OSSMDNet: An Omni-Selective Scanning Mechanism for a Remote Sensing Image Denoising Network Based on the State-Space Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We designed an end-to-end image denoising framework based on Mamba, enabling efficient training and inference. It offers a competitive alternative to traditional CNN and Transformer architectures for remote sensing image restoration.
- (2)
- We propose a Deep Feature Extraction Module (DEFM), which introduces the omni-selective scanning model based on Mamba for long-range dependency modeling and a Local Residual Module (LRB) to capture fine-grained spatial details, enabling multi-level feature extraction and fusion from both global and local perspectives.
- (3)
- We construct a new benchmark dataset for remote sensing image denoising. Extensive experiments demonstrate that OSSMDNet outperforms both classical methods and state-of-the-art methods in restoring high-quality natural images and remote sensing images.
2. Related Works
3. Methodology
3.1. Preliminaries
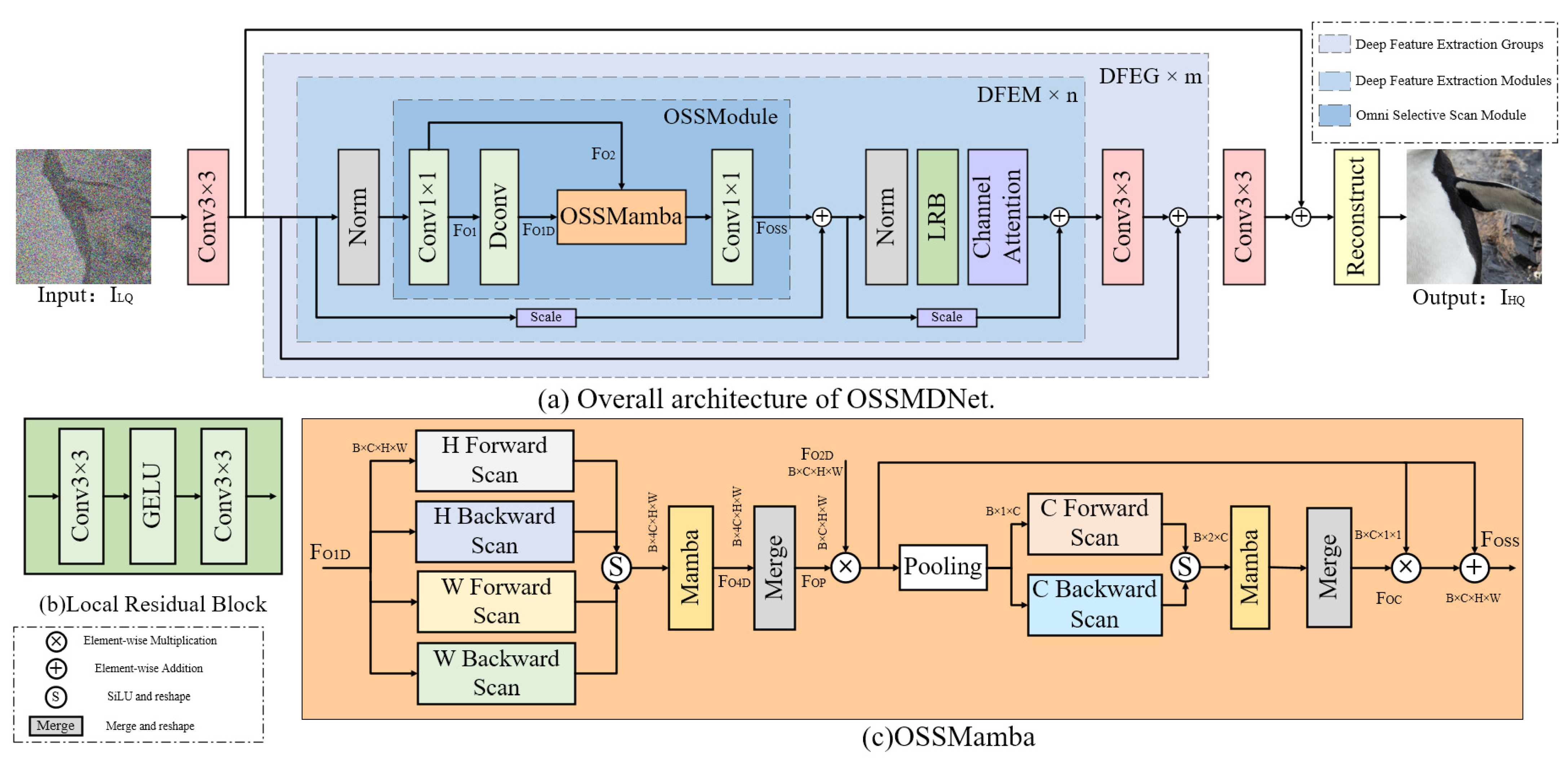
3.2. OSSMDNet Architecture
- (1)
- Shallow feature extraction stage: The input image first undergoes preliminary processing in a shallow feature extraction stage, which mainly consists of a 3 × 3 convolution layer that extracts shallow features from the input image to enhance the ability of images to represent details. The formula is as follows:
- (2)
- Deep Feature Extraction Group (DFEG): DFEG is composed of multiple DFEG modules stacked in sequence, aiming to progressively extract deeper information from shallow features. Each DFEG contains six Deep Feature Extraction Modules (DFEM) and an additional convolutional layer. As the core unit of deep feature extraction, DFEM combines the proposed OSSMamba module and a custom scanning mechanism to effectively capture long-range dependencies for expressing remote contextual information. Therefore, DFEG not only promotes the restoration of similarity between spatially adjacent pixels, improving the expression of local features, but also aids in the precise reconstruction of image details. The mathematical expression for multiple stacked DFEGs is:
- (3)
- Image Reconstruction Stage: This stage restores the image to its original RGB resolution through a convolutional mapping process, applies residual enhancement by combining the result with the input image, and finally performs denormalization to recover the original value range, yielding a high-quality output image , as shown in the following formula:
3.3. Deep Feature Extraction Module (DFEM)
3.4. OSSMamba Block Design Details
- (1)
- A 1 × 1 convolution layer;
- (2)
- A depth-wise convolution layer;
- (3)
- A core OSSMamba mechanism.
3.5. Loss Function
3.6. FLOPs, Computation Complexity and Robustness Analysis
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
- (1)
- Horizontal flipping—mirroring images along the horizontal axis;
- (2)
- Random rotation—rotating images by 90°, 180°, or 270°;
- (3)
- Image cropping—dividing the original images into 128 × 128 patches.
4.2. Evaluation Indicators
4.3. Classic Image Denoising Tasks
4.4. Remote Sensing Image Denoising Task
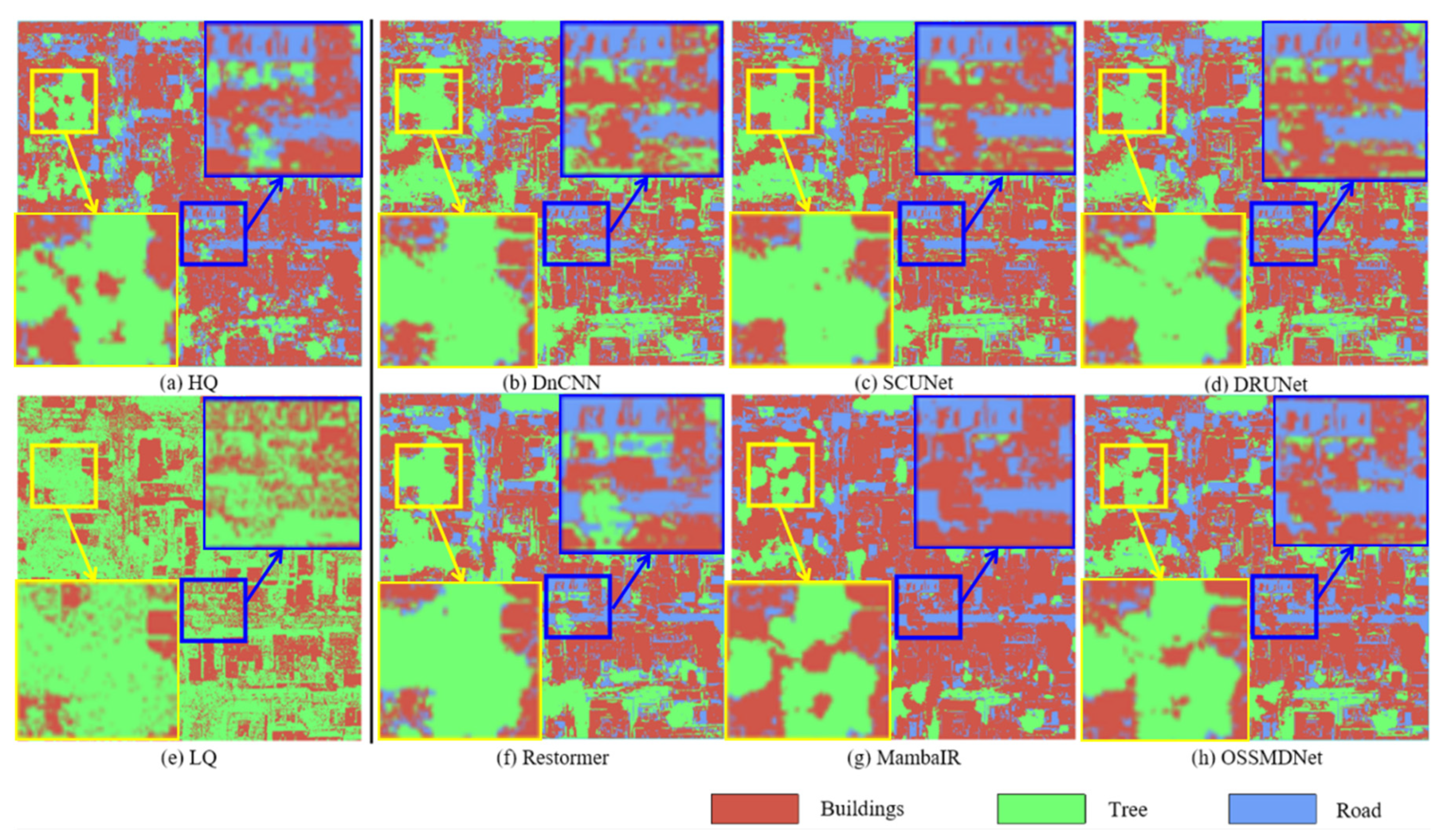
4.5. Downstream Classification Experimental Verification
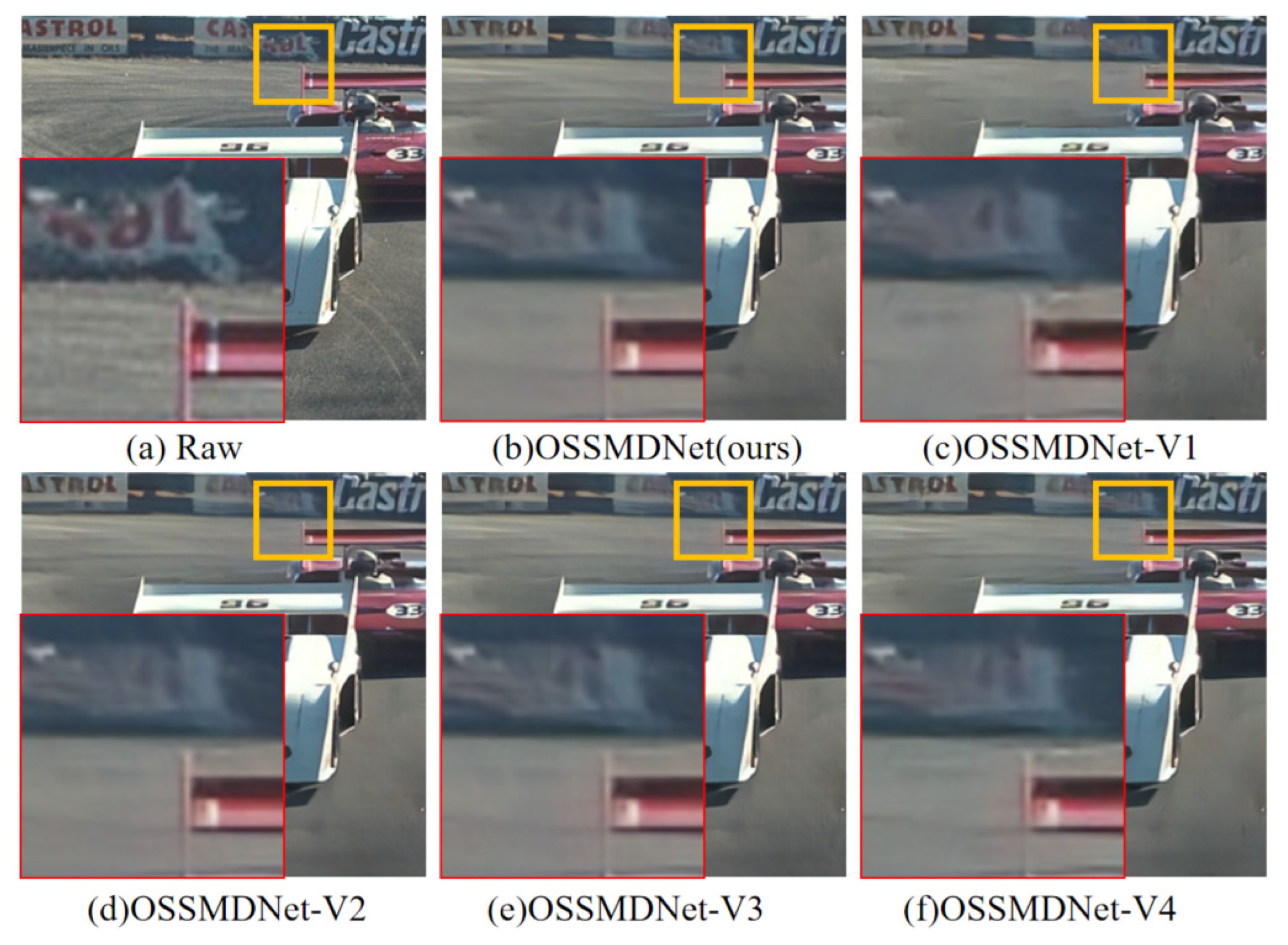
4.6. Ablation Experiments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saleem, H.; Ahmed, R.; Mushtaq, S.; Saleem, S.; Rajesh, M. Remote sensing-based analysis of land use, land cover, and land surface temperature changes in Jammu District, India. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2024, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zahidi, I. Environmental hazards posed by mine dust, and monitoring method of mine dust pollution using remote sensing technologies: An overview. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 864, 161135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiakos, C.A.D.; Chalkias, C. Use of machine learning and remote sensing techniques for shoreline monitoring: A review of recent literature. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Driscol, J.; Sarigai, S.; Wu, Q.; Lippitt, C.D.; Morgan, M. Towards synoptic water monitoring systems: A review of AI methods for automating water body detection and water quality monitoring using remote sensing. Sensors 2022, 22, 2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, S.; Durairaj, M.; Reenadevi, R.; Subbulakshmi, R.; Gupta, V.; Ramesh, J.V.N. Spatiotemporal data fusion and deep learning for remote sensing-based sustainable urban planning. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2024, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Chen, X. Intelligent Computing Characterization of Urban Images. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakria, Z.; Deng, J.; Kumar, R.; Khokhar, M.S.; Cai, J.; Kumar, J. Multiscale and Direction Target Detecting in Remote Sensing Images via Modified YOLO-V4. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Shen, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J. Underwater Forward-Looking Sonar Images Target Detection via Speckle Reduction and Scene Prior. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5604413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J. Spatio-Temporal Tensor Ring Norm Regularization for Infrared Small Target Detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 7000205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Sun, X.; Diao, W.; Yan, Z.; Yao, F.; Fu, K. Multimodal remote sensing image segmentation with intuition-inspired hypergraph modeling. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 1474–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Cheng, B.; Xiao, B.; Dong, Y.; Chen, J. Multilevel heterogeneous domain adaptation method for remote sensing image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5601916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Xia, M.; Weng, L.; Hu, K.; Lin, H.; Qian, M. Multi-scale location attention network for building and water segmentation of remote sensing image. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5609519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Matgen, P.; Chini, M. Urban flood mapping using satellite synthetic aperture radar data: A review of characteristics, approaches, and datasets. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2025, 13, 237–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Shen, H. Hyperspectral image denoising via noise-adjusted iterative low-rank matrix approximation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 3050–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Qian, Y.; Zhou, J. Multitask sparse nonnegative matrix factorization for joint spectral-spatial hyperspectral imagery denoising. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2621–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Li, S.; Fang, L.; Ma, Y.; Benediktsson, J.A. Spectral-spatial adaptive sparse representation for hyperspectral image denoising. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, G.D.; Simone, A.D.; Iodice, A.; Riccio, D. Scattering-based nonlocal means SAR despeckling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 3574–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, P.; Wang, R. Multiple-spectral-band CRFs for denoising junk bands of hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 2260–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, T.; Ren, J.; Wang, Z.; Zabalza, J.; Sun, M.; Zhao, H.; Li, S.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Dai, Q.; Marshall, S. Effective denoising and classification of hyperspectral images using curvelet transform and singular spectrum analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Song, H. Remote sensing image denoising based on wavelet transform and improved DnCNN network. Comput. Meas. Control. 2022, 30, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, L. Beyond a Gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3142–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabov, K.; Foi, A.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 2080–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canavoy, S.N.; Krishnan, S.B.; Chakrabarti, P. CNN-based restoration of remote sensing imagery through denoising schemes. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Recent Trends in Microelectronics, Automation, Computing and Communication Systems (RTMC), Hyderabad, India, 18–21 December 2024; pp. 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Zhi, K.; Zeng, J.; Tian, C.; You, L. A hybrid CNN for image denoising. J. Artif. Intell. Technol. 2022, 2, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, J.; Tian, C.; Chun-Wei Lin, J.; Zhang, S. A robust deformed convolutional neural network (CNN) for image denoising. CAAI Trans. Intell. Technol. 2023, 8, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamir, S.W.; Arora, A.; Khan, S.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S.; Yang, M.-H.; Shah, M. Learning Enriched Features for Real Image Restoration and Enhancement. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2020, Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glassgow, UK, 23–28 August 2025; Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 12370, pp. 492–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Gu, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Joint analysis and weighted synthesis sparsity priors for simultaneous denoising and destriping optical remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 6958–6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Ma, S. CSformer: Cross-scale features fusion based transformer for image denoising. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 29, 1809–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.; Dao, T. Mamba: Linear-time sequence modeling with selective state spaces. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.00752. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.00752 (accessed on 13 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Hou, W.; Van Gool, L.; Timofte, R. MatIR: A hybrid Mamba-Transformer image restoration model. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.18401. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.18401 (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Guo, H.; Li, J.; Dai, T.; Ouyang, Z.; Ren, X.; Xia, S.-T. MambaIR: A Simple Baseline for Image Restoration with State-Space Model. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2024 Workshops, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Del Bue, A., Canton, C., Pont-Tuset, J., Tommasi, T., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 15624, pp. 222–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Xia, B.; Jin, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, T.; Xia, X.; Xiao, X.; Yang, W. VmambaIR: Visual State Space Model for Image Restoration. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.11423. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.11423 (accessed on 20 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.C.; Woods, R.E. Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed.; Electronic Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2011; pp. 12–45. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.S.; Yang, G.J.; Tang, G.Y. A fast two-dimensional median filtering algorithm. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1979, 27, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.L. De-noising by thresholding. In Wavelets and Statistics; Antoniadis, A., Oppenheim, G., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 261–280. [Google Scholar]
- Candès, E.J.; Donoho, D.L. Curvelets: A Surprisingly Effective Nonadaptive Representation for Objects with Edges; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 1999; Available online: https://statistics.stanford.edu (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Do, M.N.; Vetterli, M. The contourlet transform: An efficient directional multiresolution image representation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2005, 14, 2091–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buades, A.; Coll, B.; Morel, J.M. A non-local algorithm for image denoising. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; Volume 2, pp. 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, W.; Zhang, L.; Shen, H.; Yuan, Q. Hyperspectral image restoration using low-rank matrix recovery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 4729–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elad, M.; Aharon, M. Image denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 3736–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucher, S. SAR image filtering via learned dictionaries and sparse representations. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Boston, MA, USA, 6–11 July 2008; Volume 1, pp. I–229–I–232. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, L. FFDNet: Toward a fast and flexible solution for image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 4679–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.Q.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, X.; Shen, H. Hyperspectral image denoising employing a spatial–spectral deep residual convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chierchia, G.; Scarpa, G.; Poggi, G.; Verdoliva, L. SAR image despeckling through convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 2280–2283. [Google Scholar]
- Zamir, S.W.; Arora, A.; Khan, S.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S.; Yang, M.H. Restormer: Efficient transformer for high-resolution image restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Cao, J.; Sun, G.; Zhang, K.; Van Gool, L.; Timofte, R. SwinIR: Image restoration using swin transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Cun, X.; Bao, J.; Zhou, W.; Liu, J.; Li, H. Uformer: A general u-shaped transformer for image restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, J.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, P.; Yang, H.; Wang, F. HSIDMamba: Exploring bidirectional state-space models for hyperspectral denoising. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.09697. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.09697 (accessed on 13 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Xiong, F.; Lu, J.; Zhou, J. SSUMamba: Spatial-spectral selective state space model for hyperspectral image denoising. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5601933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, H.; Xie, L.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Jiao, J.; Liu, Y. VMamba: Visual state space model. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.10166. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Cheng, X.; Xu, Z. MambaHR: State space model for hyperspectral image restoration under stray light interference. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wu, C. U-shaped Vision Mamba for Single Image Dehazing. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.04139. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.04139 (accessed on 30 January 2025). [CrossRef]
- Zamir, S.W.; Arora, A.; Khan, S.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S.; Yang, M.-H.; Shah, M. Multi-stage progressive image restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 14821–14831. [Google Scholar]
- Timofte, R.; Agustsson, E.; Van Gool, L.; Yang, M.H.; Zhang, L. NTIRE 2017 challenge on single image super-resolution: Methods and results. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 114–125. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, B.; Son, S.; Kim, H.; Nah, S.; Mu Lee, K. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L. DOTA: A large-scale dataset for object detection in aerial images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3974–3983. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, D.; Fowlkes, C.; Tal, D.; Malik, J. A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms and measuring ecological statistics. In Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–14 July 2001; Volume 2, pp. 416–423. [Google Scholar]
- Franzen, R. Kodak Lossless True Color Image Suite. 2021. Available online: http://r0k.us/graphics/kodak/ (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Zhang, L.; Wu, X.; Buades, A.; Li, X. Color demosaicking by local directional interpolation and nonlocal adaptive thresholding. J. Electron. Imaging 2011, 20, 023016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, K.M. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1646–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L. AID: Aerial image dataset for remote sensing image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2018; pp. 3564–3572. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980 (accessed on 13 June 2025).
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Gu, S.; Zhang, L. Plug-and-play image restoration with deep denoiser prior. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 6360–6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Liang, J.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, H.; Fan, D.-P.; Timofte, R.; van Goll, L. Practical blind image denoising via Swin-Conv-UNet and data synthesis. Mach. Intell. Res. 2023, 20, 822–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
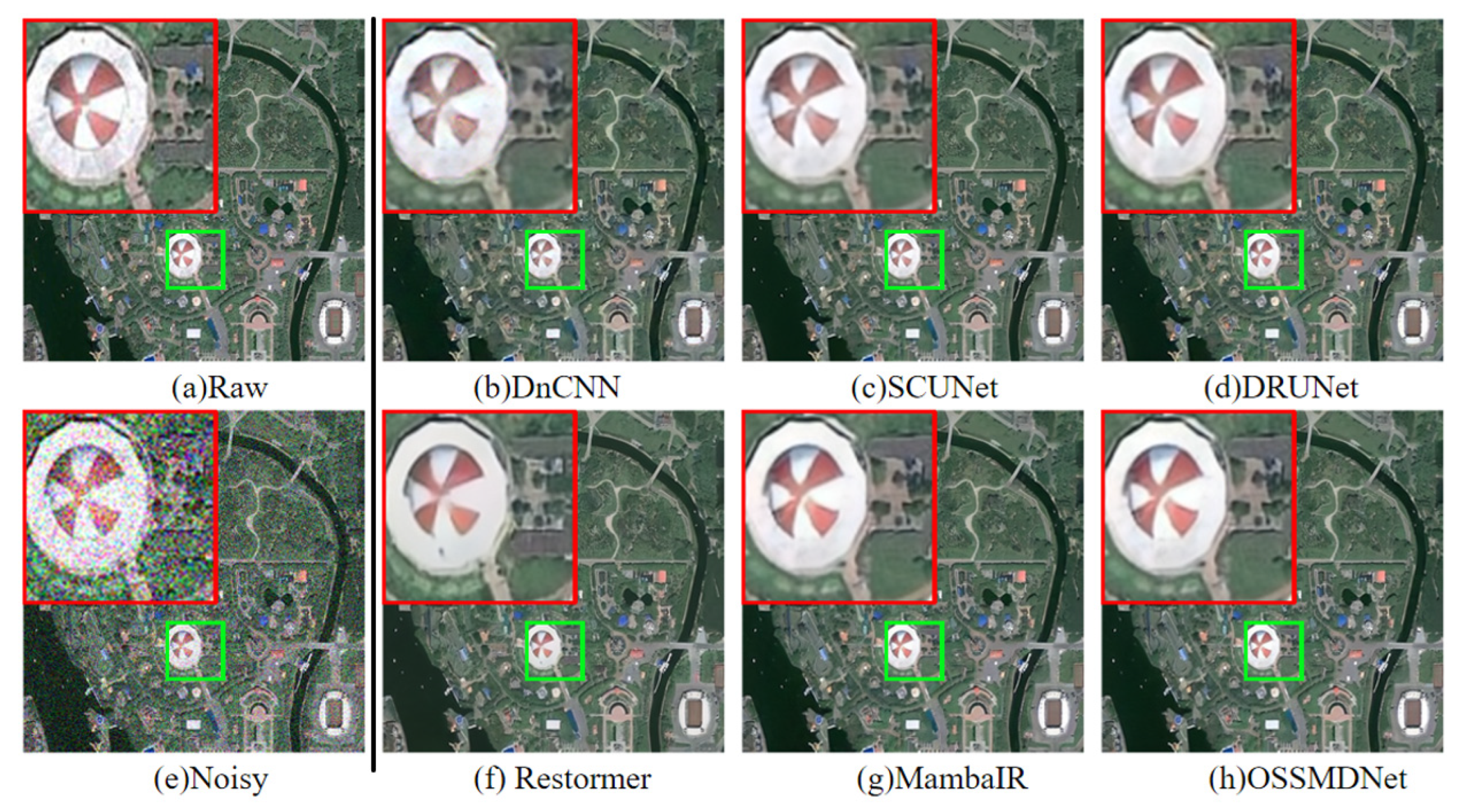







| DataSets | Noise Level | DnCNN | DRUNet | SCUNet | Restormer | MambaIR | OSSMDNet | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | ||
| CBSD68 | 25 | 30.46 | 0.8700 | 30.89 | 0.8816 | 30.92 | 0.8833 | 30.50 | 0.8839 | 30.99 | 0.8841 | 31.03 | 0.8858 |
| 50 | 27.01 | 0.7654 | 27.63 | 0.7898 | 27.61 | 0.7894 | 26.37 | 0.7787 | 27.70 | 0.7917 | 27.74 | 0.7913 | |
| Kodak24 | 25 | 31.33 | 0.8614 | 31.95 | 0.8772 | 31.92 | 0.8782 | 31.68 | 0.8786 | 32.10 | 0.8807 | 32.11 | 0.8819 |
| 50 | 27.99 | 0.7645 | 28.80 | 0.7946 | 28.76 | 0.7938 | 26.67 | 0.7866 | 28.92 | 0.7982 | 28.92 | 0.7977 | |
| McMaster | 25 | 31.43 | 0.8684 | 32.25 | 0.8896 | 32.26 | 0.8913 | 31.13 | 0.8491 | 32.47 | 0.8918 | 32.47 | 0.8924 |
| 50 | 28.07 | 0.7827 | 29.16 | 0.8239 | 29.16 | 0.8234 | 26.08 | 0.7282 | 29.31 | 0.8241 | 29.32 | 0.8249 | |
| Urban100 | 25 | 30.02 | 0.8969 | 30.87 | 0.9125 | 30.72 | 0.9110 | 30.56 | 0.9033 | 31.25 | 0.9173 | 31.30 | 0.9188 |
| 50 | 26.04 | 0.8001 | 27.51 | 0.8457 | 27.33 | 0.8437 | 26.09 | 0.8256 | 27.89 | 0.8545 | 27.96 | 0.8553 | |
| DataSets | Noise Level | DnCNN | DRUNet | SCUNet | Restormer | MambaIR | OSSMDNet | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | ||
| AID | 25 | 32.15 | 0.8740 | 32.57 | 0.8827 | 32.61 | 0.8829 | 32.52 | 0.8850 | 32.50 | 0.8806 | 32.64 | 0.8839 |
| 50 | 28.82 | 0.7703 | 29.63 | 0.8045 | 29.64 | 0.8019 | 28.80 | 0.7935 | 29.70 | 0.8047 | 29.72 | 0.8067 | |
| DOTA | 25 | 32.97 | 0.8823 | 33.66 | 0.8930 | 33.69 | 0.8926 | 33.54 | 0.8893 | 33.44 | 0.8879 | 33.74 | 0.8940 |
| 50 | 29.76 | 0.7971 | 30.72 | 0.8283 | 30.73 | 0.8261 | 29.61 | 0.8120 | 30.81 | 0.8289 | 30.84 | 0.8305 | |
| WHU-RS19 | 25 | 32.57 | 0.8946 | 32.97 | 0.9018 | 33.03 | 0.9030 | 32.39 | 0.9025 | 32.90 | 0.9000 | 33.08 | 0.9035 |
| 50 | 28.75 | 0.7952 | 29.92 | 0.8309 | 29.91 | 0.8293 | 28.25 | 0.8174 | 30.00 | 0.8315 | 30.04 | 0.8334 | |
| Evaluation Indicators | DnCNN | DRUNet | SCUNet | Restormer | MambaIR | OSSMDNet | Noisy | Raw |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall accuracy(OA) (%) | 92.96% | 95.47% | 96.57% | 97.83% | 98.33% | 99.76% | 77.10% | 100% |
| Kappa Improvement (%) | 84.06% | 91.51% | 93.42% | 96.21% | 97.77% | 98.43% | 47.60% | 100% |
| Method | OSSMamba | CA | LRB | Number of Stacks | PSNR(dB) | SSIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSSMDNet | √ | √ | √ | [6,6,6,6,6,6] | 27.96 | 0.8555 |
| OSSMDNet-v1 | × | √ | √ | [6,6,6,6,6,6] | 26.97 | 0.8287 |
| OSSMDNet-v2 | √ | × | √ | [6,6,6,6,6,6] | 27.94 | 0.8553 |
| OSSMDNet-v3 | √ | √ | × | [6,6,6,6,6,6] | 27.75 | 0.8505 |
| OSSMDNet-v4 | √ | √ | √ | [1,1,1,1,1,1] | 27.46 | 0.8451 |
| Datasets | Noise Level | OSSMDNet | OSSMDNet-v1 | OSSMDNet-v2 | OSSMDNet-v3 | OSSMDNet-v4 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | ||
| CBSD68 | 50 | 27.74 | 0.7913 | 27.38 | 0.7769 | 27.72 | 0.7913 | 27.67 | 0.7895 | 27.59 | 0.7890 |
| Kodak24 | 28.92 | 0.7977 | 28.42 | 0.7774 | 28.92 | 0.7980 | 28.80 | 0.7945 | 28.67 | 0.7931 | |
| McMaster | 29.32 | 0.8249 | 28.77 | 0.8072 | 29.32 | 0.8246 | 29.18 | 0.8203 | 28.98 | 0.8158 | |
| Urban100 | 27.96 | 0.8555 | 26.97 | 0.8287 | 27.94 | 0.8553 | 27.75 | 0.8505 | 27.46 | 0.8451 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, N.; Han, J.; Ding, H.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Song, W.; Tong, X. OSSMDNet: An Omni-Selective Scanning Mechanism for a Remote Sensing Image Denoising Network Based on the State-Space Model. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2759. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162759
Deng N, Han J, Ding H, Liu D, Zhang Z, Song W, Tong X. OSSMDNet: An Omni-Selective Scanning Mechanism for a Remote Sensing Image Denoising Network Based on the State-Space Model. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(16):2759. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162759
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Na, Jie Han, Haiyong Ding, Dongsheng Liu, Zhichao Zhang, Wenping Song, and Xudong Tong. 2025. "OSSMDNet: An Omni-Selective Scanning Mechanism for a Remote Sensing Image Denoising Network Based on the State-Space Model" Remote Sensing 17, no. 16: 2759. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162759
APA StyleDeng, N., Han, J., Ding, H., Liu, D., Zhang, Z., Song, W., & Tong, X. (2025). OSSMDNet: An Omni-Selective Scanning Mechanism for a Remote Sensing Image Denoising Network Based on the State-Space Model. Remote Sensing, 17(16), 2759. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162759







