Optimizing Amendment Ratios for Sustainable Recovery of Aeolian Sandy Soils in Coal Mining Subsidence Areas: An Orthogonal Experiment on Medicago sativa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Plant Sample Preparation and Analysis
2.4. Soil Sample Preparation and Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Plant Growth and Nutrient Uptake
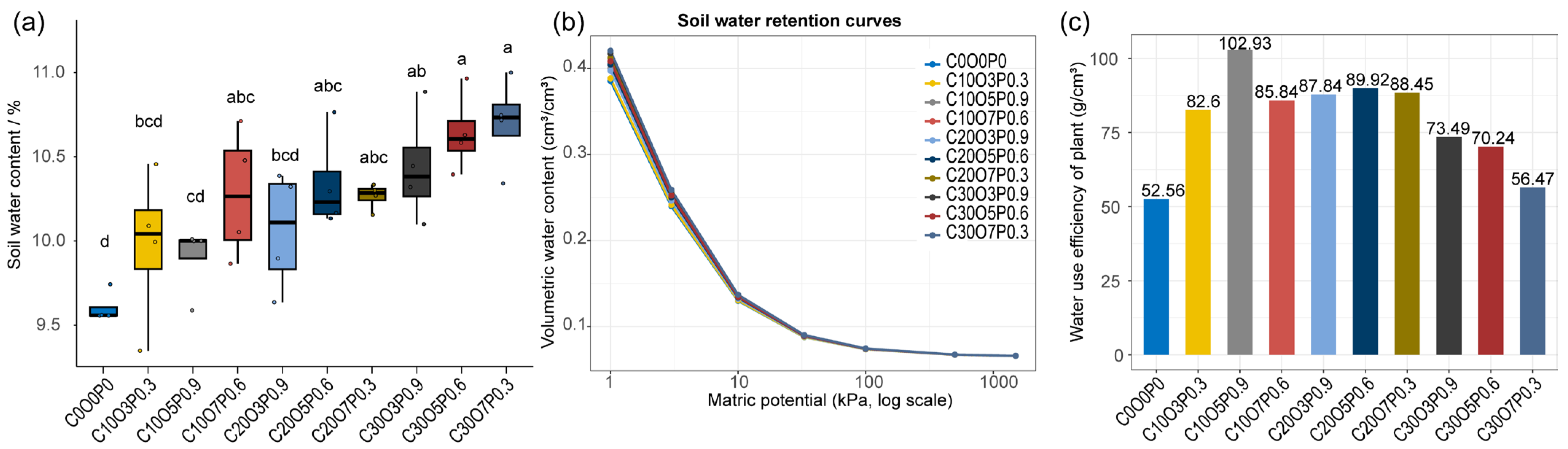
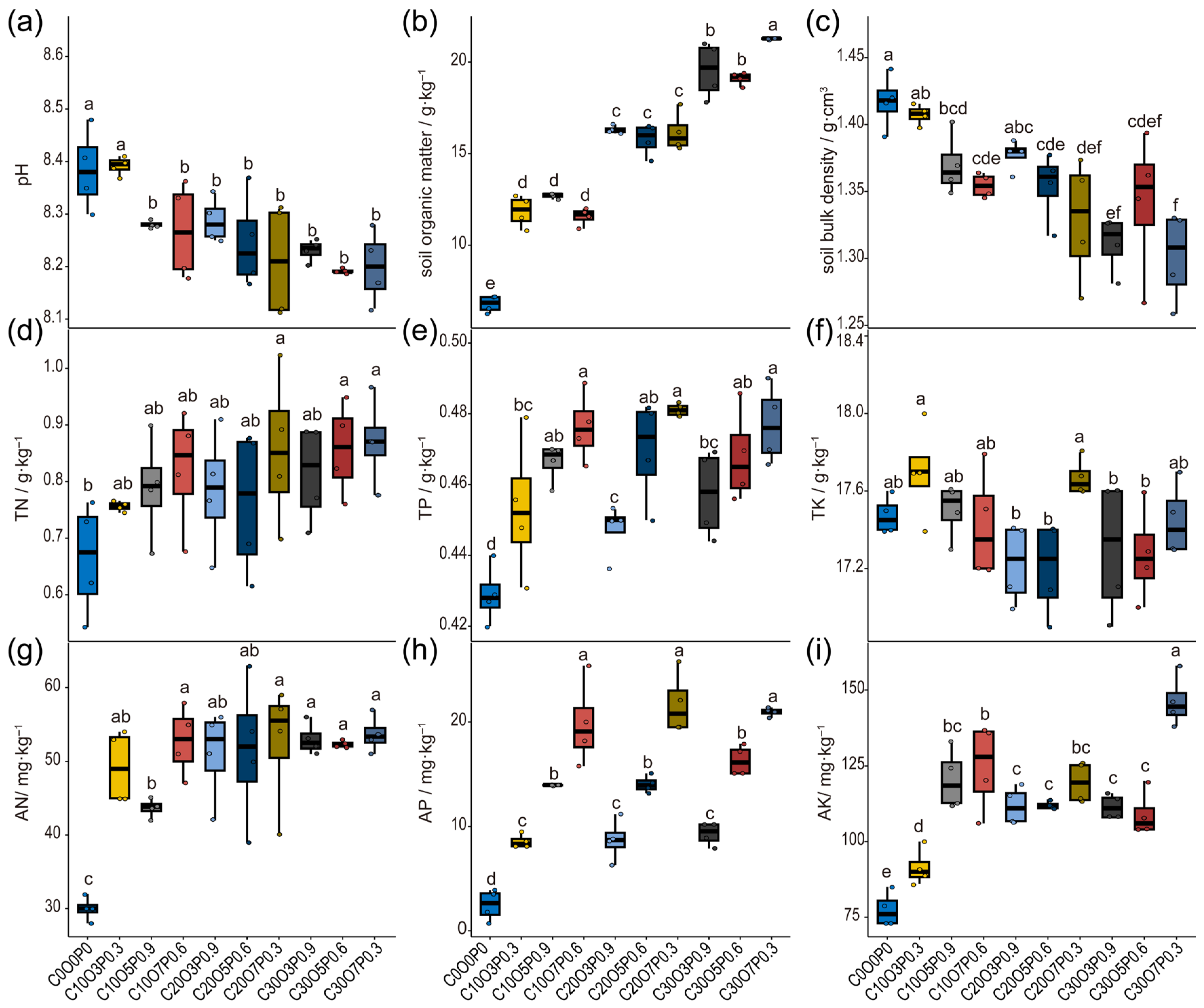
3.2. Sandy Soil Properties
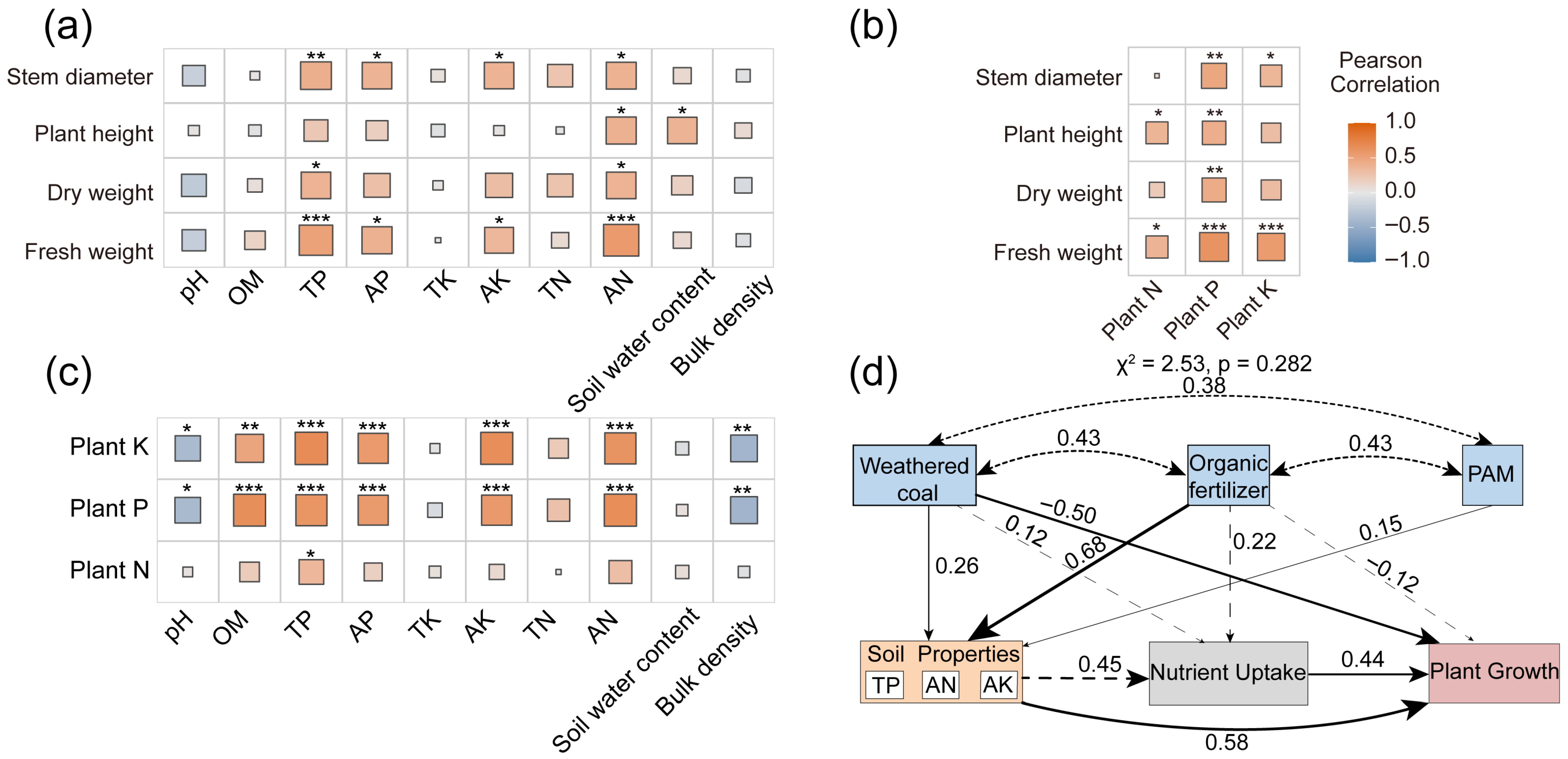
3.3. Correlation Analysis and Structural Equation Modeling (SEM)
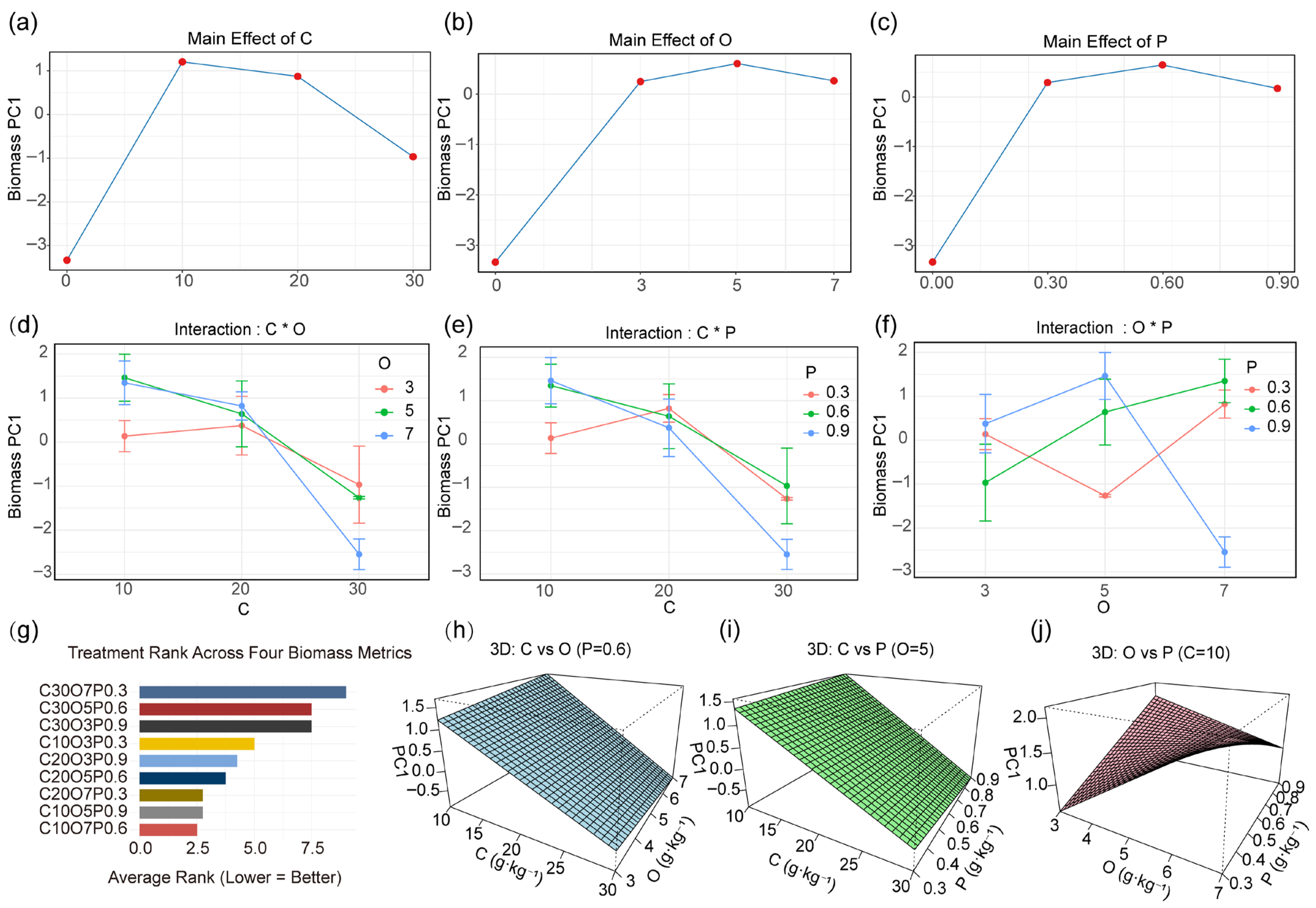
3.4. Main Effects, Interactions, and Integrated Responses of Soil Amendments on Plant Growth
4. Discussion
4.1. Optimal Ratios and Mechanisms of Soil Amendment–Induced Plant Growth Promotion
4.2. Interaction Effects of Soil Amendments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OM | Organic Matter |
| TN | Total Nitrogen |
| TP | Total Phosphorus |
| TK | Total Potassium |
| AN | Available Nitrogen |
| AP | Available Phosphorus |
| AK | Available Potassium |
| AW | Available Water |
| WUE | Water Use Efficiency |
| C | weathered coal |
| O | cow manure organic fertilizer |
| P | potassium polyacrylate |
Appendix A. Dosage Selection and Rationale for Soil Amendments
References
- Han, C.; Zheng, J.; Guan, J.; Yu, D.; Lu, B. Evaluating and Simulating Resource and Environmental Carrying Capacity in Arid and Semiarid Regions: A Case Study of Xinjiang, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, F.; Qiu, Y.; Ma, C. Sustainable Development Assessment of Ecological Vulnerability in Arid Areas Under the Influence of Multiple Indicators. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 436, 140629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, P.; Wang, E.; Chen, D.; Li, C. Characteristics of Coal Resources in China and Statistical Analysis and Preventive Measures for Coal Mine Accidents. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2023, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Qiu, H.; Yang, D.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Tang, B.; Sun, K.; Cao, M. Surface Multi-Hazard Effect of Underground Coal Mining. Landslides 2023, 20, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Li, J. Research Progress of Soil and Vegetation Restoration Technology in Open-Pit Coal Mine: A Review. Agriculture 2023, 13, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdugo, M.; Vidiella, B.; Solé, R.V.; Maestre, F.T. Ecological Mechanisms Underlying Aridity Thresholds in Global Drylands. Funct. Ecol. 2022, 36, 4–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Stringer, L.C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, W. Drivers and Impacts of Changes in China’s Drylands. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 858–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albalasmeh, A.A.; Hamdan, E.H.; Gharaibeh, M.A.; Hanandeh, A.E. Improving Aggregate Stability and Hydraulic Properties of Sandy Loam Soil by Applying Polyacrylamide Polymer. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 206, 104821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Wu, L.; Ding, X. Combined Organic Amendments and Mineral Fertilizer Application Increase Rice Yield by Improving Soil Structure, P Availability and Root Growth in Saline-Alkaline Soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 212, 105060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheir, A.M.S.; Govind, A.; Zoghdan, M.G.; Khalifa, T.H.; Aboelsoud, H.M.; Shabana, M.M.A. The Fusion Impact of Compost, Biochar, and Polymer on Sandy Soil Properties and Bean Productivity. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Wang, J.; Kader, M.A.; Sarker, T.; Hasan, A.K.; Dindaroglu, T. Cattle Manure Compost and Biochar Supplementation Improve Growth of Onobrychis viciifolia in Coal-Mined Spoils Under Water Stress Conditions. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, J.; Wu, D.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Ji, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ai, Y. Optimizing Organic Amendment Applications to Enhance Carbon Sequestration and Economic Benefits in an Infertile Sandy Soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 303, 114129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.V.; Carballo, M.T.; Calvo, L.F. Fertilization of Maize with Compost from Cattle Manure Supplemented with Additional Mineral Nutrients. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Cui, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Sun, J.; Niu, W. Effects of Manure Fertilizer on Crop Yield and Soil Properties in China: A Meta-Analysis. Catena 2020, 193, 104617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Tu, S.; Lu, X.; Li, X. Coupling of Biochar and Manure Improves Soil Carbon Pool Stability, Pore Structure, and Microbial Diversity. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, F.; Guo, H.; Dong, Z.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Xu, X. Influence Mechanism of Different Weathering Degrees on Conversion of Coal to Biogas. Nat. Resour. Res. 2022, 31, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, W.; Jia, J.; Lv, J.; Liu, S.; Xia, D. Feasibility Analysis of the in Situ Conversion of Biomethane in Surface Weathered Coal. Fuel 2020, 268, 117273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yuan, L.; Zhao, B.; Li, Y.; Lin, Z. Structural Characteristics of Humic Acids Derived from Chinese Weathered Coal Under Different Oxidizing Conditions. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, X.; Cai, J. Greater Mineral and Aggregate Protection for Organic Carbon in the Soil Amended by Weathered Coal than by Biochar: Based On a 3-Year Field Experiment. Geoderma 2023, 438, 116639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, J.; Wang, X. Amended Soils with Weathered Coal Exhibited Greater Resistance to Aggregate Breakdown than those with Biochar: From the Viewpoint of Soil Internal Forces. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 244, 106244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Sun, C.; Yang, K.; Zheng, J. Differences in Soil Physical Properties Caused by Applying Three Organic Amendments to Loamy Clay Soil Under Field Conditions. J. Soil Sediments 2022, 22, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, P.; Ren, J.; Hao, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, R. Decades of Weathering Improves Coal Waste Biogeochemical Properties by Altering Dissolved Organic Matter and Microbial Communities: A Case-Study of a Coal Waste Pile. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 1708–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampong, K.; Thilakaranthna, M.S.; Gorim, L.Y. Understanding the Role of Humic Acids on Crop Performance and Soil Health. Front. Agron. 2022, 4, 848621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, G.; Zeng, D.; Liang, C. Effects of Peat and Weathered Coal on the Growth of Pinus Sylvestris Var. Mongolica Seedlings on Aeolian Sandy Soil. J. Forestry Res. 2002, 13, 251–254. [Google Scholar]
- Özan, K.; Kanik, M.; Özer, S.S. Investigation of Water Absorption Performance of Polyester-Woven Fabrics Coated with Super Absorbent Polymer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e54837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, S.; Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yin, H.; Yu, D. Research Advances in Superabsorbent Polymers. Polymers 2024, 16, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Mei, P.; Wang, W.; Yin, Y.; Li, H.; Zheng, M.; Ou, X.; Cui, Z. Effects of Super Absorbent Polymer on Crop Yield, Water Productivity and Soil Properties: A Global Meta-Analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 282, 108290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, H.; Alsharaeh, E. Improving Water Retention in Sandy Soils with High-Performance Superabsorbents Hydrogel Polymer. Acs Omega 2024, 9, 23531–23541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelgelil, A.A.; Omer, A.M.; Hassan, A.F.; Moustafa, A.A.; Mohy Eldin, M.S. Enhancement of Sandy Soil Water Retention Using Superabsorbent Carboxymethyl Cellulose Grafted with Polyacrylamide and Polyacrylamidomethyl Propanesulfonic Acid Copolymer. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 16604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Zheng, H.; Jiang, Z.; Xing, B. Combined Effects of Biochar Properties and Soil Conditions on Plant Growth: A Meta-Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Bei, S.; Li, X.; Reinsch, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J. Contrasting Impacts of Manure and Inorganic Fertilizer Applications for Nine Years on Soil Organic Carbon and its Labile Fractions in Bulk Soil and Soil Aggregates. Catena 2020, 194, 104739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. Advances in Basic Biology of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.): A Comprehensive Overview. Hortic. Res. 2025, 12, uhaf081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Xu, X.; Xie, Y.; Huang, T.; Wang, W.; Zhao, L.; Ma, D. Comparative Metabolomic Analysis of the Metabolism Pathways Under Drought Stress in Alfalfa Leaves. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 183, 104329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, P. Research on Drought Stress in Medicago Sativa L. From 1998 to 2023: A Bibliometric Analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1406256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ali, G.; Wang, Z. Deep Soil Water Depletion and Soil Organic Carbon and Total Nitrogen Accumulation in a Long-Term Alfalfa Pasture. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 2164–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Fang, C.; Yuan, Z.; Li, F. Long-Term Growth of Alfalfa Increased Soil Organic Matter Accumulation and Nutrient Mineralization in a Semi-Arid Environment. Front. Env. Sci. 2021, 9, 649346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhou, X.; Shen, Y.; Ma, H.; Fu, B.; Lan, J. Long-Term Alfalfa Planting Mediates the Coupling of Soil Water and Organic Carbon Storage in a Semi-Arid Area of the Loess Plateau, China. PeerJ 2024, 12, e18373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, Y. Examining the Effect of Spontaneous Combustion on Vegetation Restoration at Coal Waste Dumps After Reclamation: Taking Medicago sativa L. (Alfalfa) as an Indicator. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 165668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, O.M.; Deedar, J.M.; Shadia, A.A.; Shram, H.K. Influence of Animal Manures on Carbon Mineralization and Nutrient Availability in Calcareous Soil. Sulaimani J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2020, 22, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senila, M. Recent Advances in the Determination of Major and Trace Elements in Plants Using Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry. Molecules 2024, 29, 3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, L.; Ding, Y.; Yao, M.; Liu, Q.; Zeng, R.; Chen, D.; Song, Y. Aboveground Herbivory Does Not Affect Mycorrhiza-Dependent Nitrogen Acquisition from Soil but Inhibits Mycorrhizal Network-Mediated Nitrogen Interplant Transfer in Maize. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1080416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, D.; Carrión, V.J.; Revillini, D.; Yin, S.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M. Acidification Suppresses the Natural Capacity of Soil Microbiome to Fight Pathogenic Fusarium Infections. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Xie, M.; Li, H.; Zhao, W.; Hu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Ji, W.; Li, S.; Hong, Y.; Yang, M.; et al. Stoichiometry of Soil Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus in Farmland Soils in Southern China: Spatial Pattern and Related Dominates. Catena 2022, 217, 106468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Yang, J.; Hao, B.; Hao, L.; Diao, F.; Wang, L.; Bao, Z.; Guo, W. A New Strategy for Evaluating the Improvement Effectiveness of Degraded Soil Based on the Synergy and Diversity of Microbial Ecological Function. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Ye, W.; Wang, H.; He, W.; Tian, Y.; Hu, G.; Lou, Y.; Pan, H.; Yang, Q.; Zhuge, Y. Straw and Phosphorus Applications Promote Maize (Zea mays L.) Growth in Saline Soil through Changing Soil Carbon and Phosphorus Fractions. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1336300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; He, M.; Lu, X.; Meng, Z.; Liu, J.; Mo, X. Biochar Addition Can Negatively Affect Plant Community Performance When Altering Soil Properties in Saline-Alkali Wetlands. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1347658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carsel, R.F.; Parrish, R.S. Developing Joint Probability Distributions of Soil Water Retention Characteristics. Water Resour. Res. 1988, 24, 755–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulieman, S.; Tran, L.P. Phosphorus Homeostasis in Legume Nodules as an Adaptive Strategy to Phosphorus Deficiency. Plant Sci. 2015, 239, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, C.P.; Uhde Stone, C.; Allan, D.L. Phosphorus Acquisition and Use: Critical Adaptations by Plants for Securing a Nonrenewable Resource. New Phytol. 2003, 157, 423–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, X.; Fan, W.; Meng, Q.; Liu, F.; Wang, G. Effects of Humic Acid from Weathered Coal on Water-Stable Aggregates and Pore Structure of a Reclaimed Cambisol. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Chang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Shaghaleh, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Qin, H.; Talpur, M.M.A.; Alhaj Hamoud, Y. Organic Fertilizer Compost Alters the Microbial Composition and Network Structure in Strongly Acidic Soil. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2024, 195, 105263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, P.L.; Behrends Kraemer, F.; Sabatté, L.; Guiroy, J.; Gutierrez Boem, F. Superabsorbent Polyacrylamide Effects on Hydrophysical Soil Properties and Plant Biomass in a Sandy Loam Soil. Commun. Soil. Sci. Plan. 2022, 53, 2892–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.B.; Coupal, R.H.; Dangi, M.B.; Stahl, P.D. An Assessment of Plant Growth and Soil Properties Using Coal Char and Biochar as a Soil Amendment. Agronomy 2024, 14, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhao, S.; Gao, C.; Pan, X.; Tang, D.W.S.; van der Ploeg, M. Effects of Long-Term Super Absorbent Polymer and Organic Manure on Soil Structure and Organic Carbon Distribution in Different Soil Layers. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 206, 104781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yuan, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B. Characteristics of Chinese Weathered Coal from Six Geographical Locations and Effects on Urease Activity Inhibition. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondrasek, G.; Rengel, Z.; Romic, D. Humic Acids Decrease Uptake and Distribution of Trace Metals, but Not the Growth of Radish Exposed to Cadmium Toxicity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2018, 151, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Situ, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, C.; Liang, S.; Mao, X.; Chen, X. Effects of Several Superabsorbent Polymers on Soil Exchangeable Cations and Crop Growth. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 30, 103126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Item | pH | OM/ g·kg−1 | AN/ mg·kg−1 | AP/ mg·kg−1 | AK/ mg·kg−1 | TN/ g·kg−1 | TP/ g·kg−1 | TK/ g·kg−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aeolian Sandy Soil | 8.56 | 8.28 | 117.00 | 18.20 | 103.00 | 0.68 | 0.47 | 16.50 |
| Weathered Coal | 6.62 | 34.80 | 157.00 | 19.50 | 75.00 | 5.79 | 0.10 | 0.89 |
| Cow Manure | 7.29 | 319.00 | 329.00 | 271.10 | 11,368.00 | 19.49 | 6.94 | 19.40 |
| Potassium Polyacrylate | 7.80 | 157.00 | - | - | - | 70.34 | 0.12 | 116.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, L.; Hu, Z.; Bian, Q.; Jiang, X.; Cao, Y.; Li, C.; Cui, R. Optimizing Amendment Ratios for Sustainable Recovery of Aeolian Sandy Soils in Coal Mining Subsidence Areas: An Orthogonal Experiment on Medicago sativa. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9010. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209010
Hao L, Hu Z, Bian Q, Jiang X, Cao Y, Li C, Cui R. Optimizing Amendment Ratios for Sustainable Recovery of Aeolian Sandy Soils in Coal Mining Subsidence Areas: An Orthogonal Experiment on Medicago sativa. Sustainability. 2025; 17(20):9010. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209010
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Lijun, Zhenqi Hu, Qi Bian, Xuyang Jiang, Yingjia Cao, Changjiang Li, and Ruihao Cui. 2025. "Optimizing Amendment Ratios for Sustainable Recovery of Aeolian Sandy Soils in Coal Mining Subsidence Areas: An Orthogonal Experiment on Medicago sativa" Sustainability 17, no. 20: 9010. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209010
APA StyleHao, L., Hu, Z., Bian, Q., Jiang, X., Cao, Y., Li, C., & Cui, R. (2025). Optimizing Amendment Ratios for Sustainable Recovery of Aeolian Sandy Soils in Coal Mining Subsidence Areas: An Orthogonal Experiment on Medicago sativa. Sustainability, 17(20), 9010. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17209010






