Masseter Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials (M-VEMPs) in Vestibular Neuritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
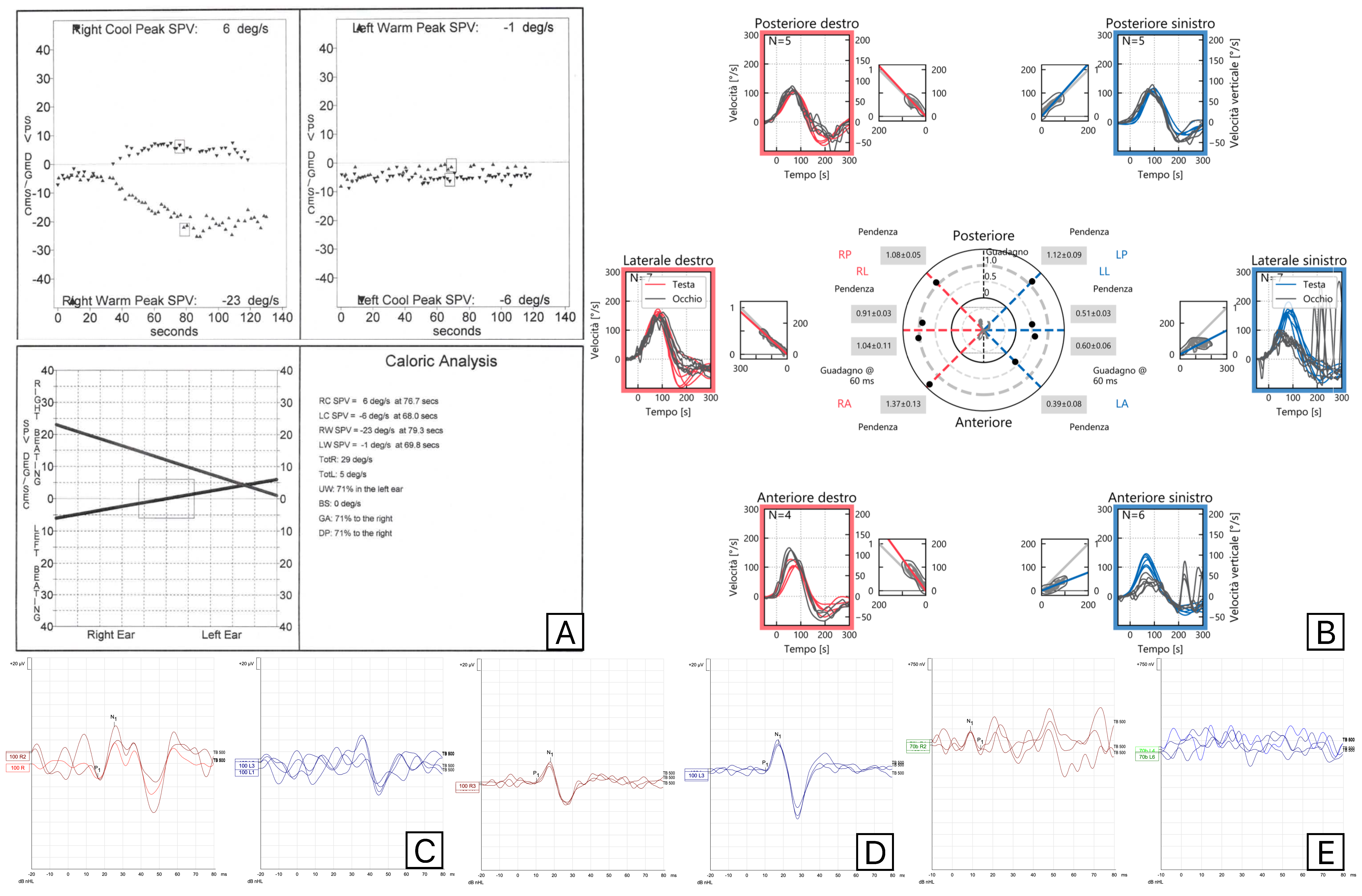
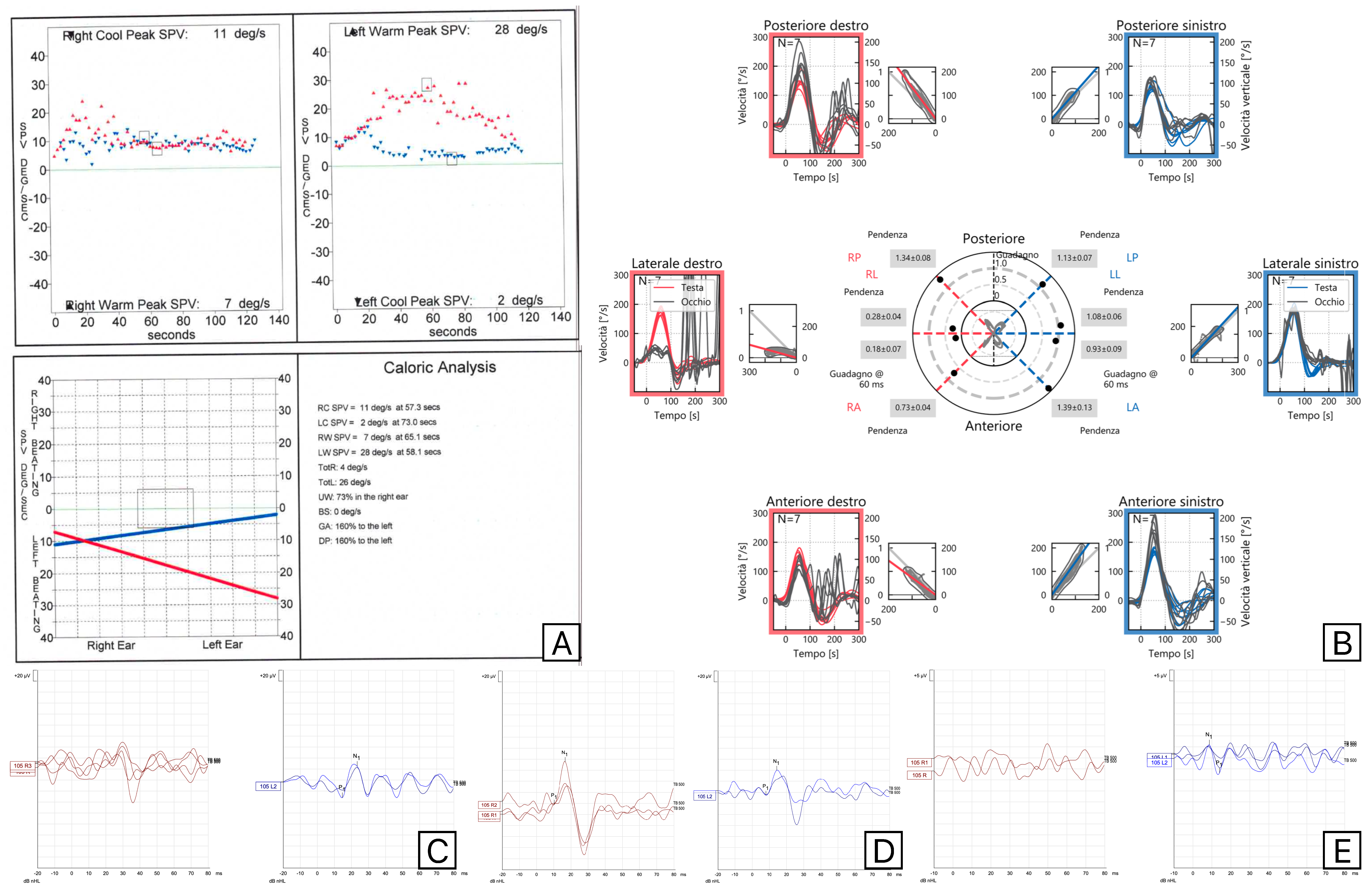
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagarajan, A.; Sinha, S. Masseter Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials: A new tool to assess the vestibulomasseteric reflex pathway. J. Otol. 2024, 19, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thirusangu, V.P.; Sinha, S.K. Masseter vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials at different tone burst frequencies in healthy individuals. Egypt. J. Otolaryngol. 2023, 39, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılınç, E.; Gençtürk, E.; Taşcı, B.; Şerbetçioğlu, M.B. Normalızatıon of masseter VEMP and comparıson wıth cervıcal VEMP ın normal ındıvıduals. Egypt. J. Otolaryngol. 2023, 39, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkadi, M.; Neupane, A. Multifrequency Analysis of Masseter Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Young Adults. Am. J. Audiol. 2023, 32, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignesh, S.; Singh, N.; Rajalakshmi, K. Tone Burst Masseter Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials: Normative Values and Test-Retest Reliability. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2021, 32, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.B.; Pushpanathan, S.; Abdullah, Y.; Patel, N.; Thontadarya, S. Comparison of Air Conduction and Bone Conduction Masseter Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potential Between Neurotypical Young Adults and Individuals With Conductive Hearing Loss. Cureus 2024, 16, e70267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ramesh, K.; Thirunavukkarasu, K. Decoding Age-Linked Masseter Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potential Changes in Healthy, Aging Individuals. Am. J. Audiol. 2024, 3, 838–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickenbottom, R.; Bishop, B.; Moriarty, T. Effects of whole-body rotation on masseteric motoneuron excitability. Exp. Neurol. 1985, 89, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Ewert, K.; Gleitsmann, K.; Reiter, F. Acoustic jaw reflex in man: Its relationship to other brain-stem and microreflexes. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1974, 36, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deriu, F.; Tolu, E.; Rothwell, J.C. A sound-evoked vestibulomasseteric reflex in healthy humans. J. Neurophysiol. 2005, 93, 2739–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deriu, F.; Ortu, E.; Capobianco, S.; Giaconi, E.; Melis, F.; Aiello, E.; Rothwell, J.C.; Tolu, E. Origin of sound-evoked EMG responses in human masseter muscle. J. Physiol. 2007, 580, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnano, I.; Pes, G.M.; Pilurzi, G.; Cabboi, M.P.; Ginatempo, F.; Giaconi, E.; Tolu, E.; Achene, A.; Salis, A.; Rothwell, J.C.; et al. Exploring brainstem function in multiple sclerosis by combining brainstem reflexes, evoked potentials, clinical and MRI investigations. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 125, 2286–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Natale, E.R.; Ginatempo, F.; Paulus, K.S.; Pes, G.M.; Manca, A.; Tolu, E.; Agnetti, V.; Deriu, F. Abnormalities of vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease are associated with clinical evidence of brainstem involvement. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 36, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Natale, E.R.; Ginatempo, F.; Laccu, I.; Figorilli, M.; Manca, A.; Mercante, B.; Puligheddu, M.; Deriu, F. Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials are abnormal in idiopathic REM sleep behavior disorders. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Vipinan, K. Cervical and Masseter Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Diabetes Mellitus Type 2. Am. J. Audiol. 2025, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behmen, M.; Konukseven, B.; Tak, A. Masseter Vestibular-Evoked Myogenic Potential Result of Possible Meniere’s Patients. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2024, 35, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tas Elibol, N.; Behmen, M.B.; Terlemez, Ş.; Konukseven, Ö. Evaluation of Masseteric Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Patients With Migraine. Am. J. Audiol. 2024, 33, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreedharan Sanitha, A.; Sinha, S. Assessment of Sacculocollic and Vestibulomasseteric Reflex Pathways in Individuals With Migraine and Vestibular Migraine. Am. J. Audiol. 2024, 33, 1257–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedik, T.Ö.; Elibol, N.; Çelik, N.; Bozali, Z. Masseteric vestibular evoked myogenic potentials findings in individuals with motion sickness susceptibility. J. Vestib. Res. 2025, 35, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajesh, A.; Neupane, A. Masseteric Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials in vestibular neuritis: A Case Series. Iran. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2024, 36, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Strupp, M.; Bisdorff, A.; Furman, J.; Hornibrook, J.; Jahn, K.; Maire, R.; Newman-Toker, D.; Magnusson, M. Acute unilateral vestibulopathy/Vestibular neuritis: Diagnostic criteria. J. Vestib. Res. 2022, 32, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comacchio, F.; Mion, M.; Armato, E.; Castellucci, A. Sequential Vestibular neuritis: Report of Four Cases and Literature Review. J. Audiol. Otol. 2021, 25, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandalà, M.; Santoro, G.P.; Awrey, J.; Nuti, D. Vestibular neuritis: Recurrence and incidence of secondary benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol. 2010, 130, 565–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppert, D.; Strupp, M.; Theil, D.; Glaser, M.; Brandt, T. Low recurrence rate of Vestibular neuritis: A long-term follow-up. Neurology 2006, 67, 1870–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comacchio, F.; Biancoli, E.; Poletto, E.; Bellemo, B.; Magnavita, P. Acute Bilateral Vestibular Neuropathy in course of Myocardial Infarction: Diagnosis and Pathophysiological Hypotheses—A Case Report. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2025. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, H.A.; Lee, H. Simultaneous occurrence of trigeminal herpes zoster and Ramsay Hunt syndrome presenting sudden prolonged vertigo. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 2049–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimisianos, N.; Ellul, J.; Salakou, S.; Tselengidou, E.; Papachristou, P.; Papathanasopoulos, P. Trigeminal herpes zoster complicated by Ramsay Hunt syndrome. Neurologist 2015, 19, 38–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbusow, V.; Schulz, P.; Strupp, M.; Dieterich, M.; Von Reinhardstoettner, A.; Rauch, E.; Brandt, T. Distribution of herpes simplex virus type 1 in human geniculate and vestibular ganglia: Implications for Vestibular neuritis. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 46, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbusow, V.; Strupp, M.; Wasicky, R.; Horn, A.; Schulz, P.; Brandt, T. Detection of herpes simplex virus type 1 in human vestibular nuclei. Neurology 2000, 55, 880–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakisaka, H.; Kobayashi, N.; Mominoki, K.; Saito, S.; Honda, N.; Hato, N.; Gyo, K.; Matsuda, S. Herpes simplex virus in the vestibular ganglion and the geniculate ganglion-role of loose myelin. J. Neurocytol. 2001, 30, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comacchio, F.; Castellucci, A. Posterior semicircular canal ossification following acute vestibular loss mimicking inferior vestibular neuritis: A case report. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 1015555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Simões, J.; Vlaminck, S.; Seiça, R.; Acke, F.; Miguéis, A. Vascular mechanisms in acute unilateral peripheral vestibulopathy: A systematic review. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2021, 41, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Oron, Y.; Shemesh, S.; Shushan, S.; Cinamon, U.; Goldfarb, A.; Dabby, R.; Ovnat, T.S. Cardiovascular Risk Factors Among Patients With Vestibular neuritis. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2017, 126, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Wang, D.; Wu, Y.; Fan, Z.; Guo, X.; Guan, Q. Correlation between vestibular neuritis and cerebrovascular risk factors. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2018, 39, 751–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navari, E.; Casani, A. Lesion Patterns and Possible Implications for Recovery in Acute Unilateral Vestibulopathy. Otol. Neurotol. 2020, 41, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yacovino, D.; Zanotti, E.; Cherchi, M. The spectrum of acute vestibular neuropathy through modern vestibular testing: A descriptive analysis. Clin. Neurophysiol. Pract. 2021, 6, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Goebel, J.A.; O’Mara, W.; Gianoli, G. Anatomic considerations in Vestibular neuritis. Otol. Neurotol. 2001, 22, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magliulo, G.; Gagliardi, S.; Ciniglio, A.M.; Iannella, G.; Re, M. Vestibular neurolabyrinthitis: A follow-up study with cervical and ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials and the video head impulse test. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2014, 123, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.; McGarvie, L.; Reid, N.; Young, A.; Halmagyi, G.; Welgampola, M. Vestibular neuritis affects both superior and inferior vestibular nerves. Neurology 2016, 87, 1704–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uffer, D.; Hegemann, S. About the pathophysiology of acute unilateral vestibular deficit—Vestibular neuritis (VN) or peripheral vestibulopathy (PVP)? J. Vestib. Res. 2016, 26, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murofushi, T.; Monobe, H.; Ochiai, A.; Ozeki, H. The site of lesion in “Vestibular neuritis”: Study by galvanic VEMP. Neurology 2003, 61, 417–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjærsgaard, J.B.; Hougaard, D.D.; Kingma, H. Thirty years with cervical vestibular myogenic potentials: A critical review on its origin. Front. Neurol. 2025, 15, 1502093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayil, M.; Keser, G.; Demir, A.; Pekiner, F. Assessment of Masseter Muscle Appearance and Thickness in Edentulous and Dentate Patients by Ultrasonography. Open Dent. J. 2018, 12, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Romero, D.; Jacobson, G.; Roberts, R. The effect of EMG magnitude on the masseter vestibular evoked myogenic potential (mVEMP). J. Otol. 2022, 17, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

| ID | Age | Sex | Impairment | Side | Herpes Zoster |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 80 | F | SIVN | R | |
| 2 | 80 | F | SIVN | L | |
| 3 | 60 | F | SIVN | R | + |
| 4 | 75 | M | SVN with ipsilateral saccule deficit | L | |
| 5 | 69 | F | SIVN | R | |
| 6 | 73 | F | SIVN | R | |
| 7 | 59 | M | SIVN | L | |
| 8 | 40 | F | SVN with ipsilateral saccule deficit | L | |
| 9 | 38 | F | SVN | L | |
| 10 | 45 | M | SVN | L | |
| 11 | 79 | M | SIVN | R | |
| 12 | 63 | M | SVN | R | |
| 13 | 76 | M | SVN | L | |
| 14 | 42 | F | SVN | R | |
| 15 | 43 | M | SVN | R | |
| 16 | 64 | M | SVN | R | + |
| 17 | 90 | F | SIVN | L | |
| 18 | 51 | M | SIVN with ipsilateral saccule sparing | R | |
| 19 | 64 | M | SIVN with ipsilateral saccule sparing | L | |
| 20 | 27 | M | SVN | R | |
| 21 | 74 | F | Utricle | L | |
| 22 | 65 | F | SVN | L | |
| 23 | 62 | M | SVN with ipsilateral saccule deficit | R | |
| 24 | 57 | M | SVN with ipsilateral saccule deficit | L | |
| 25 | 47 | M | SIVN with ipsilateral saccule sparing | L | |
| 26 | 31 | F | SVN | L | |
| 27 | 55 | M | SVN | R | |
| 28 | 77 | M | SVN | R | |
| 29 | 54 | F | SIVN | R | |
| 30 | 63 | M | SIVN | L | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Comacchio, F.; Zattoni, G.; Di Pasquale Fiasca, V.M.; Magnavita, P.; Bellemo, B.; Fasanaro, E.; Poletto, E. Masseter Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials (M-VEMPs) in Vestibular Neuritis. Audiol. Res. 2025, 15, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15030063
Comacchio F, Zattoni G, Di Pasquale Fiasca VM, Magnavita P, Bellemo B, Fasanaro E, Poletto E. Masseter Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials (M-VEMPs) in Vestibular Neuritis. Audiology Research. 2025; 15(3):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15030063
Chicago/Turabian StyleComacchio, Francesco, Giulia Zattoni, Valerio Maria Di Pasquale Fiasca, Paola Magnavita, Barbara Bellemo, Elena Fasanaro, and Elisabetta Poletto. 2025. "Masseter Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials (M-VEMPs) in Vestibular Neuritis" Audiology Research 15, no. 3: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15030063
APA StyleComacchio, F., Zattoni, G., Di Pasquale Fiasca, V. M., Magnavita, P., Bellemo, B., Fasanaro, E., & Poletto, E. (2025). Masseter Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials (M-VEMPs) in Vestibular Neuritis. Audiology Research, 15(3), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15030063








