Abstract
The BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) has completed third phase construction and currently provides global services, with a mixed constellation of BDS-2 and BDS-3. The newly launched BDS-3 satellites are equipped with rubidium and passive hydrogen maser (PHM) atomic clocks. The performance of atomic clocks is one of the cores of satellite navigation system, which will affect the performance of positioning, navigation and timing (PNT). In this paper, we systematically analyze the characteristics of BDS-2 and BDS-3 atomic clocks, based on more than one year of precise satellite clock products and broadcast ephemeris. Firstly, the results of overlapping Allan variations demonstrate that BDS-3 Rb and PHM clocks improve better in stability than BDS-2 Rb clock and are comparable to GPS IIF Rb and Galileo PHM clocks. Accordingly, the STDs of BDS-3 broadcast satellite clock are better than GPS and BDS-2, which are at the same level with that of Galileo. Secondly, the inter-system bias (ISB) between BDS-2 and BDS-3 is analyzed by satellite clock datum comparison and precise point positioning (PPP). Surprisingly, the discrepancy between BDS-2 and BDS-3 satellite clock datum has a great difference between products that could reach up to about 10 ns for WHU satellite clock products and broadcast ephemeris. Moreover, the ISBs between BDS-2 and BDS-3 satellite clocks are quite stable over one-year periods. Thirdly, due to the improved stability of BDS-3 atomic clock, the 68% positioning accuracy is better than 0.65 m at 10 min for BDS-3 PPP, based on broadcast ephemeris. Besides, the non-negligible bias between BDS-2 and BDS-3 will greatly affect the BDS precise data processing. The accuracy of positioning is greatly improved when considering the ISB.
1. Introduction
The BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS), independently constructed and developed by China, has been fully completed, following the “three-step” development strategy, as of 31 July 2020, and currently consists of a mixed constellation of BDS-2 and BDS-3 [1,2]. In 2012, the BDS-2, as the second phase started providing positioning, navigation and timing (PNT) services to the Asia Pacific region [3,4], which is now formed by a 15 satellite constellation, including 5 satellites in geostationary Earth orbit (GEO), 7 satellites in inclined geosynchronous orbit (IGSO) and 3 satellites in medium Earth orbit (MEO). Following the successful deployment and operation of the BDS-2, the global system BDS-3 was initiated with the launch of two satellites on 5 November 2017 [1,5]. On 23 June 2020, the BDS-3 reached another important milestone, which was the completion of a full constellation comprised of 30 satellites, containing 3 GEO, 3 IGSO and 24 MEO satellites [6].
The onboard atomic clock is one of the cores of a navigation satellite and greatly limits the PNT performance of real-time users [7]. Thus, the research of satellite clocks has long been a hot topic [8,9], especially the analysis of the clock stability. As the first Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), GPS clock stabilities have been studied extensively [10,11,12]. Along with the significant development of BDS, there are a growing number of publications focusing on the performance of its clocks. Hauschild et al. [13] analyzed the short-term stability of BDS-2 clocks and presented a comparison of different GNSS clocks. Similar research was conducted by Montenbruck et al. [14] and Steigenberger et al. [15]. For intervals larger than 10,000 s, all the BDS-2 clocks displayed more complex behavior due to the effects of periodic clock variations [16,17]. The performance of BDS-3 clocks has been greatly improved compared with those of BDS-2 [18]. In addition to the improved Rb atomic clocks, some BDS-3 satellites are outfitted passive hydrogen maser (PHM) clocks, which have smaller frequency drift [19,20,21]. It is well known that broadcast ephemeris provides satellite clock quadratic polynomial models for a short span of time, which means that broadcast clock offsets are predictive values. Theoretically, the broadcast ephemeris of satellite atomic clocks with better stabilities can provide more accurate prediction of clock offsets and thus provide users with better PNT services and even precise point positioning (PPP) services.
Joint BDS-2 and BDS-3 can provide sufficient observations and offer the enormous potential to enhance the accuracy, reliability and availability of PNT services [22]. However, a systematic bias between BDS-2 and BDS-3 products and observations were reported recently. For example, it was observed that there were around 4.0 ns between time group delay (TGD) reference datum of BDS-2 and BDS-3 in the broadcast ephemeris [23,24]. Moreover, it was also reported that receiver-related pseudorange biases may lead to inconsistencies in satellite clock and differential code bias (DCB) estimation when different networks of receivers were processed [25,26]. One obvious example is that the TGD values exhibit an obvious mean offset from the DCBs provided by the multi-GNSS experiment (MGEX) for BDS-2, because different correlation techniques were adopted in tracking stations before July 2017 [27,28]. Furthermore, Li et al. [29] found that receiver DCB differences between BDS-2 and BDS-3 were not close to zero and present systematic biases between different networks. In addition to TGD/DCB products, Jiao et al. [30] indicated that the broadcast ephemeris of BDS-2 and BDS-3 are calculated separately, and accordingly, the clock datum are inconsistent. Besides, the datum of precise clock products generated by international GNSS service (IGS) analysis centers (ACs) may also exist a systematic bias for BDS-2 and BDS-3, since there are many receiver types in MGEX networks, such as TRIMBLE, SEPT and JAVAD, etc. Consequently, the inter-system bias (ISB) between BDS-2 and BDS-3 actually involved the effect of products datum discrepancy and different receiver hardware delays, and must be considered in joint applications. Prior studies of the ISB between BDS-2 and BDS-3 have mostly been based on the results of PPP and focused on the impact of positioning and time transfer [31,32,33], while few touch upon the long-term characteristics of different satellite clock products.
In this paper, we focus on evaluation of BDS different satellite clock products with an emphasis on the effect of ISB between BDS-2 and BDS-3, including BDS clock stabilities and accuracy assessment, based on Allan deviation, the long-term characteristics of ISB between BDS-2 and BDS-3 satellite clocks and their impacts on PPP. The paper is organized as follows: an introduction to the Allan deviation, clock datum comparison and ionosphere-free PPP is presented in the next section. Then, a brief description of the data is presented. Next, the performance of BDS atomic clocks is evaluated with different clock products. Thereafter, we analyze the ISB between BDS-2 and BDS-3 through the comparison of satellite clock datum and receiver clock offset. Finally, the PPP performance, based on broadcast ephemeris, are evaluated and compared for five strategies.
2. Methods
The following sections introduce the Allan deviation used to assess the clock stability, the method of clock datum comparison and the principle of ionosphere-free PPP.
2.1. Satellite Clock Stability Assessment and BDS-2/BDS-3 Clock Datum Discrepancy
Due to different strategies for handling satellite clock offset, the time datum of satellite clock products of different institutions may be different. Thus, considering the different time datum, the satellite clock offset can be given by the following:
where the superscript and refer to satellites and GNSS systems, respectively; is the “true” clock offset relative to the ideal time reference; the subscript refers to the analysis center; is the estimated clock offset in products; is the clock datum with respect to the ideal time reference in products.
The Allan deviation (ADEV)—or its square, the Allan variance (AVAR)—is a common time domain measure of frequency stability. Compared with the standard variance, the AVAR has the advantage of being convergent for most types of clock noise, such as white and flicker phase noise [34]. It is defined as the infinite average of the difference in adjacent fractional frequency values averaged over the time interval and can be expressed as follows:
where is the Allan variance for the interval of interest , represents an infinite time average operation and denotes the average fractional frequency over the averaging time . In reality, the AVAR is usually calculated with phase data as follows:
where is the averaging factor and equals averaging time, , divided by basic sampling interval , is the i-th of phase values and with the round down operation .
Several improved versions of the AVAR are put forward, and one of the mostly used version now is the overlapping Allan variance, which can make maximum use of a data set and provide better statistical confidence [35]. In terms of phase data, the overlapping Allan variance used in this paper is defined as follows:
The ADEV is a more common expression of the result. In addition, gross errors are detected and eliminated by the median absolute deviation (MAD) method.
Though satellite clock stability can be assessed by substituting into Equation (4) for different product, the clock datum discrepancy between BDS-2 and BDS-3 cannot be confirmed directly with a single satellite clock offset product. Hence, the clock datum difference between different products for BDS-2 and BDS-3 is estimated firstly as follows:
where is the datum difference of the two products generated by and , and is the number of satellites. The difference between of BDS-2 and BDS-3 can thus be expressed as the difference between the BDS-2/BDS-3 clock datum discrepancy in different products, as follows:
As introduced, Equation (6), derived here, actually presents the single difference of the clock datum discrepancy between BDS-2 and BDS-3 for two ACs.
2.2. Ionosphere-Free PPP and Receiver Clock ISB
For GNSS dual-frequency data, ionosphere-free (IF) linear combination observations are widely utilized in PPP to eliminate the first-order ionospheric delay, as shown in the following expression:
where the subscript refers to receivers, and are ionosphere-free combination observations in length units of pseudorange and carrier phase, respectively, denotes the range between the receiver and the satellite with antenna phase center corrections for both and , and phase wind-up corrections for . is the speed of light, and are the receiver and satellite clock offsets, respectively. and are the hardware delay of the ionosphere-free function in the receiver and satellite. is the zenith tropospheric delay and is corresponding mapping function. is the float ionosphere-free ambiguity in units of length, and and denote observation noise. The effects of relativity, solid earth tide, ocean tide and earth rotation are corrected as well, based on existing models. Additionally, the satellite-induced, elevation-dependent code bias variation for BDS-2 is removed with the model provided by Lou et al. [36], while the effect is negligible and hence ignored for BDS-3.
B1I/B3I IF combination is adopted in the strategy of BDS-2 and BDS-3 precise clock products estimation for IGS ACs. Hence, we employed the same B1I/B3I IF combination in PPP for both BDS-2 and BDS-3. In general, the satellite IF hardware delay is assimilated to estimated precise clock offsets. Meanwhile, considering the receiver hardware delay can be absorbed by receiver clock offsets, Equation (7) can be rewritten as follows:
with
where and denote the modified receiver clock and satellite clock offset, respectively. can be eliminated directly by precise clock products. Nevertheless, it should be noted that the BDS-2 and BDS-3 broadcast clock refers to the frequency at B3I, which means it contains single B3I hardware delay that is different to the B1I/B3I IF combination counterpart [28], as follows:
in which is the hardware delay at B1I, and denote the frequencies on B1I and B3I of the BDS, respectively. BDS provides the parameter to correct the satellite clock from B3I to B1I. Thus, when the broadcast clock is aligned to B1I/B3I IF combination, the correction of hardware delay discrepancy is required to apply with and can be expressed as follows:
where is the broadcast clock offset.
With above PPP model, we can calculate the station coordinates to analyze the performance of positioning or fix the coordinates to calculate other parameters, such as the receiver clock offset. In this paper, the receiver clock offsets of BDS-2 and BDS-3 are treated as two independent white noise processes. Thus, the receiver ISB can be derived by difference of the two clock offsets.
3. Data Collection
Satellite clock products provide effective data to evaluate clock stability. As one of IGS analysis centers, Wuhan University (WHU) has been providing precise clock products for BDS-3 together with BDS-2 since 1 January 2019. Then, GeoForschungsZentrum (GFZ) started providing both BDS-2 and BDS-3 clock products since 28 November 2019. Therefore, the precise clock products generated by WHU and GFZ with a 30 s sampling interval were selected to calculate ADEV and analyze the clock datum bias between BDS-2 and BDS-3. Meanwhile, the broadcast ephemeris clock products of the same 30 s interval obtained by the second-order polynomial interpolation were also evaluated.
Moreover, seven international GNSS monitoring and assessment systems (iGMAS) and three MGEX tracking stations, which can track BDS-2 and BDS-3 satellites, were used to further calculate the ISB and evaluate the performance of PPP based on broadcast ephemeris. The experiments were performed with the FUSING (FUSing IN GNSS) software [37]. The FUSING software was developed for high precision real-time GNSS data processing [38], multi-sensor navigation [39] and atmospheric modeling [40]. The station distribution is illustrated in Figure 1. All of them are located in the Asia Pacific due to the limitation of BDS-2 regional service. The time period of selected data in this paper is from modified Julian day (MJD) 58815-59214 for a total of 400 days.
Figure 1.
Distribution of iGMAS and MGEX stations used for ISB calculation and PPP, where the color of circle indicates the station from which tracking network (red—iGMAS; blue—MGEX).
4. BDS-2/BDS-3 Clock Stabilities and Datum Discrepancy
4.1. BDS-2/BDS-3 Clock Stabilities
All of BDS-2 satellites are manufactured by China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), on which Rb atomic clocks made by Switzerland and Chinese companies are installed. Unlike BDS-2, Rb and PHM clocks used by BDS-3 satellites are all developed by China independently. Besides CASC, Shanghai Engineering Center for Microsatellites (SECM) also manufactured a part of BDS-3 satellites. More details for BDS-2 and BDS-3 satellites are listed in Table 1. There are few precise products of BDS-3 GEO satellites and the last GEO satellite C61 launched on 23 June 2020 is still under in-orbit testing. Therefore, 3 BDS-3 GEO satellites are excluded from the analysis in this paper (http://www.csno-tarc.cn/en/system/constellation, accessed on 10 December 2021).

Table 1.
BDS-2 and BDS-3 satellites information.
Figure 2 presents the overlapping Allan deviation of all BDS satellites, all GPS Block IIF satellites Rb and all Galileo Full Operational Capability (FOC) satellites PHM clocks over averaging intervals from 30 to 30,600 s. The Block IIF satellite Rb clocks (IIF-Rb) and FOC satellite PHM (FOC–PHM) clocks were selected because they have higher stabilities as the latest generation clocks for GPS and Galileo [19]. Since all IIF-Rb clocks have similar performance, we calculated the average Allan deviation values of all GPS Block IIF satellites [41]. The same was applied to FOC satellites [41,42]. Average values per satellite were derived from single-day results for the period MJD 58815-59214. The top and bottom plots were based on the precise clock products generated by GFZ and WHU, respectively, in which results were grouped according to the satellite clock types or navigation systems and depicted in different colors. To make the comparison more obvious and visible, the FOC–PHM results of GFZ products are plotted in the bottom as a reference.

Figure 2.
Overlapping Allan deviation of clock for each BDS satellite, all GPS Block IIF satellites and all Galileo FOC satellites. Average values for the period from 28 November 2019 to 31 December 2020 (MJD 58815-59214) using GFZ (top) and WHU (bottom) precise products are shown. For comparison, results of BDS-2 Rb, BDS-3 Rb, BDS-3 PHM, IIF-Rb and FOC–PHM clocks are depicted in blue, green, red, purple and cyan, respectively.
There was a good concordance between the two sets of results for BDS-2 satellite clocks. However, for BDS-3 Rb and PHM clocks, the Allan deviation based on WHU clock products is significantly higher for averaging intervals less than 1000 s. At an averaging interval of 30 s, the Allan deviation for all BDS-3 clocks based on GFZ products is between 1.7 and 2.8 10−13, while the value derived from WHU products is between 2.8 and 3.5 10−13. For averaging intervals beyond 1000 s, almost all BDS-3 PHM clocks show similar performance between the two sets of ADEV values. However, the performance of BDS-3 Rb clock stabilities for GFZ products is still better than WHU products between 1000 and 5000 s and comparable for longer intervals. Similar phenomenon also exists in IIF-Rb and FOC–PHM. Overall, these results indicate that GFZ clock products has better performance for the ADEV of the BDS-3 clock. For simplicity, the following comparison of different system clocks is based on the results calculated from GFZ products, until there is a special note.
Comparing the results of BSD-2 and BDS-3, it can be seen that the BDS-3 Rb and PHM clocks obviously have improved stability compared with the Rb clocks for BDS-2 in both plots. For the interval of 30 s, the BDS-2 Rb clocks show an Allan deviation between 3.4 and 11.0 10−13, approximately 1.2–3.9 times of the worst ADEV for the BDS-3 clocks. It is interesting to note that the majority of BDS-3 Rb and PHM clocks have virtually identical performance from averaging intervals between 30 and 10,000 s, but the ADEV for BDS-3 Rb clocks slightly increase compared with most BDS-3 PHM clocks for averaging intervals greater than 10,000 s. The PHM clocks for BDS-3 C38–C44 also show worse stability than other BDS-3 satellite PHM clocks for averaging intervals beyond about 7000 s in the two sets of results, probably owing to the lack of tracking stations. Nevertheless, the performance of BDS-2 Rb clocks exhibits significant disparity up to averaging intervals of 10,000 s and has no relevance to the satellite type. Between 500 and 2000 s, the satellite C10 and C11 show an increased ADEV compared with other BDS-2 satellites in both plots. For the averaging interval of 30,600 s, the BDS-2 Rb clocks show an Allan deviation between 2.0 and 4.5 10−14, compared with 1.4—3.1 10−14 and 1.1—2.9 10−14 for BDS-3 Rb and PHM clocks, respectively.
Over averaging intervals from 30 to 30,600 s, the decreasing range in ADEV for IIF-Rb is 23.8—1.5 10−14, and 18.1—0.7 10−14 for FOC–PHM. It is easy to find that the BDS-3 Rb and PHM clocks show better performance compared with the IIF-Rb clock in most cases from Figure 2. Moreover, the comparison of ADEV shows that the BDS-3 Rb and PHM clocks seem to be competitive with the FOC–PHM clock for averaging intervals less than 1000, but they do not reach the performance of FOC–PHM clock for longer intervals.
The plots in Figure 3 depict long-term overlapping Allan deviation for the same satellites with broadcast ephemeris (BRDC). Prior to calculating ADEV, the clock offset data were calculated from broadcast ephemeris by a second-order polynomial and stacked to 1-week periods. Then, the results derived from 1-week data for averaging intervals beyond 7200 s were averaged and shown. Inevitably, the performance of broadcast ephemeris is poorer compared with precise products in Allan deviation at the same averaging interval. The ADEV differences for BDS-3 PHM clocks are greatly small, while they are relatively large for BDS-2 and BDS-3 Rb clocks. Additionally, BDS-3 Rb clocks have a similar ADEV performance to that of BDS-3 PHM clocks for averaging intervals less than 20,000 s but show an increased Allan deviation for longer averaging intervals. However, it is interesting to note that the ADEV of C41 and C42 PHM clocks exhibits the same trend as that of BDS-3 Rb clocks, while C19, C45 and C46 Rb clocks are similar to BDS-3 PHM clocks in ADEV. At an averaging interval of 227,490 s, the median value of ADEV for BDS-2 Rb, BDS-3 Rb and BDS-3 PHM clocks is 7.5 10−14, 1.8 10−13 and 8.3 10−15, respectively.
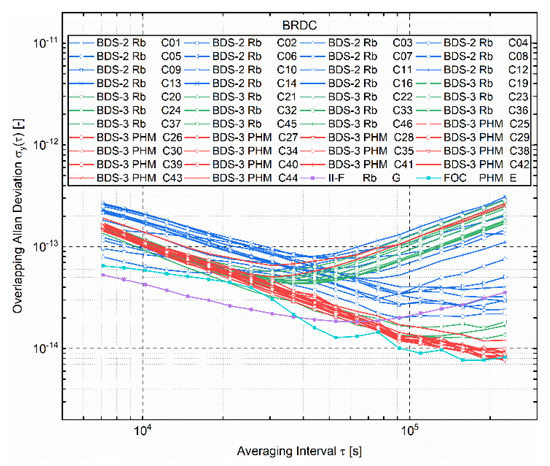
Figure 3.
Long-term overlapping Allan deviation of each BDS satellite, all GPS Block IIF satellites and all Galileo FOC satellites. Average values for the period from 28 November 2019 to 31 December 2020 (MJD 58815-59214) using broadcast ephemeris are shown.
Meanwhile, the STD values of broadcast clock offsets for all BDS, GPS and Galileo satellites were calculated corresponding to the GFZ clock products as reference values. Since the update frequency are different for different constellations, the arcs used for statistical accuracy for all constellations were uniform at 1 h. Eventually, the values were averaged over MJD 58815-59214 for all satellites in the same system and listed in Table 2. Owing to the better stability performance, the STD value of broadcast clock offsets for BDS-3 is significantly less than that of GPS and BDS-2 [22].

Table 2.
Average STD values for 1 h arc of broadcast clock offset.
4.2. Comparison of Clock Datum in Different Products
Based on the method in Section 2.1, three group differences between two sets of products from GFZ, WHU and broadcast ephemeris for the BDS-2/BDS-3 clock datum discrepancy were calculated and depicted in Figure 4. The insets enlarge respective plot of 3-day results for the time period MJD 58999-59002 to show more daily details.

Figure 4.
Difference of clock datum discrepancy between BDS-2 and BDS-3 in different products. Comparison results of GFZ–WHU (top), BRDC–GFZ (middle) and BRDC–WHU (bottom) are shown with a sampling interval of 30 s, where the satellite PCO effect in BRDC is deduced for BDS-2.
The top plot of Figure 4 presents the difference between GFZ and WHU precise clock products. Most of results are between 1 and 6 ns with a mean of 3.30 ns, which means that the datum discrepancy between BDS-2 and BDS-3 in precise products does exist. The satellite clock datum discrepancy between BDS-2 and BDS-3 of different analysis centers may be due to the different processing strategy and stations. At the day boundaries, the difference exhibits a jump due to the clock offset discontinuities. However, on the whole, the difference time series are quite stable, with a standard deviation of 0.75 ns for a total of 400 days.
The middle and bottom plots of Figure 4 present the difference between broadcast ephemeris and precise products derived from GFZ and WHU, respectively, having a mean of 3.04 ns and 6.37 ns, respectively. As mentioned above, the broadcast clock offsets with a 30 s sampling interval were obtained by second-order polynomial interpolation. Since the broadcast orbits referred to the center of mass for BDS-2, the PCO corrections are assimilated to the broadcast clock offsets [43]. Thus, the effect of satellite PCO in broadcast clock offsets must be corrected for BDS-2 when calculating the difference of clock datum discrepancy. Otherwise, it will introduce a bias of about 11 ns. Besides, the clock datum bias will jump every hour since BDS broadcast ephemeris is updated every hour and has a lager standard deviation, which is 1.61 ns for BRDC–GFZ and 1.55 ns for BRDC–WHU.
5. BDS-2 and BDS-3 ISB Analysis and PPP Solutions
5.1. Comparison of Receiver Clock Offset
In order to further validate and analyze the ISB between BDS-2 and BDS-3, ionosphere-free PPP solutions have been processed based on observation from 10 stations. For this purpose, the BDS-2 and BDS-3 were regarded as two systems and their respective receiver clock offset was estimated. The station coordinates were fixed by the weekly PPP solution. Two sets of results were obtained using precise products from GFZ and WHU, respectively. In addition, standard point positioning (SPP) solutions were also calculated with broadcast ephemeris. All solution processes were restarted at the day boundaries.
Figure 5 shows the daily average values of the difference of receiver clock offset for BDS-2 and BDS-3 from MJD 58815 to MJD 59214. The MAD method is applied to detect gross errors. Three sets of results obtained with GFZ, WHU and broadcast products are depicted in red, blue and green, respectively. Overall, the receiver clock offset difference exhibits great stability across different days. In addition, the hardware delay varies between different receivers, but it is similar for receivers of the same type [44]. Due to the effect of different receiver hardware delays, there are significant differences between the results of some stations. For instance, the difference values of receiver clock offset with GFZ precise products fluctuate around −3.06 ns for SGOC station, while fluctuating around 3.73 ns for XIA1 station. The average values of the daily average difference for each station together with the receiver type are summarized in Table 3. Moreover, the difference between the results with different products listed in the last column for an example, which is not affected by the receiver hardware delay, can greatly match respective difference of the clock datum discrepancy between BDS-2 and BDS-3 with a mean value of 3.30 ns as discussed in Section 4.2.
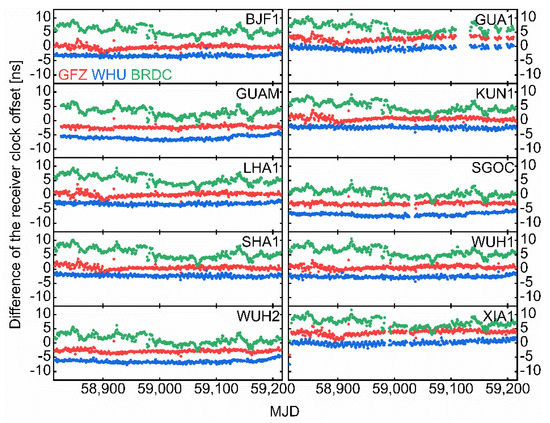
Figure 5.
Difference between the receiver clock offset for BDS-2 and BDS-3. Average values per day for 10 tracking stations are shown. The color indicates which products have been used to process (red—GFZ; blue—WHU; green—BRDC).

Table 3.
Average values (ns) of the daily average differences.
In order to analyze the daily variation of ISB, the time series of receiver clock offset difference over a 3-day period (MJD 58999–59001) are depicted in Figure 6. For the time series with precise products, the difference values jump and re-converge at the day boundaries due to the restart of PPP solution processes. After convergence, the difference seems to be a constant value. In addition, some jumps are caused by data interruption. Similarly, the results with broadcast ephemeris are more dispersed and have no obvious jump because the precision is poor for SPP solutions.
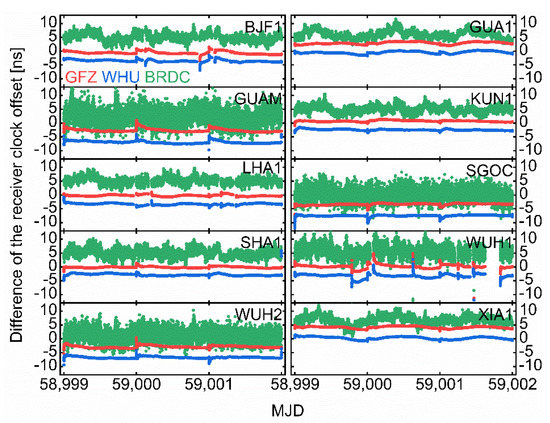
Figure 6.
Time series of the receiver clock offset difference over a 3-day period. The results of 10 tracking stations are shown with an interval of 30 s in red (GFZ), blue (WHU) and green (BRDC).
5.2. PPP Soulutions
As discussed in Section 4.1, BDS-3 atomic clock stability has been improved significantly, the accuracy of broadcast ephemeris clock model may profit thereby. Accordingly, PPP solutions were processed with broadcast ephemeris to evaluate its positioning performance. In this paper, solutions calculated with broadcast ephemeris were different to the traditional single point positioning. Both code and phase observations were adopted when using broadcast ephemeris. As comparisons, precise products of GFZ and WHU were also utilized to process PPP solutions. The two-month (MJD 59154–59214) data were selected to process kinematic PPP solutions. To avoid the effects of broadcast ephemeris update, solution processes are restarted for every hour. Taking the fixed coordinates as references, positioning errors are calculated for each epoch. For more details of PPP strategy, we refer to Table 4.

Table 4.
Details of PPP strategy.
Figure 7 presents the time series of 68% level PPP error for vertical (up) and horizontal (N–E) components. The RMS values were calculated with the results after convergence (latter 40 min) and provided in Table 5. Five strategies with broadcast ephemeris, including GPS-only (GPS), BDS-3-only (BDS-3), BDS-2+BDS-3 as one system (BDS), BDS-2+BDS-3 with ISB parameter estimation (BDS-23) and with constant ISB in Table 3 (Constant ISB), were applied for comparison. According to the character of ISB in Section 5.1, it is estimated as a constant. The 68% level visible satellite number is 9, 10 and 21 for GPS, BDS-3 and BDS-2+BDS-3, respectively. The BDS-3 positioning performs significantly better compared with GPS under the same satellite number nearly, especially in vertical. This is probably because the vertical component is relatively sensitive to the ranging error that is affected by satellite clock offset, but the horizontal component is limited by the satellite network, thus it is less affected. It is interesting to find that the PPP performance of BDS-3 is pretty close to BDS in both vertical and horizontal, despite the fact that the visible satellite number is less than half of that of BDS, which indicates that the BDS-3 positioning service improved more than BDS-2. Moreover, a better convergence speed and accuracy for BDS-23 and Constant ISB compared with BDS reflect that the precise data processing is affected by the ISB between BDS-2 and BDS-3. Similar positioning performance for BDS-23 and Constant ISB further indicate the long-term stable characteristic of ISB. The 68% PPP accuracies at 10 min for BDS-3, BDS-23 and Constant ISB are better than 0.65 and 0.60 m, respectively. Due to the similar results between estimated ISB and constant ISB with precise products from GFZ and WHU, we only present the constant ISB results that have slightly faster convergence speed compared with the strategy of estimated ISB.
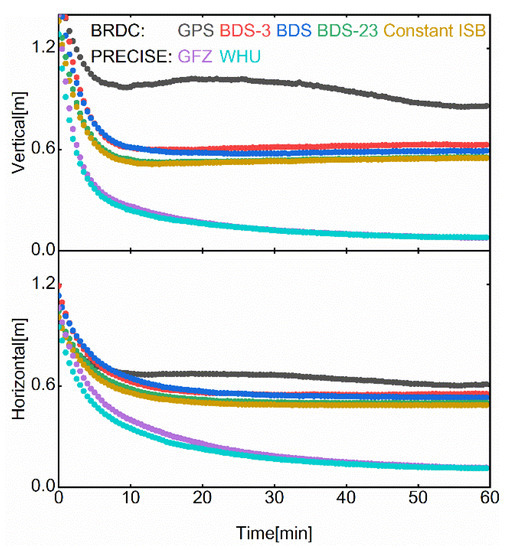
Figure 7.
Time series of 68% level PPP error in vertical (top) and horizontal (bottom). The color of scattered plots indicates different strategies (black—GPS-only; red—BDS-3-only; blue—BDS-2+BDS-3 as one system; green—BDS-2+BDS-3 with ISB parameter estimation; yellow—BDS-2+BDS-3 with constant ISB; broadcast ephemeris are used for the above strategies; purple—BDS-2+BDS-3 with constant ISB used GFZ precise products; cyan—BDS-2+BDS-3 with constant ISB used WHU precise products).

Table 5.
RMS values (m) of PPP after convergence.
6. Conclusions
The atomic clock stability of most BDS satellites is assessed systematically with overlapping Allan deviation. For comparison, three sets of results were calculated using clock products from GFZ, WHU and broadcast ephemeris, respectively, in which the results with GFZ products show a slightly better performance than that of WHU products. However, the products from GFZ and WHU have an excellent agreement in Allan deviation. The comparison of Allan deviation results for BDS-2 and BDS-3 has shown that BDS-3 Rb and PHM clocks exhibit significant improvement in stability, and BDS-3 PHM clocks are much more stable than Rb clocks for long-term intervals. Meanwhile, all GPS Block IIF and Galileo FOC satellites were selected to compare the clock stability behavior with BDS satellites. The results indicate that BDS-3 Rb and PHM clocks are comparable to GPS Block IIF Rb and Galileo FOC–PHM clocks.
Two methods, clock datum comparison and PPP, were applied to analyze the inter-system bias between BDS-2 and BDS-3. Through the comparison of clock products, the existence of clock datum discrepancy between BDS-2 and BDS-3 is confirmed indirectly. The time series of results for a total of 400 days indicates that the datum discrepancy performs quite stable. Thereafter, 10 static stations’ data were collected to investigate the receiver clock offset for BDS-2 and BDS-3 by ionosphere-free PPP solutions. As expected, there is an obvious inter-system bias between BDS-2 and BDS-3, which is not only affected by the clock datum discrepancy but also by the difference of hardware delay. Similarly, the inter-system bias seems to be a constant after convergence and is excellently stable as well, across different days. Therefore, the inter-system bias must be considered in joint BDS-2 and BDS-3 applications. Furthermore, PPP solutions of five strategies are processed with broadcast ephemeris. The comparison results indicate that BDS-3 PPP performance based on broadcast ephemeris is enormously better than GPS. Owing to the improved satellite clock stability, the 68% level positioning accuracy for BDS-3 can be better than 0.65 m at 10 min, which is ameliorated greatly compared with BDS-2. The positioning performance for BDS-2+BDS-3 has great progress when estimating the ISB parameter or taking the ISB as a constant, which demonstrates that the BDS precise data processing is affected greatly by the ISB.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.G. and X.G.; methodology, F.M.; software, S.G.; validation, F.M. and X.G.; formal analysis, X.G.; investigation, F.M.; resources, Y.L.; data curation, Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, F.M.; writing—review and editing, S.G. and X.G.; visualization, X.X.; supervision, Y.L.; project administration, Y.L.; funding acquisition, S.G. and X.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 41904016 and 42174029; and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, grant number 2019M662714.
Data Availability Statement
The precise clock products in this work were provided by the GeoForschungsZentrum and Wuhan University (ftp://igs.gnsswhu.cn/pub/gps/products/mgex, accessed on 10 December 2021).
Acknowledgments
The authors express great gratitude to IGS and iGMAS for providing the GNSS data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- CSNO. Development of BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (Version 4.0). Available online: http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/201912/P020191227430565455478.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Yuan, Y.; Freeshah, M.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, F. BDS multi-frequency PPP ambiguity resolution with new B2a/B2b/B2a + b signals and legacy B1I/B3I signals. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSNO. Report on the Development of BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (Version 2.1). Available online: http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/201805/P020180509588857259014.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Gu, S.; Lou, Y.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. BeiDou phase bias estimation and its application in precise point positioning with triple-frequency observable. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, F.; Gong, X. BDS-3 differential code bias estimation with undifferenced uncombined model based on triple-frequency observation. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X.; Tang, C.; Guo, R.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, J.; Pan, J.; Su, M. BeiDou-3 broadcast clock estimation by integration of observations of regional tracking stations and inter-satellite links. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaduszliwer, B.; Camparo, J. Past, present and future of atomic clocks for GNSS. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, H.; Dach, R.; Jäggi, A.; Beutler, G. High-rate GPS clock corrections from CODE: Support of 1 Hz applications. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Gu, S.; Gong, X.; Song, W.; Lou, Y.; Liu, J. Regional BDS satellite clock estimation with triple-frequency ambiguity resolution based on undifferenced observation. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, J.; Dass, T.; Freed, G.; Rajan, J.; D’Agostino, J.; Epstein, M. GPS block IIR clocks in space: Current performance and plans for the future. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium and Exposition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 29–31 August 2005; p. 19, ISBN 0-7803-9053-9. [Google Scholar]
- Senior, K.L.; Ray, J.R.; Beard, R.L. Characterization of periodic variations in the GPS satellite clocks. GPS Solut. 2008, 12, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griggs, E.; Kursinski, E.R.; Akos, D. An investigation of GNSS atomic clock behavior at short time intervals. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauschild, A.; Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P. Short-term analysis of GNSS clocks. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Hauschild, A.; Steigenberger, P.; Hugentobler, U.; Teunissen, P.; Nakamura, S. Initial assessment of the COMPASS/BeiDou-2 regional navigation satellite system. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigenberger, P.; Hugentobler, U.; Hauschild, A.; Montenbruck, O. Orbit and clock analysis of Compass GEO and IGSO satellites. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Q.; Maciuk, K.; Lewinska, P.; Borowski, L. Characteristics of Onefold Clocks of GPS, Galileo, BeiDou and GLONASS Systems. Sensors 2021, 21, 2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lou, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Q.; Su, X. Analysis of BDS satellite clocks in orbit. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Ge, Y.; Wei, P.; Dai, P.; Yang, X. Assessment of the BDS-3 on-board clocks and their impact on the PPP time transfer performance. Measurement 2020, 153, 107356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Huang, G.; Xie, W.; Xie, S.; Wang, H. Assessment and comparison of satellite clock offset between BeiDou-3 and other GNSSs. Acta Geod. Geophys. 2021, 56, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhou, S.; Hu, X.; Liu, L.; Shuai, T.; Xie, Y.; Tang, C.; Pan, J.; Zhu, L.; Chang, Z. Performance of the BDS3 experimental satellite passive hydrogen maser. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Mao, Y.; Sun, B. Basic performance and future developments of BeiDou global navigation satellite system. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Ouyang, C.; Huang, Y.; Peng, W. Assessment of BDS-3 global positioning service: Ephemeris, SPP, PPP, RTK, and new signal. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, Z.; Montenbruck, O.; Tang, C. Quality assessment of GPS, Galileo and BeiDou-2/3 satellite broadcast group delays. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 64, 1764–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kubo, N.; Chen, J.; Chu, F.-Y.; Wang, A.; Wang, J. Apparent clock and TGD biases between BDS-2 and BDS-3. GPS Solut. 2019, 24, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Lou, Y.; Zheng, F.; Gu, S.; Shi, C.; Liu, J.; Jing, G. Evaluation and calibration of BeiDou receiver-related pseudorange biases. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Gong, X.; Lou, Y.; Gu, S.; Jing, G.; Shi, C. Calibration of BeiDou Triple-Frequency Receiver-Related Pseudorange Biases and Their Application in BDS Precise Positioning and Ambiguity Resolution. Sensors 2019, 19, 3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montenbruck, O.; Hauschild, A.; Steigenberger, P. Differential Code Bias Estimation using Multi-GNSS Observations and Global Ionosphere Maps. J. Inst. Navig. 2014, 61, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Gong, X.; Chen, Q. The update of BDS-2 TGD and its impact on positioning. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 65, 2645–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xie, W.; Huang, J.; Ma, T.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Y. Estimation and analysis of differential code biases for BDS3/BDS2 using iGMAS and MGEX observations. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, G.; Song, S.; Liu, Y.; Su, K.; Cheng, N.; Wang, S. Analysis and Assessment of BDS-2 and BDS-3 Broadcast Ephemeris: Accuracy, the Datum of Broadcast Clocks and Its Impact on Single Point Positioning. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, G.; Song, S.; Jiao, W. Improving BDS-2 and BDS-3 joint precise point positioning with time delay bias estimation. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2020, 31, 25001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Su, H.; Wei, P.; Yang, X. Accounting BDS3–BDS2 inter-system biases for precise time transfer. Measurement 2020, 156, 107566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Chen, H.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, W.; Liu, X. Evaluation of Inter-System Bias between BDS-2 and BDS-3 Satellites and Its Impact on Precise Point Positioning. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, D.W. Statistics of atomic frequency standards. Proc. IEEE 1966, 54, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allan, D.; Hellwig, H.; Kartaschoff, P.; Vanier, J.; Vig, J.; Winkler, G.; Yannoni, N.F. Standard terminology for fundamental frequency and time metrology. In Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Frequency Control Symposium, Baltimore, MD, USA, 1–3 June 1988; pp. 419–425. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Y.; Gong, X.; Gu, S.; Zheng, F.; Feng, Y. Assessment of code bias variations of BDS triple-frequency signals and their impacts on ambiguity resolution for long baselines. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Zheng, F.; Gong, X.; Lou, Y.; Shi, C. Fusing: A Distributed Software Platform for Real-Time High Precision Multi-GNSS Service. In Proceedings of the IGS Workshop, Wuhan, China, 29 October–2 November 2018; Available online: https://files.igs.org/pub/resource/pubs/workshop/2018/IGSWS-2018-PY09-05.pdf?_ga=2.181681828.2033109928.1639203343-1862730709.1639203343 (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Gong, X.; Gu, S.; Lou, Y.; Zheng, F.; Ge, M.; Liu, J. An efficient solution of real-time data processing for multi-GNSS network. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Dai, C.; Fang, W.; Zheng, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lou, Y.; Niu, X. Multi-GNSS PPP/INS tightly coupled integration with atmospheric augmentation and its application in urban vehicle navigation. J. Geod. 2021, 95, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Lou, Y.; Gu, S.; Li, G.; Xiong, C.; Song, W.; Zhao, Z. Local ionospheric plasma bubble revealed by BDS Geostationary Earth Orbit satellite observations. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudrys, J.; Skorupa, B.; Malkin, Z. Testing the product quality of Galileo and GPS on-board oscillators. Measurement 2021, 167, 108261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Guo, F.; Zheng, J. Analysis of Galileo signal-in-space range error and positioning performance during 2015–2018. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Hauschild, A. Broadcast versus precise ephemerides: A multi-GNSS perspective. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauschild, A.; Montenbruck, O. A study on the dependency of GNSS pseudorange biases on correlator spacing. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).