Abstract
The rapid advancement of technology has led to a substantial increase in Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE), which poses significant environmental threats and increases pressure on the planet’s limited natural resources. In response, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a key enabler of the Circular Economy (CE), particularly in improving the speed and precision of waste sorting through machine learning and computer vision techniques. Despite this progress, to our knowledge, no comprehensive, systematic review has focused specifically on the role of AI in disassembling and recycling Waste-Printed Circuit Boards (WPCBs). This paper addresses this gap by systematically reviewing recent advancements in AI-driven disassembly and sorting approaches with a focus on machine learning and vision-based methodologies. The review is structured around three areas: (1) the availability and use of datasets for AI-based WPCB recycling; (2) state-of-the-art techniques for selective disassembly and component recognition to enable fast WPCB recycling; and (3) key challenges and possible solutions aimed at enhancing the recovery of critical raw materials (CRMs) from WPCBs.
1. Introduction
Electronic products that have reached their end of life are referred to as Waste from Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) or e-waste. WEEE includes large home appliances, computers, mobile phones, refrigerators, etc. Nowadays, electronic waste is a major problem worldwide that poses a significant health and environmental threat. Several toxic materials are used in electronics, including lead, mercury, and cadmium, and can be released into the environment when discarded [1]. As a consequence, soil and water can become contaminated, posing health risks to both humans and wildlife.
According to the latest survey, 56 million metric tons of e-waste are generated globally, a figure expected to reach up to 74.7 million metric tons by 2030, with only 17% properly collected and recycled [2]. On the other hand, critical raw materials (CRMs) form the foundation of Europe’s economy, ensuring industrial competitiveness, employment, and quality of life. While all raw materials contribute to economic and societal well-being, certain materials raise heightened concerns due to risks in securing their sustainable supply—such as gold, silver, and palladium. To address these challenges, the European Commission (EU) conducts a triennial criticality assessment. CRMs are defined by their high economic importance and their vulnerability to supply chain disruptions. In order to address this issue, government sectors and companies are increasingly focusing on the use of AI technologies to promote Circular Economies. AI helps predict demand for products and services more accurately, thereby reducing waste and optimizing resource use [3]. The concept of a Circular Economy (CE) has gained popularity in addressing the global generation and recycling of e-waste, offering tangible economic and environmental benefits [4]. Table 1 shows the list of acronyms used in this systematic review.

Table 1.
List of acronyms used in this paper.
Among different types of WEEE, Waste-Printed Circuit Boards (WPCBs) are the most valuable because they contain high-yield precious metals that can be reused in new production processes if recycled efficiently [5]. To enable automatic disassembly of electronic components from WPCBs, numerous recent AI applications have employed deep learning models to detect and localize electronic components mounted on the board [6,7,8,9]. Despite the promising potential of deep learning for electronic component detection, the field faces several challenges that require systematic investigation. These include the complexity of electronic component arrangements on WPCBs, issues with occlusion and overlapping components, variations in lighting conditions and viewpoints, and the need for real-time processing capabilities in industrial settings [10]. Additionally, the diversity of deep learning architectures and approaches calls for a comprehensive review to determine the most effective methods and inform future research directions.
This paper presents a comprehensive review to provide insight into how deep learning-based computer vision systems can address the rapid growth of e-waste worldwide. Furthermore, it aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the current state of research in this domain, examining available datasets, various deep learning architectures, methodologies, and applications specifically tailored for electronic component detection on WPCBs. Unlike prior reviews, which focus broadly on AI in e-waste management or component classification, this review specifically targets WPCB disassembly and sorting, offering a deep dive into dataset quality, selective disassembly models, and readiness for industrial deployment. By synthesizing findings from existing studies, identifying research gaps, and highlighting promising approaches, this review contributes to the advancement of automated e-waste recycling and support the sustainable management of electronic waste. To achieve this, three specific research questions have been formulated:
- RQ-1:
- What publicly available datasets are used in WPCB recycling, and what is their significance in deep learning-based computer vision systems?
- RQ-2:
- What are the current state-of-the-art methodologies and frameworks for the automatic disassembly and sorting of WPCBs?
- RQ-3:
- What are the main challenges and potential solutions for automating the disassembly and sorting of WPCBs using machine learning and computer vision?
This review provides the following main contributions:
- Focused Scope: It presents a systematic review specifically centered on AI-driven techniques for WPCB recycling, distinguishing it from broader studies on e-waste.
- Dataset-Centric Analysis: It highlights the role and limitations of available datasets, discussing their relevance, accessibility, and the challenges in training AI models for WPCB-specific tasks.
- Comparative Evaluation of Methods: The review critically compares various machine learning and computer vision approaches used in disassembly, sorting by component recognition, analyzing their suitability and limitations in practical settings.
- Discussion on Industrial Applicability: It examines real-world deployment potential, including scalability and cost-efficiency.
- Identification of Research Gaps: The paper outlines current limitations such as data scarcity, lack of model generalization, and integration issues, and proposes future directions to guide further research.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 defines the term critical raw materials (CRMs), their economic and environmental significance. Section 3 discusses the methodology opted for this systematic review. We outline the systematic review protocol, including our search strategy, study selection criteria, data extraction processes, and inclusion and exclusion criteria. Section 4 presents the currently available WPCB datasets and their applications. Section 5 details the state-of-the-art AI techniques used for WPCB recycling. Section 6 discusses the challenges and limitations associated with WPCB disassembly, along with potential improvements to enhance economic feasibility and environmental sustainability. Section 7 concludes the paper and presents future research directions.
2. Critical Raw Materials
Raw materials essential for the production of electronic devices are often classified as CRMs, due to their limited availability and high economic importance. Many of these materials are scarce within the European Union, and recycling efforts remain limited. To address this, the European Commission has established a road-map for a resource-efficient Europe [11,12]. According to this roadmap, the EU promotes transforming waste into valuable resources often referred to as “urban mining” which reflects a core principle of the CE. To secure a reliable supply of raw materials, particularly minerals, the Commission has developed an integrated strategy built on three main pillars:
- Recovery of critical raw materials;
- Critical raw material diplomacy;
- Sustainable sourcing of raw materials.
The first emphasizes recovering raw materials from waste to build a safe and stable domestic supply. The second focuses on raw material diplomacy to ensure fair access to global markets. The third promotes the sustainable sourcing of primary mineral raw materials from European geological deposits. The Commission acknowledges the vital role of both primary and secondary sources, such as WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment), in securing mineral resources while advancing Circular Economy (CE) goals.
According to the ProSUM project on urban mining [13], the usage and disposal of electronic devices have increased dramatically over a 20-year span, leading to a significant surge in WEEE generation. On their platform (http://www.urbanmineplatform.eu/ accessed on 15 April 2025), they provide visual data illustrating the generation of electronic waste across various WEEE categories over two decades. Figure 1 and Figure 2 show the waste generated per capita within EU states at different points in time.
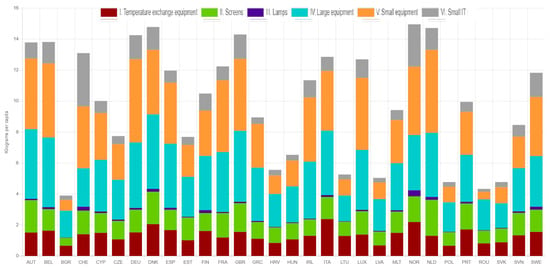
Figure 1.
Waste generated per capita within EU states in 2000 [13].
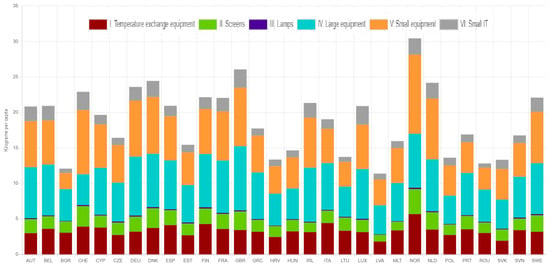
Figure 2.
Waste generated per capita within EU states in 2020 [13].
Due to the high significance of CRMs in the production of new electronic devices, the EU releases an updated list of CRMs every three years. These materials are not only crucial to the EU economy but also susceptible to supply disruptions. The CRM list plays a vital role across industries such as technology, manufacturing, and renewable energy. The first report, published in 2011 [14], identified 14 chemical elements as critical. The process of adding or removing elements from the list involves a detailed assessment of various factors, including economic importance, supply risks, and geopolitical considerations. The second list, issued in 2014 [15], designated 17 elements as critical. This trend continued with the 2017 and 2020 updates, which identified 19 and 28 critical raw materials, respectively [16,17]. Notably, the list has expanded over time rather than shrinking, largely due to inefficient and informal recycling practices. In light of these challenges, this review evaluates the key barriers to CRM recovery and explores potential AI-based solutions to address them.
The European Commission identifies 34 critical raw materials, which require focused efforts in recycling and reuse, according to its latest report [18]. The EU reviews global production and consumption of these materials every three years, updating the critical list based on recycling rates and their availability within Europe. The most recent CRM report was issued in 2023. Table 2 presents the list of identified critical elements.

Table 2.
List of critical raw materials 2023 [19]. (* Some elements do not meet the CRM thresholds but are still considered Strategic Raw Materials.)
Among different types of WEEE, WPCBs are of primary importance because they serve as the building blocks of electronic devices, and the majority of CRMs are found on their surfaces. Table 3 lists the electronic components commonly found on PCBs and their associated CRMs.

Table 3.
Electronic components present on WPCBs along with critical raw materials [19,20,21,22,23].
3. Methodology
We used the PRISMA structure [24] to organize this detailed systematic review, focusing on the role of AI-powered systems in WPCB recycling. To achieve this, the review outlines the selection of research databases, search strategies, inclusion and exclusion criteria, and data extraction procedures. The overarching goal is to provide a comprehensive understanding of how research on AI-powered systems has evolved in the context of WPCB recycling. Figure 3 presents the flow diagram of the systematic literature review.
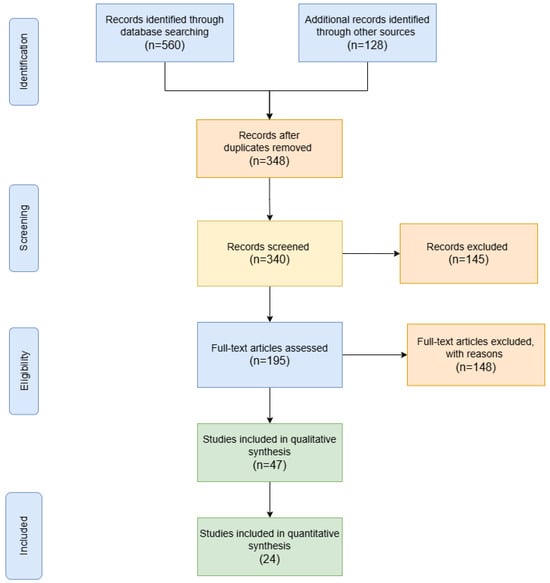
Figure 3.
Study selection flowchart for the systematic literature review.
3.1. Search Strategies
Four databases were used to search for relevant literature based on the research questions: IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar. These databases were selected because they contain the latest and most valuable research articles in WEEE. A combination of AND and OR strategies were used with various keywords, such as “Waste Printed Circuit Boards Recycling” AND “Deep Learning”, “Waste Printed Circuit Boards Datasets“ OR “State-of-the-Art Computer Visions System for WPCBs disassembly”, “Resource Recovery from Waste Printed Circuit Boards” AND “Environmental Sustainability”, “Challenges in Waste Printed Circuit Boards Recycling” AND “Limitations of Waste Printed Circuit Boards Recycling Techniques” and “ Improvement Opportunities in Recycling Strategies” OR “Sustainable E-Waste Practices” to optimize the retrieval of the most relevant articles. These keywords are closely aligned with the research questions that this study intends to address. Table 4 shows the detailed keywords used in the search strategy.

Table 4.
Search strategy on different databases.
3.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Table 5 shows the detail criteria for both study inclusion and exclusion. Inclusion criteria to select relevant paper for this detail SLR are given below:

Table 5.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria.
- Articles that focus on WPCB recycling using AI and deep learning techniques.
- Articles that include research on the recovery of CRMs from electronic boards using AI and deep learning techniques.
- Articles that report on major advancements and recent developments in AI and deep learning for WEEE recycling.
- Articles that discuss the challenges and limitations of WEEE recycling techniques.
- Articles that were published in the past 10 years.
Exclusion criteria to reject relevant paper for this detail SLR are given below:
- Articles that do not focus on electronic board waste from WEEE.
- Articles that do not include research on AI and deep learning techniques for component level detection and localization of waste PCB.
- Articles that are not in the English language.
- Articles that are not peer-reviewed research papers or conference proceedings.
- Articles that are not published in the past 10 years.
- Articles that do not align with research questions and keywords used in this review.
3.3. Study Selection
The study selection process for this review involved a thorough examination of the literature retrieved from four databases: Scopus, Web of Science, Google Scholar, and IEEE Xplore. A total of 688 papers were initially identified through a detailed keyword-based search. The first step was to remove duplicate records, resulting in 340 unique papers. Next, titles and abstracts were screened to assess their relevance to the research questions, narrowing the list to 195 papers. The full texts of these papers were then reviewed to ensure alignment with the inclusion criteria. Papers that did not meet the criteria were excluded, leading to a final selection of 24 studies considered most relevant and latest on AI and deep learning for WPCB recycling.
To ensure quality and reliability, two independent reviewers conducted the screening process, evaluating abstracts and full texts. Any discrepancies were discussed and resolved by consensus.
3.4. Data Extraction Strategy
The data extraction process for this review involved creating a structured template to capture all relevant information from the 24 selected studies. This template included fields for study ID, source database, paper title, and reference details. Each selected paper was reviewed in depth, and the extracted information is presented and analyzed in the following sections.
The extracted data was organized according to the research questions and objectives of the review. This included information on datasets, AI techniques and methodologies used for WPCB recycling, materials recovered, and performance metrics such as efficiency and accuracy. One of the reviewers reviewed the extracted data for completeness and accuracy, and any missing or incorrect information was retrieved from the original sources. Figure 4 shows the geographic distribution of the selected studies, with Asia accounting for the largest share.
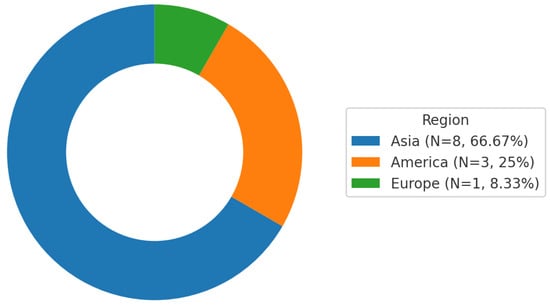
Figure 4.
Distribution of the selected studies by population location.
The data was then analyzed and synthesized to answer the research questions and identify patterns and trends in the literature. This synthesis supports conclusions and recommendations for future research in WEEE recycling using AI and deep learning approaches. The data extraction process was thoroughly documented, including any difficulties encountered, decisions made, and excluded data, to ensure transparency and replicability of the review. Figure 5 and Figure 6 show the focus areas of research for both WPCB recycling application point of view and techniques used for it. Table 6 shows the list of selected papers for systematic review.
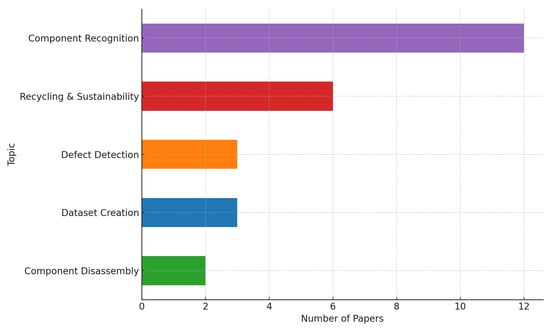
Figure 5.
Research focus areas across selected studies in WPCB recycling using AI.
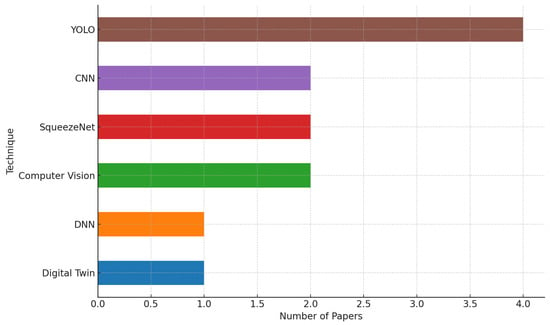
Figure 6.
AI and deep learning techniques used in selected WPCB recycling studies.

Table 6.
Total number of selected studies.
4. Datasets (RQ1)
4.1. Role of Artificial Intelligence in WEC Recycling
AI plays a crucial role in electronic waste recycling, particularly in the processing and extraction of WECs from WPCBs. The WPCB recycling process involves several essential stages, such as dismantling, resource recovery, and pollution control, which are critical for the sustainable management of e-waste [47]. AI technologies, especially computer vision and robotic systems, enable automation in the disassembly and sorting of WECs from printed circuit boards. These systems can accurately detect and classify components such as capacitors, resistors, and integrated circuits, allowing for efficient segregation [8,48,49].
Machine learning algorithms can also optimize downstream recycling processes such as mechanical shredding, pyrolysis, and hydrometallurgy by analyzing sensor data and dynamically adjusting process parameters [49,50]. As a result, material recovery rates increase, energy consumption decreases, and there is a notable reduction in environmental impact. To train these AI systems effectively, a large amount of high-quality data is required, particularly for machine vision applications. However, existing research on dataset availability remains limited. Only a few publicly accessible datasets currently support tasks such as WPCB recycling, PCB defect detection, and visual inspection. This study explores the available WPCB datasets that can be effectively used in AI-powered WEC recycling systems.
4.2. Datasets
Recent advancements in deep learning have significantly increased the data requirements of computer vision models, particularly for generalization and robustness [51]. This presents a challenge for developers, as collecting and annotating high-quality training data is time-consuming and resource-intensive. Furthermore, AI models require ongoing updates to maintain accuracy in changing environments, increasing the demand for robust dataset infrastructure.
In this section, we review state-of-the-art PCB datasets used for tasks such as quality assurance, visual inspection, and WPCB recycling:
- Pramerdorfer et al. [25] introduced a public dataset for computer vision-based PCB analysis with an emphasis on recycling-related tasks. It includes 748 high-resolution images of unique PCBs, captured using a DSLR camera under realistic conditions, and provides segmentation and bounding box information for integrated circuit (IC) chips, as well as textual annotations for some ICs.
- Mahalingam et al. [52] proposed a dataset for component-level classification. It includes 984 images from 123 boards, annotated with over 12,000 components: ICs (5844), capacitors (3175), resistors (2670), and inductors (542). This dataset is suitable for training models for WPCB component identification and classification.
- DeepPCB [28] consists of 1500 image pairs annotated for six major PCB defect types. The benchmark model achieved a mean average precision (mAP) of 98.6% at 62 FPS, highlighting its usefulness in high-speed defect detection tasks (https://github.com/tangsanli5201/DeepPCB, accessed on 12 March 2025).
- FICS-PCB [27] includes 9912 images across 31 PCB samples, with 77,347 labeled components spanning six classes. Images are provided in resolutions of 1600 × 1200 and 8256 × 440. The dataset supports both feature engineering and deep learning-based PCB classification.
- Other locally developed datasets [26,30] include PCB images annotated for a variety of tasks relevant to WPCB recycling.
The success of machine vision systems in WPCB recycling depends heavily on the characteristics of the dataset used for model development and inference. Datasets included in this review contain annotated resources relevant to the field of computer vision in the context of WPCB recycling. These annotated resources support tasks such as automatic detection of electronic components, defect detection, and automatic segmentation of different regions of the WPCB. Models vary in scale and annotation types, enabling feature engineering and deep learning for industrial recycling facilities requiring high-throughput and accurate component detection. Scalability and adaptability issues persist, as does the need to address challenges related to varying lighting and complex designs of electronic components present on the board. Addressing these issues is essential for developing robust, industrial-level AI systems for WPCB recycling.
4.3. Results and Discussion
Most of the datasets support various PCB-related tasks; however, their applicability is very limited to industrial level recycling. Most were developed for manufacturing inspections rather than for the intelligent e-waste recycling or for the recovery of high-density CRMs. The main reasons for this are the lack of availability of high-quality datasets, the complexity of designs, and the variability of conditions in controlled recycling environments.
AI models trained on these types of datasets may have difficulty generalizing to real world recycling scenarios, which can involve significant variations in lighting conditions, aging, and physical damage. The incompatibility between the characteristics of the dataset and real-world conditions reduces the robustness of the model and limits the industrial deployment of AI systems for automated dismantling and sorting. To enable practical AI applications in WPCB recycling, future datasets should better reflect recycling conditions, including diverse materials, damaged components, and accurate annotations for valuable parts of the WPCBs. Such datasets would significantly improve CRM recovery and accelerate progress in AI-driven e-waste recycling.
5. Current State of the Art for WPCB Recycling (RQ2)
AI has played a key role in the automation industry, enabling companies to accelerate production in response to the growing demand for electronic devices. As more electronic devices are discarded each year, the volume of e-waste continues to increase. Leveraging AI in e-waste management has the potential to significantly improve the speed and efficiency of recycling processes. This section addresses Research Question 2 RQ2 by examining the most recent and effective AI-based techniques used for WPCB recycling. In the context of e-waste, AI contributes to the automatic separation of different types of waste using vision-guided robots, as well as the dismantling and sorting of components from WPCBs. Among these tasks, accurate object recognition and sorting are fundamental to the success of automated recycling solutions. Therefore, this section provides a detailed overview of state-of-the-art object detection models that play a critical role in automating the disassembly and sorting of WPCBs for efficient recycling.
5.1. Object Detection: A Brief Overview
Object detection is a computer vision task that aims to identify and locate objects within an image or video. It combines both classification and localization into single operation. In recent years, object detection models have gained significant popularity due to their wide range of applications, including self-driving cars, surveillance and security systems, and medical image analysis. Given its broad applicability, various deep learning-based object detection models have been proposed over the past decade [53,54]. Most studies focus on improving both detection accuracy and real-time processing speed. Object detection models are generally categorized into three groups: (i) single-stage, (ii) two-stage, and (iii) traditional methods. In single-stage detection, region proposals and object classification are performed in a single step, enabling fast, real-time performance. Notable examples include YOLO [53] and SSD [55]. In contrast, two-stage models first generate region proposals and then perform classification and localization. Well-known two-stage models include R-CNN [54] and Mask R-CNN [56]. Traditional object detection methods, such as those based on Histograms of Oriented Gradients (HOG) [57], represent earlier approaches that relied on handcrafted features rather than deep learning. Figure 7 illustrates the overall flow and evolution of object detection models.
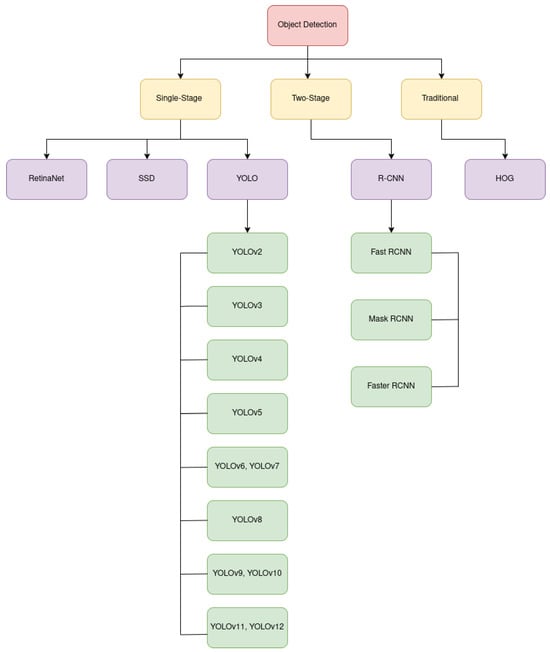
Figure 7.
Evolution and flow of fundamental object detection models (2015–2025).
5.1.1. You Only Look Once (YOLO)
YOLO [53] is one of the most widely used object detection model, known for its high citation count and popularity due to its efficiency and speed. Over the years, YOLO has undergone various updates and improvements, making it increasingly refined and effective for real-world applications. Its development includes versions from YOLOv2 through YOLOv12 [58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68]. Two key factors contribute to YOLO’s success: its compact architecture and high computational speed. Its simple structure enables it to directly predict the bounding box coordinates and class labels in a single neural network pass. This allows the model to process images quickly, making it suitable for real-time applications, including video object detection.
5.1.2. Single-Shot MultiBox Detector (SSD)
Another well-known object detection model is the SSD [55]. For each feature map location, SSD discretizes the output space of bounding boxes into a set of default boxes. Each default box is scored based on the presence of specific object categories and is adjusted to better match the object’s shape. To detect objects at different scales, SSD combines predictions from multiple feature maps with varying resolutions. SSD eliminates the need for object proposals and subsequent resampling, which simplifies training and integration. On the PASCAL VOC [69] and COCO [70] datasets, SSD is significantly faster than methods that rely on an additional object proposal stage, while providing a unified framework for both training and inference.
5.1.3. Region-Based Convolutional Neural Networks (R-CNNs)
R-CNN [71]-based models are among the most advanced deep learning approaches for object detection and are comparable to the YOLO family. R-CNN can accurately detect and classify objects in an image across various categories. It uses a combination of convolutional neural networks and region proposal algorithms to achieve high detection performance along with precise localization of the detected objects. The model follows a two-stage object detection pipeline, which performs detection in three main steps: (1) Region Proposal, (2) Feature Extraction, and (3) Classification and Localization of the detected objects. In this paper, we adopt the more advanced Faster R-CNN [54], which introduces a Region Proposal Network (RPN) that shares convolutional features with the detection network, allowing nearly cost-free generation of region proposals.
The RPN simultaneously predicts object boundaries and objectness scores, generating high-quality region proposals for detection. By integrating the RPN with Fast R-CNN into a unified network, the system streamlines the detection process. Upon evaluation on multiple benchmark datasets, the model achieves a frame rate of 5 frames per second (FPS) while maintaining state-of-the-art accuracy in object detection.
5.1.4. RetinaNet
In RetinaNet [72], the authors investigate the limitations of one-stage object detectors, which, while generally faster and simpler, tend to be less accurate than two-stage detectors. One major limitation is the extreme class imbalance between background and foreground examples during training, which significantly hampers the performance of dense detectors. To address this, RetinaNet introduces a novel loss called Focal Loss, which assigns lower weights to well-classified examples and focuses the model’s attention on harder, misclassified instances. This approach prevents easy negatives from dominating the training process, thereby improving performance. As a dense detector trained with Focal Loss, RetinaNet presents a compelling solution to the speed-versus-accuracy trade-off in object detection. It achieves the efficiency of one-stage detectors while surpassing the accuracy of many existing two-stage methods.
5.1.5. HOG
Histograms of Oriented Gradients (HOG) for human detection [57] is one of the classical object detection algorithms. In this paper, the authors investigate the use of HOG for robust visual object recognition, specifically in the context of human detection. Their results show that HOG descriptors outperform existing feature sets for this task and highlight the impact of various computational stages on overall performance. They also introduce a more challenging dataset for human detection, containing over 1800 annotated images of humans in a wide range of poses and backgrounds.
In object detection tasks, it is evident that while both two-stage and single-stage models are employed, their performance in terms of speed, accuracy, and flexibility varies depending on the specific requirement of the task. If high inference speed is crucial, single-stage models like YOLO are often a good choice. Conversely, if higher accuracy is needed, two-stage models may offer better performance, though this comes with increased computational complexity.
5.1.6. Automatic Methods for WPCB Recycling
This section discusses the current state of the art in deep learning-based algorithms for recycling WEEE.
In this study [73], the authors present a fast recognition method for electronic components in complex backgrounds using deep learning. The method is based on an improved YOLOv3 network, which balances detection accuracy and speed. The authors used an image dataset for electronic components, which included image acquisition, augmentation, and annotation. The dataset was divided into three parts: the training set, the validation set, and the test set, with a composition ratio of 35%, 35%, and 30%, respectively. Professional software was used to create image labels, which were then combined with the images to generate the dataset. The labels were uniformly converted into the PASCAL VOC 2007 format. The authors focused only on the upper electronic components; components that were more than 70% occluded were not considered. Additionally, the two ends of the components were excluded. The proposed method can be used to detect electronic components in complex backgrounds, and other object recognition tasks can benefit from the lightweight improvement of the YOLOv3 model. This improvement is achieved by combining YOLOv3 with MobileNet. The method achieved a detection accuracy of 95.21% and inference speed of 0.0794 s per image, outperforming several popular detection approaches. These results indicate that the model is well-suited for applications in electronic manufacturing and recycling scenarios.
With the advancement in electronic technology, the generation of e-waste has increased rapidly. According to Jun Chen [31], when a PCB reaches the end of its life, numerous electronic components present on the PCB can be recycled and reused in new products. Therefore, Chen proposed a YOLOv5-based algorithm combined with a hierarchical classification method to recognize the electronic components on the board that can be dismantled at later stages. The proposed method achieved 38% higher accuracy than the original YOLOv5 algorithm.
The study highlights that most e-waste recycling still relies on traditional methods, such as mechanical treatment, which have serious consequences for both environment and human health. For model training, after a series of data augmentations techniques such as horizontal and vertical flipping, rotation, scaling, cropping, contrast adjustment, etc., a total of 12,150 images were used for training and 1688 images for testing.
In [32], the author used a local PCB image dataset and conducted a simulation. He proposed an improved YOLOv3 algorithm by adding an additional layer to detect tiny components on the board. According to the author, the number of WECs present on the board is large and their shapes are different, which contributes to the relatively low detection accuracy achieved so far.
Another study [34] proposed PCB recycling using a robot manipulator integrated with deep learning techniques. A Faster R-CNN model is used for recognizing different components present on a conveyor belt, and a robotic arm is used to pick and place the components in a specified position. The paper also introduces a class-learning-based approach for detecting modifications in PCB. A loss function is proposed to train deep convolutional neural networks on unmodified boards in order to solve the challenge of producing numerous training examples containing anomalies. By comparing input images and autoencoder reconstructions, they propose a function that explores higher-level features.
In a different study [38], the authors explored the efficient segregation of waste using the YOLOv3 Darknet model. The model was trained for six object classes: cardboard, glass, metal, paper, plastic, and organic waste, and was validated using the YOLOv3-tiny model as a validation assessment. The findings of the paper are based on the segregation of biodegradable and non-biodegradable items in a garbage dataset. This study also elaborates on a detailed assessment of the YOLOv3 model along with YOLOv3-tiny’s usability for real-time detection of different e-waste products, which opens a window for future researchers in waste recycling. Although there are different complexities, the authors deal with challenges during image acquisition for detecting smaller objects.
For sorting the WPCBs, the author of [39] proposes a solution used in various factories that employ automatic robot manipulators to pick and place different electronic boards. For detection and training, the YOLOv5 model with its variants—nano, small, medium, and large neural networks were used to select the best-performing model. The evaluation of the model was performed based on mean average precision (mAP), precision, recall, and F1-score. They found that large computationally demanding neural networks are not required for this task, and the small model of YOLOv5 achieved an mAP of 0.994, and precision, recall, and F1-score of 0.996 each for detecting and classifying PCBs.
In another study [40], authors explored computer vision-based techniques for detecting PCB components to ensure hardware reliability. They described different types of features—color, shape, and texture—for better generalization. In this paper, they performed an analysis of various computer vision-based features using the semantic PCB dataset for WPCB component detection. A detailed comparison with different PCB datasets was performed, and it was reported that color-based features were the most effective for detecting components and improving model generalization.
Further, in another study [41], the authors used the PCB-DSLR [25] dataset and proposed a method to evaluate the financial return of recycling integrated circuits on PCBs. This dataset contains 748 RGB images of WPCBs, with a resolution of 4928 × 3280 pixels, collected from 165 different boards. The study aims to help the electronics recycling industry estimate the value of electronic components recovered from PCBs, with a particular focus on integrated circuits, which contribute significantly to much of the value of recovered materials.
The method proposed in this study, called WPCB-EFA, evaluates the economic viability of recycling PCBs by detecting integrated circuits using computer vision. The method uses image processing algorithms to identify the integrated circuits on a board and then estimates the amount of recoverable valuable metals present in these components. Precision, recall, and mAP metrics were used to evaluate the IC detector model. The YOLOv3 model was used for IC detection from PCBs and for estimating the recycling materials from those ICs, achieving a mAP of 0.965.
In the paper [42], the authors explained a computer vision deep learning-based approach for detecting electronic components, especially ICs, and validated its performance. A deep learning CNN model was used for detecting small IC components. They compared different object detection algorithms along with loss boosting techniques to achieve better results. Similarly, in paper [33], the author presented an approach for the intelligent disassembly of electronic components from PCBs instead of using the traditional hydro-metallurgical process. Both mechanical and chemical processes for disassembly are time-consuming and require significant time for separating valuable materials.
Following the main idea, in paper [44], an AI-based model was used for automatic segregation. The author used the SSD deep learning model with MobileNet as the base network for the classification of biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste. The SSD model integrated with MobileNet achieved 90% accuracy.
Furthermore, the study [36] proposed a semantic segmentation method based on depth images for electronic component recognition through pixel classification. Depth difference features were extracted from synthetic depth images, and a random forest classifier was used for training. The proposed model achieved state-of-the-art results on synthetic depth images and achieved 98% accuracy; while on real depth images, it achieved 85% accuracy overall.
In the study [37], the authors presented a novel digital twin-based system for WEEE recovery to support manufacturing/re-manufacturing operations throughout the product’s life cycle, from design to recovery. The proposed digital twin-based system for WEEE recovery supports manufacturing/re-manufacturing operations throughout the product’s life cycle, from design to recovery. The WEEE digital twin is initiated based on cyber knowledge acquired during the product design phase. The geometry, components, materials, and most importantly, hazardous substances are integrated and maintained in the product documentation. The feasibility of the proposed system and methodologies was validated and evaluated through implementations in the cloud and a cyber-physical system. The results show that the proposed digital twin-based system for WEEE recovery can provide an integrated and reliable cyber-avatar of the individual WEEE, thus forming a personalized service system. Overall, this paper provides valuable insights into the use of digital twin technology in the recycling and re-manufacturing of WEEE.
In another study [74], the authors examined the disassembly of electronic components from WPCBs and their physical separation using a self-designed disassembling apparatus: a three-step separation process of sieving, magnetic separation, and dense medium separation. The main purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of the dismantling apparatus in disassembling layered electronic components from WPCBs under various treatment conditions and to determine the concentration of minor metals in the electronic components by the physical separation of the detached electronic components.
Furthermore, another detailed study [43] explained the detection of PCB defects using a deep learning CNN-powered approach. They used a locally developed PCB dataset consisting of 41,387 images and divided the data into training, testing, and validation sets. The author used a conventional CNN architecture for training and achieved 85% overall accuracy. Deep learning-based models are divided into single-stage, two-stage, and conventional approaches used for WPCB recycling. Table 7 shows the AI techniques used in our selected studies for WPCB recycling.

Table 7.
Overview of AI and deep learning techniques applied in selected studies.
5.2. Results and Discussion
The methodologies adopted for recycling WPCBs are increasingly relying on deep learning techniques, particularly single-stage object detectors like YOLO variants and two-stage models such as Faster R-CNN, to automate the recycling process. YOLO-based models, including improved versions such as YOLOv3-MobileNet and YOLOv5, are the best choice because they balance detection accuracy with computational efficiency. These models perform well in real-time detection tasks. Studies described in Table 7 show that lightweight models often match or exceed the accuracy as compared to more complex architectures, suggesting an optimized trade-off suited for real-world deployment.
However, performance is still challenged by issues such as component occlusion, tiny object detection, and environmental variability. Some research has also explored advanced approaches, such as semantic segmentation with depth images and digital twin systems, to model and optimize the entire recycling life cycle. While these methods show significant potential, their effectiveness depends heavily on tuning the models for specific tasks, ensuring dataset relevance, and integrating them with physical recycling infrastructure. Overall, AI-driven methods are maturing rapidly; however, they still require greater standardization, interpretability, and practical validation in industrial recycling settings.
5.3. Critical Analysis of AI Techniques in WPCB Recycling
Although a wide range of AI techniques have been applied to WPCB recycling tasks, their suitability varies depending on the application context, dataset availability, and deployment constraints. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) such as ResNet and EfficientNet provide strong performance in image-based component classification but require large labeled datasets and struggle with generalization across varying PCB designs.
Object detection models like YOLOv5 offer a favorable trade-off between speed and accuracy, making them suitable for real-time disassembly and sorting applications. However, their performance can degrade in cluttered or noisy environments, and they often require significant retraining when applied to new PCB layouts. Transformer-based models (e.g., DETR) have demonstrated improved robustness and contextual understanding but are computationally intensive and less explored in the recycling domain. Classical machine learning models (e.g., SVM, k-NN, Random Forest) have been used for simpler tasks such as material classification, but they generally lack the capacity to handle high-dimensional visual features and perform poorly in complex disassembly scenarios.
Overall, there is no one-size-fits-all solution; model selection must consider not only performance metrics but also computational demands, dataset constraints, and alignment with real-world recycling workflows. Critical gaps remain in model adaptability, robustness to visual noise, and integration with hardware systems used in recycling facilities.
6. Challenges in the Adaptation of AI-Based Systems in WEC Recycling (RQ3)
This section of the paper discusses the challenges associated with the adoption of AI-based systems in WEC recycling and possible solutions. In the study [33], the authors address the challenges posed by inefficient and damage-prone manual disassembly processes. Traditional methods often struggle with with the complexity of densely packed components on PCBs. To address these issues, the study proposes an AI-based system that integrates deep learning algorithms and robotic arms to accurately identify and extract components. This intelligent approach improves component reuse, reduces labor costs, and supports sustainable e-waste recycling.
6.1. Challenges: Survey of the Literature
In the study [34], the authors highlight the challenges of automating the disassembly process for complex PCB structures. Manual recycling methods are time-consuming and expose workers to hazardous materials. To address these issues, the study integrates deep learning for component recognition with robotic manipulators to perform automated pick-and-place operations. This integration improves the safety, efficiency, and precision of component recovery from electronic waste.
Subsequently, in the study [41], the authors address the challenge of quantifying the economic value of recoverable components from WPCBs. Traditional estimation methods are imprecise and inefficient for large-scale recycling. The proposed solution uses computer vision and deep learning to detect integrated circuits and estimate the quantity of valuable materials they contain. This approach enables more accurate estimations of material value and supports data-driven decision-making in e-waste management.
In another study [37], the authors explore the challenges of managing complex product data and hazardous components throughout the recycling life cycle. Conventional recycling lacks integration with product design and real-time tracking. To address these issues, the study proposes a digital twin system that generates a virtual replica of electronic products, including their geometry, materials, and hazardous content. This system enables more informed recycling decisions and supports end-to-end traceability within a cyber-physical Industry 4.0 framework.
Furthermore, in the study [38], the authors address the issue of inefficient and inaccurate manual waste sorting processes. Traditional methods struggle with with the real-time identification and classification of different types of waste. The proposed solution uses an enhanced YOLOv3 deep learning model to automate the separation of biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste. This system improves sorting accuracy and speed, providing a scalable solution for smart and sustainable waste management.
In a further study [44], the authors address the challenge of accurately classifying waste materials based on their environmental impact. Manual sorting is inconsistent and unsuitable for increasing waste volumes. The proposed deep learning model, based on SSD with MobileNet, classifies waste as biodegradable or non-biodegradable with high accuracy. This automated approach improves the efficiency and reliability of waste segregation processes in smart recycling systems.
In the last study [46], the authors address the difficulty of accurately identifying different types of PCBs in mixed electronic waste streams. Manual sorting is error-prone and limits recovery efficiency. The study proposes using a convolutional neural network (CNN) for automated PCB classification. This method improves identification speed and accuracy, streamlining the recycling process and supporting better material recovery. Table 8 shows challenges and proposed solutions formulated in the selected studies.

Table 8.
Challenges and proposed solutions in WPCB recycling.
6.2. Industrial Adoption and Feasibility
Despite significant academic progress in AI applications for WPCB recycling, real-world industrial adoption remains limited. Most proposed models are validated using laboratory datasets or in controlled settings, and there are few documented pilot implementations in operational recycling facilities. Key barriers to adoption include a lack of standardized, high-quality annotated datasets; high variability in PCB designs; and the cost of integrating AI with existing mechanical disassembly infrastructure.
Real-time deployment of AI models, particularly object detection and classification systems, requires robust hardware, reliable vision systems, and resilience to noise, dust, and lighting inconsistencies. While models such as YOLOv5 offer promising speed for industrial automation, their reliance on extensive retraining limits adaptability across diverse WPCB types.
Another major challenge is economic feasibility, as the return on investment is difficult to quantify especially in regions where manual labor remains cost-effective. However, pilot studies have demonstrated the potential for AI to enhance recovery rates of valuable materials and reduce processing time. For instance, Mohsin et al. proposed [7], an automated computer vision system for selective disassembly and sorting of WPCBs through AI and IoT. In their pilot studies, the researchers prepared a high-quality custom WPCB dataset for computer vision analysis, aiming to maximize the recovery of high-density CRMs through selective disassembly and sorting.
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
7.1. General Conclusions
This paper presents a comprehensive, systematic review of recent advancements in AI, with a focus on deep learning techniques applied to the automated disassembly and sorting of WPCBs for recycling. The review is organized into three main themes:
- Datasets: A review of publicly available datasets relevant to deep learning–based WPCB analysis that highlights their role in supporting electronic component detection, automated disassembly and sorting.
- Methods: An evaluation of state-of-the-art AI techniques used for visual analysis and automatic detection of electronic components, including object detection models and robotic integration.
- Challenges and Solutions: A discussion of the primary technical and practical challenges in vision-based recycling systems and potential AI-driven solutions to improve accuracy, efficiency, and scalability.
This study follows the PRISMA methodology to ensure a transparent and systematic approach to literature selection, screening, and inclusion. The review reveals a significant gap in publicly accessible, recycling-specific datasets; most existing datasets focus on quality assurance, defect detection, or generic component recognition. This underscores the necessity of more targeted data resources and integrated AI frameworks to improve the precision and sustainability of WPCB recycling systems.
7.2. Limitations and Future Directions
Recent advancements in AI have opened new possibilities for automating WPCB recycling. However, several limitations still hinder the practical adoption of these technologies. First, the scarcity of high-quality, annotated WPCB image datasets limits the training and benchmarking of models. Existing datasets are often small and domain-specific or lack diversity in PCB layouts and component types.
Second, the generalizability of AI models is still a challenge. Most approaches are trained on limited data and tend to underperform when applied to unfamiliar board designs or varying environmental conditions, such as different lighting, occlusion, or surface damage.
Third, integrating with industrial hardware systems presents practical challenges. Many proposed models assume static imaging setups and controlled conditions, both of which are rarely available in actual recycling lines.
Looking ahead, future research should prioritize developing large, diverse, and standardized WPCB datasets, possibly through collaborations between academia and industry. Additionally, there is a need to explore domain adaptation, transfer learning, and robust model training to improve performance in variable real-world conditions. Finally, when designing AI-powered recycling systems, it is crucial to consider not only accuracy, but also real-time performance, energy efficiency, and ease of integration with mechanical disassembly and sorting systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M., S.R., F.M., and A.C.; Methodology, M.M., S.R., F.M., and A.C.; Software, M.M. and S.R.; Validation, M.M., S.R., F.M., and A.C.; Resources, M.M., S.R., and F.M.; Data Curation, M.M.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, M.M.; Writing—Review and Editing, M.M., S.R., F.M., and A.C.; Visualization, M.M., S.R., F.M., and A.C.; Supervision, S.R. and F.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Part of this work was funded by the European Union and Italian “Fondo di Rotazione per l’Attuazione delle Politiche Comunitarie” under the Interreg Marittimo/Maritime IT-FR grant 00271.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available upon request from the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Stefano Rovetta, Francesco Masulli and Alberto Cabri are employed by Vega Research Laboratories s.r.l, Italy. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Jung, Y.H.; Zhang, H.; Gong, S.; Ma, Z. High-performance green semiconductor devices: Materials, designs, and fabrication. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2017, 32, 063002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forti, V.; Baldé, C.P.; Kuehr, R.; Bel, G. The Global e-Waste Monitor 2020. Quantities, Flows, and the Circular Economy Potential; International Telecommunication Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–119. [Google Scholar]
- Waltersmann, L.; Kiemel, S.; Stuhlsatz, J.; Sauer, A.; Miehe, R. Artificial Intelligence Applications for Increasing Resource Efficiency in Manufacturing Companies—A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressanelli, G.; Saccani, N.; Pigosso, D.C.; Perona, M. Circular Economy in the WEEE industry: A systematic literature review and a research agenda. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2020, 23, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Awasthi, A.K.; Qin, W.; Liu, W.; Yang, C. Recycling value materials from waste PCBs focus on electronic components: A review on technologies, obstruction and prospects. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, M.; Rovetta, S.; Masulli, F.; Cabri, A. Adaptive Multi-Stage Transfer Learning Approach for Electronic Component Detection in Waste Printed Circuit Boards. In Proceedings of the 2025 International Conference on Advanced Sustainability Engineering and Technology (ICASET), Kenitra, Morocco, 17–18 April 2025; pp. 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsin, M.; Rovetta, S.; Masulli, F.; Cabri, A. Automated Disassembly of Waste Printed Circuit Boards: The Role of Edge Computing and IoT. Computers 2025, 14, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, M.; Rovetta, S.; Masulli, F.; Cabri, A. Virtual Mines–Component-level recycling of printed circuit boards using deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 Italian Workshop on Neural Networks (WIRN), Vietri sul Mare, Italy, 7–9 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsin, M.; Rovetta, S.; Masulli, F.; Greco, D.; Cabri, A. Deep learning-powered computer vision system for selective disassembly of waste printed circuit boards. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 8th Forum on Research and Technologies for Society and Industry Innovation (RTSI), Lecco, Italy, 18–20 September 2024; pp. 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsin, M.; Zeng, X.; Rovetta, S.; Masulli, F. Measuring the recyclability of electronic components to assist automatic disassembly and sorting waste printed circuit boards. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.16593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Roadmap to a Resource Efficient Europe; Communication of the European Commission; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2011.
- Commission of the European Communities. The Raw Materials Initiative—Meeting Our Critical Needs for Growth and Jobs in Europe; Communication of the European Commission; Commission of the European Communities: Brussels, Belgium, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Urban Mine Platform. Weight of EEE per Capita. Available online: http://www.urbanmineplatform.eu/urbanmine/eee/weightpercapita (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- European Commission. Tackling the Challenges in Commodity Markets and on Raw Materials; Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2011; 25.
- European Commission. On the Review of the List of Critical Raw Materials for the EU and the Implementation of the Raw Materials Initiative; Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2014; 297.
- European Commission. On the 2017 List of Critical Raw Materials for the EU; Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2017; 490.
- European Commission. Critical Raw Materials Resilience: Charting a Path Towards Greater Security and Sustainability; Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020; 474.
- Grohol, M.; Veeh, C. Study on the Critical Raw Materials for the EU 2023; Final Report DG GROW; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2023.
- European Commission, Joint Research Centre (JRC). EU Critical Raw Materials. 2023. Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/57318397-fdd4-11ed-a05c-01aa75ed71a1 (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Vafeas, N.; Slezak, P.; Hitzman, M. Analysis of critical raw materials policy for electrical and electronic equipment: Planning for a truly circular economy. Resour. Policy 2024, 99, 105380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobba, S.; Carrara, S.; Huisman, J.; Mathieux, F.; Pavel, C. Critical Raw Materials for Strategic Technologies and Sectors in the EU. A Foresight Study; IRIS: Porto, Portugal, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- ComponentSense. Rare Earth Elements and Electronic Components: Your Questions Answered. 2023. Available online: https://www.componentsense.com/blog/rare-earth-elements-and-electronic-components-your-questions-answered (accessed on 7 March 2025).
- Resource Hub for Technical Documents and Datasheets. Available online: https://accuristech.com/resources/ (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramerdorfer, C.; Kampel, M. A dataset for computer-vision-based PCB analysis. In Proceedings of the 2015 14th IAPR International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA), Tokyo, Japan, 18–22 May 2015; pp. 378–381. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Wei, P. A PCB dataset for defects detection and classification. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.08204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Mehta, D.; Paradis, O.; Asadizanjani, N.; Tehranipoor, M.; Woodard, D.L. Fics-pcb: A multi-modal image dataset for automated printed circuit board visual inspection. Cryptol. ePrint Arch. 2020. Available online: https://eprint.iacr.org/2020/366 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Tang, S.; He, F.; Huang, X.; Yang, J. Online PCB defect detector on a new PCB defect dataset. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.06197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagelüken, C.; Lee-Shin, J.U.; Carpentier, A.; Heron, C. The EU circular economy and its relevance to metal recycling. Recycling 2016, 1, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herchenbach, D.; Li, W.; Breier, M. Segmentation and classification of THCs on PCBAs. In Proceedings of the 2013 11th IEEE International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Bochum, Germany, 29–31 July 2013; pp. 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Bao, E.; Pan, J. Classification and Positioning of Circuit Board Components Based on Improved YOLOv5. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 208, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gu, J.; Huang, Z.; Wen, J. Application research of improved YOLO V3 algorithm in PCB electronic component detection. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopacek, B. Intelligent disassembly of components from printed circuit boards to enable re-use and more efficient recovery of critical metals. In Proceedings of the 2016 Electronics Goes Green 2016+(EGG), Berlin, Germany, 6–9 September 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Naito, K.; Shirai, A.; Kaneko, S.i.; Capi, G. Recycling of printed circuit boards by robot manipulator: A Deep Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Robotic and Sensors Environments (ROSE), Virtual, 28–29 October 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Candido de Oliveira, D.; Nassu, B.T.; Wehrmeister, M.A. Image-Based Detection of Modifications in Assembled PCBs with Deep Convolutional Autoencoders. Sensors 2023, 23, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, C.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Z. Semantic segmentation of a printed circuit board for component recognition based on depth images. Sensors 2020, 20, 5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.V.; Wang, L. Digital twin-based WEEE recycling, recovery and remanufacturing in the background of Industry 4.0. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 3892–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Yadav, D.; Gupta, H.; Verma, O.P.; Ansari, I.A.; Ahn, C.W. A novel yolov3 algorithm-based deep learning approach for waste segregation: Towards smart waste management. Electronics 2020, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glučina, M.; Anđelić, N.; Lorencin, I.; Car, Z. Detection and Classification of Printed Circuit Boards Using YOLO Algorithm. Electronics 2023, 12, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Gurudu, S.R.; Taheri, S.; Ghosh, S.; Mallaiyan Sathiaseelan, M.A.; Asadizanjani, N. Pcb component detection using computer vision for hardware assurance. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2022, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.H.d.S.; Júnior, A.A.; Azevedo, G.O.; Oliveira, S.C.; Fernandes, B.J. Estimating recycling return of integrated circuits using computer vision on printed circuit boards. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.A.; Chen, Z.; Crandall, D.J. Deep neural network–based detection and verification of microelectronic images. J. Hardw. Syst. Secur. 2020, 4, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adibhatla, V.A.; Shieh, J.S.; Abbod, M.F.; Chih, H.C.; Hsu, C.C.; Cheng, J. Detecting defects in PCB using deep learning via convolution neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th International Microsystems, Packaging, Assembly and Circuits Technology Conference (IMPACT), Taipei, Taiwan, 24–26 October 2018; pp. 202–205. [Google Scholar]
- Koganti, S.K.; Purnima, G.; Bhavana, P.; Raghava, Y.V.; Resmi, R. Deep Learning based Automated Waste Segregation System based on degradability. In Proceedings of the 2021 Second International Conference on Electronics and Sustainable Communication Systems (ICESC), Coimbatore, India, 4–6 August 2021; pp. 1953–1956. [Google Scholar]
- Soomro, I.A.; Ahmad, A.; Raza, R.H. Printed Circuit Board identification using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks to facilitate recycling. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 177, 105963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, G.; Luo, J.; He, J. An Electronic component recognition algorithm based on deep learning with a faster SqueezeNet. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 2940286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, M.; Shi, Q.; Kuang, X.; Qi, H.J.; Wang, T. Recycling waste circuit board efficiently and environmentally friendly through small-molecule assisted dissolution. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, M.; Rovetta, S.; Masulli, F.; Cabri, A. Extraction of Critical Raw Materials from Waste Printed Circuit Boards Using Machine Learning and Computer Vision. TechRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Yken, J.; Boxall, N.J.; Cheng, K.Y.; Nikoloski, A.N.; Moheimani, N.R.; Kaksonen, A.H. E-waste recycling and resource recovery: A review on technologies, barriers and enablers with a focus on oceania. Metals 2021, 11, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajwan, D.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, M.; Krishnan, V. Upcycling of Plastic Waste Using Photo-, Electro-, and Photoelectrocatalytic Approaches: A Way toward Circular Economy. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 4865–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, M.; Shaukat, A.; Akram, U.; Zarrar, M.K. Automatic Prostate Cancer Grading Using Deep Architectures. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/ACS 18th International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA), Tangier, Morocco, 30 November–3 December 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mahalingam, G.; Gay, K.M.; Ricanek, K. Pcb-metal: A pcb image dataset for advanced computer vision machine learning component analysis. In Proceedings of the 2019 16th International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA), Tokyo, Japan, 27–31 May 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Part I 14. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; Volume 1, pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Zheng, P.; Xu, S.t.; Wu, X. Object detection with deep learning: A review. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 2019, 30, 3212–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X. A review of object detection techniques. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Smart Grid and Electrical Automation (ICSGEA), Xiangtan, China, 10–11 August 2019; pp. 251–254. [Google Scholar]
- Laroca, R.; Severo, E.; Zanlorensi, L.A.; Oliveira, L.S.; Gonçalves, G.R.; Schwartz, W.R.; Menotti, D. A robust real-time automatic license plate recognition based on the YOLO detector. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, E.; Liang, Z. Apple detection during different growth stages in orchards using the improved YOLO-V3 model. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 157, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamtsho, Y.; Riyamongkol, P.; Waranusast, R. Real-time license plate detection for non-helmeted motorcyclist using YOLO. Ict Express 2021, 7, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Li, S. Target fusion detection of LiDAR and camera based on the improved YOLO algorithm. Mathematics 2018, 6, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Qiu, J. Ultralytics YOLOv8. GitHub Repository. 2023. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 22 October 2024).
- Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv9: Learning What You Want to Learn Using Programmable Gradient Information. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.13616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, J. YOLOv10: Real-Time End-to-End Object Detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.14458. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G.; Qiu, J. Ultralytics YOLO11. 2024. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Tian, Y.; Ye, Q.; Doermann, D. Yolov12: Attention-centric real-time object detectors. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.12524. [Google Scholar]
- Everingham, M.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The pascal visual object classes (voc) challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2010, 88, 303–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Part V 13. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Region-based convolutional networks for accurate object detection and segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 38, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.; Gu, J.; Sun, X.; Hou, Y.; Uddin, S. A rapid recognition method for electronic components based on the improved YOLO-V3 network. Electronics 2019, 8, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.c. Disassembly and physical separation of electric/electronic components layered in printed circuit boards (PCB). J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 241, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).