Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Practical Review of Prospective Trials
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
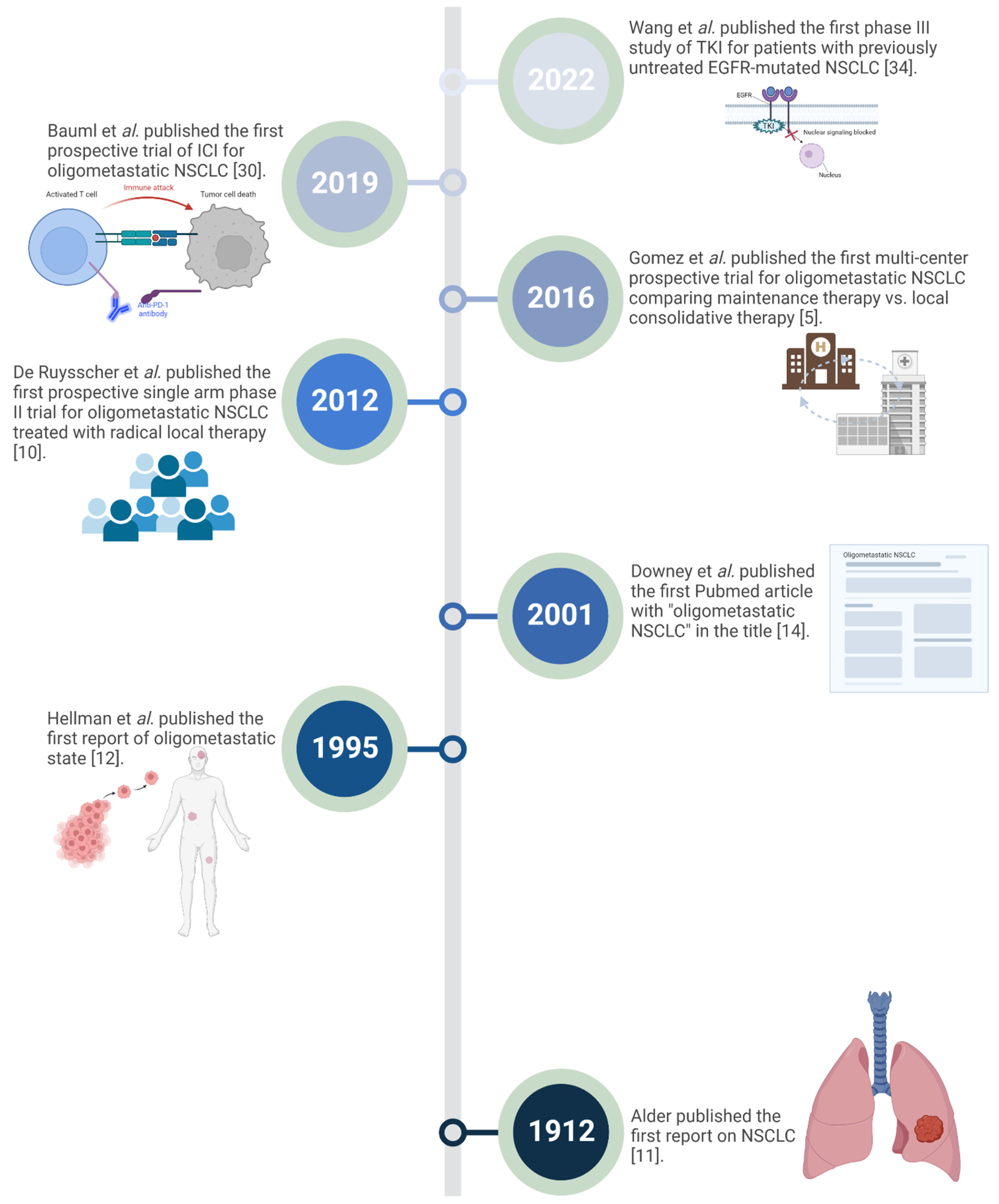
1. Introduction
2. Search Strategy
3. The Current Concept of Oligometastatic NSCLC
4. Prospective Trials for Local Ablative Therapy in Oligometastatic NSCLC
5. Immunotherapy in Oligometastatic NSCLC
6. Oligometastatic EGFR Mutated NSCLC
7. Ongoing Trials
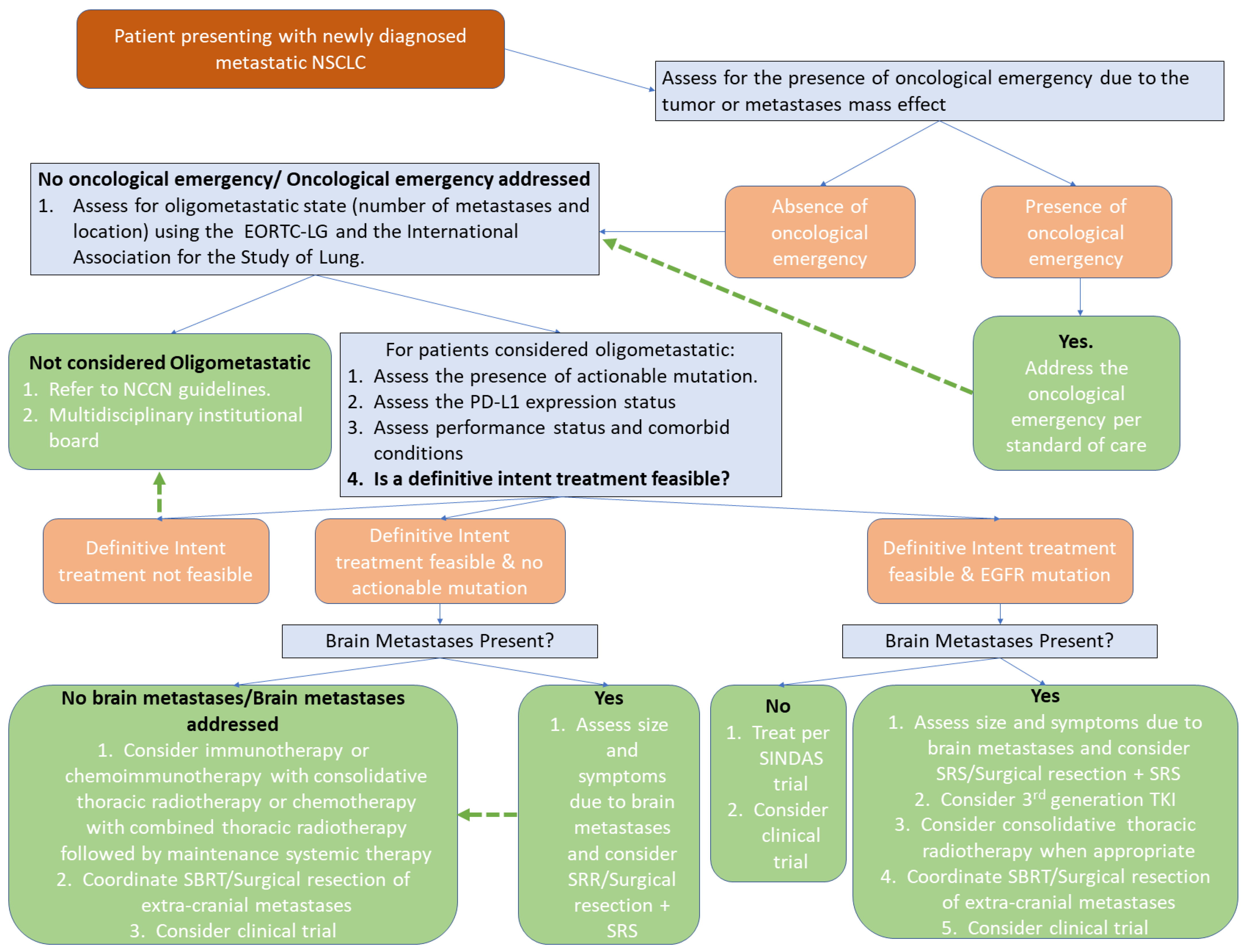
8. Oligometastatic NSCLC: Initial Therapeutic Approach
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Planchard, D.; Popat, S.; Kerr, K.; Novello, S.; Smit, E.F.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Mok, T.S.; Reck, M.; Van Schil, P.E.; Hellmann, M.D.; et al. Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, iv192–iv237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- No, H.J.; Raja, N.; Von Eyben, R.; Das, M.; Roy, M.; Myall, N.; Neal, J.; Wakelee, H.; Chin, A.; Diehn, M.; et al. Characterization of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Oligometastatic Incidence in an Era of Changing Treatment Paradigms. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 114, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mentink, J.F.; Paats, M.S.; Dumoulin, D.W.; Cornelissen, R.; Elbers, J.B.W.; Maat, A.; von der Thusen, J.H.; Dingemans, A.C. Defining oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer: Concept versus biology, a literature review. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 3329–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyengar, P.; Wardak, Z.; Gerber, D.E.; Tumati, V.; Ahn, C.; Hughes, R.S.; Dowell, J.E.; Cheedella, N.; Nedzi, L.; Westover, K.D.; et al. Consolidative Radiotherapy for Limited Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, e173501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, D.R.; Blumenschein, G.R.; Lee, J.J.; Hernandez, M.; Ye, R.; Camidge, D.R.; Doebele, R.C.; Skoulidis, F.; Gaspar, L.E.; Gibbons, D.L.; et al. Local consolidative therapy versus maintenance therapy or observation for patients with oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer without progression after first-line systemic therapy: A multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1672–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bai, Y.F.; Zeng, M. First-Line Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor with or Without Aggressive Upfront Local Radiation Therapy in Patients with EGFRm Oligometastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Interim Results of a Randomized Phase III, Open-Label Clinical Trial (SINDAS) (NCT02893332). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 108, e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remon, J.; Menis, J.; Levy, A.; De Ruysscher, D.K.M.; Hendriks, L.E.L. How to optimize the incorporation of immunotherapy in trials for oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer: A narrative review. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 3486–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schanne, D.H.; Heitmann, J.; Guckenberger, M.; Andratschke, N.H.J. Evolution of treatment strategies for oligometastatic NSCLC patients—A systematic review of the literature. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2019, 80, 101892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congedo, M.T.; Cesario, A.; Lococo, F.; De Waure, C.; Apolone, G.; Meacci, E.; Cavuto, S.; Granone, P. Surgery for oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer: Long-term results from a single center experience. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2012, 144, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruysscher, D.; Wanders, R.; van Baardwijk, A.; Dingemans, A.M.; Reymen, B.; Houben, R.; Bootsma, G.; Pitz, C.; van Eijsden, L.; Geraedts, W.; et al. Radical treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer patients with synchronous oligometastases: Long-term results of a prospective phase II trial (Nct01282450). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, I. Primary Malignant Growths of the Lungs and Bronchi: A Pathological and Clinical Study; Longmans, Green: New York, NY, USA, 1912. [Google Scholar]
- Hellman, S.; Weichselbaum, R.R. Oligometastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treasure, T. Oligometastatic cancer: An entity, a useful concept, or a therapeutic opportunity? J. R. Soc. Med. 2012, 105, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downey, R.J.; Ng, K.K. The management of non-small-cell lung cancer with oligometastases. Chest Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2001, 11, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szturz, P.; Vermorken, J.B. Oligometastatic Cancer: Key Concepts and Research Opportunities for 2021 and Beyond. Cancers 2021, 13, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Yu, J.; Nuerjiang, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Xie, C. Stereotactic body radiotherapy improves the survival of patients with oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 4605–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashworth, A.B.; Senan, S.; Palma, D.A.; Riquet, M.; Ahn, Y.C.; Ricardi, U.; Congedo, M.T.; Gomez, D.R.; Wright, G.M.; Melloni, G.; et al. An individual patient data metaanalysis of outcomes and prognostic factors after treatment of oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2014, 15, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lievens, Y.; Guckenberger, M.; Gomez, D.; Hoyer, M.; Iyengar, P.; Kindts, I.; Mendez Romero, A.; Nevens, D.; Palma, D.; Park, C.; et al. Defining oligometastatic disease from a radiation oncology perspective: An ESTRO-ASTRO consensus document. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 148, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, A.; Hendriks, L.E.; Berghmans, T.; Faivre-Finn, C.; GiajLevra, M.; GiajLevra, N.; Hasan, B.; Pochesci, A.; Girard, N.; Greillier, L.; et al. EORTC Lung Cancer Group survey on the definition of NSCLC synchronous oligometastatic disease. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 122, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingemans, A.C.; Hendriks, L.E.L.; Berghmans, T.; Levy, A.; Hasan, B.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Giaj-Levra, M.; Giaj-Levra, N.; Girard, N.; Greillier, L.; et al. Definition of Synchronous Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer-A Consensus Report. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 2109–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detterbeck, F.C.; Boffa, D.J.; Kim, A.W.; Tanoue, L.T. The eighth edition lung cancer stage classification. Chest 2017, 151, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belluomini, L.; Dodi, A.; Caldart, A.; Kadrija, D.; Sposito, M.; Casali, M.; Sartori, G.; Ferrara, M.G.; Avancini, A.; Bria, E. A narrative review on tumor microenvironment in oligometastatic and oligoprogressive non-small cell lung cancer: A lot remains to be done. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, A.; Verma, V.; Simone, C.B., 2nd; Chetty, I.J.; Chun, S.G.; Donington, J.; Edelman, M.J.; Higgins, K.A.; Kestin, L.L.; Movsas, B.; et al. American Radium Society Appropriate Use Criteria for Radiation Therapy in Oligometastatic or Oligoprogressive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 112, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurie, S.; Banerji, S.; Blais, N.; Brule, S.; Cheema, P.; Cheung, P.; Daaboul, N.; Hao, D.; Hirsh, V.; Juergens, R. Canadian consensus: Oligoprogressive, pseudoprogressive, and oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2019, 26, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collen, C.; Christian, N.; Schallier, D.; Meysman, M.; Duchateau, M.; Storme, G.; De Ridder, M. Phase II study of stereotactic body radiotherapy to primary tumor and metastatic locations in oligometastatic nonsmall-cell lung cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 1954–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petty, W.J.; Urbanic, J.J.; Ahmed, T.; Hughes, R.; Levine, B.; Rusthoven, K.; Papagikos, M.; Ruiz, J.R.; Lally, B.E.; Chan, M.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes of a Phase 2 Trial of Chemotherapy with Consolidative Radiation Therapy for Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, O.; Barron, F.; Maldonado, F.; Cabrera, L.; Corona-Cruz, J.F.; Blake, M.; Ramirez-Tirado, L.A.; Zatarain-Barron, Z.L.; Cardona, A.F.; Garcia, O.; et al. Radical consolidative treatment provides a clinical benefit and long-term survival in patients with synchronous oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer: A phase II study. Lung Cancer 2019, 130, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, D.R.; Tang, C.; Zhang, J.; Blumenschein, G.R., Jr.; Hernandez, M.; Lee, J.J.; Ye, R.; Palma, D.A.; Louie, A.V.; Camidge, D.R. Local consolidative therapy vs. maintenance therapy or observation for patients with oligometastatic non–small-cell lung cancer: Long-term results of a multi-institutional, phase II, randomized study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, D.A.; Olson, R.; Harrow, S.; Gaede, S.; Louie, A.V.; Haasbeek, C.; Mulroy, L.; Lock, M.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Yaremko, B.P. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for the comprehensive treatment of oligometastatic cancers: Long-term results of the SABR-COMET phase II randomized trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauml, J.M.; Mick, R.; Ciunci, C.; Aggarwal, C.; Davis, C.; Evans, T.; Deshpande, C.; Miller, L.; Patel, P.; Alley, E.; et al. Pembrolizumab After Completion of Locally Ablative Therapy for Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase 2 Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theelen, W.; Peulen, H.M.U.; Lalezari, F.; van der Noort, V.; de Vries, J.F.; Aerts, J.; Dumoulin, D.W.; Bahce, I.; Niemeijer, A.N.; de Langen, A.J.; et al. Effect of Pembrolizumab After Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy vs. Pembrolizumab Alone on Tumor Response in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results of the PEMBRO-RT Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Hu, M.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, F.; Zhang, B.; Wang, S.; Wang, K.; et al. Local consolidative therapy for synchronous oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer treated with first-line pembrolizumab: A retrospective observational study. Thorac. Cancer 2022, 13, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Zhou, F.; Liu, H.; Jiang, T.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, C. Consolidative Local Ablative Therapy Improves the Survival of Patients with Synchronous Oligometastatic NSCLC Harboring EGFR Activating Mutation Treated with First-Line EGFR-TKIs. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S.; Bai, Y.F.; Verma, V.; Yu, R.L.; Tian, W.; Ao, R.; Deng, Y.; Xia, J.L.; Zhu, X.Q.; Liu, H.; et al. Randomized Trial of First-Line Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor with or Without Radiotherapy for Synchronous Oligometastatic EGFR-Mutated NSCLC. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrava, U.H. Consolidation Conventional Radiotherapy + Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy at 3 Months after First-Line Chemotherapy in Stage IV Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. 2021. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04758481 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- University of Wisconsin-Madison. AstraZeneca: Phase Ib Study of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) in Oligometastatic Non-Small Lung Cancer (NSCLC) With Dual Immune Checkpoint Inhibition. 2018. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT03275597 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Esslingen, K. Prospective Trial of Induction Immunotherapy in Locally Advanced or Oligometastatic NSCLC Without a Primary Curative Option. 2017. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04926584 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Hospital TMUS. Sintilimab after Stereotactic Ablation Brachytherapy for Refractory Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. 2020. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04486287 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- OMEGA, Local Ablative Therapy in Oligometastatic NSCLC (OMEGA). 2019. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT03827577 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Tata Memorial Hospital. Local Consolidative Radiation Therapy Plus TKI Versus TKI Alone in Driver Mutated OM-NSCLC. 2019. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT05277844 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Sichuan Cancer Hospital and Research Institute; Mianyang Central Hospital; Cancer Hospital of Guizhou Province; The Optimal Intervention Time of Radiotherapy for Oligometastatic Stage IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). 2014. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT02076477 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Wu Jieping Medical Foundation; Shanghai Chest Hospital; Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital, Shanghai, China. The Value of Radiotherapy in the Oligometastatic Non-Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Clinical Benefits from Erlotinib as Second-Line Treatment. 2012. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT01796288 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Tata Memorial Hospital. Standard Maintenance Therapy (SMT) vs. Local Consolidative Radiation Therapy and SMT in OM-NSCLC. 2020. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT05278052 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Shanghai Chest Hospital. Phase II Trial of SBRT Compared with Conventional Radiotherapy for Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. 2016. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT02975609 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- University College, London, Cancer Research UK. Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. 2016. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT02417662 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University. Local Non-Salvage Radiotherapy for Synchronous Oligometastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. 2017. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT03119519 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Yonsei University. The Safety and Efficacy of First-Line Lazertinib and Locally Ablative Radiotherapy in Patients with Synchronous Oligo-Metastatic EGFR-mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. 2021. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT05167851 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Shandong Cancer Hospital and Institute. Chemotherapy Combination with Local Radiotherapy and rhGM-CSF for Oligometastatic Stage IV NSCLC Patients. 2018. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT03489616 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, National Cancer Institute (NCI). Surgery and/or Radiation Therapy or Standard Therapy and/or Clinical Observation in Treating Patients with Previously Treated Stage IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. 2012. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT01725165 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- ETOP IBCSG Partners Foundation, AstraZeneca. AstraZeneca: Immunotherapy, Chemotherapy, Radiotherapy and Surgery for Synchronous Oligo-Metastatic NSCLC. 2019. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT03965468 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Institut Claudius Regaud. A Trial Evaluating Stereotactic Radiotherapy Plus Durvalumab Continuation for Patients with NSCLC Metachronous Oligometastatic Disease Under Durvalumab Consolidation Following Chemoradiation. 2021. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT03955198 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Chia Tai Tianqing Pharmaceutical Group Co. L. A Study of TQB2450 Injection Combined with Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) in Subjects with Advanced Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. 2020. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04306926 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- ETOP IBCSG Partners Foundation, AstraZeneca. AstraZeneca: Osimertinib and Locally Ablative Radiotherapy in Patients with Synchronous Oligo-Metastatic EGFR Mutant NSCLC (STEREO). 2021. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04908956 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Zhejiang Cancer Hospital. Durvalumab Combined with Chemotherapy and Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) in Patients with Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). 2020. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04255836 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Instituto Nacional de Cancerologia de Mexico: Radical Treatment of Synchronous Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma. 2015. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT02805530 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Lawson Health Research Institute, Academic Medical Organization of Southwestern Ontario. Chest Lymph Node Sampling in Patients with Advanced Lung Cancer to be Treated with Curative-Intent Radiation Treatment. 2021. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04852588 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Roswell Park Cancer Institute. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy After Surgery in Treating Patients with Stage III-IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. 2013. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT01781741 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Tang-Du Hospital. Toripalimab in Combination with Platinum-Based Chemotherapy for Mutation-Negative Stage IV Oligometastatic NSCLC. 2021. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT05055583 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Shandong Cancer Hospital and Institute, Jiangsu HengRui Medicine Co., Ltd. A Trial of SHR-1210 (an Anti-PD-1 Inhibitor) in Combination with Hypofraction Radiotherapy in Patients With NSCLC. 2018. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT03557411 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- NRG Oncology, National Cancer Institute. Maintenance Chemotherapy with or without Local Consolidative Therapy in Treating Patients With Stage IV Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT03137771 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Maastricht Radiation Oncology. Concurrent and Non-Concurrent Chemo-Radiotherapy or Radiotherapy Alone for Patients with Oligo-Metastatic Stage IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). 2006. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT01282450 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Universitaire Ziekenhuizen KU Leuven. LAT for Oligoprogressive NSCLC Treated with First-Line OSImertinib. 2021. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04216121 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Sun Yat-sen University. A Study of Furmonertinib Combined with Radiotherapy for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with Oligoprogression. 2021. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04970693 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- M.D. Anderson Cancer Center. Local Consolidative Therapy and Durvalumab for Oligoprogressive and Polyprogressive Stage III NSCLC After Chemoradiation and Anti-PD-L1 Therapy. 2021. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04892953 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Oncology Institute of Southern Switzerland; Ente Ospedaliero Cantonale, Bellinzona; Istituto Cantonale di Patologia; Clinical Trial Unit Ente Ospedaliero Cantonale. Atezolizumab Plus 8 Gy Single-Fraction Radiotherapy for Advanced Oligoprogressive NSCLC. 2020. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04549428 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Montréal ChdlUd. Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Oligo-Progressive Non Small Cell Lung Cancer. 2021. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04405401 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Center MSKC. Randomized Study of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) in Patients with Oligoprogressive Metastatic Cancers of the Breast and Lung. 2019. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT03808662 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Institute of Cancer Research UK. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for the Treatment of OPD. 2017. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT03256981 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Counago, F.; Luna, J.; Guerrero, L.L.; Vaquero, B.; Guillen-Sacoto, M.C.; Gonzalez-Merino, T.; Taboada, B.; Diaz, V.; Rubio-Viqueira, B.; Diaz-Gavela, A.A.; et al. Management of oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients: Current controversies and future directions. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 10, 318–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, J.C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, D.-W.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Pérol, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus Crizotinib in Untreated ALK-Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmer, J.R.; Govindan, R.; Anders, R.A.; Antonia, S.J.; Sagorsky, S.; Davies, M.J.; Dubinett, S.M.; Ferris, A.; Gandhi, L.; Garon, E.B.; et al. The Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer consensus statement on immunotherapy for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Society—Year of Publication | Number of Metastatic Sites (Agreement) | Number of Organs Involved (Agreement) | Mediastinal Lymph Node Inclusion (Agreement) | Pulmonary Metastases Status (Agreement) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EORTC-LCG * 2019 | 1 (12%) | 1 (24%) | Yes (72%) | Yes (87%) |
| ≤3 (42%) | 2 (31%) | No (22%) | No (10%) | |
| >5 (17%) | 3 (25%) | N/A (6%) | N/A (3%) | |
| EORTC-LG and the International Association for the Study of Lung cancer 2019 | ≤5 | ≤3 | Not included in Metastatic Sites Count | Included in Metastatic Sites Count |
| Study Title and Number | Treated Condition | Oligometastatic Definition | Study Design | Treatment Scheme | SBRT/SRS | Surgical Excision | Number of Participants | Primary Outcome | Start Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toripalimab in Combination With Platinum-based Chemotherapy for Mutation-negative Stage IV Oligometastatic NSCLC NCT05055583 | Mutation-negative histologically or cytologically confirmed oligometastatic NSCLC | 1–3 and only 1 other organ excluding the primary organ involved | Single-arm prospective phase II study | Toripalimbab in combination with neoadjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy followed by surgery | N | Y | 30 | PFS | August 2021 |
| OMEGA, Local Ablative Therapy in Oligometastatic NSCLC (OMEGA) NCT03827577 | Synchronous or metachronous pathologically confirmed oligometastatic NSCLC | 1–3 | Two-arm prospective phase III study | Standard medical treatment * | SBRT/SRS * (N/A) | Y | 195 | OS | October 2019 |
| Surgery and/or local therapy radiation | |||||||||
| Prospective Trial of Induction Immunotherapy in Locally Advanced or Oligometastatic NSCLC Without a Primary Curative Option (KOMPASSneo) NCT04926584 | Histologically or cytologically confirmed locally advanced or oligometastatic NSCLC that cannot undergo initial curative treatment due to large tumor size or functional reasons | Not provided | Prospective observational study | Induction immuno-chemotherapy or immunotherapy * prior to resection or definitive chemoradiotherapy * | N | N | 50 | Completion of definitive therapy | December 2017 |
| A Trial of SHR-1210 (an Anti-PD-1 Inhibitor) in Combination With Hypofraction Radiotherapy in Patients With NSCLC NCT03557411 | Previously treated oligometastatic NSCLC | 1–5 | Single-arm prospective phase II study | SHR-1210 in combination with hypofractionated radiotherapy | N | N | 42 | Clinically significant toxicity | July 2018 |
| PFS | |||||||||
| Immunotherapy, Chemotherapy, Radiotherapy and Surgery for Synchronous Oligo-metastatic NSCLC (CHESS) NCT03965468 | Histologically confirmed synchronous oligometastatic NSCLC | 1–3 At least 1 must be extra-cerebral | Single-arm prospective phase II study | Induction with Durvalumab, platinum-based including Carboplatin and Paclitaxel, and SBRT followed by definitive local therapy * and continuation of Durvalumab until disease relapses or up to 1 year | SBRT/SRS (max. 10 F over 2 weeks) | Y * | 47 | PFS | November 2019 |
| Local Consolidative Radiation Therapy Plus TKI Versus TKI Alone in Driver Mutated OM-NSCLC (TARGET-01) NCT05277844 | Pathologically confirmed driver mutated oligometastatic NSCLC | 1–5 and excluding the primary tumor and regional nodes 1–3 in 1 organ | Two-arm prospective phase II study | Continuation of TKI therapy only | SBRT/SRS * (N/A) | N | 106 | PFS | November 2019 |
| Continuation of TKI therapy in combination with local consolidative radiation therapy | |||||||||
| The Optimal Intervention Time of Radiotherapy for Oligometastatic Stage IV Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) (OITROLC) NCT02076477 | Pathologically or cytologically confirmed oligometastatic NSCLC | 1–5 | Two-arm prospective phase III study | Initial concurrent chemoradiotherapy followed by chemotherapy (Docetaxel, Pemetrexed, or Cisplatin) | N | N | 420 | Short-term effects RR | January 2014 |
| Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy | |||||||||
| The Value of Radiotherapy in the Oligometastatic Non-squamous Non-small Cell Lung Cancer With Clinical Benefits From Erlotinib as Second-line Treatment (ROLE) NCT01796288 | Histologically or cytologically confirmed non-squamous oligometastatic NSCLC and received second-line erlotinib treatment | 1–5 1–4 in 1 organ | Two-arm prospective phase II study | Erlotinib only | N | N | 200 | PFS | October 2012 |
| Erlotinib simultaneously with radiotherapy | |||||||||
| A Trial Evaluating Stereotactic Radiotherapy Plus Durvalumab Continuation for Patients With NSCLC Metachronous Oligometastatic Disease Under Durvalumab Consolidation Following Chemoradiation (SILK BM) NCT03955198 | Metachronous oligometastatic NSCLC patients under durvalumab consolidation following chemoradiotherapy for previous stage III NSCLC | 1–5 in 1–3 organs and less than 4 cm | Single-arm prospective phase II study | SBRT/SRS in combination with Durvalumab | SBRT/SRS (N/A) | N | 50 | PFS | May 2021 |
| Standard Maintenance Therapy (SMT) vs. Local Consolidative Radiation Therapy and SMT in OM-NSCLC (TARGET-02) NCT05278052 | Pathologically confirmed and previously treated oligometastatic NSCLC | 1–5 and excluding the primary tumor and regional nodes 1–3 in 1 organ | Two-arm prospective phase III study | Standard medical treatment | N | N | 190 | OS | April 2020 |
| Local consolidative radiation therapy and standard medical treatment | |||||||||
| A Study of TQB2450 Injection Combined With Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) in Subjects With Advanced Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer NCT04306926 | Histologically or pathologically confirmed advanced oligometastatic NSCLC intolerable to first-line chemotherapy | 1–5 | Single-arm prospective phase II study | SBRT followed by TQB2450 | SBRT* | N | 59 | PFS | March 2020 |
| Phase II Trial of SBRT Compared With Conventional Radiotherapy for Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer NCT02975609 | Histologically confirmed, received chemotherapy with response, oligometastatic NSCLC | 1–5 less than 5 cm | Two-arm prospective phase II study | Platinum-based chemotherapy followed by conventional fractionated radiotherapy | SBRT (30 Gy/3–5 F) | N | 100 | PFS | November 2016 |
| Platinum-based chemotherapy followed by SBRT | |||||||||
| Osimertinib and Locally Ablative Radiotherapy in Patients With Synchronous Oligo-metastatic EGFR Mutant NSCLC (STEREO) (STEREO) NCT04908956 | Histologically confirmed EGFR-mutant synchronous oligometastatic NSCLC | 1–5 excluding primary tumor | Single-arm prospective phase II study | Osimertinib in combination with SBRT/SRS | SBRT/SRS (max. 5 F) | N | 60 | Safety of Osimertinib and SBRT | December 2021 |
| Concurrent and Non-concurrent Chemo-radiotherapy or Radiotherapy Alone for Patients With Oligo-metastatic Stage IV Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) NCT01282450 | Histologically or cytologically confirmed oligometastatic NSCLC | 1–4 | Single-arm prospective phase II study | Radical radiotherapy | N | Y * | 60 | OS | May 2006 |
| Phase Ib Study of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) in Oligometastatic Non-small Lung Cancer (NSCLC) With Dual Immune Checkpoint Inhibition NCT03275597 | Histologically or cytologically confirmed and previously received chemotherapy oligometastatic NSCLC | 1–6 extracranial sites Gross tumor volume of less than 8 cm | Single-arm prospective phase I study | SBRT followed by Durvalumab and Tremelimumab | SBRT (30–50 Gy/5 F) | N | 17 | Safety and tolerability of treatment | February 2018 |
| Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Oligometastatic Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (SARON) NCT02417662 | Histologically or cytologically confirmed oligometastatic NSCLC | 1–5 in 1–3 organs | Two-arm prospective phase III study | Systemic anti-cancer therapy | SBRT/SRS (N/A) | N | 340 | OS | August 2016 |
| Systemic anti-cancer therapy followed by SBRT/SRS | |||||||||
| Local Non-salvage Radiotherapy for Synchronous Oligometastatic Non-small-cell Lung Cancer. NCT03119519 | Histologically or cytologically confirmed synchronous oligometastatic NSCLC | 1–5 excluding primary tumor | Two-arm prospective phase II study | Platinum-based chemotherapy or Geffitinib or Erlotinib followed by 3D CRT or IMRT | N | N | 148 | PFS | December 2017 |
| Platinum based chemotherapy or Geffitinib or Erlotinib only | |||||||||
| Consolidation Conventional Radiotherapy + Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy at 3 Months After First-line Chemotherapy in Stage IV Oligometastatic Non-small Cell Lung Cancer NCT04758481 | Oligometastatic NSCLC | 3–10 | Single-arm prospective phase I/II study | Platinum-based chemotherapy followed by local radiotherapy then SBRT/SRS then maintenance local therapy | SBRT/SRS (30 Gy/1 F, or 50–60 Gy/3–5 F) | N | 20 | Acute and late toxicity PFS | May 2021 |
| The Safety and Efficacy of First-line Lazertinib and Locally Ablative Radiotherapy in Patients With Synchronous Oligo-metastatic EGFR-mutant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer NCT05167851 | Histologically confirmed synchronous EGFR-mutant oligometastatic NSCLC | 1–5 excluding primary tumor | Two-arm prospective phase II study | Lazertinib in combination with SBRT/SRS | SBRT/SRS (max. 5 F) | N | 68 | PFS | December 2021 |
| Lazertinib only | |||||||||
| Sintilimab After Stereotactic Ablation Brachytherapy for Refractory Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer NCT04486287 | Refractory oligometastatic NSCLC with failed second-line systemic therapy | Not provided | Single-arm prospective phase II study | Stereotactic ablation brachytherapy followed by Sintilimab | N | N | 44 | ORR | September 2020 |
| Chemotherapy Combination With Local Radiotherapy and rhGM-CSF for Oligometastatic Stage IV NSCLC Patients (CRAGMOLC) NCT03489616 | PR or SD after first-line chemotherapy oligometastatic NSCLC | 2–5 1 distant lesion outside the radiation site | Two-arm prospective study | Single agent chemotherapy in combination with local radiotherapy followed by rhGM-CSF | N | N | 45 | PFS | January 2018 |
| Single agent chemotherapy only | |||||||||
| Durvalumab Combined With Chemotherapy and Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) in Patients With Oligometastatic Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) NCT04255836 | Histologically confirmed oligometastatic NSCLC | 1–5 in 1–3 organs | Single-arm prospective phase II study | Durvalumab combined with Paclitaxel + Carboplatin OR Pemetrexed + cisplatin followed by SBRT/SRS | SBRT/SRS (50–60 Gy/1–10 F) | N | 35 | PFS | September 2020 |
| Radical Treatment of Synchronous Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma NCT02805530 | Pathologically confirmed synchronous oligometastatic advanced NSCLC | 1–5 | Single-arm prospective study | EGFR/TKI therapy * or platinum-based chemotherapy followed by radical local therapy | SBRT/SRS (N/A) | Y * | 25 | OS | June 2015 |
| Chest Lymph Node Sampling in Patients With Advanced Lung Cancer to be Treated With Curative-intent Radiation Treatment NCT04852588 | Oligometastatic NSCLC | 1–5 excluding primary tumor | Single-arm prospective study | Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial fine needle aspiration (EBUS-TFNA) or transesophageal ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) followed by SBRT/SRS | SBRT/SRS (N/A) | N | 29 | Changes to treatment plan | November 2021 |
| Surgery and/or Radiation Therapy or Standard Therapy and/or Clinical Observation in Treating Patients With Previously Treated Stage IV Non-small Cell Lung Cancer NCT01725165 | Pathologically confirmed previously treated oligometastatic NSCLC | 1–3 | Two-arm prospective phase II study | Surgical removal and/or local radiation therapy | N | Y * | 94 | PFS | November 2012 |
| Standard medical treatment or clinical observation per physician choice with choice of crossing to experimental arm | |||||||||
| Maintenance Systemic Therapy Versus Local Consolidative Therapy (LCT) Plus Maintenance Systemic Therapy for Limited Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A Randomized Phase II/III Trial (NRG-LU002) NCT03137771 | Patients with histologically confirmed metastatic NSCLC with after first-line/induction systemic therapy and no evidence of progression and limited (≤3 discrete sites) metastatic disease, all of which must be amenable to SBRT +/− Surgery | 1–3 | Phase II/III randomized prospective study | Maintenance systemic therapy alone | SBRT | Y | 378 | PFS for the phase II | April 2017 |
| SBRT or SBRT and Surgery to all sites of metastases (≤3 discrete sites) plus irradiation (SBRT or hypofractionated RT) of the primary site followed by maintenance systemic therapy. | OS for the phase III | ||||||||
| Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy After Surgery in Treating Patients With Stage III–IV Non-small Cell Lung Cancer NCT01781741 | Histologically confirmed oligometastatic NSCLC | 1–3 | Single-arm early prospective phase I study | Lymphadenectomy followed by SBRT/SRS | SBRT/SRS | Y | 10 | Portion of patients with ≥ Grade 3 treatment-related toxicities | March 2013 |
| Study Title and Number | Treated Condition | Oligoprogressive Definition | Study Design | Treatment Scheme | SBRT/SRS | Surgical Excision | Number of Participants | Primary Outcome | Start Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBRT for Oligoprogressive NSCLC After First Line Treatment With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors NCT05387044 | Pathologically confirmed oligoprogressive NSCLC after first line treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors | 1–5 in 1–3 organs and max 5 cm. | Single-arm prospective phase II study | SBRT/SRS | SBRT/SRS (N/A) | N | 28 | PFS | May 2022 |
| SBRT for Oligoprogressive NSCLC After Treatment With PD-1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors NCT04767009 | Pathologically confirmed oligoprogressive NSCLC after treatment with PD-1 inhibitors | Not provided. | Single-arm prospective phase II study | SBRT/SRS * | SBRT/SRS (N/A) | N | 59 | Percentage of participants with adverse events | January 2021 |
| 1-year new lesion-free survival rate | |||||||||
| Atezolizumab Plus 8 Gy Single-fraction Radiotherapy for Advanced Oligoprogressive NSCLC NCT04549428 | Histologically or cytologically confirmed oligoprogressive NSCLC after anti PD-1 agent and first-line of chemotherapy | 1–4 in 1–3 organs. 1–3 in 1 organ. | Single-arm prospective phase II study | Atezolizumab intravenously followed by SBRT/SRS | SBRT/SRS (8 Gy/1 F) | N | 20 | ORR | October 2020 |
| LAT for Oligoprogressive NSCLC Treated With First-line OSImertinib (LAT-FLOSI) NCT04216121 | Histologically confirmed EGFR mutated oligoprogressive NSCLC not suitable for radical treatment after first-line TKI therapy with osimertinib | 1–3 | Prospective observational study | SBRT/SRS followed by surgery | SBRT/SRS (N/A) | Y | 39 | PFS 2 | May 2021 |
| A Study of Furmonertinib Combined With Radiotherapy for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer With Oligoprogression NCT04970693 | Histologically or cytologically confirmed oligoprogressive NSCLC after first-line EGFR-TKI therapy | 3–5 after receiving the first or second generation of EGFR-TKI or after receiving Osimertinib and chemotherapy was refused. | Single-arm prospective phase II study | Furmonertinib in combination with local radiotherapy | N | N | 64 | PFS | June 2021 |
| Local Consolidative Therapy and Durvalumab for Oligoprogressive and Polyprogressive Stage III NSCLC After Chemoradiation and Anti-PD-L1 Therapy NCT04892953 | Oligoprogressive or polyprogressive NSCLC and received standard chemoradiation and anti-PD-l1 durvalumab therapy. | 1–3 | Two-arm prospective phase II study | Local consolidative therapy in combination with Durvalumab intravenously | N | Y * | 51 | PFS | July 2021 |
| Local consolidative therapy in combination with Durvalumab intravenously and chemotherapy | |||||||||
| Local Ablative Therapy for Treatment of Oligoprogressive, EGFR-Mutated, Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer After Treatment With Osimertinib NCT02759835 | (1) Histologically confirmed advanced lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR-sensitizing somatic mutations or a germline T790M mutation with no prior EGFR TKI therapy. (2) Progressive disease after 1st or 2nd generation EGFR TKI therapy harboring somatic T790 M mutation. (3) Progressive disease after treatment with Osimertinib who are eligible for local ablative therapy. | Not provided | Two-arm prospective phase II study | Osimertinib followed by LAT * followed by Osimertinib | N | Y * | 37 | PFS 2 | April 2016 |
| LAT * followed by Osimertinib | PFS | ||||||||
| Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Oligo-Progressive Non Small Cell Lung Cancer (SUPPRESS-NSCLC) NCT04405401 | Oligoprogressive NSCLC while on ICI or TKI | 1–5 extracranial in 1–3 organs and max. 5 cm | Two-arm prospective phase II study | Systemic therapy * | SBRT (N/A) | N | 68 | PFS | January 2021 |
| SBRT in combination with systemic therapy * | OS | ||||||||
| Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for the Treatment of OPD (HALT) NCT03256981 | Histologically confirmed mutation positive advanced oligoprogressive NSCLC following initial response to a TKI | 1–3 extracranial | Two-arm prospective phase III study | Continued TKI therapy only | SBRT (N/A) | N | 110 | PFS | November 2017 |
| Continued TKI therapy in combination with SBRT | |||||||||
| Randomized Study of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) in Patients With Oligoprogressive Metastatic Cancers of the Breast and Lung NCT03808662 | Histologically confirmed triple negative breast cancer, or NSCLC (without known EGFR mutation or ALK/ROPS1 rearrangement), or other high-risk breast cancer progressed on hormone or systemic therapy, or NSCLC with EGFR, ALK, or ROS1 targetable molecular alterations with disease progression on first line TKI. | 1–5 in 1 extracranial organ | Two-arm prospective phase II study | Standard medical treatment * | SBRT/SRS (*) | N | 107 | PFS | January 2019 |
| SBRT/SRS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baydoun, A.; Lee, V.L.; Biswas, T. Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Practical Review of Prospective Trials. Cancers 2022, 14, 5339. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215339
Baydoun A, Lee VL, Biswas T. Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Practical Review of Prospective Trials. Cancers. 2022; 14(21):5339. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215339
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaydoun, Atallah, VeAnn L. Lee, and Tithi Biswas. 2022. "Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Practical Review of Prospective Trials" Cancers 14, no. 21: 5339. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215339
APA StyleBaydoun, A., Lee, V. L., & Biswas, T. (2022). Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Practical Review of Prospective Trials. Cancers, 14(21), 5339. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215339








