Agronomic and Intercropping Performance of Newly Developed Elite Cowpea Lines for the West African Savannas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Genotype Selection
2.2. Multi-Location Evaluation for Agronomic Performance
2.3. Evaluation for Adaptation to Intercropping
2.4. Data Collection and Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
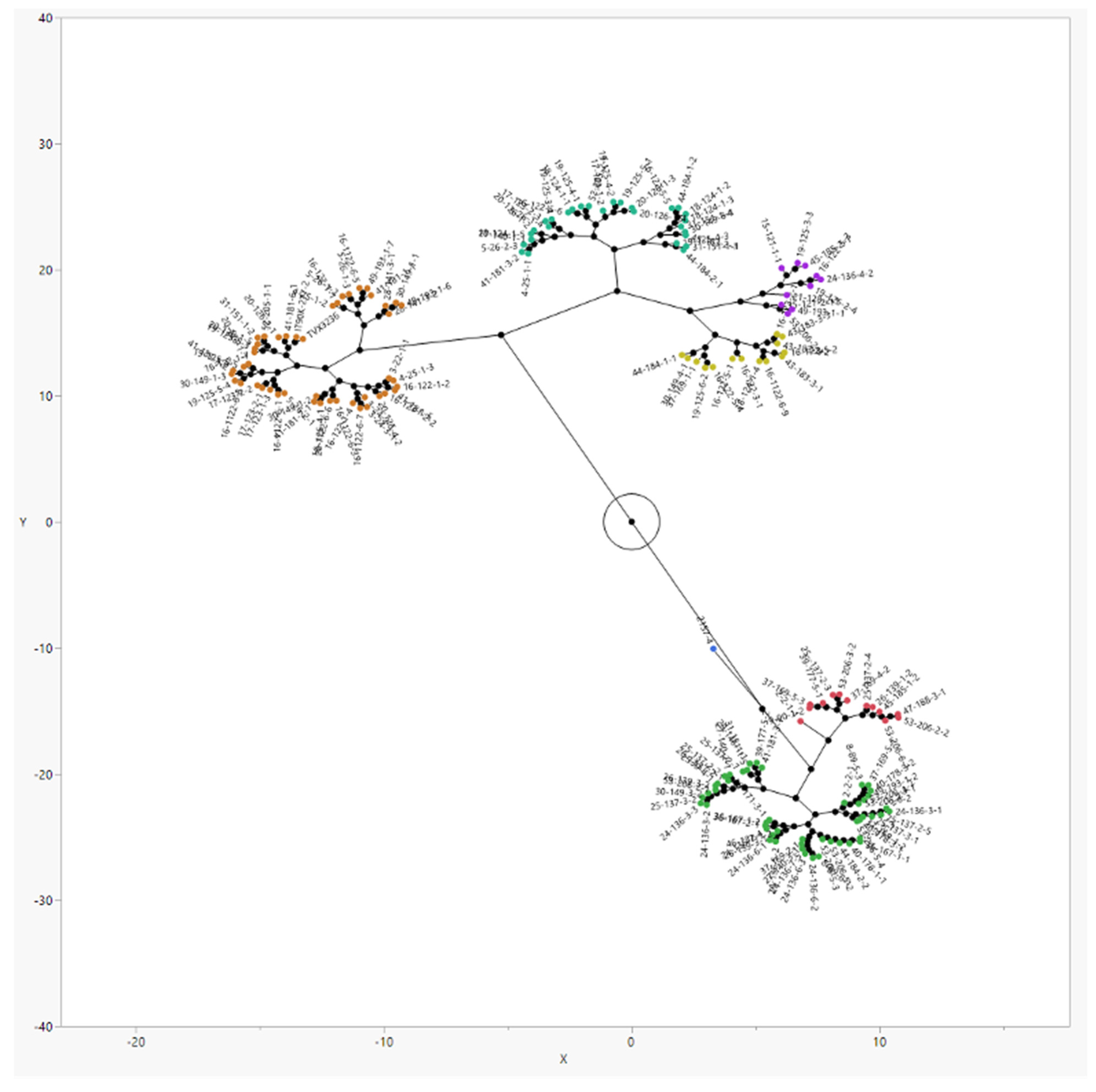
3.1. Screening of the Breeding Lines for Striga Resistance
3.2. Agronomic Performance of Elite Cowpea Lines
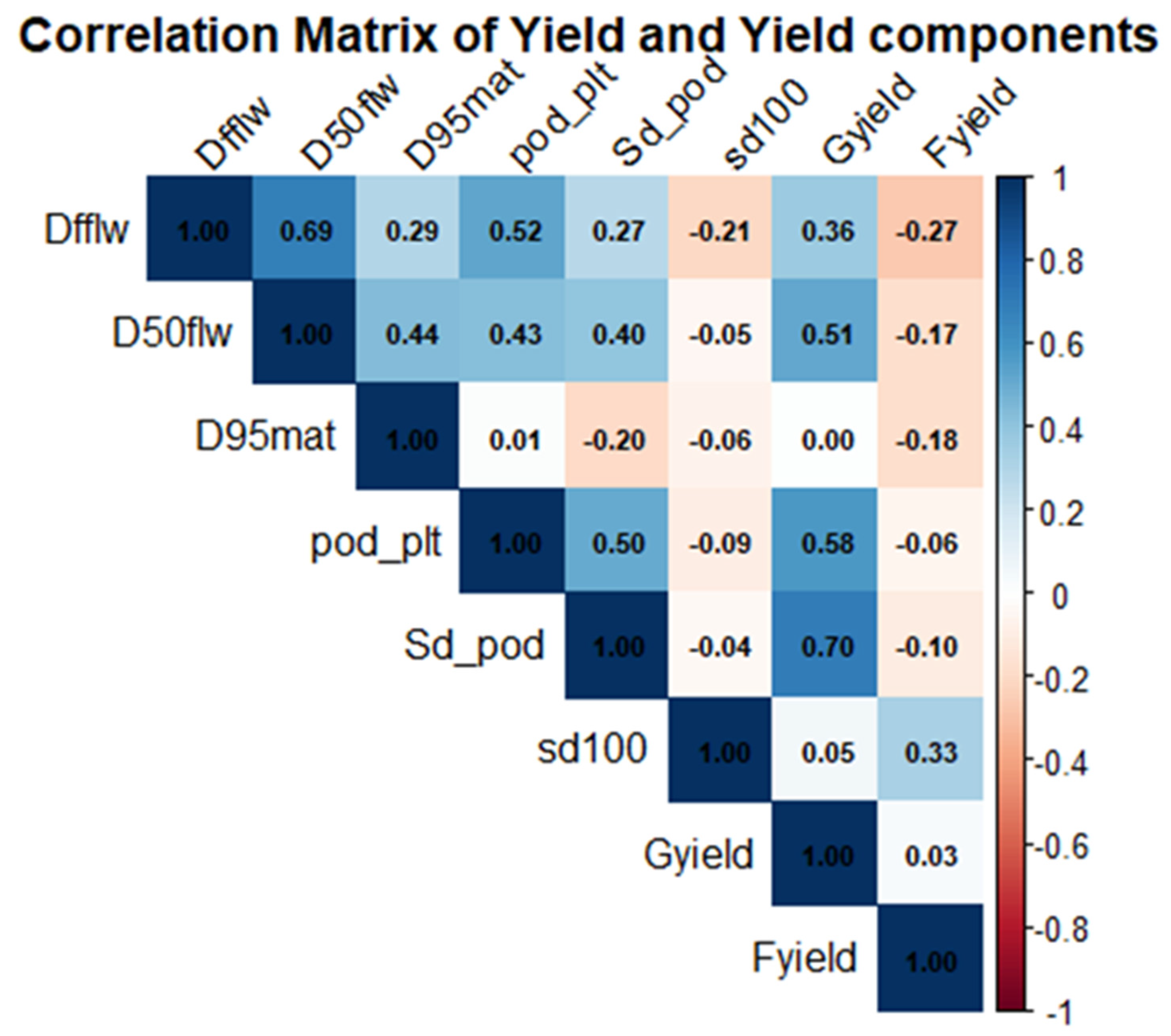
3.3. Correlation Among Traits of the Cowpea Genotypes
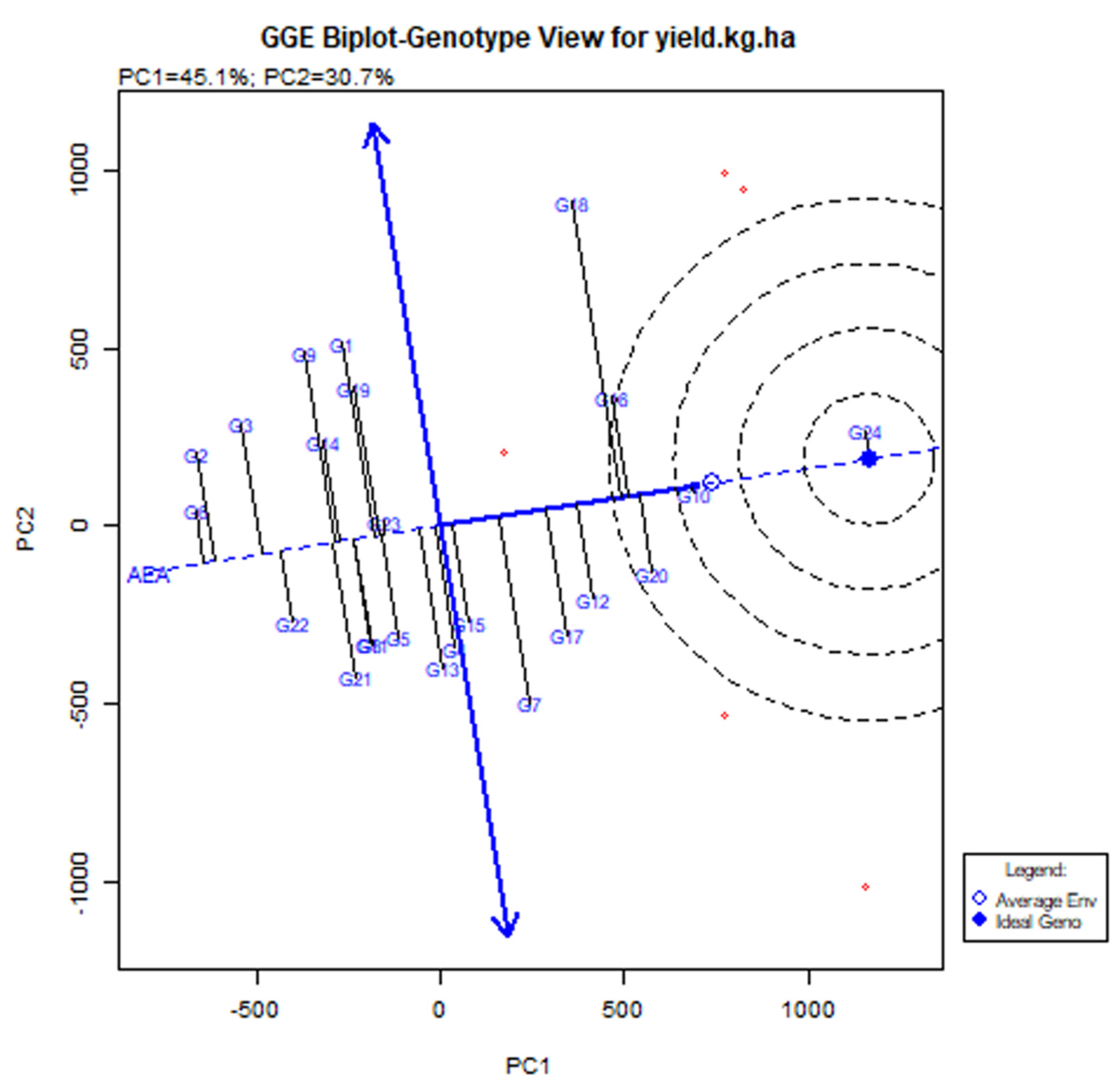
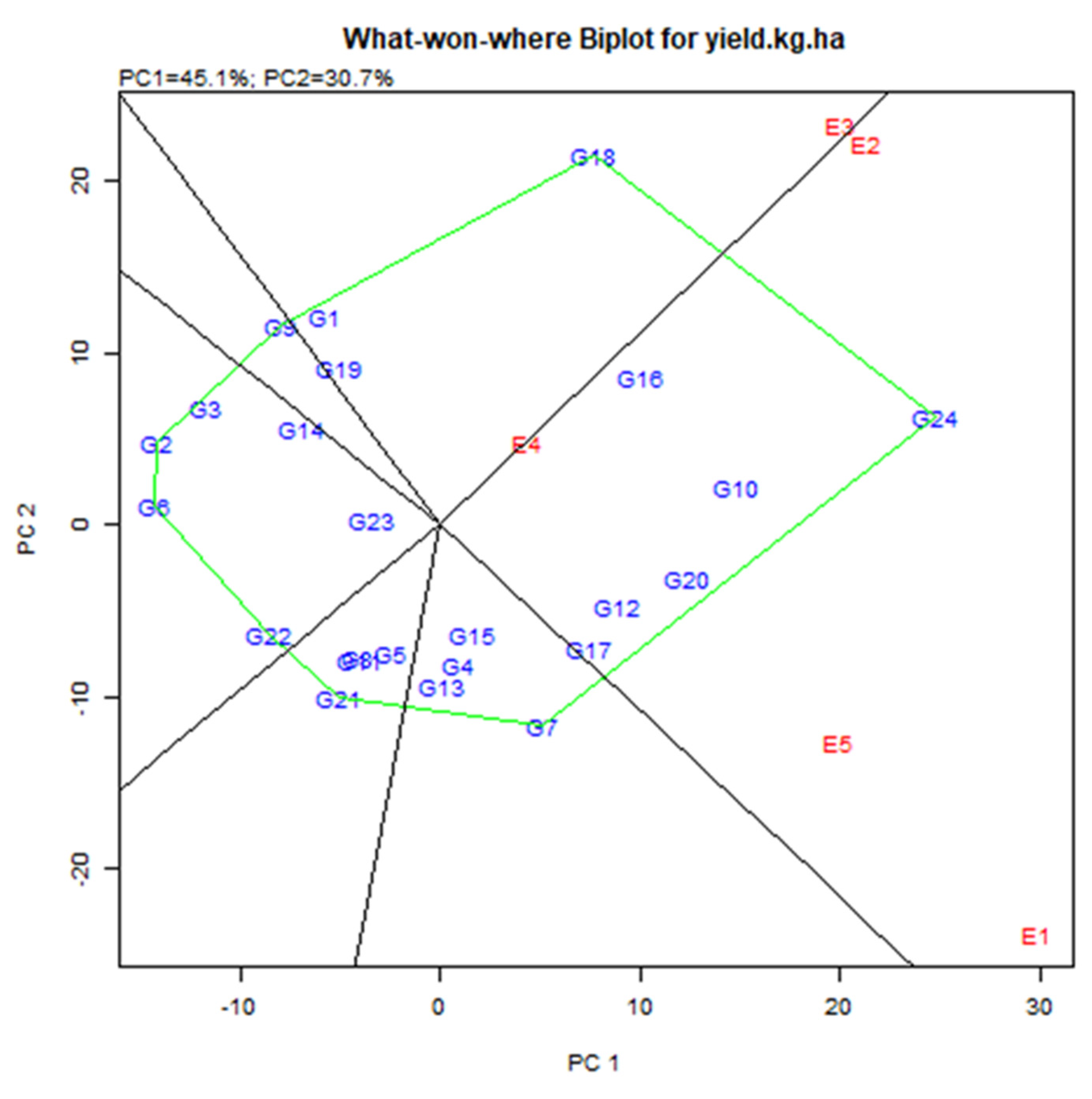
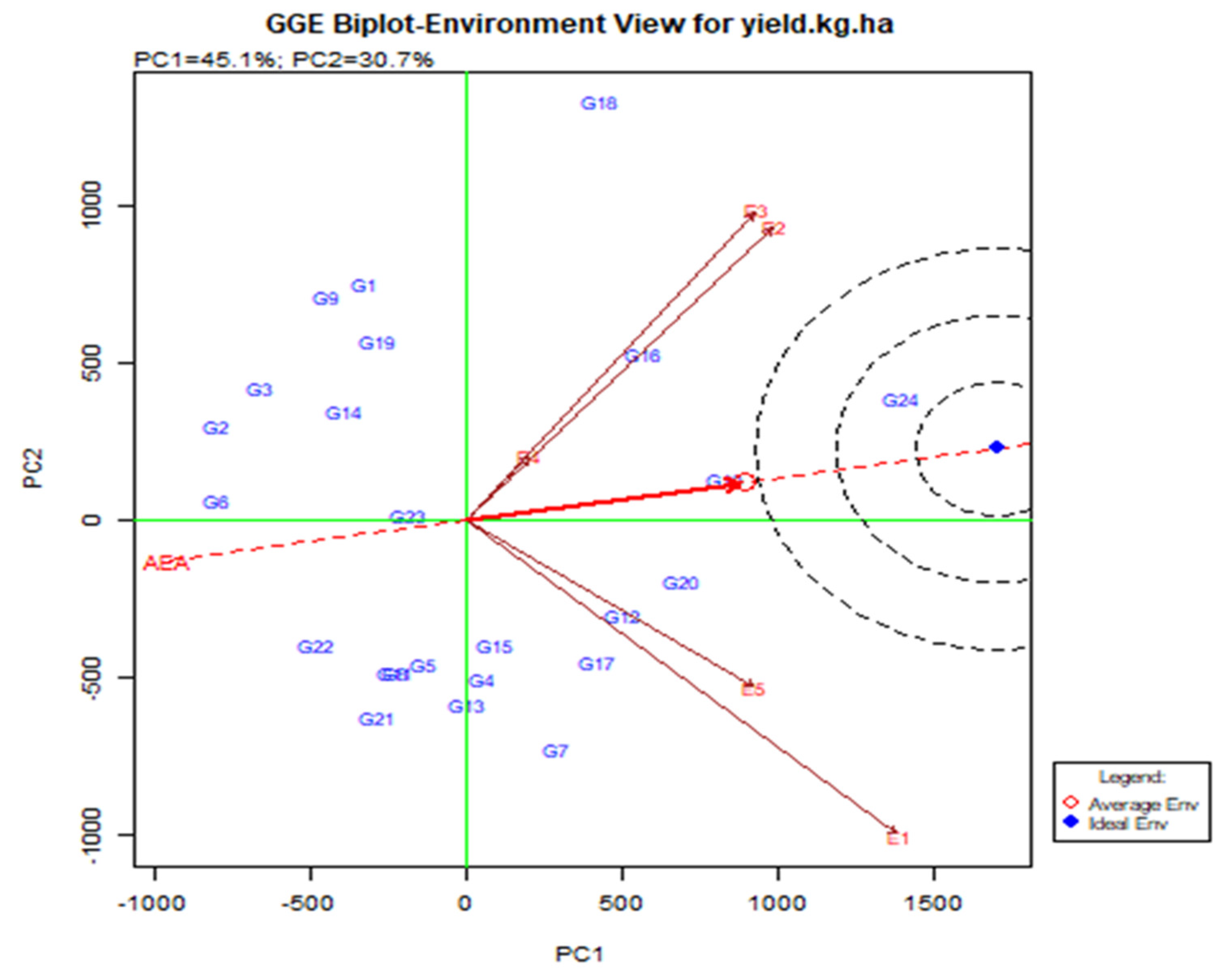
3.4. Stability of the Cowpea Genotypes
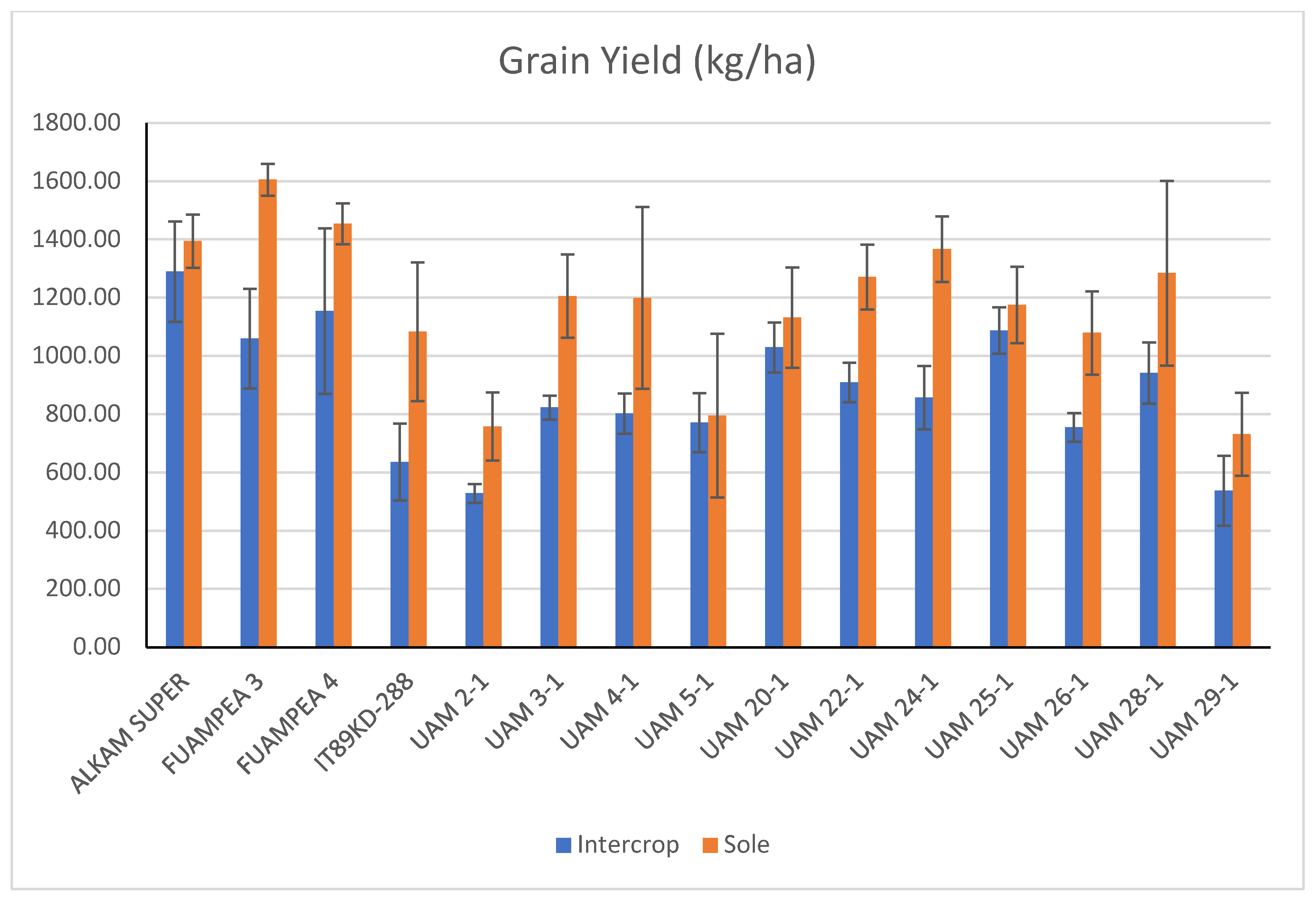
3.5. Cowpea Performance in Intercropping Systems
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Timko, M.P.; Singh, B.B. Cowpea, a multifunctional legume. In Genomics Trop Crop Plants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 227–258. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Jain, P.; Ujinwal, M.; Langyan, S. Escalate protein plates from legumes for sustainable human nutrition. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 977986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwagboso, C.; Andam, K.S.; Amare, M.; Bamiwuye, T.; Fasoranti, A. The Economic Importance of Cowpea in Nigeria: Trends and Implications for Achieving Agri-Food System Transformation; IFPRI Discussion Paper 2241; International Food Policy Research: Washington, DC, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Omoigui, L.O.; Danmaigona, C.C.; Kamara, A.Y.; Ekefan, E.J.; Timko, M.P. Genetic analysis of Fusarium wilt resistance in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata Walp.). Plant Breed. 2018, 137, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Statistics Division. 2021. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat (accessed on 16 October 2024).
- FAOSTAT. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Statistics Division. 2023. Available online: https://doi.org/10.4060/cc8166en (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Horn, L.; Shimelis, H.; Laing, M. Participatory appraisal of production constraints, preferred traits and farming system of cowpea in northern Namibia: Implication for breeding. Legume Res. 2015, 38, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namatsheve, T.; Chikowo, R.; Corbeels, M.; Mouquet-Rivier, C.; Icard-Vernière, C.; Cardinael, R. Maize–cowpea intercropping as an ecological intensification option for low-input systems in sub-humid Zimbabwe: Productivity, biological N2-fixation and grain mineral content. Field Crops Res. 2021, 263, 108052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.; Carlsson, G.; Englund, J.E.; Flöhr, A.; Pelzer, E.; Jeuffroy, M.H.; Makowski, D.; Jensen, E.S. Grain legume-cereal intercropping enhances the use of soil-derived and biologically fixed nitrogen in temperate agroecosystems. A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Agron. 2020, 118, 126077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landschoot, S.; Zustovi, R.; Dewitte, K.; Randall, N.P.; Maenhout, S.; Haesaert, G. Cereal-legume intercropping: A smart review using topic modelling. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1228850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiao, S.; Han, G.; Zhao, M.; Ding, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Ayers, E.L.; Willms, W.D.; Avstad, K.; et al. Effects of stocking rate on the variability of peak standing crop in a desert steppe of Eurasia grassland. Environ. Manag. 2014, 53, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogale, T.E.; Ayisi, K.K.; Munjonji, L.; Kifle, Y.G.; Mabitsela, K.E. Understanding the impact of the intercropping system on carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and soil carbon stocks in Limpopo Province, South Africa. Int. J. Agron. 2023, 2023, 6307673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, K.; Prithiviraj, B.; Fe, Q.; Cloutier, D.; Martin, R.; Smith, D. Intercropping corn with soybean, lupin and forages: Yield component responses. Eur. J. Agron. 2000, 12, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karikari, B.; Maale, M.D.; Anning, E.; Akakpo, D.B.; Abujaja, A.M.; Addai, I.K. Cowpea cropping systems, traits preference, and production constraints in the Upper West Region of Ghana: Farmers’ consultation and implications for breeding. CABI Agric. Biosci. 2023, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.M.F.; Nhantumbo, N.; Ferreira, I.C.; Rodrigues, P.; Patto, M.C.V. Breeding elite cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp] varieties for improved food security and income in Africa. In Legume Crops—Characterization and Breeding for Improved Food Security; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 235–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoigui, L.O.; Kamara, A.Y.; Alunyo, G.I.; Bello, L.L.; Oluoch, M.; Timko, M.P.; Boukar, O. Identification of new sources of resistance to Striga gesnerioides in cowpea Vigna unguiculata accessions. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2017, 64, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Yan, W. GGEbiplot—A Windows Application for Graphical Analysis of Multienvironment Trial Data and Other Types of Two-Way Data. Agron. J. 2001, 93, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, D.; Dutta, S. The robustness of land equivalent ratio as a measure of yield advantage of multi-crop systems over monocultures. Exp. Results 2022, 3, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larweh, V.; Akromah, K.; Amoah, S.; Asibuo, J.Y.; Kusi, F. Effect of Striga gesnerioides on Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp) Yield Components. Res. Sq. 2019, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlson, E.W.; Timko, M.P. Race structure of cowpea witchweed (Striga gesnerioides) in West Africa and its implications for Striga resistance breeding of cowpea. Weed Sci. 2020, 68, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Shi, A.; Mou, B.; Qin, J.; Motes, D.; Lu, W.; Ma, J.; Weng, Y.; Yang, W.; Wu, D. Genetic diversity and population structure of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, M.A.; Menkir, A.; Blay, E.; Gracen, V.; Danquah, E.; Hearne, S. Genetic analysis of drought tolerance in adapted × exotic crosses of maize inbred lines under managed stress conditions. Euphytica 2014, 196, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, B.O.; Ongom, P.O.; Mohammed, S.B.; Togola, A.; Ishaya, D.J.; Bala, G.; Fatokun, C.; Boukar, O. Assessing the Impact of Genotype-By-Environment Interactions on Agronomic Traits in Elite Cowpea Lines Across Agro-Ecologies in Nigeria. Agronomy 2024, 14, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adugna, W.; Labuschagne, M.T. Genotype-environment interactions and phenotypic stability analyses of linseed in Ethiopia. Plant Breed. 2002, 121, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbuma, N.W.; Gerrano, A.S.; Labaka, N.; Lauschagne, M. Interrelationship between grain yield components and nutritional quality traits in cowpea genotypes. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 150, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakshit, S.; Ganapathy, K.N.; Gomashe, S.S.; Rathore, A.; Ghorade, R.B.; Kumar, M.V.N.; Ganesmurthy, K.; Jain, S.K.; Kamtar, M.Y.; Sachan, J.S.; et al. GGE biplot analysis to evaluate genotype, environment and their interactions in sorghum multi-location data. Euphytica 2012, 185, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidnia, F.; Majidi, M.M.; Mirlohi, A.; Ahmadi, B. Graphical analysis of multi-environmental trials for wheat grain yield based on GGE-biplot analysis under diverse climate conditions. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinwale, R.O.; Fakorede, M.A.B.; Badu-Apraku, B.; Oluwaranti, A. Assessing the usefulness of GGE biplot as a statistical tool for plant breeders and agronomists. Cereal Res. Commun. 2014, 42, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Kang, M.S.; Ma, B.; Woods, S.; Cornelius, P.L. GGE Biplot Vs. AMMI Analysis of Genotype-By-Environment Data. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongom, P.O.; Fatokun, C.; Togola, A.; Dieng, I.; Salvo, S.; Gardunia, B.; Mohammed, S.B.; Boukar, O. Genetic progress in cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.] stemming from breeding modernization efforts at the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture. Plant Genome 2024, 17, e20462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansa, O.O.; Ariyo, O.J.; Ayo-Vaughan, M.A.; Ekanem, U.O.; Ntukidem, S.O.; Abberton, M.T.; Oyatomi, O.A. Genetic variability, inter-character correlation, and stability performance in cowpea for drought tolerance. J. Crop Improv. 2024, 39, 43–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agoyi, E.E.; Odong, T.L.; Tumuhairwe, J.B.; Chigeza, G.; Diers, B.W.; Tukamuhabwa, P. Genotype by Environment Effects on Promiscuous Nodulation in Soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill). Agric. Food Secur. 2017, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demie, T.; Hailemariam, B.N.; Bultosa, G.; Daba, C. Effect of genotype in cereal-legume intercropping: A review. Cogent Food Agric. 2022, 8, 2063391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoigui, L.O.; Kamara, A.Y.; Shaibu, A.S.; Aliyu, K.T.; Tofa, A.I.; Solomon, R.; Olasan, O.J. Breeding Cowpea for Adaptation to Intercropping for Sustainable Intensification in the Guinea Savannas of Nigeria. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithourgidis, A.S.; Vlachostergios, D.N.; Dordas, C.A.; Damalas, C.A. Dry matter yield, nitrogen content, and competition in pea–cereal intercropping systems. Eur. J. Agron. 2011, 34, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimonyo, V.G.P.; Modi, A.T.; Mabhaudhi, T. Can cereal-legume intercrop systems contribute to sustainable intensification? A review. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 10, 1098730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondwe, T.M.; Alamu, E.O.; Mdziniso, P. Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp) for food security: An evaluation of end-user traits of improved varieties in Swaziland. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No | Genotype Name | Origin | Seed Colour | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IAR-09-1042-4 | IAR/ABU | White | Breeding line |
| 2 | IAR-17-1015 | IAR/ABU | White | Breeding line |
| 3 | IARD-17-10177 | IAR/ABU | White | Breeding line |
| 4 | IT08K-126-19 | IITA | White | Breeding line |
| 5 | IT08K-150-12 | IITA | White | Variety |
| 6 | IT14K-2188-1 | IITA | White | Breeding line |
| 7 | IT16K-1685-2 | IITA | White | Breeding line |
| 8 | IT16K-1968-3 | IITA | White | Breeding line |
| 9 | IT16K-2287-4 | IITA | White | Breeding line |
| 10 | IT16K-2556-2 | IITA | White | Breeding line |
| 11 | IT17K-1095-2-1 | IITA | White | Breeding line |
| 12 | IT17K-1266-2-1 | IITA | White | Breeding line |
| 13 | IT17K-1403-1-1 | IITA | White | Breeding line |
| 14 | IT17K-1707-2-2 | IITA | White | Breeding line |
| 15 | IT17K-1809-4 | IITA | White | Breeding line |
| 16 | IT17K-2024-4 | IITA | White | Breeding line |
| 17 | IT17K-2357-1 | IITA | White | Breeding line |
| 18 | IT17K-3217-1 | IITA | White | Breeding line |
| 19 | IT17K1802-1 | IITA | White | Breeding line |
| 20 | UAM14-126-L2 | UAM | White | Breeding line |
| 21 | UAM14-126-L28 | UAM | White | Breeding line |
| 22 | UAM14-126-L29 | UAM | White | Breeding line |
| 23 | UAM14-126-L31-1 | UAM | White | Breeding line |
| 24 | UAM15-2157-4 | UAM | Light Brown | Breeding line |
| SOV | df | Days to First Flower | Days to 50% Flowering | Days to 95% Pod Maturity | Pods/Plants | Seed/Pod | 100-Seed Weight | Grain Yield kg/ha | Fodder Yield kg/ha |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rep(Environment) | 10 | 232.10 ** | 17.04 | 24.26 * | 4.58 | 177.99 | 5.37 | 59,4954.80 ** | 685,830.50 |
| Genotype (G) | 23 | 57.08 ** | 86.67 ** | 8.50 | 3.71 | 111.32 | 116.17 ** | 533,449.96 ** | 1,668,775.96 ** |
| Environment (E) | 4 | 4763.93 ** | 3061.46 ** | 3616.42 ** | 271.30 ** | 58,890.12 ** | 129.17 ** | 26,891,006.75 ** | 3,6259,677.50 ** |
| G × E | 92 | 18.03 ** | 24.89 ** | 9.19 | 3.75 * | 69.53 | 10.45 ** | 20,750.55 ** | 803,406.98 ** |
| Error | 230 | 9.34 | 15.59 | 9.06 | 3.54 | 135.82 | 3.84 | 81,187.00 | 492,023.00 |
| Genotype | Days to First Flower | Days to 50% Flowering | Days to 95% POD Maturity | Seeds/Pod | Pods/Plant | 100-Seed Weight (g) | Grain Yield kg/ha | Fodder kg/ha |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IAR-09-1042-4 | 48.27 | 57.40 | 78.83 | 9.43 | 29.23 | 16.79 | 1087.06 | 1778.34 |
| IAR-17-1015 | 43.40 | 52.80 | 77.83 | 8.72 | 26.82 | 18.25 | 901.80 | 1476.10 |
| IARD-17-10177 | 42.13 | 49.67 | 79.17 | 9.27 | 23.00 | 19.45 | 951.28 | 1206.12 |
| IT08K-126-19 | 44.67 | 52.33 | 80.25 | 9.29 | 25.05 | 18.92 | 1141.23 | 1435.55 |
| IT08K-150-12 | 46.47 | 53.73 | 79.25 | 9.77 | 28.24 | 17.93 | 1109.38 | 1667.21 |
| IT14K-2188-1 | 46.27 | 53.87 | 78.50 | 9.25 | 25.12 | 17.73 | 869.79 | 1365.00 |
| IT16K-1685-2 | 47.13 | 54.93 | 77.92 | 9.39 | 27.66 | 17.66 | 1207.85 | 1525.55 |
| IT16K-1968-3 | 48.73 | 57.60 | 78.75 | 9.25 | 22.96 | 20.91 | 1051.98 | 1718.88 |
| IT16K-2287-4 | 44.40 | 53.47 | 77.17 | 9.86 | 27.78 | 18.87 | 1015.49 | 1446.11 |
| IT16K-2556-2 | 47.20 | 55.53 | 79.83 | 9.90 | 25.16 | 21.79 | 1424.75 | 1687.22 |
| IT17K-1095-2-1 | 45.33 | 56.60 | 79.17 | 9.83 | 31.39 | 20.04 | 1060.76 | 1831.66 |
| IT17K-1266-2-1 | 48.73 | 57.80 | 78.83 | 9.63 | 26.08 | 18.59 | 1291.83 | 1555.55 |
| IT17K-1403-1-1 | 46.53 | 54.07 | 77.83 | 10.36 | 30.03 | 18.53 | 1125.72 | 1458.89 |
| IT17K-1707-2-2 | 45.67 | 56.33 | 79.00 | 9.75 | 31.48 | 20.17 | 1034.78 | 1230.00 |
| IT17K-1802-1 | 45.93 | 54.53 | 79.00 | 10.37 | 23.70 | 20.71 | 1136.57 | 1493.33 |
| IT17K-1809-4 | 47.13 | 56.60 | 79.25 | 9.05 | 23.70 | 21.60 | 1333.37 | 1615.89 |
| IT17K-2024-4 | 47.87 | 57.73 | 80.00 | 10.37 | 25.97 | 18.57 | 1297.75 | 1608.33 |
| IT17K-2357-1 | 50.13 | 57.80 | 79.00 | 10.42 | 26.79 | 20.87 | 1361.54 | 1571.66 |
| IT17K-3217-1 | 47.13 | 58.47 | 78.33 | 9.07 | 29.95 | 19.41 | 1107.88 | 1428.33 |
| UAM14-126-L2 | 45.60 | 54.73 | 78.08 | 10.98 | 23.29 | 21.97 | 1406.59 | 1967.22 |
| UAM14-126-L28 | 48.93 | 59.20 | 79.08 | 10.31 | 30.96 | 19.43 | 1021.59 | 2322.77 |
| UAM14-126-L29 | 46.87 | 57.07 | 79.67 | 9.91 | 30.88 | 23.34 | 992.53 | 2243.88 |
| UAM14-126-L33-1 | 44.36 | 52.57 | 79.45 | 9.45 | 30.25 | 19.79 | 1161.94 | 1527.97 |
| UAM15-2157-4 | 49.93 | 58.87 | 80.00 | 10.39 | 21.11 | 30.82 | 1674.11 | 2566.66 |
| Mean | 46.62 | 55.57 | 78.93 | 9.75 | 26.94 | 20.09 | 1156.98 | 1655.34 |
| Heritability | 0.684 | 0.713 | 0.02 | 0.016 | 0.064 | 0.910 | 0.611 | 0.519 |
| SE ± | 2.20 | 1.88 | 2.33 | 0.78 | 9.15 | 0.67 | 177.62 | 263.05 |
| Locations | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIU | MAKURDI | SAMARU | Grain Yield Advantage of UAM15-2157-4 (%) | |||
| Genotype | 2022 | 2023 | 2022 | 2023 | 2023 | |
| IAR-09-1042-4 | 419.43 | 2566.67 | 1000.67 | 631.83 | 816.72 | 35.1 |
| IAR-17-1015 | 641.64 | 1796.39 | 1093.1 | 697.53 | 280.33 | 46.1 |
| IARD-1710177 | 797.19 | 1976.11 | 1115.27 | 777.47 | 90.39 | 43.2 |
| IT08K-126-19 | 1455.5 | 1886.11 | 1056.33 | 655.97 | 652.22 | 31.8 |
| IT08K-150-12 | 1119.95 | 1716.67 | 1080.03 | 684.53 | 945.72 | 57.6 |
| IT14K-2188-1 | 652.75 | 1952.78 | 785.77 | 523.7 | 433.94 | 48.0 |
| IT16K-1685-2 | 1597.16 | 2128.89 | 830.23 | 593.63 | 889.33 | 27.9 |
| IT16K-1968-3 | 1177.73 | 2016.67 | 727.1 | 606.57 | 731.83 | 37.2 |
| IT16K-2287-4 | 652.75 | 2230.56 | 1256.37 | 602.73 | 335.06 | 39.3 |
| IT16K-2556-2 | 1561.05 | 2297.22 | 1706.13 | 639.57 | 919.78 | 14.9 |
| IT17K-1095-21 | 1119.4 | 1800 | 935.07 | 597.83 | 851.5 | 36.6 |
| IT17K-1266-2-1 | 1513.83 | 2011.11 | 1427.93 | 558.4 | 947.89 | 22.8 |
| IT17K-1403-1-1 | 1394.39 | 1858.33 | 985.83 | 623.9 | 766.17 | 32.8 |
| IT17K-1707-2-2 | 805.53 | 2277.78 | 962.5 | 677.17 | 450.94 | 38.2 |
| IT17K-1802-1 | 1366.61 | 2225 | 856.33 | 493.23 | 741.67 | 32.1 |
| IT17K-1809-4 | 1322.17 | 2594.44 | 1528.67 | 588.87 | 632.72 | 20.4 |
| IT17K-2024-4 | 1394.39 | 2252.78 | 960 | 737.9 | 1143.67 | 22.5 |
| IT17K-2357-1 | 738.86 | 2916.67 | 1649.77 | 754.07 | 748.33 | 18.7 |
| IT17K-3217-1 | 733.3 | 2278.89 | 1167.17 | 836.47 | 523.56 | 33.8 |
| UAM14-126-L2 | 1579.38 | 2572.22 | 1026.17 | 896.07 | 959.11 | 16.0 |
| UAM14-126-L28 | 1038.85 | 2358.33 | 246.57 | 479.6 | 984.61 | 39.0 |
| UAM14-126-L29 | 931.63 | 1957.22 | 633.5 | 691.5 | 748.78 | 40.7 |
| UAM14-126-L33-1 | 1158.29 | 1950 | 1151.5 | 798.93 | 544.23 | 33.1 |
| UAM15-2157-4 | 1663.27 | 2945 | 1595.07 | 967.23 | 1200 | 0.0 |
| Mean | 1118.13 | 2190.24 | 1074.05 | 671.45 | 722.44 | |
| Genotype | Cercospora Leaf Spot (0–5) | Bacteria Blight (0–5) | Septoria (0–5) | Pod Scab | Virus Severity (0–5) | Aphid (0–5) | Maruca (0–5) | Striga Count (m2) @ 63 DAP | Alectra Count (m2) @ 63 DAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IAR-09-1042-4 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 1.5 |
| IAR-17-1015 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 2.0 | 11.2 |
| IARD-17-10177 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.8 |
| IT08K-126-19 | 1.2 | 2.3 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| IT08K-150-12 | 0.8 | 2.3 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| IT14K-2188-1 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| IT16K-1685-2 | 1.2 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.8 |
| IT16K-1968-3 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| IT16K-2287-4 | 1.3 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| IT16K-2556-2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| IT17K-1095-2-1 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| IT17K-1266-2-1 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| IT17K-1403-1-1 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| IT17K-1707-2-2 | 1.0 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| IT17K-1809-4 | 1.0 | 1.3 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| IT17K-2024-4 | 1.2 | 1.8 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| IT17K-2357-1 | 1.0 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| IT17K-3217-1 | 1.2 | 2.0 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| IT17K1802-1 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| UAM14-126-L2 | 1.0 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| UAM14-126-L28 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| UAM14-126-L29 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| UAM14-126-L31-1 | 1.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| UAM15-2157-4 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Mean | 1.0 | 1.1 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.6 |
| SE ± | 0.228 | 0.378 | 0.230 | 0.097 | 0.141 | 0.048 | 0.084 | 0.441 | 1.028 |
| SOV | df | Number of Branches per Plant | Number of Peduncles per Plant | 100-Seed Weight (g) | Grain Yield kg/ha | Fodder Yield kg/ha |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rep(Location) | 2 | 2.96 * | 0.10 | 14.30 * | 22,084.20 | 1,190,274.50 |
| Genotype (G) | 14 | 1.26 | 4.09 | 92.64 ** | 408,958.34 ** | 1,248,104.64 * |
| Cropping system (CS) | 1 | 0.18 | 607.95 ** | 79.54 ** | 4,297,133.60 ** | 167,962,814.00 ** |
| G × CS | 14 | 0.90 | 3.52 | 2.68 | 56,845.31 ** | 718,141.07 |
| Location (L) | 1 | 92.58 ** | 3289.67 ** | 23.32 * | 1,710,185.50 ** | 11,331,577.00 ** |
| G × L | 14 | 0.89 | 1.18 | 6.37 | 236,972.11 ** | 2,313,856.14 ** |
| CS × L | 1 | 8.64 ** | 693.60 ** | 45.76 ** | 1,711,159.90 ** | 41,041,264.00 ** |
| G × CS × L | 14 | 1.31 | 4.42 | 4.39 | 48,619.59 ** | 13,64,608.71 ** |
| Error | 58 | 0.86 | 3.07 | 3.59 | 22,280.00 * | 563,496.00 ** |
| Number of Branches per Plant | Number of Peduncles per Plant | Fodder Yield (kg/ha) | 100-Seed Weight (g) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VARIETY | Sole | Inter | Sole | Inter | Sole | Inter | Sole | Inter |
| UAM15-2157-4 | 3.80 | 3.65 | 12.15 | 7.13 | 4291.68 | 2037.50 | 29.95 | 31.08 |
| FUAMPEA 3 | 3.60 | 3.20 | 9.70 | 6.40 | 4252.78 | 1736.79 | 24.98 | 27.13 |
| FUAMPEA 4 | 3.65 | 3.05 | 12.55 | 6.35 | 2752.08 | 1557.63 | 26.98 | 26.75 |
| IT89KD-288 | 3.90 | 3.40 | 11.00 | 6.90 | 4609.74 | 2134.03 | 16.78 | 20.18 |
| UAM 2-1 | 3.70 | 2.40 | 12.80 | 4.98 | 3784.03 | 1240.96 | 28.33 | 32.80 |
| UAM 3-1 | 3.65 | 3.30 | 13.15 | 8.30 | 3811.82 | 1535.42 | 23.78 | 25.30 |
| UAM 4-1 | 3.00 | 2.35 | 12.55 | 8.00 | 3909.74 | 1728.48 | 24.25 | 25.15 |
| UAM 5-1 | 2.63 | 3.10 | 11.75 | 7.40 | 5078.48 | 2215.29 | 22.85 | 24.70 |
| UAM 20-1 | 3.25 | 3.20 | 11.50 | 6.90 | 4828.47 | 2033.34 | 21.03 | 23.33 |
| UAM 22-1 | 3.75 | 4.40 | 11.15 | 7.15 | 4635.40 | 1535.40 | 22.33 | 23.65 |
| UAM 24-1 | 2.75 | 4.25 | 11.60 | 8.15 | 3995.13 | 2569.44 | 21.00 | 22.80 |
| UAM 25-1 | 4.10 | 3.95 | 11.30 | 8.65 | 3395.46 | 1962.03 | 21.88 | 22.28 |
| UAM 26-1 | 2.98 | 3.40 | 12.25 | 7.90 | 4345.16 | 1884.72 | 21.95 | 23.30 |
| UAM 28-1 | 3.30 | 3.65 | 11.85 | 9.05 | 4254.88 | 1390.98 | 19.10 | 20.33 |
| UAM 29-1 | 3.20 | 2.80 | 13.10 | 7.63 | 4221.53 | 1111.79 | 23.18 | 24.00 |
| Mean | 3.42 | 3.34 | 11.89 | 7.39 | 4144.42 | 1778.25 | 23.22 | 24.85 |
| SE ± | 0.2933 | 0.5590 | 1.0403 | 0.5820 | 392.7887 | 352.0880 | 1.0403 | 0.8190 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Omoigui, L.O.; Kamara, A.Y.; Shaibu, A.S.; Iorlamen, T.; Ekeruo, G.; Eseigbe, O.B.; Solomon, R.; Adeleke, M.A.; Tofa, A.I.; Ibrahim, E.A. Agronomic and Intercropping Performance of Newly Developed Elite Cowpea Lines for the West African Savannas. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2548. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112548
Omoigui LO, Kamara AY, Shaibu AS, Iorlamen T, Ekeruo G, Eseigbe OB, Solomon R, Adeleke MA, Tofa AI, Ibrahim EA. Agronomic and Intercropping Performance of Newly Developed Elite Cowpea Lines for the West African Savannas. Agronomy. 2025; 15(11):2548. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112548
Chicago/Turabian StyleOmoigui, Lucky Osabuohien, Alpha Yaya Kamara, Abdulwahab Saliu Shaibu, Teryima Iorlamen, Godspower Ekeruo, Osagie Bright Eseigbe, Reuben Solomon, Musibau Abiodun Adeleke, Abdullahi Ibrahim Tofa, and Esther Afor Ibrahim. 2025. "Agronomic and Intercropping Performance of Newly Developed Elite Cowpea Lines for the West African Savannas" Agronomy 15, no. 11: 2548. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112548
APA StyleOmoigui, L. O., Kamara, A. Y., Shaibu, A. S., Iorlamen, T., Ekeruo, G., Eseigbe, O. B., Solomon, R., Adeleke, M. A., Tofa, A. I., & Ibrahim, E. A. (2025). Agronomic and Intercropping Performance of Newly Developed Elite Cowpea Lines for the West African Savannas. Agronomy, 15(11), 2548. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112548






