Abstract
The shortening tendency of fly ash (FA), together with a reduction in the clinker factor of Portland cement, has driven the search for alternative supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs). Coal bottom ash (CBA) is a byproduct of coal combustion in thermal power plants and has the potential to be used as an SCM. This work assessed the optimization of CBA’s performance as an SCM through particle grinding. Reactivity (R3 test), rheological, and compressive strength tests were conducted, in addition to a thorough characterization of CBA. The results showed that increasing the grinding time progressively increased the reactivity of CBA (R3 heat release), matching the reactivity of FA with 10 min of grinding. Compressive strength tests demonstrated that grinding the CBA for 10 min led to an equivalent performance compared to FA, while increasing the grinding time did not result in additional strength gains. Rheological tests showed that CBA incorporation increased the yield stress and viscosity of pastes (associated with finer and more angular CBA particles); about 40–45% more superplasticizer (SP) was required for CBA-containing pastes to reach a target yield stress compared with FA-containing samples. Overall, properly grinding CBA allowed for obtaining an equivalent reactivity and strength performance to FA, but more SP was required to obtain the same workability.
1. Introduction
The growing use of coal as a fuel source in power plants and industrial facilities in many countries over the past few decades has been linked to the production of undesirable combustion byproducts [1]. Coal bottom ash (CBA) is a byproduct of coal combustion in thermal power plants, generated in substantial volumes worldwide. In India alone, approximately 30 million tons of CBA is produced annually from the combustion of 407 million tons of coal [2]. Similarly, Malaysia generates about 1.7 million tons of CBA annually, alongside 6.8 million tons of coal fly ash [3]. Globally, it is estimated that coal combustion results in approximately 730 million tons of CBA, with Asian countries contributing more than 66% of this total [4]. Despite this large production, the reuse of CBA remains limited, especially compared to coal fly ash. For instance, in the United States, only about 33% of the CBA produced is repurposed, often for low-value applications such as road base material [5].
The open disposal of CBA poses serious environmental pollution, in addition to occupying a large area of valuable land. The disposal of CBA has raised environmental concerns due to the extensive land usage required and the potential for the leaching of hazardous substances. These challenges have prompted interest in valorizing CBA as a supplementary cementitious material (SCM) in cement and concrete, a strategy that aligns with the global push for sustainable construction practices [6]. SCMs such as fly ash, slag, and calcined clays are widely used to improve the performance and sustainability of cement-based materials, but the potential of CBA remains underexplored. Utilizing CBA has a lot of potential for use in the production of SCMs [7].
Research on the application of CBA in concrete has demonstrated its viability both as an aggregate and as a pozzolanic material. Studies focusing on its use as a partial replacement for natural sand have reported mixed results. Siddique et al., 2012 [8], produced self-compacting concrete with 10–30% CBA as a sand replacement, observing reductions in 7-day compressive strength but improvements at 90 days due to pozzolanic activity. Similarly, Rafieizonooz et al., 2016 [9], found that increasing CBA content reduced workability but allowed compressive strength to recover over time, matching or exceeding the reference concrete after prolonged curing. Gooi et al., 2020 [1], reported that the concrete and mortar with the highest compressive strength, utilizing CBA as a cement substitute, were mostly achieved with about 10% and 20% replacement.
Ground CBA has also been investigated as an SCM. For example, Aydın, 2016 [10], evaluated mortar mixes with 25–70% CBA as a replacement for Portland cement, reporting satisfactory mechanical and durability properties with optimized compositions. The fine grinding of CBA significantly enhances its reactivity, as demonstrated by Oruji et al., 2017 [5], who showed that finely ground CBA (D50 ≈ 5 µm) exhibited pozzolanic activity comparable to fly ash. For Guan et al., 2023 [11], grinding was beneficial for improving the hydration reactivity of coal CBA. The finer the coal CBA particles, the higher the compressive strength of cement mortars. Still, regarding reactivity, bottom ash powders improve the hydration of mortar at an early stage compared to fly ash [11,12]. Menéndez et al., 2021 [13], investigated a mixture of coal bottom ash and fly ash and concluded that the mixture of the two ashes is promising, because they can complement each other.
Coal bottom ash increases concrete/mortar workability, with yield stress becoming at least 1.5–2 times smaller than a reference blend with cement only [14]. According to Singh et al., 2022 [15], chemical additives have a great influence over the rheological properties of CBA slurry. Viscosity and shear stress decrease with the addition of chemical additives at low shear rates and show non-Newtonian behavior with a non-zero yield stress.
The porous characteristics of CBA enhance concrete’s ability to absorb water. Using CBA as a supplementary cementitious material (SCM) and aggregate in concrete construction can potentially boost long-term strength and decrease permeability [6]. In a study by Beddu et al., 2022 [16], the optimal percentage of CBA with a particle size smaller than 75 μm was equivalent to 6% within (45 curing days), producing a compressive strength of 40 MPa. When the CBA particle size was increased to 100 μm (passing the 100 μm sieve), the optimal percentage of CBA was 12% (51 curing days, producing a compressive strength of 50 MPa). This suggests that for a greater CBA particle size, the content should be increased. Ankura et al., 2024 [17], investigated the carbonation resistance of coal bottom ash concrete. The optimized mix with the highest carbonation resistance contained 29.8% CBA and resulted in a 19.40% lower carbon footprint compared to control.
According to Eun Kim et al., 2023 [18], the CO2 emissions related to bottom ash aggregate were insignificant (6 and 9 CO2-kg/t for raw and pretreated bottom ash respectively), less than 1% of those contributed by the binder in concrete and slightly higher than those of crushed sand. This is another feature to encourage the use of CBA as an SCM.
Despite these advances, some gaps remain in optimizing the performance of CBA in cement-based systems—while increasing CBA fineness tends to increase its reactivity, excessive grinding may lead to a poor rheological performance.
In this context, the current study aims to optimize the performance of CBA as an SCM through particle grinding. The study aims to develop procedures for processing bottom ash in relation to particle size fraction and grinding time. It seeks to investigate the factors that may contribute to a bottom ash reactivity equivalent to that of fly ash using cement pastes. It also seeks to evaluate the performance of processed bottom ash regarding the properties of mortars in fresh and hardened states. Unlike previous studies that primarily focused on setting times and workability, this research offers a detailed quantitative analysis of the rheological behavior of cement pastes incorporating ground coal bottom ash (CBA). By measuring yield stress and plastic viscosity, the study provides deeper insights into how grinding time influences the flow properties of cementitious materials. Furthermore, the study integrates the R3 hydration test to assess the pozzolanic activity of CBA-blended pastes. This method enables a precise evaluation of hydration kinetics and their correlation with particle fineness, offering a comprehensive understanding of CBA reactivity. A key practical contribution of this research is the optimization of grinding time, balancing energy efficiency with an enhanced rheological and hydration performance. The findings offer practical guidance for the sustainable processing of CBA, facilitating its use as a cost-effective supplementary cementitious material (SCM).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
Commercial Portland cement (PC) was supplied by Pozosul Cimentos (Capivari de Baixo, SC, Brazil), composed of ~90 wt% clinker, 3.9 wt% calcium sulfate (gypsum and bassanite), and 6.2 wt% limestone filler (calcite and dolomite), was used as determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD). The XRD pattern of PC is shown in Figure S1 (see Supplementary Materials). Coal bottom ash (CBA) deriving from the Jorge Lacerda Thermal Company (Capivari de Baixo, SC, Brazil)—the largest thermal plan in Latin America—was used in this work. CBA was supplied by Pozosul Cimentos (Capivari de Baixo, SC, Brazil) and collected in a batch of ~100 kg with a moisture content of ~13 wt%. The material was homogenized and dried in an electric oven at 100 °C for 24 h. The CBA was characterized in terms of particle size distribution by manual sieving according to NBR 17054 [19], using sieves of 2.4 mm, 1.2 mm, 0.600 mm, 0.300 mm, 0.150 mm, and 0.075 mm. Thus, the material was divided into the following 7 fractions: (i) <0.075 mm; (ii) 0.075–0.150 mm; (iii) 0.150–0.300 mm; (iv) 0.300–0.600 mm; (v) 0.600–1.20 mm; (vi) 1.2–2.4 mm; and (vii) >2.4 mm. It was found that the material in fractions larger than 1.2 mm (0.5%) consisted only of impurities, with no retained CBA. Therefore, only the material passing through the 1.2 mm sieve was considered for processing and grinding in the ball mill—see Section 2.2. Figure 1 shows the particle size distribution (PSD) of the raw CBA. Fly ash (FA) was provided by the same cement company, supplied in the ground form at the PSD used in cement. A polycarboxylate-based superplasticizer (SP) was used for the pastes used in the rheological tests. For the mortar production process, natural quartz sand was used with a specific mass of 2.639 g/cm3 and a grain size of less than 600 μm.
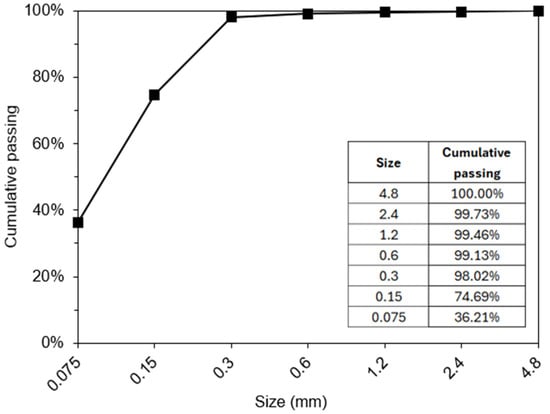
Figure 1.
PSD of the raw bottom ash.
Table 1 shows the chemical composition and physical properties of the raw materials used, with the former determined through X-ray fluorescence (XRF) using Puma S2 from Bruker (Karlsruhe, Germany) equipment. The loss on ignition was determined through thermogravimetric analysis using SDT650 from TA Instruments (New Castle, DE, USA) equipment under a N2 atmosphere at a heating rate of 20 °C/min; the mass loss (TG) and derivative mass loss (DTG) curves of CBA and FA are shown in Figure 2. The TGs of the individual size fractions of CBA are shown in Figure S2; the mass loss within 500–850 °C is attributed to the thermal decomposition of (uncombusted) coal, indicating that the 0.30–0.15 mm fraction contained the largest content of coal. Figure 3 shows the X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the materials used, measured using a D6 Phaser from Bruker (Karlsruhe, Germany) diffractometer operating at 40 kV and 15 mA with CuKα1,2 radiation (λ = 1.5418 Å).

Table 1.
Chemical composition and physical properties of the raw material.
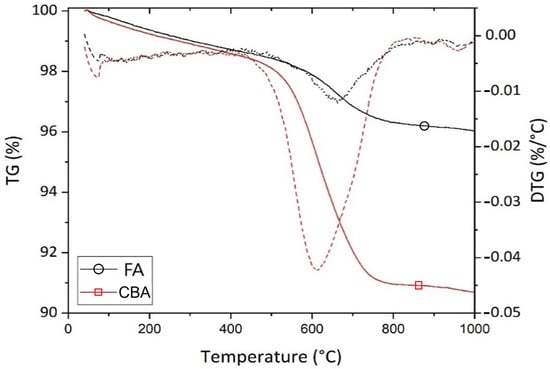
Figure 2.
TG (solid lines) and DTG (dashed lines) of the fly ash and bottom ash used.
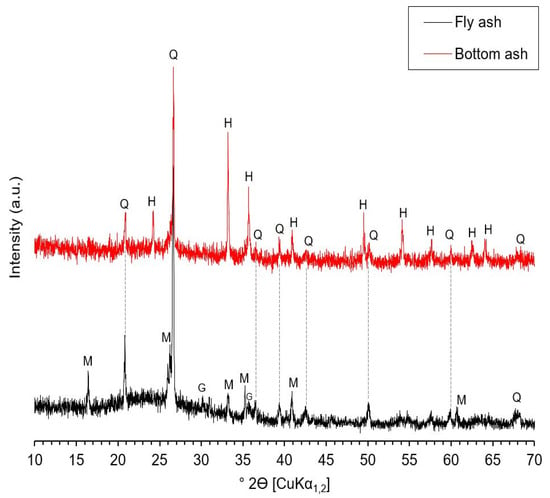
Figure 3.
XRD pattern of fly ash and bottom ash. Q: quatz; H: hematite; M: mullite; G: Goethite.
Gooi et al., 2020 [1], compared CBA samples from different countries. The typical concentrations of silica, alumina, ferric oxide, and carbon in CBA showed that most countries met the chemical composition criteria for either class “F” or class “C” pozzolan. The silica content was generally the highest, ranging from 26.2% to 79.2%, followed by alumina (9.3% to 35.0%) and ferric oxide (1.0% to 20.9%). The loss on ignition (LOI) content varied widely, with values ranging from 0.4% to 19.5%. The physical properties of CBA are mainly influenced by the coal combustion process. Rapid combustion causes the CBA to break apart into a less granulated form, a phenomenon that is significant because it leads to the formation of particles of varying sizes in the CBA [6].
Figure 4 shows scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images and the energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) results of FA and CBA (ground for 10 min). Analysis was conducted using a JCM-7000 from JEOL (Akishima, Tóquio, Japão) microscope operating at 15 kV in Au-coated samples. The EDS mapping analysis of the areas in Figure 4 is shown in Figure S3. An appreciable amount of fly ash particles (e.g., marked as “1”) can be seen in CBA, in addition to Fe-rich coarse particles (e.g., marked as “4”). This is in line with the relatively high Fe2O3 content found in XRF for CBA (Table 1).
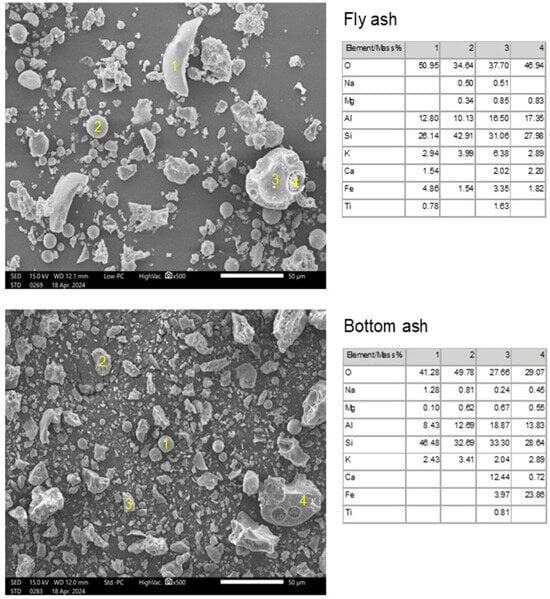
Figure 4.
SEM-EDS of the fly ash (top) and bottom ash (bottom) used.
2.2. Bottom Ash Processing
CBA was ground in the laboratory using a CT-241 from Servitech (Tubarão, SC, Brazil) ball mill operating at 380 rpm. For this purpose, batches of 150 g of CBA were ground with a ball/sample mass ratio of 5:1 (32 balls of 20 mm in diameter and 53 balls of 13 mm in diameter). Grinding cycles of 10 min were used, and ~2 g of sample was collected for PSD measurement. Figure 5 shows the PSD results of the CBA ground at different times, obtained through laser diffraction using PSA 1090 equipment from Anton Paar (Graz, Austria) with isopropanol dispersant. The 1.2–0.3 mm size fraction was not tested separately due to its low CBA content (see Figure 1). A grinding time of 10 min was enough to reach the target median diameter of 10–15 µm for all size fractions.
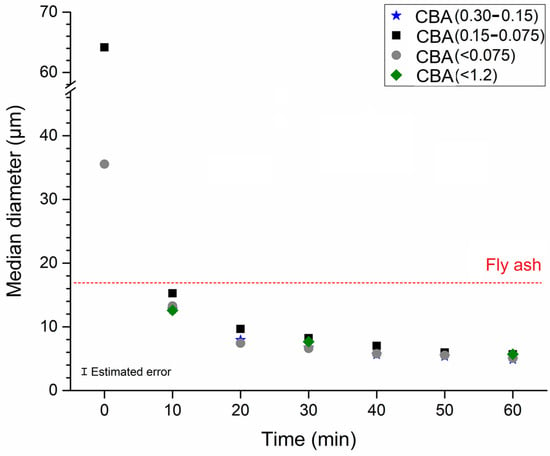
Figure 5.
Median diameter of bottom ash (CBA) as a function of the grinding time.
2.3. Mixture Proportions and Sample Preparation
Blended cements were produced by replacing 25 wt% PC with both CBA and FA, besides “REF” for the system containing only PC. Cement mixtures were prepared for rheological tests with a fixed water/binder ratio of 0.35 by weight. The superplasticizer (SP) content was gradually increased by 0.1% by weight each time (based on the binder weight) until reaching a consistency of 21 ± 1 cm, measured using the flow table method according to NBR 13276 [20]. The maximum SP content used to achieve the desired consistency was approximately 0.4%. The SP was added directly into the mixing bowl while the mixer was running and was the last material to be incorporated. The pastes were prepared in batches of ~100 mL, mixing the sample at 2800 rpm for 2 min. Mortars were produced for compressive strength test with a binder/sand/water ratio of 1:3:0.48 by weight. Batches of 1.5 L were produced in a 5 L capacity standard planetary mortar mixer at 140 rpm for 5 min and then 285 rpm for another 5 min.
2.4. Testing Methods
The R3 test was conducted following ASTM C1897 [21] at 20°C. For this purpose, appropriate amounts of CBA and FA were mixed with Ca(OH)2, CaCO3, and the standardized potassium solution. This test was also carried out for a fly ash, with the aim of using the values obtained as a reference. Solutions containing each of the different ash fractions, calcium hydroxide, calcium carbonate, and a solution of potassium hydroxide and sulfate, at a proportion of 1:3:0.5:5.4, were qualified. After, 6.00 ± 0.05 g of the sample was placed into a calorimeter container, and the appropriate amount of water was used as the reference material. The heat release was recorded for 7 days using a TAM Air from TA Instruments (New Castle, DE, USA) isothermal calorimeter. The cumulative heat was normalized per gram of SCM.
Compressive strength tests were carried out at 3, 7, and 28 days of hydration, in mixtures detailed in the previous section. Two cylindrical (Ø = 50 mm, h = 100 mm) specimens were cast for each age. The specimens were demolded 24 h after casting, being immersed in lime-saturated water until the testing age.
Rotational rheometry tests were conducted using a Haake Viscotester iQ Air from Thermo Scientific (Karlsruhe, Germany) rheometer with a vane-in-cup setup. The yield stress was determined as the peak stress before flow onset when applying a constant shear rate of 0.05 s−1 for 60 s. Subsequently, the shear rate was kept at 100 s−1 for 30 s and was then decreased down to 0.1 s−1 in 9 steps of 20 s each, logarithmically distributed. The plastic viscosity was determined as the slope of the shear stress vs. shear rate curve, assuming a Bingham flow behavior.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. R3 Test
Figure 6 shows the heat release during the R3 test and the 168 h cumulative heat at the legend. One can see that grinding the CBA for 10 min was enough to reach the R3 heat release of FA, considered the “standard” SCM for comparison. Although CBA tends to be less reactive than FA due to the presence of impurities such as uncombusted coal and hematite (discussed in Section 2.1), the 10 min ground CBA reached a fineness significantly higher than that of FA (Blaine = 6072 vs. 3580 m2/g), followed by a smaller PSD (median diameter = 13.2 vs. 17.1 µm). This grinding time was enough to compensate for the lower reactivity of CBA and match the R3 heat release of FA. Further grinding CBA progressively increased the reactivity of the material, as demonstrated by the R3 heat release. However, excessive grinding may lead to excessive water demand, potentially leading to workability issues. This will be further discussed in Section 3.3. Therefore, the 10 min grinding time was adopted as the optimum protocol. Yoon et al. [22] employed machine learning models to investigate the influence of physical and chemical properties on the reactivity of various supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs), including ground coal fly ash (CFA) and coal bottom ash (CBA). In their study [22], each SCM underwent grinding for 6 min to achieve a median particle size (d50) of approximately 5 μm. This fine grinding process enhanced the reactivity of the SCMs, as measured by the R3 test, which assesses pozzolanic activity through cumulative heat release.
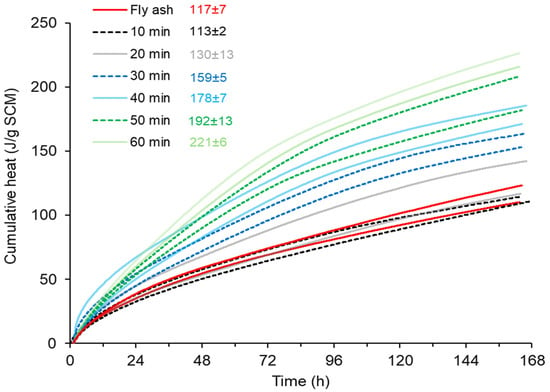
Figure 6.
R3 heat release (20 °C) of fly ash and bottom ash with different grinding times (n = 2).
The main phases present in CFA and CBA quartz, hematite and unburned carbon, affect the kinetics of cement hydration and the evolution of heat. Quartz is chemically inert and does not participate in cement hydration. Its inclusion can lead to a dilution effect, reducing the overall heat of hydration. However, fine quartz particles can act as nucleation sites, potentially accelerating early hydration reactions [23]. Hematite (α-Fe2O3) can act as a nucleation site for C-S-H gel, contributing positively to the early hydration of cement. However, high contents (typically > 1%) may reduce the hydration heat peak, negatively affecting the reaction kinetics, especially when combined with other inert phases [24]. Unburned carbon in ash can adsorb chemical admixtures, especially superplasticizers, compromising cement dispersion and the efficiency of hydration reactions. Its high surface area and hydrophobic nature can also reduce heat release and slow down hydration rates [25].
3.2. Compressive Strength
Figure 7 shows the compressive strength of the mortars produced without ash (REF), those with a 25 wt% replacement of PC with CBA ground for 10 min (CBA-10′) and 30 min (CBA-30′), and those with FA in different contents. FA contents of 30 and 46% were chosen for comparison, since these contents are used in 40 and 32 (MPa)-grade commercial cements, respectively, marketed by the manufacturer that provided the materials used here. Further grinding CBA from 10 to 30 min did not improve the compressive strength of the mortar. Although further grinding increased the reactivity of the material—as revealed by the R3 test—it also tended to increase the specific surface area and consequently the viscosity (discussed in the next section). As a result, it may increase the entrained air content and reduce the mechanical performance of the material. Figure 8 shows the correlation between the 28-day strength and the FA content, in addition to the data for CBA ground for 10 and 30 min. A strong linear correlation was observed (R2 = 0.99), suggesting that the compressive strength of mortar (which corresponds to the nominal/grade cement strength according to the standard used) can be accurately predicted based on the FA content used, adjusting the PC-to-FA proportion to tailor the mechanical strength of the material. In addition, the plotted CBA data matched the FA data fit, suggesting that such a correlation could also be used for CBA. It is worth stressing that although replacing Portland cement with either ash progressively reduced the compressive strength of mortar, the strength reduction was relatively smaller than the amount of cement replaced. For instance, the CBA-10′ mortar contained 25% less cement than REF, while the strength reduction was 19.6%. The same holds true for the sample containing the highest content of ash (46% fly ash), which had a 28-day strength 29.4% lower than that of REF. This demonstrates the feasibility of using coal ash to reduce cement consumption in mortar/concrete. Singh and ShriRam, 2023 [26], investigated the use of fly ash (FA), copper slag, and bottom ash (CS + CBA) as partial replacements for cement and natural fine aggregate, respectively. The optimal proportions found were 20% FA as a substitute for cement and a combination of 20% CS and 20% CBA as a replacement for sand. The spherical shape of fly ash, along with the low moisture absorption and gelatinous texture of copper slag, enhanced the workability of the concrete mixture. Compared to the reference mix, both the compressive and split tensile strengths increased as the replacement percentage rose, reaching improvements up to 25% [26]. The results of Chuang et al., 2023 [27], showed an optimal replacement rate of 20% for finely ground bottom ash. The maximum strength achieved with finely ground coal bottom ash was 97.7% that of the control group with pure cement, while coal fly ash reached 114.0% [27]. According to Tamanna et al., 2023 [6], the application of CBA as an SCM and aggregate in concrete construction may improve long-term strength and reduce permeability [6].
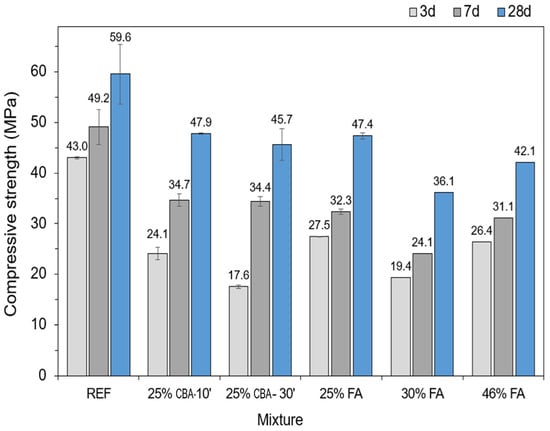
Figure 7.
Compressive strength of the mortars at 3, 7, and 28 days (n = 2).
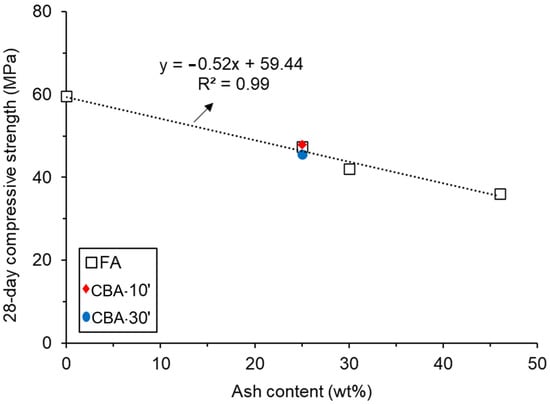
Figure 8.
Correlation between the 28-day compressive strength and fly ash (FA) content. The data for bottom ash ground for 10 min (CBA-10′) and 30 min (CBA-30′) are also plotted.
3.3. Rheometry
Figure 9 shows the rheological properties of the pastes containing FA and CBA with different SP contents (over the binder weight). Regarding pastes without SP, CBA incorporation led to higher yield stress and viscosity values, as follows: yield stresses of 427.9 vs. 250.5 Pa and viscosities of 2.7 vs. 2.4 Pa·s for pastes with CBA and FA, respectively. This can be associated with the higher specific surface area (Blaine fineness: 6072 vs. 3850 cm2/g) and finer PSD (D50: 13.2 vs. 17.1 µm) of CBA, which tend to reduce the inter-particle distance and increase their interaction, reducing the paste flowability. In addition, the greater presence of angular particles in CBA compared to the spherical particles of FA (see Figure 4) also reduced flowability. It is known that the inter-particle distance of the suspension is inversely proportional to the specific surface area of its solid fraction [28]. In addition, the greater presence of angular particles in CBA compared to the spherical particles of FA (see Figure 4) also reduced the paste flowability. According to Kumar [29], comparing the morphology of CBA and fly ash, fly ash particles are finer, more regular, and have a smooth surface texture. CBA has irregularly shaped coarser particles. Relative viscosity is reduced with an increasing temperature of fly ash slurry with and without the addition of bottom ash [29]. Angular particles impair the fluidity of cement paste, primarily due to their irregular shape and rough surface texture, which increase inter-particle friction and hinder the movement of particles within the mixture. This elevated friction leads to a higher yield stress and plastic viscosity, making the paste more resistant to flow. In contrast, spherical particles, such as those found in unground fly ash, act like ball bearings, facilitating easier movement and reducing internal resistance. The grinding process, while reducing particle size, often transforms these beneficial spherical particles into angular ones, thereby diminishing their positive impact on workability [30]. Furthermore, angular particles tend to pack less efficiently, creating a more open structure that requires additional water to achieve the desired consistency. This increased water demand can further compromise the rheological properties of cement paste. Therefore, the presence of angular particles, resulting from processes like grinding, can significantly impair the fluidity of cement paste by increasing internal friction and disrupting optimal particle packing.
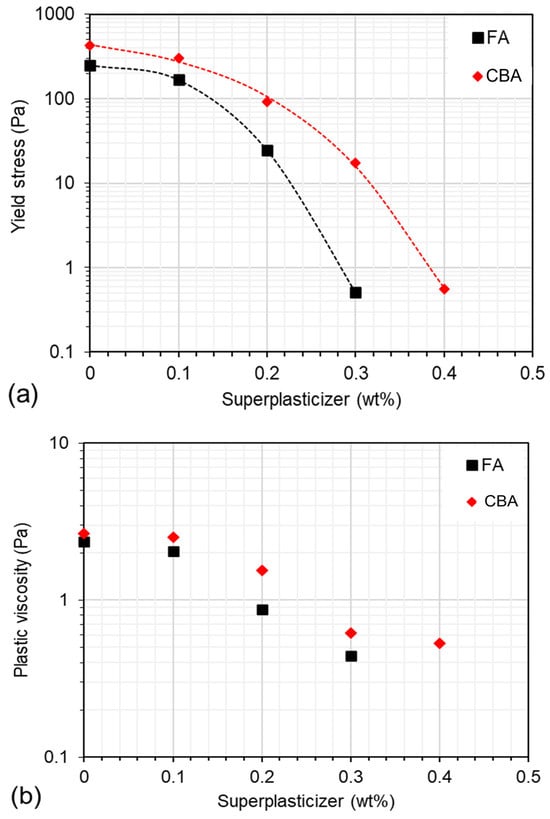
Figure 9.
Rheological properties of cement pastes containing fly ash (FA) and bottom ash (CBA) with different contents of superplasticizer. (a) Yield stress and (b) plastic viscosity.
As the SP content increased, the yield stress and viscosity decreased (as expected), but pastes with CBA presented higher yield stress and viscosity values compared to FA-containing pastes for a given SP content. In practice, the CBA-containing samples required higher SP dosages (of the order of 40–45% higher) to reach the target flowability for a fixed w/b ratio. For instance, to reach a yield stress of 100 Pa, the FA and CBA samples would require 0.14 and 0.20 wt% SP, respectively; to reach a yield stress of 10 Pa, the SP contents required are 0.23 and 0.32 wt%, respectively, for FA and CBA. These rheological results indicate that although ground CBA has good potential as an SCM—yielding an equivalent reactivity and mechanical performance to FA when the appropriate PSD is reached—its practical application requires adjustments in SP content (for a fixed w/b ratio), which requires additional attention to possible cost and hydration delay issues. Nonetheless, additional investigation into this matter is needed. According to Chuang et al., 2023 [27], the inclusion of finely ground bottom ash requires the addition of a superplasticizer to achieve the desired slump at the same replacement rate. The demand of water for the workability of concrete is governed by particle fineness and its characteristics. With a fixed water-to-cement ratio (w/c), the workability is reduced with CBA utilization as cement substitution in concrete [31].
4. Conclusions
This work assessed the reactivity (R3 test), mechanical performance, and rheology of cement pastes and mortars containing ground coal bottom ash (CBA), comparing it with fly ash (FA) as a reference SCM. The results showed that the reactivity of CBA was progressively increased by grinding it, matching or overcoming the FA reactivity by controlling the PSD. In order to match FA’s R3 reactivity, CBA required a finer PSD (D50: 13.2 µm for CBA vs. 17.1 µm for FA) and greater fineness (Blaine 70% higher). Furthermore, controlling the reactivity of CBA through the R3 test was effective, since the 10 min ground CBA and FA yielded equivalent compressive strength results. In turn, extensive grinding did not result in additional compressive strength gain. The 28-day mortar compressive strength progressively reduced with CBA and FA incorporation but at lower levels than the corresponding cement reduction, e.g., a 19.6% strength reduction for 25% FA/CBA incorporation. Rheological tests revealed that CBA incorporation led to higher yield stress and viscosity values than FA did, due to particle characteristics (fineness, particle size, and angularity). The superplasticizer content required to reach a target yield stress was about 40–45% higher for CBA than FA. Overall, it was observed that CBA presented a comparable reactivity and performance (in terms of mechanical strength) to FA, but it required additional superplasticizer addition to maintain flowability. CBA, when properly ground, can be a viable alternative to FA as a complementary cementitious material. To maintain focus and effectively control the variables, the bottom ash content was fixed at a single percentage, in accordance with the Brazilian standard for pozzolanic materials testing (i.e., 25 wt% replacement of cement). This decision allowed us to isolate the effects of grinding time without the added complexity of varying ash percentages. However, future studies should explore different grinding times and analyze reactivity, in addition to seeking strategies to minimize the demand for superplasticizer additives. Excessive grinding may not only increase costs unnecessarily, but also compromise particle shape, requiring additional additives. Thus, optimizing grinding time is a key practical outcome of this research.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su17115031/s1, Figure S1: XRD-Rietveld analysis of PC; Figure S2: Mass loss curves of CBA and FA obtained by TGA; Figure S3: SEM-EDS mapping of FA (top) and BA (bottom).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.R.d.M. and L.H.; methodology, P.R.d.M. and L.H.; validation, P.R.d.M. and L.H.; formal analysis, P.R.d.M. and L.H.; investigation, P.R.d.M. and L.H.; resources, P.R.d.M., A.S., A.P.K., E.D.R.M. and M.V.F.; data curation, P.R.d.M., L.H., A.S., and J.d.S.A.N.; writing—original draft preparation, P.R.d.M. and L.H.; writing—review and editing, P.R.d.M., A.S., and J.d.S.A.N.; supervision, P.R.d.M.; project administration, P.R.d.M. and J.d.S.A.N.; funding acquisition, P.R.d.M. and J.d.S.A.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa e Inovação do Estado de Santa Catarina (FAPESC) under the project VALTERM: Valorization of thermoelectric waste through the development of alternative binders (2023TR001444).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the staff from NIMMA/UDESC and LINCE/UFRGS for the assistance in the laboratory tests. The authors are thankful for the Multi-User Facility infrastructure of Center for Technological Sciences, Santa Catarina State University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gooi, S.; Mousa, A.A.; Kong, D. A Critical Review and Gap Analysis on the Use of Coal Bottom Ash as a Substitute Constituent in Concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 121752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Siddique, R. Strength Properties and Micro-Structural Properties of Concrete Containing Coal Bottom Ash as Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 50, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafieizonooz, M.; Mirza, J.; Salim, M.R.; Hussin, M.W.; Khankhaje, E. Investigation of Coal Bottom Ash and Fly Ash in Concrete as Replacement for Sand and Cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 116, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World of Coal Ash 2020—Website of the World of Coal Ash Conference. Available online: https://worldofcoalash.org/ (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- Oruji, S.; Brake, N.A.; Nalluri, L.; Guduru, R.K. Strength Activity and Microstructure of Blended Ultra-Fine Coal Bottom Ash-Cement Mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 153, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamanna, K.; Raman, S.N.; Jamil, M.; Hamid, R. Coal Bottom Ash as Supplementary Material for Sustainable Construction: A Comprehensive Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 389, 131679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.L.; John, V.M.; Gartner, E.M. Eco-Efficient Cements: Potential Economically Viable Solutions for a Low-CO2 Cement-Based Materials Industry. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 114, 2–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, R.; Aggarwal, P.; Aggarwal, Y. Influence of Water/Powder Ratio on Strength Properties of Self-Compacting Concrete Containing Coal Fly Ash and Bottom Ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafieizonooz, M.; Salim, M.R.; Hussin, M.W.; Mirza, J.; Yunus, S.M.; Khankhaje, E. Workability, Compressive Strength and Leachability of Coal Ash Concrete. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2017, 56, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, E. Novel Coal Bottom Ash Waste Composites for Sustainable Construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Wang, L.; Mo, L. Effects of Ground Coal Bottom Ash on the Properties of Cement-Based Materials under Various Curing Temperatures. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 69, 106196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K. Utilization of Sieved and Ground Coal Bottom Ash Powders as a Coarse Binder in High-Strength Mortar to Improve Workability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 91, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez, E.; Argiz, C.; Sanjuán, M.Á. Reactivity of Ground Coal Bottom Ash to Be Used in Portland Cement. J 2021, 4, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brás, A.; Faustino, P. Repair Mortars and New Concretes with Coal Bottom and Biomass Ashes Using Rheological Optimisation. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2016, 10, 203–216. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.P.; Kumar, A.; Kaushal, D.R. Experimental Investigation on Effects of Solid Concentration, Chemical Additives, and Shear Rate on the Rheological Properties of Bottom Ash (BA) Slurry. Int. J. Coal Prep. Util. 2022, 42, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beddu, S.; Abd Manan, T.S.B.; Mohamed Nazri, F.; Kamal, N.L.M.; Mohamad, D.; Itam, Z.; Ahmad, M. Sustainable Energy Recovery From the Malaysian Coal Bottom Ash and the Effects of Fineness in Improving Concrete Properties. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 940883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankura, N.; Singh, N.; Ankur, N. An Investigation on Optimizing the Carbonation Resistance of Coal Bottom Ash Concrete with Its Carbon Footprints and Eco-Costs. Res. Eng. Struct. Mat. 2024, 10, 135–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Seo, J.; Yang, K.H.; Kim, H.K. Cost and CO2 Emission of Concrete Incorporating Pretreated Coal Bottom Ash as Fine Aggregate: A Case Study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 408, 133706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABNT NBR 17054; Aggregates—Determination of Granulometric Composition—Test Method. Brazilian Association for Technical Standards: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2022.
- ABNT NBR 13276; Mortars Applied on Walls and Ceilings—Determination of the Consistence Index. Brazilian Association of Technical Standards: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2016.
- ASTM C1897-20; Standard Test Methods for Measuring the Reactivity of Supplementary Cementitious Materials by Isothermal Calorimetry and Bound Water Measurements. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Yoon, J.; Yonis, A.; Park, S.; Rajabipour, F.; Pyo, S. Prediction of the R3 Test-Based Reactivity of Supplementary Cementitious Materials: A Machine Learning Approach Utilizing Physical and Chemical Properties. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2024, 18, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Y.; Oh, S.; Lu, C.; Han, Y.; Lin, R.S.; Wang, X.Y. The Influence of Quartz Powder on the Mechanical–Thermal–Chemical–Durability Properties of Cement-Based Materials. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongsat, P.; Sinthupinyo, S.; O’rear, E.A.; Pongprayoon, T. Effect of Morphologically Controlled Hematite Nanoparticles on the Properties of Fly Ash Blended Cement. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, T.H.; Muralidharan, S.; Bae, J.H.; Ha, Y.C.; Lee, H.G.; Park, K.W.; Kim, D.K. Effect of Unburnt Carbon on the Corrosion Performance of Fly Ash Cement Mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2005, 19, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; ShriRam. Microstructural and Other Properties of Copper Slag–Coal Bottom Ash Incorporated Concrete Using Fly Ash as Cement Replacement. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2023, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.W.; Chen, T.A.; Huang, R. Effect of Finely Ground Coal Bottom Ash as Replacement for Portland Cement on the Properties of Ordinary Concrete. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 13212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, G.A.; de Matos, P.R.; Pelisser, F.; Gleize, P.J.P. Effect of Porcelain Tile Polishing Residue on Eco-Efficient Geopolymer: Rheological Performance of Pastes and Mortars. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 32, 101699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, M.; Garg, H.C. Effect of Addition of Bottom Ash on the Rheological Properties of Fly Ash Slurry at Varying Temperature. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 149, 012044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, D.; Wang, H.; Chen, G. Rheological Properties of Cement Paste Containing Ground Fly Ash Based on Particle Morphology Analysis. Crystals 2022, 12, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangi, S.A.; Ibrahim, M.H.W.; Jamaluddin, N.; Arshad, M.F.; Memon, F.A.; Jaya, R.P.; Shahidan, S. A Review on Potential Use of Coal Bottom Ash as a Supplementary Cementing Material in Sustainable Concrete Construction. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 2018, 10, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).