Cashmere Blended with Calcium Alginate Fibers: Eco-Friendly Improvement of Flame Retardancy and Maintenance of Hygroscopicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Cashmere/Calcium Alginate Blended Fibers
2.3. Characterization
3. Results
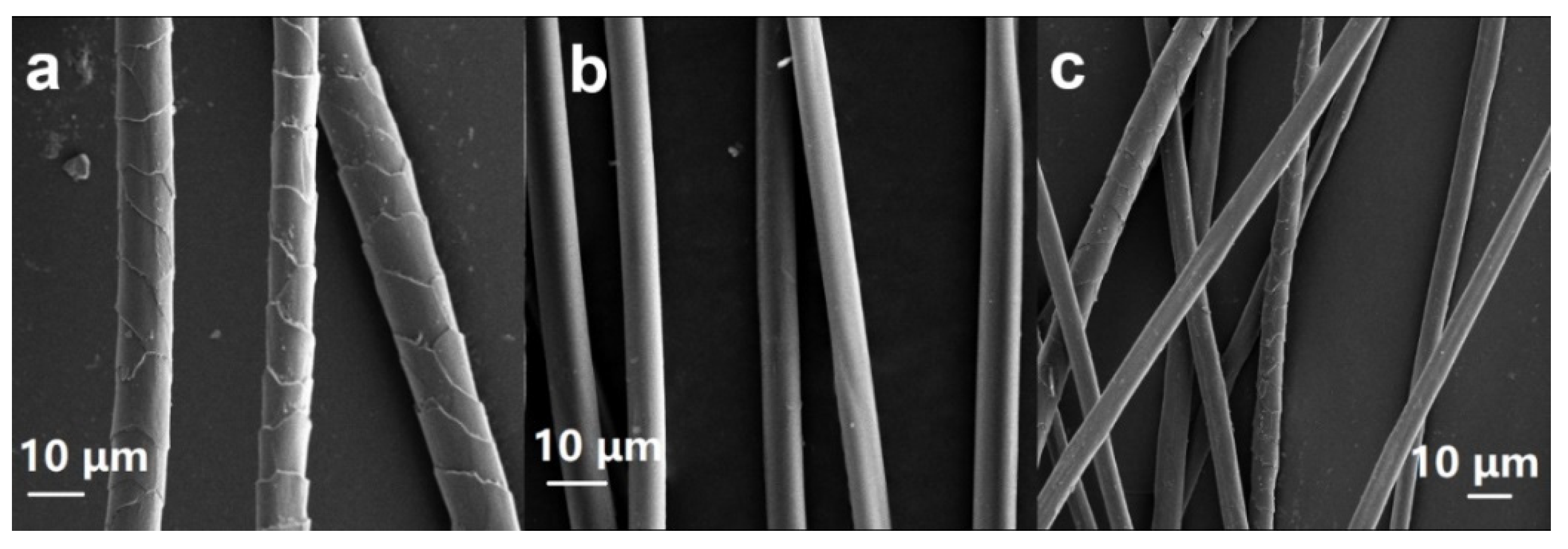
3.1. Structural Characterizations
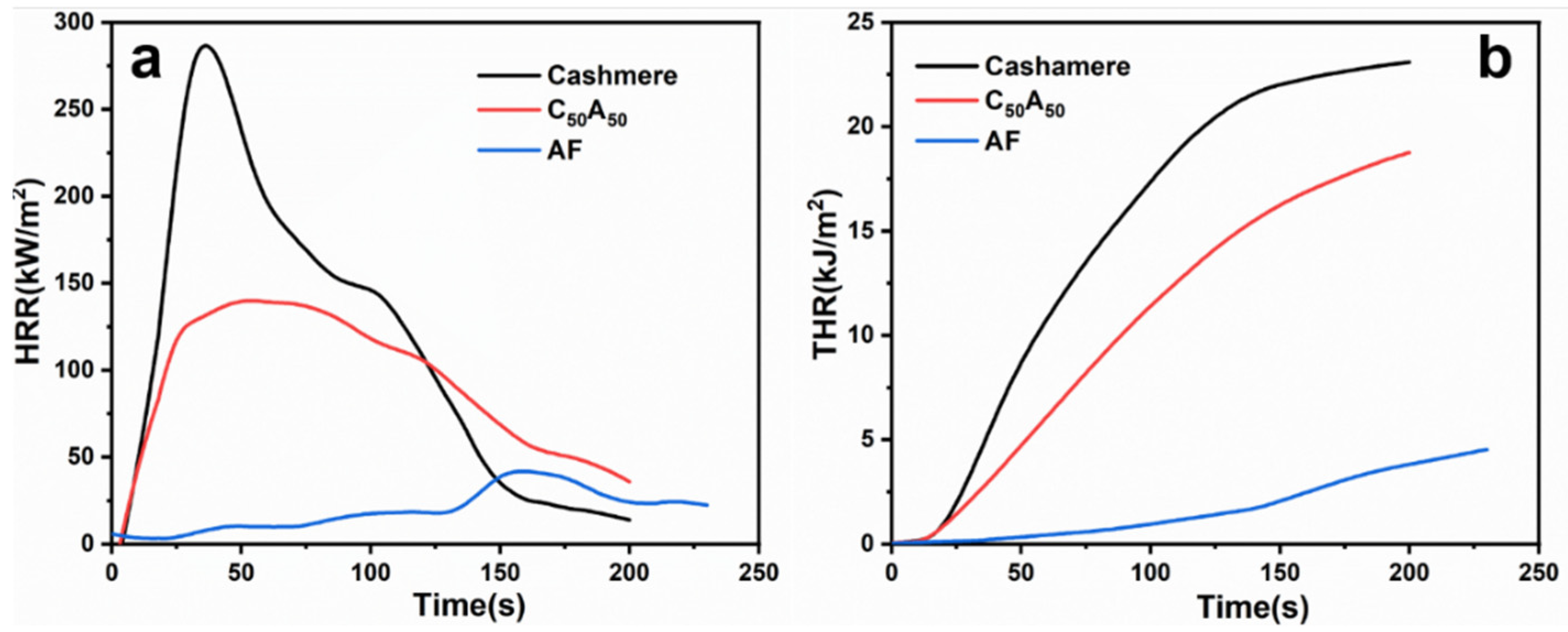
3.2. Flame Properties
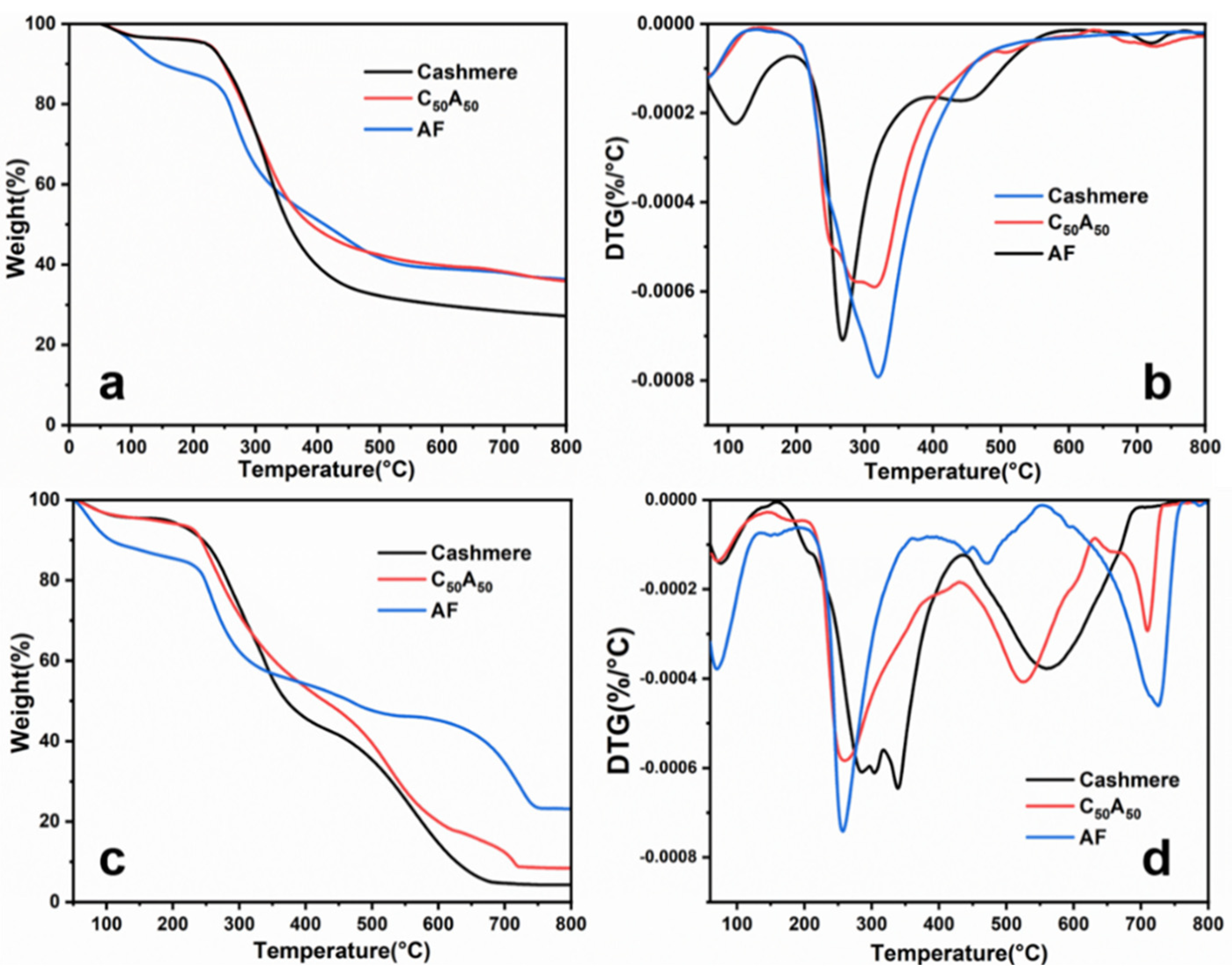
3.3. Thermal Stability
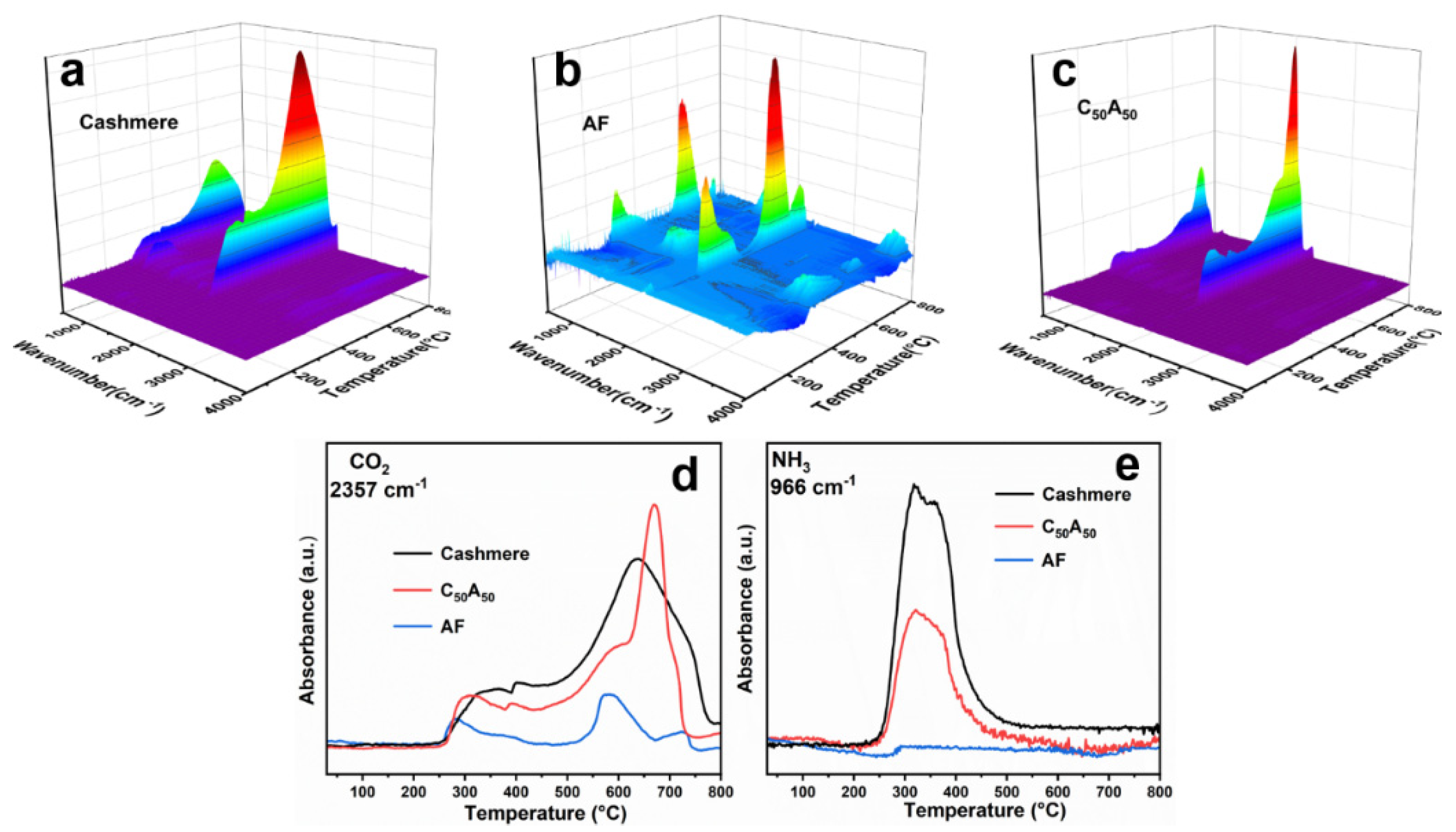
3.4. TG-FTIR Analysis
3.5. Char Residues Analysis
3.6. Flame Retardancy Mechanism of Blended Fiber
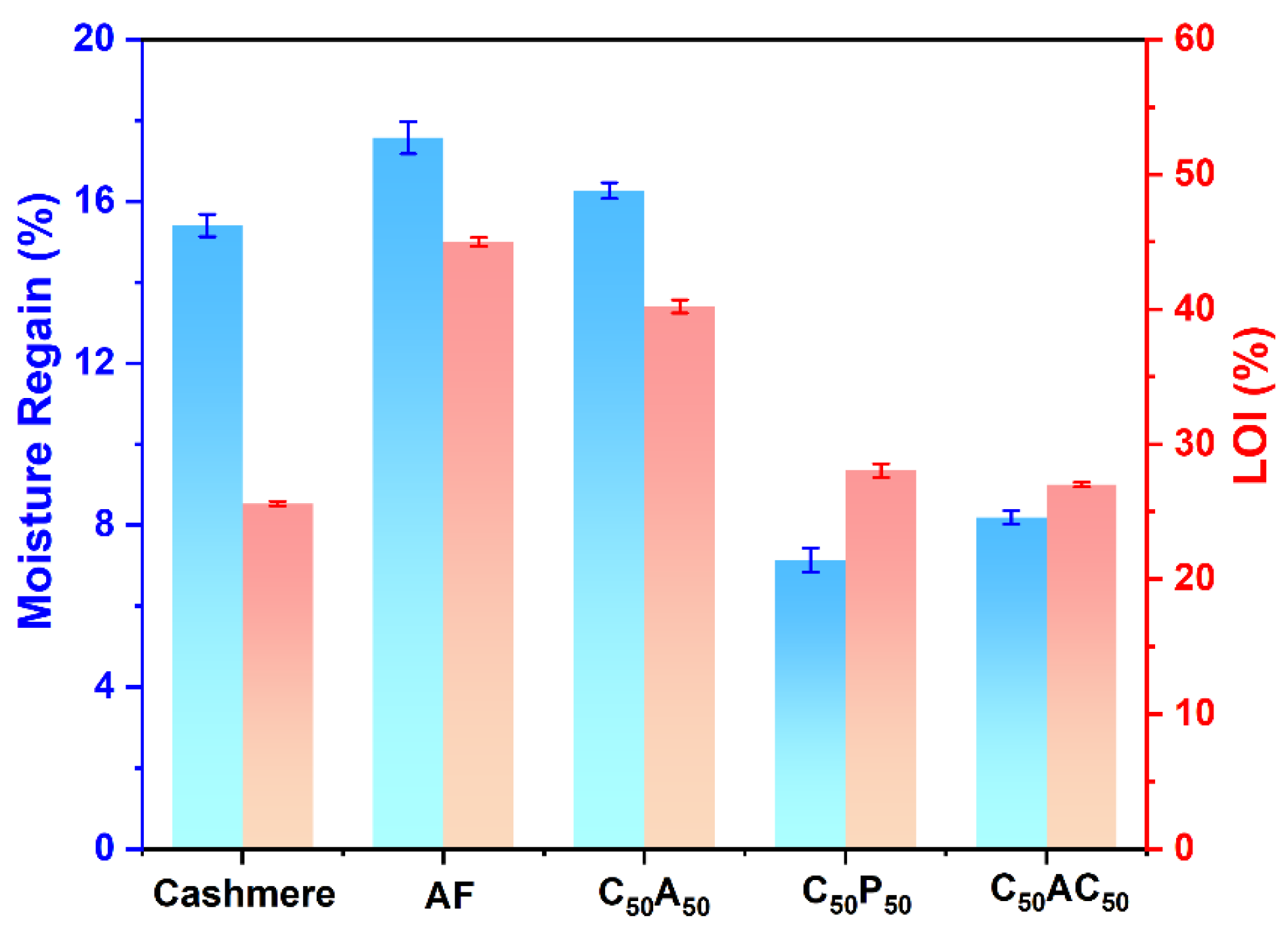
3.7. Hygroscopicity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGregor, B.A. Variation in the Softness and Fibre Curvature of Cashmere, Alpaca, Mohair and Other Rare Animal Fibres. J. Text. Inst. 2014, 105, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, R.; Wu, X.; Xu, B. Fiber-Content Measurement of Wool–Cashmere Blends Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2017, 71, 2367–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrimatopoulos, C.; Tummino, M.L.; Iliadis, E.; Tonetti, C.; Sakkas, V. Attenuated Total Reflection Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy and Chemometrics for the Discrimination of Animal Hair Fibers for the Textile Sector. Appl. Spectrosc. 2024, 11, 00037028241292372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, R.; Wang, W.; Zhao, H.; Yang, S.; Dong, Z.; Wang, D.-Y.; Pan, Y.-T. Cyclodextrin-Based Host-Guest Hierarchical Fire Retardants: Synthesis and Novel Strategy to Endow Polylactic Acid Fire Retardancy and UV Resistance. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 341, 122313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhang, W.; Song, X.; Vahabi, H.; Pan, Y.-T.; Zhang, W.; Yang, R. Fast Char Formation Induced by POSS Confining Co-MOF Hollow Prisms in Epoxy Composites with Mitigated Heat and Smoke Hazards. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Song, K.; Pan, Y.; Barreneche, C.; Vahabi, H.; He, J.; Yang, R. Hollow Superstructure In Situ Assembled by Single-Layer Janus Nanospheres toward Electromagnetic Shielding Flame-Retardant Polyurea Composites. Small 2024, 20, 2307492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Han, Z.; Song, X.; Pan, Y.-T.; Geng, Z.; Vahabi, H.; Realinho, V.; Yang, R. Enhancing Char Formation of Flame Retardant Epoxy Composites: Onigiri-like ZIF-67 Modification with Carboxymethyl β-Cyclodextrin Crosslinking. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 333, 121980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, S.; Shanmugam, N.; Das, S.; Kumar, A.; Pandit, P. Coating of Lightweight Wool Fabric with Nano Clay for Fire Retardancy. J. Text. Inst. 2019, 110, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.-W.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Y.-X.; Ma, Y.-D.; Xu, J.-T.; Guan, J.-P. Borate Functionalized Caramel as Effective Intumescent Flame Retardant for Wool Fabric. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2021, 186, 109469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykam, K.; Försth, M.; Sas, G.; Restás, Á.; Das, O. Phytic Acid: A Bio-Based Flame Retardant for Cotton and Wool Fabrics. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 164, 113349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Liu, X. Phosphorylation of Sodium Copper Chlorophyll Enables Color-Fasten and Durable Flame Retardant Wool Fibers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 179, 109286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essaket, M.; Allam, I.; Boukhriss, A.; Tahiri, M.; El Maliki, A.; Essaket, I.; Cherkaoui, O. Wool: Applications, Insect-Proofing Treatments and the Preparation of Wool Powder. Text. Prog. 2023, 55, 165–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.-W.; Guan, J.-P.; Kiekens, P.; Yang, X.-H.; Tang, R.-C. Preparation and Evaluation of an Eco-Friendly, Reactive, and Phytic Acid-Based Flame Retardant for Wool. React. Funct. Polym. 2019, 134, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Huang, J.; Lai, Y.; Xing, T.; Chen, G.; Jin, W.; Liu, H.; Sun, B. Flame Retardance and Thermal Stability of Wool Fabric Treated by Boron Containing Silica Sols. Mater. Des. 2015, 85, 796–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flambard, X.; Bourbigot, S.; Ferreira, M.; Vermeulen, B.; Poutch, F. Wool/Para-Aramid Fibres Blended in Spun Yarns as Heat and Fire Resistant Fabrics. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2002, 77, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Xi, C.; Qin, J.; Pan, H.; Wang, S.; Cao, G.; Tao, D.; Jiang, S. Polyimide/Wool Blended Woven Fabrics for Comfortable Fire Protective Clothing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e53870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.-J.; Zhao, J.-C.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, P.; Wang, D.-Y. Bio-Based Barium Alginate Film: Preparation, Flame Retardancy and Thermal Degradation Behavior. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 139, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Fan, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Weng, L. Fabrication, Property and Application of Calcium Alginate Fiber: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tao, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, P.; Xu, Y.-J.; Jiang, Z.-M.; Dong, C.-H.; Zhu, P. Fully Bio-Based Fire-Safety Viscose/Alginate Blended Nonwoven Fabrics: Thermal Degradation Behavior, Flammability, and Smoke Suppression. Cellulose 2020, 27, 6037–6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-S.; Xia, Y.-Z.; Shi, M.-W.; Yan, X. The Flame Retardancy of Alginate/Flame Retardant Viscose Fibers Investigated by Vertical Burning Test and Cone Calorimeter. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.-Q.; Wang, B.; Xu, Y.-J.; Li, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, P. Convenient Blending of Alginate Fibers with Polyamide Fibers for Flame-Retardant Non-Woven Fabrics. Cellulose 2020, 27, 8341–8349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, C.; Li, P.; Xu, Y.-J.; Jiang, Z.-M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, P. Cotton/Alginate Blended Knitted Fabrics: Flame Retardancy, Flame-retardant Mechanism, Water Absorption and Mechanical Properties. Cellulose 2021, 28, 4495–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, Q.-Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Xu, Y.-J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, P. Blending Alginate Fibers with Polyester Fibers for Flame-Retardant Filling Materials: Thermal Decomposition Behaviors and Fire Performance. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2021, 183, 109470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 2406.3-2022; Plastics—Determination of Burning Behaviour by Oxygen Index—Part 3: Elevated-Temperature Test. National Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- ISO Standard 5660-1; Reaction-to-Fire Tests—Heat Release, Smoke Production and Mass Loss Rate. International Standards Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- GB/T 9994-2018; Conventional Moisture Regains of Textile Materials: Elevated-Temperature Test. National Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- GB/T 12411-2006; Test Methods for Jute and Kenaf Fibres: Elevated-Temperature Test. National Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Cavdar, A.D. Effect of Various Wood Preservatives on Limiting Oxygen Index Levels of Fir Wood. Measurement 2014, 50, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, W.-H.; Hu, Z.-Y.; Xu, H.-X.; Xu, Y.-J.; Qi, M.; Liao, W.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.-Z. Flame-Retardant Flexible Polyurethane Foams with Highly Efficient Melamine Salt. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 7112–7119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Wang, B.; Han, X.; Ma, B.; Li, J. Synthesis and Characterization of Flame Retardant Rigid Polyurethane Foam Based on a Reactive Flame Retardant Containing Phosphazene and Cyclophosphonate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 144, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-E.; Yan, Y.-W.; Zhao, H.-B.; Jian, R.-K.; Wang, Y.-Z. A Facile and Efficient Flame-Retardant and Smoke-Suppressant Resin Coating for Expanded Polystyrene Foams. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 185, 107797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-J.; Liu, Y.; Cui, L.; Yan, C.; Zhu, P. Bio-Based Calcium Alginate Nonwoven Fabrics: Flame Retardant and Thermal Degradation Properties. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 122, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, P.; Xu, Y.-J.; Jiang, Z.-M.; Dong, C.-H.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, P. Bio-Based, Nontoxic and Flame-Retardant Cotton/Alginate Blended Fibres as Filling Materials: Thermal Degradation Properties, Flammability and Flame-Retardant Mechanism. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 194, 108038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-J.; Qu, L.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, P. An Overview of Alginates as Flame-Retardant Materials: Pyrolysis Behaviors, Flame Retardancy, and Applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 260, 117827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Deng, Y.; Xue, Y.; Li, Q. Flame Retardancy and Thermal Degradation Mechanism of Calcium Alginate/CaCO3 Composites Prepared via in Situ Method. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 131, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, K.; Yoon, S.G.; Lee, S.B.; Kang, C. Eco-Friendly Surface Coating of Wool/Polyester Blend Fabric Using a Combination of Montmorillonite and Polyquaternium 10: Enhanced Flame-Retardant Performance Using Layer-by-Layer Assembly. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 688, 133691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Quan, F.; Tian, X.; Xia, Y. Synergistic Flame Retardancy of Metal-Ion/Nitrogen in Composite Fibers Prepared from All-Seaweed Biomass. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 227, 110884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, F.; Carletto, R.A.; Alongi, J.; Marmo, L.; Di Blasio, A.; Malucelli, G. Thermal Stability and Flame Resistance of Cotton Fabrics Treated with Whey Proteins. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ji, Q.; Shen, X.; Xia, Y.; Tan, L.; Kong, Q. Pyrolysis Products and Thermal Degradation Mechanism of Intrinsically Flame-Retardant Calcium Alginate Fibre. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, J.; Qiu, W.; Cheng, Q.; Fan, G.; Song, G.; Zhang, S. Kinetics and Behavior Analysis of Lobster Shell Pyrolysis by TG-FTIR and Py-GC/MS. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 165, 105580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Li, A.; Quan, C.; Du, L.; Duan, Y. TG–FTIR and Py–GC/MS Analysis on Pyrolysis and Combustion of Pine Sawdust. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 100, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, C.; Duan, Z.; Yu, B.; Liu, M.; Song, P. Interface Engineering of MXene towards Super-Tough and Strong Polymer Nanocomposites with High Ductility and Excellent Fire Safety. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 399, 125829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.U.; Shaker, K.; Nawab, Y.; Hamdani, S.T.A.; Abdullah, H.M.; Umair, M. Thermo-Physiological Comfort of Woven Fabrics Made from Different Cellulosic Yarns. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 4050–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Wei, Z.; Gao, Y. Evaluation of Luster, Hand Feel and Comfort Properties of Modified Polyester Woven Fabrics. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2017, 12, 155892501701200409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
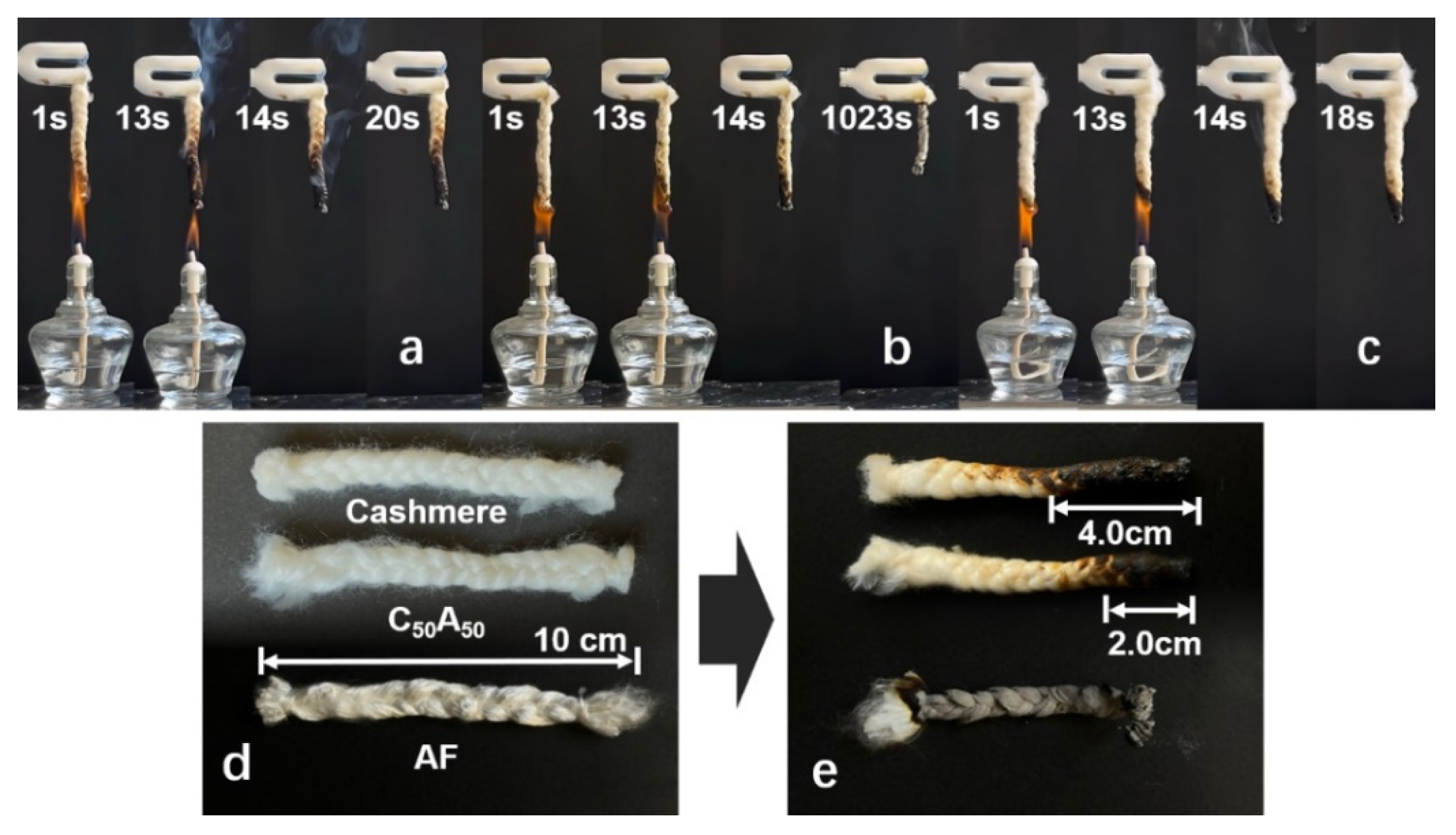

| Samples | LOI (%) | Afterflame Time (s) | Afterglow Time (s) | Damage Length (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cashmere | 25.6 ± 0.2 | 7 | 0 | 40 |
| C80A20 | 27.3 ± 0.3 | 6 | 0 | 37 |
| C60A40 | 33.4 ± 0.2 | 6 | 0 | 28 |
| C50A50 | 40.2 ± 0.6 | 5 | 0 | 20 |
| C40A60 | 40.8 ± 0.2 | 0 | 502 | 85 |
| C20A80 | 43.4 ± 0.4 | 0 | 1033 | 100 |
| AF | 45.0 ± 0.4 | 0 | 1010 | 100 |
| Samples | p-HRR | Tp-HRR | TTI | THR | TSP | FIGRA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (kW/m2) | (s) | (s) | (MJ/m2) | (m2) | (kW/m2 s) | |
| Cashmere | 289.5 ± 15.8 | 36 ± 2 | 8 ± 1 | 23.1 ± 0.8 | 0.79 ± 0.13 | 9.2 |
| C50A50 | 141.1 ± 9.0 | 46 ± 1 | 11 ± 1 | 18.8 ± 0.5 | 0.27 ± 0.06 | 5.4 |
| AF | 42.6 ± 2.5 | 154 ± 5 | 138 ± 8 | 4.5 ± 0.2 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | 0.3 |
| Samples | T1max (°C) | T2max (°C) | T3max (°C) | T4max (°C) | Residues (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cashmere | 70.2 | 319.4 | — | — | 27.18 |
| C50A50 | 72.0 | 314.8 | 505.5 | 733.3 | 35.87 |
| AF | 109.9 | 267.1 | 454.4 | 724.9 | 36.32 |
| Samples | T1max (°C) | T2max (°C) | T3max (°C) | T4max (°C) | Residues (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cashmere | 70.5 | 340.3 | 561.7 | — | 4.23 |
| C50A50 | 71.2 | 258.6 | 525.5 | 709.7 | 8.38 |
| AF | 78.7 | 256.8 | 472.8 | 725.6 | 23.17 |
| Sample | Cashmere | AF | C50A50 | C50P50 | C50AC50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breaking twist number (twists/10 cm) | 10 ± 2 | 10 ± 1 | 10 ± 1 | 7 ± 1 | 9 ± 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Xu, C.; Tian, X.; Quan, F. Cashmere Blended with Calcium Alginate Fibers: Eco-Friendly Improvement of Flame Retardancy and Maintenance of Hygroscopicity. Polymers 2025, 17, 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111497
Cai Y, Li Z, Wang B, Xu C, Tian X, Quan F. Cashmere Blended with Calcium Alginate Fibers: Eco-Friendly Improvement of Flame Retardancy and Maintenance of Hygroscopicity. Polymers. 2025; 17(11):1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111497
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Yujie, Zewen Li, Bin Wang, Chao Xu, Xing Tian, and Fengyu Quan. 2025. "Cashmere Blended with Calcium Alginate Fibers: Eco-Friendly Improvement of Flame Retardancy and Maintenance of Hygroscopicity" Polymers 17, no. 11: 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111497
APA StyleCai, Y., Li, Z., Wang, B., Xu, C., Tian, X., & Quan, F. (2025). Cashmere Blended with Calcium Alginate Fibers: Eco-Friendly Improvement of Flame Retardancy and Maintenance of Hygroscopicity. Polymers, 17(11), 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111497








