Chai, Z.; Niu, J.P.; Shi, Z.Y. Effects of microbial organic fertilizers on Astragalus membranaceus growth and rhizosphere microbial community. Ann. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Tian, L.; Nasir, F.; Bahadur, A.; Batool, A.; Luo, S.; Yang, F.; Wang, Z.; Tian, C. Response of Microbial Communities and Enzyme Activities to Amendments in Saline-Alkaline Soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 135, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, F.T.; Griffiths, R.I.; Bailey, M.; Craig, H.; Girlanda, M.; Gweon, H.S.; Hallin, S.; Kaisermann, A.; Keith, A.M.; Kretzschmar, M.; et al. Soil Bacterial Networks Are Less Stable under Drought than Fungal Networks. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Luo, X.; Liao, H.; Chen, W.; Wei, D.; Cai, P.; Huang, Q. Ureolytic Microbial Community Is Modulated by Fertilization Regimes and Particle-Size Fractions in a Black Soil of Northeastern China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 116, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Xia, W.Y.; Zhao, H.; Zeng, M. Effects of deep vertical rotary tillage on soil enzyme activity, microbial community structure and functional diversity of cultivated land. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 5009–5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Wang, X.L.; He, J.; Yang, S.M.Y.; Zheng, Q.W.; Li, M.R. Effects of Replacing Chemical Nitrogen Fertilizer with Organic Fertilizer on Active Organic Carbon Fractions, Enzyme Activities, and Crop Yield in Yellow Soil. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 4196–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.K.; Yang, G.H.; Ren, C.J.; Han, X.H. Effects of Farmland Abandonment on Soil Enzymatic Activity and Enzymatic Stoichiometry in the Loess Hilly Region, China. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.X.; Wang, Z.T.; Zhao, D.Q.; Wu, G.; Ling, J.; Zhou, S.L.; Wen, Y. Effects of soil warming and straw return on soil nutrients and extracellular enzyme activities. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 9867–9876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, W.; He, Y.; Zou, D.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Bai, Y. Plant-Root Microbiota Interactions in Nutrient Utilization. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2025, 12, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.S.; Tian, W.F.; Yan, D.D.; Li, Y.; Cao, A.C.; Wang, Q.X. Linkages between soil nutrient turnover and above-ground crop nutrient metabolism: The role of soil microbes. iMetaOmics 2025, 2, e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.S.; Zhang, C.P.; Dong, Q.M.; Yang, Z.Z.; Zhang, X.F.; Huo, L.A.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, Z.S.; Yu, Y.; Yang, X.X. Effects of Different Forms of Nitrogen Addition on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Microbial Community Structure of Perennial Alpine Cultivated Grassland. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 3595–3604. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Lei, S.; Wu, H.; Liao, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, G.; Wang, G.; Fang, L.; Song, Z. Simplified Microbial Network Reduced Microbial Structure Stability and Soil Functionality in Alpine Grassland along a Natural Aridity Gradient. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 191, 109366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Depth (cm) | Bulk Density (g·cm−3) | Field Capacity (%) | Saturated Water Content (%) | Total Nitrogen Content (mg·kg−1) | Total Phosphorus Content (mg·kg−1) | Rapidly Available Potassium (mg·kg−1) | Organic Matter (g·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~20 | 1.60 | 21.00 | 24.00 | 0.39 | 0.53 | 197.25 | 5.75 |
| 20~40 | 1.55 | 24.00 | 30.00 | 0.25 | 0.48 | 192.57 | 4.71 |
| 40~60 | 1.58 | 25.00 | 33.00 | 0.17 | 0.42 | 139.71 | 3.49 |
| 60~80 | 1.59 | 25.00 | 32.00 | 0.12 | 0.39 | 90.19 | 2.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, P.; Zhou, B.; Bi, Y.; Chen, X.; Yao, S. Study on the Microbial Mechanism of Bacillus subtilis in Improving Drought Tolerance and Cotton Yield in Arid Areas. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1932. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081932
Ren P, Zhou B, Bi Y, Chen X, Yao S. Study on the Microbial Mechanism of Bacillus subtilis in Improving Drought Tolerance and Cotton Yield in Arid Areas. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1932. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081932
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Peiqi, Beibei Zhou, Yanpeng Bi, Xiaopeng Chen, and Shaoxiong Yao. 2025. "Study on the Microbial Mechanism of Bacillus subtilis in Improving Drought Tolerance and Cotton Yield in Arid Areas" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1932. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081932
APA StyleRen, P., Zhou, B., Bi, Y., Chen, X., & Yao, S. (2025). Study on the Microbial Mechanism of Bacillus subtilis in Improving Drought Tolerance and Cotton Yield in Arid Areas. Agronomy, 15(8), 1932. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081932






