Abstract
Currently, few studies have revealed the comprehensive effects of environmental organic matter, freeze–thaw and oxidative aging on the adsorption performance of cadmium (Cd(II)), which is essential for the sustainable stability evaluation of the adsorbent. Herein, we observed that humic acids (HAs) extracted from different soils inhibited the adsorption performance of Cd(II) onto the cuttlebone-derived samples by occupying the different major adsorption active sites of the adsorbent, and the lower cadmium-complexation ability of HAs would increase the occupation of adsorption sites. The freeze–thaw process increased the pore size and volume of the cuttlebone-derived samples, while oxidative aging enhanced the specific surface area and introduced additional C–O/C=O groups. These changes promoted the adsorption performance of Cd(II) in the cuttlebone-derived samples after freeze–thaw or oxidative aging. Additionally, the resistances of cuttlebone-based adsorbents to HAs, freeze–thaw, and oxidative aging were elucidated and optimized by simple alkali boiling or carbonization treatment. Furthermore, the adsorption capacities of Cd(II) by samples in the natural cadmium-contaminated river ranged from 548.99 mg g−1 to 571.55 mg g−1, which are higher values than those of most reported adsorbents. Therefore, this work provides an important experimental basis for the practical application and sustainable design of adsorbents under real environmental conditions.
1. Introduction
A significant volume of cadmium-containing wastewater is discharged during various industrial processes, including mining, electroplating, electrolysis, and pesticide production [1,2]. Due to the chemical stability and high toxicity, cadmium poses serious risks to ecological systems and human health [3,4]. Several technologies have been developed to remediate cadmium pollution, such as membrane separation [5], ion exchange [6], adsorption [7], chemical precipitation [8], and bio-remediation [9]. Among these technologies, adsorption has been widely regarded as an economically viable and efficient method due to its operational simplicity, excellent reusability, and high removal efficiency [10,11].
An adsorbent, as the core component of adsorption technology, plays a decisive role in determining its overall efficacy and practical applicability [12,13]. Numerous studies have confirmed that adsorbents with abundant functional groups (e.g., carbonyl, carboxyl, hydroxyl, amino, and pyrrole groups) and a well-developed pore structure are key factors in achieving high adsorption capacity for Cd(II) [10,13,14,15,16,17]. However, some promising adsorbents have been limited in terms of the complex preparation methods, high cost, and potential ecological risks, such as functionalized graphene nanosheets, graphene oxide, and multi-walled carbon nanotubes [13,16,17]. Therefore, developing efficient, low-cost, and environmentally friendly adsorbents is essential for the remediation of cadmium-contaminated water.
Recently, marine bio-derived adsorbents have received extensive attention for heavy metal removal owing to their wide availability, high biodegradability, and excellent reusability [18,19,20]. As an important representative, cuttlebone has a skeleton structure with supporting and water storage functions [21], with a low density, high porosity, and excellent mechanical stability [22,23]. Its highly flexible organic polymers (e.g., β-chitin and proteins), combined with nanolayered aragonite (CaCO3), are key to its efficient adsorption of heavy metals, demonstrating a removal efficiency up to three times higher than that of inorganic CaCO3 [24].
As has been reported [25,26,27,28,29], the adsorption capacity and stability of cuttlebone has been the primary focus of research, and surface modification and carbonization have been the commonly employed enhancement methods. In our previous work [27], the organic membrane of cuttlebone was deacetylated to improve its capacity to adsorb metal ions through the formation of stronger complexation via amino groups. In addition, we investigated the effect of pyrolysis treatment on the adsorption stability and the transformation of aragonite CaCO3 in cuttlebone [28]. However, the specific roles of the organic and inorganic components of cuttlebone in the adsorption of Cd(II) have not been elucidated in detail, particularly under various natural environmental conditions.
Additionally, the evaluation of cadmium adsorption by many adsorbents often overlooks the effects of organic matter, freeze–thaw, and oxidative aging that occur in natural environments, thereby compromising the practical assessment of the adsorbent [25,26,27,28,29]. Humic acids (HAs), a major component of humus in natural organic matter, are widely present in soil and aquatic systems [30]. HAs contain numerous hydrophilic and hydrophobic branched chains along with functional groups (e.g., hydroxyl, carboxyl, and carbonyl) [30,31], which could form complexes with Cd(II) and influence its adsorption and migration behavior in the environment [32,33]. Furthermore, in the long-term application of adsorbents, it has been essential to account for regional seasonal variations and diurnal temperature fluctuations [34], particularly freeze–thaw aging induced by extreme temperature changes, as well as varying degrees of oxidative aging caused by sunlight, dissolved oxygen, and other oxidizing factors.
Herein, we systematically investigate the effect mechanisms of two self-extracted soluble humic acids on the adsorption performance of cadmium onto cuttlebone-derived adsorbents (Y, Z3, S300) by using adsorption kinetics, isotherms, thermodynamics, and multiple characterization techniques. Furthermore, the effects of freeze–thaw and oxidative aging on the structure of the cuttlebone-derived adsorbents are analyzed. Additionally, the effect of pH and various ion types, and the remediation of the natural cadmium-contaminated river are also studied. In brief, we analyze the practical application and sustainable design of adsorbents under real environmental conditions by exploring, in detail, the effects of various environmental factors on the adsorption of Cd(II) by cuttlebone-derived samples, such as organic matter (humic acids), freeze–thaw cycles (−20~25 °C) and oxidative aging (H2O2: 5~20%), pH (3~11), ion types (Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl−, NO3−, SO42−, CO32−, PO43−), and the natural cadmium-contaminated river.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
The cuttlebone was sourced from Bozhou Cuttlefish Bone Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Bozhou, China). All reagents used were of analytical grade. Specifically, Cd(NO3)2·4H2O (99%), NaOH (98%), and HNO3 (36~38%) were purchased from Xilong Scientific Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China). H2O2 (30%) and HCl (98%) were obtained from Damao Chemical Reagent Factory (Tianjin, China). NaCl (99.5%), KCl (99.5%), CaCl2 (99.5%), MgCl2 (99.5%), NaNO3, Na2SO4 (99%), NaHCO3 (99.5%), Na4P2O7 (99%), NaH2PO4 (99%), and HF (40%) were supplied by Sinopharm Group Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Additionally, two types of humic acids were extracted from red soil in Yunnan Province and black soil in Heilongjiang Province. The natural river water sample was collected from the Beng River in Linyi City, Shandong Province.
2.2. Synthesis of the Cuttlebone-Derived Samples
The cuttlebone was washed with water to remove impurities and then vacuum-dried at 80 °C for 72 h. Subsequently, the cuttlebone sample was ground, passed through a 100-mesh sieve, and denoted as Y. The calcined sample, designated as S300, was prepared by heating Y under an N2 atmosphere at 300 °C for 2 h with a heating rate of 10 °C min−1. The deacetylated sample was obtained by boiling Y in 3 mol L−1 NaOH solution for 1 h at a solid-to-liquid ratio (Y/NaOH) of 1:50. The deacetylated sample was collected, washed thoroughly with water, dried at 80 °C for 72 h, and labeled as Z3.
2.3. Extraction of Humic Acids from Different Soils
Two types of humic acids were extracted from red soil in Yunnan Province and black soil in Heilongjiang Province using an alkaline extraction–acid precipitation method, and denoted as HAs-R and HAs-B, respectively. The collected soil was first washed with 0.005 mol L−1 HCl. A mixed solution of NaOH and Na4P2O7 (0.1 mol L−1, 1:1 v/v) was then added to the above suspension at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:10 (g mL−1). The mixture was stirred uniformly and equilibrated for 12 h. After centrifugation, the supernatant was filtered through a polyethersulfone membrane (0.45 μm). The filtrate was acidified with 0.01 mol L−1 HCl to precipitate the humic acids, which were then washed with 10% HF and ultrapure water.
2.4. Adsorption Experiment
The experiments investigating the adsorption of Cd(II) onto the cuttlebone-derived samples in the presence of HAs were conducted in 100 mL glass bottles. Each reaction system contained 4.8 mg of adsorbent, 50 mL of deionized water, 25 mL of Cd(II) solution (5~60 mg L−1), and 25 mL of humic acid solution (10 mg L−1). After adsorption, the concentrations of HA and Cd(II) were determined using an ultraviolet spectrophotometer (UV-2600, Shimadzu Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) at 300 nm and an atomic absorption spectrometer (Z-2000, Hitachi, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), respectively. All adsorption experimental data are the average of three measurements. Additionally, the detailed descriptions of the adsorption performance of Cd(II) onto the cuttlebone-derived samples are provided in the Supplementary Materials, including kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics.
2.5. Freeze–Thaw and Oxidative Aging Experiment
Samples (Y, S300, Z3) were mixed with 60% water, frozen at −20 °C for 16 h, and then thawed at 25 °C for 32 h to simulate one freeze–thaw cycle. This cycle was repeated 15 times. The freeze–thaw-aged samples were designated as Y-D, S300-D, and Z3-D, respectively.
For oxidative aging, samples (Y, S300, Z3) were placed in a closed container and treated with different mass concentrations of H2O2 (5%, 10%, 15%, 20%) at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:20 (g mL−1). The mixtures were agitated on a magnetic stirrer for 6 h. Thereafter, samples were washed with ultrapure water until a stable pH was reached. The H2O2-aged samples were labeled as Y-5, Y-10, Y-15, Y-20, S300-5, S300-10, S300-15, S300-20, Z3-5, Z3-10, Z3-15, and Z3-20, respectively. The corresponding adsorption performances of Cd(II) in the cuttlebone-derived samples were evaluated after different numbers of freeze–thaw cycles or under various oxidative aging conditions.
2.6. Characterization Methods of the Cuttlebone-Derived Samples and the Self-Extracted HAs
The crystalline structures of the cuttlebone-derived samples were determined using X-ray diffraction (XRD, Rigaku SmartLab SE, Tokyo, Japan), with the diffraction angle (2θ) ranging from 10° to 70° at a scan speed of 10° min−1. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) was performed on Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA) Nicolet iS20 to identify the surface functional groups, with a wavenumber range from 500 cm−1 to 4000 cm−1. The N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms of the samples were measured using an Autosorb-IQ physisorption analyzer (Quantachrome Instruments, Boynton Beach, FL, USA) at 77 K. The elemental compositions were obtained with a MicroCube elemental analyzer (Elementar, Langenselbold, Germany), and the zeta potentials were measured using a ZetaPlus analyzer (Brookhaven, Nashua, NH, USA). A Bruker Avance III 400 MHz nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer (Bruker Corporation, Billerica, MA, USA) was used to analyze the structural carbon in the extracted humic acids (HAs).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization Analysis of the Cuttlebone-Derived Samples and the Self-Extracted HAs
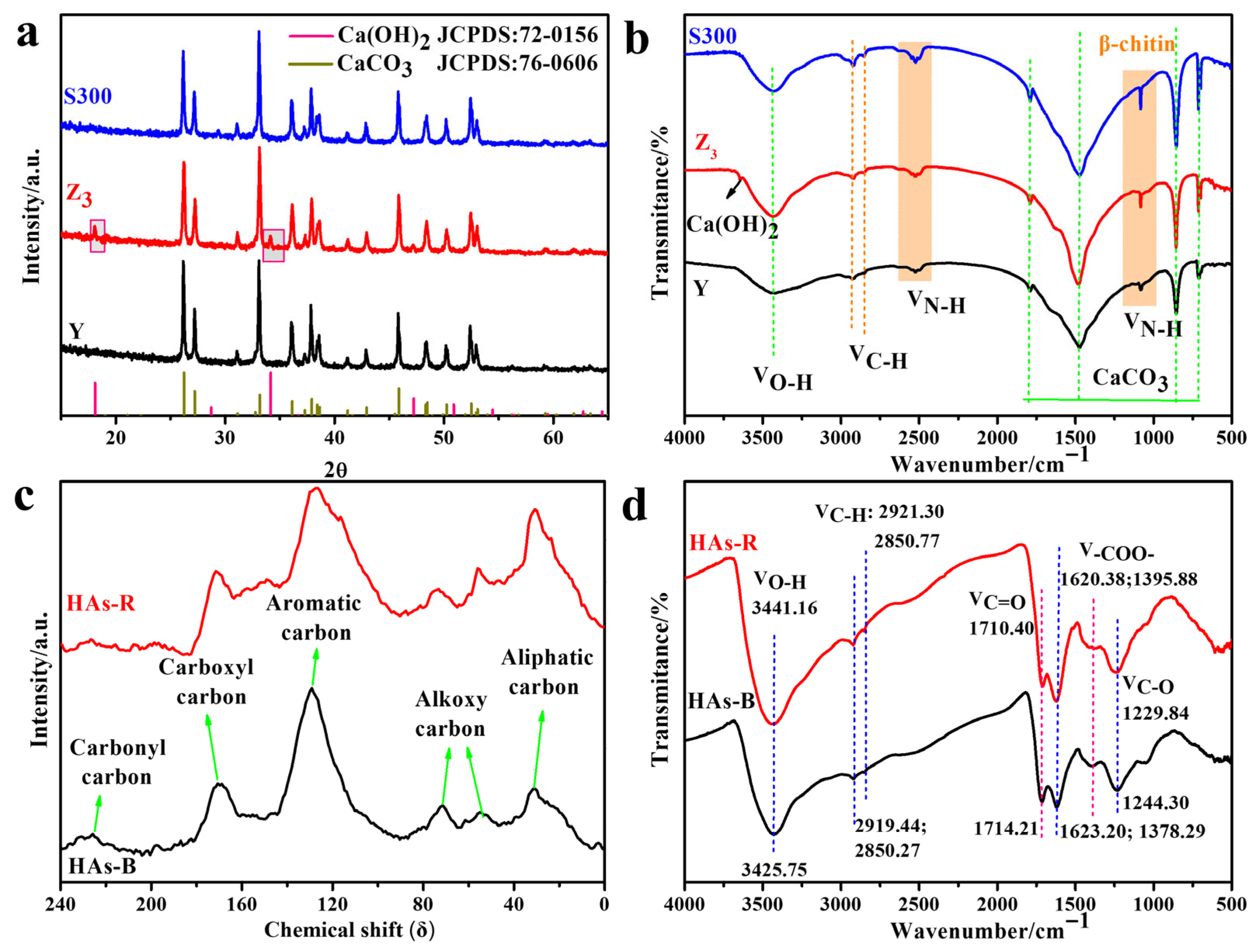
As shown in Figure 1a, the cuttlebone sample (Y) exhibited a typical aragonite calcium carbonate phase (CaCO3, JCPDS: 76-0606), which was retained after carbonization at 300 °C (S300) and alkali boiling treatment (Z3). Notably, new diffraction peaks at 18° and 34° appeared in Z3, indicating the presence of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2, JCPDS: 72-0156). The FT-IR spectra of the cuttlebone-derived samples further supported these findings (Figure 1b). All samples displayed characteristic vibration absorption peaks of aragonite CaCO3 at 710 cm−1, 854 cm−1, 1474 cm−1, and 1789 cm−1, along with functional groups associated with β-chitin, including −C−NH2 (1082 cm−1), −NH3+X− (2523 cm−1), and aliphatic −CH2− (2858 cm−1 and 2923 cm−1), as well as the absorbed water at 3423 cm−1 [22,26].
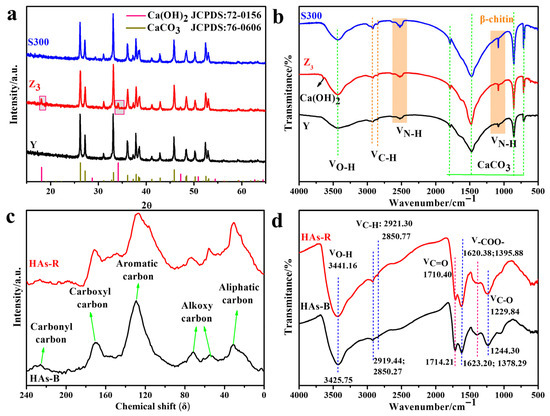
Figure 1.
The XRD (a) and FT-IR (b) spectrum of the derived cuttlebones (Y, S300, Z3); the 13C NMR (c) and FT-IR (d) spectrum of the self-extracted humic acids (HAs-B, HAs-R).
Compared to Y (Figure 1b and Table S1), Z3 showed enhanced amino group vibration peaks and an increased H/N atomic ratio, indicating that alkali boiling with NaOH promoted deacetylation, leading to the formation of more amino groups on the surface of cuttlebone [26,27]. These amino groups could readily become protonated in aqueous solution, reducing the negative surface charge and resulting in a higher zeta potential [35]. Additionally, Z3 exhibited an increased pore volume and average pore size, along with a decreased specific surface area, suggesting that alkali treatment corrodes impurities, loosens the surface pore structure, and promotes the interconnection of micropores. In contrast, S300 showed a decreased H/C atomic ratio and specific surface area, along with an increased average pore size. These results indicated that pyrolysis decomposes organic matter, disrupts the pore structure, and exposes more negatively charged calcium carbonate surfaces [36].
The physicochemical properties of the self-extracted humic acids (HAs-R and HAs-B) from different soil sources were analyzed, including the composition, aromaticity, hydrophilicity, distribution of carbon species, functional groups, zeta potential, and particle size. As shown in Figure 1c, the 13C NMR spectra of HAs-R and HAs-B exhibited similar profiles, but differed in absorption intensity and peak area across various carbon functional groups: aliphatic carbon (δ: 0–35), alkoxy carbon (δ: 35–109), aromatic carbon (δ: 109–159), carboxyl carbon (δ: 159–200), and carbonyl carbon (δ: 200–250) [37]. HAs-B demonstrated higher aromaticity and hydrophobicity than HAs-R, as evidenced by its greater aromatic carbon content and total aromaticity (Table S2), along with a higher proportion of hydrophobic carbon (aliphatic and aromatic carbon), which might facilitate its interaction with adsorbents [22]. Additionally, the lower H/C and (O + N)/C ratios of HAs-B further supported its stronger aromatic and hydrophobic character compared to HAs-R (Table S3). In contrast, the higher N/C ratio of HAs-R suggested a higher degree of humification, which also contributed to its more negatively charged surface and lower zeta potential.
The FT-IR spectra of HAs-B and HAs-R were similar, as shown in Figure 1d. HA-B and HAs-R both exhibited characteristic absorption bands corresponding to C−O vibrations in phenols and carboxylic acids (1050 cm−1, 1244 cm−1), antisymmetric and symmetric vibrations of −COO− groups (1378 cm−1, 1623 cm−1), C=O stretching from carboxyl, aldehyde, or ketone functionalities (1710 cm−1), and the absorbed water (3425 cm−1) [38,39]. However, HAs-B displayed weaker aliphatic −CH2− vibration bands (2850 cm−1 and 2921 cm−1) and stronger C−O vibration bands attributed to phenols compared to HAs-R [38], suggesting the lower aliphatic content and the higher proportion of acidic phenolic functional groups in HAs-B.
3.2. Effects of HAs on the Adsorption of Cd(II) by the Cuttlebone-Derived Samples
3.2.1. Adsorption Performance of Cd(II) by the Cuttlebone-Derived Samples with HAs
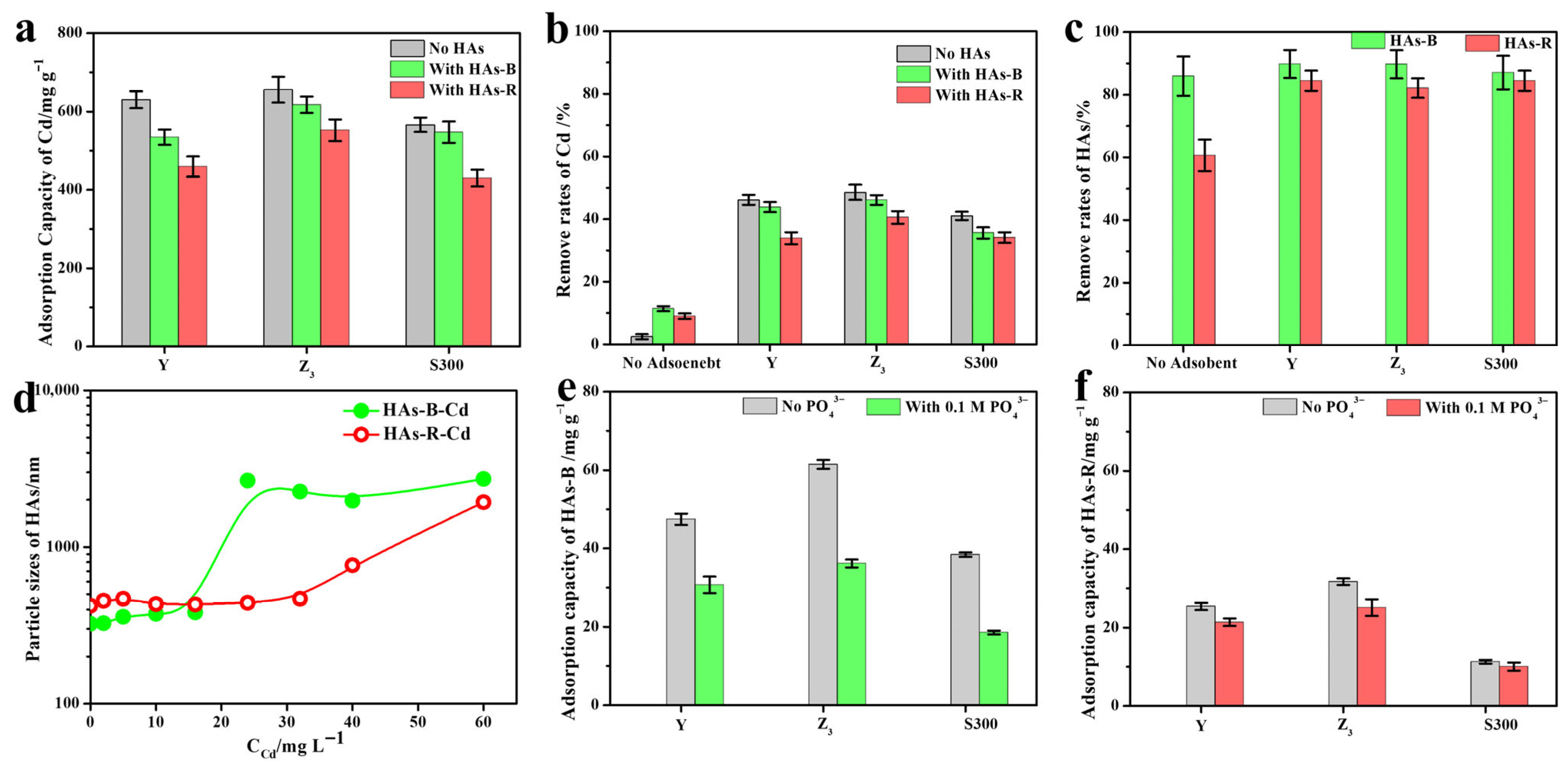
As shown in Figure 2a, the adsorption capacity of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples decreased in the presence of humic acids (HAs-B or HAs-R), with a more pronounced reduction observed for HAs-R. This indicated that HAs inhibit the adsorption of Cd(II), and HAs-R exhibited a stronger inhibitory effect than HAs-B. Compared to the high Cd(II) removal rates achieved by the cuttlebone-derived samples (Figure 2b), the removal rates by HAs-B or HAs-R alone were considerably lower, confirming that the adsorption of Cd(II) is primarily attributable to the cuttlebone-derived samples rather than to the HAs. The increase in HA removal upon the addition of adsorbents suggested that partial adsorption of HAs onto the cuttlebone-derived samples occurred during the adsorption process of Cd(II) (Figure 2c). Furthermore, a strong complexation–precipitation interaction between HAs and Cd(II) was evident, as reflected by the high removal rates of HAs (over 60%, Figure 2c), even in the absence of adsorbents. As the concentration of cadmium increased (Figure 2d), HAs-B showed a greater increase in particle size than HAs-R, indicating its stronger complexation–precipitation with Cd(II). This is consistent with the higher removal rate of Cd(II) by HAs-B alone compared to HAs-R (Figure 2b).
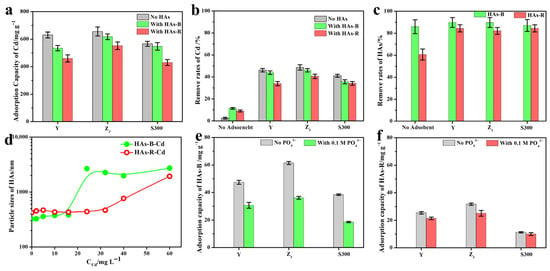
Figure 2.
The adsorption capacities (a) and removal rate (b) of Cd(II) by Y, Z3, and S300 with or without HAs (HAs-B or HAs-R); the removal rates of HAs-B or HAs-R in the cadmium solution with or without adsorbents (c); the particle size of HAs-B or HAs-R in the different concentrations of cadmium solution (d); the adsorption capacities of HAs-B (e) and HAs-R (f) by Y, Z3, and S300 with or without PO43−.
As shown in Figure 2e,f, the adsorption capacity of HAs-B onto the cuttlebone-derived samples was higher than that of HAs-R. This could be attributed to the reduced electrostatic repulsion between HAs-B (zeta potential: −35.74 mV) and cuttlebone-derived samples (Z3: −5.55 mV, Y: −21.59 mV, S300: −36.78 mV), the stronger π–π interactions resulting from the higher total aromaticity of HAs-B (1.36 vs. 0.91 for HAs-R), and the greater accessibility of active adsorption sites due to the smaller particle size of HAs-B (323.82 nm vs. 421.91 nm for HAs-R). In the presence of phosphate as a competing ion, the adsorption of HAs all decreased, with a more pronounced reduction observed for HAs-B. This suggested that ligand exchange and calcium ion bridging also contribute to the adsorption of HAs [40,41] and that these mechanisms play a more significant role in the adsorption of HAs-B. Nevertheless, the inhibitory effect of HAs-B on the adsorption of Cd(II) was lower than that of HAs-R, indicating that the stronger complexation ability between HAs-B and Cd(II) compensates for its occupation of adsorption sites on those samples.
Thus, the decreased adsorption performance of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples in the presence of HAs could be attributed to the adsorption of HAs onto the surface of adsorbents via ligand exchange and calcium ion bridging, which masked the active adsorption sites. Additionally, differences in the complexation–precipitation behavior between the two types of HAs and Cd(II) led to varying degrees of inhibition on the adsorption of Cd(II). The following sections provide a detailed analysis of the effects of HAs on the adsorption performance and behavior of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples, including adsorption kinetics, isotherms, thermodynamics, and mechanisms.
3.2.2. Adsorption Kinetics of Cd(II) by the Cuttlebone-Derived Samples with HAs
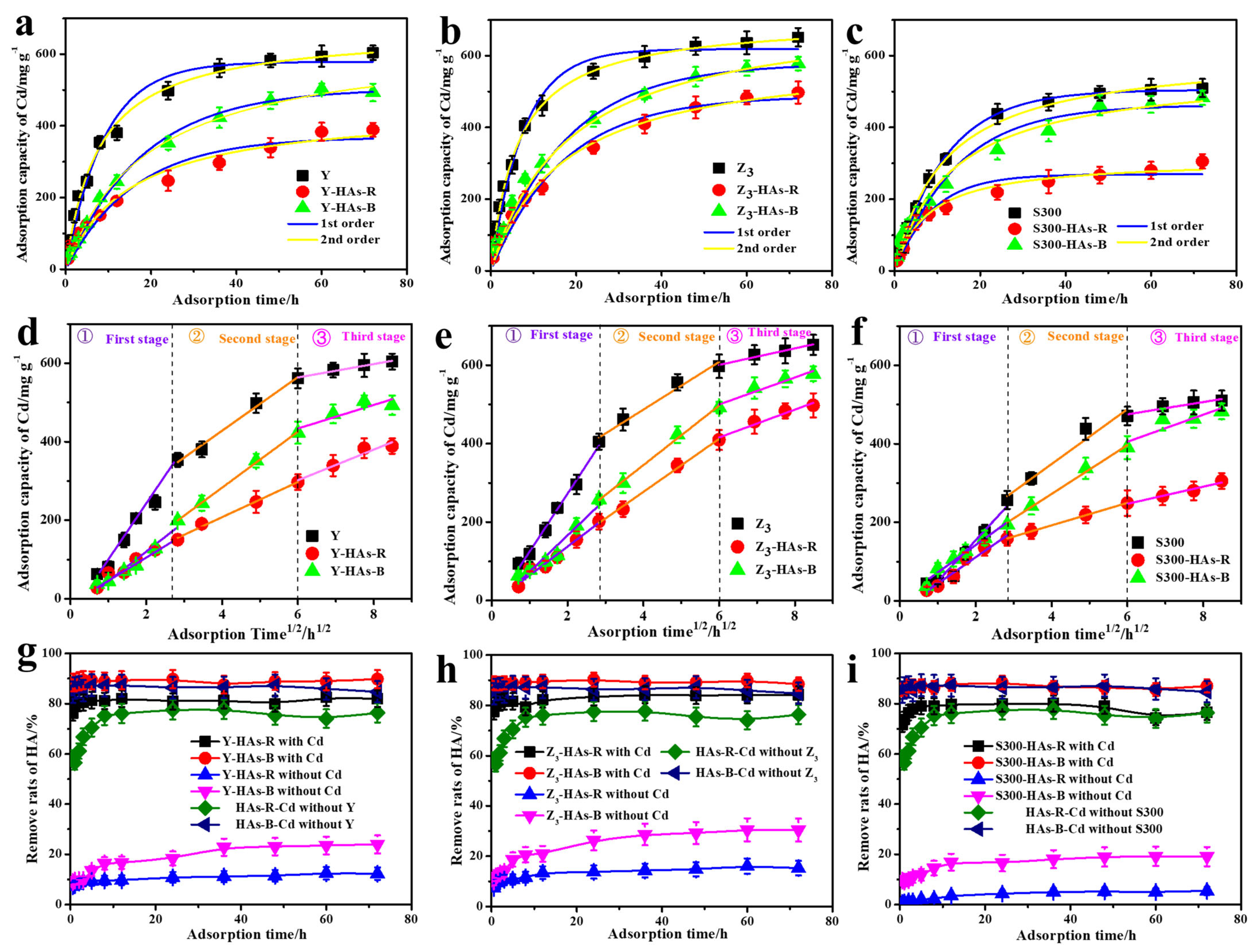
As shown in Figure 3a–c, the addition of humic acids (HAs-B or HAs-R) reduced the adsorption capacity of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples over time, with HAs-R exhibiting a stronger inhibitory effect than HAs-B. Approximately 58% of HAs-R was rapidly removed in the cadmium-containing solution (Figure 3g–i), and the presence of the cuttlebone-derived samples further increased the removal of HAs-R to 72~78%. In contrast, only about 0.6~7.0% of HAs-R was removed by the cuttlebone-derived samples in the absence of cadmium. These results confirm that complexation with Cd(II) is the primary mechanism for the removal of HAs in this system. The higher removal rates of HAs-B could be attributed to its stronger complexation affinity with Cd(II) (Figure 2c) and its higher capacity for adsorption onto the cuttlebone-derived samples (Figure 2e,f). Based on the higher correlation coefficients (R2, Table S4), the adsorption of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived adsorbents more closely followed pseudo-second-order kinetics, indicating that chemisorption is the dominant adsorption mechanism, both in the presence and absence of HAs [7]. Furthermore, the decreased adsorption rate constant (k2) suggested that the addition of HAs reduces the rate of adsorption of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples, with a more pronounced reduction observed for HAs-R than for HAs-B. Nevertheless, the high R2 values for the pseudo-first-order model (Table S4) also indicated that physical adsorption may contribute to the overall adsorption process [26].
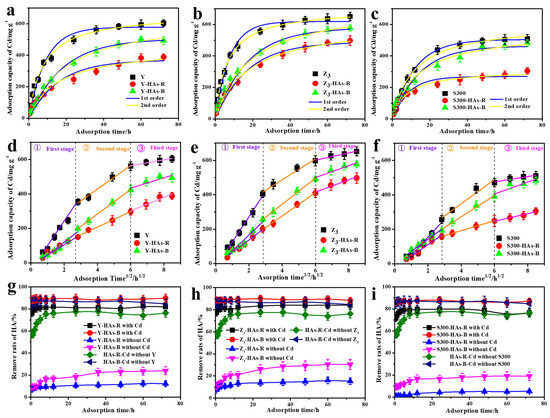
Figure 3.
The fitted adsorption kinetic models of Cd(II) in the cuttlebone-derived samples with or without different HAs: pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order ((a): Y; (b): Z3; (c): S300), Weber–Morris model ((d): Y; (e): Z3; (f): S300). The corresponding removal rates of HAs-B or HAs-R in the adsorption process of Cd (II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples ((g): Y; (h): Z3; (i): S300).
To further investigate the adsorption process, the adsorption kinetics of Cd(II) in the cuttlebone-derived samples, both with and without HAs, were analyzed using the Weber–Morris model. The fitted results (Figure 3d–f, Table S5) showed multi-linear curves with intercepts not passing through the origin, indicating that the adsorption process of Cd(II) in the cuttlebone-derived samples, both with and without HAs, involves multiple steps [42]. These include (1) rapid diffusion of Cd(II) from the solution to the surface of the cuttlebone-derived samples; (2) slower intra-particle diffusion within the pores of the cuttlebone-derived samples; (3) a final slow equilibrium adsorption stage [43]. However, the presence of HAs reduced the adsorption rate constant (K1) of the Weber–Morris model, with a more pronounced decrease observed for HAs-R than for HAs-B. These results suggest that the HAs occupied surface active sites on the cuttlebone-derived samples during the initial rapid diffusion-adsorption stage. The weaker complexation ability of HAs-R with Cd(II) further resulted in the lower removal of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples in its presence.
3.2.3. Adsorption Isotherms and Thermodynamics of Cd (II) in the Cuttlebone-Derived Samples with HAs
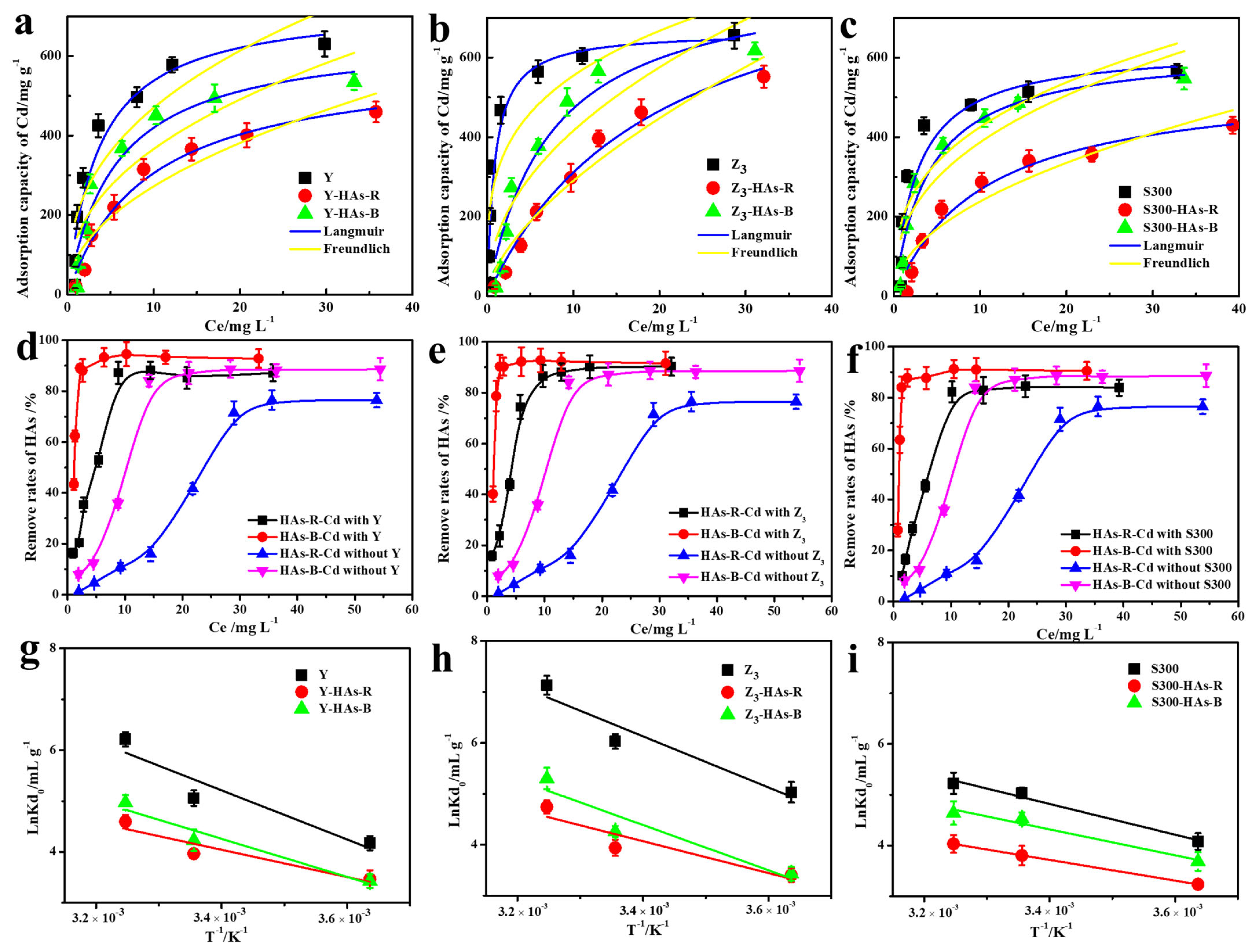
As the cadmium concentration increased (Figure 4a–c), the capacity to adsorb Cd(II) of the cuttlebone-derived samples, both with and without HAs, rose rapidly before reaching the adsorption equilibrium. This trend could be attributed to the enhanced mass transfer driving force at higher Cd(II) concentrations and the eventual saturation of available adsorption sites on the cuttlebone-derived samples [44,45,46]. As shown in Figure 4d–f, the removal rate of HAs by the cuttlebone-derived samples also increased with rising cadmium concentration, even in the absence of adsorbents. Owing to the stronger complexation ability with Cd(II), HAs-B exhibited higher removal rates than HAs-R, and had less of an inhibitory effect on the adsorption of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples, which was consistent with the above kinetic results. Similar trends were observed at different temperatures (Figures S1–S3), where elevated temperatures led to an increase in the adsorption of Cd(II) and HAs, indicating that the above adsorption processes are endothermic.
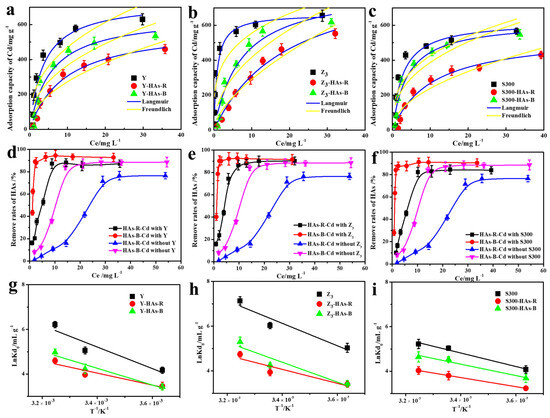
Figure 4.
The fitted Langmuir and Freundich adsorption isotherms models of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples with or without HAs ((a): Y; (b): Z3; (c): S300); the corresponding remove rates of HA ((d): Y; (e): Z3; (f): S300), and the relationship curves lnKd°and 1/T ((g): Y; (h): Z3; (i): S300).
Based on the higher correlation coefficients (R2) obtained from the Langmuir model (Table S6), the behavior of Cd(II)’s adsorption on the cuttlebone-derived samples, both with and without HAs, more closely followed that of monolayer adsorption across different temperatures [14,47]. Furthermore, all calculated equilibrium parameter values (RL) fell within the range of 0 to 1 (0.0057 ~ 0.43, Table S6), indicating the favorable adsorption of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples under the above conditions [48]. However, the presence of HAs reduced the adsorption favorability of Cd(II), as reflected by the higher RL values in HAs-containing systems. Specifically, HAs-R resulted in a less favorable adsorption process compared to HAs-B, due to its higher RL values. As summarized in Table 1, the maximum adsorption capacities of Cd(II) in the cuttlebone-derived samples in the presence of HAs ranged from 426.70 mg g−1 to 617.37 mg g−1, values which exceed those of many reported nano- and biomass-based adsorbents [13,42,49,50,51,52,53,54,55]. This demonstrated the excellent adsorption performance of Cd(II) in the cuttlebone-derived samples even in complex systems containing humic acids. Although the cuttlebone-derived samples exhibit a lower adsorption capacity for Cd(II) compared to synthesized nanomaterials (e.g., MgFe Layered Double Hydroxide, 869.6 mg g−1) [56], this drawback is offset by their markedly lower cost, rendering them a cost-effective and practical alternative for wastewater remediation.

Table 1.
Comparison of the adsorption capacities for Cd(II) of the cuttlebone-derived samples with some reported adsorbents.
The thermodynamic parameters for the adsorption of Cd(II) onto the cuttlebone-derived samples, with and without HAs, were calculated based on the adsorption isotherms at different temperatures, including the standard enthalpy change (ΔH0), standard Gibbs free energy change (ΔG0), and entropy change (ΔS0) [24]. As shown in Figure 4g–i and Table S7, the calculated ΔG0 values were negative at all temperatures and became more negative with increasing temperature, indicating that the adsorption processes of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples with or without HAs are all spontaneous, and that the degree of spontaneity increases at higher temperatures [15]. Moreover, the positive values of ΔS0 and ΔH0 suggested that the adsorption processes of Cd (II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples, with or without HAs, are all endothermic and increase the randomness at the solid–liquid interface [57,58]. The presence of HAs reduced the adsorption spontaneity and randomness of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples [16], as evidenced by the increased ΔG0 and decreased ΔS0 and ΔH0 values, with HAs-R exhibiting a more pronounced effect. These results further confirmed that HAs inhibit the adsorption performance of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples to varying degrees.
3.2.4. Adsorption Mechanism and Process of Cd(II) by the Cuttlebone-Derived Samples with HAs
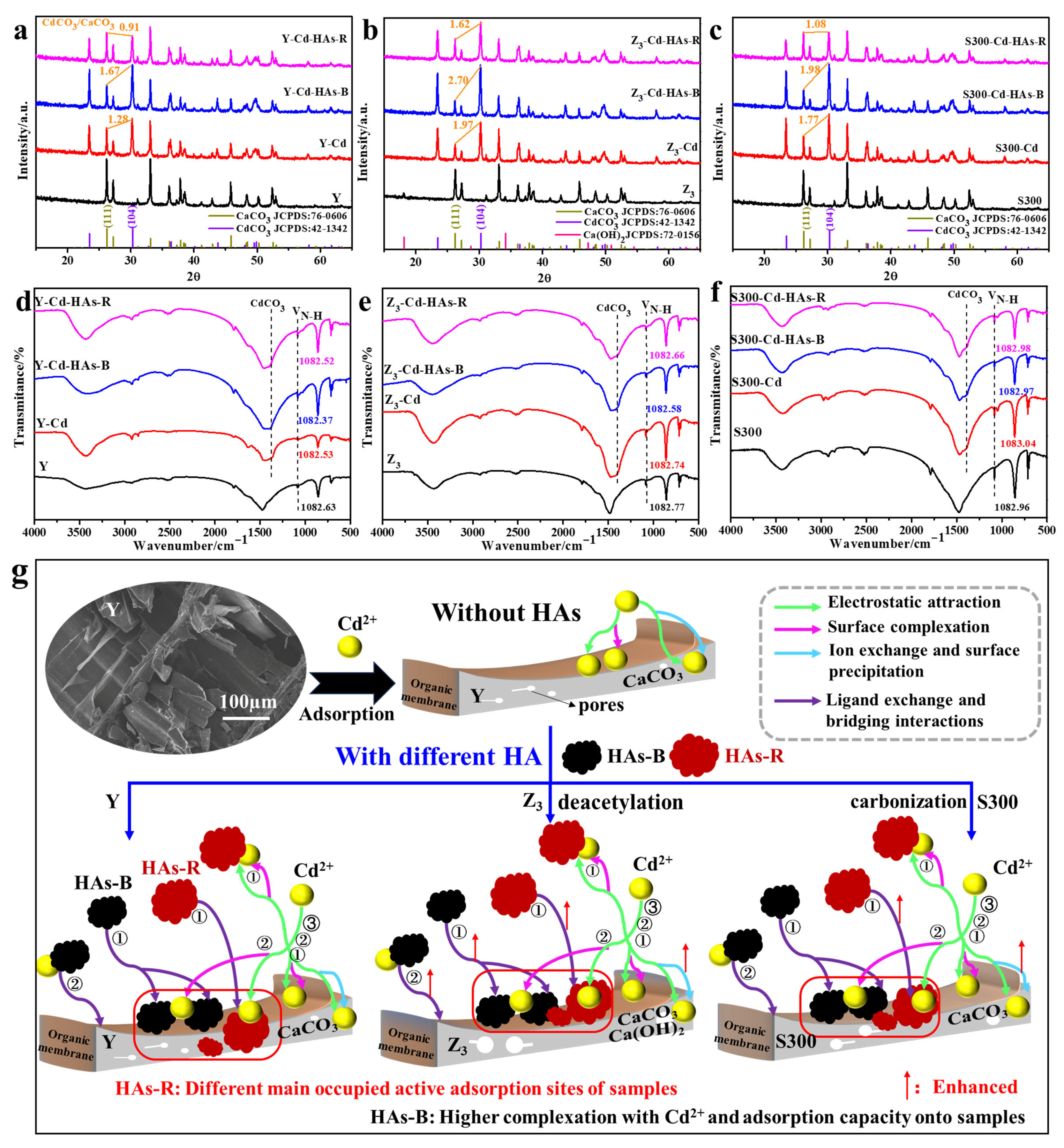
The adsorption mechanisms of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples, with and without HAs, were further investigated using XRD and FT-IR analyses of the samples before and after adsorption. As shown in Figure 5a–c, the appearance of the diffraction peaks corresponding to CdCO3 (JCPDS: 42-1432) confirmed the successful adsorption of Cd(II) onto the cuttlebone-derived samples, and indicated that ion exchange between Cd(II) and Ca(II) is an important adsorption mechanism, both in the presence and absence of HAs. Based on changes in the diffraction intensity of CaCO3 and the formation of CdCO3 after adsorption, the addition of HAs-B increased the proportion of the formed CdCO3, whereas HAs-R reduced it. These results demonstrated that HAs-B and HAs-R exerted different influences on the involvement of the inorganic component (CaCO3) of the cuttlebone-derived samples in the adsorption of Cd(II) [10,42,59,60]. Specifically, HAs-B promoted the ion exchange between Cd(II) and Ca(II) to form the crystalline CdCO3, while HAs-R inhibited this mechanism. However, the overall adsorption capacity of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples decreased in the presence of HAs-B or HAs-R (Figure 2a), indicating that ion exchange is not the sole mechanism in this system, and that HA may also affect the adsorption of Cd(II) through interactions with the organic membrane of the cuttlebone-derived samples.
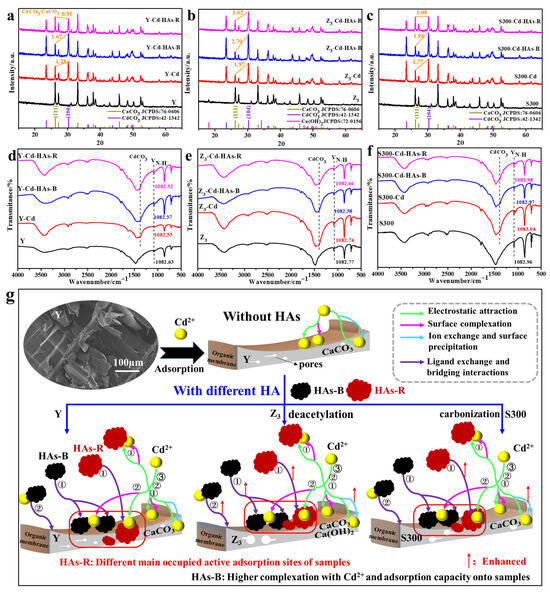
Figure 5.
The XRD pattern ((a): Y; (b): Z3; (c): S300) and FTIR spectra ((d): Y; (e): Z3; (f): S300) of the cuttlebone-derived samples with HAs before and after the adsorption of Cd(II), and the projected adsorption mechanism and process of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples with HAs (g); ①, ②, and ③ represent three different adsorption stages of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples with HAs, respectively.
As shown in Figure 5d–f, the inhibitory effect of HAs on the adsorption of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples was further supported by changes in the FT-IR spectra before and after adsorption. In all cases, new CO32− vibration bands corresponding to CdCO3 appeared after the adsorption of Cd(II), both with and without HAs [56]. Additionally, the −NH2 vibration band at 1082 cm−1 shifted after the adsorption of Cd(II), as well as the −OH, C−O, and C=O vibration bands [22,26,61]. Those results indicated the complexation between Cd(II) and various groups (−NH2, −OH, C−O, C=O) in the organic membrane of the adsorbents. Notably, this shift in the −NH2 band also occurred in the presence of HAs, with a more pronounced change observed for HAs-B than for HAs-R, suggesting that HAs-B exerts a stronger effect on the organic membrane during the adsorption of Cd(II). Combined with the XRD results, these findings implied that HAs-B is primarily adsorbed onto the organic membrane via ligand exchange, whereas HAs-R is mainly retained on the surface of calcium carbonate through calcium ion bridging.
Based on the above experimental and characterization results, the proposed adsorption mechanisms and processes of Cd(II) in the cuttlebone-derived samples in the presence of HAs were illustrated in Figure 5g. Initially, Cd(II) was rapidly adsorbed onto the surface of the cuttlebone-derived samples via electrostatic attraction, ion exchange, surface precipitation, and complexation. Simultaneously, a portion of HAs was adsorbed onto the surface of the cuttlebone-derived samples through ligand exchange and calcium ion bridging. Meanwhile, Cd(II) interacted with free HAs in the solution to form HAs–Cd complexes via surface complexation, and these aggregates were subsequently adsorbed onto the cuttlebone-derived samples. The remaining Cd(II) continued to be adsorbed through the mechanisms until equilibrium was reached in the cuttlebone–HAs–Cd system. Throughout this process, HAs occupied adsorption sites on the cuttlebone-derived samples, thereby reducing the adsorption capacity and rate of Cd(II). Due to the stronger complexation ability with Cd(II), HAs-B exhibited a relatively lower inhibitory effect compared to HAs-R. Furthermore, HAs-B was primarily adsorbed onto the organic membrane of the cuttlebone-derived samples through ligand exchange, while HAs-R tended to bind to the surface of calcium carbonate via calcium ion bridging. The modified surface properties of the cuttlebone after alkali boiling or carbonization also led to differences in the active sites occupied by HAs.
3.3. Effects of Freeze–Thaw and Oxidative Aging on the Adsorption of Cd(II) by the Cuttlebone-Derived Samples
3.3.1. Adsorption Performance of Cd(II) by the Cuttlebone-Derived Samples After Freeze–Thaw and Oxidative Aging
The effects of diurnal/seasonal temperature variations and environmental oxidation represented a critical factor in assessing the practical applicability and long-term performance of adsorbents [2]. Therefore, we further examined and analyzed the adsorption of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples after multiple freeze–thaw cycles or hydrogen peroxide oxidation treatments.
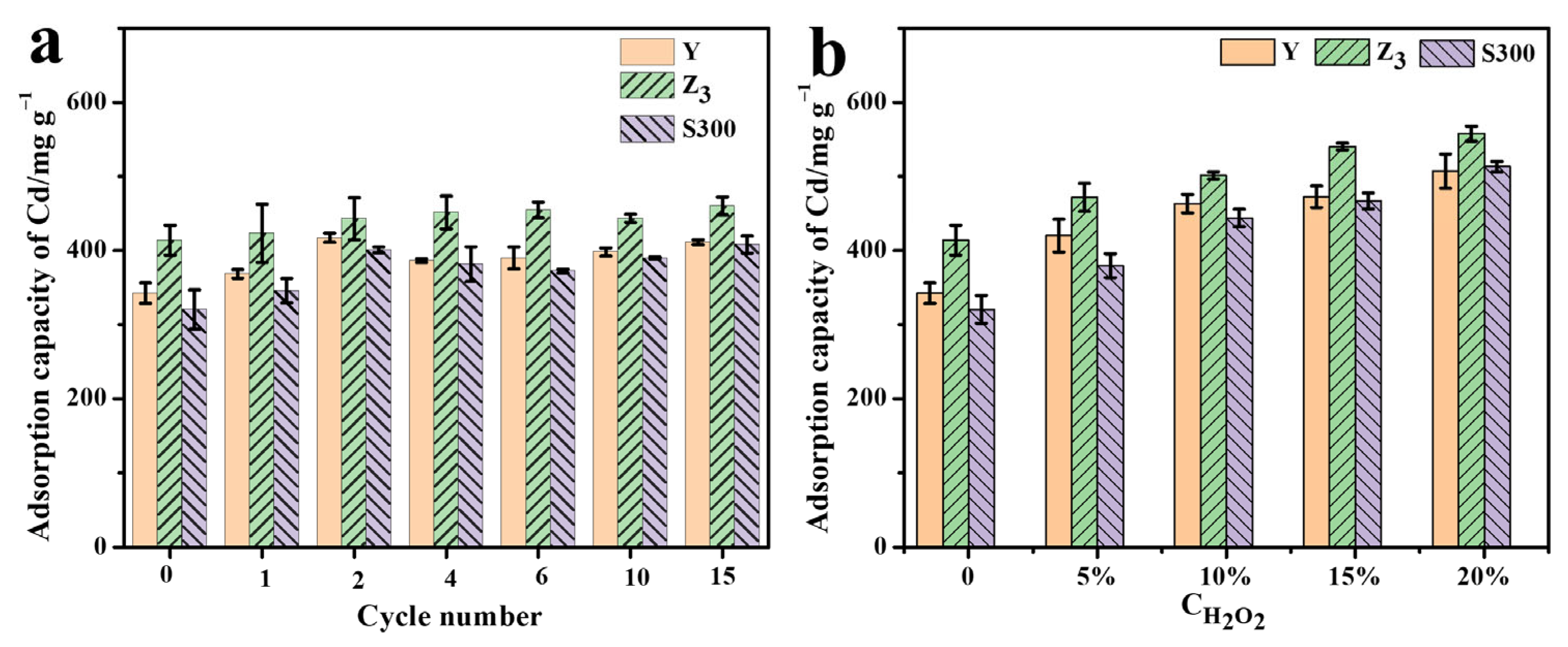
As shown in Figure 6a, the adsorption performance of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples improved to varying extents after multiple freeze–thaw treatments. For instance, the adsorption capacity of Cd(II) by sample (Y) increased from 342.40 mg g−1 to 411.20 mg g−1 following fifteen freeze–thaw cycles. Similarly, the adsorption capacity of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples increased significantly under the hydrogen peroxide oxidation treatment (Figure 6b). The adsorption capacity of Cd(II) by Y increased from 342.40 mg g−1 to 420.03 mg g−1 after treatment with 5% H2O2, and further rose to 507.14 mg g−1 with 20% H2O2. Z3 and S300 exhibited a similar trend of enhanced adsorption of Cd(II), which could be attributed to changes in their surface physicochemical properties (Table S8).
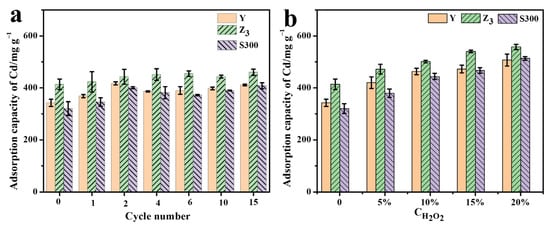
Figure 6.
The adsorption capacities of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples after the multiple freeze–thaw cycles (a) or hydrogen peroxide oxidation treatment (b).
3.3.2. Adsorption Mechanism of Cd(II) by the Cuttlebone-Derived Samples After Freeze–Thaw and Oxidative Aging
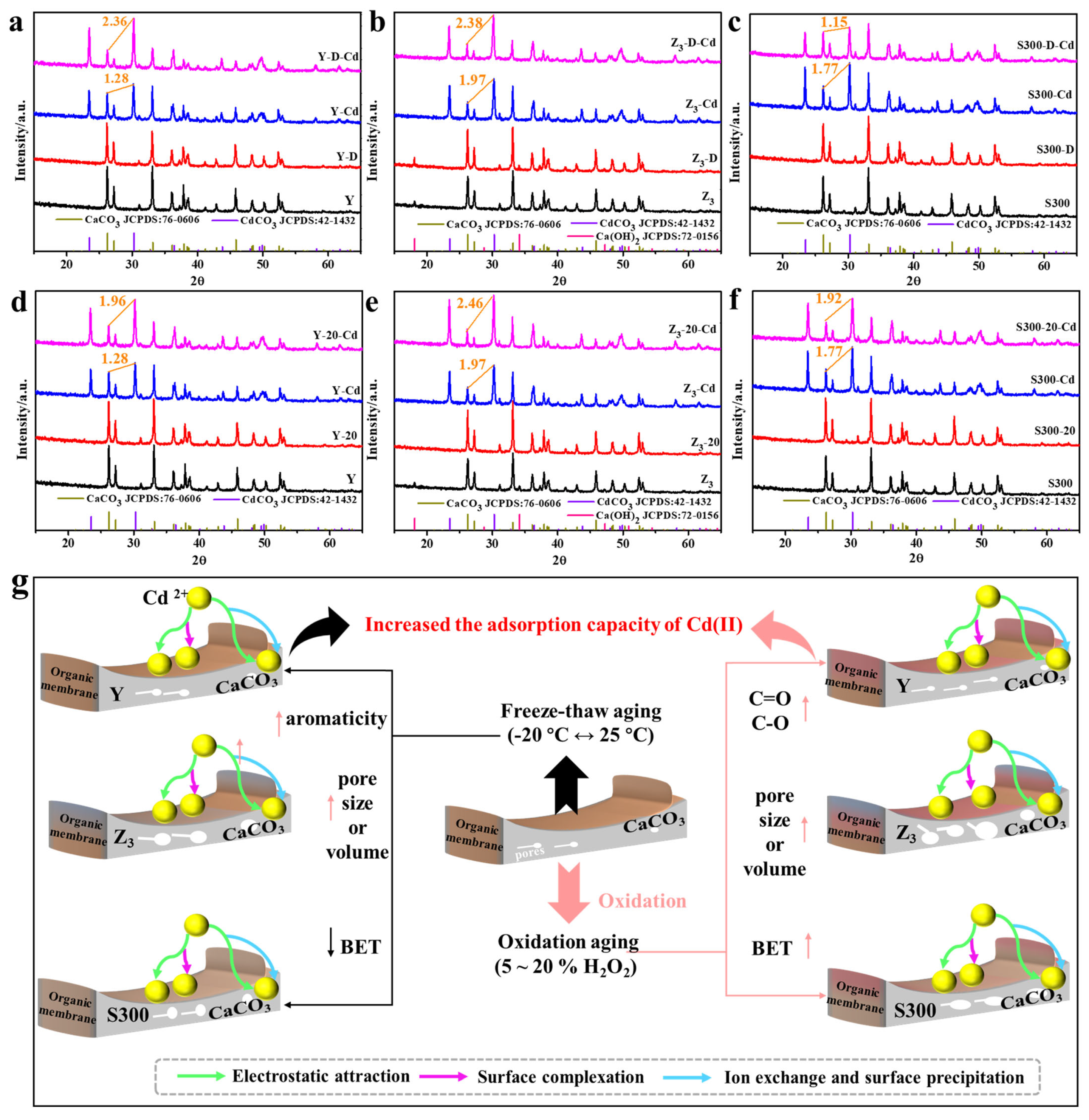
As shown in Figure 7a–c and Figure S4a–c, the calcium carbonate structure and organic functional groups of the cuttlebone-derived samples remained intact after freeze–thaw treatment. However, the freeze–thaw treatment led to a partial loss of organic matter, as indicated by the reduced proportions of hydrogen and nitrogen atoms (Table S8). The increased average pore size, coupled with organic matter loss, suggested that freeze–thaw exposure may uncover additional calcium carbonate surfaces, thereby enhancing ion exchange between Cd(II) and Ca(II). Furthermore, freeze–thaw aging increased the aromaticity of the cuttlebone-derived samples, as reflected by decreased H/C, N/C, and (O + N)/C atomic ratios, which facilitated the formation of coordination bonds between the π-electron cloud of the adsorbent and Cd(II) [52,53]. Nevertheless, partial pore blockage or collapse occurred during freeze–thaw aging, resulting in a reduced specific surface area. Therefore, the freeze–thaw process simultaneously involved enhancements in electrostatic interaction, ion exchange, and surface precipitation, collectively leading to the improved adsorption performance of Cd(II) (Figure 7g). Additionally, the smaller changes in the cadmium carbonate/calcium carbonate ratio before and after freeze–thaw suggested that Z3 may exhibit better freeze–thaw resistance among the cuttlebone-derived samples (Figure 7a–c).
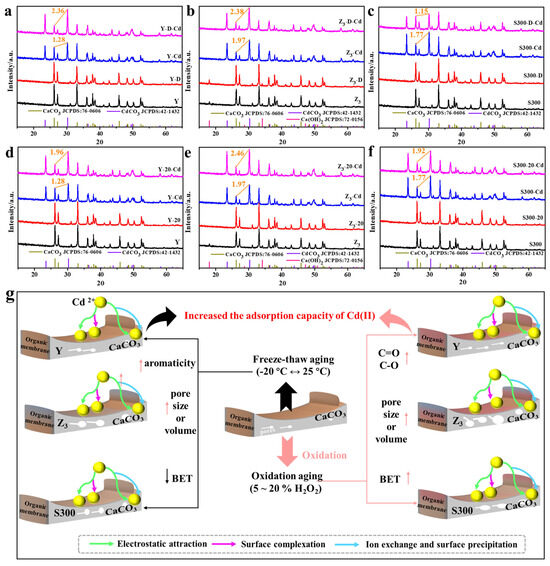
Figure 7.
The XRD spectra of the cuttlebone-derived samples with freeze–thaw aging ((a): Y; (b): Z3; (c): S300) or oxidative aging ((d): Y; (e): Z3; (f): S300) before and after the adsorption of Cd(II), and the projected adsorption mechanism and process of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples with freeze–thaw aging or oxidative aging (g).
As shown in Figure 7e–f, the calcium carbonate structure of the cuttlebone-derived samples remained intact after oxidative aging, although the oxidative treatment resulted in a partial loss of organic matter, as evidenced by the reduced proportions of hydrogen and nitrogen atoms (Table S8). The oxidative effect of hydrogen peroxide was further reflected in the increased O/C atomic ratios, indicating the formation of more oxygen-containing functional groups on the surface of the cuttlebone-derived samples (Figure S4e–f, Table S8). Consequently, oxidative aging reduced surface impurities, increased the specific surface area and pore volume, and provided additional adsorption sites. These changes in physicochemical properties collectively enhanced the adsorption performance of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples (Figure 7g). Notably, S300 might exhibit better oxidation resistance, as suggested by the smaller change in the cadmium carbonate/calcium carbonate ratio before and after oxidative aging (Figure 7d–f).
3.4. Remediation of the Natural Cadmium-Contaminated River by the Cuttlebone-Derived Samples
As a key environmental parameter, pH strongly influences the speciation of cadmium ions. As shown in Figure S5, the cuttlebone-derived samples exhibited a similar trend in Cd(II) adsorption capacity with increasing pH. When the pH increased from 3.0 to 9.0, cadmium ions primarily existed as Cd2+ [62]. The decrease in H+ concentration, as a competitive ion, enhanced Cd(II) adsorption in the cuttlebone-derived samples. When the pH further increased from 9.0 to 11.0, cadmium ions were mainly—present in the form of Cd2+, Cd(OH)+, and Cd(OH)2(aq) [62], which reduced the electrostatic attraction between the adsorbent and Cd(II), leading to a decrease in adsorption capacity.
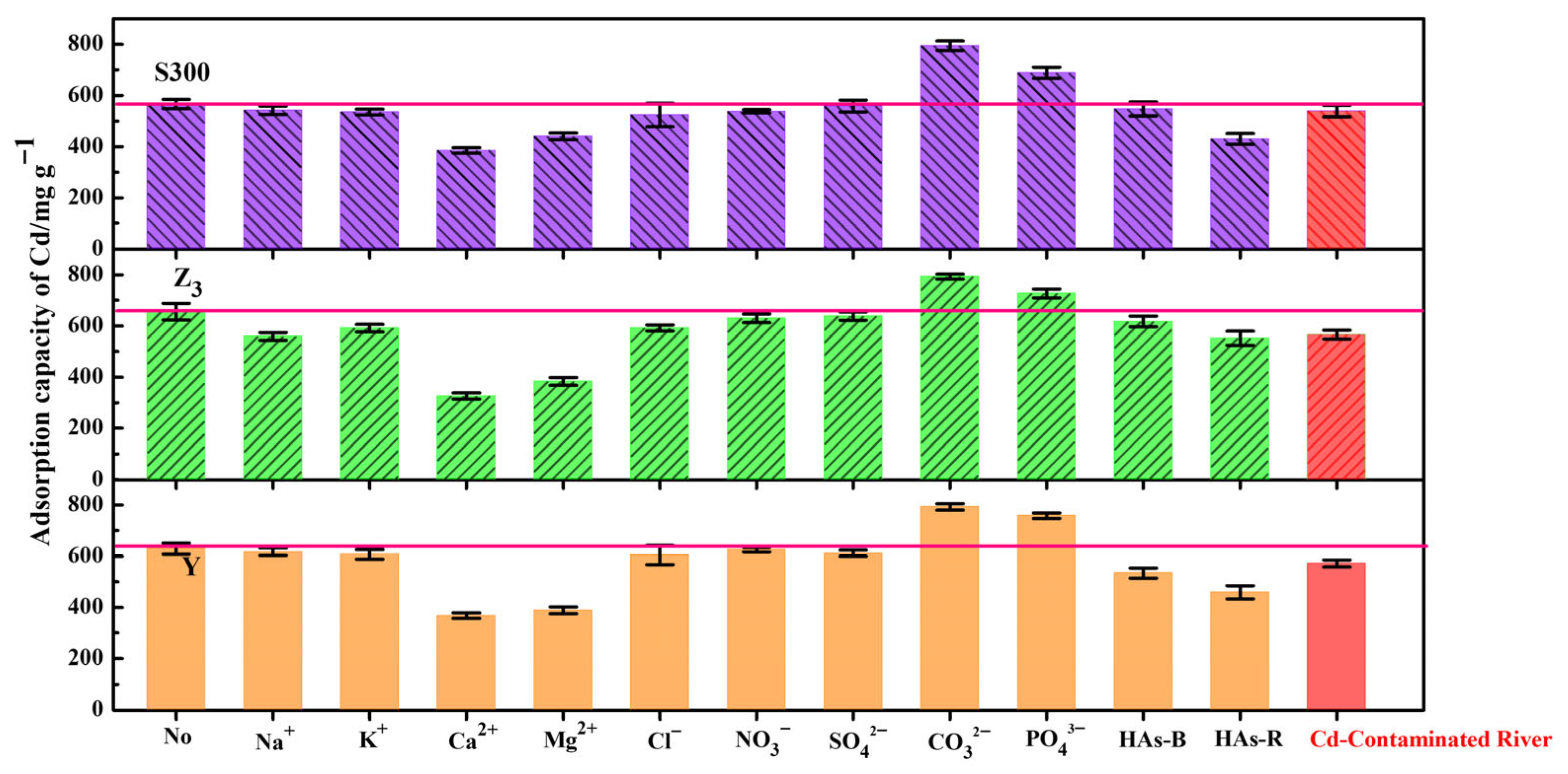
We further explored, in detail, the effects of common ion types on the adsorption of cadmium by the cuttlebone-derived samples. Compared to monovalent cations (Na+, K+), divalent cations (Ca2+, Mg2+) exhibited stronger competitive adsorption effect against Cd2+ due to their similar valence states [10]. Among the anions, CO32− and PO43− could form complex precipitates with Cd2+ [55,63], thereby enhancing the adsorption capacity for Cd(II). Conversely, the presence of organic matter masked the adsorption sites of the samples, resulting in the reduced adsorption capacity of Cd(II). As shown in Figure 8, we applied these cuttlebone-derived samples to remediate a cadmium-contaminated natural river. All samples showed high adsorption capacities for Cd(II) (S300: 548.99 mg g−1; Y: 566.16 mg g−1; Z3: 571.55 mg g−1), demonstrating their excellent remediation performance for cadmium-contaminated rivers.
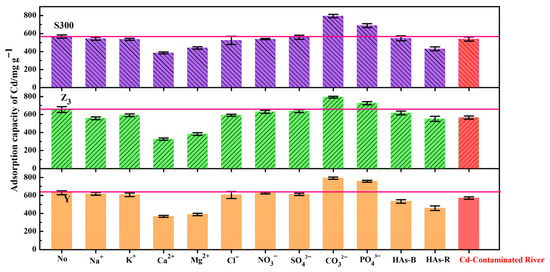
Figure 8.
The adsorption capacities of Cd(II) in the cuttlebone-derived samples from the cadmium-contaminated natural river, and in the presence of the various cations and anions (each ion: 0.05 mol L−1, Cd2+: 40 mg L−1; HAs-B/HAs-R: 20 mg L−1).
4. Conclusions
In this study, we investigated the effects of two types of humic acids (HAs-B and HAs-R), freeze–thaw cycling, and oxidative aging on the adsorption performance for Cd(II) of three cuttlebone-derived adsorbents. Based on comprehensive experiments and characterization, HAs were found to occupy the surface adsorption active sites of the samples primarily through ligand exchange and calcium ion bridging during the adsorption of cadmium. Their limited complexation capacity with Cd(II) further exacerbated the inhibition of adsorption performance. During freeze–thaw aging, a reduction in adsorption sites occurred alongside enhancements in electrostatic interaction, ion exchange, and surface precipitation. Oxidative aging reduced surface impurities, increased the specific surface area and pore volume, and introduced more oxygen-containing functional groups. These physicochemical changes collectively improved the adsorption performance of Cd(II) after freeze–thaw or oxidative aging. Finally, the high adsorption capacity of the cuttlebone-derived samples in a natural cadmium-contaminated river verified their excellent practical remediation potential. This study also clarified the differential effects and resistances of the cuttlebone-derived samples to HAs, freeze–thaw, and oxidative aging, providing important insights for the development of sustainably stable and practical adsorbents.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su17219628/s1: Calculation of adsorption performance for Cd(II) of the cuttlebone-derived samples; adsorption kinetic models; adsorption isotherm models; adsorption thermodynamics; Figure S1: The adsorption isotherms of Cd(II) in the cuttlebone-derived samples at different temperatures (a: Y; b: Z3; c: S300). Figure S2: The adsorption isotherms of Cd (II) in the cuttlebone-derived samples with HAs-R at different temperatures (a: Y; b: Z3; c: S300), and the corresponding removal rates of HAs-R with or without the cuttlebone-derived samples (d: Y; e: Z3; f: S300); Figure S3: The adsorption isotherms of Cd (II) in the cuttlebone-derived samples with HAs-B at different temperatures (a: Y; b: Z3; c: S300), and the corresponding remove rates of HAs-B with or without the cuttlebone-derived samples (d: Y; e: Z3; f: S300); Figure S4: The FTIR spectra of the derived cuttlebones with freeze–thaw aging (a: Y; b: Z3; c: S300) or oxidative aging (d: Y; e: Z3; f: S300) before and after the adsorption of Cd(II); Figure S5. The adsorption capacities for Cd(II) of the cuttlebone-derived samples under different pH conditions. Table S1: Physicochemical properties of the cuttlebone-derived samples; Table S2: The carbon integration results of HAs-R and HAs-B from the corresponding NMRs; Table S3: The surface potentials, particle size and elemental analyses of HAs-R and HAs-B; Table S4: Pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order adsorption kinetics model-fitted results of Cd(II) by the cuttlebone-derived samples with or without HAs; Table S5: Weber–Morris adsorption kinetics model-fitted results of Cd(II) in the cuttlebone-derived samples with or without HAs; Table S6: Langmuir and Freundich adsorption isotherm-fitted results of Cd(II) in the cuttlebone-derived samples with or without HAs; Table S7: Thermodynamic parameters of Cd(II) in the cuttlebone-derived samples with or without HAs; Table S8: Physicochemical properties of the cuttlebone-derived samples with freeze–thaw or oxidative aging.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.H. and L.S.; methodology, D.W., H.X. and Y.X.; validation, D.W. and Z.H.; formal analysis, Z.H., D.W. and L.S.; investigation, D.Z.; resources, D.Z.; data curation, D.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.H. and D.W.; writing—review and editing, D.W. and D.Z.; supervision, D.Z.; funding acquisition, D.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Taishan Scholar Foundation of Shandong Province (tsqn202306276), Natural Science Foundation of China (42167030), and Linyi University High-level Talents (Doctor) Research Foundation (Z6122037).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wu, W.P.; Han, L.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhang, W.Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, H.P.; Hou, S.L.; Li, J.; Chen, M.F. The impact of heteroaggregation between nZVI and SNPs on the co-transport of Cd (II) in saturated sand columns. Water Res. 2024, 258, 121822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Q.; Lawluvy, Y.; Shi, Y.; Ighalo, J.O.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yap, P.S. Adsorption of cadmium and lead from aqueous solution using modified biochar: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.D.; Xu, R.H.; Ma, C.L.; Yu, J.; Lei, S.; Han, Q.Y.; Wang, H.J. Potential functions of engineered nanomaterials in cadmium remediation in soil-plant system: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 336, 122340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, X.; Jeyakumar, P.; Wang, Z.; Sun, S.Y.; Qiu, T.Y.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, M.; et al. Unveiling the impacts of microplastics on cadmium transfer in the soil-plant-human system: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 477, 135221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazkhani, S.; Aminsharei, F.; Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi, S.A.; Malekzadeh, A.; Ameri, E. Synthesis and modification of nanofiltration membranes with dendrimer-modified graphene oxide to remove lead and cadmium ions from aqueous solutions. Cleaner Eng. Technol. 2024, 23, 100843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marszałek, M.; Knapik, E.; Piotrowski, M.; Chruszcz-Lipska, K. Removal of cadmium from phosphoric acid in the presence of chloride ions using commercially available anion exchange resins. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2023, 118, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M.M.; Liao, C.H.; Venkatesan, S.; Liu, Y.T.; Tzou, Y.M.; Jien, S.H.; Lin, M.C.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Osman, A.I. Sulfur-functionalized sawdust biochar for enhanced cadmium adsorption and environmental remediation: A multidisciplinary approach and density functional theory insights. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Singha, T.; Nambissan, P.M.G. Defect characteristics of cadmium oxide nanocrystallites synthesized via a chemical precipitation method. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2023, 181, 111513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.X.; Zhao, J.T.; Ding, Z.D.; Xiong, F.; Liu, X.Q.; Tian, J.; Wu, N.F. Cadmium-absorptive Bacillus vietnamensis 151-6 reduces the grain cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.): Potential for cadmium bioremediation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 254, 114760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Li, L.; Chen, W.D.; Tong, Y.J.; Wang, X.S. Controllable synthesis of coral-like hierarchical porous magnesium hydroxide with various surface area and pore volume for lead and cadmium ion adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.W.; Chen, K.P.; Wu, J.C.; Li, P. Reactive transport of Cd2+ in porous media in the presence of xanthate: Experimental and modeling study. Water Res. 2024, 266, 122402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.F.; Wang, D.; Cao, R.Y.; Sun, F.W.; Li, J.X. Magnetically separable h-Fe3O4@phosphate/polydopamine nanospheres for U(VI) removal from wastewater and soil. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbosiuba, T.C.; Egwunyenga, M.C.; Tijani, J.O.; Mustapha, S.; Abdulkareem, A.S.; Kovo, A.S.; Krikstolaityte, V.; Veksha, A.; Wagner, M.; Lisak, G. Activated multi-walled carbon nanotubes decorated with zero valent nickel nanoparticles for arsenic, cadmium and lead adsorption from wastewater in a batch and continuous flow modes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 126993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, K.; Wei, C.Z.; Liang, B.; Huang, H.L.; Huang, G.; Li, S.H.; Liang, J.; Huang, K. Thiol and amino co-grafting modification of sugarcane bagasse lignin nanospheres to enhance the adsorption capacity of cadmium ion. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2024, 222, 119982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmonem, H.A.; Hassanein, T.F.; Sharafeldin, H.E.; Gomaa, H.; Ahmed, A.S.A.; Abdel-lateef, A.M.; Allam, E.M.; Cheira, M.F.; Eissa, M.E.; Tilp, A.H. Cellulose-embedded polyacrylonitrile/amidoxime for the removal of cadmium (II) from wastewater: Adsorption performance and proposed mechanism. Colloid. Surf. A 2024, 684, 133081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalajiolyaie, A.; Jian, C. Advancing wastewater treatment from cadmium contamination via functionalized graphene nanosheets. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 63, 105491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yin, J.; Ma, Q.; Baihetiyaer, B.; Sun, J.X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.J.; Wang, J.; Yin, X.Q. Montmorillonite-reduced graphene oxide composite aerogel (M−rGO): A green adsorbent for the dynamic removal of cadmium and methylene blue from wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 296, 121416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.K.; Khatoon, S.; Nizami, G.; Fatma, U.K.; Ali, M.; Singh, B.; Quraishi, A.; Assiri, M.A.; Ahamad, S.; Saquib, M. Unleashing the power of bio-adsorbents: Efficient heavy metal removal for sustainable water purification. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 64, 105705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Mondal, A.; Hinkley, C.; Kondaveeti, S.; Vo, P.H.N.; Ralph, P.; Kuzhiumparambil, U. Influence of pyrolysis time on removal of heavy metals using biochar derived from macroalgal biomass (Oedogonium sp.). Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 414, 131562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.C.; Jabeur, F.; Pontoni, L.; Mechri, S.; Jaouadi, B.; Sannino, F. Sustainable removal of arsenic from waters by adsorption on blue crab, Portunus segnis (Forskål, 1775) chitosan-based adsorbents. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 33, 103491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.F.; Cao, R.; Li, M.S.; Chen, G.X.; Tian, J.F. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic cuttlebone with an inherent lamellar structure for continuous and effective oil spill cleanup. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, D.; Yang, M.Y.; Li, F.F.; Zhao, J.F.; He, Z.H.; Bai, Y.W. New discovery of extremely high adsorption of environmental DNA on cuttlefish bone pyrolysis derivative via large pore structure and carbon film. Waste Manag. 2024, 175, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.T.; Chen, C.Y.; Shiao, J.C.; Lin, S.; Wang, C.H. Temperature-dependent fractionation of stable oxygen isotopes differs between cuttlefish statoliths and cuttlebones. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 106457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.L.; Liu, W.Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Ou, X.W.; Tian, C.; Lin, Z.; Dang, Z. Biogenic calcium carbonate with hierarchical organic-inorganic composite structure enhancing the removal of Pb(II) from wastewater. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 35785–35793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazid, H.; Bouzid, T.; Naboulsi, A.; Grich, A.; Mountassir, E.M.; Regti, A.; El Himri, M.; El Haddad, M. Adsorption of malachite green using waste marine cuttlefish bone powder: Experimental and theoretical investigations. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 209, 117210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagyaraj, S.; Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Khan, M.; Kasak, P.; Krupa, I. Modified os sepiae of Sepiella inermis as a low cost, sustainable, bio-based adsorbent for the effective remediation of boron from aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2022, 29, 71014–71032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.Q.; Liu, J.; Sun, X.; Bai, X.A.; He, Z.H. Adsorption of Cd(II) from Wastewater by Cuttlebone and Its Derived Materials. In Advances in Watersheds Water Pollution and Ecological Restoration; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.Q.; Qin, P.R.; Sun, X.; Yin, M.N.; He, Z.H.; Wang, B. Adsorption of Pb(II) by cuttlebone-derived materials and its stability. E3S Web Conf. 2024, 490, 01011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakootian, M.; Shiri, M.A. Investigating the removal of tetracycline antibiotic from aqueous solution using synthesized Fe3O4@Cuttlebone magnetic nanocomposite. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 221, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salati, S.; Papa, G.; Adani, F. Perspective on the use of humic acids from biomass as natural surfactants for industrial applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.J.; Shao, T.; Karanfil, T.J. The effects of dissolved natural organic matter on the adsorption of synthetic organic chemicals by activated carbons and carbon nanotubes. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, Z.W.; Chen, J.; Jin, C.S.; Cao, W.C.; Peng, B. Humic-like components in dissolved organic matter inhibit cadmium sequestration by sediment. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 150, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.X.; Li, J.X.; Ren, X.M.; Chen, C.L.; Wang, X.K. Few-Layered graphene oxide nanosheets as superior sorbents for heavy metal ion pollution management. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 10454–10462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.D.; Shen, L.; Cao, Y.Q. Animal or plant waste-derived biochar for Cd(II) immobilization: Effects of freeze-thaw-wet-dry cyclic aging on adsorption behavior in tea garden soils. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 182, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of chitosan with ultra high molecular weight. Carbohyd. Polym. 2016, 148, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.F.; Cao, J.M.; Li, Y.X.; Howard, A.; Yu, K.W. Effect of pyrolysis temperature on characteristics of biochars derived from different feedstocks: A case study on ammonium adsorption capacity. Waste Manag. 2019, 87, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.M.; An, T.T.; Chi, F.Q.; Wei, D.; Zhou, B.K.; Hao, X.Y.; Jin, L.; Wang, J.K. Evolution over years of structural characteristics of humic acids in Black Soil as a function of various fertilization treatments. J. Soil. Sediment. 2018, 19, 1959–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Hodson, M.E. The impact of varying abiotic humification conditions and the resultant structural characteristics on the copper complexation ability of synthetic humic-like acids in aquatic environments. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 165, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Yang, Z.P.; Zhang, Q.X.; Fu, D.J.; Chen, P.; Li, R.B.; Liu, H.J.; Wang, Y.L.; Liu, Y.; Lv, W.Y.; et al. Effect of tartaric acid on the adsorption of Pb (II) via humin: Kinetics and mechanism. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2020, 107, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.; Huang, Q.Y.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, D.H.; Zhou, X.Y.; Rong, X.M.; Liang, W. Effects of low-molecular-weight organic ligands and phosphate on DNA adsorption by soil colloids and minerals. Colloid. Surf. B 2007, 54, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.T.; Zheng, Y.M.; Chen, J.P. Enhanced adsorption of arsenate onto a natural polymer-based sorbent by surface atom transfer radical polymerization. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2011, 356, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, W. Effects of macromolecular humic/fulvic acid on Cd(II) adsorption onto reed-derived biochar as compared with tannic acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.F.; Shu, Y.; Zhang, R.Q.; Li, X.; Song, J.F.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.T.; Ou, D.L. Comparison of the removal and adsorption mechanisms of cadmium and lead from aqueous solution by activated carbons prepared from Typha angustifolia and Salix matsudana. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 16092–16103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.T.; Li, G.X.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q.S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, D.D. Adsorption mechanism of arsenic(V) on aged polyethylene microplastics: Isotherms, kinetics and effect of environmental factors. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 18, 100711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, S.; Wongrod, S.; Simon, S.; Guibaud, G.; Vinitnantharat, S. Simultaneous sequestration of cadmium and lead in brackish aquaculture water by biochars: A mechanistic insight. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 16, 100501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, H.Y.; Zhang, J.F.; Li, J.X. Easily synthesized mesoporous aluminum phosphate for the enhanced adsorption performance of U(VI) from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 432, 128675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, J.X. Efficient remediation and synchronous recovery of uranium by phosphate-functionalized magnetic carbon-based flow electrode capacitive deionization. Water Res. 2025, 281, 123707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, S.X.; Wang, Y.N.; Liu, X.; Shao, D.D.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.; Li, J.X. Removal of U(VI) from aqueous solution by amino functionalized flake graphite prepared by plasma treatment. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4073–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, W.; Xiong, L.; Xu, N.; Ni, J. Influence of pH, ionic strength and humic acid on competitive adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cr(III) onto titanate nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 215, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Ma, J.; Ouyang, X.X.; Weng, L.P.; Chen, Y.L.; Li, Y.T. Enhanced cadmium removal by biochar and iron oxides composite: Material interactions and pore structure. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.Z.; Guo, Y.Y.; Li, B.; Xue, Z.L.; Jin, Z.W.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, L.X.; Zhao, C.H.; Yin, K.; Jouha, J.; et al. Highly efficient capture of cadmium ions by dual-layer calcium sulfide-calcium carbonate-loaded kelp biochar: Synthesis, adsorption and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 495, 138842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, D.J.; Xu, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gui, X.Y.; Song, B.Q.; Xu, N. Biochar nanoparticles with different pyrolysis temperatures mediate cadmium transport in water-saturated soils: Effects of ionic strength and humic acid. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Ma, J.; Li, Y.T.; Weng, L.P. Enhanced cadmium immobilization in saturated media by gradual stabilization of goethite in the presence of humic acid with increasing pH. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toprak, M.; Yıldız, B.; Zaman, B.T.; Bozyiğit, G.D.; Temuge, İ.D.; Çetin, G.; Bakırdere, S. Microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of zinc-tin based nanoflower for the adsorptive removal of cadmium from synthetic wastewater. Water Air Soil Poll. 2024, 235, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profeta, D.O.; Silva, M.A.; Faria, D.N.; Cipriano, D.F.; Freitas, J.C.C.; Santos, F.S.; Lima, T.M.; Vasconcelos, S.C.; Pietre, M.K. Zeolite/calcium carbonate composite for a synergistic adsorption of cadmium in aqueous solution. Next Mater. 2025, 6, 100493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Zhang, S.Y.; Li, Q.Y.; Li, A.Y.; Gan, W.X.; Hu, L.N. Efficient removal of lead, cadmium, and zinc from water and soil by MgFe layered double hydroxide: Adsorption properties and mechanisms. Sustainability 2024, 16, 11037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Hu, L.; He, N.; Jiang, Z.P.; Gong, J.Y.; Jiang, C.Y.Z.; Zhao, H.B. Lead and cadmium adsorption by phanerochaete chrysosporium under the protection of phosphorus-containing biochar: Effects and mechanisms. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 117330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.X.; Zhu, B.W.; Yu, J.X.; Wang, X.T.; Zhang, C.; Qin, Y. A biomass carbon prepared from agricultural discarded walnut green peel: Investigations into its adsorption characteristics of heavy metal ions in wastewater treatment. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 13, 12833–12847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, C.M.; Rivera-Hernández, M.; Álvarez, L.H.; Acosta-Rodríguez, I.; Ruíz, F.; Compeán-García, V.D. Biosynthesis and characterization of cadmium carbonate crystals by anaerobic granular sludge capable of precipitate cadmium. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 246, 122797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Y.; Liu, J.H.; Li, S.M.; Yang, W.H.; Wang, W.Y.; Li, K.; Sun, Y.Z.; Han, W.P.; Li, R.; Zhang, J.; et al. Effects of steady magnetic fields on NiRuO2 nanofibers for the electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction and oxygen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2025, 13, 31585–31591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simić, M.; Petrović, J.; Šoštarić, T.; Ercegović, M.; Milojković, J.; Lopičić, Z.; Kojić, M. A mechanism assessment and differences of cadmium adsorption on raw and alkali-modified agricultural waste. Processes 2022, 10, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xv, C.H.; Zhao, Z.R.; Wang, F.Y.; Lei, W.; Xia, M.Z.; Wang, Z.H. The facile preparation of polydopamine-modified sepiolite and its adsorption properties and microscopic mechanism for cadmium ion. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.T.; Xu, Y.; Gu, L.T.; Zhu, M.Q.; Yang, P.; Gu, C.H.; Liu, Z.; Feng, X.H.; Tan, W.F.; Huang, Q.Y.; et al. Elucidating phosphate and cadmium cosorption mechanisms on mineral surfaces with direct spectroscopic and modeling evidence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 20211–20223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).