Simple Summary
Epidemiological evidence has suggested that modifiable factors play an essential role in the risk of head and neck cancer (HNC). However, few studies have established HNC prediction models based on sex and tumor subsites. In this study, we establish sex- and subsite-specific HNC risk prediction models for the general Taiwanese population. Our study draws from a large sample size of 14,423 participants. The HNC prediction models may be applied in clinical risk assessments for health promotion programs.
Abstract
Epidemiological evidence has suggested that modifiable lifestyle factors play a significant role in the risk of head and neck cancer (HNC). However, few studies have established risk prediction models of HNC based on sex and tumor subsites. Therefore, we predicted HNC risk by creating a risk prediction model based on sex- and tumor subsites for the general Taiwanese population. This study adopted a case-control study design, including 2961 patients with HNC and 11,462 healthy controls. Multivariate logistic regression and nomograms were used to establish HNC risk prediction models, which were internally validated using bootstrap sampling. The multivariate logistic regression model indicated that age, education level, alcohol consumption, cigarette smoking, passive smoking, coffee consumption, and body mass index are common HNC predictors in both sexes, while the father’s ethnicity, betel-nut-chewing habits, and tea consumption were male-specific HNC predictors. The risk factors of the prediction model for the HNC tumor subsite among men were the same as those for all patients with HNC. Additionally, the risks of alcohol consumption, cigarette smoking, and betel nut chewing varied, based on the tumor subsite. A c-index ranging from 0.93 to 0.98 indicated that all prediction models had excellent predictive ability. We developed several HNC risk prediction models that may be useful in health promotion programs.
1. Introduction
Head and neck cancer (HNC) includes malignancies of the oral cavity, oropharynx, hypopharynx, and larynx [1]. Each year, over 900,000 HNC cases are diagnosed and 400,000 deaths from HNC occur worldwide [2]. In Taiwan, oral cavity (73.9%), oropharyngeal (11.2%), and hypopharyngeal (14.7%) cancers accounted for the majority of HNC in 2018. The incidence of HNC among men is higher than that among women. The age-adjusted incidence rate of oral cancer (including oropharyngeal and hypopharyngeal cancer) for men and women is 42.15 per 100,000 people and 3.92 per 100,000 people, respectively [3].
Epidemiological evidence suggests that modifiable lifestyle factors significantly affect the risk of HNC, but the associations vary, based on sex and tumor subsites. Studies have indicated that male smokers had a significantly greater risk of HNC than female smokers [4]. However, passive smoking and exposure to cooking oil fumes were reported to significantly increase the risk of oral cancer among Chinese women but not in men [5]. Alcohol consumption is another major risk factor for HNC, particularly for oropharyngeal and hypopharyngeal cancer [6]. Additionally, betel-nut chewing is a well-established risk factor for oral cancer, while combining tobacco consumption with betel-nut chewing is associated with a greater risk of oral cancer than oropharyngeal cancer [7].
Risk prediction models have been developed for many types of cancer, including breast, colorectal, prostate, lung, ovarian, and esophageal [8] cancers, but those for cancers in the head and neck are limited. Two studies in Japan have developed risk prediction models for upper aerodigestive tract cancer that included both genetic and environmental factors [9,10]. Hung et al. established a predictive model for oral cancer among high-risk individuals who had a habit of smoking or betel nut chewing in Taiwan [11]. As mentioned above, the risk of HNC varies by gender and tumor subsite. However, no study has established a risk prediction model of HNC that is based on sex and tumor subsites for a Taiwanese population. In the present study, we predicted the risk of HNC by using sex- and tumor subsite-specific models in the general Taiwanese population.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
We conducted a case-control study by combining a large series of HNC cases from a medical center in northern Taiwan with a large series of general noncancer controls of the Taiwanese population from the Taiwan Biobank (TBB). The TBB is an ongoing prospective cohort study, recruiting over 160,000 participants from the community across Taiwan since 2012 [12]. Eligible participants are aged over 30 years old and have no prior diagnosis of any cancer or human immunodeficiency virus infection. Upon their recruitment, the participants completed written informed consent, a demographic questionnaire, a physical examination, and laboratory blood and urine tests. A total of 3313 patients with HNC were recruited from the Department of Head and Neck Oncology at Linkou Chang Gung Memorial Hospital between 1999 and 2019. After the exclusion of patients without oral cancer, oropharyngeal cancer, or hypopharyngeal cancer and patients with missing demographic information and information on behavioral factors, 2961 eligible patients (2788 male and 173 female) were included. The distribution of the clinicopathological characteristics of the HNC patients is shown in Table S1 of the Supplementary Materials. A total of 11,462 healthy controls (5650 male and 5812 female) were selected from the Taiwan Biobank (n = 122,071), according to the age- and sex-specific distribution of the general Taiwanese population in 2013 (Figure 1).
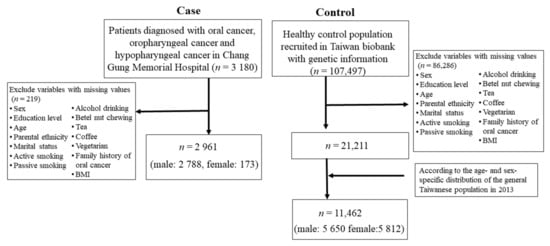
Figure 1.
Selection procedure of participants with head and neck cancer.
2.2. Data Collection
Data from the participants were collected in face-to-face interviews using a structured lifestyle questionnaire that included questions regarding sociodemographic characteristics (age, sex, education, parental ethnicity, and marital status), lifestyle habits (active and passive smoking, alcohol consumption, betel-nut chewing, and tea and coffee consumption), dietary habits, family history of oral cancer, and body mass index (BMI). Additionally, the clinicopathological data, including tumor differentiation, tumor stage, tumor size, treatment methods, and prognosis, were gathered from the medical records.
The variables measured in the present study were the following: age (<40, 40–49, 50–59, ≥60 years); sex (male or female); education (junior high and below, senior high school, or college and above); parental ethnicity (Taiwanese, Hakka, or other); occupation (non-white collar or white collar); family history of oral cancer (yes or no); BMI (<18.5, 18.5–23.9, ≥24); active smoking, passive smoking, betel-nut chewing, and alcohol consumption (never or ever); and tea consumption, coffee consumption, and a vegetarian diet (yes or no).
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The chi-square test was performed to compare the categorical demographic characteristics between the case and control groups. Univariate logistic regression was used to observe the relationship between risk factors and the risk of HNC and to estimate the odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). All variables with p < 0.05 in the univariate logistic analyses were further assessed using multivariable logistic regression and stepwise selection. Based on the results from the final multivariate logistic regression models, we generated nomograms to estimate the risk of HNC. Calibration curves were plotted to calibrate the HNC risk-prediction models. The C-index was used to evaluate the discriminative ability; 0.5 indicated that the model had no predictive effect, with 1 indicating that the model’s prediction results were consistent with the actual results. Additionally, the risk-prediction models were subjected to 100, 500, and 1000 bootstrap resamples for internal validation, to assess the predictive accuracy. All statistical analyses were conducted using SAS software, version 9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA). Statistical significance was considered at p < 0.05.
3. Results
In total, 2961 patients with HNC (2788 men and 173 women) and 11,462 controls (5650 men and 5812 women) were included in the study. Regarding the tumor subsites among male cases, 2440 were oral cavity tumors, 175 were oropharyngeal tumors, and 173 were hypopharyngeal tumors. The demographic and lifestyle habits of the cases and controls are listed in Table 1. Patients with HNC were primarily male, older, predominantly Hakka, and had a history of alcohol and tobacco use, passive smoking, betel-nut chewing, tea consumption, and a lower BMI compared with the controls (all p < 0.001). In the univariate analysis, being male, old age, married status, Hakka ethnicity, occupation (non-white collar), ever using alcohol and tobacco, passive smoking, ever chewing betel nuts, tea consumption, a family history of oral cancer, and having a BMI of <18.5 were associated with an increased risk of HNC. Higher education level, coffee consumption, and a BMI ≥ 24 were associated with a protective effect against HNC. In the multivariate model, being male (OR: 2.86, 95% CI: 2.25–3.64), aged ≥ 60 (OR: 1.45, 95% CI: 1.12–1.87), of Hakka ethnicity (OR: 2.21, 95% CI: 1.80–2.71), ever consuming alcohol (OR: 3.33, 95% CI: 2.85–3.89), ever smoking cigarettes (OR: 2.34, 95% CI: 1.91–2.85), passive smoking (OR: 5.81, 95% CI: 5.00–6.75), ever chewing betel nuts (OR: 6.83, 95% CI: 5.76–8.11), tea consumption (OR: 1.47, 95% CI: 1.27–1.70), and a BMI of <18.5 (OR: 4.95, 95% CI: 3.32–7.39) were significantly associated with an increased risk of HNC. However, a higher education level (OR: 0.04, 95% CI: 0.04–0.06), coffee consumption (OR: 0.65, 95% CI: 0.55–0.77), and a BMI ≥ 24 (OR: 0.57, 95% CI: 0.49–0.67) were significantly protective against HNC.

Table 1.
Demographic characteristics and lifestyle associated with the risk of head and neck cancer.
Table 2 presents the demographic characteristics and lifestyle habits associated with HNC risk among male patients. The distribution of demographic characteristics and lifestyle habits is similar to that in Table 1. In the univariate analysis, older age, marital status, Hakka ethnicity, occupation (non-white collar), ever consuming alcohol, ever smoking cigarettes, passive smoking, ever chewing betel nuts, tea consumption, a BMI of <18.5, and a family history of oral cancer were associated with an increased risk of HNC. A higher education level, coffee consumption, a vegetarian diet, and a BMI ≥ 24 were associated with a lower risk of HNC. In the multivariate model, an age of 40–49 years (OR: 1.46, 95% CI: 1.15–1.84), Hakka ethnicity (OR: 2.38, 95% CI: 1.90–2.97), ever consuming alcohol (OR: 3.32, 95% CI: 2.82–3.89), ever smoking cigarettes (OR: 2.52, 95% CI: 2.04–3.12), passive smoking (OR: 4.86, 95% CI: 4.13–5.70), ever chewing betel nuts (OR: 6.15, 95% CI: 5.17–7.32), tea consumption (OR: 1.49, 95% CI: 1.27–1.74), and a BMI of <18.5 (OR: 4.32, 95% CI: 2.60–7.18) were significantly associated with an increased risk of HNC. A higher education level (OR: 0.04–0.18), coffee consumption (OR: 0.67 95%, CI: 0.56–0.80), and a BMI ≥ 24 (OR: 0.53, 95% CI: 0.45–0.62) were significantly protective against HNC.

Table 2.
Demographic characteristics and lifestyle associated with the risk of head and neck cancer among male patients.
Table 3 presents the demographic characteristics and lifestyle habits associated with HNC risk among female patients. Marital status, the father’s ethnicity, tea consumption, a vegetarian diet, and a family history of oral cancer were similarly distributed between cases and controls (all p > 0.05). In the univariate analysis, older age, Hakka ethnicity, occupation (non-white collar), ever consuming alcohol, ever smoking cigarettes, passive smoking, ever chewing betel nuts, and a BMI of <18.5 were associated with an increased risk of HNC. In the multivariate model, age, ever consuming alcohol (OR: 5.31, 95% CI: 2.96–9.54), ever smoking cigarettes (OR: 2.73, 95% CI: 1.55–4.82), passive smoking (OR: 19.0, 95% CI: 12.8–28.3), and a BMI of <18.5 (OR: 9.46, 95% CI: 4.73–18.9) were significantly associated with an increased risk of HNC. A higher education level (OR: 0.05, 95% CI: 0.02–0.09), coffee consumption (OR: 0.61, 95% CI: 0.39–0.94) and a BMI ≥ 24 (OR: 0.83, 95% CI: 0.56–1.24) were significant protective factors against HNC.

Table 3.
Demographic characteristics and lifestyle associated with the risk of head and neck cancer among female patients.
Table 4 shows tumor site-specific multivariate models for the risk of HNC among male patients. Age, Hakka ethnicity, ever consuming alcohol, ever smoking cigarettes, passive smoking, ever chewing betel nuts, and a BMI of <18.5 significantly increased the risks for all HNC subsites. Additionally, alcohol consumption exhibited the strongest positive association with cancer in the hypopharynx (OR: 14.3), followed by cancers in the oropharynx (OR: 9.67) and oral cavity (OR: 2.98). Cigarette smoking presented the strongest positive association with tumor subsites in the hypopharynx (OR: 6.94), followed by tumor subsites in the oropharynx (OR: 3.35) and oral cavity (OR: 2.39). Betel-nut chewing had the strongest positive association with oral cavity cancer (OR: 6.34), followed by hypopharyngeal cancer (OR: 4.74) and oropharyngeal cancer (OR: 3.68). Education level and a BMI ≥ 24 had significant protective effects against all HNC subsites. Coffee consumption exhibited a specific protective factor against oral cancer (OR: 0.68) and hypopharyngeal cancer (OR: 0.28). However, tea consumption was a specific risk factor for oral cancer (OR: 1.53).

Table 4.
Tumor site-specific multivariable models for the risk of head and neck cancer among male participants.
Based on the independent risk factors for HNC, we plotted nomograms to predict the probability of developing HNC for all participants, for participants according to sex, and for participants with specific tumor subsites (Figure 2 and Figure 3). The score for each independent variable can be determined by drawing a vertical line to the point axis. The total risk score was then calculated by summing each variable score. Finally, the probability of HNC occurrence can be determined on the total point axis. Furthermore, the prediction models were internally validated using bootstrap resampling, which assessed the optimism-corrected discrimination and calibration (Table S2 in the Supplementary Materials). Across the 100, 500, and 1000 bootstrap repetitions, the optimism-corrected c-index for predicting the risk of HNC in all prediction models ranged from 0.93 to 0.98. The expected and observed risks were plotted for all prediction models, and all models had good calibration. The 45° line indicates perfect calibration (Figures S1–S6 in the Supplementary Materials).
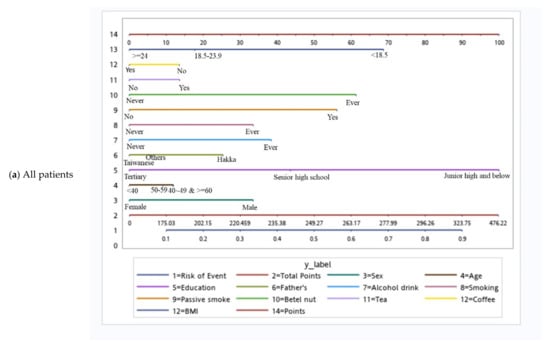

Figure 2.
Nomograms of patients.

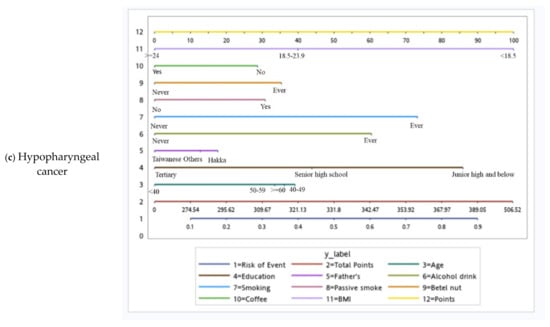
Figure 3.
Tumor site-specific nomograms for male head and neck cancer.
4. Discussion
We established sex-specific and tumor subsite-specific prediction models of HNC risks for the general Taiwanese population. The HNC risk prediction models included sex, age, education level, father’s ethnicity, alcohol consumption, cigarette smoking, passive smoking, betel-nut chewing, tea consumption, coffee consumption, and BMI.
Among all sociodemographic factors, education level was the strongest predictor, which is consistent with other studies [13,14]. Previous analyses have demonstrated that lower education and income levels are associated with a higher risk of HNC. Among all lifestyle factors, alcohol consumption, cigarette smoking, and betel-nut chewing are major risk factors for HNC, and the effect of betel-nut chewing is greater than those of alcohol drinking or cigarette smoking, which is consistent with other studies in East Asia [4,15]. Betel-nut chewing is a key predictor in East Asian countries and increases the risk of oropharyngeal cancer, oral leukoplakia, oral mucosal lesions, and oral cancer [16,17]. Tobacco is a known human carcinogen [18]; one study suggested that secondhand smoke may increase the risk of breast cancer, nasal sinus cavity cancer, and nasopharyngeal cancer among adults [19]. Our research indicated that passive smoking is a risk factor for HNC, which is consistent with the literature [20]; however, the magnitude is higher in the present study than in other studies, which may be due to the exposure time and dose. Further studies are required to clarify the association between passive smoking and HNC.
Tea consumption is identified as a risk factor in our study, but a significant inverse association between tea consumption and HNC has been reported in five other studies [21,22,23,24,25]. Several factors may contribute to inconsistencies in the results. First, most of the studies were conducted in Europe and the United States, where tea consumption is not as prevalent as in Taiwan. Moreover, the types of tea that are consumed vary; for example, black tea is consumed the most in Europe and the United States. Second, the association between smoking and drinking tea is high in Asia [26]. This was also true in our study sample (the prevalence of tea consumption was 48.2% among patients who smoked and 32.6% among patients who did not smoke in the control group). Consequently, our results may be biased toward the null or overestimated. Consistent with the results of other studies [27], our analysis revealed that coffee consumption is protective against HNC. Our results also indicated that being underweight is significantly associated with a higher risk of HNC, while being overweight or obese is significantly associated with a lower risk of HNC. In another study that explored the association between BMI and 22 specific cancer sites, the results indicated that obesity has a protective effect against tumors in certain locations [28]; this phenomenon has been termed the “obesity paradox” [28]. A possible explanation for this phenomenon is that an increase in nutritional reserves and a higher body mass protect the body during periods of acute sickness.
Age, education level, alcohol consumption, cigarette smoking, passive smoking, coffee consumption, and BMI are common predictors of HNC among both men and women, and these predictors are consistent with other studies [29,30]. The father’s ethnicity, betel-nut chewing habits, and tea consumption are specific predictors of HNC among men. In particular, betel-nut chewing is much more prevalent among men over 18 years old than among women (22% vs. 1%) [31]. The risk of tea consumption between men and women is inconsistent with other studies [32,33]. Other studies may have evaluated participants who did not smoke or drink, so the confounding effects caused by these two factors can be excluded. Furthermore, the previous studies recruited more female participants, which may have affected the results.
In the prediction model for tumor subsites among men, the risk factors are the same as those for HNC. Coffee consumption is associated with the risk of oral cancer and hypopharyngeal cancer, which is consistent with other studies [27,34,35]. Additionally, the risks of alcohol consumption, cigarette smoking, and betel nut chewing vary based on the tumor sites. Alcohol consumption is associated with the greatest risk of hypopharyngeal cancer (OR: 14.32), followed by oropharyngeal (OR: 9.67) and oral cancer (OR: 2.98). Studies have reported that pharyngeal cancer is strongly associated with alcohol consumption [36]. In Taiwan, the incidence of hypopharyngeal cancer has risen the fastest at sites unrelated to human papillomavirus (HPV) [37], which may be explained by the high level of alcohol consumption among the Taiwanese population. We speculate that the reason why drinking has a greater effect on the hypopharynx may be related to the Taiwanese “bottoms-up” drinking tradition of ganbei [38] because it increases the exposure to alcohol in the hypopharynx, which subsequently increases the risk of lesions in the hypopharyngeal tissue [39,40,41]. Smoking posed the greatest risk of hypopharyngeal cancer (OR: 6.94), followed by oropharyngeal cancer (OR: 3.35) and oral cancer (OR: 2.39), which is consistent with other studies [42] and may be associated with differences in smoking patterns (e.g., inhalation). In a Japanese study on cigarette smoke inhalation and lung cancer risk, smokers who inhaled cigarette smoke had a 1.5-fold increase in risk compared with those who did not inhale cigarette smoke [43]. Unfortunately, evaluating smoking patterns is outside the scope of the present study. Finally, the risk of betel-nut chewing was the highest among patients with oral cancer (OR: 6.34), followed by hypopharyngeal (OR: 4.74) and oropharyngeal cancer (OR: 3.68). The risk of betel-nut chewing also depends on individual chewing habits. In Taiwan, betel nut is often held in the mouth for a long time before swallowing [44], which may increase the exposure time in the oral cavity.
The present study has several strengths. First, our study recruited a relatively large sample size, which drew upon patient records in the Taiwan Biobank. Second, we included more predictors (demographic factors, lifestyle factors) that could predict the risk of developing HNC in the general population more widely. Third, using nomograms could easily construct risk scores for each individual’s probability of the occurrence of HNC. However, this study has some limitations. First, few female patients with HNC were included in our study, which may have resulted in a type-2 error, an overestimation of the results, and a less stratified analysis of the tumor subsites. Second, the present study was a case-control study; therefore, recall bias may have occurred. Patients with HNC may have exaggerated their tobacco or alcohol use, compared with the controls. Third, selection bias may have also occurred. Linkou Chang Gung Memorial Hospital is close to several industrial parks in northern Taiwan; many individuals seeking medical services from this hospital are blue-collar laborers. Therefore, the patient cohort may include more men who are younger and have a lower socioeconomic status, which may have caused an overestimation of the effect of each predictor on HNC risk. However, these factors were adjusted for in the multivariate model. Fourth, although other risk factors, such as dietary habits, serological and genetic biomarkers, and HPV infection status were not collected, all established prediction models with c-indices of >0.9 indicated excellent discrimination in the analysis. Finally, although our prediction models were initially validated using bootstrap sampling methods, further research with larger multicenter cohorts is necessary to validate our findings.
5. Conclusions
For this study, we developed HNC risk prediction models for all patients, male patients, female patients, and male patients with specific tumor sites. The results indicate that the risk factors of HNC vary based on sex and tumor subsite. Our group-specific HNC risk prediction models may be used in clinical settings or communities to identify high-risk individuals, as well as to promote healthier behaviors, such as ceasing or reducing cigarette smoking, alcohol drinking, and betel-nut chewing. Such preventive efforts are the most effective way to reduce the occurrence of HNC in Taiwan. Furthermore, additional serological and genetic biomarkers should be included to increase the discriminatory ability of HNC risk prediction models.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cancers14215338/s1, Table S1: Clinicopathological characteristics of head and neck cancer patients; Table S2: Original c-index and optimism, adjusting performance for the risk prediction model; Figure S1: Calibration plot for the head and neck cancer prediction model; Figure S2: Calibration plot for the men’s head and neck cancer prediction model; Figure S3: Calibration plot for the women’s head and neck cancer prediction model; Figure S4: Calibration plot for the oral cancer prediction model; Figure S5: Calibration plot for the oropharyngeal cancer prediction model; Figure S6: Calibration plot for the hypopharyngeal cancer prediction model.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.-Z.Y., M.-M.W., H.-T.C., C.-T.L., M.-J.S., S.-F.H. and C.-C.Y.; methodology, M.-Z.Y., S.-F.H. and C.-C.Y.; validation, M.-Z.Y., M.-M.W., H.-T.C., C.-T.L., M.-J.S., S.-F.H. and C.-C.Y.; formal analysis, M.-Z.Y. and M.-M.W.; investigation, H.-T.C., C.-T.L., M.-J.S. and S.-F.H.; resources, C.-T.L., S.-F.H. and C.-C.Y.; data curation, S.-F.H. and C.-C.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, M.-Z.Y., M.-M.W. and C.-C.Y.; writing—review and editing, M.-Z.Y., M.-M.W., H.-T.C., C.-T.L., M.-J.S., S.-F.H. and C.-C.Y.; visualization, M.-Z.Y.; supervision, S.-F.H. and C.-C.Y.; project administration, S.-F.H. and C.-C.Y.; funding acquisition, S.-F.H. and C.-C.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Science and Technology Council (MOST 108-2314-B-038-088, MOST 110-2314-B-038-053, MOST 111-2314-B-038-046), and Taipei Medical University (TMU109-F-001).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (IRB No.: 201800213B0) and Taipei Medical University IRB (Nos. N201802083, N202103125, and N202203077).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this article (and Supplementary Materials).
Acknowledgments
We thank all the members of the Cancer Center and Tissue Bank, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou, Taiwan.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chow, L.Q.M. Head and Neck Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Cancer Observatory. International Agency for Research on Cancer; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Taiwan Cancer Registration Center. Long-Term Trend of Age-Standardized Incidence Rate (Data only Includes Invasive Cancer); Taiwan Cancer Registration Center: Taipei City, Taiwan, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-C.A.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Chen, C.-J.; Hsu, W.-L.; Lou, P.-J.; Zhu, C.; Pan, J.; Shen, H.; et al. Tobacco smoking, alcohol drinking, betel quid chewing, and the risk of head and neck cancer in an East Asian population. Head Neck 2019, 41, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Chen, F.; Yan, L.; Huang, J.; Liu, F.; Qiu, Y.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, L. Independent and joint exposure to passive smoking and cooking oil fumes on oral cancer in Chinese women: A hospital-based case-control study. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2016, 136, 1074–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Hsiao, J.R.; Lee, W.T.; Lee, Y.C.; Ou, C.Y.; Chang, C.C.; Lu, Y.C.; Huang, J.S.; Wong, T.Y.; Chen, K.C.; et al. Investigating the Association between Alcohol and Risk of Head and Neck Cancer in Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, N.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; Vlaanderen, J.; Straif, K. Betel quid chewing and the risk of oral and oropharyngeal cancers: A meta-analysis with implications for cancer control. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, A.N.; Seminara, D.; Gail, M.H.; Hartge, P.; Colditz, G.A.; Ballard-Barbash, R.; Pfeiffer, R.M. Cancer risk prediction models: A workshop on development, evaluation, and application. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2005, 97, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyanagi, Y.N.; Ito, H.; Oze, I.; Hosono, S.; Tanaka, H.; Abe, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Matsuo, K. Development of a prediction model and estimation of cumulative risk for upper aerodigestive tract cancer on the basis of the aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 genotype and alcohol consumption in a Japanese population. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 26, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, M.; Budhathoki, S.; Yamaji, T.; Tanaka-Mizuno, S.; Kuchiba, A.; Sawada, N.; Goto, A.; Shimazu, T.; Inoue, M.; Tsugane, S. Inclusion of a gene-environment interaction between alcohol consumption and the aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 genotype in a risk prediction model for upper aerodigestive tract cancer in Japanese men. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 3835–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, L.C.; Kung, P.T.; Lung, C.H.; Tsai, M.H.; Liu, S.A.; Chiu, L.T.; Huang, K.H.; Tsai, W.C. Assessment of the Risk of Oral Cancer Incidence in A High-Risk Population and Establishment of a Predictive Model for Oral Cancer Incidence Using a Population-Based Cohort in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwan Biobank. Available online: https://www.twbiobank.org.tw/article.php?id=17 (accessed on 10 August 2022).
- Conway, D.I.; Petticrew, M.; Marlborough, H.; Berthiller, J.; Hashibe, M.; Macpherson, L.M. Socioeconomic inequalities and oral cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control studies. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 2811–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, J.R.; Huang, C.C.; Ou, C.Y.; Chang, C.C.; Lee, W.T.; Tsai, S.T.; Huang, J.S.; Chen, K.C.; Lai, Y.H.; Wu, Y.H.; et al. Investigating the health disparities in the association between lifestyle behaviors and the risk of head and neck cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 2974–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.J.; Jiang, R.S.; Wu, S.H.; Chen, F.J.; Liu, S.A. Smoking, alcohol, and betel quid and oral cancer: A prospective cohort study. J. Oncol. 2011, 2011, 525976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.C.; Ray, C.S. Epidemiology of betel quid usage. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2004, 33, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.E.; Huang, T.J.; Huang, J.C.; Lin, M.S.; Hong, R.M.; Chang, C.H.; Chen, M.Y. Alcohol, betel-nut and cigarette consumption are negatively associated with health promoting behaviors in Taiwan: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Tobacco Smoke and Involuntary Smoking. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 83, pp. 1–1438. [Google Scholar]
- National Toxicology Program. Tobacco-related exposures: Environmental tobacco smoke. Rep. Carcinog. Carcinog. Profiles 2011, 12, 410–412. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Morgenstern, H.; Spitz, M.R.; Tashkin, D.P.; Yu, G.P.; Hsu, T.C.; Schantz, S.P. Environmental tobacco smoking, mutagen sensitivity, and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2000, 9, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar]
- Franceschi, S.; Barra, S.; La Vecchia, C.; Bidoli, E.; Negri, E.; Talamini, R. Risk factors for cancer of the tongue and the mouth. A case-control study from northern Italy. Cancer 1992, 70, 2227–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagiou, P.; Talamini, R.; Samoli, E.; Lagiou, A.; Ahrens, W.; Pohlabeln, H.; Benhamou, S.; Bouchardy, C.; Slamova, A.; Schejbalova, M.; et al. Diet and upper-aerodigestive tract cancer in Europe: The ARCAGE study. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 2671–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoï, L.; Paget-Bailly, S.; Menvielle, G.; Cyr, D.; Schmaus, A.; Carton, M.; Guida, F.; Cénée, S.; Sanchez, M.; Guizard, A.V.; et al. Tea and coffee consumption and risk of oral cavity cancer: Results of a large population-based case-control study, the ICARE study. Cancer Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.S.; Freedman, N.D.; Kamangar, F.; Dawsey, S.M.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Schatzkin, A.; Abnet, C.C. Tea, coffee, carbonated soft drinks and upper gastrointestinal tract cancer risk in a large United States prospective cohort study. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zheng, J.W.; Luo, J.F.; Zhong, L.P.; Xiang, Y.B. Tea consumption and the risk of oral cancer incidence: A case-control study from China. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 918–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.C.; Lee, W.T.; Tsai, S.T.; Ou, C.Y.; Lo, H.I.; Wong, T.Y.; Fang, S.Y.; Chen, K.C.; Huang, J.S.; Wu, J.L.; et al. Tea consumption and risk of head and neck cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Cui, D. Association between coffee consumption and the risk of oral cancer: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 11657–11665. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhaskaran, K.; Douglas, I.; Forbes, H.; dos-Santos-Silva, I.; Leon, D.A.; Smeeth, L. Body-mass index and risk of 22 specific cancers: A population-based cohort study of 5·24 million UK adults. Lancet 2014, 384, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Lin, L.; Yan, L.; Liu, F.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; Wu, J.; Bao, X.; Lin, L.; et al. Nomograms and risk scores for predicting the risk of oral cancer in different sexes: A large-scale case-control study. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 2543–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.A.; Al-Temimi, M.; Ying, J.; Muscat, J.; Olshan, A.F.; Zevallos, J.P.; Winn, D.M.; Li, G.; Sturgis, E.M.; Morgenstern, H.; et al. Risk Prediction Models for Head and Neck Cancer in the US Population from the INHANCE Consortium. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 189, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health and Welfare National Health Service. Percentage of Betel Nut Chewing among People over 18 Years Old; Ministry of Health and Welfare: New Delhi, India, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; He, B.; Huang, J.; Liu, F.; Yan, L.; Hu, Z.; Lin, L.; He, F. Effect of tea on oral cancer in nonsmokers and nondrinkers: A case-control study. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2015, 49, 683–687. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; He, B.C.; Yan, L.J.; Liu, F.P.; Huang, J.F.; Hu, Z.J.; Lin, Z.; Zheng, X.Y.; Lin, L.S.; Zhang, Z.F.; et al. Tea consumption and its interactions with tobacco smoking and alcohol drinking on oral cancer in southeast China. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biazevic, M.G.; Toporcov, T.N.; Antunes, J.L.; Rotundo, L.D.; Brasileiro, R.S.; de Carvalho, M.B.; de Góis Filho, J.F.; Kowalski, L.P. Cumulative coffee consumption and reduced risk of oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavani, A.; Bertuzzi, M.; Talamini, R.; Gallus, S.; Parpinel, M.; Franceschi, S.; Levi, F.; La Vecchia, C. Coffee and tea intake and risk of oral, pharyngeal and esophageal cancer. Oral Oncol. 2003, 39, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Miao, L.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, H.; Yuan, H. Different levels in alcohol and tobacco consumption in head and neck cancer patients from 1957 to 2013. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, T.Z.; Hsiao, J.R.; Tsai, C.R.; Chang, J.S. Incidence trends of human papillomavirus-related head and neck cancer in Taiwan, 1995–2009. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.F. A Preliminary Exploration of Young Nurses’ Alcohol Drinking Behavior, Attitude and Mental Health Status. Master’s Thesis, National Taipei University of Nursing and Health Sciences, New Taipei, Taiwan, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Brennan, P.; Boffetta, P. Mechanistic considerations in the molecular epidemiology of head and neck cancer. IARC Sci. Publ. 2004, 157, 393–414. [Google Scholar]
- Pai, S.I.; Westra, W.H. Molecular pathology of head and neck cancer: Implications for diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2009, 4, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraguti, G.; Terracina, S.; Petrella, C.; Greco, A.; Minni, A.; Lucarelli, M.; Agostinelli, E.; Ralli, M.; de Vincentiis, M.; Raponi, G.; et al. Alcohol and Head and Neck Cancer: Updates on the Role of Oxidative Stress, Genetic, Epigenetics, Oral Microbiota, Antioxidants, and Alkylating Agents. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubin, J.H.; Muscat, J.; Gaudet, M.M.; Olshan, A.F.; Curado, M.P.; Dal Maso, L.; Wünsch-Filho, V.; Sturgis, E.M.; Szeszenia-Dabrowska, N.; Castellsague, X.; et al. An examination of male and female odds ratios by BMI, cigarette smoking, and alcohol consumption for cancers of the oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx in pooled data from 15 case-control studies. Cancer Causes Control CCC 2011, 22, 1217–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, K.; Ito, H.; Matsuo, K.; Tanaka, H.; Yokoi, K.; Tajima, K.; Takezaki, T. Cigarette smoke inhalation and risk of lung cancer: A case-control study in a large Japanese population. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. Off. J. Eur. Cancer Prev. Organ. ECP 2015, 24, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Lee, K.W.; Fang, F.M.; Wu, D.C.; Tsai, S.M.; Chen, P.H.; Shieh, T.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Wu, I.C.; Huang, H.L.; et al. The neoplastic impact of tobacco-free betel-quid on the histological type and the anatomical site of aerodigestive tract cancers. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, E733–E743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).