Abstract
The deposition and dispersion of particulate matter from diesel combustion in confined spaces pose significant challenges to air quality and public health, with important implications for sustainable development goals. While previous studies have focused on particle behavior inside diesel engines, the external environmental effects remain poorly understood. This study systematically investigated the mass concentrations and deposition characteristics of PM1, PM2.5, and PM10 particles in a 1 m3 environmental chamber under both sealed and ventilated conditions. The experimental results demonstrated that natural deposition ratios reached 50–75% after 8 h across all particle sizes. A comparative evaluation of ventilation strategies showed lateral ventilation achieved superior particle reduction ratios of 36%, outperforming direct ventilation at 14–22% and non-ventilated conditions at 23%. The study revealed that ventilation-induced convective removal was more effective than gravitational settling alone, providing important technical insights for air quality management in enclosed environments. These findings offer valuable scientific guidance for optimizing ventilation systems while contributing to the development of sustainable solutions for particulate pollution control. The research advances our understanding of particle behavior in confined spaces and supports technological innovations for cleaner air in urban infrastructure.
1. Introduction
The particles formed during diesel fuel combustion are discharged in the form of solid particle clumps together with other gases [1], containing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, alkanes, and their derivatives [2,3]. These particles range in size from 0.01 to 300 μm [4] and pose severe health risks, including cardiovascular disease, respiratory disease, and mental illness [5,6,7], with significant mortality implications [8]. In addition to the adverse effects on health, they degrade atmospheric visibility [9] and inhibit the photosynthesis of plants [10], and gases such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides produced by diesel combustion also damage the ecological environment [11].
Given the significant negative effects of diesel combustion particles on human health and the environment, it is essential that we further study their diffusion characteristics in air to develop methods to mitigate their impact. Research on the diffusion and transport of particles is usually carried out through field tests and simulations to determine the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of particle concentration.
Most current field studies are conducted to sample particles in specific areas, and the distribution of particles is related to the wind direction [12], wind speed [13], altitude [14], population density [15], vegetation density [16], and other factors. However, the research on regional particles covers a wide range, making it difficult to completely determine and quantify pollution sources. The particle composition from diesel combustion can be basically determined, making the study of particle diffusion from a single combustion source more valuable. Zuo et al. [17] measured a particle size of 0.18–0.32 μm at the engine exhaust port and 0.32–0.56 μm at the engine laboratory chimney vent, yet failed to fully characterize the diffusion process.
Confined-space studies provide a higher precision. Huang et al. [18] identified six sources of particles in subway stations, while Carteni et al. [19] observed concentration spikes from train-induced particle resuspension. Park et al. [20] concluded that the particles in subway stations were caused by train-induced wind. Licbinsky et al. [21] linked cave particle concentrations to ventilation. These studies confirm that the diffusion of particles in a limited space correlates with size, sedimentation, and wind direction. However, there are few reports on the diffusion and settlement of diesel combustion particles in a confined space.
Field tests require extensive experimentation, and it is challenging to determine particle diffusion laws. Therefore, the diffusion laws are often carried out by simulation. The current simulation studies on atmospheric particle have found that the concentration of atmospheric particles was related to height [22], temperature [23], ventilation volume [24], wind speed [25], and humidity [26]. The experiments and simulation studies on the diffusion and transport of particles in the atmosphere are all based on specific environments. Environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, wind field, terrain, and height have significant effects on the diffusion and transport of particles. On one hand, there are many sources of particle pollution in the atmospheric environment, making it difficult to trace their sources accurately. On the other hand, the comprehensive testing of the entire diffusion process has not been conducted, which is also difficult to carry out.
Several simulations on the diffusion of particles within a confined space have been carried out. Izadi et al. [27] demonstrated particle accumulation at train rears during subway piston-effect winds. Goldasteh et al. [28] proved the floor-type-dependent dust resuspension. Romain et al. [29] linked the vehicle rear inclination to particle distribution uniformity. However, these simulations involve only one correlation factor, making it impossible to judge the mutual influence of multiple factors.
In terms of diesel engine particle emissions, more emphasis is placed on measuring the concentration and number density of particles inside the engine exhaust pipe and removing them using the diesel particulate filter (DPF). However, there are few reports on tracking the diffusion and deposition of particles discharged from diesel engine exhaust entering a confined space. In fact, there are two questions that are not well-understood. First, what is the deposition ratio of particles by diesel fuel combustion in the air at different times? Second, what is the contribution of ventilation conditions to the deposition of these particles? Introducing diesel exhaust particles into a larger confined space for research would add complexity and high testing costs. Therefore, in this study, a small environmental chamber was used as the diffusion space for particles by diesel fuel combustion and an alcohol lamp fueled with diesel serving as a combustion source instead of a diesel engine to generate particles. Nine particle sensors installed at different positions in the environmental chamber were used for the long-term monitoring of the particle concentration. The spatiotemporal distributions of the particle concentration were simulated under closed conditions and different ventilation conditions. One innovation of this paper lies in studying the diffusion and settling behavior of particles by diesel fuel combustion directly released in a confined space through experimental and simulation methods. Additionally, the contribution of deposition and ventilation to the particle removal ratio was quantitatively described. The relationship between different ventilation inlet velocities, ventilation opening positions, air exchange rates, and particle reduction rates was obtained. This provides deep insight into the concentration distribution characteristics of particles emitted by diesel fuel combustion in a confined space during the diffusion process under enclosure and ventilation.
2. Experimental Devices and Methods
Fuel combustion and emissions studies were typically conducted under atmospheric conditions [30,31,32]. Although the morphology, size, and concentration of the particles generated under atmospheric conditions differ from those produced under high-pressure and high-temperature combustion conditions of diesel engines [33,34], this difference does not affect the fundamental research findings. In this study, an alcohol lamp burning diesel was used as a combustion source to generate particles.
The experiment was conducted in an environmental chamber with dimensions of 1 m in length, width, and height. The environmental chamber’s airtightness was checked prior to testing. A circular platform was installed on one side wall of the environmental chamber to hold the alcohol lamp. Nine laser particle sensors numbered 1# to 9# were arranged in three layers, with 3#, 4#, and 8# belonging to the upper layer, 5#, 6#, 7#, and 9# in the middle layer, and 1# and 2# in the lower layer. Sensors 1# to 7# monitored wall-adjacent particulate mass concentrations at different heights, while 8# and 9# tracked concentrations directly above the combustion source and at the center of the chamber, respectively. All measurements were performed using D5 particle detectors with a range of 0–5000 μg/m3, ±10% accuracy, and 1 Hz sampling frequency. These sensors were newly purchased and calibrated by the manufacturer. Figure 1 shows the experimental devices.
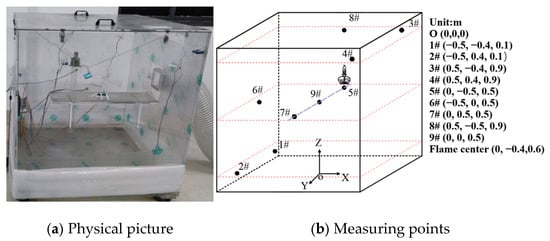
Figure 1.
Experimental devices.
Prior to experiments, the wick of the alcohol lamp was soaked in 0# diesel for 10 min and trimmed to 1 cm extension. The commercially available 0# diesel fuel was used in this study, with a cetane number of 51, a lower heating value of 43.5 MJ/kg, a density of 845 kg/m3 at 20 °C, and a dynamic viscosity of 3.5 mm2/s at 40 °C. The air in the chamber was also purified using an air cleaner to minimize measurement errors. The alcohol lamp’s burning time was set to 1 min. The 0# diesel fuel consumed in 1 min was 1.49 g, weighed by an electronic scale with a resolution of 0.01 g. Particle monitoring continued for 8 h.
According to references [35,36], the deposition ratio () of different particle size levels at each sampling point is defined as follows:
where is the maximum mass concentration of particles with a diameter size level of i and is the mass concentration of particles at time t.
3. Setup of Particle Diffusion Model
In order to characterize the spatial distribution of combustion particles in detail, the diffusion of diesel combustion particles in the environmental chamber was simulated. Due to the effective reduction in particle concentration by ventilation, the distributions of the particle concentration under ventilation conditions including the ventilation inlet velocities and ventilation vent positions were also simulated. Table 1 shows the particle diffusion simulation schemes. All inlet and outlet vents were square with a side length of 20 cm. For cases 2–4 under directly facing ventilation, the inlet and outlet were located at the center of the left and right chamber walls, respectively. For case 5 under side ventilation, the centers of the inlet and outlet of case 3 were offset upward and downward by 40 cm, respectively. Case 6 was obtained by swapping the inlet and outlet of case 5.

Table 1.
Particle diffusion simulation schemes.
Since the Discrete Random Walk Model was employed, it was not suitable to use the data from a single monitoring point for grid independence verification. Therefore, the final total mass of particulate matter suspended in the environmental chamber was selected as the verification parameter for grid independence testing.
Figure 2 shows the remaining particulate mass under different grid numbers. It is found that the particulate mass gradually decreases with increasing grid number. When the grid number exceeds 1,001,600, the particulate mass remains almost unchanged. Therefore, a grid number of 1,016,000 was ultimately selected.
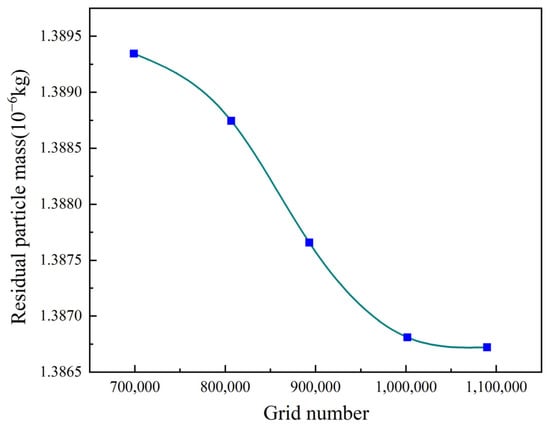
Figure 2.
Grid independence verification.
The bottom center of the cube model was taken as the origin to establish a coordinate axis. The particle injection source was set to replace the fuel combustion release source at the coordinate (0, −0.4, 0.6). Taking the directly facing ventilation as an example, the numbers cells and nodes in the mesh are 1,001,600 and 1,032,065, respectively. The mesh was created using a multi-zone method with the hexahedral grid type. The grid information under the ventilation schemes is completely identical. The number of mesh cells and nodes under closed conditions is slightly less than that under ventilation schemes. Figure 3 shows the grid diagrams of the chamber under the directly facing ventilation.
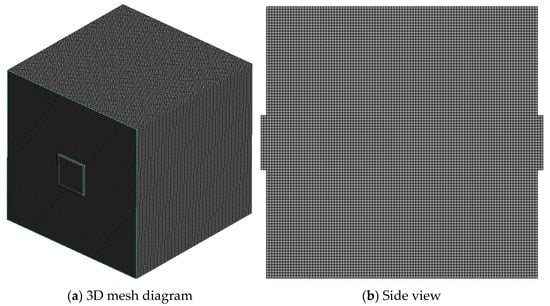
Figure 3.
Grid schematic diagram of the chamber.
In this paper, the particle diffusion was simulated using Fluent 2021R1 software. The effect of gravity was considered by applying an acceleration of −9.8 m/s2 in the Z-direction. The standard k-epsilon turbulence model was selected to simulate the viscous flow [37,38]. In the Discrete Phase Model (DPM), continuous phase interaction was enabled to update the DPM source at each iteration. Table 2 shows the properties of the particle injection point. The non-fixed-length particle tracking was selected to process the particles with a time step size of the particles of 0.001 s, a maximum of 2000 tracking steps, and a length size of 0.0001 m. Considering that the particulate plume produced by fuel combustion was not a single straight line, cone injection was selected as the injection source type. The spraying time of particles was set to 30 s. The inert ash-solid particles were selected as a substitute for diesel combustion particles with the size distribution following the Rosin–Rammler model. In the physical model, the Saffman lift force, virtual mass force, and pressure gradient force were considered.

Table 2.
Spray point property settings.
In boundary conditions, the discrete phase boundary type was set as ‘trap’ for the bottom wall and ‘reflect’ for other walls. As a comparison, the impact of the ventilation on the particle reduction rate was only considered when the discrete phase boundary type was set as ‘reflect’ for all walls. Under ventilated conditions, the inlet type and outlet boundary types were set as ‘velocity inlet’ and ‘outlet-vent’. For the outlet, the discrete phase boundary condition was ‘escape’. A function was used to control the ventilation start time (30 s) once the particle spraying was complete. The particle diffusion time was 30 s and the total calculation time was 60 s.
In this simulation, we obtain the mass of the particles () after the spraying is completed, and the remaining particles () is obtained after deposition, ventilation, and diffusion. Therefore, the particle reduction ratio () is written as follows:
The total mass of particles can be expressed as follows:
where is the mass flow rate and is the injection time of particles.
During ventilation, the fresh air flow () is given by the following:
where is the inlet air velocity and is the area of the inlet.
The air exchange rate () can be calculated by the following:
where represents the volume of the environmental chamber.
The fresh air volume () during ventilation is written as follows:
where is the ventilation time.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Measured Particle Concentration
Figure 4 shows the temporal variation of particle mass concentrations at nine monitoring points. During the initial stage of the diffusion (0–600 s), all measured points show concentration increases with fluctuations due to the turbulent smoke ascent. Points 3#, 4#, and 7# exhibit smaller fluctuations as they rise slowly along the chamber walls.
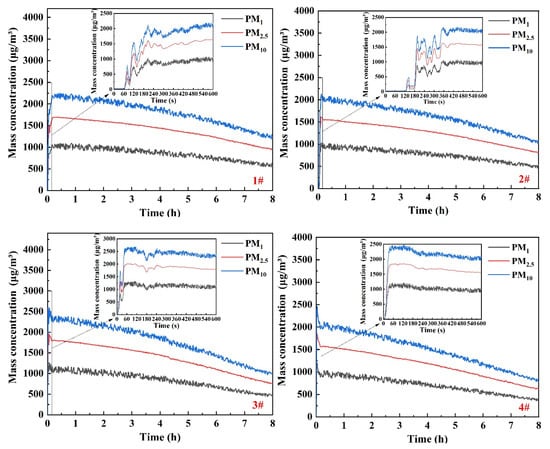
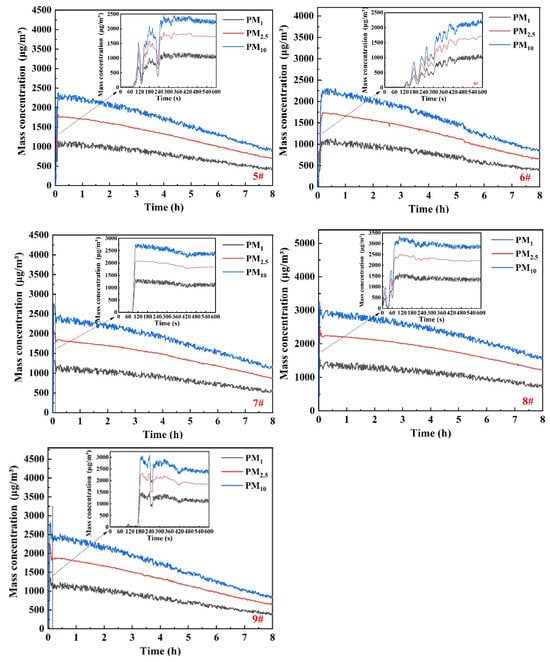
Figure 4.
Concentration curves of particles at measuring points.
The time at which the particle mass concentrations for all measuring points rise to the peak are related to the distance from the combustion source. Points 3#, 4#, and 8# nearest to the source increase rapidly, peaking within about 60–90 s. All measuring points reach the peak concentrations within 420 s, maintaining stable levels for approximately 1 h thereafter.
The peak concentrations of PM1, PM2.5, and PM10 at several points near the wall are proportional to their height. For upper points 3# and 4# at the same height, the concentration peaks of PM1, PM2.5, and PM10 are approximately 1250, 2000, and 2500 μg/m3. The peak concentrations of PM1, PM2.5, and PM10 at middle points 5# and 6# at the same height are approximately 1000, 1600, and 2200 μg/m3. Compared with the four aforementioned points, the peak concentrations of PM1, PM2.5, and PM10 at the bottom points 1 and 2# decrease to 800, 1500, and 2000 μg/m3 due to wall adhesion loss and deposition. Additionally, the peak mass concentrations of PM10, PM2.5, and PM1 at point 8# located above the combustion source are 3338, 2492, and 1635 μg/m3, respectively.
Due to the effect of gravity, the particles gradually settle after about 1 h, resulting in a gradual decrease in concentration. Correspondingly, the concentrations of PM1, PM2.5, and PM10 decrease by approximately 540–830, 710–1170, and 1020–1640 μg/m3, respectively. The concentration of larger particles decreases more, which is consistent with the results in reference [39].
After 8 h, the deposition ratios of PM1, PM2.5, and PM10 at upper points 3# and 4# are about 65% and those at middle points 5#, 6#, and 7# are about 60%. However, the deposition ratios of PM1, PM2.5, and PM10 at the bottom points 1# and 2# decrease to 50%. Additionally, the deposition ratios of PM1, PM2.5, and PM10 at points 8# and 9# are approximately 55% and 75%, respectively. The results indicate that the deposition ratios of particulate matter basically decrease from top to bottom. This is mainly due to the deposition caused by gravity. When the concentration of particles in the top area decreases, the concentration of particles in the bottom area increases, resulting in a decrease in the deposition ratio of particles in the bottom area.
However, the central area (9#) exhibits an exceptionally high deposition ratio due to the influence of the localized airflow, which accelerates particle deposition in this zone. The particle concentration at measuring point 8# above the combustion source has a maximum value. When the particle concentration in the same layer decreases, the deposition ratio at measuring point 8# is lower.
The PM concentrations in diesel exhaust exceed those observed in our study by a considerable margin [40,41], whereas post-emission measurements in expansive areas demonstrate markedly reduced levels [42]. Diesel engines operate under high-pressure, high-temperature environments with complex fuel–air mixing processes, leading to a more heterogeneous combustion and a broader particle size distribution compared to the alcohol lamp’s steady, low-pressure flame. This may lead to differences in deposition behavior. Diesel engines exhibit a significantly higher exhaust flow velocity compared to the combustion source used in this study, greatly affecting the temporal and spatial distribution of particles in confined spaces. Despite these differences, this study provides foundational insights into particle diffusion and deposition mechanisms.
4.2. Simulated Particle Concentration Distributions in the Closed Environment Chamber
Considering that the combustion source is located at the coordinates of X = −0.4 m and Z = 0.6 m, the contours of the particle concentration distribution on the sections at X = −0.4, 0, and 0.4 m and Z = 0.3, 0.6, and 0.9 m, were selected for analysis. In addition to the particle concentration distribution cloud maps of the six cross-sections, the particle distribution maps along the XYZ coordinate axes are also presented, as shown in Figure 5. It is found that the simulated particle concentrations align with the measured values in terms of magnitude, confirming the reliability of the simulation model.
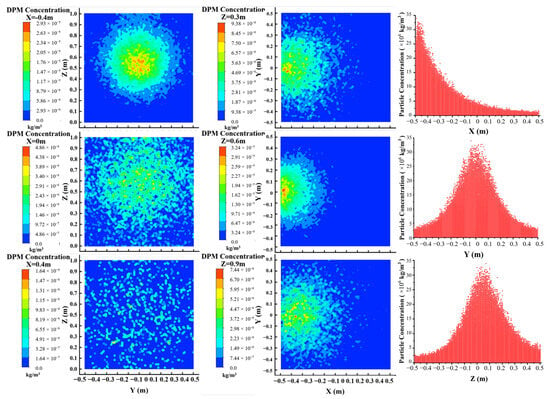
Figure 5.
Particle concentration distributions (left column: X section; middle column: Z sections; and right column: scatterplot along the XYZ axis).
It is easily seen that the concentration of the particles at and near the combustion source is higher and more concentrated compared to other areas. The particle mass concentration at the X = −0.4 m section is higher with the peak value of 2.931 × 10−5 kg/m3 and more concentrated than at the X = 0 m and 0.4 m sections. This is because the particles diffused from the jet source cannot be evenly distributed throughout the space within a short time. Similarly, the particle mass concentration at the Z = 0.6 m section is higher and more concentrated than those at the Z = 0.3 m and 0.9 m sections.
It is also found that the concentrations of the particles along the Y-axis and Z-axis direction are generally normally distributed. However, the concentration of the particles along the X-axis direction shows basically half of a normal distribution. As can be seen from the scatterplot of the X-coordinate, the particle concentration at X = −0.45 m is higher than that at X = 0.4 m. The reason is that the particles rebound after colliding with the wall, causing an increase in concentration near the X = −0.45 section.
4.3. Influence of Ventilation on the Particle Concentrations
Considering that the facing ventilation inlet is located at Z = 0.5 m, the particle mass concentration distribution and velocity contour at the Z = 0.1, 0.5, and 0.9 m sections for case 1 and case 3 are compared, as shown in Figure 6. It is evident that the particle concentration at the Z = 0.5 m section for case 3 is lower and more dispersed than that for case 1. This is because some particles at the Z = 0.5 m section are directly carried away within the range of the ventilation inlet area. However, the particle concentrations at the Z = 0.1 m and 0.9 m sections for case 3 is higher than that for case 1. It is seen from the figure that airflow recirculation occurs both above and below the chamber during ventilation, moving towards the inlet direction. This recirculation pattern reduces both particle removal through the outlet and the deposition ratio of particles.
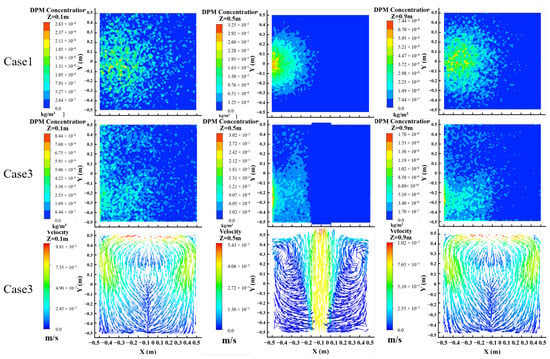
Figure 6.
Comparison of particle concentration distributions and velocity fields between closeness and ventilation.
Figure 7 shows the scatterplots of the particle mass concentration at different ventilation inlet velocities and vent positions. The plots illustrate the variation range of the particle mass concentration with changes in X (Y and Z). A larger range at the same vertical coordinate generally indicates a higher concentration level. It is found that the particle mass concentrations for all cases are still closely related to the distance from the combustion source. When the inlet velocities increase during directly facing ventilation, the concentrations of the particles near the combustion source increase and become more concentrated, while the concentrations of the particles in other areas decrease. This finding suggests potential limitations with direct ventilation along the Y-axis towards the opening. Compared to the directly facing ventilation for all inlet velocities, side ventilation at the medium inlet velocity of 0.4 m/s effectively reduces the concentration of the particles throughout the chamber. The subsequent analysis will focus on the impact of the two ventilation methods on the particle concentration based on the velocity field.
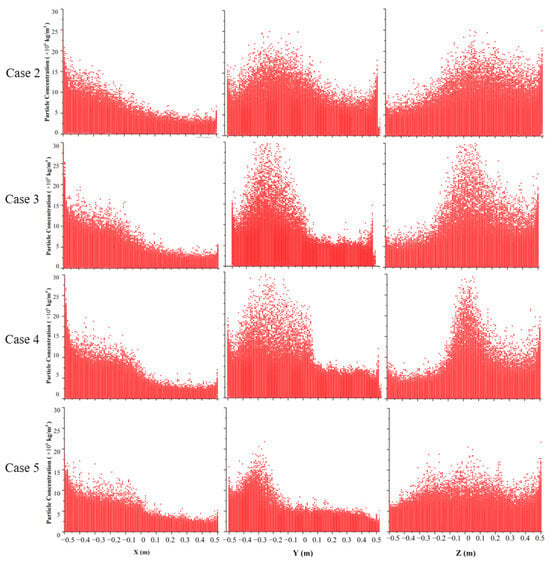
Figure 7.
Scatterplots of particle mass concentrations at different ventilation inlet velocities and vent positions.
Figure 8 compares the velocity fields and the relationship between flow velocity and particle concentrations at an inlet velocity of 0.4 m/s for directly facing ventilation and side ventilation. Under directly facing ventilation, two vortices form along the upper and lower sides of the ventilation airflow position, hindering the outflow of some particles from the outlet. In contrast, the main airflow under side ventilation follows the bottom direction and then moves upward along the right wall. Additionally, a top-down airflow is generated within the chamber and flows out together with the main airflow, facilitating the effective removal of the particles. The scatterplot of the particle concentration versus velocity reveals that the low velocity observed during directly facing ventilation corresponds to higher particle concentrations than those observed during side ventilation.
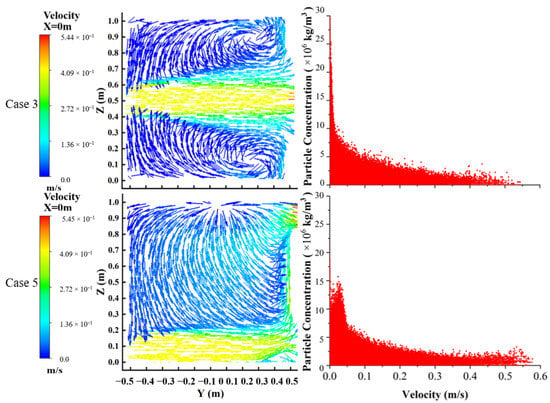
Figure 8.
Velocity field and concentration–velocity scatterplot for case 3 and case 5.
4.4. Comparison of Ventilation Effect
Table 3 presents the statistical results for particles under ventilated and non-ventilated conditions. In case 1 (closed conditions), no fresh air enters the enclosure, resulting in zero fresh air volume. However, a particle reduction rate of 23% occurs due to the effect of gravitational settling. Under the directly facing ventilation, increasing the inlet velocities leads to a linear increase in the ventilation airflow, air exchange rate, and particle reduction rate. Nevertheless, the particle reduction ratios of 14%, 18%, and 22% for case 2 to case 4 remain below the 23% reduction achieved without ventilation. Although directly facing ventilation can remove some particles, it also significantly hinders the settling of the particles due to the movement of airflow. It is found that side ventilation for case 5 achieves a higher particle reduction ratio of 36% compared to directly facing ventilation for three cases. The main reason is that reasonable airflow in case 5 carries away more particles out though the outlet. It can be seen that the particle removal ratio in case 6 is lower than in case 5, as the top-down ventilation method causes more particles to be suspended in the air.

Table 3.
Statistical results of the particles for six cases.
In order to quantify these versus deposition contributions, the reduction ratios of the particles caused by the ventilation are presented. The particle reduction ratios caused by the ventilation for case 1 to case 6 are 0, 11%, 14%, 18%, 33%, and 27%, respectively. Conversely, the reduction ratios of the particles caused by deposition for case 1 to 6 are 23%, 4%, 4%, 4%, 3%, and 3%, respectively. Obviously, the airflow movement prevents the particle deposition. Additionally, the air exchange rate has a minor impact on the particle deposition ratio, which is consistent with the results in reference [43]. Overall, the proportion of the particle reduction caused by deposition is lower during ventilation, while the proportion of the particle reduction by ventilation is higher. The results also indicate that both inlet velocities and ventilation positions significantly affect the particle removal efficiency in the chamber.
4.5. Limitations and Future Research
The mass concentrations of diesel fuel combustion particles emitted from the alcohol lamp were measured at nine monitoring points within a small environmental chamber due to experimental limitations. While the confined space sizes and sources of particles differ from real-world conditions, the environmental characteristics in this study maintain relevant similarities with practical scenarios [44,45].
It is necessary that we study the diffusion and deposition characteristics of diesel combustion particulate matter under more realistic conditions in the future. The volume of the confined space needs to be enlarged significantly and more particle sensors should be arranged in the corresponding positions. It is best to use wireless particle sensors to reduce interference with measurements. Moreover, a real diesel engine should be used to replace the alcohol lamp in generating particles and the exhaust pipe of the engine will be connected to the confined space in future studies. The exhaust amount of the engine into the space should be quantitatively controlled to match the volume of the space. More factors should also be considered, such as engine fuels and operating conditions, airflow, and temperature and ventilation.
In the calculation, only the rebound or capture of particles was considered due to the wall effects. The actual effect of the wall on particles should be considered through defined functions in future work. The current particle diffusion model will be improved based on the measured concentration attenuation curve of the particles. The relationship between the deposition velocity of particulate matter and the particle size should also be studied in theoretical calculations.
5. Conclusions
In this study, the mass concentrations and deposition of particles emitted by diesel fuel combustion in a closed environmental chamber were experimentally studied. On this basis, the numerical simulation of the particle diffusion was conducted to clarify the relationship between the particle deposition and ventilation conditions for six cases. The main conclusions of the study are summarized as follows:
(1) The mass concentration of the particles remains nearly constant for approximately 1 h after reaching its peak, followed by a slow decline over the next 1 to 8 h. After 8 h, the deposition ratios of PM1, PM2.5, and PM10 at all monitoring points range from 50% to 75%.
(2) The measured particle concentrations at closure are consistent in magnitude with the simulated values, validating the accuracy of the model. The particle concentration at and near the combustion source is higher and more concentrated compared to other areas in the closed chamber. The concentrations of particles along the Y-axis and Z-axis generally follow a normal distribution.
(3) Under the directly facing ventilation with the inlet velocities of 0.2, 0.4, and 0.6 m/s, the particle reduction ratios of 14%, 18%, and 22% are still lower than the 23% reduction achieved without ventilation. In contrast, side ventilation achieves a higher particle reduction ratio of 36% compared to directly facing ventilation. Furthermore, bottom-to-top ventilation removes more particles than top-to-bottom ventilation. Ventilation contributes more to the removal of the particles than the gravitational settling. This is primarily because the airflow movement inhibits the settling of many particles.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.N.; data curation, Z.D.; methodology, P.N.; investigation, Z.D. and X.W.; software, Z.D.; supervision, X.W. and X.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.D.; writing—review and editing, P.N. and X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Thangavel, P.; Park, D.; Lee, Y.C. Recent insights into particulate matter (PM2.5)-mediated toxicity in humans: An overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Li, Z.L.; Yu, L.; Wang, X.L.; Lu, X.C. Review of the state-of-the-art of particulate matter emissions from modern gasoline fueled engines. Appl. Energy 2019, 238, 1269–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, N.; Vigil, F.M.; Donaldson, B. Fuel effects on PAH formation, toxicity and regulated pollutants: Detailed comparison of biodiesel blends with propanol, butanol and pentanol. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 849, 157839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovicheva, O.B.; Irimiea, C.; Carpentier, Y.; Ortega, I.K.; Kireeva, E.D.; Shonija, N.K.; Schwarz, J.; Vojtisek-Lom, M.; Focsa, C. Chemical composition of diesel/biodiesel particulate exhaust by FTIR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry: Impact of fuel and driving cycle. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 1717–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.C.; Liu, F.C.; Huang, K.Y.; Yang, Y.X.; Li, J.X.; Xiao, Q.Y.; Chen, J.C.; Liu, X.Q.; Cao, J.; Shen, C. Long-term exposure to fine particulate matter and cardiovascular disease in China. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyung, S.Y.; Jeong, S.H. Particulate-matter related respiratory diseases. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2020, 83, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braithwaite, I.; Zhang, S.; Kirkbride, J.B.; Osborn, D.P.J.; Hayes, J.F. Air pollution (particulate matter) exposure and associations with depression, anxiety, bipolar, psychosis and suicide risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 127, 126002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puett, R.C.; Hart, J.E.; Suh, H.; Mittleman, M.; Laden, F. Particulate matter exposures, mortality, and cardiovascular disease in the health professionals follow-up study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1130–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, S.D.; Lee, B.K.; Han, J.S. Fine particulate matter characteristics and its impact on visibility impairment at two urban sites in Korea: Seoul and Incheon. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Agrawal, M. World air particulate matter: Sources, distribution and health effects. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2017, 15, 283–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.N.; Shabbir, M.; Tahir, E.; Iftikhar, M.; Saif, H.; Murtaza, M.A.; Khokhar, M.F.; Rehan, M.; Aghbashlo, M. Emerging challenges of air pollution and particulate matter in China, India, and Pakistan and mitigating solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birmili, W.; Tomsche, L.; Sonntag, A.; Opelt, C.; Weinhold, K.; Nordmann, S.; Schmidt, W. Variability of aerosol particles in the urban atmosphere of Dresden (Germany): Effects of spatial scale and particle size. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.G.; Feng, X.Y.; Zeng, X.Q.; Ma, Y.X.; Shang, K.Z. A study on variations of concentrations of particulate matter with different sizes in Lanzhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2823–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Z.Z.; Liu, Y.B.; Zhao, T.L.; Zhou, Y.B.; Habtemicheal, B.A.; Shen, L.J.; Hu, J.; Ma, X.D.; Sun, X.Y. Long-term variations in aerosol optical properties, types, and radiative forcing in the Sichuan Basin, Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.Y.; Ren, X.D.; Xiong, K.N.; Li, L.Q.; Bi, X.C.; Wu, Q.L. Analysis of the driving factors of PM2.5 concentration in the air: A case study of the Yangtze River Delta, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Brimblecombe, P. Role of vegetation in deposition and dispersion of air pollution in urban parks. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 201, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Mei, D.Q.; Yuan, Y.N.; Zhu, Z.N.; Mei, C.W. A comparative study on the size distribution and carbon components of particulate matters from typical sources. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2020, 39, e13462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chen, P.X.; Hu, K.Y.; Qiu, Y.C.; Feng, W.W.; Ren, Z.P.; Wang, X.L.; Huang, T.; Wu, D.S. Characteristics and source identification of fine particles in the Nanchang subway, China. Build Environ. 2021, 199, 107925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carteni, A.; Cascetta, F.; Henke, I.; Molitierno, C. The role of particle resuspension within PM concentrations in underground subway systems. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 4075–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Woo, Y.H.; Park, J.C. Major factors affecting the aerosol particulate concentration in the underground stations. Indoor Built Environ. 2014, 23, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licbinsky, R.; Faimon, J.; Tanda, S.; Hegrova, J.; Goessler, W.; Uberhuberova, J. Changes in the elemental composition of particulate matter in a speleotherapeutic cave. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1142–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, M.J.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, J.S.; Buccolieri, R. Neighborhood-scale dispersion of traffic-related PM2.5: Simulations of nine typical residential cases from Nanjing. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 90, 104393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Wei, C.H.; Zhu, W.C.; Zhang, M. Temperature-and pressure-dependent gas diffusion in coal particles: Numerical model and experiments. Fuel 2020, 266, 117054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnat, S.E.; Coull, B.A.; Schwartz, J.; Gold, D.R.; Suh, H.H. Factors affecting the association between ambient concentrations and personal exposures to particles and gases. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Hong, B.; He, L.; Cheng, F.; Zhao, P.; Wei, C.L.; Liu, Y.H. Temporal and spatial simulation of atmospheric pollutant PM2.5 changes and risk assessment of population exposure to pollution using optimization algorithms of the back propagation-artificial neural network model and GIS. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 12171–12195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.X.; Ma, J.; Zhang, L.L.; Jia, Z.K.; Ma, L.Y. Microclimate simulation and model optimization of the effect of roadway green space on atmospheric particulate matter. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, T.; Mehrabian, M.A.; Ahmadi, G.; Abouali, O. Numerical analysis of the mirco-particles distribution inside an underground subway system due to train piston effect. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2021, 211, 104533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldasteh, I.; Ahmadi, G.; Ferro, A.R. Wind tunnel study and numerical simulation of dust particle resuspension from indoor surfaces in turbulent flows. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.; Murzyn, F.; Mehel, A.; Larrarte, F. Dispersion of ultrafine particles in the wake of car models: A wind tunnel study. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerod. 2020, 198, 104109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, G.P.; Shao, S. Experimental research on the flame temperature of n-butanol–diesel fuel blends in atmospheric conditions. J. Energy Eng. 2016, 142, 4015037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, I.S.; Khalid, A.; Jaat, N.; Nursal, R.S.; Koten, H.; Karagoz, Y. A study of ignition delay, combustion process and emissions in a high ambient temperature of diesel combustion. Fuel 2021, 297, 120706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, G.P.; Shi, T.C.; Huang, M.; Hu, P. Investigating the fractal dimension of flame fronts of the biodiesel-diesel blends combustion in atmospheric conditions and engine cylinders: An experimental study. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2024, 197, 108802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.Q.; Zhang, D.P.; Chen, B.; Xu, J.P.; Mei, D.Q.; Yuan, Y.Y. Study on microstructure and extinction characteristics of particulate matter in diesel engine fueled with different biodiesels. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 22458–72240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, P.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Xu, H.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Xia, Q. Diffusion and hygroscopicity of particles from diesel and biodiesel combustion in an environmental chamber. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 8271–8281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.W.; Chen, Z.X.; Shen, B.X.; Wang, J.; Yang, L. Numerical study on characteristics of particle deposition efficiency on different walls of 90° square bend. Powder Technol. 2020, 364, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.P.; Wang, X.; Zheng, J.X. Numerical study on particle deposition in rough channels with different structure parameters of rough elements. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 2895–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A.; Huckaby, E.D. Simulation of a swirling gas-particle flow using different k-epsilon models and particle-parcel relationships. Eng. Lett. 2010, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, W.L.; Xia, Y.S.; Dong, C.J.; Ren, C.X.; Zhang, W. The effect of particle size on aluminum dust dispersion based on numerical simulation. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2024, 89, 105290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, X.X.; Liu, S.; Franky, K.; Li, W.W.; Bi, W.F. The effects of warm air heater on the dispersion and deposition of particles in an enclosed environment. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 200620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, X.R.; Xie, L.; Chang, J.; Kang, Y.N.; Zhang, Z. Experimental studies on the particulate matter emission characteristics of a lateral swirl combustion system for direct injection diesel engines. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 330, 121756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljohani, S.; Aljohani, K.; Kandasamy, M.; Vellaiyan, S.; Nagappan, B. Enhancement of diesel engine performance and emission reduction using ZnS nanoparticles and water emulsions with electrostatic precipitator integration. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2025, 71, 106157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferree, P.L.; Polat, M.; Nøjgaard, J.K.; Jensen, K.A. Airborne particulate matter and diesel engine exhaust on infrastructure construction sites in the Copenhagen metropolitan area. Ann. Work. Expo. Health 2024, 68, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.R.; Li, F.; Cai, H.; Zhou, B.; Shi, S.S.; Liu, J.X. A numerical investigation on the mixing factor and particle deposition velocity for enclosed spaces under natural ventilation. Build. Simul. 2019, 12, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Y.; Lu, Q.C.; Peng, Z.R. Spatial distribution of fine particulate matter in underground passageways. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.B.; Namgung, H.G.; Jeong, W.; Park, D.; Eom, J.K. Transient variation of aerosol size distribution in an underground subway station. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).