Abstract
Though biological and ecological characteristics of Scopimera globosa have been intensively investigated, little has been understood on bioturbation, especially sediment reworking. This study was designed to evaluate variation on sediment reworking of S. globosa based on feeding pellet production (FP) and burrowing pellet production (BP) with influencing factors and estimating the chlorophyll content reduction within the surface sediment by its feeding. The FP and BP largely fluctuated according to chlorophyll a concentration and crab density, but both were not influenced by temperature. The FP was enhanced by chlorophyll a concentration, whereas both FP and BP were restricted by crab density. The daily individual production was highest in spring, followed by fall and summer, with values of 25.61, 20.70 and 3.90 g ind.−1 d−1, respectively, while the total daily production was highest in fall, followed by summer and spring 2150, 1660 and 660 g m−2 d−1, respectively. The daily sediment reworking based on the FP and BP of Scopimera was highest in fall, followed by summer and spring, with values of 1.91, 1.70 and 0.77 mm d-1 and the annual sediment reworking rate of this species was calculated 40 cm year−1 based on its density in this study area. The chlorophyll a reduction ratio was estimated from 11 to 24% in one day by its feeding. These results imply that the sediment reworking of S. globosa is regulated by food abundance and its density, and Scopimera is an important bioturbator, greatly influencing biogeochemical changes in the intertidal sediments.
1. Introduction
Bioturbation by the activities of benthic organisms, such as feeding and burrowing, is one of the important processes influencing the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of intertidal sediments. Through feeding and burrowing activities, macrofauna increase the surface area of sediment exposed to overlying water or air and also modify the surface sediments. Macrofauna modifies sediment characteristics and enhances the exchange of solute and solids across the sediment–water interface during the process of bioturbation [1,2,3]. In particular, the sediment reworking that results from feeding and burrowing of macrofauna is essential to the organic matter mineralization, microphytobenthos reduction and nutrient exchange from the sediment to the water column [4,5,6,7]. Organic matter decomposition in intertidal sediments is mediated by the activity of macrofauna, which increases the capacity of organic matter degradation and transport processes via burrow dwelling. Burrowing crabs induce sediment transport and mixing during burrow maintenance and feeding activities modifying sediment dynamics and food resource availability for the microbial. Sediment disturbance and particle erosion through burrowing, feeding and movement of burrowing crabs enhance both the direct release of nutrients sequestered in water and nutrient cycling, through oxygenation of the sediment and increasing the surface area available for microbial activity [8,9,10]. Therefore, bioturbation has an important influence on material cycles in intertidal sediments.
The sediment reworking depends on the biotic factors such as feeding, burrowing, and density of inhabitant, depending on abiotic factors, such as temperature, water content, organic matter contents, chlorophyll contents and food availability [5,7,11,12,13]. The influence of these factors in sediment reworking has been largely assessed via in situ measurements and laboratory experiments [7,13,14,15]. The overall sediment reworking rate of deposit-feeder increases with an increase in density, but that of individual decrease with density due to competition for trophic resources and territory [16]. The sediment reworking by deposit-feeders is strongly temperature-dependent and organic matter-dependent. The feeding activity of the deposit-feeder increases as temperature and organic matter increase [7,17]. These studies have stressed that the sediment reworking of natural communities varies depending on changes in a few dominant species. Thus, previous studies emphasize the crucial importance of considering temporal changes in ecological/environmental parameters when up-scaling sediment reworking rates to a longer period than the one over which actual measurements were carried out.
The surface deposit-feeding sand bubbler crab, Scopimera globosa, is one of the most abundant burrowing crab species in the upper tidal zone of Anmyeon Island, Korea [18]. A few studies have investigated the biological and ecological information of this species such as population ecology, life history and behavioral characteristics [19,20,21,22]. It lives in the sandy intertidals and ingests surface sediments and egests the remaining particles around the burrow in the shape of beans [23]. The recruitment of this crab occurs from July to August resulting in a high juvenile proportion in the population during summer. The newly settled juveniles in summer grow up until fall and stop to grow without feeding in winter through early spring due to low temperature resulting in stable density except for the decreases by mortality. However, little research has been conducted on temporal variation in sediment reworking rate of this species with abiotic/biotic factors influencing that or its effects on sediment environments.
Therefore, the objective of this study is to evaluate variation on the sediment reworking with influencing factors of sand bubble crab S. globosa and estimate its effects on chlorophyll content of surface sediments. Specifically, the present study aimed (a) to assess variation on sediment reworking based on quantification of feeding and burrowing pellets of S. globosa (b) to evaluate biotic/abiotic factors influencing its sediment reworking and (c) to estimate chlorophyll content reduction in surface sediment by the feeding of this species. The results of the present study provide ecological characteristics and bioturbation effects on intertidal sediments of S. globosa, one of the abundant burrowing crab species in this study area, for the management and conservation of Anmyeon Island tidal flat ecosystem.
2. Materials and Methods
This study was conducted in the upper tidal zone of Anmyeon Island, on the west coast of Korea (36°26′42.17″ N 126°20′5.02″ E, Figure 1). The mean tidal range is 4.3 m, with spring and neap tide at 6.0 m and 3.0 m, respectively. The sediment in the study area consists primarily of sand, with a mean grain size of 2.19 ∅, and is positioned 1.3 m above mean sea level (MSL). The sand bubbler crab S. globosa is one of the most abundant burrowing crab species in the study area, with annual mean density of 175 ind. m−2.
Figure 1.
Location and layout of the study site in the Anmyeon Island tidal flat, on the western coast of Korea. Red rectangle represents study area; gray area represents tidal flat.
Field surveys were seasonally conducted at spring tide in September 2016, February, May, and August 2017. A series of three quadrats, 0.25 m−2 (50 cm × 50 cm) in area, was established at the study site in each season. Immediately after the site was exposed, existing feeding pellets and burrowing pellets in the quadrat were cleared without any surface disturbance. After 2 h, brushes with spatula were used to carefully load the newly produced feeding and burrowing pellets into each glass vial. This collection process was repeated until before the site was submerged by the flood tide. The collection was conducted at 2 h intervals to evaluate accurate pellet production during the emergence period and repeated eight times in spring and six times in summer and fall during a consecutive day and night (Figure 2). Since any pellet was not produced, it was not conducted in winter. The wet weights of both pellet samples were measured with an electronic scale after the collection process at each sampling occasion. The feeding pellet production (FP) and burrowing pellet production (BP) were estimated as each pellet quantity produced by an inhabitant in an hour because the crab density varied among seasons.
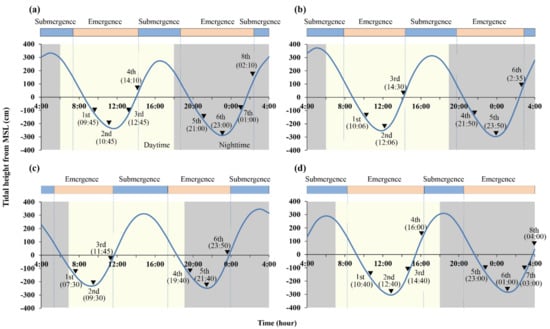
Figure 2.
Sampling times for collection of Scopimera globosa feeding pellet and burrowing pellet by tidal height: (a) spring, (b) summer, (c) fall, (d) winter. Blue line represents tidal height. Black triangles represent pellet collection for quantification and chlorophyll content analysis.
A defaunated plot (0.25 m−2) was independently established at the study site to measure chlorophyll a concentration one day before the collection in each season. All crabs were removed within the plot, and a square stainless steel frame (0.25 m−2) with 20 cm height was placed on the edge of the defaunated plot to prevent recolonization of crabs. The frame extended 15 cm aboveground, penetrating the sediment to 5 cm below ground. The surface sediments were collected within the defaunated plot to estimate the chlorophyll a reduction ratio (CR). The chlorophyll a concentration between the surface sediments in defaunated plot and non-bioturbated surrounding surface sediments was compared to evaluate sediment mixing effects by crab removal. The chlorophyll a concentration was not significantly different between them (Table S1); thus it was assumed that the chlorophyll a concentration of surface sediments in defaunated plot was unaffected by sediment mixing.
The collection was repeated for each sampling occasion over the season (Figure 2). The CR was calculated based on differences in chlorophyll a concentration between the feeding pellet in the quadrat and surface sediment in the defaunated plot. The samples were extracted with 10 mL of 90% acetone in 15-mL conical tubes for 24 h at −20 °C in the dark. The chlorophyll a concentration was then determined using a Turner Designs fluorometer (RF-5301PC; Shimadzu Corporation, Japan).
After these collections, all the crabs within the quadrats were captured for density, body length and biomass measurements. The length of the crab carapace and the feeding pellet length were measured with calipers, and the masses of crabs were obtained by weighing. The sediments were collected at depths of 0–1, 5–6, 10–11, 15–16 and 20–21 cm to estimate water content, and the weight–volume conversion factor for sediment reworking rate calculations. These sediment depths were determined based on the burrow depth of S. globosa observed in this study area.
The wet weight of the sediment was measured initially, and the dry weight was then obtained after drying the samples for 3 days at 60 °C. The sediment–water content was estimated based on the difference between the wet and dry weights. The wet weight per volume of sediment was measured using a syringe, and the weight–volume conversion factor was determined as the specific gravity of water divided by the wet weight per volume of sediment.
The sediment reworking rate (SRR) was expressed as reworked sediment depth to decide how much deep sediment had been reworked by the crab, based on the feeding and burrowing pellets weights. The wet weights of both pellets were converted into a volume using a weight–volume conversion factor. The reworked depth was calculated as the converted pellet volumes divided by the reworked area (see [7]). The SRR was given by the sediment depth reworked over one day by the crab. The annual SRR was calculated arithmetically as the daily sediment reworking rate per individual multiplied by 365 days and crab density.
The air temperature was measured 1.5 m above the sediment surface, and sediment temperature was obtained by placing a thermometer directly at a sediment depth of 10 cm during each collection period. The elevation from MSL was measured using a real-time kinetic differential global positioning system (RTK DGPS) at the study site. Tidal records for the study area were obtained from the Korean Hydrographic and Oceanographic Agency (KHOA).
Differences in density, morphometric dimensions, water content, pellet production, and sediment reworking rate among seasons were tested using non-parametric analysis of variances (Kruskal–Wallis test) due to non-homoscedasticity of data. The results were considered statistically significant when p < 0.05.
3. Results
Daily variation in air and sediment temperatures followed similar curves in four seasons, showing a peak in the early afternoon. The mean temperature was highest in summer, followed by fall, spring and winter, with values of 29, 21, 16, and 5 °C in the sediment and 28, 20, 18, and 3 °C in the air, respectively (Figure 3).
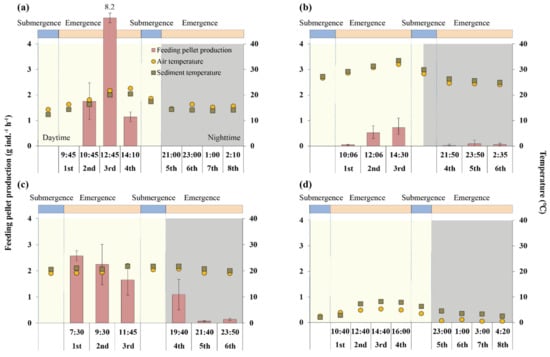
Figure 3.
Variation in feeding pellet production (FP) at each sampling time: (a) spring, (b) summer, (c) fall, (d) winter.
The sediment–water content was highest in summer, followed by fall and spring, with mean values of 22.4, 22.3 and 20.6%, respectively, but without significance-p > 0.05 (Table 1, Tables S2–S7).

Table 1.
Comparison of density and morphometric data for Scopimera globosa and sediment–water content (mean value ± standard deviation). Different superscripts indicate the significant differences among seasons at 0.05.
The density and morphometric dimensions of S. globosa were compared among seasons (Table 1, Tables S2–S7). The mean density was 7 ± 5, 114 ± 40, 26 ± 4 and 28 ± 9 ind. 0.25 m−2 in spring, summer, fall and winter, respectively. The mean body length and biomass were highest in winter while those were lowest in summer. The density of juveniles, whose carapace length was less than 2.0 mm, intensively appeared in summer and sharply decreased in fall from 97% to 10% in composition, but the juveniles did not appear in spring and winter.
In spring, the diurnal and nocturnal FP and BP were significantly different, at 2.76 and 0 g ind.−1 h−1 for FP and 9.77 and 0.72 g ind.−1 h−1 for BP, respectively (Table 2, Tables S8–S11). The feeding and burrowing pellets were intensively produced in the daytime except for the first sampling occasion, whereas only the burrowing pellet was generated in nighttime (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Daily individual and total productions were 25.61 g ind.−1 d−1 and 660 g m−2 d−1, respectively. The mean sediment temperature was higher in the daytime than nighttime with values of 18 and 14 °C, respectively, but the sediment temperature of the first sampling occasion in the daytime was similar to nighttime at 14 °C.

Table 2.
Comparison of feeding pellet and burrowing pellet productions during daytime and nighttime and sediment reworking rates (mean value ± standard deviation). Different superscripts indicate the significant differences among seasons at 0.05.
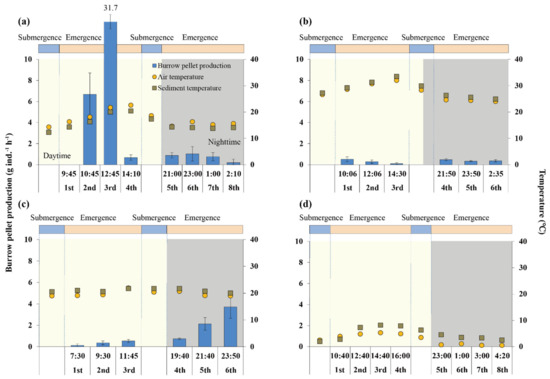
Figure 4.
Variation in burrowing pellet production (BP) at each sampling time: (a) spring, (b) summer, (c) fall, (d) winter.
The diurnal FP was about 9 times higher than nocturnal FP in summer, at 0.43 and 0.05 g ind.−1 h−1, respectively (Table 2, Tables S8–S11). In daylight, the FP was gradually increased over time, whereas no specific trend was found in nighttime (Figure 3). The BF was similar between daytime and nighttime with no specific tendency (Figure 4). Daily individual and total productions were 3.90 g ind.−1 d−1 and 1660 g m−2 d−1, respectively.
In fall, the daytime FP was highest during the first sampling occasion with gradually decreasing values over time, and nighttime one also showed a similar tendency (Figure 3). The diurnal FP was 5 times higher than nocturnal FP, at 2.15 and 0.44 g ind.−1 h−1, respectively (Table 2, Tables S8–S11). Unlike FP, the BP was gradually increased over time during both daytime and nighttime (Figure 4). Daily individual and total productions were 20.70 g ind.−1 d−1 and 2150 g m−2 d−1, respectively.
The FP was positively correlated with chlorophyll a concentration of surface sediments over the entire study period except for winter (Figure 5). FP increased as chlorophyll a concentration increased in spring and fall, whereas a negative correlation between these factors was seen in summer.
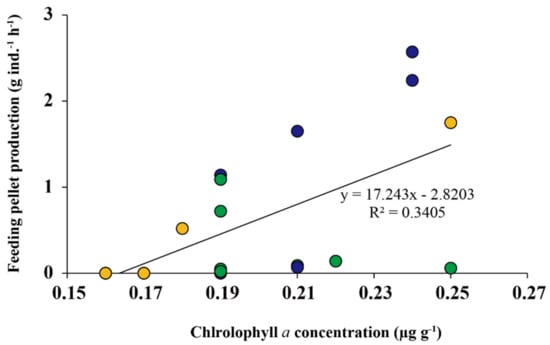
Figure 5.
Correlation between chlorophyll a concentration and feeding pellet production over the entire study period except for winter. Yellow, green and blue circles represent spring, summer and fall, respectively.
The FP and BP were plotted against density during the entire study period except for winter (Figure 6). The crab density ranged from 4 to 156 ind. 0.25 m−2, and FP and BP ranged from 0.11 to 3.48 g ind−1 h−1 and 0.24 to 14.00 g ind−1 h−1, respectively. The FP and BP were decreased as the density increased with a negative correlation.
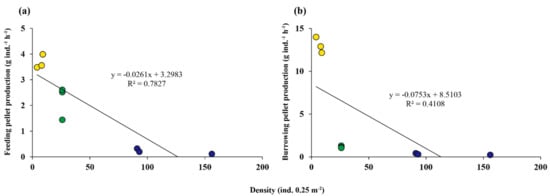
Figure 6.
(a) Correlation between FP and density over the entire study period except for winter, (b) Correlation between BP and density over the entire study period except for winter. Yellow, green and blue circles represent spring, summer and fall, respectively.
The FP and temperature between 14 and 32 °C in the air and between 14.3 and 33.5 °C in the sediment showed no significant correlation over the entire study period (Figure 7).
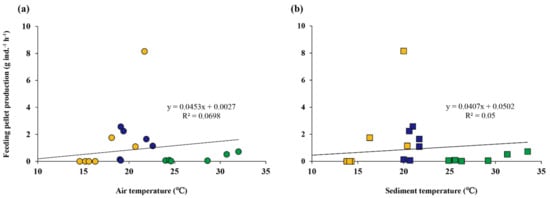
Figure 7.
(a) Correlation between air temperature and feeding pellet production over the entire study period, (b) Correlation between sediment temperature and feeding pellet production over the entire study period. Yellow, green and blue circles represent spring, summer and fall, respectively.
The individual SRR, representing the reworked sediment depth based on FP and BP by an inhabitant in a day, was highest in spring, followed by fall and summer at 0.12, 0.07 and 0.02 mm ind.−1 d−1, respectively (Table 2). However, given the crab density, the total SRR was highest in fall, followed by summer and spring, with values of 1.91, 1.70 and 0.77 mm d−1, respectively.
The mean chlorophyll a concentration of surface sediments showed similar values among spring, summer and fall, but the lowest value was observed in winter (Table 3, Tables S8–S11). The chlorophyll content was reduced by the feeding activity of crab in all seasons except for winter. The daily mean CR was highest in spring, followed by fall and summer, with values of 24.1, 12.3, and 11.2%, respectively.

Table 3.
Comparison of chlorophyll a concentrations and chlorophyll a reduction ratio (mean value ± standard deviation).
4. Discussion
The density and morphometric data of Scopimera differed among seasons. The density and juvenile proportion of Scopimera were highest in summer, whereas its body was significantly longer and heavier in winter. The recruitment of this crab occurs from July to August resulting in a high juvenile proportion in the population during summer [20]. The newly settled juveniles in summer grow up until fall and stop to grow without feeding in winter through early spring due to low temperature resulting in stable density except for the decreases by mortality. In this study, the crab density rapidly increased in summer due to great recruitment in juvenile proportion in the population and then sharply decreased in fall, which is consistent with previous studies. Therefore, our results on seasonal variation in the density and morphometric characteristics of S. globosa reflect the life history of this species.
The correlation between FP and chlorophyll a concentration showed that the feeding activity of S. globosa was enhanced by food abundance. The microphytobenthos attached to sediment particles is the main nitrogen source for surface deposit-feeders and is an important factor influencing feeding activity [24,25,26]. Previous studies have demonstrated that the feeding activity of surface deposit-feeding crabs increases with chlorophyll a concentration of surface sediments [27,28]. The feeding activity of sand fiddler crab, Uca pugilator, was 200-fold increased when chlorophyll a concentration was 5-fold increased [27] and the feeding rate of the other fiddler crab, Uca pugnax, was 2-fold increased as chlorophyll a concentration 2-fold increase [28]. In the present study, the chlorophyll a concentration was positively correlated with FP production in spring and fall, but negative correlation between these factors was observed in summer (Figure 5). However, the overall correlation between FP and chlorophyll a concentration showed that the former was increased as the latter increased (Figure 5), which indicates that the FP of this species is strongly dependent on chlorophyll a concentration of surface sediments.
The relationship between crab density and pellet production (FP and BP) showed that the latter was restricted by the former directly and indirectly. Crab density is an important factor influencing the feeding activity of the surface deposit feeder. At high crab densities, food resources decrease faster throughout the exploitative competition and the presence of more neighbors could reduce the available time for feeding due to interference [29,30]. In addition, high densities of crabs need larger areas and feed for longer periods to compensate for competition costs. In the current study, the FP was sharply decreased as crab density increased over the entire study period with negative correlation, especially in high density during summer (Figure 6a). These results suggest that density is an important factor regulating the feeding activity of S. globosa.
As with FP, the BP was negatively correlated with crab density, decreasing tendency as density increased (Figure 6). However, it is expected to be caused by indirect effects rather than direct effects of crab density. The burrowing crabs need more energy for burrowing than for the other activities, since crabs have to walk many times up and down inside burrows to push newly entered sediments up to the surface; thus, burrowing activities such as reconstruction and maintenance take place after feeding activity [31]. Since crabs need more time to do feeding activities to gain more energy as their density increases, the burrowing activity may have been restricted through enhanced feeding activity. Therefore, crab density is believed to affect the feeding and burrowing activities of Scopimera directly and indirectly. However, more detailed studies are necessary to evaluate the influences of crab density on the burrowing activity of S. globosa.
The temperature is one of the important factors influencing feeding activity on the surface of deposit-feeding crabs [5,29,32]. A few studies have reported that the surface deposit-feeding crabs require a temperature of at least 13 to 15 °C for feeding activity on the surface [20,33]. In spring, the FP and BP were intensively produced in the daytime where the air and sediment temperatures were above 14 °C, while only the BP was generated at nighttime below that temperature. The mean air and sediment temperatures in the nighttime of spring were 14.5 and 14.3 °C, which would not have been enough to be active on the surface. Thus, our results suggest that the minimum temperature of S. globosa for feeding activity on the surface is 14.5 °C.
The correlation between FP and temperature (air and sediment) showed that the former was uninfluenced by the latter within the range of this study. The effects of temperature on the feeding activity of deposit-feeding crabs differ by crab species. Some studies have reported that feeding activity is temperature-dependent. Fishelson [34] found that the feeding rate of sand bubbler crab, Dotilla sulcata, was increased with temperature and the other study showed a significant correlation between them in the sand fiddler crab, U. pugilator [35]. Meanwhile, Bradshaw and Scoffin [36] and Allen et al. [37] concluded that the temperature had no effect on the feeding activity of Dotilla myctiroides and Dotilla intermedia without a significant correlation between them. In this study, a significant correlation was not observed between FP and temperature over the entire study period (Figure 7), and no specific tendency in FP according to temperature variation was found (Figure 3). Therefore, our results revealed that the temperature under our condition between 14 and 34 °C is not a crucial factor affecting FP of Scopimera.
The annual SRR of Scopimera, as recorded during all seasons except for winter, was 18.9 mm ind.−1 year−1, which is remarkably higher than that of other deposit-feeding crab species. The annual SRR of deposit-feeding crabs of Uca annulipes and Uca inversa were estimated to be both 13.5 mm ind.−1 year−1 [38]. Since the SRR depends on various factors such as species, density, sediment organic contents and food availability, direct comparisons are generally inadequate. Nonetheless, the annual SRR of S. globosa based on the density observed in this study area was estimated at 40 cm year−1, which indicates that S. globosa is an important bioturbator, greatly influencing biogeochemical changes in intertidal sediments.
Some field studies have reported that chlorophyll a is reduced by the crab feeding on the surface sediments [5,26,35]. Reinsel [35] found that the sand fiddler crab, U. pugilator, contributed to 20–70% chlorophyll a reduction, and another study showed 30–60% chlorophyll a reduction by Uca uruguayensis [5]. In addition, Bulcao and Hodgson [39] have reported 40% chlorophyll a reduction by feeding of sand bubbler crab, Dotilla fenestrate. The CR of this study was shown to be relatively low compared to the previous studies at 11 to 24% (Table 3). Experimental studies have reported that the feeding efficiency of surface deposit-feeding crab depends on food abundance in their habitat [5,40]. The feeding activity of crabs is increased with food concentration, whereas the feeding efficiency is decreased by decreasing extraction time [28]. Under low food conditions, crabs enhance their feeding activity to gain more energy; but the extraction time for detaching food resources from particles decreases due to the rapid feeding process. The mean chlorophyll a concentration of surface sediments with respect to unfed sediments in the current study (0.18 µg g−1) was significantly lower than that of previous studies (10 by Reinsel [35], 1000 by Ribeiro and Iribarne [5] and 5 µg g−1 by Bulcao and Hodgson [39], respectively), which indicated that the low CR of S. globosa in this study might be due to low chlorophyll a concentration of surface sediments in this study area. Although we could not fully evaluate the factors affecting CR of S. globosa, our results did show that chlorophyll content was reduced 11, 12, and 24% in summer, fall, and spring, respectively, by its feeding. These findings suggest that S. globosa may play an important role in the microphytobenthos cycle in this intertidal sediments.
We examined ecological characteristics and evaluated temporal variation on sediment reworking rate of S. globosa with influencing biotic/abiotic factors and estimated chlorophyll content reduction by its feeding activity. The proportion of juveniles of this crab dramatically increased in summer and then decreased in fall, indicating the reproduction of this crab occurs in summer. The SRR was restricted by crab density and enhanced by chlorophyll a concentration of surface sediments. The annual SRR of this species was remarkably higher than that of other deposit-feeding crab species and the CR was comparable with other crab species, which indicated that S. globosa is an important bioturbator, greatly influencing biogeochemical changes in intertidal sediments. However, we could not fully evaluate accurate annual SRR of S. globosa, and the effects of juvenile proportion on that due to insufficient data. Thus, the accurate SRR of this species should be evaluated further through longer time series and more frequent sampling. In addition, the effects of juvenile proportion on SRR should be investigated to better understand the seasonal dynamics of this species. Nonetheless, the findings in this study can offer information on ecological characteristics and bioturbation effects of S. globosa on intertidal sediments for management and conservation planning of study area and can be used as baseline data for the estimation of ecosystem services of tidal flat. In Korea, there are no plans for the protection of the habitat of this species at the national or local level so far.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su13105703/s1, Table S1: Comparison of chlorophyll a concentration between the surface sediments in defaunated plot and non-bioturbated surrounding surface sediments (mean value ± standard deviation). Significant differences by t-test at 0.05. Table S2: Comparison of density of S. globosa among seasons. Significant differences by Kruskal-Wallis test at 0.05. Table S3: Comparison of length of S. globosa among seasons. Significant differences by Kruskal-Wallis test at 0.05. Table S4: Comparison of biomass of S. globosa among seasons. Significant differences by Kruskal-Wallis test at 0.05. Table S5: Comparison of juvenile proportion of S. globosa among seasons. Significant differences by Kruskal-Wallis test at 0.05. Table S6: Comparison of feeding pellet length of S. globosa among seasons. Significant differences by Kruskal-Wallis test at 0.05. Table S7: Comparison of sediment-water content among seasons. Significant differences by Kruskal-Wallis test at 0.05. Table S8: The air and sediment temperatures, density, feeding and burrowing pellet productions and chlorophyll a concentration (mean value ± standard deviation) over the entire study period in spring. Table S9: The air and sediment temperatures, density, feeding and burrowing pellet productions and chlorophyll a concentration (mean value ± standard deviation) over the entire study period in summer. Table S10: The air and sediment temperatures, density, feeding and burrowing pellet productions and chlorophyll a concentration (mean value ± standard deviation) over the entire study period in fall. Table S11: The air and sediment temperatures, density, feeding and burrowing pellet productions and chlorophyll a concentration (mean value ± standard deviation) over the entire study period in winter.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.S. and B.J.K.; formal analysis, J.S. and B.J.K.; writing—original draft preparation, J.S. and B.J.K.; writing—review and editing, B.J.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the project “Development of technology for constructing biological and environmental spatial information system of tidal flats through machine learning of remotely sensed visual data (PE99915)” funded by Korea Institute of Ocean Science and Technology.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank M. Kim and M. Jang for their assistance in the field.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Koo, B.J.; Kwon, K.K.; Hyun, J.H. Effect of environmental conditions on variation in the sediment-water interface created by complex macrofaunal burrows on a tidal flat. J. Sea Res. 2007, 58, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, B.J.; Koh, C.H. Oxygen penetration through invertebrate burrow walls in Korean tidal flat. Ocean Sci. J. 2013, 48, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez-Cardenas, D.; Quintana, C.O.; Meysman, F.J.R.; Kristensen, E.; Boschker, H.T.S. Species-specific effects of two bioturbation polychaetes on sediment chemoautotrophic bacteria. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 549, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, F.; Hulth, S.; Grossi, V.; Poggiale, J.C.; Desrosiers, G.; Rosenberg, R.; Gérino, M.; François-Caracaillet, F.; Michaud, E.; Stora, G. Sediment reworking by marine benthic species from the Gullmar Fjord (Western Sweden): Importance of faunal biovolume. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 348, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P.D.; Iribarne, O.O. Coupling between microphytobenthic biomass and fiddler crab feeding. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2011, 407, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, E.; Penha-Lopes, G.; Delefosse, M.; Valdemarsen, T.; Quintana, C.O.; Banta, G.T. What is bioturbation? The need for a precise definition for fauna in aquatic sciences. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 446, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Koo, B.J. Spring-neap variation on sediment reworking with organic matter contents by a polychaete, Perinereis aibuhitensis, in the intertidal sediments of the Gomso Bay, Korea Mar. Biol. 2019, 166, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, K.; Hansen, J.I.; Blackburn, T.H. The influence of benthic infauna on exchange rates of inorganic nitrogen between sediment and water. Ophelia 1980, 1, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Fry, J.C. Interactions between bacteria and benthic invertebrates. In Sediment Microbiology; Nedwell, D.B., Brown, C.M., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1982; pp. 171–201. [Google Scholar]
- Biles, C.L.; Paterson, D.M.; Ford, R.B.; Solan, M.; Raffaelli, D.G. Bioturbation, ecosystem functioning and community structure. Hydrol. Earth. Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermillod-Blondin, F.; François-Caracaillet, F.; Rosenberg, R. Biodiversity of benthic invertebrates and organic matter processing in shallow marine sediments: An experimental study. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2005, 315, 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maire, O.; Duchêne, J.C.; Grémare, A.; Malyuga, V.S.; Meysman, F.J.R. A comparison of sediment reworking rates by the surface deposit-feeding bivalve Abra ovata during summertime and wintertime, with a comparison between two models of sediment reworking. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 343, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, B.J.; Seo, J. Sediment reworking by a polychaete, Perinereis aibuhitensis, in the intertidal sediments of the Gomso Bay, Korea. Ocean Sci. J. 2017, 52, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugnai, C.; Gerino, M.; Frignani, M.; Sauvage, S.; Bellucci, L.G. Bioturbation experiments in the Venice Lagoon. Hydrobiologia 2003, 464, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecroart, P.; Schmidt, S.; Jouanneau, J.M.; Weber, O. Be-7 and Th-234 as tracers of sediment mixing on seasonal time scale at the water-sediment interface of the Thau Lagoon. Radioprotection 2005, 40, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duport, E.; Stora, G.; Tremblay, P.; Gilbert, F. Effects of population density on the sediment mixing induced by the gallery-diffusor Hediste (Nereis) diversicolor O.F. Müller, 1776. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 336, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, D.L.; Bianchi, T.S.; Roper, E.H. Experimental studies of sediment reworking and growth of Scoloplos spp. (Orbiniidae: Polychaeta). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1986, 30, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Khim, J.S.; Choi, J.W.; Shin, H.C.; An, S.; Park, J.; Kang, D.; Lee, C.H.; Koh, C.H. Environmentally associated spatial changes of a macrozoobenthic community in the Saemangeum tidal flat, Korea. J. Sea Res. 2011, 65, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, K. Movement of burrow location in Scopimera globosa and Ilyoplax pusillus. Physiol. Ecol. Jpn. 1983, 20, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, H. Studies on the life history of sand bubble crab, Scopimera globosa De Haan, at Tomioka Bay, West Kyushu—I. Seasonal changes of population structure. Mem. Fac. Fish. Kagoshima Univ. 1983, 32, 55–69. [Google Scholar]
- Sassa, S.; Watabe, Y. Threshold, optimum and critical geoenvironmental conditions for burrowing activity of sand bubbler crab, Scopimera globosa. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 354, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaida, S.; Kimura, T.; Toyohara, H. Habitat segregation of two dotillid crabs Scopimera globosa and Ilyoplax pusilla in relation to their cellulase activity on a marsh-dominated estuarine tidal flat in central Japan. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2013, 449, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, B.J. Burrows of Macroinvertebrates in the Korean Tidal Flats; Korea Institute of Ocean Science and Technology (KIOST): Busan, Korea, 2017; ISBN 978-89-444-9060-6. [Google Scholar]
- Botto, F.; Valiela, I.; Iribarne, O.O.; Martinetto, P.M.D.R.; Alberti, J. Impact of burrowing crabs on C and N sources, control, and transformations in sediments and food webs of SW Atlantic estuaries. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 293, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaya, G.; Takagi, S.; Kikuchi, E. Dietary contribution of the microphytobenthos to infaunal deposit feeders in an estuarine mudflat in Japan. Mar. Biol. 2008, 155, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, B.J.; Kim, S.H.; Hyun, J.H. Feeding behavior of the ocypodid crab Macrophthalmus japonicus and its effects on oxygen-penetration depth and organic-matter removal in intertidal sediments. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 228, 106366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.R.; Bancroft, K.; Vermeer, G.; Plaisier, K. Experimental studies on the foraging behavior of the sand fiddler crab Uca pugilator (Bose, 1802). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1980, 44, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissburg, M. Functional analysis of fiddler crab foraging: Sex-specific mechanics and constraints in Uca pugnax (Smith). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1992, 156, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.S. Pattern and process in competition. Adv. Ecol. Res. 1967, 4, 1–74. [Google Scholar]
- Virgilio, A.; Ribeiro, P.D. Spatial and temporal patterns in the feeding behavior of a fiddler crab. Mar. Biol. 2013, 160, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordhaus, I.; Diele, K.; Wolff, M. Activity patterns, feeding and burrowing behavior of the crab Ucides cordatus (Ucididae) in a high intertidal mangrove forest in North Brazil. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2009, 374, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.C. The feeding mechanism of fiddler crabs, with ecological considerations of feeding adaptations. Zoologica 1961, 46, 89–101. [Google Scholar]
- Bortolus, A.; Schwindt, E.; Iribarne, O.O. Positive plant-animal interactions in the high marsh of an Argentinean coastal lagoon. Ecology 2002, 83, 733–742. [Google Scholar]
- Fishelson, L. Population ecology and biology of Dotilla sulcate (Crustacea, Ocypodidae) typical for sandy beaches of the red sea. In Sandy Beaches as Ecosystems; McLachlan, A., Erasmus, T., Eds.; Dr. W. Junk Publishers: The Hague, The Netherlands, 1983; pp. 643–654. [Google Scholar]
- Reinsel, K.A. Impact of fiddler crab foraging and tidal inundation on an intertidal sandflat: Season-dependent effects in one tidal cycle. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 313, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, C.; Scoffin, T.P. Factors limiting distribution and activity patterns of the soldier crab Dotilla myctiroides in Phuket, South Thailand. Mar. Biol. 1999, 135, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.J.; Paterson, G.L.J.; Hawkins, L.E.; Hauton, C.; Clark, P.F.; Aryuthaka, C. Zonation on sandy tropical beaches: A case study using Dotilla intermedia (Brachyura: Ocypodidae). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 408, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penha-Lopes, G.; Bartolini, F.; Limbu, S.; Cannicci, S.; Kritensen, E.; Paula, J. Are fiddler crabs potentially useful ecosystem engineers in mangrove wastewater wetlands? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1694–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulcao, C.; Hodgson, A.N. Activity and feeding of Dotilla fenestrata (Brachyura: Ocypodidae) in a warm, temperate South African estuary. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 37, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citadin, M.; Costa, T.M.; Netto, S.A. The response of meiofauna and microphytobenthos to engineering effects of fiddler crabs on a subtropical intertidal sandflat. Austral Ecol. 2016, 41, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).