Abstract
Background/Objectives: The growing prevalence of out-of-home eating is reflected in the contract catering sector, which worldwide generates billions of euros annually. Considering its large economic value and workforce, as well as the meals it offers in institutions, the sector may greatly impact human and planetary health. Thus, this scoping review aimed to analyze the availability of evidence on the nutritional quality (NQ) and environmental impact (EI) of institutional canteen menus/meals. Methods: The search was conducted using PubMed and Scopus databases and was limited to the period from 2013 to 2025. Quantitative articles that considered the NQ and/or EI of institutional canteen menus/meals were included. Results: Results revealed that most of the 107 articles included were conducted in high-income countries and in early-education centers. Additionally, most studies evaluated NQ in comparison to EI (n = 76 and n = 13, respectively), while only 18 studies evaluated both. It was also noted that interest in EI increased in recent years, with greenhouse gas emission being the most common indicator. Conclusions: This review contributes to identifying an imbalance in the available evidence, with substantially more data on the nutritional quality of institutional canteen menus and meals than on their environmental footprints, which are often assessed through greenhouse gas emissions while other environmental indicators remain largely overlooked. Moreover, the heterogeneity of study settings and the predominance of research conducted in developed countries limit the generalizability of current findings. Future studies should adopt a broader scope to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of the nutritional and environmental sustainability of institutional catering systems.
1. Introduction
Despite the term “sustainable diet” being coined almost 40 years ago, the currently acknowledged definition comes from the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) that described sustainable diets as “…protective and respectful of biodiversity and ecosystems, culturally acceptable, accessible, economically fair and affordable; nutritionally adequate, safe and healthy; while optimizing natural and human resources” [1]. This view was reinforced in the sixteen guiding principles crafted by the World Health Organization (WHO) and FAO [2]. The principles set the basis for “Sustainable Healthy Diets,” a concept that is a current focal point for various stakeholders, including governments, international organizations, civil society groups, the private sector, and academia [2].
Nowadays, research overall agrees that the dietary patterns most likely to confer health and environmental benefits simultaneously (i.e., sustainable healthy diets) are those that are rich in vegetables, fruits, nuts, whole grains, and legumes; have low to moderate amounts of fish, poultry, eggs, and low-fat dairy; and limit red and processed meats, added sugars, and refined carbohydrates [2,3]. Although results vary depending on the different parameters and dietary patterns compared, it has been estimated that shifting towards diets featuring these characteristics could allow a risk reduction for type 2 diabetes by 21%, cardiovascular disease by 15%, and cancer by 14% [4]. A review also estimated that the adoption of a dietary pattern mostly based on plant-based foods may decrease diet-related land use, greenhouse gas emissions, green water use, and blue water up to 76%, 49%, 21%, and 14%, respectively [5].
Despite food systems having achieved many positive results so far, including keeping up with a growing global population, offering a wide choice of foods to consumers, meliorating some forms of malnutrition, and reducing poverty, the sustainability of current production and consumption patterns also raise several major concerns [6]. The reciprocal interaction between environmental footprints, dietary patterns, and food systems may exacerbate bioavailability, nutrient composition, and food production, leading to environmental, nutritional, and economic consequences [7]. On the other hand, food systems play a critical role in shaping human health and environmental sustainability since they involve all actors and activities connected to producing, processing, distributing, consuming, and disposing of food products [8]. Particularly during distribution and consumption, the role of food catering services in the shift to more health-conscious and sustainable food systems is of interest [9]. Catering services are categorized into commercial catering and institutional catering. Commercial catering includes establishments such as restaurants, fast-food chain outlets, and cafés, while institutional catering serves canteens of institutions such as factories, hospitals, schools, and nursing homes [10,11]. In 2024, the global market size of institutional catering was valued at USD 543.14 billion, and it is projected to grow in the next years [12].
In Europe, the institutional sector has the highest purchase volume of food services, with health/welfare being responsible for 42.7% of total meals served, followed by education at 31.4%, and business and industry at 17.8% [13]. Moreover, the contract catering sector in Europe produces an annual turnover that reaches €25 billion, with a workforce of roughly 600,000 people delivering about 6 billion meals per year to employees, public servants, students, hospital patients and nursing home residents [14]. Considering the sector’s large size and economic value, data on the types and nutritional composition of the food served within catering services cannot be overlooked, as these services can shape the public’s dietary habits by improving access to and availability of sustainable healthy diets [15,16]. In this regard, institutional canteens represent a crucial setting for promoting healthy and sustainable eating habits, as they constitute a major component of the organizational food environment [17,18]. Indeed, they provide a substantial proportion of meals consumed out-of-home, particularly in schools, workplaces, hospitals, and universities, where daily eating routines are largely shaped by menu availability and food service practices [19,20,21]. Because of their structured nature and centralized procurement systems, canteens offer unique opportunities to implement and evaluate nutritional and environmental interventions at a large scale [22]. At the same time, besides influencing the dietary behaviors of individuals, institutional catering can affect the entire food supply chains and purchasing standards, thus fostering sustainability transitions within the food system [23,24,25].
Previous studies have aimed to analyze the nutritional and environmental impact of menus and meals in canteens. However, they mostly focused on either one aspect or the other, were limited to a specific country, or were conducted within a particular institution.
Given the current limited understanding of the nutritional quality and environmental impact of canteen menus and meals within the institutional catering system, the present scoping review aimed to fill this gap by mapping and analyzing existing evidence across various institutional settings. The review also examined differences across various settings and population groups.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
This scoping review was conducted following the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) methodology for scoping reviews. The research question was formulated using the PCC (Population, Concept, Context) framework, where the Population included users of institutional canteens (e.g., students, employees, patients, residents in nursing homes) worldwide; the Concept focused on studies evaluating the nutritional quality and/or environmental impact of canteen menus and meals; and the Context referred to institutional catering systems across different settings. Accordingly, the research question was: “What is the current evidence on the nutritional quality and environmental impact of meals provided in institutional canteens worldwide?” After identifying the research question, a literature search was performed using PubMed and Scopus databases [26,27]. Within the search strategy, research terms were incorporated within carefully crafted search syntaxes. These included the following terms: (canteen* OR school* OR hospital* OR nursing home OR “center* OR care home OR institut* OR cafeteria* OR food court OR universit*) AND (meal* OR lunch* OR menu OR menus) AND (diet* OR food* OR nutrition* OR environment* OR sustain*) AND (consum* OR optim* OR impact* OR intak*). Syntaxes were properly adapted for each database. Additional citations were also sought by examining reference lists of selected articles. The search was limited to the period from 2013 to 2025 in order to focus on the most recent and relevant evidence and to capture contemporary research on the nutritional quality and environmental impact of meals provided in institutional canteens. The search was conducted in November 2023 and updated in October 2025 to ensure the review incorporates the latest available evidence.
The literature identification process was conducted in compliance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement [28] and the PRISMA checklist can be found in Supplementary Table S1. Since scoping reviews are not currently eligible for registration on PROSPERO [29], neither the present review nor the protocol was registered prior to data extraction and analysis.
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
In this review, articles were included if they were quantitative research articles that presented quantitative data considering nutritional quality and/or environmental impact of menus and meals served in institutional canteens. These articles had to be in English and peer-reviewed, and be based on studies conducted in different institutions such as schools, nursing homes, hospitals, etc. The following types of articles were excluded: non-English articles, qualitative research, articles that did not examine actual served menus and meals (e.g., examined theoretical menus), school initiatives that occurred outside of the school year (e.g., summer vacations), interventions that only involved specific diets (e.g., therapeutic diets), studies that examined menus/meals of private restaurants not associated with public institutions, studies that evaluated only one nutrient, articles without a methodology section, or studies that were published before 2013. There were no exclusion criteria based on the country of the study.
2.3. Study Selection and Data Extraction
First, articles were collected through electronic databases and reference lists and then exported to an Excel spreadsheet (Microsoft Excel, version 2410). Duplicates were then detected and deleted. Subsequently, articles were screened for titles and abstracts. Finally, the full text of the selected articles was screened to assess their eligibility. Two authors (L.C. and M.T.) independently reviewed the titles, abstracts, and full texts of eligible studies. When conflicts arose between the authors regarding the eligibility of certain articles, a third independent reviewer (D.M.) was consulted to reach an agreement.
The extracted data included publication year, country and setting of the study, study design, whether it involved menus or meals, meal types (breakfast, lunch, dinner, full-day, half-day), whether it involved a nutritional evaluation and/or an environmental evaluation, and the nutritional and environmental components it considered. In this review, analyses including meals collected over five or more consecutive days were considered representative of a “menu,” to distinguish them from studies assessing single meals. Conclusions regarding nutritional and environmental adequacy were also extracted. A study was considered to have evaluated adequacy only if it both mentioned and discussed the differences between its results regarding the served menus or meals and the reference recommendations.
3. Results and Discussion
The PRISMA flow diagram that describes the screening and selection process is shown in Figure 1. A total of 13,316 studies were retrieved from PubMed and Scopus, of which 4153 were duplicates. Out of the 9163 articles that remained, 8777 were excluded based on their title or abstract. After that, 386 articles were sought for retrieval, but 9 articles could not be accessed. Of the 377 articles that were evaluated, 270 articles were excluded according to the exclusion criteria. Overall, a total of 107 articles were included in this review.
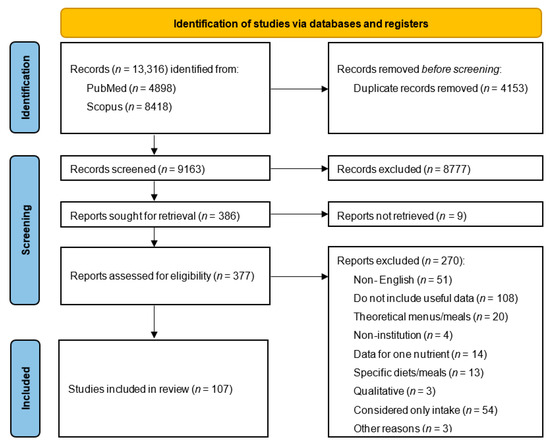
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow chart describing the identification, screening, and selecting process of the included studies (n = 107).
3.1. Geographical Distribution
Figure 2 depicts a geographical distribution of the included studies. They were conducted in over 37 countries, with those conducted in the United States of America being the most common (n = 19), followed by Italy and Spain (n = 9 each), and Brazil and the UK (n = 8 each). The analysis revealed that 93% of the studies (n = 100) were conducted in countries of high-income or upper-middle-income according to income classifications by the World Bank [30]. These findings are in line with a recent scoping review on environmental footprints in food services, in which all the studies included were classified as high- or upper-middle-income countries [31]. Despite the influence of globalization, which is often linked to economic, political, social, and cultural standardization across countries [32,33], food environments still differ greatly between those of high income and low-middle income [34]. Therefore, the lack of consideration for low or lower-middle income countries in research can limit the generalizability to these countries. It may also introduce biases that should be considered when developing interventions aimed at fostering the implementation of sustainable healthy menus.
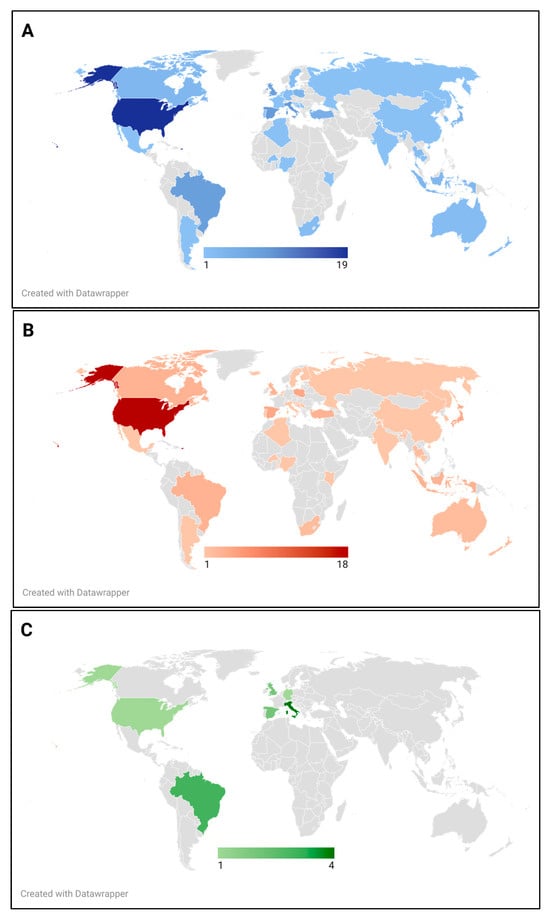
Figure 2.
Geographical distribution of (A) all studies included, (B) studies on nutritional quality, (C) studies on environmental impact. Lighter colors indicate fewer available studies, while darker colors represent a greater number of studies per country.
3.2. Setting Distribution
Regarding the setting of the study, most of the studies included in this review were conducted in schools (37%) or nurseries (21%), as shown in Table 1, which presents the characteristics of the included studies. The commonality of these settings as targets of research may be due to the association between early nutrition and health. Research has shown that a poor diet during childhood may lead to obesity and NCDs in adulthood [35,36,37,38]. Therefore, ensuring that children have access to adequate and sustainable diets may promote optimal growth and development, and can reduce the risk of malnutrition later in life. It is important to note that there was a clear variation within the settings. For example, among the 38 studies that were conducted in schools, 20 were conducted in elementary/primary schools, 3 in elementary and middle schools, 3 in middle schools, and 3 in preschool and primary school. Additionally, 2 studies were conducted in boarding high schools, 3 were conducted in full school districts, 1 combined nursery, primary and secondary schools, 2 combined nursery, preschool, elementary, secondary, young adults, and adult education, and 4 did not specify the type of school. This variation across settings reflects a variation in the needs and wants of target populations as well.

Table 1.
Characteristics of included studies.
3.3. Research Trends
Regarding the design of the studies, the most common types were observational studies (n = 91), of which 92% were cross-sectional and 8% were longitudinal (Table 1).
Out of the 107 studies included in the present review, 76 focused only on nutritional quality, 13 focused only on environmental impact, and 18 focused on both nutritional quality and environmental impact (Table 1). These results indicated a higher interest in the nutritional evaluation of menus and meals in comparison to their environmental evaluation. Moreover, as shown in Figure 3, an analysis of the publication trend between 2013 and 2025 showed a brief shift in research interest, with the focus on EI and the combination of NQ and EI being observed in the later years of the review’s specified period, despite the periodic decrease in attention noted in EI every few years (2015, 2019, and 2023). Research that focused on NQ was consistent throughout the years, with a higher percentage of NQ publications (67–100% of publications per year) being published every year in comparison to those focusing on NQ and EI combined, and only EI. The exception was 2025, where the number of studies that focused on both NQ and EI was higher than the number of those that focused solely on NQ (Figure 3). The publication pattern and the generally higher number of NQ studies across the years could have stemmed from nutrition being a more consolidated research field and the major role it has played in food policy throughout history [44,45]. Only recently, due to the alarming climate change levels and concerns about food waste, as well as efforts to ensure sustainable development, environmental footprint research has gained and is continuing to gain popularity [46,47]. In fact, the use of environmental footprints as a method of environmental sustainability assessment is relatively recent, as it was labeled a new indicator only about 10 years ago [48]. Moreover, the rise of international frameworks, such as the Paris Agreement and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, has emphasized reducing environmental impact and the importance of sustainable food systems [49,50]. These frameworks, along with others, may have also contributed to shifting the scientific community’s focus towards environmental sustainability.
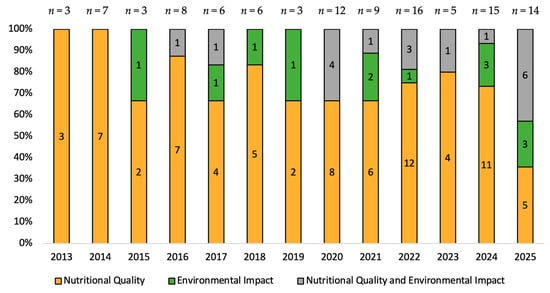
Figure 3.
Distribution of publications across the years (2013–2025).
3.4. Assessment of Nutritional and Environmental Components
The studies in this review varied greatly in the nutritional and environmental components they measured. Table 2 lists the different nutritional and environmental components considered within the articles. Considering the studies that assessed nutritional quality, the number of studies evaluating each nutritional component (energy, protein, carbohydrate, fat, and vitamins and minerals) was similar, ranging from 80 to 89 studies. Among the vitamins and minerals, the most considered were iron (n = 62), salt/sodium (n = 61), calcium (n = 61), vitamin A (n = 55), vitamin C (n = 52), and zinc (n = 41). Fiber was also commonly mentioned, as it appeared in 64 studies.
Concerning the different environmental components, there was a clear variation in the number of studies that evaluated them. Of the 31 studies that considered environmental evaluations (13 on EI and 18 on both NQ and EI), 10 studies assessed GHG emissions among other components, while 17 studies (55%) assessed only GHG emissions. Fewer studies considered water use (n = 14), land use (n = 2), and energy use (n = 3) (Table 2). The high research interest in GHG emissions noted in the present study may be due to their role in driving an unprecedented global rise in temperatures (up to 1.1 °C) since the late 19th [51,52]. Another reason for the higher focus on GHG emissions compared to other environmental indices may be that GHGs are well mixed in the atmosphere. This means that the amount of GHGs measured in the atmosphere is roughly similar all over the world, regardless of the source of the emissions [53]. In contrast, water use, energy use, and land use are more affected by region and supply, therefore greatly differ from one area to another [54,55,56,57]. This makes it harder to compare these markers globally and may contribute to them being less studied in comparison to GHG emissions. Another reason for the greater focus on GHG emissions could be the high availability of data. The SU-EATABLE LIFE Database, which compiles carbon and water footprint values of food commodities from peer-reviewed articles and grey literature, included a total of 3349 carbon footprint values from 841 publications and 937 water footprint values from 88 publications [58]. Overall, more data is available for carbon footprint than water footprint. This difference in the availability of data may have pushed researchers to conduct more research on one environmental footprint indicator than the other, which may explain the emphasis on GHG emissions. More details regarding the macronutrients, micronutrients, and indicators of environmental impact evaluated in each article, along with their units, are provided in Supplementary Table S2.

Table 2.
Nutritional and environmental components evaluated within the included studies.
Table 2.
Nutritional and environmental components evaluated within the included studies.
| Author | Year | Nutritional Quality Components | Environmental Impact Components | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | Protein | Carbohydrate | Fat | Vitamins & Minerals | Nutritional Adequacy | GHG Emission | Water Use | Land Use | Energy Use | ||
| Adiyan et al. [41] | 2025 | x | x | x | x | - | - | x | x | - | - |
| Andersen et al. [59] | 2025 | x | x | x | x | x | - | ||||
| Barcina-Perez et al. [60] | 2023 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Batista and Diaz [61] | 2024 | - | x | - | - | ||||||
| Biasini et al. [62] | 2024 | x | x | x | x | x | - | ||||
| Blondin et al. [63] | 2020 | x | x | x | x | x | - | ||||
| Boronowski et al. [64] | 2025 | x | - | - | - | ||||||
| Boutata et al. [65] | 2024 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Buckinx et al. [66] | 2017 | x | x | x | x | - | x | ||||
| Bux et al. [43] | 2025 | x | - | - | - | ||||||
| Chapman et al. [67] | 2022 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Cohen et al. [68] | 2021 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Colombo et al. [69] | 2020 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | - | - | - |
| Compaoré et al. [70] | 2024 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Conti et al. [71] | 2024 | x | - | - | - | ||||||
| Cummings et al. [72] | 2014 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Dahmani et al. [73] | 2022 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | - | - | - |
| Deagan and Lawson [74] | 2024 | x | x | - | - | - | - | ||||
| De Laurentiis et al. [75] | 2017 | x | x | - | - | ||||||
| de Oliveira et al. [76] | 2022 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| De Seymour et al. [77] | 2022 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Đermanović et al. [78] | 2016 | - | - | - | - | x | x | ||||
| Dixon et al. [79] | 2016 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Doorduijn et al. [80] | 2016 | x | x | - | - | - | x | ||||
| Elinder et al. [81] | 2020 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | - | - | - |
| Everitt et al. [82] | 2020 | x | - | - | - | x | x | ||||
| Farapti et al. [83] | 2023 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Fitriani and Sulistiyani [84] | 2024 | x | x | x | x | - | x | ||||
| Flynn et al. [85] | 2025 | x | - | - | - | ||||||
| Frampton et al. [86] | 2014 | - | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Gajdoš Kljusuri et al. [87] | 2016 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| González-García et al. [88] 1 | 2020 | x | x | x | x | x | - | x | x | - | x |
| González-García et al. [89] | 2021 | x | x | - | - | ||||||
| Harrison et al. [90] | 2024 | x | - | - | - | ||||||
| Hassan et al. [91] | 2025 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Hatjiathanassiadou et al. [92] | 2019 | - | x | - | - | ||||||
| Holliday et al. [93] | 2021 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Imamura et al. [94] | 2024 | x | x | - | - | x | - | ||||
| Jaworowski et al. [95] | 2018 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Jindrich et al. [96] | 2022 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Jiyana and Ncube [97] | 2025 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Joyce et al. [98] | 2018 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Joyce et al. [99] | 2020 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Juniusdottir et al. [100] | 2018 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Kaiser et al. [101] | 2022 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Kesa and Onyenweaku [102] | 2024 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Kilian et al. [103] | 2021 | - | x | - | - | ||||||
| Kluczkovski et al. [39] | 2022 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | - | - | - |
| Knight et al. [104] | 2014 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Kuruvilla et al. [105] | 2021 | x | x | - | x | x | x | ||||
| Lavall et al. [106] | 2020 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Lavriša et al. [107] | 2024 | x | x | x | x | - | x | ||||
| Lazarevic et al. [108] | 2014 | x | x | x | x | - | x | ||||
| Leão et al. [109] | 2018 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Lin et al. [110] | 2024 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Lir et al. [111] | 2020 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Lizuka et al. [112] | 2022 | x | x | x | x | x | - | ||||
| Makurat et al. [113] | 2017 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Martinez-Perez et al. [114] | 2025 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | - | - | - |
| Martins et al. [115] | 2021 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Mendes et al. [116] | 2025 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Menis et al. [117] | 2024 | x | x | x | x | - | - | x | x | - | - |
| Mistretta et al. [10] 2 | 2018 | x | - | - | x | ||||||
| Mizéhoun-Adissoda et al. [118] | 2022 | - | - | - | - | x | x | ||||
| Moran et al. [119] | 2015 | x | - | - | x | x | x | ||||
| Moyano et al. [120] | 2020 | x | - | x | x | x | - | ||||
| Myszkowska-Ryciak and Harton [121] | 2018 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Myszkowska-Ryciak and Harton [122] | 2019 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Nanayakkara et al. [123] | 2019 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Neelon et al. [124] | 2013 | x | x | x | x | - | x | ||||
| Nicklas et al. [125] | 2013 | x | x | x | x | - | x | ||||
| Nogueira et al. [126] | 2020 | x | x | x | x | x | x | - | x | - | - |
| Okuda et al. [127] | 2024 | - | - | - | - | x | - | ||||
| Ongan et al. [128] | 2014 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Pepito et al. [129] | 2022 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Petchoo et al. [130] | 2022 | x | x | x | x | - | x | ||||
| Poličnik et al. [131] | 2021 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Pörtner et al. [132] 2 | 2025 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | - |
| Poulter et al. [133] | 2024 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Rasbold et al. [134] | 2016 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Retondario et al. [135] | 2016 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Rodríguez-Rejón et al. [136] | 2017 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Rosi et al. [42] | 2022 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | - |
| Rossi et al. [137] | 2021 | x | x | x | x | x | - | x | - | - | - |
| Sahin and Caferoglu [138] | 2022 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Sakai et al. [139] | 2022 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Sato et al. [140] | 2025 | x | x | x | x | x | - | ||||
| Seiquer et al. [141] | 2016 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Serrem et al. [142] | 2020 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Shin [143] | 2014 | - | - | - | - | x | x | ||||
| Simon et al. [40] | 2023 | x | x | - | x | - | - | x | - | - | x |
| Sossen et al. [144] | 2021 | x | x | - | - | - | x | ||||
| Stanikowski et al. [145] | 2020 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Takacs et al. [146] 2 | 2025 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | - | - |
| Trafalska [147] | 2014 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Trang et al. [148] | 2015 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Turner-McGrievy et al. [149] | 2013 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Vici et al. [150] | 2025 | x | x | x | x | - | - | x | x | - | - |
| Vidal et al. [151] | 2015 | x | - | - | - | ||||||
| Volanti et al. [152] | 2022 | x | - | - | - | ||||||
| Vucea et al. [153] | 2017 | x | x | x | - | x | x | ||||
| Wall and Pearce [154] | 2023 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Wickramasinghe et al. [155] | 2016 | x | - | - | - | x | x | x | - | - | - |
| Wickramasinghe et al. [156] | 2017 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | - | - | - |
| Wungrath et al. [157] | 2022 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Yesildemir [158] | 2025 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | - | - |
| Zailani et al. [159] | 2023 | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||
| Total | 89 | 86 | 81 | 83 | 80 | 79 | 27 | 14 | 2 | 3 | |
Articles are marked with an “x” in the column of “Nutritional Adequacy” only if they both mentioned and discussed the differences in nutritional adequacy. 1 The study included the recommended values for nutrients but did not provide a clear comparison. 2 These studies included more environmental components, including acidification (kg SO2eq), eutrophication (kg PO43−eq), and photochemical oxidation (kgC2H4eq). Note: GHG: greenhouse gas emissions.
3.5. Assessment of Nutritional and Environmental Adequacy
Regarding Nutritional Adequacy, 79 of the 94 articles that considered nutritional evaluations (76 focusing on NQ and 18 on both NQ and EI) performed a nutritional adequacy assessment. The articles made a comparison with the Dietary Reference Intakes, national dietary guidelines, feeding program standards, or WHO recommendations, while others used indices such as the Healthy Eating Index (HEI) and the Nutrient Rich Food (NRF) index to evaluate nutritional adequacy. Given the differences in the menus and meals evaluated, as well as the guidelines and requirements used among the different studies, nutritional adequacy evaluations varied greatly. However, despite the variation in results, there was a clear trend of menus or meals being nutritionally inadequate. In particular, this inadequacy was due to the insufficient levels of fiber and essential micronutrients such as vitamin D, vitamin E, calcium, and iron, as well as the high levels of sodium. This inadequacy may be partly explained by the limited inclusion of foods that provide fiber and micronutrients (e.g., whole grains, legumes), combined with the frequent presence of high-sodium foods, including refined bread, processed meats, and cheeses, in institutional menus. These issues may be particularly evident in institutional catering settings, where economic constraints, menu standardization, and logistical limitations often restrict the variety and frequency of nutrient-dense foods. Summaries of the nutritional adequacy conclusions of the included studies are presented in Supplementary Table S3.
Among the 31 articles that considered EI, only 5 articles compared their results against clear environmental cut-off values, which is necessary to enable a proper evaluation. Two articles compared their results with the cut-off values suggested by the SU-EATABLE LIFE project led by the Barilla Center for Food and Nutrition. In the first study, the meals showed high carbon emission and water consumption in comparison to the cut-offs [42]. In the second study, the meals offered in two out of three hospital canteens exceeded the carbon emission and the water consumption cut-offs [117]. Two other articles compared their results with the EAT–Lancet planetary boundaries [160]. Boronowsky et al. [64] showed that the calculated average of carbon emissions per meal exceeded the boundary by 3 times across all school districts they evaluated, and Conti et al. [71] reported that 99% of the menus they evaluated in a long-term care facility exceeded the carbon footprint boundary. Finally, one article compared its results with the World Wildlife Fund’s target for school lunches, showing that the baseline diet exceeded the target [81]. Different dietary guidelines and diets can greatly influence EI. For example, Gonzalez et al. summarized a list of articles that demonstrated significant variability of environmental footprint values depending on the dietary guidelines, where carbon footprint values of school lunches ranged from 1.23 to 2.35 kg CO2eq, and water footprint ranged from 680 to 1808 L [89]. This variation, along with the many different factors that are usually considered when calculating different environmental footprints, can only make it more difficult to establish a single universal threshold, which further complicates the assessment of environmental adequacy [161]. It was noted that, to validate their findings, most authors compared their results with baseline levels or different meal scenarios within the same study, evaluated reductions in EI in percentages, or compared results from existing research. Since the environmental impact is mostly assessed through GHG emissions given the methodological and data availability constraints discussed above, this narrow focus overlooks other critical dimensions of sustainability, such as water use, but also land occupation, and effects on biodiversity and thus limits the comprehensiveness and applicability of current findings, particularly in contexts where water scarcity or local ecosystem impacts are major concerns. Moreover, future research should also address food waste generation and management to provide a more comprehensive assessment of the environmental impact of institutional catering. In fact, food loss and waste represents a drain of the embedded environmental footprint and reducing them would directly translate into lower overall emissions and resource use.
The present scoping review has some strengths and limitations worth noting. Among the strengths, to the best of our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive review to explore available data on the nutritional quality and environmental impact of menus and meals within the institutional catering system. A previous scoping review by Guimarães et al. [31] specifically focused on the assessment of carbon and water footprints and the methodologies applied to food services, but did not consider the nutritional aspect, other environmental footprints, or the institutional catering system. In contrast to the review by Guimarães et al. [31], the present review aimed to simultaneously evaluate the availability of data for both the nutritional quality and the environmental impact of menus and meals served in institutional catering. Some findings from Guimarães et al. [31] overlap with those of the present review, particularly regarding mitigation actions such as promoting plant-based dishes and implementing educational interventions. However, our findings also highlight the need for future research to adopt an integrated nutritional and environmental impact assessment, as well as the continued need to improve the nutritional quality of institutional meals, considering the practical challenges of finding a nexus between nutritional adequacy and environmental impact reduction [162,163]. However, the harmonization of environmental impact assessments, including and expanding the use of different indicators, emerges as a key priority also from our results. Among the limitations, the search of this review was restricted to studies published in English. This language restriction may have led to the exclusion of relevant studies such as those conducted in underdeveloped or developing countries, potentially limiting the global representation of the findings. Another limitation of this review is that the menu/meal quality was assessed only in terms of energy and nutrient content. However, quality is a multidimensional concept that goes beyond nutritional composition and includes aspects related to food preparation, cooking and transport methods, meal presentation, and sensory attributes. These aspects were not considered in this review due to the limited and non-standardized nature of the available data. Finally, it is important to acknowledge that the social dimension of sustainability was not addressed in this review. Social sustainability encompasses aspects such as equity, cultural acceptability, fair working conditions, and accessibility of healthy and sustainable meals. Considering these factors in future research would allow for a more holistic assessment of institutional catering systems and support the development of policies that promote not only nutritional and environmental sustainability, but also social equity.
4. Conclusions
The findings of this review indicate that the availability of data is higher for the evaluation of nutritional quality than for environmental footprints, with a consistent trend of inadequacy for specific micronutrients, including vitamin D, vitamin E, calcium, iron, and high sodium content. Environmental analyses remain limited, mostly focusing on GHG emissions, while other critical dimensions such as water use, land use, and energy use are largely unexplored. Broader geographical coverage, particularly through studies conducted in low- and middle-income countries, is also needed to improve generalizability and reflect diverse food systems and resource constraints.
Thus, future research should aim to adopt standardized and comparable indicators for environmental impact assessment, allowing consistent cross-study comparisons and meta-analyses. In this regard, developing a shared repository of studies assessing both nutritional and environmental parameters in institutional meal settings would support data harmonization and comparison. The integration of nutritional and environmental dimensions should become a common practice in institutional menu planning, encouraging nutritionists and canteen managers to jointly design meals that are both nutritionally adequate and environmentally sustainable. In addition to nutritional and environmental dimensions, future research should also consider the social aspects of sustainability, such as equity, cultural acceptability, and accessibility, to provide a truly comprehensive evaluation of institutional catering systems.
This comprehensive approach will provide a more holistic understanding of the nutritional quality and environmental impact of canteen menus in an institutional context, which will facilitate the identification of gaps that need addressing, and foster progress toward sustainable and healthy diets at a global level.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nu17223550/s1, Table S1: PRISMA 2020 checklist; Table S2: Characteristics of the studies evaluating nutritional quality and/or environmental impact of menus or meals in institutional settings; Table S3: Summary of Nutritional Adequacy Conclusions of Menus/Meals served in Included Studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.M. and C.D.B.; methodology, D.M.; validation, M.T. and D.M.; formal analysis, L.C.; investigation, L.C. and M.T.; data curation, L.C. and M.T.; writing—original draft preparation, L.C. and M.T.; writing—review and editing, M.T., P.R., C.D.B. and D.M.; visualization, L.C.; supervision, D.M.; funding acquisition, D.M. and P.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded under the National Recovery and Resilience Plan (NRRP), Mission 4 Component 2 Investment 1.3—Call for tender No. 341 of 15 March 2022 of Italian Ministry of University and Research funded by the European Union—NextGenerationEU; Award Number: Project code PE00000003, Concession Decree No. 1550 of 11 October 2022 adopted by the Italian Ministry of University and Research, CUP D93C22000890001, Project title “ON Foods—Research and innovation network on food and nutrition Sustainability, Safety and Security—Working ON Foods”.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Sustainable Diets and Biodiversity—Directions and Solutions for Policy, Research and Actions. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/i3004e/i3004e00.htm (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Food and Agriculture Organization; World Health Organization. Sustainable Healthy Diets: Guiding Principles. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241516648 (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Li, Y.; He, P.; Shan, Y.; Li, Y.; Hang, Y.; Shao, S.; Ruzzenenti, F.; Hubacek, K. Reducing Climate Change Impacts from the Global Food System through Diet Shifts. Nat. Clim. Change 2024, 14, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Han, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Rimm, E.B.; Hu, F.B.; Sun, Q. Associations between Plant-Based Dietary Patterns and Risks of Type 2 Diabetes, Cardiovascular Disease, Cancer, and Mortality—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutr. J. 2023, 22, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, J.; Cappuccio, F.P. Plant-Based Dietary Patterns for Human and Planetary Health. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agriculture. Sustainable Food Systems in Italy: Policies, Movements and Markets. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/journal/agriculture/special_issues/Sustainable_Food_Systems (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Michel, M.; Eldridge, A.L.; Hartmann, C.; Klassen, P.; Ingram, J.; Meijer, G.W. Benefits and Challenges of Food Processing in the Context of Food Systems, Value Chains and Sustainable Development Goals. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 153, 104703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Sustainable Food Systems Concept and Framework. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/b620989c-407b-4caf-a152-f790f55fec71/content (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Reinders, M.J.; Battjes-Fries, M.C.E.; Bouwman, E.P.; Meeusen–van Onna, M.J.G. Effectively Implementing Healthy and Sustainable Food Practices in Out-of-Home Food Service Locations: The Perspective of the Catering Staff Members. Appetite 2024, 193, 107152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistretta, M.; Caputo, P.; Cellura, M.; Cusenza, M.A. Energy and Environmental Life Cycle Assessment of an Institutional Catering Service: An Italian Case Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.S.A. The Foodservice Industry: Eating out Is More than Just a Meal. Food Qual. Prefer. 2013, 27, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortune Business Insights. Institutional Food Service Market Size, Share & Industry Analysis, by Restaurant Type (Chained and Independent), by Service Type (Dine-In and Takeout), and Regional Forecast, 2025–2032. Available online: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/institutional-food-service-market-113738 (accessed on 16 October 2025).
- Boyano, A.; Espinosa, N.; Quintero, R.; Neto, R. Revision of the EU GPP Criteria for Food Procurement and Catering Services. Available online: https://susproc.jrc.ec.europa.eu/product-bureau/sites/default/files/contentype/product_group_documents/1581683081/EU_GPP_Food_catering_criteria_TR3.0.pdf (accessed on 3 April 2024).
- Food Service Europe. For the Strategic Deployment of Contract in the Aftermath of COVID-19. Available online: https://foodserviceeurope.org/gallery/152/FSE-Call%20to%20Action.pdf (accessed on 3 April 2024).
- Kraak, V.I.; Englund, T.; Misyak, S.; Serrano, E.L. A Novel Marketing Mix and Choice Architecture Framework to Nudge Restaurant Customers toward Healthy Food Environments to Reduce Obesity in the United States. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 852–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, B.A.; Langen, N. Determinants of How Individuals Choose, Eat and Waste: Providing Common Ground to Enhance Sustainable Food Consumption out-of-Home. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2018, 42, 35–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzer, S.; Theurich, M.A.; Mareis, T.; Proebstl, S.; Holliday, N.; Yan, S.; Leibinger, A.; Monsef, I.; Bach, L.; Camargo, D.R.; et al. Promoting Healthy and Sustainable Diets through Food Service Interventions in University Settings: A Scoping Review. BMC Nutr. 2025, 11, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesteiro, E.; García-Carro, A.; Aparicio-Ugarriza, R.; González-Gross, M. Eating out of Home: Influence on Nutrition, Health, and Policies: A Scoping Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Rodrigues, S.S.P.; Correia, D.M.E.; Rei, M.C.C.; Severo, M.; Costa, A.I.A.; Torres, D.P.M.; Lopes, C.M.M. Eating out of Home in Portugal: Characterisation and Effects on Dietary Intake. Br. J. Nutr. 2024, 132, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliarino, E. State School Catering in Italy during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Qualitative Study. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1387100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsen, A.V.; Lassen, A.D.; Andersen, J.S.; Mikkelsen, B.E. Workforce Gender, Company Size and Corporate Financial Support Are Predictors of Availability of Healthy Meals in Danish Worksite Canteens. Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 2068–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasini, B.; Tiboni-Oschilewski, O.; Monica, E.; Deon, V.; Rapetti, V.; Scazzina, F.; Rosi, A. Evaluation of the Potential of Promoting Healthy and Sustainable Food Choices in a Worksite Canteen through an App-Based Intervention. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 76, 634–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, S.S.; Rocha, A.; Viegas, C. Strategies for Increased Adherence to the Mediterranean or Healthy Diet in University Food Services: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 76, 239–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graça, J.; Campos, L.; Guedes, D.; Roque, L.; Brazão, V.; Truninger, M.; Godinho, C. How to Enable Healthier and More Sustainable Food Practices in Collective Meal Contexts: A Scoping Review. Appetite 2023, 187, 106597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcotrigiano, V.; Stingi, G.D.; Nugnes, P.T.; Mancano, S.; Lagreca, V.M.; Tarricone, T.; Salerno, G.; Pasquale, P.; Marchet, P.; Sava, G.A.; et al. Collective Catering Activities and Official Controls: Dietary Promotion, Sustainability and Future Perspectives. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PubMed. Advanced Search Results. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/advanced/ (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- Scopus. Advanced Search. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/search/form.uri?display=advanced (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science. Systematic Reviews, Scoping Reviews & Other Evidence Synthesis Projects. Available online: https://guides.rosalindfranklin.edu/sysreviews/protocols (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- The World Bank. The World by Income and Region. Available online: https://datatopics.worldbank.org/world-development-indicators/the-world-by-income-and-region.html (accessed on 14 October 2024).
- Guimarães, N.S.; Reis, M.G.; Costa, B.V.D.L.; Zandonadi, R.P.; Carrascosa, C.; Teixeira-Lemos, E.; Costa, C.A.; Alturki, H.A.; Raposo, A. Environmental Footprints in Food Services: A Scoping Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Chen, H.; Rong, Z. Environmental Homogenization or Heterogenization? The Effects of Globalization on Carbon Dioxide Emissions, 1970–2014. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas Garciá-Dorado, S.; Cornselsen, L.; Smith, R.; Walls, H. Economic Globalization, Nutrition and Health: A Review of Quantitative Evidence. Glob. Health 2019, 15, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westbury, S.; Ghosh, I.; Jones, H.M.; Mensah, D.; Samuel, F.; Irache, A.; Azhar, N.; Al-Khudairy, L.; Iqbal, R.; Oyebode, O. The Influence of the Urban Food Environment on Diet, Nutrition and Health Outcomes in Low-Income and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Review. BMJ Glob. Health 2021, 6, e006358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, T.L.; Petersen, K.S.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. Early Nutrition and Development of Cardiovascular Disease. In Early Nutrition and Long-Term Health: Mechanisms, Consequences, and Opportunities, 2nd ed.; Saavedra, J.M., Dattilo, A.M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Kidlington, UK, 2022; pp. 309–325. [Google Scholar]
- NCD Child. Children & Non-Communicable Disease: Global Burden Report. 2019. Available online: https://www.ncdchild.org/2019/01/28/children-non-communicable-disease-global-burden-report-2019/ (accessed on 25 October 2024).
- Alves, J.G.B.; Alves, L.V. Early-Life Nutrition and Adult-Life Outcomes. J. Pediatr. 2024, 100, S4–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari-Beni, M. Early Life Nutrition and Non-Communicable Disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1121, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kluczkovski, A.; Menezes, C.A.; Tereza da Silva, J.; Bastos, L.; Lait, R.; Cook, J.; Cruz, B.; Cerqueira, B.; Lago, R.M.R.S.; Gomes, A.N.; et al. An Environmental and Nutritional Evaluation of School Food Menus in Bahia, Brazil That Contribute to Local Public Policy to Promote Sustainability. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, X.; Copena, D.; Pérez-Neira, D. Assessment of the Diet-Environment-Health-Cost Quadrilemma in Public School Canteens. An LCA Case Study in Galicia (Spain). Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 12543–12567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiyan, N.N.; Beyhan, Y.; Dayi, T. Evaluation of the Carbon Footprint, Water Footprint, Nutrient Profiles and Cost of Sustainable Menus Planned with Digital Modeling. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e70977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, A.; Biasini, B.; Monica, E.; Rapetti, V.; Deon, V.; Scazzina, F. Nutritional Composition and Environmental Impact of Meals Selected in Workplace Canteens before and after an Intervention Promoting the Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bux, C.; Zizzo, G.; Roe, B.E.; Amicarelli, V. A Comparative Assessment of Food Waste and Carbon Footprint toward a More Sustainable Healthcare Foodservice. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 495, 145102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byerlee, D.; Fanzo, J. The SDG of Zero Hunger 75 years on: Turning Full Circle on Agriculture and Nutrition. Glob. Food Secur. 2019, 21, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkovich, M. Feeding the Hungry: Advocacy and Blame in the Global Fight Against Hunger; Cornell University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia, L.; Jha, H.; Sarkar, T.; Sarangi, P.K. Food Waste Utilization for Reducing Carbon Footprints towards Sustainable and Cleaner Environment: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohli, K.; Prajapati, R.; Shah, R.; Das, M.; Sharma, B.K. Food Waste: Environmental Impact and Possible Solutions. Sustain. Food Technol. 2024, 2, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simion, I.M.; Ghinea, C.; Maxineasa, S.G.; Taranu, N.; Bonoli, A.; Gavrilescu, M. Ecological Footprint Applied in the Assessment of Construction and Demolition Waste Integrated Management. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2013, 12, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Climate Change. The Paris Agreement. Available online: https://unfccc.int/process-and-meetings/the-paris-agreement (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- United Nations: Department of Economic and Social Affairs. The 17 Goals. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/resources/climate-change-in-data/ (accessed on 25 October 2024).
- Xu, Z.; Sun, D.W.; Zeng, X.A.; Liu, D.; Pu, H. Research Developments in Methods to Reduce the Carbon Footprint of the Food System: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 1270–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Overview of Greenhouse Gases. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/overview-greenhouse-gases (accessed on 25 November 2024).
- Water Footprint Network. Frequently Asked Questions. Available online: https://www.waterfootprint.org/water-footprint-2/frequently-asked-questions/ (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Land Use. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/report-environment/land-use (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Elliott, R.J.R.; Sun, P.; Zhu, T. Energy Abundance, the Geographical Distribution of Manufacturing, and International Trade. Rev. World Econ. 2024, 160, 1361–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, S.; Fischer, A.; Lechtenböhmer, S. The Renewables Pull Effect: How Regional Differences in Renewable Energy Costs Could Influence Where Industrial Production is Located in the Future. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2023, 104, 103257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersson, T.; Secondi, L.; Magnani, A.; Antonelli, M.; Dembska, K.; Valentini, R.; Varotto, A.; Castaldi, S. A Multilevel Carbon and Water Footprint Dataset of Food Commodities. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, C.J.; Murray, K.; Gaito, A.; Dupree, L.; Cintrón-Rivera, L. Nutritional Quality of University Dining Options Varies by Location, Level of Convenience, and Accessibility: Pilot Study Perspectives on Assessing University Food Environments. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025, 22, 102057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcina-Pérez, P.; Lucas-Abellán, C.; Abellán-Aynés, O.; Mercader-Ros, M.T.; Victoria-Montesinos, D.; Hernández-Sánchez, P.; Serrano-Martínez, A. Assessment of Nutrient Levels Provided by General Hospital Patient Menus: A Cross-Sectional Study Carried Out in the Region of Murcia (Spain). Healthcare 2023, 11, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jesus Silva Batista, M.; Dias, G.P. Food and Sustainability: The Water Footprint Assessment of the Menus Served in a University Restaurant. Sustain. Debate 2024, 15, 294–324. [Google Scholar]
- Biasini, B.; Donati, M.; Rosi, A.; Giopp, F.; Colić Barić, I.; Bituh, M.; Brečić, R.; Brennan, M.; Ilić, A.; Quarrie, S.; et al. Nutritional, Environmental and Economic Implications of Children Plate Waste at School: A Comparison between Two Italian Case Studies. Public Health Nutr. 2024, 27, e143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondin, S.A.; Cash, S.B.; Griffin, T.S.; Goldberg, J.P.; Economos, C.D. Meatless Monday National School Meal Program Evaluation: Impact on Nutrition, Cost, and Sustainability. J. Hunger. Environ. Nutr. 2022, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boronowsky, R.; Lin-Yang, K.; Natanson, L.; Presley, K.; Reddy, Y.; Shenkiryk, A.; Wang, M.; Slusser, W.; Koch, P.A.; Cleveland, D.A.; et al. The Carbon Footprint of School Lunch: Moving Toward a Healthy and Sustainable Future for the Next Generation. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutata, F.Z.; Sersar, I.; Bencharif, M. Algerian Initiative Guidelines on Hospital Nutrition. Nutr. Clin. Metab. 2024, 38, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckinx, F.; Allepaerts, S.; Paquot, N.; Reginster, J.Y.; de Cock, C.; Petermans, J.; Bruyère, O. Energy and Nutrient Content of Food Served and Consumed by Nursing Home Residents. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2017, 21, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, L.E.; Richardson, S.; Harb, A.A.; Fear, E.; Daly, T.P.; Olarte, D.A.; Hawley, M.; Zukowski, E.; Schwartz, C.; Maroney, M.; et al. Nutrient Content and Compliance with Sodium Standards in Elementary School Meals in the United States Pre- and Post-COVID-19. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.F.W.; Richardson, S.; Roberto, C.A.; Rimm, E.B. Availability of Lower-Sodium School Lunches and the Association with Selection and Consumption among Elementary and Middle School Students. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2021, 121, 105–111.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustachio Colombo, P.; Patterson, E.; Lindroos, A.K.; Parlesak, A.; Elinder, L.S. Sustainable and Acceptable School Meals through Optimization Analysis: An Intervention Study. Nutr. J. 2020, 19, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compaoré, E.W.R.; Ouédraogo, O.; Souho, T.; Bengaly, M.D.; Simporé, M.P.; Dicko, M.H. Analysis of the Nutritional Composition and Organization of School Meals in the Province of Kadiogo in Burkina Faso: Challenges and Prospects. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1309730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, A.; Opizzi, A.; Binala, J.G.; Cortese, L.; Barone-Adesi, F.; Panella, M. Evaluation of the Climate Impact and Nutritional Quality of Menus in an Italian Long-Term Care Facility. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, P.L.; Welch, S.B.; Mason, M.; Burbage, L.; Kwon, S.; Kuo, T. Nutrient Content of School Meals before and after Implementation of Nutrition Recommendations in Five School Districts across Two U.S. Counties. Prev. Med. 2014, 67, S21–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dahmani, J.; Nicklaus, S.; Grenier, J.M.; Marty, L. Nutritional Quality and Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Vegetarian and Non-Vegetarian Primary School Meals: A Case Study in Dijon, France. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 997144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deagan, C.; Lawson, N. Using a Pictorial Menu in Hospital Enhances Patient Satisfaction Without Improving Nutritional Intake or Plate Waste: A Pre-Post Mixed-Methods Pilot Study. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2025, 38, e70062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Laurentiis, V.; Hunt, D.V.L.; Rogers, C.D.F. Contribution of School Meals to Climate Change and Water Use in England. Energy Procedia 2017, 123, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, E.C.V.; Madruga, F.P.; Retondario, A.; Jagher, A.; de Oliveira, P.D.P.; Alves, R.C.; Almeida, C.C.B.; Cerqueira, M.M.O. de School Food in Child Daycare Centers: Poor in Macro and Micronutrients. Clin. Nutr. Open Sci. 2022, 43, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Seymour, J.; Stollenwerk Cavallaro, A.; Wharemate-Keung, L.; Ching, S.; Jackson, J. Nutrient-Level Evaluation of Meals Provided on the Government-Funded School Lunch Program in New Zealand. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đermanović, M.; Miletić, I.; Pavlović, Z. A Comparative Analysis of the Contents of Iron, Zinc, Copper, Manganese, and Calcium in the Collective Diet Of Preschool Children in the Northwestern Region of Bosnia. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 175, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, L.B.; Breck, A.; Kettel Khan, L. Comparison of Children’s Food and Beverage Intakes with National Recommendations in New York City Child-Care Centres. Public Health Nutr. 2016, 19, 2451–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorduijn, A.S.; van Gameren, Y.; Vasse, E.; de Roos, N.M. At Your Request Room Service Dining Improves Patient Satisfac-tion, Maintains Nutritional Status, and Offers Opportunities to Improve Intake. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 1174–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elinder, L.S.; Colombo, P.E.; Patterson, E.; Parlesak, A.; Lindroos, A.K. Successful Implementation of Climate-Friendly, Nu-tritious, and Acceptable School Meals in Practice: The OPTIMATTM Intervention Study. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everitt, T.; Engler-Stringer, R.; Martin, W.; Vatanparast, H. Comparing Diet Quality of School Meals versus Food Brought from Home. Can. J. Diet. Pract. Res. 2020, 81, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farapti, F.; Wangi, M.P.; Adiningsih, S. The Assessment of Daily Menus in Nursing Home Residents for Improving Intake and Nutritional Status in Elderly. Amerta Nutr. 2023, 7, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitriani, J.I. Sulistiyani Student Characteristics, Acceptability, and Suitability of Portion Standards with Recommended Dietary Allowance in School Meals at Al Furqan Primary School, Jember Regency. Amerta Nutr. 2024, 8, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, A.N.; Takahashi, T.; Sim, A.; Brunstrom, J.M. Dish Swap across a Weekly Menu Can Deliver Health and Sustainability Gains. Nat. Food 2025, 6, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, A.M.; Sisson, S.B.; Horm, D.; Campbell, J.E.; Lora, K.; Ladner, J.L. What’s for Lunch? An Analysis of Lunch Menus in 83 Urban and Rural Oklahoma Child-Care Centers Providing All-Day Care to Preschool Children. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 114, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdoš Kljusurić, J.; Bosanac, V.; Šanko, K.; Colić Barić, I. Establishing Energy-Nutritional Variety of Boarding School Daily Menus as a Result of Regional Differences Using Multivariate Analysis. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016, 51, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-García, S.; González-García, R.; González Vázquez, L.; Moreira, M.T.; Leis, R. Tracking the Environmental Footprints of Institutional Restaurant Service in Nursery Schools. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-García, S.; Esteve-Llorens, X.; González-García, R.; González, L.; Feijoo, G.; Moreira, M.T.; Leis, R. Environmental Assessment of Menus for Toddlers Serviced at Nursery Canteen Following the Atlantic Diet Recommendations. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 145342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, L.; Herrmann, A.; Quitmann, C.; Stieglbauer, G.; Zeitz, C.; Franke, B.; Danquah, I. Effects of a Cafeteria-Based Sustainable Diet Intervention on the Adherence to the EAT-Lancet Planetary Health Diet and Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Consumers: A Quasi-Experimental Study at a Large German Hospital. Nutr. J. 2024, 23, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.F.; Malli, D.; Antar, E.; Khattar, M.; Badereddine, N.; Fattouh, F.; El Cheikh Mohamad, J.; Khatib, S.E.; Abiad, M.; Hoteit, M. Evaluating Adherence of Hospital Meals to Mediterranean Diet: The Case of a Developing Country. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2025, 44, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatjiathanassiadou, M.; de Souza, S.R.G.; Nogueira, J.P.; de Medeiros Oliveira, L.; Strasburg, V.J.; Rolim, P.M.; Seabra, L.M.A.J. Environmental Impacts of University Restaurant Menus: A Case Study in Brazil. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holliday, M.K.; Richardson, K.M. Nutrition in Midwestern State Department of Corrections Prisons: A Comparison of Nutritional Offerings with Commonly Utilized Nutritional Standards. J. Correct. Health Care 2021, 27, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, T.; Narang, N.; Kinugawa, K. Validation of Artificial Intelligence-Based Application to Estimate Nutrients in Daily Meals. J. Cardiol. 2025, 85, 424–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworowska, A.; Rotaru, G.; Christides, T. Nutritional Quality of Lunches Served in South East England Hospital Staff Canteens. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindrich, C.; Joyce, J.; Daniels, E.; Procter, S.B.; Sauer, K.; Jindrich, C.; Joyce, J.; Daniels, E.; Procter, S.B.; Sauer, K.; et al. The Nutritional Adequacy and Diet Quality of Vegetarian Menu Substitutions in Urban Kansas Childcare Centers. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiyana, M.J.; Ncube, L.J. Nutrient Composition of Meals Served to Adult Inpatients in Public Hospitals in North West, South Africa. Health SA Gesondheid 2025, 30, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, J.M.; Rosenkranz, R.R.; Rosenkranz, S.K. Variation in Nutritional Quality of School Lunches with Implementation of National School Lunch Program Guidelines. J. Sch. Health 2018, 88, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, J.M.; Rosenkranz, R.R.; Rosenkranz, S.K. Evaluation of Variability in Dietary Quality of School Lunches Meeting Na-tional School Lunch Program Guidelines by Socioeconomic Status and Rurality. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juniusdottir, R.; Hörnell, A.; Gunnarsdottir, I.; Lagstrom, H.; Waling, M.; Olsson, C.; Talvia, S.; Olafsdottir, A.S. Composition of School Meals in Sweden, Finland, and Iceland: Official Guidelines and Comparison with Practice and Availability. J. Sch. Health 2018, 88, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, R.; Hamlin, D. The National School Lunch Program and Healthy Eating: An Analysis of Food Selection and Con-sumption in an Urban Title I Middle School. Educ. Urban. Soc. 2022, 56, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesa, H.; Onyenweaku, E. Menu Evaluation versus Health and Well-Being of Children Participating in School Feeding Programmes in South Africa. Int. J. Sch. Health 2024, 11, 2–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kilian, L.; Triches, R.M.; Ruiz, E.N.F. Food and Sustainability at University Restaurants: Analysis of Water Footprint and Consumer Opinion. Sustain. Debate 2021, 12, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, K.B.; Hickey, R.; Aloia, C.R.; Oakley, C.B.; Bomba, A.K. The Use of the USDA Nutrient Analysis Protocol in the Evaluation of Child-Care Menus in North Mississippi. Early Child. Dev. Care 2015, 185, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruvilla, A.; Panchasara, K.; Panchal, N. Improving Maternal Nutrition in Public Health Facilities by Strengthening the Dietary Component of Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram—A Government of India Programme. Malays. J. Nutr. 2021, 27, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavall, M.J.; Blesa, J.; Frigola, A.; Esteve, M.J. Nutritional Assessment of the School Menus Offered in Spain’s Mediterranean Area. Nutrition 2020, 78, 110872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavriša, Ž.; Pravst, I.; Krušič, S.; Hren, N.; Gregorič, N.; Hren, I.; Koroušić Seljak, B.; Hristov, H. Nutrition among Nursing Home Residents: Results from the NutriCare Study. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1423658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarevic, K.; Stojanovic, D.; Bogdanović, D. Energy and nutritional value of the meals in kindergartens in Nis (Serbia). Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 2014, 65, 127–131. [Google Scholar]
- Leão, P.V.; Dias, R.M.; Das Graças Ferreira Frazão, A.; Dias, I.A.; Da Silva, I.R.P.; Corrêa, N.A.F.; Cavalcanti, C.D.T.D. Nutri-tional Analysis of the School Feeding Program Menus Offered in a Municipality of Pará. Mundo Saúde 2018, 42, 181–198. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Lv, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; He, L.; Wang, Z. Quality and Quantity of School Lunch in Nanjing: Based on Data from the Sunshine Restaurant Supervision Platform. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lir, D.N.; Perevalov, A.Y.; Tapeshkina, N.V.; Sherstobitova, A.V.; Misharina, E.A. Analyzing Nutrition Rations at Pre-School Children Facilities in a Large Industrial City in Russia. Health Risk Anal. 2020, 1, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, K.; Ishihara, T.; Watanabe, M.; Ito, A.; Sarai, M.; Miyahara, R.; Suzuki, A.; Saitoh, E.; Sasaki, H. Nutritional Assessment of Hospital Meals by Food-Recording Applications. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makurat, J.; Pillai, A.; Wieringa, F.T.; Chamnan, C.; Krawinkel, M.B. Estimated Nutritive Value of Low-Price Model Lunch Sets Provided to Garment Workers in Cambodia. Nutrients 2017, 9, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Perez, N.; Barrena-Barbadillo, R.; Irastorza-Terradillos, I. Nutritional and Environmental Assessment of School Meals Served, Consumed and Wasted in Primary Schools in Spain: A Comparison of Public and Charter Schools. Public Health Nutr. 2025, 28, e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liz Martins, M.; Rodrigues, S.S.P.; Cunha, L.M.; Rocha, A. School Lunch Nutritional Adequacy: What Is Served, Consumed and Wasted. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 4277–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, B.; Gunes Bayir, A.; Aksoy, A.S.; Toluk, O. A Retrospective Study: Do Hospital Menus Carry a Risk of Malnutrition? Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e70669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menis, D.; Fiori, F.; Cautero, P.; Zago, D.; Beorchia, Y.; Dallan, L.; Vettorazzo, P.; Lesa, L.; Conte, A.; Scarpis, E.; et al. Sustainability and Nutritional Composition of Food Offer and Choices in Three Hospital Canteens in Italy. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizéhoun-Adissoda, C.; Alouki, K.; Adjobimey, M.; Yémoa, A.; Itiblitse, R.; Alihonou, F.; Aglago, E.K.; Desport, J.C. Nutri-tional and Hygienic Quality of Meals Served in School Canteens in Togo: A Cross-Sectional Study. Food Control 2022, 135, 108680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, A.; Lederer, A.; Johnson Curtis, C. Use of Nutrition Standards to Improve Nutritional Quality of Hospital Patient Meals: Findings from New York City’s Healthy Hospital Food Initiative. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 115, 1847–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyano, D.; Rodriguez, E.R.; Perovic, N.R. An Analysis of Policy Interventions Regarding School Lunch Programs and Their Role in the Healthy Nutrition of Children in Córdoba, Argentina. Salud Colect. 2021, 16, e2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myszkowska-Ryciak, J.; Harton, A. Implementation of Dietary Reference Intake Standards in Preschool Menus in Poland. Nutrients 2018, 10, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myszkowska-Ryciak, J.; Harton, A. Eating Healthy, Growing Healthy: Outcome Evaluation of the Nutrition Education Program Optimizing the Nutritional Value of Preschool Menus, Poland. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayakkara, W.S.; Skidmore, P.; O’Brien, L.; Wilkinson, T.; Frampton, C.; Gearry, R. From Menu to Mouth: The Decay Pathway of Nutrient Intake from Planned Menu to Consumed and Characteristics of Residents in an Aged Care Facility with Greater Nutrient Decay Rates: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e024044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin Neelon, S.E.; Reyes-Morales, H.; Haines, J.; Gillman, M.W.; Taveras, E.M. Nutritional Quality of Foods and Beverages on Child-Care Centre Menus in Mexico. Public Health Nutr. 2013, 16, 2014–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicklas, T.A.; Liu, Y.; Stuff, J.E.; Fisher, J.O.; Mendoza, J.A.; O’Neil, C.E. Characterizing Lunch Meals Served and Consumed by Pre-School Children in Head Start. Public Health Nutr. 2013, 16, 2169–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, J.P.; Hatjiathanassiadou, M.; de Souza, S.R.G.; Strasburg, V.J.; Rolim, P.M.; Seabra, L.M.A.J. Sustainable Perspective in Public Educational Institutions Restaurants: From Foodstuffs Purchase to Meal Offer. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, N.; Higashiyama, A.; Tanno, K.; Yonekura, Y.; Miura, M.; Kuno, H.; Nakajima, T.; Nagahata, T.; Taniguchi, H.; Kosami, K.; et al. Na and K Intake from Lunches Served in a Japanese Company Cafeteria and the Estimated Improvement in the Dietary Na/K Ratio Using Low-Na/K Seasonings and Dairy to Prevent Hypertension. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ongan, D.; Inanc, N.; Cicek, B. Comparing School Lunch and Canteen Foods Consumption of Children in Kayseri, Turkey. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 30, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepito, B.M.; Dawes, J.; Hildebrand, D.; Joyce, J. Analysis of a State Police Academy Menu Cycle for Dietary Quality and Performance Nutrition Adequacy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petchoo, J.; Kaewchutima, N.; Tangsuphoom, N. Nutritional Quality of Lunch Meals and Plate Waste in School Lunch Pro-gramme in Southern Thailand. J. Nutr. Sci. 2022, 11, e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poličnik, R.; Rostohar, K.; Škrjanc, B.; Seljak, B.K.; Blaznik, U.; Farkaš, J. Energy and Nutritional Composition of School Lunches in Slovenia: The Results of a Chemical Analysis in the Framework of the National School Meals Survey. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pörtner, L.M.; Schlenger, L.; Gabrysch, S.; Lambrecht, N.J. Dietary Quality and Environmental Footprint of Health-Care Foodservice: A Quantitative Analysis Using Dietary Indices and Lifecycle Assessment Data. Lancet Planet. Health 2025, 9, 101274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulter, M.; Coe, S.; Graham, C.A.M.; Leach, B.; Tammam, J. Menu Provision in a Young Offenders Institution, Comparison with Dietary Guidelines, and Previous Menu Allocation: A Cross-Sectional Nutritional Analysis. J. Nutr. Sci. 2024, 13, e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasbold, A.H.; Adamiec, R.; Anderson, M.P.; Campbell, J.E.; Horm, D.M.; Sitton, L.K.; Sisson, S.B. Macronutrient and Micro-nutrient Intakes of Children in Oklahoma Child-Care Centres, USA. Public Health Nutr. 2016, 19, 1498–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retondario, A.; Silva, D.L.F.; Salgado, S.M.; De Oliveira Alves, M.A.; Ferreira, S.M.R. Nutritional Composition of School Meals Serving Children from 7 to 36 Months of Age in Municipal Day-Care Centres in the Metropolitan Area of Curitiba, Paraná, Brazil. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 2203–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rejón, A.I.; Ruiz-López, M.D.; Malafarina, V.; Puerta, A.; Zuñiga, A.; Artacho, R. Menus Offered in Long-Term Care Homes: Quality of Meal Service and Nutritional Analysis. Nutr. Hosp. 2017, 34, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, L.; Ferrari, M.; Martone, D.; Benvenuti, L.; De Santis, A. The Promotions of Sustainable Lunch Meals in School Feeding Programs: The Case of Italy. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytekin Sahin, G.; Caferoglu, Z. The Food Service Quality and Its Effects on Nutritional Status in Nursing Home Residents. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 47, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, Y.; Rahayu, Y.Y.S.; Araki, T. Nutritional Value of Canteen Menus and Dietary Habits and Intakes of University Students in Indonesia. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Inagaki, R.; Shimamoto, K.; Tsuji, H. Validating Nutritional Values of Daycare Lunches Using Recipe Calculation Based on Standard Tables of Food Composition in Japan. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 143, 107614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiquer, I.; Haro, A.; Cabrera-Vique, C.; Muñoz-Hoyos, A.; Galdó, G. Nutritional Assessment of the Menus Served in Municipal Nursery Schools in Granada. An. De Pediatría 2016, 85, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrem, K.; Dunay, A.; Serrem, C.; Atubukha, B.; Oláh, J.; Illés, C.B. Paucity of Nutrition Guidelines and Nutrient Quality of Meals Served to Kenyan Boarding High School Students. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D. Analysis of Micromineral Contents of School Meals. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2014, 8, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sossen, L.; Bonham, M.; Porter, J. An Investigation of Recommended Serve Food Portions and Attaining Energy and Protein Requirements in Older Adults Living in Residential Care. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2021, 34, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanikowski, P.; Michalak-majewska, M.; Domagała, D.; Jabłońska-ryś, E.; Sławińska, A. Implementation of Dietary Reference Intake Standards in Prison Menus in Poland. Nutrients 2020, 12, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takacs, B.; Kalea, A.Z.; Borrion, A. Menu Dilemmas: An Integrated Assessment of the Nutritional Quality, Environmental Impact, and Cost of Vegan, Vegetarian, and Meat-Based Versions of Meals. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trafalska, E. Assessing Diets for Energy and Nutrients Content in Nursery School Children from Lodz, Poland. Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 2014, 65, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Trang, S.; Fraser, J.; Wilkinson, L.; Steckham, K.; Oliphant, H.; Fletcher, H.; Tzianetas, R.; Arcand, J. A Multi-Center Assessment of Nutrient Levels and Foods Provided by Hospital Patient Menus. Nutrients 2015, 7, 9256–9264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner-McGrievy, G.M.; Hales, S.B.; Baum, A.C. Transitioning to New Child-Care Nutrition Policies: Nutrient Content of Preschool Menus Differs by Presence of Vegetarian Main Entrée. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 114, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vici, G.; Giustozzi, D.; Camilletti, D.; Zufolino, S.; Malandrino, L.; Renzi, S.; Pucciarelli, S.; Vincenzetti, S.; Belli, L.; Polzonetti, V. An Evaluation and Optimization of Nutrition, Environmental Footprint, and Food Waste in Italian Primary School Menus: A Case Study. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, R.; Moliner, E.; Pikula, A.; Mena-Nieto, A.; Ortega, A. Comparison of the Carbon Footprint of Different Patient Diets in a Spanish Hospital. J. Health Serv. Res. Policy 2015, 20, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volanti, M.; Arfelli, F.; Neri, E.; Saliani, A.; Passarini, F.; Vassura, I.; Cristallo, G. Environmental Impact of Meals: How Big Is the Carbon Footprint in the School Canteens? Foods 2022, 11, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vucea, V.; Keller, H.H.; Morrison, J.M.; Duncan, A.M.; Duizer, L.M.; Carrier, N.; Lengyel, C.O.; Slaughter, S.E. Nutritional Quality of Regular and Pureed Menus in Canadian Long Term Care Homes: An Analysis of the Making the Most of Mealtimes (M3) Project. BMC Nutr. 2017, 3, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, K.K.; Rayner, M.; Goldacre, M.; Townsend, N.; Scarborough, P. Contribution of Healthy and Unhealthy Primary School Meals to Greenhouse Gas Emissions in England: Linking Nutritional Data and Greenhouse Gas Emission Data of Diets. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, C.J.; Pearce, J. Energy and Nutrient Content of School Lunches Provided for Children Attending School-Based Nurseries: A Cross-Sectional Study. Public Health Nutr. 2023, 26, 2641–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, K.; Rayner, M.; Goldacre, M.; Townsend, N.; Scarborough, P. Environmental and Nutrition Impact of Achieving New School Food Plan Recommendations in the Primary School Meals Sector in England. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e013840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wungrath, J.; Yutabootr, S.; Limvilai, T.; Kapheak, K. Nutritional Value of Lunches Served in the Remote Rural Area Child-Care Centers in Chiang Mai, Thailand. Open Public Health J. 2022, 15, e187494452208182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesildemir, O. Energy and Nutritional Content of Lunch Menus in Turkish Universities: The Impact on Ecological Footprint. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e70149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zailani, H.; Owolabi, O.A.; Sallau, A.B. Contribution of School Meals to the Recommended Nutrient and Energy Intake of Children Enrolled in the National Homegrown School Feeding Program in Zaria, Nigeria. Arch. Pédiatrie 2023, 30, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willett, W.; Rockström, J.; Loken, B.; Springmann, M.; Lang, T.; Vermeulen, S.; Garnett, T.; Tilman, D.; DeClerck, F.; Wood, A.; et al. Food in the Anthropocene: The EAT-Lancet Commission on Healthy Diets from Sustainable Food Systems. Lancet 2019, 393, 447–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclaren, S.; Berardy, A.; Henderson, A.; Holden, N.; Huppertz, T.; Jolliet, O.; De Camillis, C.; Renouf, M.; Ru-Gani, B.; Saarinen, M.; et al. Integration of Environment and Nutrition in Life Cycle Assessment of Food Items: Opportunities and Challenges; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Contribution of Terrestrial Animal Source Food to Healthy Diets for Improved Nutrition and Health Outcomes—An Evidence and Policy Overview on the State of Knowledge and Gaps; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Leonard, U.M.; Leydon, C.L.; Arranz, E.; Kiely, M.E. Impact of Consuming an Environmentally Protective Diet on Micronutrients: A Systematic Literature Review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 119, 927–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).