Optimization of 4-Cyano-4’-pentylbiphenyl Liquid Crystal Dispersed with Photopolymer: Application Towards Smart Windows and Aerospace Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
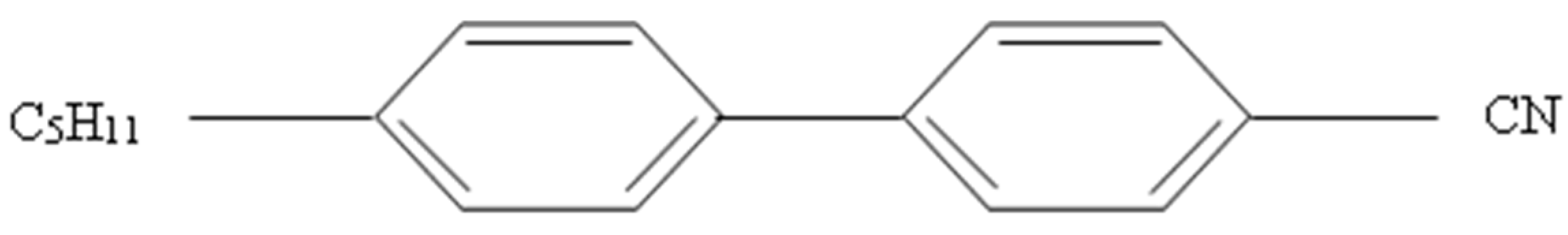
2.1.1. Liquid Crystalline Material
2.1.2. Polymer Used
2.2. Mixing of Liquid Crystal and Polymer
2.3. Fabrication of Liquid Crystal Cell
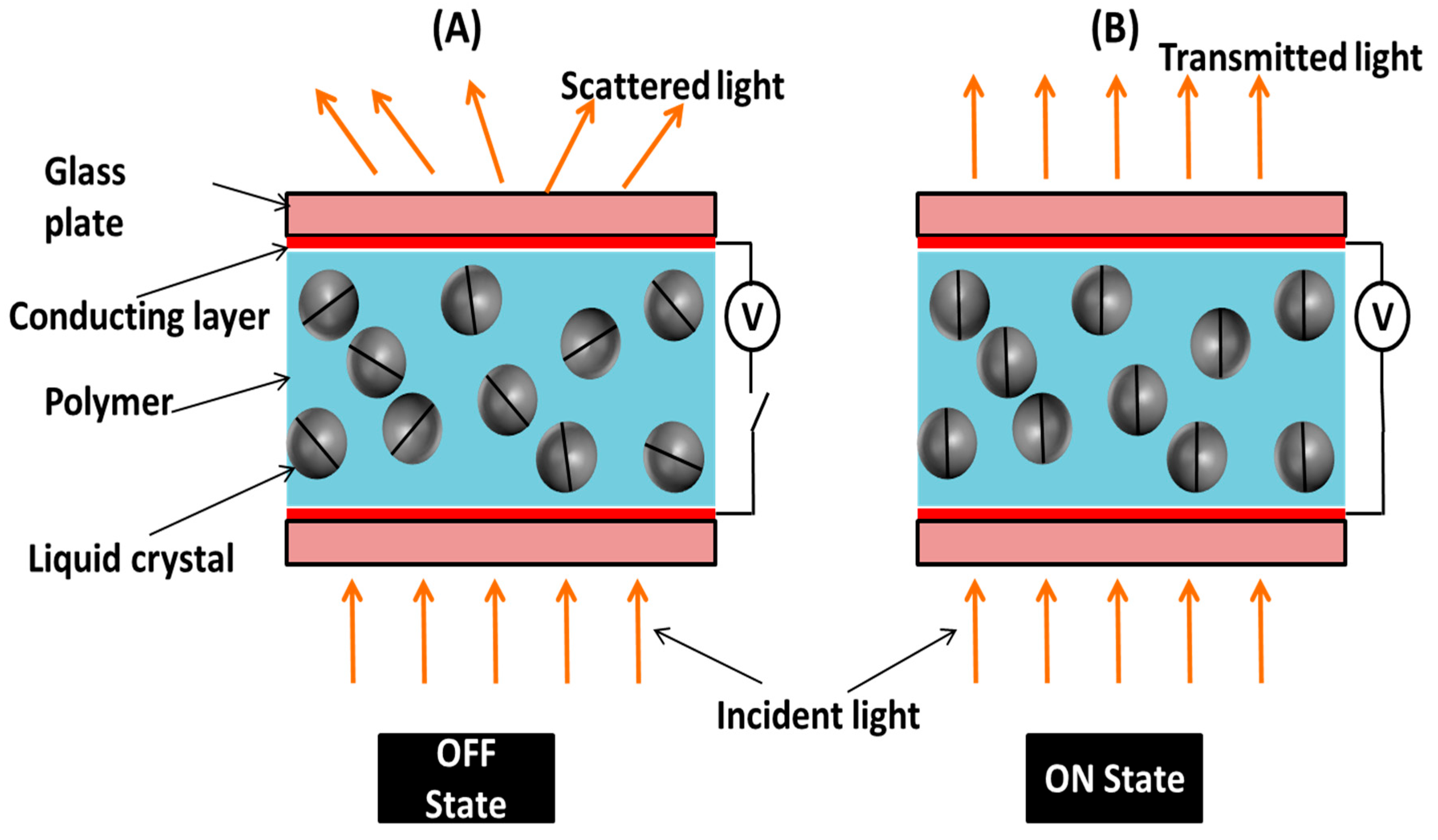
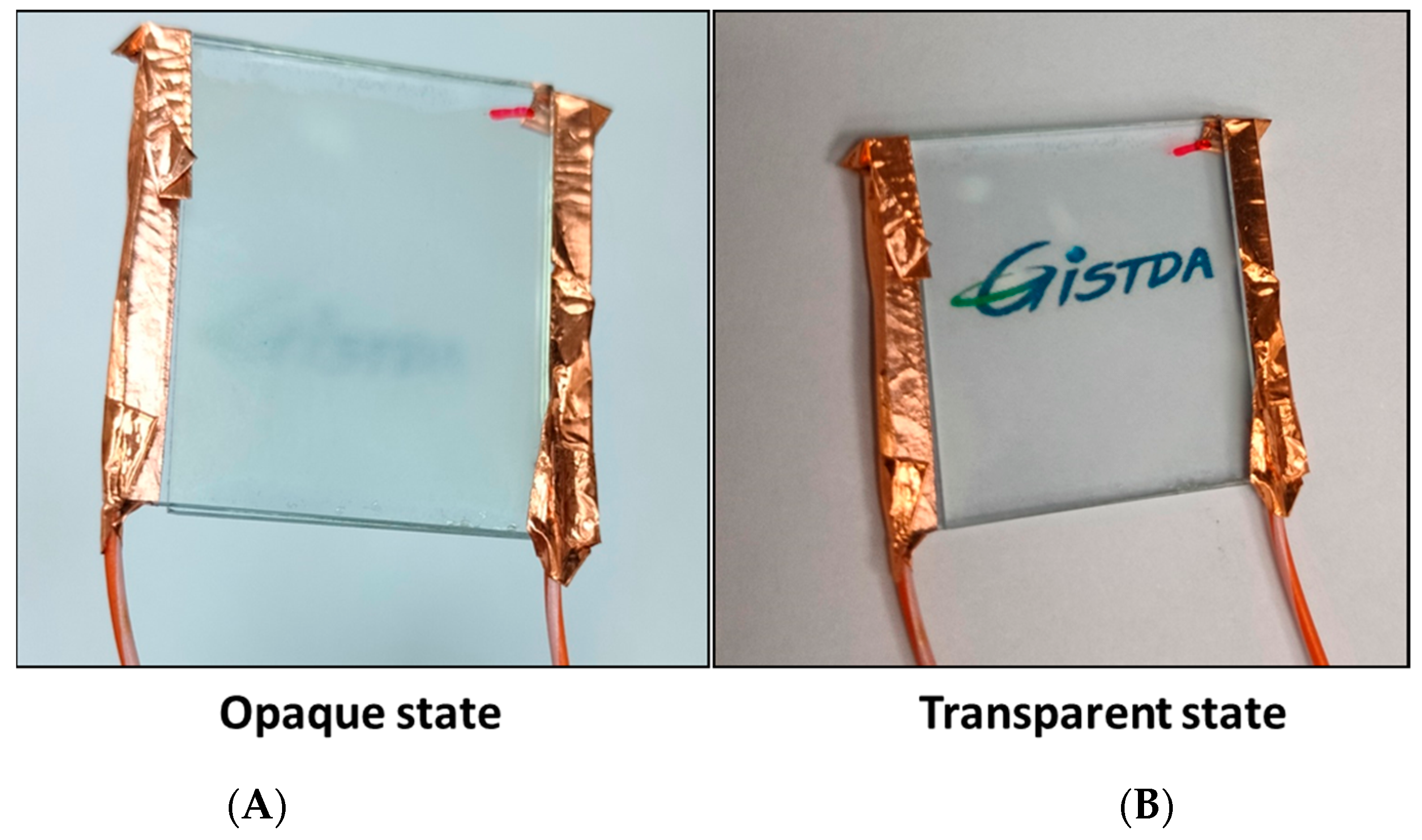
2.4. Filling of LC–Polymer Mixture in LC Cell and UV Exposure: Smart Window
2.5. Instruments Used
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Textural Study
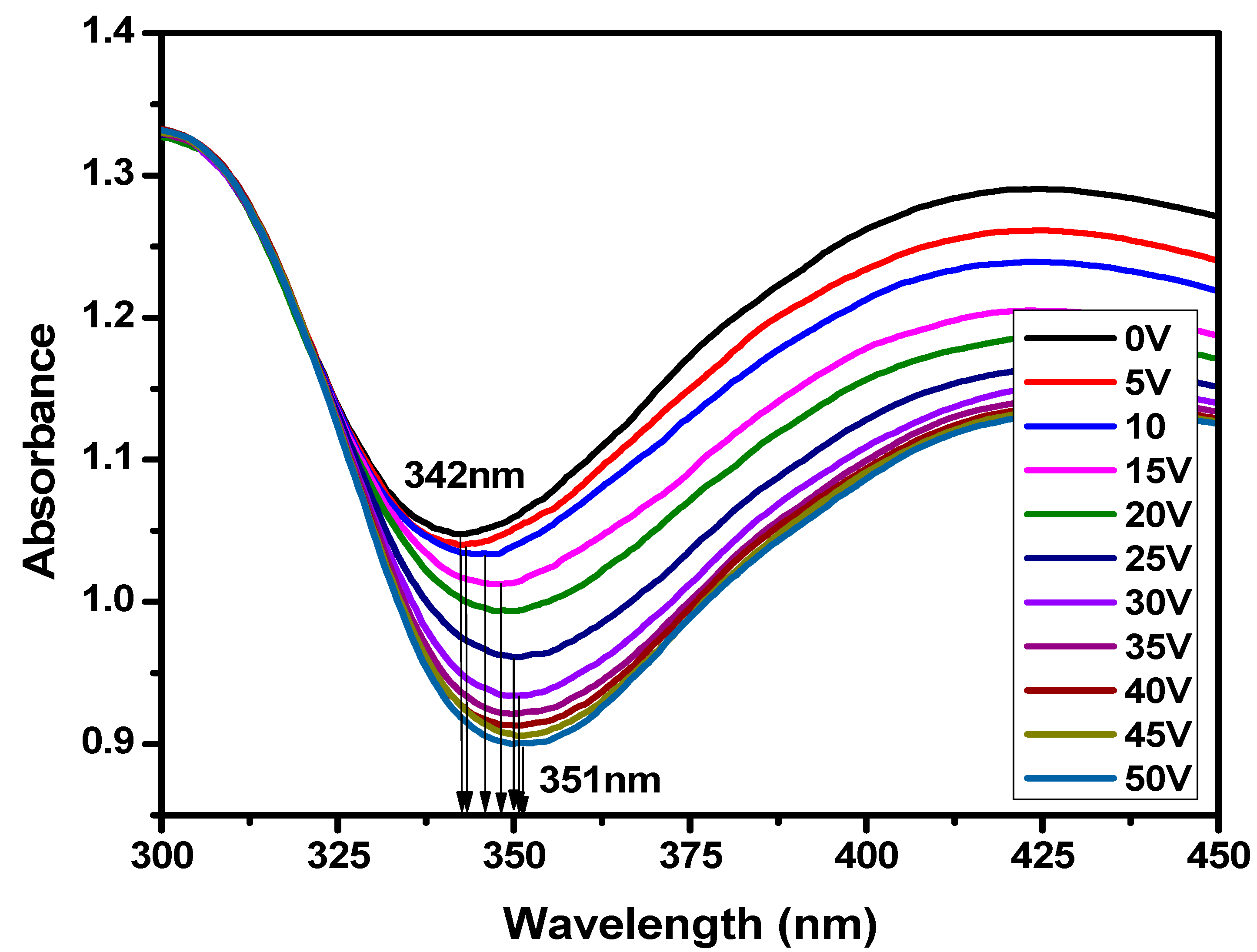
3.2. Optical Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrienko, D. Introduction to Liquid Crystals. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 267, 520–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Temiz, M.; El-Makadema, A. Determining dielectric properties of nematic liquid crystals at microwave frequencies using inverted microstrip lines. Liq. Cryst. 2022, 49, 2069–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.S.; Geng, Y.; Majumdar, Y.; Lagerwall, J.P.F. Tunable templating of photonic microparticles via liquid crystal order-guided adsorption of amphiphilic polymers in emulsions. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukusoglu, E.; Bedolla Pantoja, M.; Mushenheim, P.C.; Wang, X.; Abbott, N.L. Design of Responsive and Active (Soft) Materials Using Liquid Crystals. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2016, 7, 163–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Han, J.; Li, C.; Zhao, T.; Jin, X.; Duan, P. Recyclable soft photonic crystal film with overall improved circularly polarized luminescence. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tan, N.; Pivnenko, M.; Sibik, J.; Zeitler, J.A.; Chu, D. High-Birefringence Nematic Liquid Crystal for Broadband THz Applications. Liq. Cryst. 2016, 46, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, I.C. Liquid Crystals: Physical Properties and Nonlinear Optical Phenomena; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Klysubun, P. Nonlinear Optical Studies of Dye-Doped Nematic Liquid Crystals. Ph.D. Dissertation, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, S.; Bozkurt, A. Spectroscopic measurement of liquid crystal anisotropy in the ultraviolet/visible region. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 107, 410–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilsum, C. Flat-panel electronic displays: A triumph of physics, chemistry and engineering. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2010, 368, 1027–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Miyama, T.; Akiyama, H.; Ikemura, A.; Kitamura, M. Development of Liquid Crystal Displays and Related Improvements to Their Performances. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2022, 98, 493–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devadiga, D.; Ahipa, T.N. A Review on the Emerging Applications of 4-Cyano-40-Alkylbiphenyl (nCB) Liquid Crystals Beyond Display. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2022, 275, 115522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.W.; Ji, S.M.; Han, C.H.; Yoon, T.H. A cholesteric liquid crystal smart window with a low operating voltage. Dye. Pigment. 2022, 197, 109843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinov, L.M. Structure and Properties of Liquid Crystals; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Zhang, B.; Kelly, S.M.; Cui, J.; Zhang, K.; Hu, W.; Min, D.; Ding, S.; Huang, W. Photopolymerisable liquid crystals for additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 55, 102861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zheng, J.; Xing, C.; Sang, J.; Shen, T. Applications of liquid crystal planer optical elements based on photoalignment technology in display and photonic devices. Displays 2024, 82, 102632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, P.; Weitz, D.A. Inverted and multiple nematic emulsions. Phys. Rev. E 1998, 57, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, P.; Stark, H.; Lubensky, T.C.; Weitz, D.A. Novel Colloidal Interactions in Anisotropic Fluids. Science 1997, 275, 1770–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerwall, J.P.F.; Giesselmann, F. Current Topics in Smectic Liquid Crystal Research. ChemPhysChem 2006, 7, 20–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipanah, Z.; Zakerhamidi, M.S.; Ranjkesh, A. Temperature- Dependent Optical Properties of Some Mixtures Nematic Liquid Crystal. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscari, P.; DiCarlo, A.; Turzi, S.S. Anisotropic Wave Propagation in Nematic Liquid Crystals. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 8296–8307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayeb, H.; Alaya, S.; Derbali, M.; Samet, L.; Bennaceur, J.; Jomni, F.; Soltani, T. Dielectrical, Electro-Optical and Textural Studies of 5CB Nematic Liquid Crystal Doped With TiO2 and Cu-TiO2 Nanoparticle. Liq. Cryst. 2020, 48, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Daoudi, A.; Dubois, F.; Blach, J.F.; Henninot, J.F.; Kurochkin, O.; Grabar, A.; Segovia-Mera, A.; Legrand, C.; Douali, R. A comparative study of nematic liquid crystals doped with harvested and non-harvested ferroelectric nanoparticles: Phase transitions and dielectric properties. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 35438–35444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Kinkead, B.; Hegmann, T. Effects of functionalized metal and semiconductor nanoparticles in nematic liquid crystal phases. Proc. SPIE 2008, 6911, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, S.-M.; Oh, S.-W.; Yoon, T.-H. SmartWindow Based on Angular-Selective Absorption of Solar Radiation with Guest–Host Liquid Crystals. Crystals 2021, 11, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.W. Temperature dependence of electro-optical characteristics of polymer dispersed liquid crystal films. Liq. Cryst. 2001, 28, 1487–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trushkevych, O.; Reshetnyak, V.; Turvey, M.; Edwards, R.S. Polymer-dispersed liquid-crystal coatings for ultrasound visualization: Experiment and theory. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 109, 064701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trushkevych, O.; Eriksson, T.J.R.; Ramadas, S.N.; Dixon, S.; Edwards, R.S. Acousto-optics with polymer dispersed liquid crystals for ultrasound sensing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 054102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.S.; Ward, J.; Zhou, L.; Trushkevych, O. The interaction of polymer dispersed liquid crystal sensors with ultrasound. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 044104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, S.E.; Hurley, S.P.; Yang, Y.C.; Yang, D.K. Electric polarization frozen by a polymer network in nematic liquid crystals. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 3834–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanks, R.A.; Staszczyk, D. Thermal and Optical Characterization of Polymer-Dispersed Liquid Crystals. Int. J. Pol. Sci. 2012, 2012, 767581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Cuevas, K.G.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Z.G.; Bisoyi, H.K.; Li, G.; Tan, L.S.; Vaia, R.A.; Li, Q. Frequency-Driven Self-Organized Helical Superstructures Loadedwith Mesogen-Grafted Silica Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13090–13094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocakulah, G.; Balci, L.; Koysal, O. Determination of Phase Transition and Electro-optical Behaviors of Quantum Dot Doped Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystal. J. Elect. Mater. 2020, 49, 3427–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gridyakina, A.; Kasian, N.; Chychłowski, M.S.; Kajkowska, M.; Lesiak, P. Advances in multicomponent systems: Liquid crystal/nanoparticles/polymer. Mater. Today Phys. 2023, 38, 101258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.P.; Hsieh, C.F.; Pan, C.L.; Chen, C.Y. Temperature-dependent optical constants and birefringence of nematic liquid crystal 5CB in the terahertz frequency range. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 093523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Wang, L.; Zhong, T.; Chen, G.; Li, C.; Chen, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, K.; Yang, Z.; et al. Electrically switchable light transmittance of epoxy-mercaptan polymer/nematic liquid crystal composites with controllable microstructures. Polymer 2019, 160, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pathak, G.; Phettong, B.; Chattham, N. Optimization of 4-Cyano-4’-pentylbiphenyl Liquid Crystal Dispersed with Photopolymer: Application Towards Smart Windows and Aerospace Technology. Polymers 2025, 17, 2232. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17162232
Pathak G, Phettong B, Chattham N. Optimization of 4-Cyano-4’-pentylbiphenyl Liquid Crystal Dispersed with Photopolymer: Application Towards Smart Windows and Aerospace Technology. Polymers. 2025; 17(16):2232. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17162232
Chicago/Turabian StylePathak, Govind, Busayamas Phettong, and Nattaporn Chattham. 2025. "Optimization of 4-Cyano-4’-pentylbiphenyl Liquid Crystal Dispersed with Photopolymer: Application Towards Smart Windows and Aerospace Technology" Polymers 17, no. 16: 2232. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17162232
APA StylePathak, G., Phettong, B., & Chattham, N. (2025). Optimization of 4-Cyano-4’-pentylbiphenyl Liquid Crystal Dispersed with Photopolymer: Application Towards Smart Windows and Aerospace Technology. Polymers, 17(16), 2232. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17162232





