Abstract
In synthetic aperture radar (SAR) maritime target detection tasks, corner reflector targets (CRTs) and their arrays can easily interfere with the accurate detection of ship targets, significantly increasing the misdetection rate and false alarm rate of detectors. Current deep learning-based research on SAR maritime target detection primarily focuses on ship targets, while dedicated detection methods addressing corner reflector interference have not yet established a comprehensive research framework. There remains a lack of theoretical innovation in detection principles for such targets. To address these issues, utilizing the prior knowledge of cross-shaped structures exhibited by marine CRTs in SAR images, we propose an innovative cross-shaped bounding box (CSBB) annotation strategy and design a novel dedicated detection network CSBBNet. The proposed method is constructed through three innovative component modules, namely the cross-shaped spatial feature perception (CSSFP) module, the wavelet cross-shaped attention downsampling (WCSAD) module, and the cross-shaped attention detection head (CSAD-Head). Additionally, to ensure effective training, we propose a cross-shaped intersection over union (CS-IoU) loss function. Comparative experiments with state-of-the-art methods demonstrate that our approach exhibits efficient detection capabilities for CRTs. Ablation experiment results validate the effectiveness of the proposed component architectures.
1. Introduction
Under the macro context of high-quality marine economic growth and the maritime power strategy, radar technology [1,2] demonstrates indispensable scientific merits and application potential. Compared with traditional sea-surface target monitoring methods, synthetic aperture radar (SAR) [3,4] overcomes optical sensors’ dependence on meteorological conditions through its active microwave remote sensing characteristics. In recent years, deep-learning-based maritime target detection technology has made rapid progress. By utilizing high-resolution SAR images [5,6] as input data for deep learning algorithms, researchers have achieved breakthroughs in applications, such as ship target detection and recognition [7], accurate tracing of oil spill pollution [8], and monitoring of illegal fishing activities [9].
Due to the electromagnetic wave reflection-based working principle of radar, the imaging process is susceptible to system noise, environmental clutter, external electromagnetic interference, and strong scatterers. In particular, when a strongly-scattering floating target (SSFT) represented by corner reflectors is illuminated by radar beams, its polyhedral structures generate coupled superposition effects of specular reflection and edge diffraction. This phenomenon arises from the superposition effect of specular reflection and edge diffraction [10], creating structures that closely resemble ship components, including bridges, masts, and shipboards. To simulate the echo characteristics of different ship target types, we construct the diverse corner reflector array targets (CRATs) by manually controlling the placement intervals and quantities of corner reflectors targets (CRTs) [11]. This poses significant challenges for ship target detection tasks. Therefore, how to quickly, accurately, and robustly eliminate interference caused by CRTs on ship target detection tasks is a challenging problem to be solved.
The conventional neural network-based object detection methods mainly regress the target position through horizontal bounding box (HBB) [12,13]. In recent years, in order to achieve a more refined description of the target, researchers have developed oriented bounding box (OBB) detection technology [14,15,16]. The OBB method adjusts the direction of the bounding box by rotating the angle, which can fit the object contour more closely and significantly reduce the overlapping false detection rate.
However, in remote sensing scenarios, particularly for corner reflectors target (CRT) detection tasks, both HBB and OBB methods exhibit significant limitations in key feature extraction and background suppression. Due to the physical characteristics of multi-scattering surface structures, it possesses a stable radar cross-section (RCS) and demonstrates low sensitivity to variations in incident wave direction and polarization states [11]. Consequently, CRTs appear in SAR images as dense distributed features characterized by high intensity and stable morphology (typically cross-shaped bright spots). Specifically, they appear as follows:
- (1)
- HBB encompasses substantial redundant background regions, often introducing side-lobe clutter and interference from adjacent targets. This leads to feature confusion during training and hinders accurate network detection.
- (2)
- The principal axes of CRT cross-shaped patterns remain consistent aligned with coordinate axes in SAR images, rendering OBB rotational degrees of freedom unnecessary. This yields no additional information gain while needlessly increasing model complexity and computational burden.
Thus, existing HBB/OBB methods struggle to effectively adapt to CRT detection requirements, necessitating specialized detection approaches for efficient and robust CRT identification.
In response to the above issues, the main contributions of this manuscript are summarized as follows:
- Leveraging the inherent cross-shaped prior of corner reflectors, a novel bounding box annotation strategy called cross-shaped bounding box (CSBB) is proposed. As illustrated in Figure 1, when two CRTs are spatially adjacent in SAR images, traditional annotation approaches using HBB or OBB inevitably produce ground-truth labels containing substantial background redundancy and coupled features from neighboring targets. In stark contrast, the CSBB format maximally suppresses such interference to guide neural networks to focus on intrinsic target feature extraction during training, enhancing detection robustness. Notably, differing from HBB-based methods (regressing four parameters) and OBB-based methods (regressing five parameters), CSBB requires regression of six spatial parameters to precisely characterize CRTs with distinct cross-shaped features. Although these six parameters substantially enhance spatial representation capability, they also introduce new challenges of higher inter-parameter coupling and increased regression difficulty.
 Figure 1. Differences in the coverage of CRTs features with different types of bounding boxes.
Figure 1. Differences in the coverage of CRTs features with different types of bounding boxes.
- 2.
- We propose a dedicated CRT detection network based on CSBB, naming it CSBBNet. This network directly regresses six parameters in an end-to-end manner using the CSBB strategy and decodes them to form cross-shaped target areas. Such processing significantly reduces mutual interference between features of adjacent targets, thereby improving CRT detection accuracy.
The upper part of Figure 2a shows a typical sea-surface target detection scenario, showing two small ship targets at the right edge and multiple CRATs distributed in the central area. The lower part provides an enlarged view of this central region, clearly demonstrating how tightly arranged CRATs and sea clutter couple and superimpose in the radar echo domain. This interaction generates SAR image features exhibiting high similarity to ship target scattering characteristics, imposing extreme demands on detector performance. Figure 2b proves that even in such dense small-target scenarios, CSBBNet achieves accurate detection and localization.
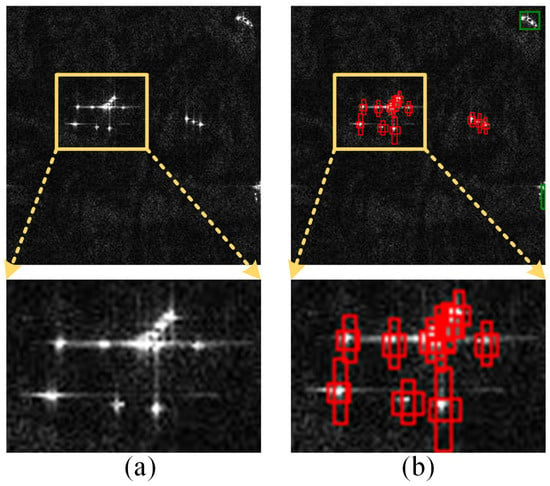
Figure 2.
CSBBNet detection results. (a) Raw data; (b) CSBBNet detection results.
- 3.
- We propose the cross-shaped spatial feature perception (CSSFP) module and the wavelet cross-shaped attention downsampling (WCSAD) module. CSSFP combines convolution and a cross-shaped self-attention (CSSA) mechanism to achieve fine-grained feature extraction of cross shaped regions. WCSAD first applies Haar wavelet transform to the input feature map to obtain approximate, horizontal, vertical, and diagonal sub feature maps. Subsequently, the CSSA is constructed using horizontal and vertical channels to achieve lossless downsampling of the input feature map.
- 4.
- We modify the existing decoupled detection head by integrating the CSSA mechanism into the coordinate prediction branch, thereby forming a cross-shaped attention decoupling head (CSAD-Head). Furthermore, to ensure stable model training, we propose a cross-shaped IoU (CS-IoU) loss function that effectively guides the network in regression prediction of the six-dimensional parameters required for constructing CSBB.
This novel bounding box representation method constitutes the fundamental distinction between CSBBNet and existing deep learning approaches. Crucially, CSBBNet does not merely substitute bounding box strategies within existing frameworks. Instead, it centers on CSBB as the core innovation, implementing collaborative and necessary redesigns of critical components (feature extractors, detection heads, and loss functions) to address the unique challenges of 6D parameter regression.
The rest of this manuscript is organized as follows: Section 2 surveys CRT and ship target detection research. Section 3 details the CSBBNet methodology. Section 4 presents experimental setups and results analysis. Section 5 analyzes detection performance in complex scenarios, discusses limitations, and proposes future research directions. Section 6 concludes the work.
2. Related Works
2.1. Sea-Surface Corner Reflector Target Detection and Recognition
Chen et al. [17] developed an ocean target imaging method based on modified clean technology combined with time–frequency analysis, enabling precise extraction of Doppler parameters from CRTs. Utilizing three distinct time–frequency characteristics (micro-motion period, time–frequency spectrum entropy, and the maximum micro-Doppler half-period frequency difference), Hong et al. [18] achieved effective distinction between CRTs and ship targets. To address the recognition problem of high-resolution range profiles (HRRP) for CRATs, Xia et al. [19] introduced a method based on mismatch filters. This approach extracted differential features between CRATs and ship targets by modifying the frequency modulation slope of the chirp signal within the filter and subsequently employed a support vector machine (SVM) for target recognition. Studies in [20,21] first provided a theoretical analysis of the differences in physical structure and polarization characteristics between ships and CRTs. Building on this, polarization decomposition was then applied to extract polarization invariant features from both target types, serving as the basis for recognition, which was ultimately accomplished using the SVM method. An alternative approach based on HRRP differences was presented by Yuan et al. [22], who employed an extreme learning machine (ELM) to successfully recognize ships, CRTs, and CRATs. Lv et al. [23] described a sea-surface target recognition method leveraging a feature fusion network. This technique facilitated the automatic weighted fusion of manually extracted features through a channel attention mechanism, resulting in significantly enhanced recognition accuracy compared to methods relying solely on manual features or convolutional neural networks (CNNs). For countering CRAT deception interference, Liang et al. [24] proposed a method combining Pauli polarization decomposition with a back propagation (BP) neural network, effectively increasing the accuracy of radar detection and tracking for critical targets. Targeting the challenge of CRAT recognition, Wang et al. [25] designed a recognition network model based on an improved time convolutional network and double-gate recurrent unit. By extracting hidden temporal information from HRRP and incorporating the Swish activation function, this model demonstrated improved recognition capability under low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) conditions. Guan et al. [26] combined time convolutional networks (TCNs) with long short-term memory networks (LSTM) to effectively capture multi-scale temporal features, thereby mitigating the performance degradation caused by limited CRT samples. Rapid recognition of CRT HRRP was achieved in [27] using a 1D-CNN network. Reference [28] innovatively addressed the issues of single features and low classification efficiency in CRAT recognition by combining multi-domain feature extraction with a CatBoost classifier. The proposed solution involved segmenting mixed-echo HRRP using adaptive density peak clustering, extracting 21-dimensional features, applying LightGBM for dimensionality reduction, and finally utilizing CatBoost for effective target classification, leading to enhanced CRAT identification performance.
A literature survey reveals that current research on sea-surface CRT detection primarily focuses on two technical approaches, namely (1) Feature extraction methods based on radar scattering model analysis combined with traditional machine learning classifiers (mainly SVM-based), and (2) end-to-end deep learning methods (such as LSTM and 1D-CNN) for feature extraction and recognition of HRRP. However, these approaches predominantly process one-dimensional HRRP data. As these models are specifically designed for 1D signals, they struggle to effectively detect CRT in 2D SAR images. Notably, while deep learning has achieved breakthroughs in optical image target detection, SAR image-based methods for sea-surface CRT detection remain scarcely explored in public research. Therefore, we hope to seek references and insights from relevant studies in the field of sea-surface ship target detection.
2.2. Ship Target Detection
The development of classic deep learning object detection models, including Faster R-CNN [29], YOLO [30], and SSD [31], has significantly advanced computer vision technology, providing crucial technical support for the robust progress in ship object detection. Building upon YOLOv8, Dong et al. [32] enhanced the detection strategy. By decomposing the ship detection task into independent detection and topological correlation analysis of the head, hull, and tail, they achieved improved accuracy for large ship targets. Fan et al. [33] introduced the CSDP-YOLO method. This approach strengthened the network’s shallow feature extraction capability through deep large kernel convolution within the CSDP module, while employing the MPDIoU loss function to achieve precise perception of small remote sensing targets. Aimed at compact high-frequency surface wave radar (HFSWR) applications, reference [34] presented DS-YOLOv5s, a ship target detection method leveraging a triple-attention mechanism and dynamic snake convolution. Compared to the YOLOv5s baseline model, the method demonstrated significant improvements of 15.3% in F1 score and 6.3% in AP75. To enhance the model’s ability to capture spatial semantic information, Min et al. [35] developed a dual path context enhancement neck (DCEN) module and a multi-context boosted (MCB) detection head. These innovations led to leading detection results on three measured datasets. Tang et al. [36] optimized the YOLOv7-tiny network structure by incorporating deformable convolution and the BiFormer attention mechanism, resulting in enhanced detection accuracy for small ship targets. For fine-grained perception of 3D spatial features, Jiang et al. [37] integrated a resolution-adjustable 3D weighted attention (RA3-DWA) mechanism before the decoupling detection head. This mechanism assigned specific 3D weights to small targets, effectively boosting the model’s detection performance. Gao et al. [38] proposed CGTC-RYOLO, which is a rotating object detection network designed to capture global contextual spatial relationships through the integration of a multi-head self-attention mechanism within the cross-stage partial (CSP) module. Additionally, a probability and distribution loss function (PrfoIoU) was designed to optimize regression performance. To address fine-grained remote sensing ship target detection, Zhan et al. [39] devised a multi-scale object enhancement module (MSOEM) to mitigate feature confusion caused by complex backgrounds. Concurrently, the introduction of a comparative embedding classification loss term into the multi-task loss function significantly improved fine-grained ship target classification accuracy. For detecting ship targets in large-scale remote sensing images, Chen et al. [40] presented P2RNet. Inspired by two-stage object detection networks, this method first divided the original image into sub-images using a keypoint extraction network and region generator. Subsequently, a lightweight object detection network with an embedded attention mechanism detected ship targets within these sub-images, achieving an optimal balance between detection accuracy and speed.
The above methods not only demonstrate the successful application of neural network technology in ship target detection tasks but also demonstrate that introducing an attention mechanism can enhance the network’s ability to fuse multi-scale features and robust target representation. This provides inspiration for us to develop a specialized detection scheme, which combines the structural prior characteristics of CRTs with deep neural networks and enhances the semantic expression ability of the network using attention mechanism to achieve lightweight and efficient detection performance. It should be specifically clarified that the core objective of this work is to validate the unique advantages of the proposed CSBB annotation strategy for CRT detection tasks. Since the aforementioned methodologies all rely on HBB or OBB strategies, we select the representative official YOLO version as the experimental baseline, given its superior public accessibility, code stability, and industry recognition.
3. Materials and Methods
Unlike deep learning methods that use HBB or OBB as regression targets, CSBBNet directly regress 6D coordinate parameters to achieve accurate detection of cross-shaped target areas. This section first introduces the overall architecture of CSBBNet, and then details three core innovative modules, namely CSSFP, WCSAD, and CSAD-Head. Finally, the CS-IoU loss function is derived to guide the normal training.
3.1. Overview
The overall architecture of CSBBNet is shown in Figure 3. The model is based on a three-stage architecture consisting of a backbone network, neck network, and detection head. Given an input image of size , the backbone network first performs multi-level feature extraction on the input and outputs a feature map of size . Among them, CBS (Convolution-BatchNorm-SiLU) and C2F (CSP with two convolutions and feature extraction) are classic spatial feature extraction modules. Subsequently, the neck network performs multi-feature fusion processing on these feature maps, and the final detection head regress the predicted results of the target category and position. The biggest difference between our proposed method and current mainstream object detection methods is that it directly regresses the six-dimensional coordinates of the target (usually four-dimensional coordinates) via the decoupling detection head and then decodes and converts them into a cross-shaped detection area (usually a rectangle). For other types of targets (such as ships), the network will automatically degrade to HBB detection mode. The challenge here lies in the fact that the receptive field of convolution kernels is rectangular. When performing feature extraction on cross-shaped regions, they are inevitably influenced by a significant number of irrelevant features present in the background areas. This interference ultimately impairs the model’s ability to extract fine-grained features from cross-shaped regions. We were inspired by the CSSA mechanism and Haar wavelet transform to propose the CSSFP module and WCSAD module, and we applied them to the backbone network and neck network of the model. At the same time, we also proposed CSAD-Head and CS-IoU loss functions to achieve prediction and training guidance for CSBB. In the Section 3.2, Section 3.3, Section 3.4, and Section 3.5, we provide a detailed introduction to the above structures and methods.
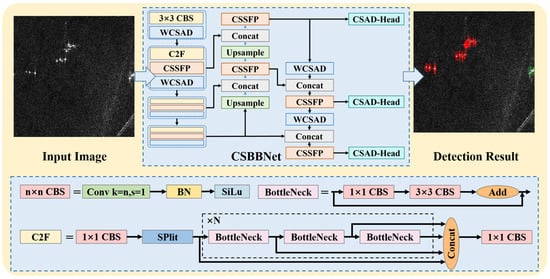
Figure 3.
Overall architecture of CSBBNet.
3.2. Cross-Shaped Spatial Feature Perception Module
In order to improve the adaptability of the proposed method in the CRT detection task, we need to strengthen the network’s feature perception ability for the cross-shaped spatial region by optimizing the structural design of the feature extraction module. However, standard convolution operators integrate features in local areas through a fixed size sliding window, and their receptive field size is directly limited by the size of the convolution kernel. When handling complex task scenarios, this locality makes models struggle to capture semantic correlations between distant targets in images, often leading to contextual information fragmentation. While the translation invariance of convolution kernels effectively enhances model generalization, it also limits their adaptive capability for irregularly shaped regions. Researchers can effectively expand the theoretical receptive field by stacking multiple layers of convolution and achieve adaptive adjustment of receptive field shape through the dynamic offset characteristics of deformable convolution. However, these improvement measures often come with significant increases in computational complexity and parameter size, making it difficult to meet the strict requirements of real-time detection tasks for inference speed and resource consumption.
Meanwhile, the self-attention mechanism has demonstrated remarkable performance in long-range contextual modeling due to its superior capability in global dependency modeling. However, its computational complexity exhibits quadratic growth relative to feature map dimensions, leading to memory consumption and computational latency proportional to the square of feature map area when applied to high-resolution dense prediction vision tasks (e.g., object detection and semantic segmentation). This severely limits its practical application value in scenarios where computing resources are constrained. Dong et al. [41] developed a self-attention mechanism based on a cross-shaped window and proposed the CSWin Transformer network architecture to reduce the computational cost of the self-attention mechanism. By segmenting the feature map into equally wide strips, powerful spatial modeling capability is preserved while reducing computational burden. Qiu et al. [42] proposed the CrossDet++ network, which flexibly represented the object to be detected through intersecting lines that could grow along both horizontal and vertical axes, effectively suppressing interference from background noise. The YOLOv12 network proposed by Tian et al. [43] utilized area attention mechanism, which effectively reduced computational cost while ensuring a large receptive field.
Therefore, in order to better utilize the prior information of the cross-shaped structural features of angular targets and fully leverage the advantages of the two methods mentioned above, we propose the CSSFP module, as shown in Figure 4. The CSSFP module first extracts local information from the feature map through 3 × 3 convolution.

Figure 4.
The structure of the CSSFP module.
Subsequently, self-attention calculations are performed in parallel within horizontal and vertical windows, forming the CSSA mechanism. Finally, the extracted spatial features are integrated through a 3 × 3 convolution.
The CSSA mechanism is mainly composed of parallel horizontal self-attention (HSA) branches and vertical self-attention (VSA) branches. For the feature map with an input size of , we first divide it equally along the channel dimension to obtain a horizontal feature map and a vertical feature map with both sizes of . Subsequently, is vertically divided into horizontal stripe regions with as the step size without overlap, and then the horizontal multi-head feature is obtained through multi-head self-attention aggregation. Similarly, is horizontally divided into vertical stripe regions with as the step size, and then the vertical multi-head feature is obtained. Through channel concatenation and projection operations, the final output feature map with the same input size is obtained.
3.3. Wavelet Cross-Shaped Attention Downsampling Module
Object detection networks often use max-pooling or strided convolution operations to downsample feature maps. However, due to not meeting the requirements of the Nyquist sampling theorem, the above method may cause aliasing effects of high-frequency components during the downsampling process: this not only results in the loss of high-frequency information, such as target edges and textures, but also introduces artifact noise due to spectral overlap. For sea-surface target detection tasks, targets, such as ships and CRTs, usually have rich local high-frequency features. Downsampling operations can significantly weaken the network’s ability to represent these key features, resulting in a decrease in semantic discrimination between different types of targets. Especially in complex scenes, aliasing effects can further blur the distribution patterns of the target body, sea clutter, and interfering targets, resulting in a weakening of the network model’s ability to distinguish differences between target classes, thereby exacerbating the risks of false positives and false negatives.
However, through the construction of efficient and concise scaling/wavelet functions, the Haar wavelet transform could achieve rapid multi-scale lossless decomposition of input signals, generating four sub-bands, namely low-frequency approximation (LL), horizontal detail (HL), vertical detail (LH), and diagonal detail (HH) [44]. Over the years, it has played a significant role in image processing and computer vision tasks. Inspired by the concept of lossless information transformation, a method integrating Haar wavelets with CNNs was proposed in [45]. This approach implemented HWD downsampling modules to replace conventional pooling and strided convolution operations, demonstrating outstanding performance in segmentation tasks.
Inspired by the above research, we propose the WCSAD module, with the overall structure shown in Figure 5. The core objective of this module is to effectively alleviate the information attenuation problem of the cross-shaped prior features during the downsampling process, thereby laying the foundation for the effective representation of CRTs in deep networks for continuous learning. The specific implementation includes three key steps. Firstly, Haar wavelet transform is performed on the input feature map , and four sub-band features are obtained by decomposition.

Figure 5.
The overall structure of WCSAD.
Secondly, differentiated processing strategies are implemented according to the distinct frequency-domain characteristics inherent to each sub-band. The horizontal detail sub-band is processed through an HSA to capture fine-grained features along the horizontal orientation, while the vertical detail sub-band is analyzed via VSA to extract detailed information in the vertical axial direction. Using standard 3 × 3 convolution for spatial feature extraction on the low-frequency approximation sub-band and diagonal detail sub-band , respectively, we obtain and .
Finally, the fusion of multi-frequency features is achieved through channel dimension concatenation, and channel compression and information integration are completed using 1 × 1 convolution to obtain the output feature map . The above process can be expressed as follows:
3.4. Cross-Shaped Attention Decoupling Head
Detection boxes are usually represented in two forms, namely HBB or OBB. Specifically, the HBB detection method describes the rectangular bounding box of the target by regressing four parameters, namely center coordinates , width , and height . The OBB detection strategy is an extension of HBB, which not only regresses the center coordinates and height and width parameters, but also requires an additional parameter to represent the rotation angle of the bounding box. Finally, five parameters are used to describe the target bounding box with any rotation angle. The most significant distinction of the CSBB method compared to the aforementioned two methods lies in its composition of two orthogonal bounding boxes sharing a common center point. When CRTs exist in the scene, the network detection head will directly regress the six-dimensional coordinate parameters to describe the prediction results of the cross-shaped region at the current anchor point. is the offset relative to the coordinate of the anchor point, represents the width and height of the horizontal bounding box, and represents the width and height of the vertical bounding box. Figure 6 illustrates the coordinate representation method of CSBB.
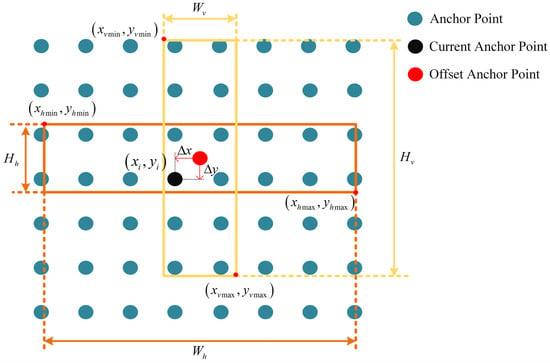
Figure 6.
Coordinate representation method of CSBB.
Therefore, in order to further improve the prediction accuracy of the network for the six-dimensional parameters of CSBB, we propose the CSAD-Head structure, as shown in Figure 7. This structure inherits the design concept of YOLO series decoupling detection head. The parallel dual-branch architecture is used to realize category prediction and coordinate prediction, respectively. It is worth noting that for the coordinate prediction branch, in addition to the six-dimensional parameters of CSBB, the proposed method also needs to regress an additional flag parameter as a switch to enable the CSBB coordinate format. For instance, in the case of CRTs, the model activates the CSBB mode through , and outputs six-dimensional coordinate parameters to precisely locate the cross-shaped region. However, for other objectives , the effective output predicted by the network will degrade to the conventional HBB method, only outputting four-dimensional axis aligned bounding box parameters. Finally, the output size of the category prediction branch is , and the output size of the coordinate prediction branch is . and are the width and height of the current input feature map, respectively, and is the number of target species in the dataset. represents the number of coordinate discretization points, usually set to 16, used for subsequent calculation of distribution focal loss (DFL) [46,47].
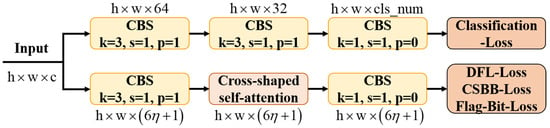
Figure 7.
The overall structure of the CSAD-Head.
3.5. Cross-Shaped Intersection over Union Loss
To enable the proposed method to effectively adapt to the detection task of cross-shaped targets, it is essential to specifically design gradient-optimization-oriented loss functions that achieve precise alignment between prediction results and ground truth annotations. For this purpose, we propose the CS-IoU Loss as shown in (5). This composite loss function consists of four core components, namely cross-shaped bounding box loss , classification loss , DFL loss , and flag bit loss , where serves as the loss adjustment factor. Through synergistic interaction, these components enable quantitative evaluation of prediction deviations and guide stable parameter updates along the optimization direction.
There are two feasible methods for calculating the , as follows: (1) Directly calculate the IoU loss between the minimum enclosing rectangle bounding box (MERBB) of CSBB and the ground truth. (2) Decouple CSBB into horizontal and vertical sets of rectangular boxes, calculate the IoU loss between each component and the ground-truth box, and then compute the weighted sum of these losses. To evaluate the geometric sensitivity difference between the two strategies, we analyzed the translation sensitivity characteristics of the bounding box. Figure 8a and Figure 8c show the overlapping area when the MERBB is horizontally shifted by half a width and diagonally shifted by half a diagonal length, respectively. The corresponding Figure 8b and Figure 8d show the overlapping area of the CSBB in the same direction and amount of movement, respectively. It can be clearly seen that whether offset horizontally or diagonally, the overlapping area calculated by method (2) is significantly smaller than that calculated by method (1). In addition, we also quantitatively analyzed the relationship between the offset and IoU of the two methods mentioned above. Figure 9a and Figure 9b display, respectively, the 3D surface plots showing the variation of IoU with two-dimensional offsets for MERBB and CSBB. Figure 9c,d provide clear comparative curves of IoU variations with horizontal/vertical offsets for both schemes. Compared to MERBB, the decoupled computation strategy using CSBB demonstrates more pronounced peak characteristics and steeper decay properties in IoU calculation results. This response characteristic indicates that the decoupled computation strategy exhibits higher geometric sensitivity to bounding box offsets, which facilitates faster identification of gradient directions for localization errors during network training. This provides a crucial theoretical foundation for loss function design.
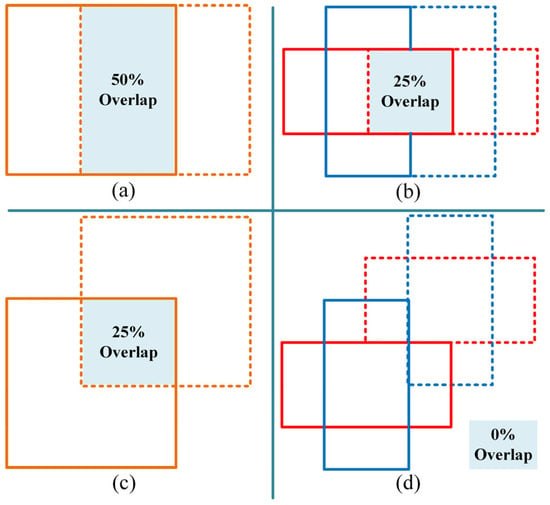
Figure 8.
Effects of different offsets on overlapping regions. (a) MERBB with 50% horizontal offset; (b) CSBB with 50% lateral offset; (c) MERBB with 50% diagonal offset; (d) CSBB with 50% diagonal offset.
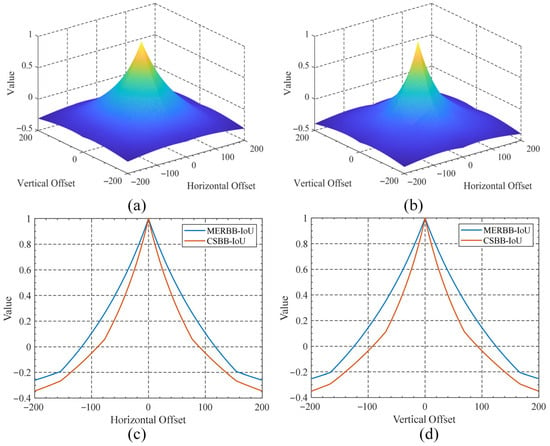
Figure 9.
Sensitivity analysis of IoU under different offsets. (a) Variation patterns of IoU with offsets for MERBB; (b) variation characteristics of IoU with offsets for CSBB; (c) comparative analysis of IoU variations with horizontal offsets between the two strategies; (d) comparative analysis of IoU variations with vertical offsets between the two strategies.
Therefore, according to the CSBB decoupling strategy, we design the specific calculation process of the loss function . Firstly, the six-dimensional coordinate parameters obtained by the network prediction are decoupled and transformed into the vertex coordinate format of the horizontal rectangular bounding box and the vertical rectangular bounding box according to Equations (6) and (7), respectively, as follows:
where is the grid coordinate corresponding to the current anchor point, is the upper left vertex coordinate of the horizontal rectangular bounding box, is the lower right vertex coordinate of the horizontal rectangular bounding box, is the upper left vertex coordinate of the vertical rectangular bounding box, and is the lower right vertex coordinate of the horizontal rectangular bounding box. Subsequently, the CIoU loss of the and are calculated separately from the ground truth, then weighted and added, as follows:
where represents the CIoU loss calculation operation. and represent, respectively, the ground truth of the horizontal/vertical rectangular bounding box. Due to the fact that the CSBB strategy only applies to CRTs, the traditional HBB coordinate format is still used for other types of targets. Therefore, a flag parameter is needed to control the switching between the two coordinate formats. The modified positioning loss function calculation method is shown in Equation (9). It should be pointed out that when , the localization loss function will degenerate into the CIoU loss function in the standard HBB format.
Since it is necessary to switch the type of bounding box loss function for different types of targets, the task of predicting this flag parameter is essentially a binary classification optimization problem. Its corresponding loss function typically requires optimization under imbalanced sample conditions. We employ the focal loss method [48] for loss computation, as shown in (10). Let the true value of the type flag for the predicted bounding box be , where 0 indicates a ship target and 1 indicates a CRT. The type probability output by the network is , computed by the sigmoid activation function.
The hyperparameter controls the weights for positive and negative samples (set to 0.7 in our experiments), while the hyperparameter controls the down-weighting degree for easy-to-classify samples (set to 2 in our experiments).
Specifically, the classification loss ensures target semantic consistency by minimizing the cross-entropy between the category posterior probability distribution and one-hot labels. The DFL loss discretizes the bounding box position distribution, with its optimization objective being to minimize the Kullback–Leibler (KL) divergence between the predicted distribution and the Dirac delta distribution, thereby refining the granularity of coordinate regression. The cross-shaped bounding box loss jointly optimizes the CIoU loss for horizontal and vertical rectangular boxes, aiming to maximize geometric overlap between predicted boxes and ground truth (GT) while suppressing misalignment errors in cross-shaped regions, thus improving localization accuracy. The flag bit loss performs binary classification to determine whether the current target is a CRT, with the optimization goal of reducing misclassification probability for CRT under imbalanced sample conditions while enabling modulation of the cross-shaped bounding box loss .
During network training, we adopt an adaptive weighting strategy to achieve interactive balancing among different loss components. This strategy stems from the observation that the four components of the total loss exhibit significant magnitude differences in the early convergence phase (with classification loss and DFL loss being approximately 1–2 orders of magnitude greater than cross-shaped bounding box loss and flag bit loss ). To prevent any single loss term from prematurely dominating the training process, we design weights based on the following two heuristic principles: (1) Magnitude normalization: After the first training epoch, we record the unweighted raw mean values of each loss term, and set initial weights as , thereby ensuring all four losses contribute to gradients at comparable magnitudes on average. (2) Task prioritization: Based on object detection task characteristics, classification loss and cross-shaped bounding box loss are treated as primary tasks, and their weights are kept relatively high throughout the training process. In contrast, DFL loss and flag bit loss are considered auxiliary tasks and are assigned weights at 50% of their initial values.
4. Results
In this section, we first provide a detailed introduction to the SSFT dataset used for experimental validation. Subsequent comparative experiments and ablation experiments verify the effectiveness and progressiveness of the proposed method.
The computer hardware environment used in the experiment is the Intel(R) Xeon(R) W-2295 CPU and NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 24GB, with a software environment of Python 3.9 and PyTorch 1.9. All methods were trained using an image size of 640 × 640, with the maximum training iterations and batch size set to 200 and 16, respectively. The dataset is divided into training, validation, and test datasets in a 7:1:2 ratio. The Adam optimizer is employed with an initial learning rate of 0.001, incorporating a learning rate decay strategy during training.
4.1. Introduction of Experimental Datasets
The design of CSBBNet stems from the critical need for accurate and efficient detection of CRTs in marine remote sensing. However, existing public marine remote sensing datasets generally lack annotated samples for such targets, significantly increasing the difficulty of algorithm development. Benefiting from breakthrough advances in modern electromagnetic simulation techniques [49,50], the construction of refined electromagnetic models for CRT and their arrays enables the efficient generation of high-fidelity simulated echoes that closely approximate the scattering characteristics of measured data. This provides a reliable data foundation for algorithm training and validation.
Therefore, we construct the experimental dataset by superimposing electromagnetic simulated echoes onto real remote sensing data. Using the three-dimensional model of an icosahedral corner reflector (ICR) shown in Figure 10a as the fundamental unit, we systematically build CRAT models with varying numbers of units and spatial configurations. Their echo signals are calculated using the image-based fast shooting and bouncing ray (IFSBR) method (Figure 10b–i display SAR images of arrays containing 2–4 corner reflectors). Following the parameter settings in references [51,52], the spacings between CRTs are randomly set within the range of 10–30 m. This approach ensures the physical plausibility of the spacing configuration, significantly enhances scene realism, and improves dataset diversity through randomization.
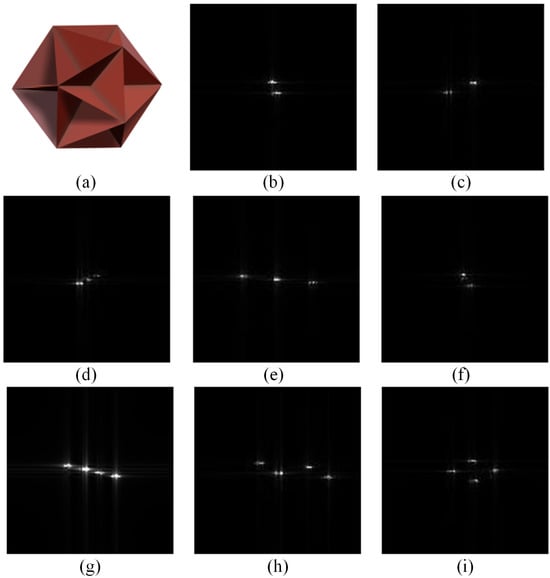
Figure 10.
ICR model and electromagnetic simulation results of its arrays. (a) Three-dimensional model of the ICR; (b,c) array composed of two ICRs; (d–f) complex array composed of three ICRs; (g–i) complex array composed of four ICRs.
Based on the FAIR-CSAR-V1.0 complex image dataset [53] open-sourced by researchers including Wu, we randomly superimposed 2–6 sets of CRAT simulated echoes onto each scene. This process ultimately formed the sea-surface SSFT dataset. The dataset comprises 4093 images, containing 40,816 CRT instances and 7452 ship target instances. The significantly higher number of CRTs compared to ships aligns with the characteristic multi-unit deployment of CRATs in real-world scenarios. Partial sample visualizations of SSFT dataset are shown in Figure 11.

Figure 11.
Partial sample visualizations of SSFT dataset.
4.2. Experimental Evaluation Criteria
To scientifically evaluate the detection performance of different methods for CRTs, this manuscript constructs a multidimensional evaluation system using the following indicators and objectively measures the detection efficiency through quantitative analysis of the accuracy and comprehensiveness.
- (1)
- Precision: Refers to the proportion of correctly detected positive samples relative to the total number of positive samples in the detection results. Its mathematical expression is as follows:where (true positive) represents the target of correct detection and (false positive) represents the target of error detection. In the object detection tasks, this metric reflects the effective proportion of the real target in the detection result, which is used to measure the ability of the algorithm to eliminate false alarms.
- (2)
- Recall: Refers to the proportion of the number of correctly detected positive samples to the total number of true positive samples; its mathematical expression is as follows:where (false negative) represents the target of missed detection. This metric represents the algorithm’s ability to cover real targets and reflects the effectiveness of the detection system in discovering targets.
- (3)
- F1-Score: Defined as the harmonic mean of precision and recall, particularly when the sample distribution is imbalanced or when both types of errors (FP and FN) need to be considered simultaneously, providing a more comprehensive performance measure. Its mathematical expression is as follows:
- (4)
- Average precision (AP): Obtained by integrating the area under the precision–recall curve, calculated using the following formula:
This metric comprehensively considers the dynamic balance between precision and recall under different confidence thresholds, evaluating single-class detection performance by quantifying the stability of detection results. In this manuscript, AP50 is adopted as the evaluation metric, which refers to the AP value calculated when the IoU threshold is fixed at 0.5.
- (5)
- Mean average precision (mAP): As a unified evaluation standard for multi class detection, it is defined as follows:
By calculating the arithmetic means of the AP values for all categories, the overall detection performance of the algorithm in complex scenarios is comprehensively reflected, which is a key indicator for measuring the comprehensive ability of the object detection system. MAP50 and mAP50-95 are used as evaluation metrics in this manuscript.
4.3. Comparative Experimental Results and Analysis
In order to fully verify the progressiveness and effectiveness of the proposed method in the CRT detection task, we compare its performance with the current mainstream single-stage detection methods, including YOLOv5-n, YOLOv8-n, YOLOv8-s and the latest YOLOv12-n [43]. As shown in Table 1, comparative analysis of model parameters and floating point operations (FLOPs) across different methods reveals that the lightweight architecture-based CSBBNet demonstrates significant advantages in parameter scale. The proposed method has 1.7 M parameters, which is 10.5% lower than the suboptimal YOLOv5-n. Regarding computational efficiency, while the proposed method’s 6.4 G FLOPs slightly exceed YOLOv5-n’s 4.5 G, it remains comparable to the latest lightweight network YOLOv12-n (6.5 G) and shows marked improvement over YOLOv8-n (8.7 G) and the larger-scale YOLOv8-s (28.6 G). This balanced characteristic of the minimized parameter count and controllable computational overhead makes the method particularly suitable for deployment scenarios on computationally constrained mobile and edge devices.

Table 1.
Comparison of parameter quantity and calculation quantity for different methods.
The quantitative evaluation results of different methods on the SSFT test dataset are presented in Table 2, where P (CR), R (CR), F1 (CR), and AP50 (CR) represent precision, recall, F1-score, and AP50 evaluation metrics for CRT detection, respectively. Similarly, P (SH), R (SH), F1 (SH), and AP50 (SH) denote the corresponding metrics calculated for ship target detection.

Table 2.
Comparison of metric quantification results of different methods on the SSFT test dataset.
A comprehensive analysis of all metric results demonstrates that the proposed method exhibits comprehensively superior performance. On the critical metric mAP50, the proposed method achieves 0.8872, representing a 3.37% increase over the suboptimal model YOLOv8-s (0.8535). Regarding the mAP50-0.95 metric, which characterizes localization accuracy, the proposed method has a score of 0.4533 compared to YOLOv8-s’s 0.3887. This advantage primarily stems from the following two factors: (1) Individual CRT occupy minimal pixels in images, belonging to the category of difficult small targets. Even slight deviations in detection bounding boxes can cause significant declines in localization accuracy metrics. (2) The number of CRTs in the dataset substantially exceeds that of ship targets. This sample imbalance increases the difficulty of network training.
On the CRT detection metric R (CR), the proposed method achieves an absolute improvement of 35.43% compared to YOLOv5-n. Even when compared to the YOLOv8-s model, which has several times the parameters, it still leads by 6.09%. This underscores the significant effectiveness of the proposed method in mitigating the problem of missed detections for dense small objects. Regarding the P (CR) and AP50 (CR) metrics, improvements of 2.03% and 5.11% are achieved over the suboptimal model YOLOv8-s, respectively, further validating its superior performance in corner reflector detection.
In ship target detection, the proposed method maintains its advantage even when the CSBB degenerates into a conventional HBB. Experimental results show that, despite having significantly lower model parameters and computational complexity than YOLOv8-s, the proposed method achieves relative advantages of 2.3%, 7.23%, 4.83%, and 1.64% on the four metrics P (SH), R (SH), F1 (SH), and AP50 (SH), respectively. This indicates that the proposed method maintains better detection capabilities for targets than other reference methods while preserving its lightweight nature.
4.4. Ablation Experiment
In this section, we validate the effectiveness of three core components, namely CSSFP, WCSAD, and CSAD-Head, through ablation experiments. It should be noted that the baseline model for ablation studies is constructed by replacing these three core components in the CSBBNet network, specifically including the following structural modifications: (1) Replace all CSSFP modules with a standard convolution layer with a kernel size of 3 × 3. (2) The WCSAD module is replaced by the maximum pooling downsampling layer with step size of 2. (3) Replace the CSSA mechanism in CSAD-Head with a 3 × 3 standard convolutional layer. Based on this baseline model, we progressively integrate each component using the control variable method to build comparative models. The detection performance of various combined models is quantitatively evaluated on the SSFT test dataset using mAP50 and mAP50-95 metrics, with all comparative experiments maintaining identical training strategies and hyperparameter settings.
As demonstrated by the ablation experimental results in Table 3, the baseline model achieves an mAP50 of 0.8128 and an mAP50-0.95 of 0.4062. The integration of three modules (CSSFP, WCSAD, and CSAD-Head) yields progressive performance improvements. Notably, each component contributes differently to the enhancements. Among single-module additions, CSSFP provides the most significant gains: when incorporated alone, it elevates mAP50 to 0.8559 (+4.31% over baseline) and mAP50-0.95 to 0.4443 (+3.81%), indicating its substantial impact on localization accuracy. WCSAD ranks second (mAP50: 0.8471, +3.43%), while CSAD-Head shows limited efficacy (mAP50: 0.8252, +1.24%), suggesting its performance gain may depend on other modules. For dual-module configurations, the CSSFP + WCSAD pairing achieves optimal performance (mAP50: 0.8750, +6.22%; mAP50-0.95: 0.4515, +4.53%), highlighting strong complementarity between them. The WCSAD + CSAD-Head combination yields an mAP50 of 0.8624 (+4.96%), notably exceeding the sum of their individual gains (+4.67%), which reveals promising complementary optimization potential. Finally, the full integration of all three modules achieves peak performance, with an mAP50 of 0.8872 (+7.44%) and mAP50-0.95 of 0.4533 (+4.71%), significantly outperforming any single- or dual-module variant and confirming their synergistic enhancement effect.

Table 3.
Ablation experimental results of CSBBNet.
5. Discussion
5.1. The Impact of Different Scenarios on the Performance of Various Detectors
Figure 12a shows the original image, while Figure 12b–e present the detection results of YOLOv8-n, YOLOv12-n, YOLOv8-s, and the proposed method on the SSFT test dataset, respectively. The figure contains four typical scenarios: the first row represents a strong scattering scenario, the second row represents a multi-target complex scenario, the third and fourth rows represent interference scenarios in adjacent areas, and the fifth row represents a land background scenario. The following analysis details the detection performance of each method according to the scenario sequence.

Figure 12.
Comparison of detection results using different methods on the SSFT dataset. (a) Raw data; (b) YOLOv8-n; (c) YOLOv12-n; (d) YOLOv8-s; (e) CSBBNet.
- (1)
- The strong scattering scenario
The results in the first row of Figure 12 show the detection performance differences of various methods in a strong scattering scenario (containing three ship targets). The original image reveals that the scattering intensities of Ship1 and Ship2 are significantly lower than other targets in the scene, providing a critical test for each method’s weak-target detection capability. Comparative detection results demonstrate that both YOLOv8-n and YOLOv8-s miss Ship1, whereas YOLOv12-n and the proposed method perform better, successfully detecting both weak ship targets.
Notably, ship targets inherently contain complex scattering structures and may form cross-shaped strong scattering points under specific viewing angles (e.g., Ship3). Figure 13 provides an enlarged view of local detection results near Ship3 across different methods. This detailed perspective clearly shows not only the intrinsic cross-shaped scattering structure of Ship3 but also two strong scattering CRTs in its right adjacent area. These factors collectively increase detection difficulty in this region. Comparing detection results in Figure 13 reveals that only the proposed method accurately identifies all targets in this local scene (i.e., Ship3 and two CRTs). The other three methods mistakenly detect Ship3 as a CRAT formed by multiple superimposed reflectors.
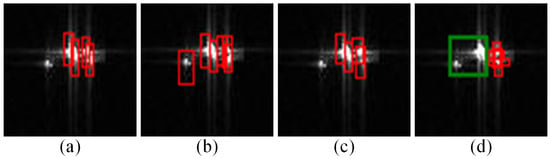
Figure 13.
Comparison of local detection results in the vicinity of Ship3 (the scenario presented in the first row of Figure 12) across different methods. (a) YOLOv8-n; (b) YOLOv12-n; (c) YOLOv8-s; (d) CSBBNet.
- (2)
- The multi-target complex scenario
The results in the second row of Figure 12 compares the detection performance of different methods in a multi-target complex scenario. This scenario presents significant challenges, as multiple ship targets coexist with CRATs amidst widespread clutter interference in the background. Such complexity imposes high demands on the target recognition and detection capabilities of network models. Notably, all methods demonstrate strong robustness in clutter suppression without generating false alarms. However, a decoy target array composed of multiple CRTs exists in the immediate vicinity below Ship1, exhibiting structural contours highly similar to an actual ship. The comparative local detection results for this area are enlarged in Figure 14.
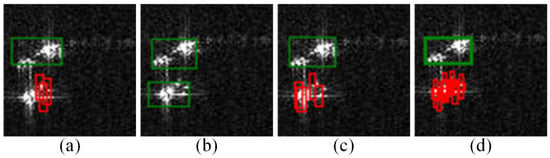
Figure 14.
Comparison of local detection results in the vicinity of Ship1 (the scenario presented in the second row of Figure 12) across different methods. (a) YOLOv8-n; (b) YOLOv12-n; (c) YOLOv8-s; (d) CSBBNet.
Figure 14b reveals that YOLOv12-n misidentifies the entire CRAT as a single ship target. Although YOLOv8-n (Figure 14a) and YOLOv8-s (Figure 14c) avoid this misclassification, they exhibit varying degrees of missed detections. Furthermore, both methods show insufficient localization precision for densely distributed CRTs, frequently generating oversized bounding boxes that encompass multiple adjacent targets (i.e., failing to distinguish closely spaced objects).
In contrast, the proposed method significantly enhances localization accuracy and discrimination capability for CRTs, attributable to the incorporation of the CSBB mechanism.
- (3)
- The interference scenario in adjacent areas
The third and fourth rows of Figure 12 demonstrate the detection robustness comparison of different methods under different SNR conditions when ship targets are subjected to strong scattering CRT interference in adjacent areas. Specifically, in the higher SNR scenario shown in the third row of Figure 12, several CRTs appear as interference near the upper adjacent region of Ship1. Furthermore, the strong scattering points formed by Ship1’s bow and stern exhibit characteristics in SAR images that closely resemble CRTs. A comparative analysis of locally magnified detection results from this region is presented in Figure 15. As shown, both the YOLOv8-n and YOLOv12-n models with smaller parameter counts fail to correctly detect the Ship1 target. Additionally, they misclassify the strong scattering points on Ship1 as CRTs. While YOLOv8-s successfully detects the presence of a ship target in this region, it incorrectly identifies a CRT located in the adjacent area above Ship1 as part of the ship’s structure.
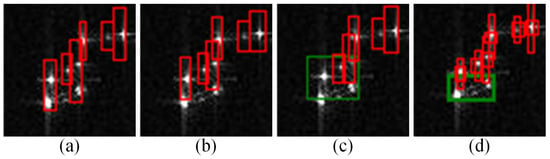
Figure 15.
Comparison of local detection results in the vicinity of Ship1 (the scenario presented in the third row of Figure 12) across different methods. (a) YOLOv8-n; (b) YOLOv12-n; (c) YOLOv8-s; (d) CSBBNet.
In the low-SNR scenario depicted in the fourth row of Figure 12, the coupling effect between noise and sea clutter causes the boundaries between ship targets and adjacent CRTs to become increasingly blurred, which further elevates detection difficulty. A comparative analysis of locally magnified detection results from this region is shown in Figure 16. As observed in Figure 16, YOLOv8-n not only misses the ship target but also generates false alarms for CRTs. YOLOv12-n detects the ship and adjacent CRTs as a single entity. While YOLOv8-s correctly detects and distinguishes the ship target, it exhibits insufficient localization accuracy for the CRTs and produces a single detection box that encompasses multiple CRTs.

Figure 16.
Comparison of local detection results in the vicinity of the ship (the scenario presented in the fourth row of Figure 12) across different methods. (a) YOLOv8-n; (b) YOLOv12-n; (c) YOLOv8-s; (d) CSBBNet.
- (4)
- The land background scenario
The fifth row of Figure 12 demonstrates the detection robustness of four methods under land background interference. This scenario contains two ship targets (Ship1 and Ship2), four CRATs, and extensive island shoreline backgrounds. The detection results show that only YOLOv12-n fails to detect Ship2, while YOLOv8-n, YOLOv8-s, and the proposed method successfully detect all ship targets. However, strong scattering points on the island shoreline cause all three comparison methods to generate false alarms. Additionally, a CRAT exhibiting spatial distribution characteristics highly similar to those of a ship target is present at the scene center. The locally enlarged comparison is shown in Figure 17. This array is falsely detected as multiple ship targets by the aforementioned three comparison methods. Only the proposed method correctly detects and precisely locates the four individual CRTs constituting the array.

Figure 17.
Comparison of detection results in the central region of the scene shown in the fifth row of Figure 12 among different methods. (a) YOLOv8-n; (b) YOLOv12-n; (c) YOLOv8-s; (d) CSBBNet.
Based on the comparative experimental results presented above, when it performs detection tasks for CRTs, CSBBNet delivers optimal detection accuracy across diverse scenarios through its innovative architecture design and demonstrates potential as an efficient solution for resource-constrained applications.
5.2. Proposal for Future Work
Although designed for traditional static CRTs, this method utilizes cross-shaped feature priors to enhance detection model representation, theoretically extending to novel targets with similar scattering characteristics. Time-varying trihedral corner reflectors incorporating metasurfaces now attract significant attention due to programmable electromagnetic properties [54,55,56,57]. Despite dynamic modulation mechanisms, these targets retain dominant scattering modes appearing as cross-shaped bright spots in SAR imagery. This context reveals CSBB’s advantages for detecting novel targets, as follows: (1) Cross-shape adaptability: By directly regressing cross-shaped principal axis parameters, CSBB accurately delineates the core scattering energy region of metasurface CRTs. This avoids localization noise from traditional HBB or OBB strategies that introduce excess background pixels and rotational complexity. (2) Background suppression enhancement: Metasurface dynamic modulation may intensify sidelobe clutter or adjacent target interference. CSBB’s compact structured representation minimizes irrelevant background pixel inclusion during training.
However, CSBB application to dynamic programmable metasurface CRTs presents the following unique challenges: (1) Dynamic scattering complexity: Rapid metasurface element switching causes transient distortion or energy fluctuations in cross-shaped scatter patterns. This requires feature extraction networks with enhanced temporal modeling and robustness for non-stationary scattering behavior. (2) Dataset scarcity: Public real-world SAR datasets containing dynamic programmable metasurface CRTs remain limited. Constructing benchmark datasets through high-fidelity electromagnetic simulations with experimental validation urgently supports method evaluation.
CSBB also has current limitations, as follows: (1) For targets lacking distinct cross-shaped scattering signatures (e.g., ships), CSBB defaults to HBB in localization. This indicates limitations in detecting rotated or structurally complex targets, marking key optimization directions, like enhanced rotation invariance. (2) While focusing on sea-surface CRT detection, other strong-scattering decoys exist (e.g., chaff clouds) with different scattering mechanisms. Future work should also explore applying CSBB variants to broader floating targets to improve generalization.
6. Conclusions
In this manuscript, we propose a detection framework named CSBBNet for marine CRTs. Differing from conventional annotation strategies based on HBB or OBB, this work innovatively designs a CSBB representation method that achieves precise geometric modeling of targets through 6D coordinate parameters while establishing an end-to-end neural network regression framework. Leveraging the inherent cross-shaped structural priors of CRTs in SAR images, we propose three innovative modules based on CSSA mechanisms: the CSSFP module, the WCSAD module, and the CSAD-Head module, along with a dedicated CS-IoU loss function. Specifically, the CSSFP module enables refined extraction of spatial features in cross-shaped regions through synergistic operation of convolutional processing and CSSA mechanisms. The WCSAD module innovatively integrates Haar wavelet transform with CSSA mechanisms to perform downsampling while preserving information integrity, effectively replacing traditional stride convolution and max-pooling approaches. The CSAD-Head module incorporates CSSA mechanisms into the coordinate prediction branch of decoupled detection heads, significantly enhancing coordinate regression accuracy. The newly designed CS-IoU loss function decouples CSBB into mutually orthogonal horizontal and vertical rectangular components, guiding model parameter optimization by calculating individual losses against ground truth labels, thereby ensuring training stability. To validate the proposed method’s effectiveness, we first constructed the SSFT dataset and conducted comparative and ablation experiments on it. Visualization results and quantitative analysis comprehensively demonstrate CSBBNet’s superior detection performance and robust reliability in marine CRT detection tasks.
Author Contributions
W.T. created the research idea, wrote the manuscript, conducted the theoretical analyses, and verified the proposed method; M.X. (Mengdao Xing) and Y.G. were involved in improving the proposed method. M.X. (Min Xue) and H.L. designed the experiments; G.S. contributed to revising the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded in part by the National Nature Science Foundation of China under Grant U22B2015, in part by the National Nature Science Foundation of China under Grant 62271375, in part by the National Science Fund for Excellent Young Scholars under Grant 62222113, and in part by the Open Fund of the Laboratory of Pinghu.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Gu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Xiao, S. ISAR Image Transform via Joint Intra pulse and Inter pulse Periodic coded Phase Modulation. IEEE Sens. J. 2025, 25, 28788–28799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, Q.; Ai, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhao, F. Micromotion Frequency Estimation of Multiple Space Targets Based on RCD Spectrum. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, Q.; Pan, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, F. SAR Image Transform Based on Amplitude and Frequency Shifting Joint Modulation. IEEE Sens. J. 2025, 25, 7043–7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Sun, G.; Bian, H.; Xiang, J.; Xing, M. On the Role of Scene Coordinate System in Focusing of GEO SAR Data With Fast Time-Domain Algorithm. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 2355–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Lin, H.; Chen, Q.; Xing, M.; Zhou, S.; Sun, G. 2-D Autofocus for High-Squint SAR Based on Affine Coordinate Back-Projection Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5228217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Lan, P.; Deng, Y.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xing, M.; Zhang, Y. Multichannel Back Projection (MC-BP) Algorithm and Its Accelerated Form for HRWS SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5222116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, S. Bidirectional Interaction Fusion Network Based on EC-Maps and SAR Images for SAR Target Recognition. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2025, 74, 2519313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, C.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, J. Estimating Oil–Water Mixing Ratios of Marine Oil Spills From L-Band Fully Polarimetric SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 4010505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.L. Deep Nets Spotlight Illegal, Unreported, Unregulated (IUU) Fishing. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Applied Imagery Pattern Recognition Workshop (AIPR), Washington, DC, USA, 15–17 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- LI, H.; Chen, S. Electromagnetic Scattering Characteristics and Radar Identification of Sea Corner Reflectors: Advances and Prospects. J. Radars. 2023, 12, 738. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Luo, J.; Yu, Z. Research on Corner Reflector Array Fitting Method for Ship Scattering Characteristics. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Big Data and Algorithms (EEBDA), Changchun, China, 24–26 February 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Yuan, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, R.; Li, X.; Hou, Q.; Cheng, M.-M. YOLO-MS: Rethinking Multi-Scale Representation Learning for Real-Time Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2025, 47, 4240–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Wang, X.; Zou, J.; Wu, H. YOLO-Ssboat: Super-Small Ship Detection Network for Large-Scale Aerial and Remote Sensing Scenes. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Fang, M.; Peng, D. TIAR-SAR: An Oriented SAR Ship Detector Combining a Task Interaction Head Architecture with Composite Angle Regression. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, D.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, H. Center-Symmetry Representation-Based High-Quality Localization Detector for Oriented Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5617614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Hu, J.; Ren, H.; Lin, J.; Luo, X.; Zou, L.; Zhou, Y. Cross-Level Adaptive Feature Aggregation Network for Arbitrary-Oriented SAR Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, W.; Gao, Y.; Cui, L.; Chen, Q.; Fu, J.; Xing, M. An Imaging Method for Marine Targets in Corner Reflector Jamming Scenario Based on Time–Frequency Analysis and Modified Clean Technique. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, Q.; Pan, Y.; Tai, N.; Yuan, N. A sea corner-reflector jamming identification method based on time-frequency feature. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC), Ningbo, China, 19–22 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, L.; Wang, F.; Pang, C.; Li, N.; Peng, R.; Song, Z.; Li, Y. An Identification Method of Corner Reflector Array Based on Mismatched Filter through Changing the Frequency Modulation Slope. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xie, M.; Su, Q.; Fu, X. Identification of Ship and Corner Reflector Based on Invariant Features of the Polarization. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 4th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing (ICSIP), Wuxi, China, 19–21 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xie, M.; Fu, X. Identification of Ship and Corner Reflector In sea clutter environment. In Proceedings of the 2020 15th IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing (ICSP), Beijing, China, 6–9 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Fu, X.; Zhao, C.; Xie, M.; Gao, X. Ship and Corner Reflector Identification Based on Extreme Learning Machine. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Signal, Information and Data Processing (ICSIDP), Chongqing, China, 11–13 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Q.; Fan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Quan, Y.; Xing, M. Agile Frequency RCS-Based Deep Fusion Network for Ship and Corner Reflector Identification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 3504505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, B. Anti-Corner Reflector Array Method Based on Pauli Polarization Decomposition and BP Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning (PRML), Chengdu, China, 16–18 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, X.; Dong, J.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Fu, X. Combined corner reflector array interference recognition based on improved TCN and DGRU. In Proceedings of the IET International Radar Conference (IRC 2023), Chongqing, China, 3–5 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, S.; Fu, X.; Dong, J. Corner Reflector Identification Based on Improved Temporal Convolutional Network and LSTM. In Proceedings of the 2023 8th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing (ICSIP), Wuxi, China, 8–10 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Huangfu, H.; Meng, X.; Shen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P. RCS Recognition Method of Corner Reflectors based on 1D-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society (ACES-China) Symposium, Chengdu, China, 28–31 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, S.; Gao, X.; Lang, P.; Dong, J. The Corner Reflector Array Recognition based on Multi-domain Features Extraction and CatBoost. In Proceedings of the 2023 8th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Signal Processing (ICSP), Xi’an, China, 21–23 April 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, R.; Santosh, D.; Ross, G.; Ali, F. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.-Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. Comput. Vision ECCV 2016 2016, 9905, 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, T.; Wang, T.; Li, X.; Hong, J.; Jing, M.; Wei, T. A Large Ship Detection Method Based on Component Model in SAR Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 4108–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Wei, T.; Huang, Z. A Small-Ship Object Detection Method for Satellite Remote Sensing Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 11886–11898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Zhou, H.; Tian, Y.; Yang, Z.; Huang, W. A Deep Learning-Based Time-Frequency Scheme for Ship Detection Using HFSWR. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 2718–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.; Dou, F.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, D.; Li, L.; Wang, B. CM-YOLO: Context Modulated Representation Learning for Ship Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 4202414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, J.; Xia, Y.; Xiao, H. DBW-YOLO: A High-Precision SAR Ship Detection Method for Complex Environments. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 7029–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Bai, T. DSFPAP-Net: Deeper and Stronger Feature Path Aggregation Pyramid Network for Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 6010505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, G.; Yao, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Li, G. An Oriented Ship Detection Method of Remote Sensing Image With Contextual Global Attention Mechanism and Lightweight Task-Specific Context Decoupling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 4200918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, W.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.; Xiao, L. Computational Oriented Proposal for Fine-Grained Ship Detection in Complex Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 2524118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. P2RNet: Fast Maritime Object Detection From Key Points to Region Proposals in Large-Scale Remote Sensing Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 9294–9308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Bao, J.; Chen, D.; Zhang, W.; Yu, N.; Yuan, L.; Chen, D.; Guo, B. CSWin Transformer: A General Vision Transformer Backbone with Cross-Shaped Windows. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, H.; Li, H.; Wu, Q.; Cui, J.; Song, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M. CrossDet++: Growing Crossline Representation for Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 1093–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Ye, Q.; Doermann, D. YOLOv12: Attention-Centric Real-Time Object Detectors. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.12524. [Google Scholar]
- Shahaf, E.; Finder Roy, A.; Eran, T.; Oren, F. Wavelet Convolutions for Large Receptive Fields. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.05848. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Liao, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; He, X.; Wu, X. Haar wavelet downsampling: A simple but effective downsampling module for semantic segmentation. Pattern Reco. 2023, 143, 109819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.; Wu, L.; Chen, S.; Hu, X. Generalized Focal Loss: Learning Qualified and Distributed Bounding Boxes For Dense Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.04388. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Li, J.; Tang, J.; Yang, J. Generalized Focal Loss V2: Learning Reliable Localization Quality Estimation for Dense Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández López, P.; Arcambal, C.; Baudry, D.; Verdeyme, S.; Mazari, B. Simple Electromagnetic Modeling Procedure: From Near-Field Measurements to Commercial Electromagnetic Simulation Tool. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2010, 59, 3111–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.-W.; Sheng, X.-Q. Accurate and Efficient Simulation Model for the Scattering From a Ship on a Sea-Like Surface. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 2375–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Pang, C.; Li, D. Identification Method For Icosahedron Triangular Trihedral Corner Reflector And Vessels Based on Polarization Feature-Range Joint Matrix. J. Radars. 2025, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, S.; Yang, Q.; Fan, X.; Wang, P. On Optimization of Heterotypic Corner Reflector Arrays. J. Nav. Univ. Eng. 2019, 31, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Suo, Y.; Meng, Q.; Dai, W.; Miao, T.; Zhao, W.; Yan, Z.; Diao, W.; Xie, G.; Ke, Q.; et al. FAIR-CSAR: A Benchmark Dataset for Fine-Grained Object Detection and Recognition Based on Single-Look Complex SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5201022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Feng, D. An Approach for SAR Feature Reconfiguring Based on Periodic Phase Modulation with Inter-Pulse Time Bias. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Ding, C.; Guan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, T.; Meng, F.; Wang, J. Subsection-Shift-Doppler-Frequency Jamming Based on Phase-Tunable Metasurface Against SAR Imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5223415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Feng, D.; Sun, G. A Flexible Range-Doppler Modulation Method for Pulse-Doppler Radar Using Phase-Switched Screen. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2025, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, K.; Xu, K.; Luo, C.; Lv, Y.; Deng, Y. A Broadband Information Metasurface-Assisted Target Jamming System for Synthetic Aperture Radar. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).