Abstract
Land-take leads to the loss of natural and semi-natural areas. The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development highlights the important role played by land-take and degradation mitigation to promote sustainable cities. This research aims to assess (1) the temporal dynamics of land-take and land degradation, (2) their spatial configuration, and (3) their ecological effects in three Italian urban landscapes. Spatial analyses from 2006 to 2022 reveal a significant urban sprawl, with an increase in land-take across all municipalities, with the highest land-take per capita in Nardò, higher than the national value. The land-take patterns showed the highest aggregation in Galatone, the smallest municipality. This municipality showed the highest percentage of degraded land (60% of the total area), followed by Lecce (about 47%) and then Nardò (about 42%), where it is possible to notice several areas of improvements (743 ha) scattered throughout the landscape. Degraded areas have increasingly impacted natural areas (25% in Lecce, 22% in Galatone, and 10% in Nardò). The results are discussed in terms of methodology limitations and policy-making implications, highlighting the important role of tools like Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) in assessing the coherence of landscape plans with sustainable development targets.
1. Introduction
Urban sprawl is expanding at a rate overpassing the growth of the urban population [1]. This expansion is attributed to economic development and the growth of built-up urban areas [2,3] that shape the urban landscape [4,5]. Urbanization is a global, multidimensional phenomenon driven by the alteration of land use and land cover (LULC), causing the transformation of natural landscapes into impermeable built-up surfaces [3,6,7], and representing a significant anthropogenic driver of landscape reshaping. Urbanization is a form of “land take” that refers to the conversion of natural and semi-natural lands into artificial surfaces [8,9,10,11]. These changes necessitate an in-depth understanding of their socio-ecological implications to effectively mitigate their effects on both human quality of life and environmental quality [12]. In particular, the degradation of natural and semi-natural areas can affect the provision of several landscape services as defined by Termorshuizen and Opdam [13] or even result in their complete loss [10,14,15]. These services are considered the contributions of natural capital to human well-being and incorporate natural and cultural aspects, their temporal dynamics, and their spatial patterns [16]. Land-take can cause land degradation, defined as the reduction or loss of the biological or economic productivity of land [17], with the irreversible loss of biodiversity, ecological functions, and the capacity to provide landscape services.
To minimize land-take and avoid land degradation, the establishment of sustainable spatial planning at the local scale is essential to set strategic goals over time by which cities prioritize their spatial development [18,19]. These goals should consider the mitigation of land degradation effects on landscape services to enhance human well-being. Therefore, urban spatial planning represents a way to put into practice the concept of landscape services as an important tool for sustainability [16,20]. However, in the past, little attention has been given to approaches trying to integrate the temporal and spatial assessment of land-take and land degradation effects on landscape services. In the context of Agenda 2023 and with the support of European directives, this research aims to assess (1) the temporal dynamics of land-take and land degradation areas in terms of amount, (2) their spatial configuration, and (3) their ecological effects on the provision of landscape services in three urban landscapes.
How to Mitigate the Ecological Effects of Land-Take and Land Degradation Through Urban Planning
Among the several effects of land-take is landscape fragmentation [21,22,23,24,25,26]. Fragmentation leads to the formation of patch fragments [27,28,29,30], disrupts landscape spatial configuration in terms of structural connections among patches, and thus reduces landscape resilience and its ability to provide a wide range of landscape services. The presence of land-take areas among natural and semi-natural patches contributes to the lack of connections that can isolate flora and fauna by limiting wildlife access to resources and reducing both the area and the quality of habitats [28,31]. Fragmentation is also exacerbated by land degradation that influences the availability of natural resources for human communities [10] and causes socio-economic and ecological challenges for urban planning [32,33]. Growing attention is being paid to mitigating the consequences of land degradation and land-take. The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) has focused attention on these issues through three main goals. In particular, Goal 2.4 aims to ensure and implement resilient agricultural practices and sustainable food production. In line with Goal 2.4, Goal 15.3 focuses on the strategies against desertification, restoring degraded land and soil, and striving for a land degradation-neutral world [34]. The Agenda proposes to monitor these Goals through the Indicator 15.3.1“Annual change in degraded or desertified arable land (% or ha)”. Goal 11.3 aims to enhance inclusive and sustainable urbanization and capacities for participatory, integrated, and sustainable human settlement planning and management in all countries. In this case, the Agenda proposes to monitor this target through Indicator 11.3.1, “Ratio of Land Consumption Rate to Population Growth Rate” (LCRPGR).
Furthermore, land-take is taken into account in various environmental policies, including the recent European Biodiversity Strategy 2030 [35], the European Soil Strategy 2030 [11], and the recent Nature Restoration Law n. 2024/1991, which sets targets to restore degraded ecosystems with the aim of enhancing carbon storage and prevent the impact of natural disasters. At the urban scale, the most effective strategy to promote sustainability is the integration of environmental protection principles into the planning process, through instruments such as Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) [36], especially at the urban scale [37,38]. The effective implementation of the EU Directive on the Strategic Environmental Assessment (2001/42/EC) [39] has shown how to promote the inclusion of environmental aspects in the design of plans and programs [19,40,41]. This promotes a more systematic and transparent planning process, as well as more effective decision-making at the urban scale [38,42,43], given that urban is the right scale where actions against land consumption can be implemented [44,45,46,47,48].
Finally, recognizing the maintenance of sustainable and livable cities as the main challenge of urban planning [49,50], the capacity to analyze the spatial dynamics of urbanization has been implemented through the use of Earth observation datasets [51]. These data can be useful in analyzing the spatial and temporal dynamics of built-up density, land use conversion, and land-take spatial pattern [52,53,54]. When these data are integrated with landscape spatial metrics, they can quantitatively and simultaneously analyze landscape composition (amount) and configuration (spatial arrangement) [29,55,56].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas
This study was carried out in three municipalities of the province of Lecce (Apulia region, southern Italy): Lecce, Nardò, and Galatone (Figure 1). The three municipalities are part of the Salento peninsula, a subregion of southern Apulia lying between the Ionian Sea to the west and the Adriatic Sea to the east. These municipalities were selected from the same province to avoid differences related to specific social and economic trends that can vary among provinces and regions. Their landscapes mainly consist of agricultural lands, with non-irrigated arable fields being the most prominent feature, although the agricultural areas are fragmented by roads and urban settlements. Thus, the economy is based on agriculture, particularly olive growing and viticulture, and tourism. Lecce is also an important hub for the Salento economy and ranks among the most dynamic areas in southern Italy, as it is also the provincial capital. Lecce and Nardò are quite comparable to each other in terms of extent, while Galatone is the smallest, as shown in Table 1. The administrations of these municipalities have proposed new General Urban Plans (GUPs) that apply to urban, peri-urban, and rural areas. According to Italian legislation (Italian Law n. 152/2006), these GUPs are subject to the Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) to verify whether the planned actions are in line with the Agenda 2030 SDGs. As shown in Table 1, only Galatone presents a GUP adopted and implemented, while the GUPs of Lecce and Nardò are still in the design phase.
Figure 1.
Study areas are represented by the municipalities of Lecce, Nardò, and Galatone, in the province of Lecce (Apulia region, southern Italy).

Table 1.
Description of the municipalities under study in terms of area (in ha), inhabitants (number), and implementation of the General Urban Plan.
2.2. Methods
The flow chart of the research structure is presented in Figure 2. In particular, the basic layers are represented by the land-cover maps; land-cover maps for 2006 and 2011 were acquired from the regional geo-database SIT Puglia (http://www.sit.puglia.it/ accessed on 10 July 2024), which is a regional web GIS that collects regional spatial databases. Their classification is based on CORINE Land Cover level 3. The land-cover maps for 2022 were obtained by updating the land-cover maps for 2011 with the photointerpretation of orthorectified aerial imageries.
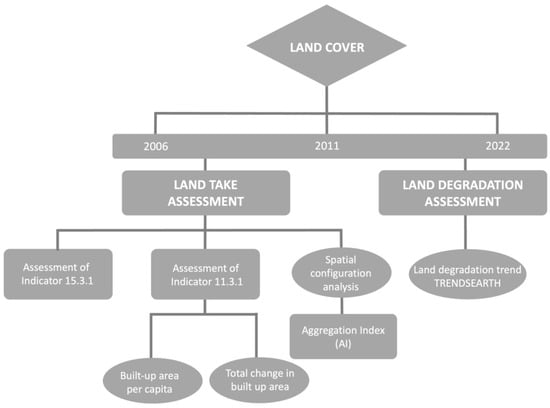
Figure 2.
Flow chart of the key steps of the methodological framework.
2.2.1. Land-Take Assessment
In this research, the assessment of land-take (Figure 2) was based on the artificial, i.e., anthropogenic, land-cover classes that describe the consumption of land, classified according to CORINE Land Cover classification level 3 and detailed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Land-cover classes that describe the land-take based on CORINE Land Cover classification level 3.
These classes were mapped in 2006, 2011, and 2022 and used to quantify Indicator 15.3.1 in terms of the extent (amount) of land-take areas (in ha) and in terms of the percentage of land-take over each municipality area, according to the relation in (1):
as well as the increment of land-take density (m2/ha) over each time range (2006–2011 and 2011–2022) according to the relation in (2):
As a second step, Indicator 11.3.1, named “Ratio of Land Consumption Rate to Population Growth Rate” (LCRPGR), of the 11th SDG was quantified according to the relation (3) proposed by [57]
where land consumption rate is the rate at which urbanized land changes during a time range (in percentage) and population growth rate is the change of a population in a defined area in the same time range (in percentage) [57]. To better analyze the land-take rate, two additional secondary indicators were used: “Built-up area per capita” (in m2/person) (4):
and “Total change in built-up area” (in % over the municipality area) (5):
The final step in the assessment of land-take was to carry out the analysis of its spatial configuration in the three municipalities in 2022, through the use of aggregation index (AI), a landscape metric computed using FRAGSTAT 4.2 software [56]. The AI has been used to describe the aggregation or connectivity between patches of land-take [58,59,60]. The AI is a value expressed in percentage, typically ranging from 0 to 100: The AI equals 0 when the patch types are maximally disaggregated and the AI equals 100 when the landscape consists of a single patch [56].
2.2.2. Land Degradation Assessment
The assessment of land degradation (Figure 2) was based on land-cover change in the time range of 2006–2022, based on a simplified classification (tree-covered, grasslands, croplands, wetlands, artificial surface, other lands, water bodies) in comparison with the CORINE classification. In this way, all of the classes in Table 2 are included in the “artificial surface” class. Indicator 15.3.1, named “Annual change in degraded or desertified arable land (in % over the municipality area)” of the 15th SDG, was quantified through TRENDSEARTH, which is a QGIS plugin. The results allowed us to characterize the study areas using three classes of change (in degradation, stable, and improvement) according to the process of land-cover change in progress that could potentially have increased or mitigated degradation during the reference time range (2006–2022).
Finally, the assessment of the ecological effects of land-take and land degradation was detected considering the high natural value areas (protected areas and European special areas of conservation). Through this analysis, it was possible to quantify how much land has been consumed or degraded in these natural areas and to identify the areas where it is possible to highlight improvement trends against land degradation.
3. Results
3.1. Assessment and Spatial Analysis of Land-Take
The maps of land-take by 2022 for the three analyzed municipalities are shown in Figure 3 and allow for spatial comparison among them.
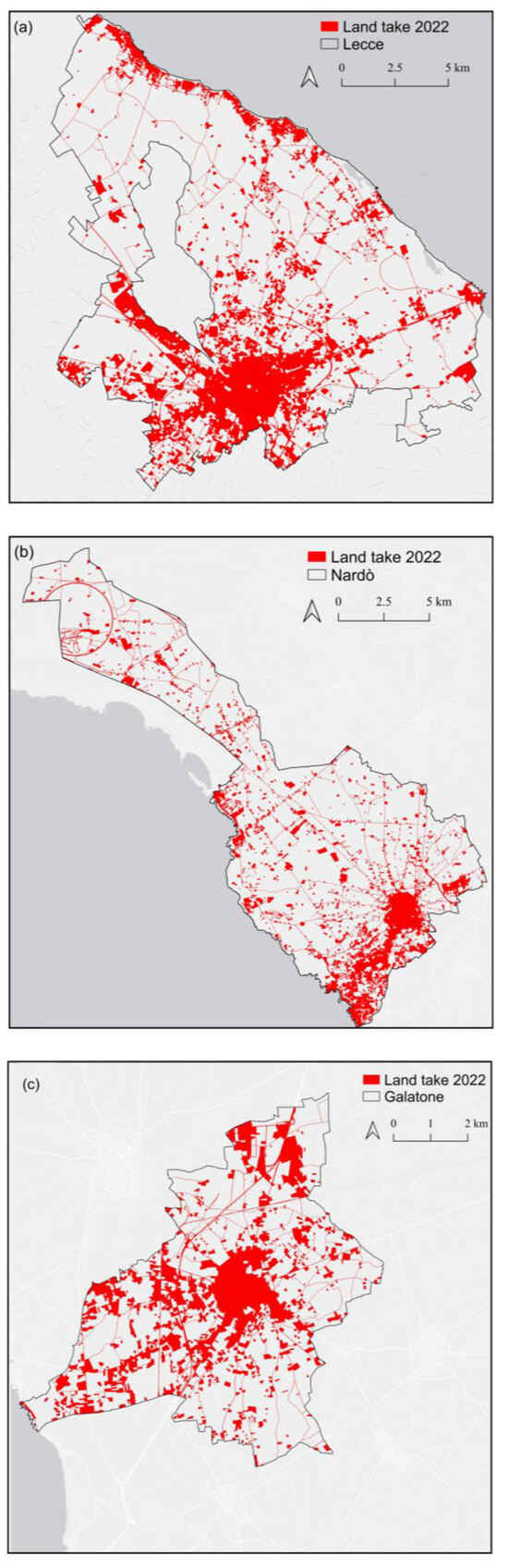
Figure 3.
Land-take maps of the municipalities of Lecce (a), Nardò (b), and Galatone (c) in 2022.
Urban and industrial settlements, road networks, and infrastructural areas most determine the land-take in the three study areas. This is in accordance with the trend observed in the Italian municipalities, where often, land-take starts from the historical city center (urban area) and branches to rural areas (Figure 3a–c). In general, the three municipalities are affected by the phenomenon of land-take throughout their landscape, sometimes with a patchy configuration. In the cases of Lecce (Figure 3a) and Nardò (Figure 3b), land-take seems more concentrated in some areas and also spreads strongly along the coast. In the municipality of Galatone (Figure 3c), land-take characterizes the entire landscape in an invasive way.
Table 3 shows for each municipality the area (in ha) and the incidence of land-take over the entire municipality area (in %) in 2006, 2011, and 2022. It is possible to underline that Galatone, the smallest municipality among the three under study, shows the highest percentage of land-take in 2006, 2011, and 2022.

Table 3.
Quantification of land-take in hectares and in percentage over the total area in the municipalities of Lecce, Nardò, and Galatone for the years 2006, 2011, and 2022.
Table 3 shows that in the case of Lecce, the increase in land-take was greater from 2006 to 2011 (+0.6%) than from 2011 to 2022 (+0.3%), while the other two municipalities show an opposite trend. Both Nardò and Galatone saw a constant increase in land-take from 2006 to 2022 (Table 3), but Galatone is the municipality that shows the highest increase in land-take in percentage from 2011 to 2022 (about +2.5%). In general, Nardò seems to be the municipality most affected by the increase in land-take (in ha) from 2006 to 2022, accounting for 414.12 ha (Table 3, Figure 4a). However, Galatone shows the highest increase in land-take (in %) compared with the other two municipalities in the time range of 2006–2022 (Table 2, Figure 4b).
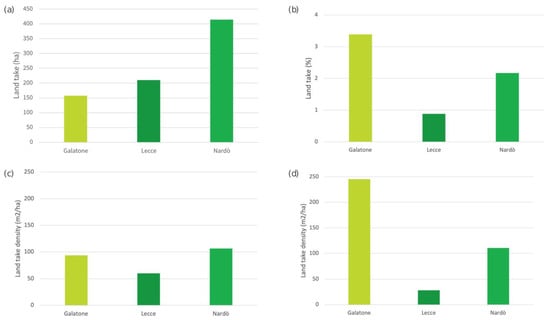
Figure 4.
(a) Land-take in 2006–2022 in ha, (b) land-take increment in 2006–2022 in %, (c) land-take density in 2006–2011 in m2/ha, and (d) land-take density in 2011–2022 in m2/ha in Galatone, Lecce, and Nardò.
The land-take density in each time range of 2006–2011 and of 2011–2022 shows completely different results (Figure 4c,d). In the first-time range (2006–2011), Nardò shows the highest land-take density followed by Galatone and then Lecce (Figure 4c). In the second time range (2011–2022), the land-take density in Galatone continues to increase, while in the other two municipalities, despite being bigger than Galatone, the land-take density decelerates its trend (Figure 4d).
The results of Indicator 11.3.1 LCRPGR (Ratio of Land Consumption Rate to Population Growth Rate) and the secondary indicators Built-Up Area Per Capita (m2/inhabitant) and Total Change in Built-Up Area (%) are shown in Table 4. The indicator LCRPGR shows a negative value for Nardò and Galatone (Table 4) explained by the decrease in the number of inhabitants from 2006 to 2022. Lecce still presents a positive LCRPGR but with a very low value (Table 4). Nardò is the municipality with the highest values of built-up area per capita every year (Table 4), followed by Galatone that has the smallest municipality area. Once again, Nardò has the highest percentage of the total change in the built-up area, while Lecce has the smallest percentage (Table 4).

Table 4.
Indicator 11.3.1 and its secondary indicators (Built-Up Area Per Capita and Total Change in Built-Up Area) for Lecce, Nardò, and Galatone.
Moving to the spatial configuration of land-take, the results of the aggregation index are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Aggregation index (AI) of land-take for Lecce, Galatone, and Nardò in 2006, 2011, and 2022.
Land-take appears to be more aggregated in Lecce, followed by Galatone, and Nardò.
3.2. Assessment and Spatial Analysis of Land Degradation
The results of Indicator 15.3.1 “Annual change in degraded or desertified arable land (in % over the municipality area)” are based on land-cover change from 2006 to 2022 and classify the landscape into three classes representing a land degradation trend (Figure 5): degradation, stable, and improvement. The results reveal that for Lecce, the areas classified as in degradation are high, representing about 47% of the total area, only 23 ha (0.10%) fall within the improvement class, and less than half of the landscape results are stable (Table 6, Figure 5a). In the case of Galatone, land in degradation characterizes 60% of the entire landscape, and about 88 ha (1.89%) are classified as in improvement (Table 6, Figure 5c). Finally, Nardò shows the lowest percentage of land in degradation (41.86%), which places the municipality in third place among the three study areas. Furthermore, it is possible to notice several areas of improvement (743 ha) scattered throughout the landscape (Table 6, Figure 5b).
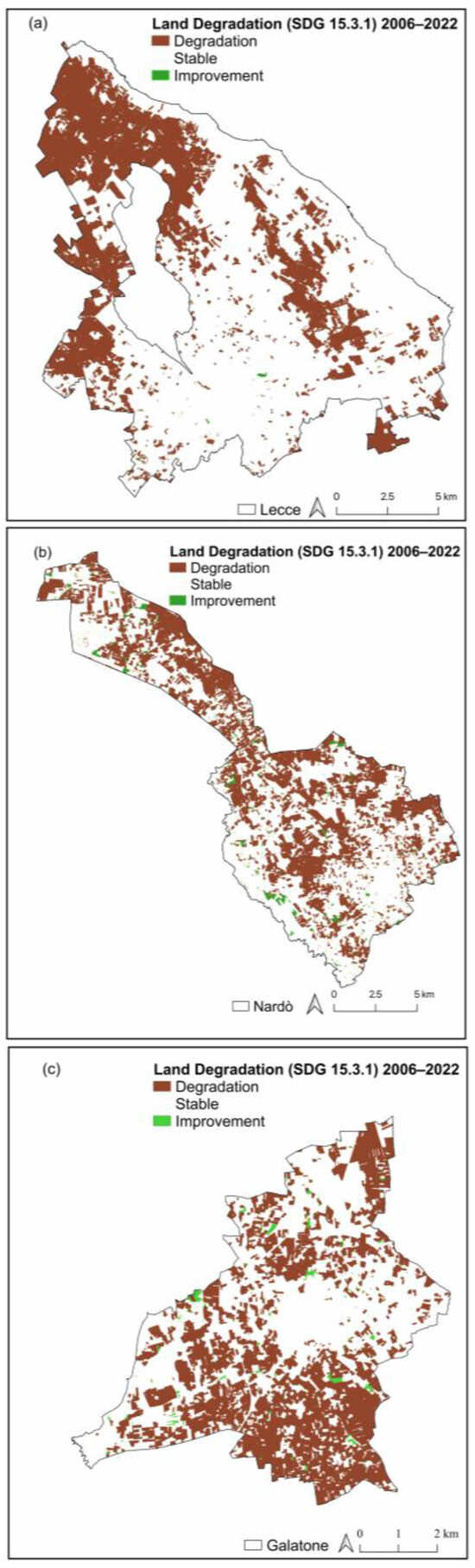
Figure 5.
Spatial distribution of land degradation from 2006 to 2022 according to Indicator 15.3.1 for Lecce (a), Nardò (b), and Galatone (c).

Table 6.
Annual change of Indicator 15.3.1 (degraded or desertified arable land (in % over the municipality area) classified into the three classes (areas in degradation, stable areas, and areas in improvement).
3.3. Ecological Effects of Land-Take and Land Degradation on Areas of High Natural Value
Land-take and land degradation can play a different role according to the landscape context where they develop. The assessment of the ecological effects of land-take and land degradation on the high natural value areas (protected areas and European special areas of conservation) was based on the land-cover change from 2006 to 2022. Figure 6 shows the integration of land degradation in 2006–2022, land-take in 2006, and areas with high natural value.
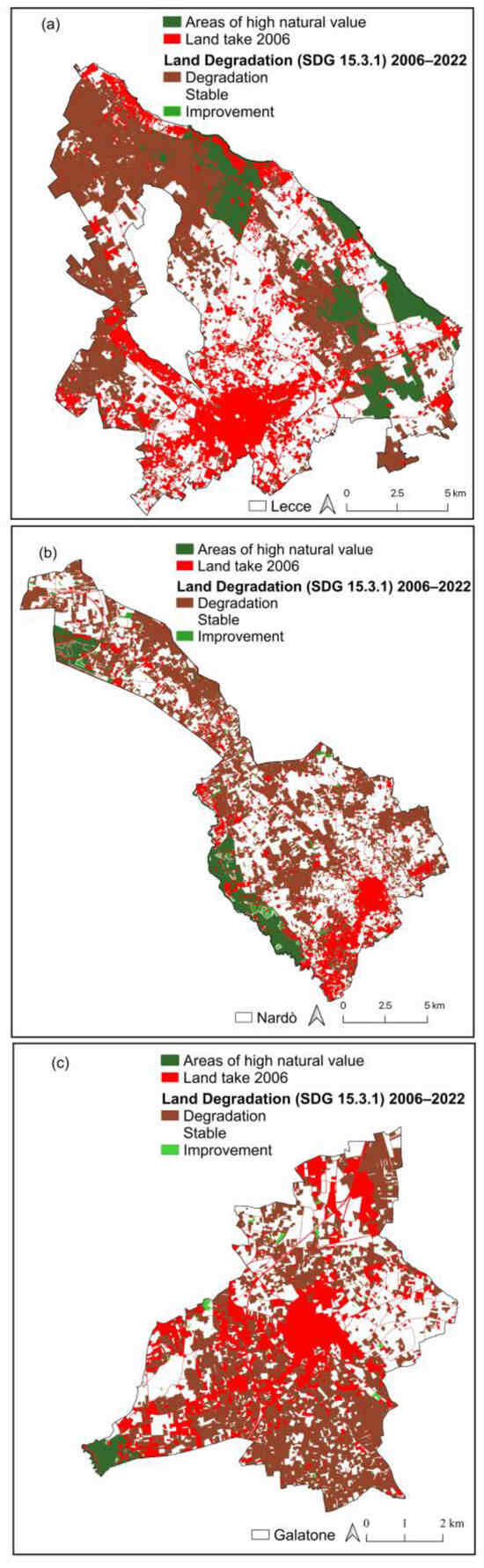
Figure 6.
Land degradation from 2006 to 2022 (SDG 15.3.1) compared with areas of higher naturalistic value for Lecce (a), Nardò (b), and Galatone (c).
As shown in Table 7, land degradation in high natural value areas was quantified. It is possible to notice that 25% of natural areas in Lecce are highly at risk of land degradation (Figure 6a, Table 7). A similar percentage was also found in the case of Galatone (Figure 6c, Table 7) where about 23% of the high natural value areas are affected by land degradation. Worthy of note is the municipality of Nardò where it is possible to highlight a smaller incidence of land degradation (about 10%) as well as several lands in improvement falling in high natural value areas (Figure 6b, Table 7).

Table 7.
Land degradation in high natural value areas in ha and in % in Lecce, Nardò, and Galatone from 2006 to 2022.
4. Discussion
Land degradation and land-take cause the disruption of physical and ecological resources and the decline of land productivity with risks to food security and sustainable livelihoods worldwide [61]. At the urban scale, these issues touch on several aspects of sustainable development, some of them are clearer, as in the case of sustainable food production systems and resilient agricultural practices since they are strongly linked with the use of land. However, there are other concerns regarding their effects on the capacity to adapt to climate change (extreme weather, drought, flooding, and other disasters), terrestrial biodiversity (habitat diversity), and, more in general, people’s quality of life. In other words, it is possible to state that land degradation and land-take affect socio-ecological sustainability because the ecological structural changes they produce strongly affect ecological functions and, consequently, the provision of landscape services. This is the reason why the basic layers of this research were the land-cover in three different years (2006, 2011, and 2022). Land-covers helped in analyzing not only the amount of land degradation but also its spatial configuration, based on the aggregation index landscape metric [51,62]. The three municipalities are all characterized by land-take and degradation, but the results have shown that there are some differences among them.
As is possible to observe in Table 8, the contribution of land-take to land degradation from 2006 to 2022 is very low in all municipalities under study for two main reasons. Firstly, the strong spread of urbanization showed its main development around the 1980s when the previous urban plans were designed and then implemented. Before 2006, in a landscape stabilized by traditional land uses like olive groves and vineyards, most of the degradation can be attributable to land-take related to the enlargement of urban centers because of an increase in population and the development of tourism. However, land-take has continued to increase in all of the study areas with varying incidence: +0.88% in Lecce, +2.17% in Nardò, and +3.39% in Galatone (Table 3). A significant amount of land has resulted as consumed in 2022: in Lecce 20.51%, in Nardò 13.88%, and in Galatone 25.78% (Table 3). However, they showed a different increase in built-up area for the total time range (16 years) (Table 4): Lecce + 4.50%, Nardò + 18.55%, and Galatone + 15.14%. High values are shown for the built-up area per capita (in m2/inhabitant) in 2022 (Table 4), resulting in very high values for Nardò (860.71 m2/inhabitant) and Galatone (792.29 m2/inhabitant), while in Lecce (521.66 m2/inhabitant), they were not as high; however, they were higher than the national land-take value in 2022 (364.46 m2/inhabitant) [63]. This is probably due to management strategies that over the last thirty years have seen these municipalities managed according to urban plans more focused on urban sprawl than on green areas and ecological restoration.

Table 8.
Contribution of land-take to land degradation from 2006 to 2022 in Lecce, Nardò, and Galatone.
After 2006, the huge amount of 2006 land-take becomes part of the stable lands. Thus, stable lands cannot be considered in a positive sense. The data that catch our attention are those related to the degraded areas from 2006 to 2022, which are sometimes even higher than the stable lands, like in the case of Galatone. These data are the result of the effect of the spread of Xylella fastidiosa subsp. pauca., which is a very dangerous phytopathogenic bacterium with negative effects on agricultural landscapes. As highlighted recently [64], one of the stabilizing land uses has been destroyed by Olive Quick Decline Syndrome, with consequences for landscape multifunctionality at different spatial scales.
At the same time, lands in improvement cover a very small extent; therefore, they provide a very small contribution to landscape functionality. In Lecce, the lands in degradation recovery are very small (Figure 5a), while in Nardò (Figure 5b) and Galatone (Figure 5c), there are several areas where it has been possible to notice areas in recovery from land degradation. In the case of Galatone, this result can be explained by the implementation of the new General Urban Plan that, according to the Italian Law n. 152/2006, has been evaluated according to the Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA). The introduction of this tool has caused changes in the way the landscape is planned since it evaluates the coherence of the landscape plan with the Agenda 2030 SDGs in terms of goals and actions. In the case of Nardò, the recovery area regards the official institution of the natural protected area named “Porto Selvaggio e Palude del Capitano” (Regional Law n. 2006/6). The managers of this area have planned and carried out several restoration projects to enhance terrestrial biodiversity, such as the removal of environmental detractors, like unauthorized buildings, the recovery of degraded areas, and more accurate environmental monitoring activities. The implementation of the General Urban Plan, still in elaboration, can strengthen this positive trajectory of the municipality of Nardò toward sustainability.
In addition, a negative correlation between the increase in land-take and the population trend has been highlighted. Despite continuous population decline, many European cities are expanding, leading to excessive land-take and changes in land-cover [65]. From the negative LCRPGR values, the strong presence of artificial surfaces for all municipalities has occurred over time despite a negative population balance. Lecce is the only municipality that has shown a weak positive value of LCRPGR.
The effects of land-take are very often considered in terms of quantity (hectares or percentages) without considering its spatial configuration [51,62]. The use of the aggregation index, a landscape metric, has helped in identifying municipalities where land-take is more fragmented and others where it is more aggregated. In the case of Nardò, with high values for 11.3.1 secondary indicators, land-take has resulted in less aggregation than in the other two municipalities. This means that land-take in this municipality is fragmented, irregular, and dispersed, affecting different areas distributed across the landscape. In the other two cases, the urban center has aggregated the land-take, while small fragments can be seen in the rural areas and along the coasts. Clearly, it is not possible to say whether it is better to have fragmented or clumped land-take, because it depends on the context where the land-take develops [62]. If the land-take is close to areas with natural value, it could be better to have small fragments than big areas, because the small areas can easily be the subject of restoration measures. Thus, it is important not only how much land-take characterizes a landscape but also where it is, and what it affects. The spatial context can make the difference [66]; urban areas with equal amounts of land-take can face different environmental impacts depending on the spatial configuration of the providers of landscape services [62]. It is, therefore, essential to monitor how the changes in land-cover can affect the landscape by spatially analyzing land degradation by considering its spatial context and the areas with high natural value, which potentially provide landscape services.
Nardò presents several degraded patches, with many of these areas located in rural regions, particularly in the north, where the realization of new infrastructures has contributed to land degradation. Policymakers could significantly benefit from the spatial analysis of Indicator 15.3.1, as it may support the identification of key areas of interest where efforts for setting back land degradation and supporting landscape restoration should be strengthened. It is likely that there are already areas wherein initiatives toward ecological recovery indicate already existing efforts for reaching the sustainability of landscape management in Nardò and Galatone. Trends.Earth is a useful tool for analyzing land degradation and making informed decisions at various administrative levels [67].
Possible Methodology Limitations and Implications for Sustainable Urban Planning
The process of stopping land degradation and the restoration and rehabilitation of degraded lands require the assessment of how much and where degraded areas are located. From this perspective, this methodology has allowed us to analyze the temporal dynamics of land-take and land degradation amount, the spatial configuration of degraded areas, and their potential ecological effects on the provision of landscape services in the study areas. The methodology is based on land-cover in three different years, which does not always allow us to clarify when a specific degradation process has started to act. This is the case of Xylella fastidiosa; it is known that this pathogen started to spread in 2013, but this methodology does not allow us to depict when the ecological effects really started. However, having a date before and a date after the diffusion supported the study of the spatial arrangement of the degraded areas.
In addition, the use of land-cover maps as basic layers for the assessment of land degradation dynamics tends to homogenize the environmental information, as each land-cover is considered a homogenous area. However, since spatial heterogeneity is also present within each land-cover, and since degradation is assessed in terms of net primary productivity capacity, an NDVI analysis based on satellite imagery could be more useful for the assessment of the effect of land degradation on ecological functionality. Finally, the landscape classification in three land degradation classes may not be clear since the “stable class” can have both positive and negative meanings: positive when an area not degraded is stable, negative when the “stable class” is a land-take area.
However, from the results, it is possible to list some sustainable management actions:
- (1)
- To avoid further land-take as far as possible.
- (2)
- When point (1) is not possible, to reuse already consumed land, by demolishing buildings or recovering the ecological functionality of lands.
- (3)
- When points (1) and (2) are not possible, then only land in poor condition (characterized by low ecological value) may be consumed.
- (4)
- In degraded areas, mitigation and compensation measures should be applied to minimize the loss of natural capital (e.g., urban green areas or rural agroforestry).
5. Conclusions
The integration of land-take and land degradation assessment within the urban planning process is crucial in achieving the United Nations’ 2030 Agenda Goals. Sustainable landscape planning could help in mitigating the risks associated with decisions causing unecological land-cover changes and in promoting more sustainable urban development. To reach this aim, tools such as SEA are essential for monitoring and evaluating the sustainability and environmental effectiveness of long-term land management policies. Nowadays, SEA in urban planning is strongly based on the assessment of its effects on land-take and land degradation over the short, medium, and long term. The different spatial and temporal perspectives can help decision-makers in understanding the potential environmental consequences of their decisions in terms of amount and spatial configuration. The results show that the three municipalities are characterized by an increase in land-take across time (2006–2022) but with a different spatial configuration and with different environmental risks for the provision of landscape services. This has demonstrated that it is useless to analyze the amount of land-take/degradation without considering how it is spatially arranged and how much it affects biodiversity and the provision of landscape services. Analyzing the spatial patterns of a specific threat, like land-take/degradation, can help in reducing the impact of human activities and in identifying specific improvement targets toward landscape restoration, such as:
- −
- Where and how much to increase urban green space and urban tree cover, also considering the EU-level commitment of planting at least three billion additional trees by 2030;
- −
- How to restore natural landscape connectivity;
- −
- Where and how to recover land-covers that act in supporting some landscape processes, like pollination;
- −
- How to put into practice measures aimed at achieving a positive trend in biodiversity conservation in forest, agricultural, and urban landscapes.
From this perspective, the use of simple and measurable indicators and their spatial assessment can help in monitoring the trends of different cities toward sustainability goals, testing and validating the different strategies, and identifying the most suitable solutions to restore and improve landscape multifunctionality.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.M.L., D.V. and I.P.; methodology, E.M.L. and D.V.; software, E.M.L.; validation, E.M.L., D.V. and I.P.; formal analysis, E.M.L.; investigation, E.M.L. and D.V.; resources, I.P.; data curation, E.M.L.; writing—original draft preparation, E.M.L., D.V. and I.P.; writing—review and editing, E.M.L., D.V. and I.P.; visualization, E.M.L. and D.V.; supervision, I.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable
Data Availability Statement
The dataset is available from the authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Richardson, B.F. Finance, Food, and Future Urban Zones: The Failure of Flexible Development in Auckland, New Zealand. Land Use Policy 2022, 119, 106203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elze, S.; Banzhaf, E. High-Precision Monitoring of Urban Structures to Understand Changes in Multiple Ecosystem Services. Urban Urban Green 2022, 73, 127616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindral, S.; Kot, R.; Hulisz, P. The Influence of City Development on Urban Pedodiversity. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia Torres, A.; Tiwari, C.; Atkinson, S.F. Sustaining Human Nutrition in an Increasingly Urban World. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medayese, S.; Magidimisha-Chipungu, H.H.; Chipungu, L. Spatial Matrices of Urban Expansion in Lafia, North-Central Nigeria. For. Geo. 2023, 37, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, B.; Zhu, Z. What Is the Spatiotemporal Relationship between Urbanization and Ecosystem Services? A Case from 110 Cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patle, S.; Ghuge, V.V. Urban Fragmentation Approach for Assessing Thermal Environment Dynamics: A Case Study of Semi-Arid City from a Comfort Perspective. Urban Clim 2024, 53, 101784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolau, R.; David, J.; Caetano, M.; Pereira, J. Ratio of Land Consumption Rate to Population Growth Rate—Analysis of Different Formulations Applied to Mainland Portugal. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Tombolini, I.; Ippolito, A.; Carlucci, M. Land Quality and the City: Monitoring Urban Growth and Land Take in 76 Southern European Metropolitan Areas. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2018, 45, 691–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency. Land Take and Land Degradation in Functional Urban Areas; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2022; p. 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council on Soil Monitoring and Resilience (Soil Monitoring Law); European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, S.S.; Zhen, L.; Miah, M.G.; Ahamed, T.; Samie, A. Impact of Land Use Change on Ecosystem Services: A Review. Environ. Dev. 2020, 34, 100527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termorshuizen, J.W.; Opdam, P. Landscape Services as a Bridge between Landscape Ecology and Sustainable Development. Landsc. Ecol. 2009, 24, 1037–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot, T.; Goldstein, B.; Gómez-Baggethun, E.; Proença, V.; Rugani, B. Ecosystem Service Deficits of European Cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourdes, K.T.; Hamel, P.; Gibbins, C.N.; Sanusi, R.; Azhar, B.; Lechner, A.M. Planning for Green Infrastructure Using Multiple Urban Ecosystem Service Models and Multicriteria Analysis. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 226, 104500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallés-Planells, M.; Galiana, F.; Van Eetvelde, V. A Classification of Landscape Services to Support Local Landscape Planning. Ecol. Soc. 2014, 19, art44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, N.C.; Newnham, G.J.; England, J.R.; Guerschman, J.; Cox, S.J.D.; Roxburgh, S.H.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Fritz, S.; Wheeler, I. Good Practice Guidance. SDG Indicator 15.3.1, Proportion of Land That Is Degraded Over Total Land Area. Version 2.0. 2021. Available online: https://www.unccd.int/sites/default/files/relevant-links/2021-03/Indicator_15.3.1_GPG_v2_29Mar_Advanced-version.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Bobylev, N.; Syrbe, R.-U.; Wende, W. Geosystem Services in Urban Planning. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 85, 104041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatz, E.-M.; Bovet, J.; Lieder, S.; Schroeter-Schlaack, C.; Strunz, S.; Marquard, E. Land Take in Environmental Assessments: Recent Advances and Persisting Challenges in Selected EU Countries. Land Use Policy 2021, 111, 105730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luiza Petroni, M.; Siqueira-Gay, J.; Lucia Casteli Figueiredo Gallardo, A. Understanding Land Use Change Impacts on Ecosystem Services within Urban Protected Areas. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 223, 104404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, E.C.; Kaplan, J.O.; Fuller, D.Q.; Vavrus, S.; Klein Goldewijk, K.; Verburg, P.H. Used Planet: A Global History. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7978–7985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, R.; Herold, M.; Verburg, P.H.; Clevers, J.G.P.W.; Eberle, J. Gross Changes in Reconstructions of Historic Land Cover/Use for Europe between 1900 and 2010. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Sluis, T.; Pedroli, B.; Kristensen, S.B.P.; Lavinia Cosor, G.; Pavlis, E. Changing Land Use Intensity in Europe—Recent Processes in Selected Case Studies. Land Use Policy 2016, 57, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levers, C.; Müller, D.; Erb, K.; Haberl, H.; Jepsen, M.R.; Metzger, M.J.; Meyfroidt, P.; Plieninger, T.; Plutzar, C.; Stürck, J.; et al. Archetypical Patterns and Trajectories of Land Systems in Europe. Reg. Environ. Change 2018, 18, 715–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulp, C.J.E.; Levers, C.; Kuemmerle, T.; Tieskens, K.F.; Verburg, P.H. Mapping and Modelling Past and Future Land Use Change in Europe’s Cultural Landscapes. Land Use Policy 2019, 80, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Martín, M.; Quintas-Soriano, C.; Torralba, M.; Wolpert, F.; Plieninger, T. Landscape Change in Europe. In Sustainable Land Management in a European Context; Weith, T., Barkmann, T., Gaasch, N., Rogga, S., Strauß, C., Zscheischler, J., Eds.; Human-Environment Interactions; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 8, pp. 17–37. ISBN 978-3-030-50840-1. [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger, J.A.G. Landscape Division, Splitting Index, and Effective Mesh Size: New Measures of Landscape Fragmentation. Landsc. Ecol. 2000, 15, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.G.E.; Bennett, E.M.; Gonzalez, A. Strong and Nonlinear Effects of Fragmentation on Ecosystem Service Provision at Multiple Scales. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 094014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarigal, K. FRAGSTATS Help; University of Massachusetts: Amherst, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ledda, A.; De Montis, A. Infrastructural Landscape Fragmentation versus Occlusion: A Sensitivity Analysis. Land Use Policy 2019, 83, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbeck, L.S.; Krumme, U.; Andersen, T.J.; Jennerjahn, T.C. Decadal Trends in Mangrove and Pond Aquaculture Cover on Hainan (China) since 1966: Mangrove Loss, Fragmentation and Associated Biogeochemical Changes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 233, 106531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, G.; Park, Y.; Bowman, A.O.M.; Lee, R.J. Vacant Urban Areas: Causes and Interconnected Factors. Cities 2018, 72, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Lin, Z.; Jiang, X.; Qiu, M.; Sun, J. How Do the Industrial Land Use Intensity and Dominant Industries Guide the Urban Land Use? Evidences from 19 Industrial Land Categories in Ten Cities of China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 53, 101978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions EU—Biodiversity Strategy for 2030 Bringing Nature Back into Our Lives; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mitincu, C.-G.; Ioja, I.-C.; Hossu, C.-A.; Artmann, M.; Nita, A.; Nita, M.-R. Licensing Sustainability Related Aspects in Strategic Environmental Assessment. Evidence from Romania’s Urban Areas. Land Use Policy 2021, 108, 105572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geneletti, D. Reasons and Options for Integrating Ecosystem Services in Strategic Environmental Assessment of Spatial Planning. Int. J. Biodivers. Sci. Ecosyst. Serv. Manag. 2011, 7, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, V.; Henríquez, C. Can Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) Contribute towards the Implementation of Biophilic Urbanism in Urban Planning? The Case of Chilean Municipal Regulatory Plans. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 95, 106765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Directive 2001/42/EC, of 27th June, on the Assessment of the Effects of Certain Plans and Programs on the Environment; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, T.; Tan, Z.; He, X. Integrating Environment into Land-Use Planning through Strategic Environmental Assessment in China: Towards Legal Frameworks and Operational Procedures. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2007, 27, 243–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.; Bekessy, S.A.; Gordon, A. Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services in Strategic Environmental Assessment: An Evaluation of Six Australian Cases. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 87, 106552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.; Gilmer, A.; Foley, R.; Sweeney, J.; Fry, J. Applying Geographic Information Systems to Support Strategic Environmental Assessment: Opportunities and Limitations in the Context of Irish Land-Use Plans. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2011, 31, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Bao, C.-K.; Shu, T.-F.; Yun, X.-X.; Jiang, D.; Brown, L. Framework for Integration of Urban Planning, Strategic Environmental Assessment and Ecological Planning for Urban Sustainability within the Context of China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2011, 31, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, K.G.; Anderson, S.; Gonzales-Chang, M.; Costanza, R.; Courville, S.; Dalgaard, T.; Dominati, E.; Kubiszewski, I.; Ogilvy, S.; Porfirio, L.; et al. A Review of Methods, Data, and Models to Assess Changes in the Value of Ecosystem Services from Land Degradation and Restoration. Ecol. Model. 2016, 319, 190–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abera, W.; Tamene, L.; Kassawmar, T.; Mulatu, K.; Kassa, H.; Verchot, L.; Quintero, M. Impacts of Land Use and Land Cover Dynamics on Ecosystem Services in the Yayo Coffee Forest Biosphere Reserve, Southwestern Ethiopia. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 50, 101338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Jiang, W.; Ling, Z.; Hou, P.; Deng, Y. Evaluating the Potential Impacts of Land Use Changes on Ecosystem Service Value under Multiple Scenarios in Support of SDG Reporting: A Case Study of the Wuhan Urban Agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raviv, O.; Zemah-Shamir, S.; Izhaki, I.; Lotan, A. The Effect of Wildfire and Land-Cover Changes on the Economic Value of Ecosystem Services in Mount Carmel Biosphere Reserve, Israel. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 49, 101291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, A.; Bongers, F.; Ramírez Marcial, N.; García Barrios, L.E.; Kuyper, T.W. Farm Diversity and Fine Scales Matter in the Assessment of Ecosystem Services and Land Use Scenarios. Agric. Syst. 2022, 196, 103329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haaland, C.; Van Den Bosch, C.K. Challenges and Strategies for Urban Green-Space Planning in Cities Undergoing Densification: A Review. Urban Urban Green 2015, 14, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, D.; Kabisch, S.; Haase, A.; Andersson, E.; Banzhaf, E.; Baró, F.; Brenck, M.; Fischer, L.K.; Frantzeskaki, N.; Kabisch, N.; et al. Greening Cities—To Be Socially Inclusive? About the Alleged Paradox of Society and Ecology in Cities. Habitat Int. 2017, 64, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Taubenböck, H.; Zhu, X.X. Land Consumption in Cities: A Comparative Study across the Globe. Cities 2021, 113, 103163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joorabian Shooshtari, S.; Silva, T.; Raheli Namin, B.; Shayesteh, K. Land Use and Cover Change Assessment and Dynamic Spatial Modeling in the Ghara-Su Basin, Northeastern Iran. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2020, 48, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.; Al-Belushi, M.; Al-Awadhi, T. Monitoring Land Use and Land Cover Changes in the Mountainous Cities of Oman Using GIS and CA-Markov Modelling Techniques. Land Use Policy 2020, 91, 104414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upreti, M.; Kumar, A. Landscape Modeling for Urban Growth Characterization and Its Impact on Ecological Infrastructure in Delhi-NCR: An Approach to Achieve SDGs. Phys. Chem. Earth 2023, 131, 103444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baude, M.; Meyer, B.C. Changes in Landscape Structure and Ecosystem Services since 1850 Analyzed Using Landscape Metrics in Two German Municipalities. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 152, 110365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.; Ene, E. FRAGSTATS v4: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorical Maps; University of Massachusetts: Amherst, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- UN-Habitat (United Nations Human Settlements Programme). DG Indicator Metadata (Harmonized Metadata Template—Format Version 1.1). 2021. Available online: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/metadata/files/Metadata-11-03-02.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Cui, P.; Xv, D.; Tang, J.; Lu, J.; Wu, Y. Assessing the Effects of Urban Green Spaces Metrics and Spatial Structure on LST and Carbon Sinks in Harbin, a Cold Region City in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 113, 105659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Wang, L.; Hou, W.; Yang, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, W. Analyzing the Dynamic Changes and Causes of Greenspace Landscape Patterns in Beijing Plains. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Gao, P.; Xu, R.; Mu, X.; Sun, W. Influence of Landscape Pattern Changes on Water Conservation Capacity: A Case Study in an Arid/Semiarid Region of China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 112082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Zhao, W.; Pereira, P. Ecosystem Restoration along the “Pattern-Process-Service-Sustainability” Path for Achieving Land Degradation Neutrality. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2025, 253, 105227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, D.; Lovello, E.M.; Giannuzzi, C.G.; Scardia Scardia, A.M.; Marinelli, M.V.; Petrosillo, I. Towards Land Consumption Neutrality and Natural Capital Enhancement at Urban Landscape Scale. Land 2023, 12, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munafò, M. Consumo Di Suolo, Dinamiche Territoriali e Servizi Ecosistemici; Report di Sistema; SNPA: Rome, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Valente, D.; Lovello, E.M.; Chirizzi, R.; Petrosillo, I. Multiscale Effects of Xylella Fastidiosa on Landscape Services. Land 2024, 13, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csomós, G.; Szalai, Á.; Farkas, J.Z. A Sacrifice for the Greater Good? On the Main Drivers of Excessive Land Take and Land Use Change in Hungary. Land Use Policy 2024, 147, 107352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beele, E.; Aerts, R.; Reyniers, M.; Somers, B. Spatial Configuration of Green Space Matters: Associations between Urban Land Cover and Air Temperature. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2024, 249, 105121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio Chaparro Torres, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Lan, Y. Temporal Analysis of Land Degradation and Urban Expansion in Central Yunnan Province Using Remote Sensing for Supporting Sustainable Development Goals 11/15. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 112058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).