Abstract
This longitudinal study applies decade-spanning socioeconomic indicators (2013–2022) from the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration. An integrated analytical framework was developed, merging the super-efficiency slack-based measurement (SBM) methodology with entropic weighting techniques to quantify tourism efficiency and economic development. Subsequent phases employed a multi-method analytical cascade: coupling coordination assessment modeling for system interaction analysis, standard deviation ellipses for spatial dispersion characterization, and Markovian transition matrices for temporal pattern identification. The investigation concludes with evolutionary trajectory projections using gray system forecasting GM(1,1) modeling. The analytical findings reveal the following patterns: (1) Within the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei metropolitan cluster, tourism efficiency demonstrates a consistent upward trajectory, manifesting spatial differentiation characteristics characterized by a dual-core structure centered on Tianjin and Baoding, with higher values observed in northwestern areas compared to southeastern regions. Concurrently, regional disparities exhibit progressive convergence over temporal progression. (2) The level of economic development in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei city cluster has been rising steadily, demonstrating a geospatial distribution of ‘central concentration with peripheral attenuation, with the north-east being better than the southwest’, and the gap between the regional differences has become broader over time. (3) The coupling between tourism efficiency and the level of economic development in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei city cluster has generally improved, with Beijing and Tianjin predominantly in a coordinated regime, and some cities in Hebei Province about to shift from dysfunctional to coordinated, and, spatially, the coupling and coordination in northern sectors demonstrate superior performance compared to southern counterparts nationally. (4) The coupling coordination degree of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei city cluster in the next eight years is predicted by the gray GM(1,1) prediction model and the overall continuation of the growth trend of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei city cluster over the past ten years, thus verifying the importance of the regional integrated policy frameworks in the system integration of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei metropolitan system.
1. Introduction
The strategic concept of ‘Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei regional integration’ was first proposed in the ‘Twelfth Five-Year Plan’, and then Comrade Xi Jinping emphasized the great significance of Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei regional synergistic development when he convened a symposium in Beijing, and the ‘Outline of the Plan for the Synergistic Development of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei’ explicitly put forward Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei transport integration requirements. After 5 years, the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei (BTH) city cluster rail ‘one-hour traffic circle’ is completed, realizing the interconnection between the three places, which can not only unite the advantages of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei triad but also drive the rapid development of neighboring cities and the Bohai Rim Economic Zone through the radiation effect of the agglomeration development of the three places to enhance the overall competitiveness and international competitiveness of the BTH city cluster and the cities of the northern part of the country [1]. Competitiveness and international competitiveness effectively promote the advancement of regional tourism ecosystems. Functioning as a catalytic mechanism for regional economic progression, tourism development induces cross-sectoral industrial symbiosis through value chain integration [2]. Parallel with China’s sustained economic expansion, the nation’s tourism sector, now positioned as a global top-three tourism economy, is transitioning into a premium service industry through operational framework enhancements and service delivery standardization. Tourism efficiency serves as a critical measure in evaluating regional tourism performance, demonstrating a strong correlation with local economic growth patterns [3]. However, the reciprocal enhancement and systemic alignment of these interdependent systems fundamentally shape environmentally conscious tourism growth within regional ecosystems.
Therefore, this study takes the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration as the research object, and based on the panel data of the last ten years, it aims to reveal the coupled and coordinated relationship between tourism efficiency, economic development level, and its evolution law. The focus is to explore (1) the characteristics of spatial and temporal differentiation of tourism efficiency and its influencing factors; (2) the multi-dimensional evolution trajectory of the economic development level; (3) the dynamic evolution path and spatial correlation characteristics of the coupling and coordination degree between the systems; and (4) the prediction of the development trend of the coordination in the future and the path of optimization. The research results can provide a decision-making basis for the high-quality coordinated development of tourism economy under the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei coordinated development strategy and empirical support for the construction of the theory of synergistic development of urban agglomeration systems.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Tourism Efficiency
Tourism efficiency is often used to judge the level of development of a region’s tourism industry, i.e., by analyzing the ratio of inputs to outputs of tourism activities to reflect the extent to which the input factors have been utilized over a certain time [4]. Regarding tourism efficiency research, foreign scholars have previously conducted studies mainly focusing on the micro-level; this research primarily related to major industries related to tourism, such as travel agencies [5], tourism transport [6], hotels [7], and so on. Domestic scholars started a little later, but they have also made fruitful achievements in the field of tourism efficiency, and their research objects involve tourism industry efficiency [8], tourism ecological efficiency [9,10], tourism poverty alleviation efficiency [11], and so on. The main methods of measurement are data envelopment analysis [12] and its related improvement models [13], the Super-SBM model [14], etc. In addition, some scholars have also studied their spatial characteristics using standard deviation ellipse [10] and center of gravity models [10], and analyzed the main driving factors affecting tourism efficiency using probe models [15]. The scale of this study encompasses the provincial [16], municipal [17], and county [18,19] levels. Revealing the spatial and temporal heterogeneity of tourism efficiency and its dynamic evolution mechanism and exploring the multi-dimensional influencing factors of tourism resource allocation efficiency can not only provide a scientific basis for optimizing the spatial layout of the tourism industry and the policy supply system but also inject innovative kinetic energy into the construction of a new pattern of coordinated development of regional tourism and the promotion of high-quality development of the tourism industry in the new era, ultimately realizing the benign interaction between the tourism industry and economic development.
2.2. Level of Economic Development
For the research related to the level of economic development, the quantitative analysis of its measurement is the main focus, and the research object focuses on the digital economy [20], ecological economy [21], green economy [22], rural economy [23], etc. Most of the research themes are based on the results of the measurement, analyzing the spatial effects, temporal and spatial changes, regional differences, and influencing factors. Individual scholars have explored the coordination, coupling, and synergy between the level of economic development and other factors, such as the level of economic growth and regional higher education [24], urban resilience [25], and the Belt and Road Initiative [26]. In addition, scholars have conducted studies on the correlation between tourism and the regional economic performance using statistical models [27]. This investigative approach establishes a conceptual framework for analyzing tourism productivity/economic progression interdependencies within the BTH metropolitan cluster, providing empirically grounded insights for regional development strategies. Through the above research, a certain theoretical and practical foundation has been laid for the coupling research of tourism efficiency and economic development level in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei city cluster.
2.3. Coordination of Tourism Efficiency and Level of Economic Development
Western scholars took the lead in researching the relationship between tourism and the economy. Bodio first paid attention to the fact that tourism development can promote economic growth and analyzed the impact and influence of tourism economic activities and tourism economic income on the national economy [28]. Modeste pointed out that the tourism industry has a significant role in driving the growth of the regional economy, and it can transform the advantages of the regional resources into economic power and drive the construction and improvement of infrastructure in the process of tourism development [29]. Pascal further studied the relationship between the two and the influencing factors and concluded that the tourism industry and regional economy are complementary and mutually reinforcing [30].
In exploring the coupled development relationship between tourism efficiency and economic development level, scholars mainly analyze the coupled spatiotemporal characteristics of the two systems and their influencing factors with the help of models and methods such as the data envelopment analysis method [31], entropy weight TOPSIS method [32], coupled coordination degree model [3], center of gravity model [33], and so on. In terms of the research scale, most of the empirical studies were selected at the provincial level based on the easy accessibility of data, such as the western provinces and regions [33], and the 31 provinces in the country [34]. With the accelerated process of urbanization and the increasingly close links between cities, urban tourism has become a significant pillar of the urban or regional economy. The study of the coupling and coordination between the efficiency of urban tourism and the level of economic development can help to enhance the level of new quality productivity of the town and promote the high-quality development of the city and even the whole region. As for the city cluster as a critical geographical unit, few scholars [35] focus on the current hotspot territory of city cluster research to study the coupled development of its tourism efficiency and economic development level. Especially for the rapidly developing and strategically important BTH city cluster, the research on the coupling development of tourism efficiency and economic development level needs to be strengthened.
In particular, although cities are often characterized by multifunctional development and tourism is only one of their economic components, in some countries, tourism has become a central driver of land development and economic growth. For example, Cyprus, with its Mediterranean location and cultural heritage resources, and its economy are highly dependent on the synergistic effect of tourism exchange and cultural heritage tourism [36]; Malta also takes tourism as its pillar industry and realizes the unitary development of its economic structure through the fusion of historical monuments and coastal resorts [37]. These cases show that under specific geographical conditions, tourism can break through the positioning of ‘complementary to multiple industries’ and become a single dominant force in regional economic development, and the coupling mechanism between its efficiency and economic level is more complex and typical. Therefore, future research needs to pay more attention to the coupling law of such special cases and strengthen the empirical exploration of emerging geographical units such as city clusters to improve the theoretical framework of the synergistic development of the tourism economy.
Building upon these foundations, taking the BTH city cluster as the study region, we examine spatiotemporal variations between the regions with the help of ArcGIS 10.8. software and a statistical model, to reveal the internal mechanism of the interaction between tourism efficiency and economic development level, and further use the gray GM(1,1) model to predict the future coupling between tourism efficiency and economic development level. The gray GM(1,1) model is further used to predict the future coupling of tourism efficiency and economic development level to provide scientific support for the BTH metropolitan cluster to advance synergistic high-quality development objectives of tourism and the economy.
3. Overview of the Study Area
The Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration (Figure 1), known as the ‘Capital Economic Circle’, occupies the core of the Bohai Rim in Northeast Asia. The geographical coordinates span from 113°04′ to 119°53′ east longitude and 36°01′ to 42°37′ north latitude, with a total area of about 218,000 square kilometers. As of 2022, the region’s Gross Regional Product (GRP) has exceeded the CNY ten trillion mark. Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei Provinces are geographically close and display strong economic, social, and cultural ties, forming a highly complementary and synergistic regional economic complex that plays a pivotal role in the Chinese and global economy. The BTH metropolitan cluster not only excels in the financial field but also has rich tourism resources. The three places are jointly committed to building a model region for all-region tourism and have put forward the slogan ‘Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Synergy, Tourism First’, aiming to promote the improvement of the economic benefits of tourism in the BTH urban agglomeration and the high-quality development of the region through the synergistic development of the tourism industry. This strategy helps to promote balanced regional economic growth and provides a new impetus for achieving high-quality, synergistic regional development.
Figure 1.
The Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration.
4. Data Sources and Research Methodology
This study establishes a systematic research framework through the construction of a dual-system evaluation index system encompassing tourism efficiency and the economic development level. As illustrated in the research workflow (Figure 2), the methodology follows a structured approach: The initial stage involves formulating a multi-dimensional indicator system grounded in established theoretical principles. Subsequent steps include employing the Super-SBM model to quantify efficiency and applying the entropy weight method for objective index weighting. A coupling coordination degree model is then constructed to evaluate synergistic relationships between systems, followed by Markov chain analysis to uncover dynamic evolutionary patterns. The final phase integrates the GM(1,1) model under gray system theory to predict future coupling coordination states. By combining static assessment, dynamic evolution analysis, and predictive modeling, this methodology ensures both theoretical robustness and empirical validity.

Figure 2.
The research flowchart.
4.1. Construction of the Indicator System
Based on the research results of existing scholars, a comprehensive assessment index system on tourism efficiency and economic development level was established in terms of data accuracy, scientificity, and accessibility in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region (Table 1). Among them, the tourism efficiency system includes two subsystems, tourism input and tourism output, and seven indicators, such as GDP per capita and disposable income per capita, are selected to measure the level of economic development, taking into account the three aspects of economic efficiency: income level, investment, and consumption. This study adopts SPSS statistical analysis software (https://www.spsspro.com/), combines the objective assignment characteristics of the entropy weight method, standardizes the indicator data through the principle of information entropy, and, finally, scientifically determines the weight value of each evaluation indicator. This quantitative analysis method effectively avoids subjective assignment bias and ensures that the results of weight assignment truly reflect the inherent informativeness differences in the indicator data.

Table 1.
Comprehensive evaluation index system of tourism efficiency and economic development level.
4.2. Source of Data
The data for this study were obtained from official statistics of Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei Provinces for the period from 2014 to 2023, specifically the Beijing Statistical Yearbook, Tianjin Statistical Yearbook, and Hebei Statistical Yearbook for each year, as well as the statistical yearbooks of the cities within Hebei Province. Some data were from the China Tourism Statistical Yearbook, 2014–2018, China Culture and Tourism Yearbook, 2019–2020, China Culture, Heritage and Tourism Statistical Yearbook, 2021–2022, China Fixed Asset Investment Statistical Yearbook, and China Investment Field Yearbook. In terms of data selection, given the availability and timeliness of the data, data from the last ten years were selected, and some of the missing data were calculated on the basis of linear regression interpolation and other calculations.
During the initial data preparation phase, standardization procedures were implemented to mitigate dimensional disparities among heterogeneous variables resulting from measurement unit variations, ensuring comparability of scale-free source information. As indicated in Equation (1), the standardization approach implemented in this study employs sum normalization, alternatively denoted as summation scaling or total proportion adjustment. This technique involves dividing individual values by their arithmetic aggregate to achieve dimensionless comparability across measurement units. To validate indicator system efficacy, an entropic weighting technique was systematically applied to determine index significance coefficients, with comprehensive computational outcomes detailed in Table 1.
4.3. Research Methodology
4.3.1. Super-Efficient SBM Model
In traditional data envelopment analysis models, assessing the relative efficiency of decision-making units relies mainly on radial and angular measures, which limits the analysis of input–output slack problems. To overcome this limitation, the super-efficient SBM (Slack-Based Measure) model has emerged, which not only inherits the advantages of the traditional DEA model and the SBM model but also takes into account the input or output slackness in particular. In addition, the model provides an in-depth study of decision-making units with efficiency values of 1 or more. Based on this, the super-efficient SBM model is applied to measure the tourism efficiency value of the BTH city cluster, and the specific formula is shown in [35].
4.3.2. Entropy Weighting (Physics)
The entropy weight method, also known as the entropy value method, is an analytical tool that measures the degree of dispersion of an indicator based on the principle of information entropy. This approach assumes that as the information entropy decreases, the dispersion of the indicator value increases and its influence (i.e., weight) on the overall judgment increases. As a result, the weight of each indicator is determined by the size of the entropy weight, which provides a scientific basis for the comprehensive judgment of multiple indicators. Its calculation formula is shown in Ref. [42].
4.3.3. Coupled Coordination Degree Model
The coupling degree is a classical indicator of the degree of interaction between two systems. The coupling degree is calculated by the formula [43]:
where represents the coupling degree between tourism efficiency and the level of economic development, with a value ranging from 0 to 1. The larger the value of the coupling degree , the stronger the correlation and interaction between tourism efficiency and economic development level. The coupling only reflects the degree of interaction between the two systems and does not provide a comprehensive picture of their coordinated development. To more effectively measure the coordinated development of tourism efficiency and the level of economic development, a comprehensive evaluation index is introduced, which combines tourism efficiency and the level of economic development, and then the coupled coordination degree model is constructed. The formula is as follows [44]:
In the formula, denotes the degree of coupled coordination between tourism efficiency and the level of economic development; is a comprehensive evaluation index that measures the coordinated development of the two systems. and represent the evaluation values of tourism efficiency index and economic development level, respectively, and and refer to the coordination weights of tourism efficiency and economic development level, respectively. The BTH urban agglomeration, as the core urban agglomeration in China, has tourism and economic development going hand in hand, so the parameter = = 0.5 is set. The value of is between 0 and 1. The larger is, the higher the coordination the two systems have; on the contrary, the smaller is, the lower the degree of coordination. Drawing on Han Dong’s study [45], the coupling coordination continuum was systematically categorized into ten distinct tiers using precise numerical thresholds: acute dysfunction [0, 0.1), [0.1, 0.2) severely dysfunctional, moderate discordance [0.2, 0.3), [0.3, 0.4) mildly dysfunctional, marginal functionality [0.4, 0.5), elementary coordination [0.5, 0.6), foundational synergy [0.6, 0.7), intermediate synchronization [0.7, 0.8), [0.8, 0.9) good coordination, and optimal alignment [0.9, 1.0]. Through critical threshold analysis, the coordination spectrum was further consolidated into three developmental phases: dysfunctional regime (<0.4), transitional phase (0.4–0.6), and coordinated state (≥0.6).
4.3.4. Markov Chain
A Markov chain is a stochastic process characterized by discrete time intervals and states, adhering to the Markov property where future states depend solely on the present state. By employing a transition probability matrix, this analytical tool effectively captures the dynamic mobility patterns of regional units, quantifying their probabilities of upward or downward transitions in developmental status. The exact formula is given in [46].
4.3.5. Gray GM(1,1) Model
The gray GM(1,1) model is a method based on gray system theory, which is based on the analysis of the existing information to predict the development trend of the research object. It is suitable for the situation of small data and insufficient information. The model first performs the level comparison test on the original data series, weakens the randomness of the original data through the cumulative operation, constructs a new data series, establishes a first-order differential equation based on the series, and solves the model parameters through the application of the least-squares method to obtain the approximate estimated value of the original data, ultimately realizing the prediction of the development trend. For detailed operations, see [47].
5. Analysis of Results
5.1. Characterization of Spatial and Temporal Variations in Tourism Efficiency
5.1.1. Characteristics of Time Series Changes in Tourism Efficiency
The tourism efficiency of the BTH city cluster is measured using the super-efficient SBM model, and the results are shown in Figure 3. In terms of time series, the 13 cities in the BTH urban agglomeration experienced a general decline in tourism efficiency between 2017 and 2020, a phenomenon that may be related to the global outbreak of the COVID-19 epidemic and the transformative impact of supply-side structural reforms on the tourism industry. Especially in Tianjin, its tourism efficiency value fluctuates a lot. The tourism efficiency value in 2013–2018 exceeds 1.20, which indicates that the development and utilization of Tianjin’s tourism resources during this period is more reasonable, and the input–output rate is higher. However, tourism efficiency in Tianjin declined sharply in 2020. Although it recovered briefly in 2021, it dropped again in 2022, finishing just above Langfang and Cangzhou, suggesting that Tianjin has been particularly hard hit by the new Crown Pneumonia epidemic and that it urgently needs to improve the efficiency of its tourism resource development to promote growth in tourism arrivals and revenues. City tourism efficiency in Hebei Province as a whole shows an upward trend, with Shijiazhuang, Baoding, Handan, Qinhuangdao, and Cangzhou cities developing more steadily. In contrast, the other towns show some fluctuations due to influencing factors at different times. Nonetheless, the uneven distribution of tourism resources across the cities of Hebei Province and the deficiencies in resource allocation and management have led to the polarization of resource distribution, which provides a broad scope for future improvement.
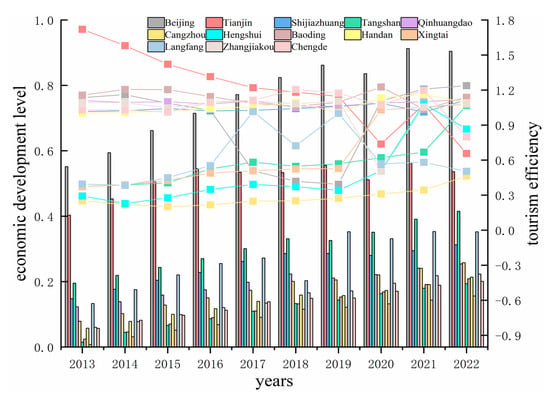
Figure 3.
Trends in tourism efficiency and comprehensive evaluation of economic development level.
In order to further analyze the regional differences in the BTH city cluster, the spatial coefficients of variation in tourism efficiency, economic development level, and coupling coordination were calculated from 2013 to 2022, and the results are shown in Table 2. Among them, the average value of tourism efficiency is generally stable between 0.81 and 0.97, indicating that the comprehensive tourism efficiency of the BTH city cluster is at a high level; the standard deviation continues to decrease from 0.45 in 2013 to 0.26 in 2022, and the coefficient of variation (CV) decreases from 0.54 to 0.27, indicating that the differences in tourism efficiency within the BTH city cluster have been narrowed, which suggests that regional synergy effects are apparent.

Table 2.
Coefficient of variation values for tourism efficiency, economic development level, and coupling coordination degree.
5.1.2. Characteristics of Spatial Differentiation in Tourism Efficiency
In terms of spatial distribution, the tourism efficiency of provinces and cities within the BTH city cluster shows apparent heterogeneity, forming an efficient region with Tianjin and Baoding at its core, and urban tourism efficiency is generally high in the northwestern region and relatively low in the southeastern region; however, overall, the tourism efficiency of the BTH city cluster is maintained at a high level. Specifically, the tourism efficiency of the BTH city cluster is divided into five echelons: the first echelon includes Tianjin and Baoding; the second echelon consists of Qinhuangdao, Chengde, Handan, Shijiazhuang, and Zhangjiakou; the third echelon consists of Beijing and Langfang; the fourth echelon consists of Xingtai, Tangshan, and Hengshui; and the fifth echelon consist of Cangzhou. The high number of cities at the medium level reflects that the tourism industry in the BTH city cluster is generally developing well, and the efficiency of resource conversion is high, but the development among cities is not balanced, mainly because of the different abundance of tourism resources in each region and the differences in the allocation of tourism factors, so the tourism efficiency of the BTH city cluster needs to be further coordinated and developed.
To deeply analyze the spatial pattern of tourism efficiency and its development dynamics in the BTH urban agglomeration, the tourism efficiency data in 2013, 2016, and 2022 were selected, and the standard deviation ellipse and center of gravity migration maps of tourism efficiency were plotted with the spatial statistical analysis tool of ArcGIS 10.8. Spatiotemporal analysis, as shown in Figure 4, reveals a distinct southward migration trajectory in the tourism efficiency centroid within the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration, transitioning from Langfang to Baoding during the 2013–2022 observational timeframe. The gradual expansion of the ellipse range and the shift in the center point coordinates to the southwest (from 116.28° E, 39.37° N in 2013 to 116.28° E, 39.32° N in 2016, and then to 116.26° E, 39.03° N in 2022) further reveal the changes in the spatial distribution of the tourism efficiency in the BTH urban agglomeration. The change in the angle of the ellipse decreases from 28.33° in 2013 to 28.29° in 2016. Then, it increases slightly to 30.16° in 2022, which indicates that the agglomeration of tourism efficiency in the direction of ‘north-east—south-west’ has increased.
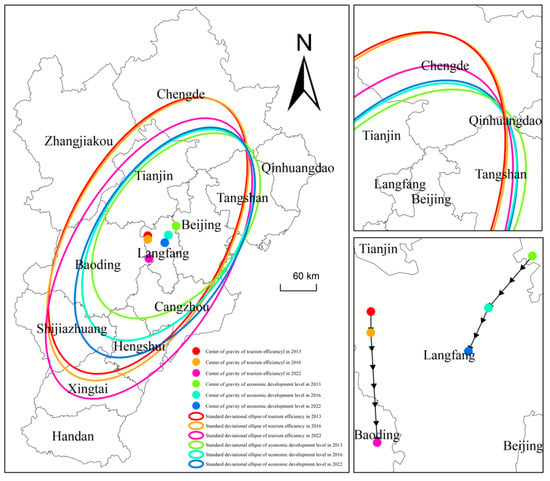
Figure 4.
The standard deviation ellipse and gravity shift in tourism efficiency and economic development level.
5.2. Characterization of Spatial and Temporal Variations in the Level of Economic Development
5.2.1. Characteristics of Temporal Changes in the Level of Economic Development
The entropy weight method was used to comprehensively evaluate and rank the economic development level of the BTH city cluster, and the results are detailed in Figure 3. The economic development level of the BTH city cluster from 2013 to 2022 shows a precise ladder distribution, with Beijing always in first place, followed by Tianjin, while the prefecture-level cities in Hebei Province are in second place, with an overall upward trend from year to year. Among them, the level of economic development of Beijing is significantly higher than that of other cities, increasing from 0.55 to 0.90 in ten years, reflecting the rapid growth of the city’s economy. Tianjin’s level of economic development continued to grow between 2013 and 2016. Still, the following years were more unstable, showing a ‘down-up-down’ mountain peak pattern, rising again in 2021 and falling in 2022, but the overall level has still increased. Meanwhile, the 11 municipal prefectures in Hebei Province have had relatively low levels of economic development over the past decade, with large gaps between them and Beijing and Tianjin. Still, they are also making progress, with Tangshan City growing from 0.20 in 2013 to 0.42 in 2022 and Langfang City growing from 0.13 in 2013 to 0.35 in 2022.
According to the data in Table 2, the mean value of the economic development level has continued to climb from 0.14 to 0.33, with an average annual growth rate of 10.7 per cent, demonstrating the rapid economic development of the BTH urban agglomeration. The standard deviation fluctuates between 0.16 and 0.21, indicating that absolute differences may increase and regional differences still exist, especially in the early period when the CV is high, and there may be a large gap. However, the CV coefficient decreases year by year, from 1.13 in 2013 to 0.63 in 2022, and the relative difference decreases, indicating that the economic development of the BTH urban agglomeration tends to be balanced in distribution and the integrated development strategy is playing a positive role.
5.2.2. Characteristics of Spatial Differentiation in Levels of Economic Development
From a spatial perspective, the economic development level of the BTH urban agglomeration shows evident regional disparities, with Beijing having the highest level, at 0.76, and Xingtai at the bottom with a low level, at 0.09. Overall, the high-level region has Beijing and Tianjin as its core, forming a spatial distribution pattern of ‘high in the center, low in the surrounding area, and better in the north-east than in the southwest’. Beijing, as the capital of China, has a well-documented level of economic development, while Tianjin also maintains a high level of economic development. However, there are significant differences in the level of economic development between cities in Hebei Province, which may be related to their geographical location. Langfang, Tangshan, and Cangzhou are close to Beijing and Tianjin, and are better developed due to economic radiation, while the other cities may be suffering from the ‘siphon effect’ that leads to the flow of resources and talents to Beijing and Tianjin, which may inhibit their economic development. The ‘siphon effect’ in other cities may lead to a flow of resources and talents to Beijing and Tianjin, thus inhibiting their economic development and making them much less developed than the core region.
In order to further analyze the spatial pattern and evolution of the economic development level of the BTH urban agglomeration, the comprehensive evaluation values of the economic development level in 2013, 2016, and 2022 were selected. Standard deviation ellipse and center of gravity migration maps of the economic development level were made with the help of the ArcGIS software (see Figure 4). Figure 4 shows that the standard deviation ellipse of the economic development level of the BTH city cluster from 2013 to 2022 exhibits the distribution characteristic of ‘Northeast-Southwest’, and the ellipse range has expanded. The deflection angle decreases from 39.20° in 2013 to 33.75° in 2016, and then further decreases to 32.08° in 2022, which indicates that there is a trend of clustering in the economic development level of the BTH city cluster. The mean centers of economic development levels are all located in Langfang City, with the coordinates of the center point moving from 116.85° E, 39.46° N in 2013 to 116.68° E, 39.34° N in 2016, and then migrating southwards to 116.60° E, 39.24° N in 2022, with an overall tendency to move along the southwest direction.
5.3. Characterization of Spatial and Temporal Variations in the Degree of Coordination of the Coupling Between Tourism Efficiency and the Level of Economic Development
5.3.1. Characteristics of Time Series Changes in the Coupled Coordination Degree of Tourism Efficiency and Level of Economic Development
Based on the combined score of tourism efficiency and economic development level obtained from the measurement, the interaction between tourism efficiency and economic development level in the BTH city cluster was quantitatively analyzed using the coupled coordination degree model. From the time evolution trend, the coupling coordination degree of the BTH metropolitan cluster is on an upward trend, showing that the tourism efficiency and the economic development level show a mutually reinforcing coordination effect at a high level.
As shown in Figure 5, the level of coupled and coordinated development between tourism efficiency and the level of economic development in Beijing has always remained high. It improved from a good coordination status in 2013 to a quality coordination status in 2017, and despite a decline in coupling coordination in 2020 due to the impact of the new Crown Pneumonia outbreak, it remained at a quality coordination status and rebounded in 2021, showing an overall favorable development. The level of coupled coordination between tourism efficiency and the level of economic development in Tianjin was in the middle of the range from 2013 to 2022. It was in a state of primary coordination in most of the years, and although there was a decline in 2020 and 2022, the overall trend of optimization of the level of coupled coordination was still shown. The coupling coordination level between tourism efficiency and economic development level is generally low in 11 cities in Hebei Province, and all cities are in a state of dislocation, which indicates that the development and utilization of tourism resources in each city does not effectively promote regional economic development, and there is a particular gap between the two, with tourism efficiency generally lagging behind the level of economic development. Overall, the coupled coordination of tourism efficiency and economic development level is improving in 11 cities in Hebei Province between 2013 and 2022, with Shijiazhuang performing better, Hengshui performing averagely, and Shijiazhuang and Tangshan about to step into the coordinated ranks, while the other prefectural-level cities still have a lot of room for improvement.
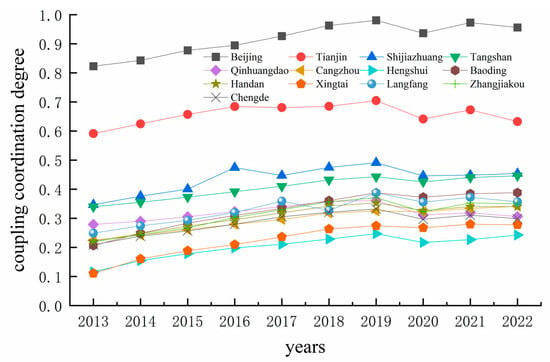
Figure 5.
The variation in coupling coordination degree between tourism efficiency and economic development level.
In addition, regional differences can be further analyzed by calculating the spatial coefficient of variation in the coupling coordination degree. As can be seen from Table 2, the mean value of the coupling coordination degree is in the range of 0.30–0.44, with an overall upward trend, although there is still a lot of room for increase. The standard deviation is stable at 0.19–0.20, and the CV coefficient decreases from 0.65 in 2013 to 0.46 in 2022, which indicates that the coupling synergistic development of tourism efficiency and economic development level of the BTH city cluster maintains a stable state as a whole, and the regional differences have not expanded significantly, in which the inter-regional differences are shrinking, which indicates that the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei regional synergistic policy is effective, but the optimization space still exists, and the relative difference in the level of economic development is still the main contradiction.
5.3.2. Characteristics of Spatial Divergence in the Coupled Coherence of Tourism Efficiency and Economic Development Levels
To accurately identify the years in which the coupled coordination degree of tourism efficiency and economic development level in the BTH city cluster changed significantly, this study conducted a mutation analysis of the coupled coordination degree of 13 cities using the Mann–Kendall mutation test. By setting the two parameters, UF and UB, and applying the method of sequence analysis, it is possible to reveal the dynamics of the sample sequence. In a sequence, a positive (or negative) UF value indicates a growing (or decreasing) movement in the sequence. If the curve UF is greater than the confidence limit, which usually corresponds to a 95 percent confidence level, it indicates that the change trend is statistically significant. If the intersection of the curves UF and UB is within this confidence limit, this is considered to be the starting point of the mutation. The results of the mutation test show that the UF and UB curves of the coupled coordination degree of the BTH urban agglomerations focus on the intersection point between 2013 and 2016. Specifically, the coupling coordination between Tianjin and Qinhuangdao changed significantly between 2013 and 2014; Shijiazhuang, Zhangjiakou, and Chengde experienced mutations between 2014 and 2015; and Beijing, Hengshui, Handan, and Langfang experienced changes between 2015 and 2016, while none of the other cities reached the 95 percent confidence level for their UF and UB intersections and did not meet the conditions for the occurrence of mutation points. Based on these findings, 2013, 2016, and 2022 were selected in this study as the key time points for visualizing the degree of coupled coordination.
Temporal analysis of Figure 5 demonstrates sustained growth trajectories in both tourism efficiency and economic development level across the BTH megaregion from 2013 to 2022. Utilizing ArcGIS 10.8’s analytical toolkit, this investigation implemented Jenks natural breaks classification to generate comparative geospatial visualizations of inter-urban coordination patterns at triennial intervals (2013, 2016, 2022), as systematically presented in Figure 6. Overall, the BTH urban agglomerations differ significantly in space, with the northern region generally having a better degree of coupling coordination than the southern region, with Shijiazhuang, located in the south, developing more prominently, while the northern region is centered on Beijing and Tianjin. It can be seen from the figure that the spatial difference in the coupled development of tourism efficiency and economic development level in the BTH city cluster is gradually narrowing from 2013 to 2016 and then to 2022, which reflects the radiation-driven effect of Beijing and Tianjin on the neighboring cities. Beijing’s level of coupled and coordinated development has always been ahead of that of Tianjin and the prefecture-level cities in Hebei Province, while Tianjin’s level of coupled and coordinated development is second to Beijing’s, although its tourism efficiency is generally higher than that of Beijing’s, mainly because of the large gap between its level of economic development and that of Beijing.
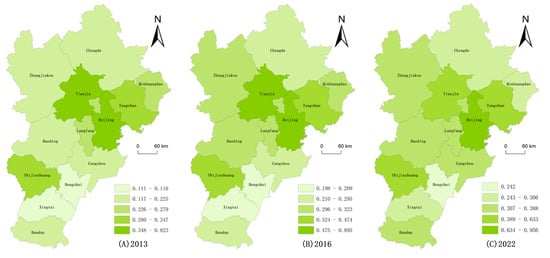
Figure 6.
Spatial distribution of the coupling coordination degree between tourism efficiency and economic development level in 2013, 2016, and 2022.
To deeply analyze the spatiotemporal evolution law of the coupled and coordinated relationship between tourism efficiency and economic development level in the BTH urban agglomeration, standard deviation ellipse and center of gravity migration maps were plotted using the spatial statistical analysis tool in ArcGIS 10.8 (Figure 7). The coupling coordination degree of the BTH urban agglomeration from 2013 to 2022 generally shows the distribution characteristic of ‘southwest-northeast’, and the coverage of the ellipse gradually expands. Its azimuth angle decreases from 32.70° in 2013 to 29.93° in 2022. From the distribution trend, the standard deviation of both the long and short axes shows an increasing trend, which indicates that the coupling coordination degree shows a diffusion in both axes. While the center of gravity of the ellipse is always located in Langfang City, the coordinates of the center point migrated from 116.58° E, 39.29° N in 2013 to the southwest, changed to 116.46° E, 39.23° N in 2016, and finally settled at 116.42° E, 39.17° N in 2022.
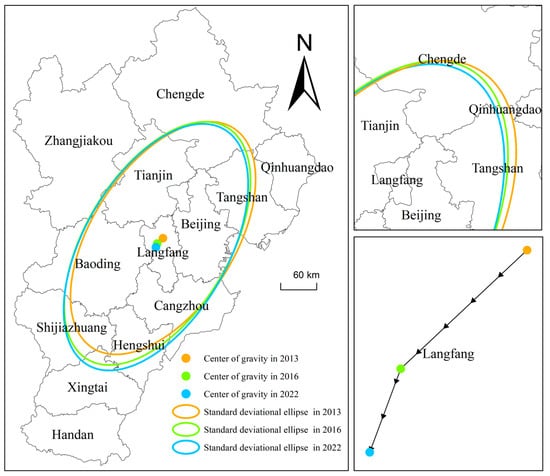
Figure 7.
Standard deviation ellipse and centroid migration of the coupling coordination degree between tourism efficiency and economic development level.
5.3.3. Markov Analysis of the Degree of Coordination of the Coupling of Tourism Efficiency and the Level of Economic Development
Investigating the evolutionary trajectory of systemic interdependencies between tourism efficiency and economic development level in the BTH megaregion, this research employs Markovian transition probability modeling to delineate longitudinal development patterns. According to the quartile method, the coupling coordination degree was classified into four intervals: [0, 0.27), [0.27, 0.33), [0.33, 0.42), and [0.42, 1], which are denoted by k = 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively.
By analyzing the Markov transfer probability matrix of the coupled coordination degree of tourism efficiency and economic development level (Table 3), we draw the following conclusions: (1) The transfer probability on the main diagonal is significantly higher than that on the non-diagonal, and the probability of the four types to keep the current state is 74.19%, 63.33%, 75%, and 100%, which suggests that the coupled coordination degree of BTH city cluster has high stability and the probability of state change is small. (2) The coupling coordination of the BTH urban agglomeration shows the characteristics of ‘club convergence’, in which the probability of upward adjustment of cities in state 2 (33.33 percent) far exceeds the probability of downward adjustment (3.33 percent), and the probability of downward adjustment of cities in state 3 (17.86 percent) exceeds the probability of upward shift (7.14 percent). (3) The odds of transferring on the upper right side of the diagonal are significantly greater than those on the lower left side of the diagonal, indicating that the likelihood of transferring from low-value to high-value areas is greater than the likelihood of transferring from high-value to low-value areas, showing that the coupling between the efficiency of tourism and the level of economic development is increasing. In addition, the transfer probabilities of non-adjacent diagonal elements are all 0, and the probability of a direct leap from state 1 to states 2, 3, and 4 is also 0. This suggests that the type of coupling coherence does not change by leaps and bounds in the short term, but rather develops through a continuous and gradual process. Therefore, to achieve coordinated regional development, the future should focus on enhancing the leading role of Status 3 and Status 4 cities and helping Status 1 and Status 2 cities to transform in a more positive direction.

Table 3.
Markov probability transition matrix.
5.4. Future Projections of the Degree of Harmonization of the Coupling Between Tourism Efficiency and the Level of Economic Development
On this basis, based on the coupled coordination degree between tourism efficiency and economic development level in the BTH city cluster from 2013 to 2022, the gray GM(1,1) model is used to predict the degree of coupled coordination between the two systems from 2023 to 2030. The average relative errors of the models were all below 20 percent, indicating a good model fit. The coupling coordination degree is expected to be improved from 2023 to 2030, which, overall, continues the trend of a steady increase in the coupling coordination degree from 2013 to 2022, which further confirms the key role of the regional synergistic development strategy in the synergistic development of the BTH urban agglomeration. In particular, projections show that Shijiazhuang and Tangshan will move from dislocation to harmonization in 2026, Baoding is expected to reach harmonization in 2027, and Zhangjiakou may rise to harmonization in 2030. However, the prediction results for Tianjin show that the coupled coordination between its tourism efficiency and economic development level remains almost linear, which reveals the existence of sizeable regional development differences in the BTH urban agglomeration. Therefore, it still takes a long time to realize the integrated development of the BTH urban agglomeration, and it is imperative to focus on the coupled and coordinated development of Tianjin to promote its development in a more coordinated direction. By strengthening the development of the ‘short board’ areas, it is possible to improve BTH city cluster tourism efficiency and the economic development level of synergistic development and overall improvement, thus achieving the ‘14th Five-Year Plan’ on the integration of BTH city cluster to achieve the strategic objectives.
In this study, the predicted values of coupling coordination for the BTH city cluster for 2023–2030 were further spatially visualized using ArcGIS 10.8 software (Figure 8). Figure 8 shows that the coupling coordination degree of the BTH urban agglomeration maintains an overall growth trend. The spatial pattern changes from ‘Beijing is higher than peripheral cities’ in 2023 to ‘the central city is higher than the north and south cities’ in 2030, indicating that Beijing, as the regional center, has a significant pulling effect on the development of the peripheral cities and a substantial influence on the development of the peripheral cities. This indicates that Beijing, as a regional center, has a significant pulling effect on the development of the surrounding cities. Based on the BTH city cluster as a whole, the gap between the coupling coordination degree of Qinhuangdao City and other cities has widened in 2028, while the coupling coordination degree of Hengshui City has been at a low level for a long time. Although regional incoherence still exists in the BTH city cluster in 2023–2030, the coupling coherence gap between cities, except for Qinhuangdao City and Hengshui City, has significantly narrowed, and the overall tendency is to be balanced.
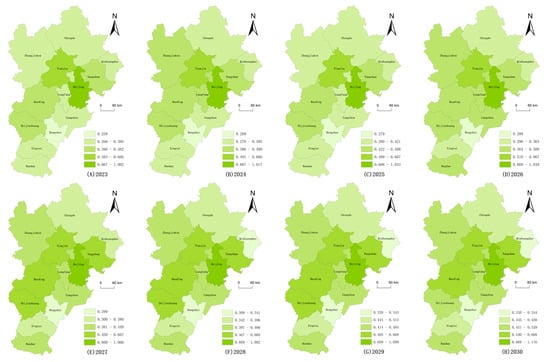
Figure 8.
Spatial distribution of coupling coordination degree between tourism efficiency and economic development level from 2023 to 2030.
6. Discussion
Taking the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration as the empirical object, this study innovatively constructs an integrated research framework containing the super-efficiency SBM model, entropy weight method, coupled coordination model, Markov chain analysis, and gray prediction GM(1,1). The framework systematically deconstructs the interaction mechanism between tourism efficiency and economic development through three dimensions: static assessment, dynamic evolution, and trend prediction. From the perspective of methodological comparison, relevant studies in Yunnan Province focus on the spatial coupling characteristics of tourism efficiency and tourism economic network dominance, and explore the structural effects of the external linkage network of tourism destinations by integrating the DEA model and the social network analysis technique [31]; empirical evidence in Jiangsu Province uses the coupling coordination model and exploratory spatial data analysis, focusing on the spatial heterogeneity and its functioning mechanism between tourism efficiency and economic development [3]. In comparison, this study has stronger systematic features and predictive functions in the methodological system, and its innovativeness is mainly reflected in the following: firstly, the three-dimensional integration of coupled measurement, spatial diagnosis, and trend prediction is realized through the synergistic use of multiple models, and secondly, the research gap of dynamic evolutionary law and trend deduction in the time series dimension is effectively bridged by introducing Markov chain analysis and the thGM(1,1) prediction model. The application of this composite method not only enhances the predictive value of the research conclusions but also provides dynamic and forward-looking decision support for regional policy formulation.
This study draws the following core conclusions through systematic analyses: The coupled coordination between tourism efficiency and economic development level in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region shows a significant enhancement, and its evolution process has a distinctive policy-oriented character. In the context of regional coordinated development strategy in-depth implementation, in Beijing and Tianjin, the core growth pole of the ‘dual-core drive’ effect continues to show, but there are still significant gradient differences in Hebei Province, especially the hinterland of the ring of Beijing and Tianjin, where a strategy for tourism resource endowment and economic development capacity has not yet been formed, and regional heterogeneity is obvious.
This study further reveals that there is a significant non-linear coupling between the two systems, and that the efficiency of tourism factor allocation and the quality of economic growth present a two-way mutual feedback mechanism. Based on this, it is urgent to build a cross-regional factor flow mechanism for the sustainable development of the tourism economy, focusing on the integration of spatial planning, innovation of industrial linkage, sharing of public services, strengthening the radiation-driven effect of the core city, and solving the problem of efficiency dissipation caused by administrative division barriers.
In addition, further in-depth research is needed: firstly, under the premise of fully considering the data availability, the research indicators of each system should be further refined, and the quantitative characterization of ‘tourism service quality’ should be added, such as tourists’ satisfaction, the degree of improvement of scenic spots, the level of protection of cultural heritage, etc., to further elucidate the synergies between tourism efficiency and economic development in the BTH urban agglomeration. Secondly, this study has not yet fully explored the intrinsic path between tourism efficiency and economic growth, and will use policy support, infrastructure, and population mobility as the mediating variables for further research in the future. The study adopts a gray GM(1,1) model for forecasting, which is slightly monolithic and weakly adaptable to non-linear relationships and non-stationary time series data, and machine learning needs to be integrated to improve the robustness of forecasting and the ability of multi-scenario simulation in the future. Finally, future research can introduce the Harken model to further explore the synergistic evolutionary relationship between tourism efficiency and economic development level in the BTH metropolitan area, providing more in-depth theoretical support and policy recommendations.
7. Conclusions and Recommendations
7.1. Conclusions
Taking the BTH city cluster as the research object, the tourism efficiency value of the region was measured by the super-efficiency SBM model using the panel data from 2013 to 2022, and the comprehensive evaluation value of the economic development level of each province and the city was calculated by the entropy weighting method. The interrelationships between tourism efficiency and the economic development level were further analyzed by using the coupling degree of the coordination model to arrive at the following main conclusions:
- (1)
- Between 2013 and 2022, the tourism efficiency of the BTH urban agglomeration shows an upward trend, and the inter-regional differences gradually decrease over time. The tourism efficiency of the BTH city cluster shows pronounced spatial heterogeneity, with Tianjin and Baoding as the core, showing a distribution of ‘high in the northwest and low in the southeast’, which may be related to the distribution of transport, economy, and tourism resources.
- (2)
- During the same period, the comprehensive evaluation index of the economic development level of the BTH urban agglomeration showed an upward trend. Still, the economic development level of most cities in Hebei Province was much lower than that of Beijing Municipality and Tianjin Municipality, and there was a tendency to widen the inter-regional differences. Regarding spatial distribution, with Beijing and Tianjin as the core, a distribution pattern of ‘high in the center, low in the surroundings, and better in the north-east than in the southwest’ has been formed.
- (3)
- The level of coupled coordination in the BTH city cluster in 2013–2022 develops in a more coordinated direction. However, in terms of spatial distribution, there are significant differences in the level of coupled coordination between the two systems in the cities in the BTH city cluster, with Beijing and Tianjin in a state of coordination, while the 11 cities in Hebei Province are in a state of dysfunction.
- (4)
- The prediction results show that the coupling coordination degree of the BTH city cluster will show a steady upward trend from 2023 to 2030. Some cities will change from a state of dissonance to a state of coordination, and the overall coupling coordination level will tend to be balanced. Nonetheless, there are still significant regional disparities within the region, suggesting that it will take a long time to realize the integrated development of the BTH city cluster, and that more emphasis needs to be placed on coordinated inter-regional development.
7.2. Recommendations
Based on the above empirical research, the following recommendations are proposed: (1) Given the convenience of the ‘one-hour traffic circle’ of the BTH city cluster, we should make full use of the characteristics of the tourism resources of different provinces and cities to develop differentiated tourism products. With Beijing and Tianjin as the core tourism cities, the tourism development of Hebei Province cities should be driven to narrow the development gap between the regions. (2) It is recommended that the BTH city cluster establish a platform for exchanging talents, so that high-quality talents can be channeled to less-developed cities through regional cooperation. This will promote a balanced flow of resources and technology and realize the integrated and synergistic development of inter-regional tourism and economy. (3) The projection analysis of coupling coordination trajectories reveals moderate synchronization potential between tourism efficiency and economic development level in Tianjin, necessitating strategic emphasis on optimizing tourism’s catalytic role within regional economic frameworks. While allocating tourism resources, tourism should be used to promote sustainable economic development in order to achieve a higher level of coordinated development.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.W. and R.L.; methodology, M.L.; software, S.W.; validation, R.L. and M.L.; formal analysis, S.W. and R.L.; investigation, S.W. and M.L.; resources, R.L. and M.L.; data curation, S.W. and R.L.; writing—original draft preparation, S.W.; writing—review and editing, S.W. and R.L.; visualization, S.W.; supervision, R.L.; project administration, M.L.; funding acquisition, S.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Soft Science Special Project of Gansu Basic Research Plan under Grant (S.W., 23JRZA421; W.F., 24JRZA079), Gansu Provincial Universities Young Doctor Support Project (S.W., 2023QB-069), Key Research Projects of Lanzhou University of Finance and Economics (S.W., Lzufe2023B-001), and Gansu Provincial Department of Education College Teachers’ Innovation Fund Project (S.W., 2024A-071).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Tian, X.; Li, W. Achievements and Realistic Reflections on the 10th Anniversary of the Coordinated Development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Reg. Econ. Rev. 2024, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhan, W.; Tu, D. An Analysis of the Coupling and Coordination Degree between Tourism Industry and Regional Economy in Ethnic Areas—A Case Study of Tibetan Region. J. Tibet Univ. 2022, 37, 205–212. [Google Scholar]
- Xuan, Y.; Zhou, N.; Yang, H. The Spatio-Temporal Pattern Evolution of Tourism Efficiency and Economic Development Level from the Perspective of Coupling Coordination—A Case Study of Jiangsu Province. J. Nanjing Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2020, 43, 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Teng, T.; Bao, H. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Urban Tourism Efficiency in the Yellow River Basin. J. Stat. Inf. 2023, 38, 105–117. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes, R. Efficiency of travel agencies: A case study of Alicante, Spain. Tour. Manag. 2011, 32, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabright, N.P. Competition, Privatisation and Productive Efficiency: Evidence from the Airline Industry. Econ. J. 2001, 111, 591–619. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.C.; Song, H.; Shen, S. New developments in tourism and hotel demand modeling and forecasting. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2017, 29, 507–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Dai, Z. Study on the Spatial and Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Tourism Industry Efficiency—An Example from Yangtze River Economic Belt. World Surv. Res. 2023, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wang, J. Study on the spatio-temporal evolution of tourism eco-economic efficiency and influencing factors in ethnic areas: A case study of three cities and towns in northwestern Yunnan Province. Times Econ. Trade 2023, 20, 130–135. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Q. The spatio-temporal evolution of tourism eco-efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt and its interactive response with tourism economy. J. Nat. Resour. 2019, 34, 1945–1961. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Fang, S.; Gan, Y.; Qin, X. Measurement and spatio-temporal evolution of tourism poverty alleviation efficiency in Guangxi border ethnic areas. World Reg. Stud. 2021, 30, 367–377. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Huang, D.; Liu, X.; Guan, J. Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and influencing factors of provincial tourism efficiency in China. Arid. Land Geogr. 2023, 46, 2052–2060. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Hu, Y.; He, J.; Gan, C. Spatial Spillover Effects of China’s Industrial Structure Upgrading on Tourism Efficiency. Areal Res. Dev. 2023, 42, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.; Tang, J. The impact of environmental system resilience on green development efficiency and spatial spillovers of tourism in China. Stat. Decis. 2024, 40, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Huang, Z.; Hu, X.; Lyu, L.; Cao, F. The Spatial Pattern Evolution and Its Influencing Factors of County-Scale Tourism Efficiency in Zhejiang Province. Econ. Geogr. 2018, 38, 197–207. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Mu, X.; Ming, Q. Spatial differences and driving factors of tourism efficiency in border regions——A case of Yunnan Province. World Reg. Stud. 2020, 29, 416–427. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.; Lu, L. The Urban Tourism Efficiencies of Cities in Anhui Province Based on DEA Model. J. Nat. Resour. 2014, 29, 313–323. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Jian, Z.; Ding, Z. A Case Study on the Spatial Pattern of Tourism Development Efficiency and Its Influencing Factors at County Scale in the Qinba Mountain Area. Tour. Forum 2021, 14, 64–76. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Q.; Song, Y.; Chen, L.; Pan, Z. The spatial pattern and influencing factors of county-scale tourism efficiency in Shaanxi province. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, M.; Wang, J. Analysis on the coupling-coordination characteristics and influencing factors of China’s provincial digital economy and high-level opening-up. World Reg. Stud. 2024, 2024, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C. Statistical Measurement of China’s Ecological Economy Development Level. Stat. Decis. 2024, 40, 106–111. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Fan, H.; Su, Y.; Zheng, Z. Research on the Driving Factors of China’s Green Economy Development Level. J. Quant. Technol. Econ. 2021, 38, 65–82. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, J.; Yang, C.; Bai, Y. Analysis of Regional Disparities of Rural Economic Development Level in China. Econ. Geogr. 2010, 30, 479–483. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L. Coordination of Higher Education and Regional Economic Development: Analysis Based on Data from 2004 to 2011. Res. Educ. Dev. 2014, 34, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.; Shen, Z. Research on Coupling Coordination of Urban Resilience and Economic Development Level—Taking Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration as an Example. Resour. Dev. Mark. 2021, 37, 820–821. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Li, S. Impact of “One Belt One Road” Initiative on China’s Economic Development Level:Based on Regression-Discontinuity Analysis. J. Technol. Econ. 2018, 37, 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H. Analysis of Coupling Coordinative Degree between Tourism Industry and Regional Economy—A Case Study of Huangshan City. J. Bus. Econ. 2013, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H. Tourism Economics; China Renmin University Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Modeste, N.C. The impact of growth in the tourism sector on economic development: The experience of selected Caribbean countries. Econ. Int./Int. Econ. 1995, 48, 375–385. [Google Scholar]
- Pascal, T. The economic organization of tourism. Ann. Tour. Res. 2015, 25, 837–859. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Ming, Q.; Shi, P.; Luo, D. Space Evolution Characteristics and Correlation between Tourism Economic Efficiency and the Advantage Sturmability of Tourism Economy Network: Taking Yunnan Province as an Example. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 37, 125–135. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Lin, H.; Gan, C.; Deng, C. Spatio-Temporal Coupling Relationship between Tourism Poverty AlleviationEfficiency and Economic Development Level in Contiguous Destitute Areas:A Case Study of Wuling Mountain Area. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 200–208. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Li, L.; Xia, S.; Gao, X. Study on the Coordinated Relationship between Tourism Efficiency and Economic Development Level in China. Stat. Decis. 2019, 35, 127–131. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q. Spatial-Temporal Pattern Evolution and Influencing Factors of Coupling Coordination between Tourism Efficiency and Ecological Well-Being Performance in the Mountainous Area of Southern Anhui Province, China. Mt. Res. 2022, 40, 597–613. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Q. The spatio-temporal evolution of tourism efficiency and its interactive response with ecological environment in urban agglomeration in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. J. Shaanxi Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 51, 24–35. [Google Scholar]
- Yeniasır, M.; Gökbulut, B. Effectiveness of usage of digital heritage in the sustainability of cultural tourism on islands: The case of northern Cyprus. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrushka, V.; Horozhankina, N.; Girman, A.; Shulyak, S.; Shcholokova, G. Malta’s tourism potential. J. Geol. Geogr. Geoecol. 2021, 30, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Ming, Q.; Liu, A.; Zhang, X. Research on the center of gravity coupling and interactive response between tourism economic efficiency and regional economic level in Western Provinces. World Reg. Stud. 2022, 31, 350–362. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Mu, Q.; Ding, Z.; Ming, Q. The coordination pattern of tourism efficiency and high-speed transportation: A case study of 41 cities in the Yangtze River Delta. Geogr. Res. 2021, 40, 1042–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Yu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, L. Coupling relationship between urbanization efficiency and economic development level in the Yangtze River Delta. Prog. Geogr. 2013, 32, 1060–1071. [Google Scholar]
- Li, E.; Cui, Z. Coupling Coordination Between China’s Regional Innovation Capability and Economic Development. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 38, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, L.; Zhang, H.; Lu, T.; Song, L.; Chen, J.; Shu, Y.; Zhang, L. A Study on Influencing Factors of Maritime Traffic Safety with Entropy Weight Method. Navig. China 2021, 44, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, L.; Ren, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Xu, G.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Y. Relationship between runoff and sediment load in Dali River Basin based on coupling coordination degree. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 86–94. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Zhou, C. Analysis on the Coordination Degree of China’s Regional Technology Finance and Technological Innovation Coupling. Product. Res. 2021, 6, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D. Spatial and temporal evolution of the coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration coupled with the degree of coordination of carbon emissions. Stat. Decis. 2024, 40, 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Z. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Differences and Dynamic Evolution of Grain Production Resilience Based on Spatial Markov Chains. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J. Grey Forecasting and Decision-Making; Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press: Wuhan, China, 1988. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).