Highlights
- Latin America has shown increased big data adoption since 2012; Ecuador is now entering this transformative field.
- Science and engineering in Ecuador have benefited most from data analysis, with untapped potential in health and services sectors.
- Big data is shaping sectors in Ecuador, including disaster prediction, agriculture, smart city development, and electoral data analysis.
- Despite public sector inefficiencies, residential ICT adoption provides opportunities for Ecuador’s smart city advancements.
- Despite some data underutilization, big data’s transformative potential is evident in Ecuador’s healthcare and education advancements.
Abstract
Data analysis is increasingly critical in aiding decision-making within public and private institutions. This paper scrutinizes the status quo of big data and data analysis and its applications within Ecuador, focusing on its societal, educational, and industrial impact. A detailed literature review was conducted from academic databases such as SpringerLink, Scopus, IEEE Xplore, Web of Science, and ACM, incorporating research from inception until May 2023. The search process adhered to the PRISMA statement, employing specific inclusion and exclusion criteria. The analysis revealed that data implementation in Ecuador, while recent, has found noteworthy applications in six principal areas, classified using ISCED: education, science, engineering, health, social, and services. In the scientific and engineering sectors, big data has notably contributed to disaster mitigation and optimizing resource allocation in smart cities. Its application in the social sector has fortified cybersecurity and election data integrity, while in services, it has enhanced residential ICT adoption and urban planning. Health sector applications are emerging, particularly in disease prediction and patient monitoring. Educational applications predominantly involve student performance analysis and curricular evaluation. This review emphasizes that while big data’s potential is being gradually realized in Ecuador, further research, data security measures, and institutional interoperability are required to fully leverage its benefits.
1. Introduction
From ancient data records to the contemporary era of information and communication technologies (ICT), one aspect remains consistent—data analysis, a process that inspects, cleans, transforms, and models data to discover useful information, which has been a cornerstone in decision-making across various societal spheres [1]. The ICT revolution of the early 20th century marked a transition from conventional to strategic information systems, leveraging technology to process data with greater efficiency [1]. During the 1930s in the United States of America, the inception of big data analysis was sparked as public institutions aimed to optimize resources by tracking citizens’ social security contributions [2]. Fast-forward to the present, the explosive growth of data—a product of rapid digitalization and interconnectivity—presents both an opportunity and a challenge.
Data are now described as the new oil, with their value and impact echoing throughout all sectors of modern society, including education, manufacturing, and public sector management [3,4]. However, extracting meaningful insights from these vast datasets requires specialized methods and technologies [5]. Despite the increasing prominence of big data, studies on its application in developing countries like Ecuador remain sparse, underscoring the significance and need for our bibliometric review.
The growth and advancement of data analysis techniques, particularly those that facilitate the study of extremely large datasets, or big data, have transformed various fields, from business to healthcare. They are now poised to revolutionize education and manufacturing, among others. In the educational context, these advanced data analysis techniques provide valuable insights into student attributes, learning behavior, and psychological state, enabling tailored, effective teaching strategies and curricular reforms [6,7]. Meanwhile, in the manufacturing industry, big data’s role is no less critical. It lies at the heart of the Industry 4.0 paradigm, driving operational efficiency and business growth [8]. However, the actualization of these benefits requires overcoming hurdles related to sustainability, privacy, and access equity [9,10].
The primary objective of our bibliometric review is to explore the current state of big data applications in various sectors within Ecuador, identifying prevalent themes and potential gaps in the existing literature. To achieve this, we utilize comprehensive databases to aggregate relevant research, applying strict inclusion and exclusion criteria to ensure the validity and relevance of the selected studies. The data analysis will encompass techniques that enable a nuanced understanding of big data’s role and potential within the Ecuadorian context. The study leverages various analysis techniques, including keyword analysis, citation analysis, and co-authorship analysis, to discern trends and patterns in the selected articles.
Our review promises to make a unique contribution to the existing body of knowledge, providing much-needed insights into the state of big data applications in a developing country context. The findings could inform decision-making and policy development, particularly in sectors like education and manufacturing where the impact of data analysis techniques and big data is profoundly felt. In turn, the relevance of our research extends to the wider scientific community, paving the way for future studies exploring similar themes in other emerging economies.
The current technological infrastructure allows for storing any type and amount of information in the cloud, leading to the exponential growth of digital information [11]. Extracting and analyzing this information from large data sets helps society and industries to predict trends, understand people’s behavior, make better business decisions, and create innovative industrial solutions [12]. On the other hand, educational big data has many applications, such as educational administration, teaching innovation, personnel selection, and research management [13]. Moreover, big data in education, together with artificial intelligence (AI), gamification, facial recognition, voice-based learning, and simulation, maximizes learning effectiveness [14,15]. This new ecosystem of data and educational tools has enabled the exponential growth of online learning, transforming education [16].
Big data analytics or big data has a significant influence on society and industry, and there are challenges related to sustainability, information gathering, and analysis that must be addressed [9]. Population growth and resource depletion force manufacturers to become more competent and sustainable [17]. Advances in manufacturing processes in manufacturing industries are increasing thanks to the use of technology [18]. In addition, it has motivated the generation of research that uses these tools to understand user relationships and experiences [19].
In Latin America, including countries like Mexico, Brazil, Argentina, Chile, and Colombia, there has been an increase in the number of companies dedicated to data analysis. As described by Correa [20], for Latin America to achieve greater industrialization, it required the use of foreign technologies to renew its infrastructure. This dynamic that has driven and maintained the private sector has also been reproduced at the governmental level to improve decision-making, seeking the benefit of citizens. However, it is not enough, which is why there is criticism of the governments of Latin American countries regarding the misuse of public resources and other social problems.
Big data answers questions that many organizations have never even asked themselves, providing a starting point for decision-making and quick problem identification. No matter the companies’ strategic sector today, they handle large amounts of data. However, if they are analyzed and used, a critical opportunity for competitiveness and growth is recovered. The importance lies in determining the root causes of failures; companies also have a better understanding of the market and their competitors.
Proper data management is particularly relevant in countries with a low level of technology, especially in the public sector. According to Toapanta et al. [21], this situation has generated dissatisfaction among citizens in Ecuador due to inefficient and slow services. In addition, it is necessary to implement more information control and supervision mechanisms since, according to current legislation, all information must be protected by the National Public Data System, guaranteeing its veracity and reliability. The study by Pazmiño-Maji et al. [22] presents a systematic review of learning analytics (LA) in Ecuador, identifying common areas of application and challenges for its implementation, such as the lack of technological resources and teacher training.
On the other hand, Pazmiño-Maji et al. [23] focused on analyzing the current state of research on LA in Ecuador through a systematic review of the scientific literature, providing a replicable methodology that can be used by other researchers interested in studying LA in Ecuador. In contrast, the study by Pin Garcia [24] shows that the discipline of process mining is relatively new in Ecuador and that its application has been mainly in the educational field. Despite this, it highlights the potential of process mining to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of processes in several application domains in Ecuador. The articles mentioned above provide valuable information on the use of technologies related to data collection and analysis in the educational and organizational environment in Ecuador. However, none of these studies specifically focus on Data Analysis applications in the country, indicating the need for further exploration of this topic.
This article is structured as follows: we begin with an introduction to Big Data and its relevance in developing countries such as Ecuador. Then, we detail our bibliometric review methodology. We then present and discuss our findings, before concluding with the implications of our research and suggestions for future studies.
2. Methodology
2.1. Objective
This paper aims to analyze the current situation of big data and its applications in Ecuador, as well as its impact on Ecuadorian society, education, and industry.
2.2. Protocol
The field of big data research in Ecuador is recent, so it was determined that there was a need to develop a literature review. The research protocol contains inclusion and exclusion criteria established according to the context of the country of study. In addition, for a better understanding of the protocol, the flow chart proposed in the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses) statement is shown in Figure 1.
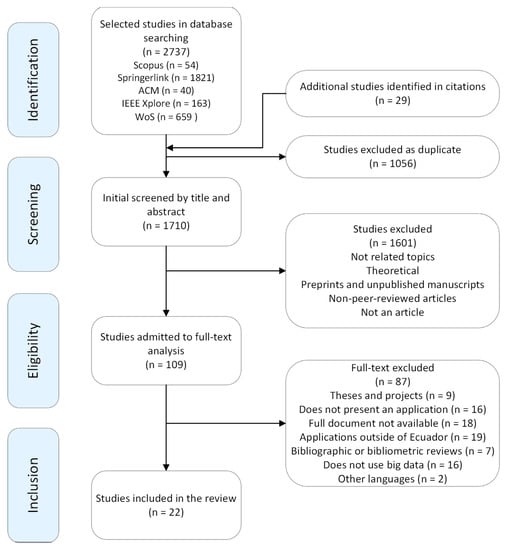
Figure 1.
PRISMA flowchart.
2.3. Search Strategy
The search was conducted in databases containing academic information: SpringerLink, Scopus, IEEE Xplore, Web of Science, and ACM. Keywords related to the subject matter were selected, and their search syntax was adapted according to the characteristics of each platform. In addition, to minimize selection bias, we included the citations of all the selected articles in our study. Finally, Supplementary Material shows the search equations and their combinations, in the Table S1.
2.4. Inclusion Criteria
A comprehensive literature search was carried out in English from inception until 30 May 2023. This search included studies carried out in the Ecuadorian territory or by institutions in the same country. The eligible works had to be original peer-reviewed articles published in books and indexed journals. Also, this review only included research by researchers based in Ecuador who had developed their research within the research fields.
2.5. Exclusion Criteria
All articles that are part of the following groups: (i) theses and project documents, (ii) articles published in non-indexed journals, (iii) research developed in a country other than Ecuador, (iv) documents without peer review, (v) any bibliographic or bibliometric review, and (vi) research that did not involve big data.
2.6. Data Sources and Search Strategies
The authors searched for relevant articles in SpringerLink, Scopus, IEEE Xplore, Web of Science and ACM databases from their inception until May 2023. Search terms included keywords related to big data (“data analysis”, “big data”, “hadoop”, and “data mining”), different areas of knowledge (“sciences”, “engineering”, “services”, “education”, “health”, and “social”), terms related to governance (“society” and “e-government”) and education (“education”, “research”, and “academia”).
2.7. Identification and Selection of Studies
The guidelines established in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement were applied to identify and select the studies. This statement consists of the following stages: identification, selection, eligibility, and inclusion. In the first identification stage, a search was carried out in Scopus, Springerlink, ACM, IEEE Xplore, and WoS, applying Boolean operators, which allowed the identification of 2737 articles. At this stage, the authors (JB and MA-Ch) reviewed the titles and abstracts of the articles found, and those considered most relevant by at least one of the reviewers were identified. If there was no consensus among the authors, the collaboration of a third author (FA-C) was requested to help decide to include or exclude the research in the review. Finally, all identified articles were in a matrix. In the second screening stage, 1056 research studies considered duplicates were excluded from the review, and 29 research studies cited in the articles identified in stage 1 were included, leaving a total of 1710 research studies in stage 2. In the third stage of eligibility, after reading and analyzing the research selected in stage 2, 109 articles were selected. Finally, in the fourth stage, called inclusion, 22 articles were left that met all the review criteria. Figure 1 shows the flow diagram of the review.
3. Results
Some Latin American countries such as Mexico, Colombia, Chile, Argentina, and Brazil have reported an increase in big data initiatives since 2012. This trend in the use of big data is intensified by the adoption and use of social networks, in addition to Google trend information that allows for the analysis of different social issues [4]. However, in Ecuador, the implementation of data analytics is a relatively new topic.
The review was conducted in five databases hosting numerous high-quality journals and publications from inception until May 2023. The information found was organized according to the International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED), used by the Secretariat of Higher Education, Science, Technology and Innovation (SENESCYT) and developed by UNESCO. This way, the research falls into six areas: education, science, engineering, health, and social services. A detailed description of the articles is given in Table 1.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the studies included in this review.
The analysis of Table 1 and Figure 2 collectively provides insightful information about the impact of various areas of knowledge on big data applications. Notably, the results suggest that the fields of engineering and science exert the greatest influence in this domain. This significant impact is discernible even when considering data from Ecuador, a country that exhibits a relatively lower number of publications compared to fields such as education and social sciences. Conversely, the fields of services, as well as health and social services, show only a limited interest and impact in the context of big data applications. These findings could serve as valuable insights for future research endeavors and inform public policy in Ecuador, potentially fostering exploration and development of big data applications in sectors that promise a greater impact.
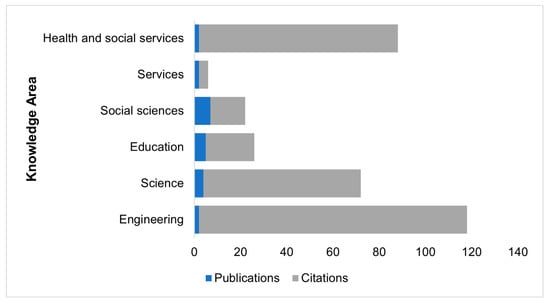
Figure 2.
Publications vs. citations.
3.1. Sciences
Ecuador is situated in the “Ring of Fire” [47], an area with high seismic activity, making it vulnerable to earthquakes [48]. The use of big data can aid in developing preventive measures and public policies to mitigate the impact of such disasters. Researchers have found a relationship between human mobility patterns and the effects of earthquakes [38], indicating that people move towards less affected areas. March, April, and May are the months most prone to earthquakes, providing essential information for risk management [37]. Big data analysis can also aid in agriculture, predicting variables such as soil moisture, relative humidity, temperature, and luminosity, allowing companies to make informed decisions [36]. The OpenStreetMap project analyzes data from Quito [39], identifying errors and proposing corrective measures. The pilot study demonstrates the usefulness of automated methods in optimizing resources.
3.2. Engineering
The versatility of the Internet of Things (IoT) allows it to be adapted to various fields of knowledge, including the implementation of sensor and actuator networks in homes, campuses, and cities to create smart environments. In a study conducted on a traditional university campus in Quito, a smart city design using the IoT and big data was applied to obtain data on mobility, student concentration, and vending machine purchases [41]. The data collected were used to plan schedules, avoid crowds, and improve processes. In ref. [40], a projection was made for the electricity consumption in the distribution system of Empresa Eléctrica Ambato Regional Centro Norte S.A. (EEASA), which covers three provinces of Ecuador, to improve the resilience of the electrical system. With the help of new technologies and automated projection processes, preventive actions can be taken to ensure the reliable and efficient supply of essential services such as drinking water, electricity, telephony, and the Internet in smart cities [49].
3.3. Social
Ecuador’s public sector faces challenges due to outdated systems for information management, leading to inefficiency, distrust in processes, and security problems such as information theft [50]. Blockchain technology and cryptography are proposed as solutions to improve computer security by minimizing security problems and protecting users [30]. The use of these technologies can also increase citizens’ confidence by providing double verification with their digital signature when accessing information.
Social network data analysis is used to assess the quality, consistency, and integrity of presidential election data in Ecuador. Apache Flum tool was used in 2017 to process data from the Twitter social network [31], while the 2021 election generated a lot of social network interaction data [27]. The analysis of tweets using numerical weights showed that there were more positive tweets towards the candidate Lasso in the province of Pichincha and more negative ones towards the candidate Arauz [26]. However, there were also fraudulent Twitter accounts that spread harmful content against the opposing candidate, known as “trolls.” These practices can be dissuaded with the use of technological systems.
Big data can be applied in various sectors, including commercial transactions in the private sector, residential electricity consumption, and socioeconomic levels of neighborhoods [51]. Despite its potential, around 90% of the data held by credit card providers is not used in data analytics applications to improve processes [52]. Even at the residential level, data analysis can provide insights that influence decision-making, such as the increasing use of low-consumption light bulbs [29] and the determination of socioeconomic levels using information from airtime recharges of cell phones [28]. In [25], a computational algorithm was developed in RStudio, and in conjunction with ArcGIS software for geographic information, spatial segregation patterns were identified in Ambato, Ecuador. The use of big data can create new communication and transaction networks, attracting new customers and entering new markets, and contribute to decision-making in various sectors.
3.4. Services
In Ecuador, there has been an increase in the adoption of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) at the residential level, with smartphones and voice assistants becoming commonplace. This has led to the generation and storage of significant amounts of data which could be integrated at the municipal level to boost the smart city concept. Latin American cities such as Santiago and Buenos Aires have already efficiently managed transportation, power grids, energy consumption, healthcare, construction, and green environments through the use of IoT technology. While communication networks are often physical, there is also a proliferation of wireless networks such as Wi-Fi, GSM, and Bluetooth.
However, in cities such as Quito, vehicular traffic congestion remains a significant issue. To address this problem, intelligent resource management could help generate smart cities [33]. Data generated by social networks and acquired by sensors can be used to identify vehicular traffic zones using historical records. With proper management proposals, these smart city initiatives could help alleviate problems caused by migration, population growth, and the automotive industry, ultimately improving the quality of life for residents [32].
3.5. Health
In Ecuador, technology can be used in health institutions to increase human well-being by using data analysis to determine behavior patterns and factors that could increase a person’s state of health. Cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cerebrovascular and hypertensive diseases are prevalent among the Ecuadorian population, and not many studies related to big data applied to health have been presented. However, a study carried out by [34] identified people at risk of developing cardiovascular disease using 13 computational algorithms and found that age, weight, drug use, constant headache, chest pain, swollen feet, elevated systolic and diastolic blood pressure, fatigue, and acute exhaustion were the most significant variables. The random forest model showed the best precision in predicting high-incidence diseases in the country by analyzing the patient’s historical information.
On the other hand, Yacchirema et al. [35] presented an innovative proposal for monitoring and treating obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in the elderly using IoT and big data technologies. The proposed system collects data from various sources, such as environmental sensors, heart rate monitors, and air pollution data from smart cities. These data are processed using a fog computing approach and analyzed using big data tools in the cloud.
These advancements in healthcare demonstrate the transformative power of big data in Ecuador. By leveraging data-driven insights, healthcare professionals can make more informed decisions, devise personalized treatment plans, and implement targeted interventions. This holds the potential to improve the overall health outcomes for individuals and contributes to the development and progression of the big data ecosystem in Ecuador. Integrating IoT and big data technologies offers a promising avenue for optimizing healthcare services, facilitating real-time monitoring, and enhancing the interoperability of heterogeneous devices. As these innovative solutions gain traction, Ecuador is poised to witness the growth and integration of big data in healthcare, paving the way for improved healthcare delivery, enhanced patient experiences, and, ultimately, a healthier population.
3.6. Education
Big data tools are being utilized in education to analyze student performance, evaluate curricula, and identify areas for improvement [53]. The Universidad Técnica Particular de Loja (UTPL) has implemented an educational system that uses Hadoop to organize and collect data on student behavior, allowing for predictions and informed decisions [46]. Studies have shown that analyzing student demographics, knowledge assessments, and performance can provide relevant information on existing patterns. For example, a study on Israel Technological University analyzed student grades from 2012 to 2018, revealing that the nineth semester had the highest approval rate, while the second and third levels had the highest losses [45]. Another study used machine learning algorithms to determine the variables that influenced mathematics performance in high school students in Ambato-Ecuador, with the random forest model generating the best prediction results [42].
However, it has also been noted that some universities lack comprehensive training in data-related subjects. A study analyzed the contents of data journalism subjects in social communication and journalism careers from six universities in Spain, Colombia, and Ecuador, revealing the need for curricular changes [44]. Therefore, using big data to identify students’ needs is essential and can be influenced by sociodemographic factors. For instance, a model proposed in a study revealed that online students in a university in Ecuador had an average grade of 6/10 due to working full-time, while face-to-face students had an average age of 20 and only 1% worked [43].
4. Discussion
As previously mentioned, research related to big data has recent precedents in Ecuador, with a notable increase primarily from 2019. Publications are grouped by research areas and their trends compared over time, making it possible to identify some dominant fields, including computer technology, international economics, computer sciences, and policy sciences. Data collected in the Ecuadorian Repository of Researchers (REDI in Spanish) suggest that, between 2016 and 2018, only 0.72% of investigations were related to data analysis and big data [54]. Simultaneously, there is evidence that contributions related to robotics, wireless, big data, computer networks, and digital television have decreased. This indicates that, despite some research evidence, the studies related to data analysis and big data conducted within the country remain insufficient. Only a handful of researchers are involved in and generate projects that aim to implement big data techniques. This situation, however, opens up opportunities to fill the knowledge gap that currently exists in Ecuador.
Social networks, like Twitter, have become invaluable resources for understanding human behavior and trends, especially in the realm of data analysis and big data. these platforms present a challenge, however, in terms of data quality evaluation. Ensuring that information adheres to quality guidelines is paramount for interpretation and reliability [31], which in turn supports decision-making within various sectors. Interestingly, the evolution of data analysis and big data tools has led to options that forego the need for cloud storage, such as Google Suite [26].
Twitter, in particular, provides a wealth of data. These data have been leveraged in research exploring interactions during electoral processes in Ecuador. For instance, the previous two elections saw high levels of engagement, with comments both in support of and against the presidential candidates. By using data analysis and big data techniques, it is possible to identify voting trends, influential proposals, and those proposals that fail to gain traction among citizens. It also enables the identification of accounts or users predominantly disseminating harmful political content intended to discredit opposing candidates [26,27]. Such damaging practices have regrettably become an integral part of the electoral process and everyday political life. Despite this, there are ongoing efforts to use data analysis and big data techniques to measure the impact of such harmful content. This information is also being used to trace the originators of such content and propose limitations for the creation of new accounts with the sole intent of discrediting others.
The public sector also employs data analysis techniques, managing and integrating millions of citizens’ records. This incorporation necessitates the implementation of infrastructure and protocols to guarantee the security, accuracy, correctness, and accessibility of the information. Initiatives such as [21] bring transparency to the operations conducted by both public and private entities. As a result, databases must adapt to the unique requirements of the projects, often requiring the augmentation of relational databases with non-relational ones. The use of open-source platforms, like Linux [54], has been found optimal to ensure the integrity and availability of the data. These processes not only guarantee data immutability but also enable the tracing of information theft attempts.
In the business sector, according to [55], 40% of Ecuadorian companies are already utilizing big data tools. Out of these, 65% use it to gather market information, 82% to generate new knowledge about their company, and 53% to analyze information swiftly. The mindset of entrepreneurs is shifting as they see big data as an opportunity to comprehend data from various sources in real-time and to innovate. Within the hotel industry, these techniques enable efficient management of company accounting based on supply and demand fluctuations throughout the year. According to [46], around 19% of a sample of three- and four-star hotels in Ecuador and Cuba are utilizing big data to streamline their operations. This strategy allows businesses to anticipate current reservations, thereby offering superior organization to their clients.
The information gathered through data analysis and big data techniques can guide specialized marketing campaigns for specific sectors. Furthermore, daily data generated from customers can be utilized to predict and cater to their future needs [56]. These techniques also provide an opportunity to identify and anticipate auxiliary services customers may require, like extended stays or gym renovations (infrastructure management). Regular interactions and inquiries from customers generate valuable data, leading to informed decision-making. Predictive insights drawn from this data can not only enhance the conditions of a particular establishment but can also contribute to a management model with positive implications for the entire country.
Transportation planning and management is another sector deriving benefits from data analysis. This component is vital in urban planning, potentially improving living conditions in large cities. Data from social networks can serve as references to understand the congestion issues in major Ecuadorian cities. Georeferenced data, supplied by smartphones, can be analyzed to create heat maps that emphasize the city’s busiest areas. This information could guide public administration, encouraging the formulation and implementation of short- and long-term policies. Other cities serve as tangible examples of how these tools can alleviate congestion problems. The study by [33] demonstrates how Twitter data, a real-time source, can enhance local management.
Likewise, data from citizens’ homes can be gathered to understand their consumption habits and waste management practices. As daily practices are continuously evolving, there is an ongoing need to create and update waste management policies. One clear instance of this is the recent trend towards energy-efficient light bulbs. While their increasing popularity positively impacts national electricity consumption reduction, it may also potentially have adverse environmental effects. Here, big data can be used to highlight different variables that signify the socioeconomic status of residents. As indicated in [28], the quantity of cell phone airtime purchased can be a reflection of residents’ living standards. The study has found that areas with higher income levels see more significant investments, while the opposite is true for areas with lower incomes. This disparity across cities underscores that spatial segregation is far from being eradicated. Data analysis provides objective information about resource access and the sectors that need them the most. Such information could be harnessed to influence local government changes and initiate substantial transformations in Ecuadorian society [25].
In the healthcare sector, data analysis can contribute to adjustments in care protocols and the existing hierarchy, based on patient needs and predispositions to specific illnesses. Analysis of various risk factors can suggest potential impacts on other conditions, such as cancer, thereby facilitating the development of local and regional predictive models. This differentiation is equally applicable to hospitalized patients and those dealing with acute and degenerative diseases. Demographic and geographic factors that impact different age groups can be customized based on needs and the resources available, as illustrated in [34]. Studying populations in smaller cohorts can simplify the implementation of policies and modifications in the Ministry of Public Health’s planning. Data related to mental health, stress, depression, and anxiety can also be integrated into a comprehensive personal analysis. This encompasses other factors such as the emergence of new viruses, pollution, environmental changes due to global warming, and other elements that society will incorporate as it progresses.
The competition for student admissions in the education sector, especially in private universities, is currently very intense. Data analysis can provide information that assists in establishing strategies to attract new students. These strategies can include creating new academic programs or expanding to other cities, all in alignment with the social and economic characteristics of the local environment and professional needs, as identified through Data analysis. Curricula that may be outdated and less appealing to applicants can be refreshed. This issue is explored in [44], where shortcomings in journalism and social communication curricula were identified, triggering updates. To enhance the effectiveness of such measures, data from other successful universities could be studied, and experiences could be shared.
Furthermore, considering sociodemographic factors can aid in the development of distance learning programs for individuals who cannot attend in-person due to personal or professional commitments. The trend towards distance or online education has seen a significant rise in the region since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, as observed by [57]. Villegas-Ch et al. found that the current activities within their case study’s online format were insufficient for proper learning [43]. The notion of self-directed learning deserves deeper exploration, as it is not a linear process; it encompasses a variety of techniques that depend on both the individual and the context. Hillier et al. [58] discuss ultra-learning, a method that allows students to choose the content they need to learn and understand its relevance. In this setting, the adoption of technology is essential, as is the regulation of its use to avoid resource misuse.
Computational algorithms enable the selection of data that can be used for pattern detection, as illustrated by the study [43]. Factors such as age, working conditions, and even the mode of study underscore the need to establish differentiated norms that adapt to the conditions of each student. However, it is crucial to understand that learning processes are varied and individual, and outcomes improve when tools and activities that align with this methodology are encouraged. In this light, with the appropriately utilized information, new educational models can be proposed. These models could focus on competency-based learning and project-based learning. Furthermore, consideration should be given to those academic programs and levels that pose significant difficulties for students, as well as those that do not [45]. Since some institutions, particularly those at the primary and secondary education levels, lack sophisticated computer systems, the implementation of simple algorithms is suggested [42]. This strategy could reduce computational costs and facilitate replication in other high-performing institutions.
Apart from employing learning analytics to extract information about student learning, big data can potentially inform educational policymaking and implementation. Internet users, particularly those who are active on social media or run blogs, often express their opinions and sentiments online. These online comments and messages serve as new sources of public opinion, proving invaluable for policymakers in their quest to understand public issues and needs, develop policies to address them, evaluate policy effectiveness, and even engage the public in generating ideas and solutions [59]. Online public opinion data sources often provide rich detail about human behavior and contextual factors, including textual information (e.g., a text message about a particular policy), temporal information (e.g., the time the message was posted), and structural information (e.g., who communicated with whom about the policy).
In Ecuador, substantial changes have occurred since the implementation of the most recent constitution. The nation is declared a country with free access to information, mandating public accessibility, and ICT plays a vital role in ensuring this regulation is upheld. From a social perspective, identifying citizens’ needs necessitates the analysis of high volumes of data. This, however, signifies extensive analysis of confidential data and a risk of information leakage; therefore, an enhancement in security measures in data processing and a guarantee of confidentiality are essential. In this regard, the importance of computer security becomes apparent, a research topic closely associated with big data. This emphasizes the need to upgrade public information storage and control systems and to reduce social inequalities.
A growing social demand to stay informed exists, guaranteeing better education and cultural, political, and economic development. One of the challenges of ICT in the educational field is to establish a proper connection with the social and productive field. Data analysis will facilitate our understanding of the professionals in demand today, the skills that need to be incorporated, and the anticipated results.
All this will facilitate the implementation of more efficient governance models that improve the quality of life for citizens. As mentioned in [60], Ecuador is beginning to change its models, and government support is essential to meet these objectives. When evaluating the trend for the development of opportunities using ICT, according to the Global Information Technology Report, Ecuador ranks number 82 worldwide. Since the migration of information to digital environments began, it is evident that the interoperability of public and private institutions is a necessity in today’s world. Most of the applications included in this review show significant heterogeneity and a need for compliance with macro-objectives. Although there are proposals in various fields of knowledge, there is a need for a centralized alignment with the current policies.
Technology advances rapidly, and the evolution of applications needs to keep pace; the governments of today and tomorrow face the challenge of continuing to promote information analysis for decision-making and the development of ICT. Simultaneously, they must manage the resources and conditions so that academia and industry continue generating valuable proposals that contribute to the comprehensive development of the country.
Limited access to documents conditioned this review; in general, conference papers are not freely accessible, so access was possible to only part of the information. In some cases, direct requests were made for research, but not all received a favorable response. On the other hand, some authors omitted the place where they conducted the study; therefore, in these cases, affiliations were taken as a selection parameter; however, in some instances, the information required a more comprehensive view and, therefore, was excluded. Another limitation is the limited research carried out in the country; therefore, performing a comprehensive analysis was impossible. Most of the documents are congress articles with low impact in the scientific field; for this reason, developing a more robust review (meta-analysis, for example) was impossible. The search also identified research with descriptive studies that explained and proposed applications in their abstracts, but upon complete review of the document, there was no concordance and integrity between the summary and the development of the document.
The low confidence of users in the proper treatment of data indicates the need to implement more big data projects in the country with high computer security protocols. In this sense, it is proposed as future work to implement big data analysis in public and private institutions to develop algorithms that facilitate the analysis of the information generated by the institutions; this will help decision-makers to choose the best option for each particular case technically, what is known as data-based decisions. Additionally, to promote the development of in Ecuador, it is advisable to include complete information on the place of application, codes, and research data to facilitate replicability.
5. Conclusions
This review highlights the state of research related to big data and data analysis in Ecuador, identifying the distinct areas where these methodologies have been employed and the potential they hold to enhance the country’s development. Although there is evidence of research related to big data, the study carried out in the country is still insufficient. Few researchers are involved in generating projects with lines of research that aim to implement big data techniques. However, the mindset of entrepreneurs is changing, and they see data analysis as an opportunity to understand data from various sources in real time and to innovate.
Big data analysis offers valuable information, contributing to the formulation of strategies in several sectors, such as education, health, transportation, and tourism, among others. By analyzing the data, it is possible to identify the needs of citizens, generate new knowledge, and make better decisions. However, it is essential to increase security measures in data processing and guarantee confidentiality to avoid the risk of information leakage. The interoperability of public and private institutions is also a need in today’s world.
There are still challenges to overcome, such as weak research carried out in the country, limited access to documents, and the low confidence of users in the proper treatment of data. In this sense, it is proposed for more big data projects in public and private institutions to be implemented and to promote the development of big data in Ecuador. Future work should focus on implementing big data analysis in different sectors and generating algorithms that facilitate decision-making based on data. The ethical and social implications of using big data in Ecuador should also be assessed.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://github.com/faviles7/BigData_Ecuador.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.-C., J.B. and F.A.-C.; methodology, M.A.-C. and J.B.; software, M.A.-C., J.B. and F.A.-C.; validation, M.A.-C. and J.B.; formal analysis, M.A.-C., J.B. and F.A.-C.; investigation, M.A.-C., J.B. and F.A.-C.; resources, M.A.-C. and F.A.-C.; data curation, J.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A.-C. and J.B.; writing—review and editing, J.B. and F.A.-C.; visualization, M.A.-C.; supervision, M.A.-C., J.B. and F.A.-C.; project administration, M.A.-C. and F.A.-C.; funding acquisition, M.A.-C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The payment of the article processing charge (APC) for this scientific article was supported by the Universidad Indoamérica under project No. 295.244.2022, entitled “Big Data and its Impact on Society, Education, and Industry”.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in Supplementary Material.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledged the support from Universidad Indoamérica.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ogunsola, L. Information and Communication Technologies and the Effects of Globalization: Twenty-First Century “Digital Slavery” for Developing Countries—Myth or Reality? E-JASL 1999–2009 (volumes 1–10). Electron. J. Acad. Spec. Librariansh. 2005, 58, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Bergeaud, A.; Cette, G.; Lecat, R. Productivity Trends in Advanced Countries between 1890 and 2012. Rev. Income Wealth 2016, 62, 420–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, J.; Kolb, J. Secrets of the Big Data Revolution; Applied Data Labs: Chicago, IL, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1490403809. [Google Scholar]
- Hilbert, M. Big Data for Development: A Review of Promises and Challenges. Dev. Policy Rev. 2016, 34, 135–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, E.S.; Lien, L.B.; Timmermans, B.; Belik, I.; Pandey, S. Stability in Turbulent Times? The Effect of Digitalization on the Sustainability of Competitive Advantage. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 128, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Palmero, J.; Colomo-Magaña, E.; Ríos-Ariza, J.M.; Gómez-García, M. Big Data in Education: Perception of Training Advisors on Its Use in the Educational System. Soc. Sci. 2020, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foresti, R.; Rossi, S.; Magnani, M.; Guarino Lo Bianco, C.; Delmonte, N. Smart Society and Artificial Intelligence: Big Data Scheduling and the Global Standard Method Applied to Smart Maintenance. Engineering 2020, 6, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Dong, T.; Luo, X. A Longitudinal Study of the Actual Value of Big Data and Analytics: The Role of Industry Environment. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 60, 102389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Godoy, J.; Otrel-Cass, K.; Toft, K.H. Transformations of Trust in Society: A Systematic Review of How Access to Big Data in Energy Systems Challenges Scandinavian Culture. Energy AI 2021, 5, 100079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Ueti, R.M.; Espinosa, D.F.; Rafferty, L.; Hung, P.C.K. Case Studies of Government Use of Big Data in Latin America: Brazil and Mexico. In Big Data Applications and Use Cases; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 197–214. [Google Scholar]
- Novikov, S.V. Data Science and Big Data Technologies Role in the Digital Economy. TEM J. 2020, 9, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.I.; Shuib, L.; Yadegaridehkordi, E. Big Data in Education: A State of the Art, Limitations, and Future Research Directions. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2020, 17, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seles, B.M.R.P.; de Sousa Jabbour, A.B.L.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; de Camargo Fiorini, P.; Mohd-Yusoff, Y.; Thomé, A.M.T. Business Opportunities and Challenges as the Two Sides of the Climate Change: Corporate Responses and Potential Implications for Big Data Management towards a Low Carbon Society. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 189, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogiannakis, M.; Papadakis, S.; Zourmpakis, A.-I. Gamification in Science Education. A Systematic Review of the Literature. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- August, S.E.; Tsaima, A. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: An Instructor’s Exoskeleton in the Future of Education BT-Innovative Learning Environments in STEM Higher Education: Opportunities, Challenges, and Looking Forward; Ryoo, J., Winkelmann, K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 79–105. ISBN 978-3-030-58948-6. [Google Scholar]
- Zalat, M.M.; Hamed, M.S.; Bolbol, S.A. The Experiences, Challenges, and Acceptance of e-Learning as a Tool for Teaching during the COVID-19 Pandemic among University Medical Staff. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, M.; Haleem, A.; Bahl, S.; Javaid, M.; Suman, R.; Nandan, D. Big Data Applications to Take up Major Challenges across Manufacturing Industries: A Brief Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 49, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-H.; Tsai, C.-C.; Wang, C.-H.; Chen, C.-J.; Lin, C.-M. Optimizing the Energy Efficiency of Chiller Systems in the Semiconductor Industry through Big Data Analytics and an Empirical Study. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 60, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, S.; Sindakis, S.; Aggarwal, S.; Chen, C.; Su, J. Managing Big Data in the Retail Industry of Singapore: Examining the Impact on Customer Satisfaction and Organizational Performance. Eur. Manag. J. 2021, 39, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, C.M. Transfer of Technology in Latin America: A Decade of Control. J. World Trade 1981, 15, 388–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toapanta, S.M.T.; Quimi, F.G.M.; Lambogglia, L.M.R.; Gallegos, L.E.M. Impact on the Information Security Management Due to the Use of Social Networks in a Public Organization in Ecuador. Smart Innov. Syst. Technol. 2020, 165, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazmiño-Maji, R.; Conde, M.; García-Peñalvo, F. Learning Analytics in Ecuador: A Systematic Review Supported by Statistical Implicative Analysis. Univers. Access Inf. Soc. 2021, 20, 495–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazmiño-Maji, R.; Naranjo-Ordoñez, L.; Conde-González, M.; García-Peñalvo, F. Learning Analytics in Ecuador: An Initial Analysis Based in a Mapping Review. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference Proceeding Series; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 304–311. [Google Scholar]
- García, L.J.P. La Minería De Procesos Y Su Aplicación En Ecuador: Una Revisión Sistemática. Rev. Espamciencia 2019, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ayala-Chauvin, M.; Maigua, P.; Medina-Enríquez, A.; Buele, J. Socio-Spatial Segregation Using Computational Algorithms: Case Study in Ambato, Ecuador. In Trends in Artificial Intelligence and Computer Engineering—ICAETT 2022; Botto-Tobar, M., Gómez, O.S., Rosero Miranda, R., Díaz Cadena, A., Luna-Encalada, W., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 619, pp. 64–75. ISBN 9783031259418. [Google Scholar]
- López-Fierro, S. Querying on Google Sheets Designing a Sentiments Analysis Alternative for Rating Tweets Regarding the Ecuadorian 2021 Presidential Campaigns. IX Jorn. Cloud Comput. Big Data Emerg. Top. 2021, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- López-Fierro, S.; Chiriboga-Calderon, C.; Pacheco-Villamar, R. If It Looks, Retweets and Follows like a Troll; Is It a Troll?: Targeting the 2021 Ecuadorian Presidential Elections Trolls. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Big Data, Big Data 2021, Orlando, FL, USA, 15–18 December 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 2503–2509. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, E.; Vaca, C.; Avendano, A. Mining Top-up Transactions and Online Classified Ads to Predict Urban Neighborhoods Socioeconomic Status. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 9–12 December 2019; pp. 4055–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Mosquera, D.; Luján-Mora, S. Framework for Big Data Integration in E-Government. DYNA 2019, 86, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toapanta, S.M.; Mafla Gallegos, L.E.; Ordoñez Baldeon, P.; Trivino Trivino, F.D. Blockchain Analysis Applied to a Process for the National Public Data System for Ecuador. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Information and Computer Technologies, ICICT 2020, San Jose, CA, USA, 9–12 March 2020; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 258–265. [Google Scholar]
- Tenesaca Luna, G.A.; Imba, D.; Mora-Arciniegas, M.-B.B.; Segarra-Faggioni, V.; Ramírez-Coronel, R.L. Use of Apache Flume in the Big Data Environment for Processing and Evaluation of the Data Quality of the Twitter Social Network. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2019, 884, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, N.I.H. Big Data Architecture Proposal for Vehicular Traffic Detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference of Digital Transformation and Innovation Technology (Incodtrin), Quito, Ecuador, 28–30 October 2020; pp. 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, N.H.; Santamaria, H.S.; Macias Macias, M.; Gomez, E. Analysis of the Factors Generating Vehicular Traffic in the City of Quito and Its Relation to the Application of Sensorial and Social Data with Big Data as a Basis for Decision Making. In Proceedings of the 2016 3rd International Conference on eDemocracy and eGovernment, ICEDEG 2016, Sangolqui, Ecuador, 30 March–1 April 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes Reyes, F.A.; Cruz Felipe, M.D.R.; Parraga-Alava, J. Prediction of Diseases in the Elderly in Manabí Through Big Data Technologies. Lect. Notes Netw. Syst. 2022, 511, 600–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacchirema, D.C.; Sarabia-Jacome, D.; Palau, C.E.; Esteve, M. A Smart System for Sleep Monitoring by Integrating IoT with Big Data Analytics. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 35988–36001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Guevara, K.L.; Palacios-Echeverria, J.A.; Maya-Olalla, E.; Dominguez-Limaico, H.M.; Suarez-Zambrano, L.E.; Rosero-Montalvo, P.D.; Peluffo-Ordonez, D.H.; Alvarado-Perez, J.C. GreenFarm-DM: A Tool for Analyzing Vegetable Crops Data from a Greenhouse Using Data Mining Techniques (First Trial). In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 2nd Ecuador Technical Chapters Meeting, ETCM 2017, Salinas, Ecuador, 16–20 October 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 2017, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Estupiñán, J.; Menéndez, J.J.D.; Arias, I.F.B.; Bermúdez, J.M.M.; Lemus, N.M. Neutrosophic K-Means for the Analysis of Earthquake Data in Ecuador. Neutrosophic Sets Syst. 2021, 44, 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, X.; Layedra, F.; Vaca, C.; Cruz, E. RiSC: Quantifying Change after Natural Disasters to Estimate Infrastructure Damage with Mobile Phone Data. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Big Data, Big Data 2018, Seattle, WA, USA, 10–13 December 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 3383–3391. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, R.; Tierra, A.; Luna, M. Assessing the Horizontal Positional Accuracy in Openstreetmap: A Big Data Approach. In Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 931, pp. 513–523. ISBN 9783030161835. [Google Scholar]
- Guaman, A.; Ramirez, J.; Mayorga, B.; Aviles, F.; Gallardo, C. Short-Term Load Forecasting in the Distribution System of the Electric Company of Ambato (EEASA) Based on Big Data Criteria. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Science (INCISCOS), Quito, Ecuador, 20–22 November 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Villegas-Ch, W.; Palacios-Pacheco, X.; Luján-Mora, S. Application of a Smart City Model to a Traditional University Campus with a Big Data Architecture: A Sustainable Smart Campus. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Pinos, C.A.; Ayala-Chauvín, I.; Buele, J. Predicting Academic Performance in Mathematics Using Machine Learning Algorithms. In Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 1658, pp. 15–29. [Google Scholar]
- Villegas-Ch, W.; Roman-Cañizares, M.; Jaramillo-Alcázar, A.; Palacios-Pacheco, X. Data Analysis as a Tool for the Application of Adaptive Learning in a University Environment. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejedor, S.; Ventin, A.; Martinez, F.; Tusa, F. Emerging Lines in the Teaching of University Communication the Inclusion of Data Journalism in Universities in Spain, Colombia and Ecuador. In Proceedings of the 2020 15th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI), Sevilla, Spain, 24–29 June 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; Volume 2020, pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Baldeon Egas, P.F.; Gaibor Saltos, M.A.; Toasa, R. Application of Data Mining and Data Visualization in Strategic Management Data at Israel Technological University of Ecuador. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2020, 1066, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urena-Torres, J.-P.; Tenesaca-Luna, G.-A.; Arciniegas, M.B. Analysis and Processing of Academic Data from a Higher Institution with Tools for Big Data. In Proceedings of the 2017 12th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI), Lisbon, Portugal, 14–17 June 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Rivadeneira, F.; Segovia, M.; Alvarado, A.; Egred, J.; Troncoso, L.; Vaca, S.; Yepes, H. Breves Fundamentos Sobre Los Terremotos En El Ecuador; Instituto Geofísico de la Escuela Politécnica Nacional, Corporación Editora Nacional: Quito, Ecuador, 2007; ISBN 978-9978-84-460-1. [Google Scholar]
- Banco Interamericano de Desarrollo. Perfil de Riesgo de Desastres Por Evento Sísmico de Ecuador; BID: Madrid, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.; Urquiza, L. Security Enhancement through Effective Encrypted Communication Using ELK. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference Proceeding Series; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, N.; Yaqoob, I.; Hashem, I.A.T.; Inayat, Z.; Mahmoud Ali, W.K.; Alam, M.; Shiraz, M.; Gani, A. Big Data: Survey, Technologies, Opportunities, and Challenges. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 712826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zikoupoulos, P.; Eaton, C. Understanding Big Data: Analytics for Enterprise Class Hadoop and Streaming; McGraw-Hill Osborne Media: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 11, ISBN 9780071790536. [Google Scholar]
- Macfadyen, L.P.; Dawson, S.; Pardo, A.; Gaševic, D. Embracing Big Data in Complex Educational Systems: The Learning Analytics Imperative and the Policy Challenge. Res. Pract. Assess. 2014, 9, 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Segarra, J.; Ortiz, J.; Gualan, R.; Saquicela, V. Discovering Research Trends in the Computer Science Area of Ecuador: An Approach Using Semantic Knowledge Bases. In Proceedings of the 2019 XLV Latin American Computing Conference (CLEI), Panama City, Panama, 30 September–4 October 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, A.; Ramirez, S.; Toasa, R.; Vargas, J.; Urvina-Barrionuevo, R.; Lavin, J.M. Performance Evaluation of NoSQL and SQL Queries in Response Time for the E-Government. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on eDemocracy & eGovernment (ICEDEG), Quito, Ecuador, 4–6 April 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 257–262. [Google Scholar]
- Quelal, R.; Villavicencio, M. A Survey of Big Data Use in Large and Medium Ecuadorian Companies. In Big Data—BigData 2018; Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 10968, pp. 334–342. ISBN 9783319943008. [Google Scholar]
- Toapanta, S.M.T.; Quintana, T.F.P.; Arellano, M.R.M.; Gallegos, L.E.M. Hyperledger Technology in Public Organizations in Ecuador. In Proceedings of the 2020 3rd International Conference on Information and Computer Technologies (ICICT), San Jose, CA, USA, 9–12 March 2020; pp. 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argüelles-Cruz, A.-J.; García-Peñalvo, F.-J.; Ramírez-Montoya, M.-S. Education in Latin America: Toward the Digital Transformation in Universities. In Radical Solutions for Digital Transformation in Latin American Universities; Lecture Notes in Educational Technology; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 93–108. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, D.; Mitchell, A.; Millwood, R. “Change of Heart!”: A New e-Learning Model Geared to Addressing Complex and Sensitive Public Health Issues. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 2005, 42, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schintler, L.A.; Kulkarni, R. Big Data for Policy Analysis: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. Rev. Policy Res. 2014, 31, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, D.E.P. Analysis of Digital Government in Ecuador: Review of Ecuadorian Agenda with Regard to the Digital Government Stage Framework. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on eDemocracy & eGovernment (ICEDEG), Quito, Ecuador, 4–6 April 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).