Toward Effective Vaccines Against Piscine Orthoreovirus: Challenges and Current Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. PRV Genotypes and Epidemiology
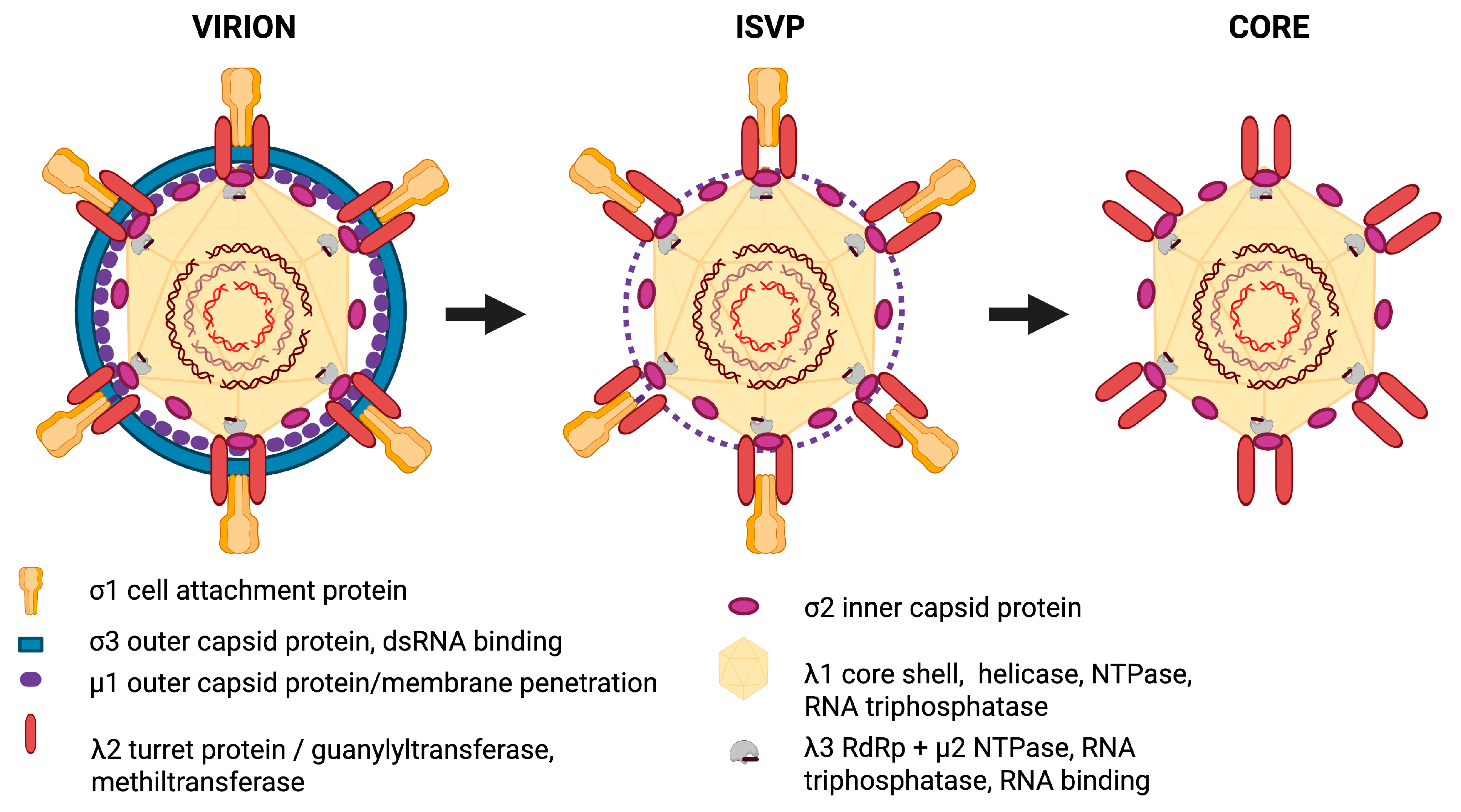
3. Genomic Structure, Viral Proteins, and Replicative Cycle
4. Pathogenesis of PRV Infection
5. Immune Response to PRV Infection
6. Immunogenicity of PRV Proteins
7. Vaccination Developed Against PRV
8. Discussion
9. Future Perspectives for PRV Vaccine Development
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PRV | Piscine orthoreovirus |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| HSMI | Heart and skeletal muscle inflammation |
| EIBS | Erythrocytic Inclusion Body Syndrome |
| MRV | Mammalian orthoreovirus |
| RdRP | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase |
| ISVP | Infectious subviral particle |
| FAST | Fusion-associated small transmembrane protein |
| EPC | Epithelioma papulosum cyprini (fish cell line) |
| AUG | Start codon (adenine-uracil-guanine) |
| IFN | Interferon |
| MHC | Major Histocompatibility Complex |
| IHNV | Infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus |
| GST | Glutathione S-transferase |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| LM | Lipid-modified |
| VHS | Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia |
| SUMO | Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier |
| TF | Trigger factor |
| APEX | Approved Piscine DNA Vaccine (APEX-IHN) |
| IHN | Infectious hematopoietic necrosis |
| VPS | Vacuolar Protein Sorting |
| SAV | Salmonid alphavirus |
| ISG | Interferon-stimulated gene |
References
- International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) Orthoreovirus Piscis. In: ICTV Taxonomy. August 2024. Available online: Https://Ictv.Global/Taxonomy/Taxondetails?Taxnode_id=202404974&taxon_name=Orthoreovirus%20piscis (accessed on 19 August 2025).
- Palacios, G.; Lovoll, M.; Tengs, T.; Hornig, M.; Hutchison, S.; Hui, J.; Kongtorp, R.T.; Savji, N.; Bussetti, A.V.; Solovyov, A.; et al. Heart and Skeletal Muscle Inflammation of Farmed Salmon Is Associated with Infection with a Novel Reovirus. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongtorp, R.T.; Kjerstad, A.; Taksdal, T.; Guttvik, A.; Falk, K. Heart and Skeletal Muscle Inflammation in Atlantic Salmon, Salmo salar L.: A New Infectious Disease. J. Fish Dis. 2004, 27, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessel, Ø.; Braaen, S.; Alarcon, M.; Haatveit, H.; Roos, N.; Markussen, T.; Tengs, T.; Dahle, M.K.; Rimstad, E. Infection with Purified Piscine orthoreovirus Demonstrates a Causal Relationship with Heart and Skeletal Muscle Inflammation in Atlantic Salmon. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kongtorp, R.T.; Taksdal, T.; Lyngøy, A. Pathology of Heart and Skeletal Muscle Inflammation (HSMI) in Farmed Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2004, 59, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessel, Ø.; Olsen, C.M.; Rimstad, E.; Dahle, M.K. Piscine orthoreovirus (PRV) Replicates in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) Erythrocytes Ex Vivo. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, M.G.; Kibenge, M.J.T.; Wang, Y.; Suarez, R.; Leiva, C.; Vallejos, F.; Kibenge, F.S.B. First Description of Clinical Presentation of Piscine orthoreovirus (PRV) Infections in Salmonid Aquaculture in Chile and Identification of a Second Genotype (Genotype II) of PRV. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cicco, E.; Ferguson, H.W.; Schulze, A.D.; Kaukinen, K.H.; Li, S.; Vanderstichel, R.; Wessel, Ø.; Rimstad, E.; Gardner, I.A.; Hammell, K.L.; et al. Heart and Skeletal Muscle Inflammation (HSMI) Disease Diagnosed on a British Columbia Salmon Farm through a Longitudinal Farm Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicco, E.D.; Ferguson, H.W.; Kaukinen, K.H.; Schulze, A.D.; Li, S.; Tabata, A.; Günther, O.P.; Mordecai, G.; Suttle, C.A.; Miller, K.M. The Same Strain of Piscine orthoreovirus (PRV-1) Is Involved in the Development of Different, but Related, Diseases in Atlantic and Pacific Salmon in British Columbia. Facets 2018, 3, 599–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongtorp, R.T.; Halse, M.; Taksdal, T.; Falk, K. Longitudinal Study of a Natural Outbreak of Heart and Skeletal Muscle Inflammation in Atlantic Salmon, Salmo salar L. J. Fish Dis. 2006, 29, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haatveit, H.M.; Wessel, Ø.; Markussen, T.; Lund, M.; Thiede, B.; Nyman, I.B.; Braaen, S.; Dahle, M.K.; Rimstad, E. Viral Protein Kinetics of Piscine orthoreovirus Infection in Atlantic Salmon Blood Cells. Viruses 2017, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polinski, M.P.; Gross, L.A.; Marty, G.D.; Garver, K.A. Heart Inflammation and Piscine orthoreovirus Genotype-1 in Pacific Canada Atlantic Salmon Net-Pen Farms: 2016–2019. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garver, K.A.; Johnson, S.C.; Polinski, M.P.; Bradshaw, J.C.; Marty, G.D.; Snyman, H.N.; Morrison, D.B.; Richard, J. Piscine orthoreovirus from Western North America Is Transmissible to Atlantic Salmon and Sockeye Salmon but Fails to Cause Heart and Skeletal Muscle Inflammation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, T.; Bauer, J.; Graff, S.; Teich, L.; Sterneberg, M.; Gebert, M.; Seibel, H.; Seeger, B.; Hellmann, J.; Wessel, Ø.; et al. Beating Cardiac Cell Cultures From Different Developmental Stages of Rainbow Trout as a Novel Approach for Replication of Cardiac Fish Viruses. J. Fish Dis. 2025, 48, e14080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, P.H.; Misk, E.; Papazotos, F.; Jones, G.; Polinski, M.P.; Contador, E.; Russell, S.; Garver, K.A.; Lumsden, J.S.; Bols, N.C. Screening of Fish Cell Lines for Piscine Orthoreovirus-1 (PRV-1) Amplification: Identification of the Non-Supportive PRV-1 Invitrome. Pathogens 2020, 9, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, Ø.; Hansen, E.F.; Løvoll, M.; Inami, M.; Husby, A.; Kruse, G.; Dahle, M.K.; Rimstad, E. Inactivation of Piscine Orthoreovirus. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamotharan, K.; Vendramin, N.; Markussen, T.; Wessel, Ø.; Cuenca, A.; Nyman, I.B.; Olsen, A.B.; Tengs, T.; Dahle, M.K.; Rimstad, E. Molecular and Antigenic Characterization of Piscine orthoreovirus (PRV) from Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Viruses 2018, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, T.; Nawata, A.; Sakai, T.; Matsuyama, T.; Ito, T.; Kurita, J.; Terashima, S.; Yasuike, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Fujiwara, A.; et al. Full-Genome Sequencing and Confirmation of the Causative Agent of Erythrocytic Inclusion Body Syndrome in Coho Salmon Identifies a New Type of Piscine Orthoreovirus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibenge, M.J.T.; Iwamoto, T.; Wang, Y.; Morton, A.; Godoy, M.G.; Kibenge, F.S.B. Whole-Genome Analysis of Piscine Reovirus (PRV) Shows PRV Represents a New Genus in Family Reoviridae and Its Genome Segment S1 Sequences Group It into Two Separate Sub-Genotypes. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, M.K.; Powers, R.L.; Taksdal, T.; McKenney, D.; Conway, C.M.; Elliott, D.G.; Polinski, M.; Garver, K.; Winton, J. Consequences of Piscine orthoreovirus Genotype 1 (PRV-1) Infections in Chinook Salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha), Coho Salmon (O. kisutch) and Rainbow Trout (O. mykiss). J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turcotte, L.D.M.; Bradshaw, J.C.; Polinski, M.P.; Johnson, S.C. Piscine orthoreovirus Genotype-1 (PRV-1) in Wild Pacific Salmon of British Columbia, Canada: 2011–2020. Fishes 2023, 8, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamek, M.; Hellmann, J.; Flamm, A.; Teitge, F.; Vendramin, N.; Fey, D.; Riße, K.; Blakey, F.; Rimstad, E.; Steinhagen, D. Detection of Piscine Orthoreoviruses (PRV-1 and PRV-3) in Atlantic Salmon and Rainbow Trout Farmed in Germany. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polinski, M.P.; Vendramin, N.; Cuenca, A.; Garver, K.A. Piscine Orthoreovirus: Biology and Distribution in Farmed and Wild Fish. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 1331–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, M.; Medina, D.A.; Suarez, R.; Valenzuela, S.; Romero, J.; Kibenge, M.; Wang, Y.; Kibenge, F. Extensive Phylogenetic Analysis of Piscine orthoreovirus Genomic Sequences Shows the Robustness of Subgenotype Classification. Pathogens 2021, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polinski, M.P.; Marty, G.D.; Snyman, H.N.; Garver, K.A. Piscine orthoreovirus Demonstrates High Infectivity but Low Virulence in Atlantic Salmon of Pacific Canada. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.S.; Teige, L.H.; Braaen, S.; Olsen, A.B.; Nordberg, M.; Amundsen, M.M.; Dhamotharan, K.; Svenning, S.; Edholm, E.S.; Takano, T.; et al. Piscine orthoreovirus (Prv)-3, but Not Prv-2, Cross-Protects against Prv-1 and Heart and Skeletal Muscle Inflammation in Atlantic Salmon. Vaccines 2021, 9, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoulia, T.; Sundaram, A.Y.M.; Amundsen, M.M.; Rimstad, E.; Wessel, Ø.; Jørgensen, J.B.; Dahle, M.K. Comparison of Transcriptome Responses in Blood Cells of Atlantic Salmon Infected by Three Genotypes of Piscine Orthoreovirus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2025, 157, 110088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garseth, Å.H.; Moldal, T.; Gåsnes, S.K.; Hjortaas, M.J.; Sollien, V.P.; Gjevre, A. Piscine Orthoreovirus-3 Is Prevalent in Wild Seatrout (Salmo Trutta L.) in Norway. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendramin, N.; Kannimuthu, D.; Olsen, A.B.; Cuenca, A.; Teige, L.H.; Wessel, Ø.; Iburg, T.M.; Dahle, M.K.; Rimstad, E.; Olesen, N.J. Piscine orthoreovirus Subtype 3 (PRV-3) Causes Heart Inflammation in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Vet. Res. 2019, 50, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauge, H.; Vendramin, N.; Taksdal, T.; Olsen, A.B.; Wessel, Ø.; Mikkelsen, S.S.; Alencar, A.L.F.; Olesen, N.J.; Dahle, M.K. Infection Experiments with Novel Piscine orthoreovirus from Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in Salmonids. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markussen, T.; Dahle, M.K.; Tengs, T.; Løvoll, M.; Finstad, Ø.W.; Wiik-Nielsen, C.R.; Grove, S.; Lauksund, S.; Robertsen, B.; Rimstad, E. Sequence Analysis of the Genome of Piscine orthoreovirus (PRV) Associated with Heart and Skeletal Muscle Inflammation (HSMI) in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, Ø.; Nyman, I.B.; Markussen, T.; Dahle, M.K.; Rimstad, E. Piscine orthoreovirus (PRV) ơ3 Protein Binds dsRNA. Virus Res. 2015, 198, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamotharan, K.; Bjørgen, H.; Malik, M.S.; Nyman, I.B.; Markussen, T.; Dahle, M.K.; Koppang, E.O.; Wessel, Ø.; Rimstad, E. Dissemination of Piscine Orthoreovirus-1 (PRV-1) in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) during the Early and Regenerating Phases of Infection. Pathogens 2020, 9, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, T.; Read, J.; Nibert, M.L.; Duncan, R. Piscine Reovirus Encodes a Cytotoxic, Non-Fusogenic, Integral Membrane Protein and Previously Unrecognized Virion Outer-Capsid Proteins. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Parker, J.S.L. The Paradoxes of Viral MRNA Translation during Mammalian Orthoreovirus Infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haatveit, H.M.; Nyman, I.B.; Markussen, T.; Wessel, Ø.; Dahle, M.K.; Rimstad, E. The Non-Structural Protein ΜnS of Piscine orthoreovirus (PRV) Forms Viral Factory-like Structures. Vet. Res. 2016, 47, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finstad, Ø.W.; Dahle, M.K.; Lindholm, T.H.; Nyman, I.B.; Løvoll, M.; Wallace, C.; Olsen, C.M.; Storset, A.K.; Rimstad, E. Piscine orthoreovirus (PRV) Infects Atlantic Salmon Erythrocytes. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooms, L.S.; Kobayashi, T.; Dermody, T.S.; Chappell, J.D. A Post-Entry Step in the Mammalian Orthoreovirus Replication Cycle Is a Determinant of Cell Tropism. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 41604–41613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillian, A.L.; Nibert, M.L. Amino Terminus of Reovirus Nonstructural Protein ΣNS Is Important for SsRNA Binding and Nucleoprotein Complex Formation. Virology 1998, 240, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.A.; Schmechel, S.C.; Williams, B.R.G.; Silverman, R.H.; Schiff, L.A. Involvement of the Interferon-Regulated Antiviral Proteins PKR and RNase L in Reovirus-Induced Shutoff of Cellular Translation. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 2240–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imani, F.; Jacobs, B.L. Inhibitory Activity for the Interferon-Induced Protein Kinase Is Associated with the Reovirus Serotype 1 Σ3 Protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 7887–7891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniert, J.; dos Santos, T.; Eaton, H.E.; Cho, W.J.; Plummer, G.; Shmulevitz, M. Reovirus Uses Temporospatial Compartmentalization to Orchestrate Core versus Outercapsid Assembly. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Xia, X.; Martynowycz, M.W.; Gonen, T.; Zhou, Z.H. Molecular Sociology of Virus-Induced Cellular Condensates Supporting Reovirus Assembly and Replication. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, A.N.; Aravamudhan, P.; Fernández de Castro, I.; Tenorio, R.; Risco, C.; Dermody, T.S. Ins and Outs of Reovirus: Vesicular Trafficking in Viral Entry and Egress. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, H.W.; Di Cicco, E.; Sandoval, C.; MacPhee, D.D.; Miller, K.M. Haemorrhagic Kidney Syndrome May Not Be a Variation of Infectious Salmon Anaemia. Aquaculture 2020, 516, 734498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polinski, M.P.; Garver, K.A. Characterization of Piscine orthoreovirus (PRV) and Associated Diseases to Inform Pathogen Transfer Risk Assessments in British Columbia; Research Document; Canadian Science Advisory Secretariat: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2019; p. 35.
- Dahle, M.K.; Wessel, Ø.; Timmerhaus, G.; Nyman, I.B.; Jørgensen, S.M.; Rimstad, E.; Krasnov, A. Transcriptome Analyses of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) Erythrocytes Infected with Piscine orthoreovirus (PRV). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 45, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendramin, N.; Cuenca, A.; Sørensen, J.; Alencar, A.L.F.; Christiansen, D.H.; Jacobsen, J.A.; Axen, C.; Lieffrig, F.; Ruane, N.M.; Martin, P.; et al. Presence and Genetic Variability of Piscine orthoreovirus Genotype 1 (PRV-1) in Wild Salmonids in Northern Europe and North Atlantic Ocean. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannimuthu, D.; Roh, H.J.; Morton, H.C.; Peñaranda, M.M.D.; Vossgård, A.; Hansen, T.; Fjelldal, P.G.; Karlsbakk, E.; Fiksdal, I.; Dahle, M.K.; et al. Experimental Transmission of Piscine Orthoreovirus-1 (PRV-1) in Different Life Stages of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) and Brown Trout (Salmo Trutta). Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1151577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Miwa, S.; Matsuyama, T.; Kiryu, I.; Honjo, M.; Sakai, T.; Matsuura, Y.; Yamasaki, M.; Kumagai, A.; Nakayasu, C. Clinical Symptoms and Histopathological Changes in Coho Salmon Affected by the Erythrocytic Inclusion Body Syndrome (EIBS) Are Caused by the Infection of Piscine orthoreovirus 2 (PRV-2). J. Fish Dis. 2024, 47, e13939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauta, P.R.; Nayak, B.; Das, S. Immune System and Immune Responses in Fish and Their Role in Comparative Immunity Study: A Model for Higher Organisms. Immunol. Lett. 2012, 148, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, S.K. The Innate Immune Response of Finfish—A Review of Current Knowledge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 23, 1127–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, D.M.; Zaccone, G.; Alesci, A.; Kuciel, M.; Hussein, M.T.; Sayed, R.K.A. Main Components of Fish Immunity: An Overview of the Fish Immune System. Fishes 2023, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Røsæg, M.V.; Lund, M.; Nyman, I.B.; Markussen, T.; Aspehaug, V.; Sindre, H.; Dahle, M.K.; Rimstad, E. Immunological Interactions between Piscine orthoreovirus and Salmonid Alphavirus Infections in Atlantic Salmon. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 64, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoulia, T.; Sundaram, A.Y.M.; Braaen, S.; Jørgensen, J.B.; Rimstad, E.; Wessel, Ø.; Dahle, M.K. Transcriptomics of Early Responses to Purified Piscine Orthoreovirus-1 in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) Red Blood Cells Compared to Non-Susceptible Cell Lines. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1359552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendramin, N.; Alencar, A.L.F.; Iburg, T.M.; Dahle, M.K.; Wessel, Ø.; Olsen, A.B.; Rimstad, E.; Olesen, N.J. Piscine orthoreovirus Infection in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Protects against Subsequent Challenge with Infectious Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus (Ihnv). Vet. Res. 2018, 49, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, L.H.; Dahle, M.K.; Wessel, Ø.; Timmerhaus, G.; Løvoll, M.; Røsæg, M.; Jørgensen, S.M.; Rimstad, E.; Krasnov, A. Differences in Gene Expression in Atlantic Salmon Parr and Smolt after Challenge with Piscine orthoreovirus (PRV). Mol. Immunol. 2016, 73, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Polinski, M.P.; Morrison, P.R.; Brauner, C.J.; Farrell, A.P.; Garver, K.A. High-Load Reovirus Infections Do Not Imply Physiological Impairment in Salmon. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.S.; Nyman, I.B.; Wessel, Ø.; Dahle, M.K.; Rimstad, E. Dynamics of Polarized Macrophages and Activated CD8+ Cells in Heart Tissue of Atlantic Salmon Infected With Piscine Orthoreovirus-1. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 729017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teige, L.H.; Lund, M.; Haatveit, H.M.; Røsæg, M.V.; Wessel, Ø.; Dahle, M.K.; Storset, A.K. A Bead Based Multiplex Immunoassay Detects Piscine orthoreovirus Specific Antibodies in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 63, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teige, L.H.; Kumar, S.; Johansen, G.M.; Wessel, Ø.; Vendramin, N.; Lund, M.; Rimstad, E.; Boysen, P.; Dahle, M.K. Detection of Salmonid IgM Specific to the Piscine orthoreovirus Outer Capsid Spike Protein Sigma 1 Using Lipid-Modified Antigens in a Bead-Based Antibody Detection Assay. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, T.; Takano, T.; Honjo, M.; Kikuta, T.; Nawata, A.; Kumagai, A.; Honda, R.; Sakai, T.; Kurita, J.; Terashima, S.; et al. Enhancement of Piscine Orthoreovirus-2 DNA Vaccine Potency by Linkage of Antigen Gene to a Trigger Factor Gene or Signal Peptide Genes. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, E.S.; Forrest, J.C.; Connolly, J.L.; Chappell, J.D.; Liu, Y.; Schnell, F.J.; Nusrat, A.; Parkos, C.A.; Dermody, T.S. Junction Adhesion Molecule Is a Receptor for Reovirus. Cell 2001, 104, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.W.K.; Hayes, E.C.; Joklik, W.K. Protein Σ1 Is the Reovirus Cell Attachment Protein. Virology 1981, 108, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, K.L.; Mann, M.A.; Fields, B.N.; Virgin, H.W. Protective Anti-Reovirus Monoclonal Antibodies and Their Effects on Viral Pathogenesis. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 3446–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preissler, S.; Deuerling, E. Ribosome-Associated Chaperones as Key Players in Proteostasis. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2012, 37, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Hackert, E.; Hendrickson, W.A. Promiscuous Substrate Recognition in Folding and Assembly Activities of the Trigger Factor Chaperone. Cell 2009, 138, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, J.; Peng, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Fan, D.; Xu, X. Human HSP70 and Modified HPV16 E7 Fusion DNA Vaccine Induces Enhanced Specific CD8+ T Cell Responses and Anti-Tumor Effects. Oncol. Rep. 2009, 22, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gül, A.; Erkunt Alak, S.; Can, H.; Karakavuk, M.; Korukluoğlu, G.; Altaş, A.B.; Gül, C.; Karakavuk, T.; Köseoğlu, A.E.; Ülbeği Polat, H.; et al. Immunogenicity and Protection Efficacy of a COVID-19 DNA Vaccine Encoding Spike Protein with D614G Mutation and Optimization of Large-Scale DNA Vaccine Production. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Fan, G.; Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Man, D.; Liu, S.; Tang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, W. Protective Effects of Membrane-Anchored and Secreted DNA Vaccines Encoding Fatty Acid-Binding Protein and Glutathione S-Transferase against Schistosoma Japonicum. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Torres, C.A.T.; Yang, K.; Mustafa, F.; Robinson, H.L. DNA Immunization: Effect of Secretion of DNA-Expressed Hemagglutinins on Antibody Responses. Vaccine 1999, 18, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatakis, D.; McMillan, M. The Signal Peptide Sequence Impacts the Immune Response Elicited by a DNA Epitope Vaccine. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 1776–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Middha, S.K.; Menon, S.V.; Paital, B.; Gokarn, S.; Nelli, M.; Rajanikanth, R.B.; Chandra, H.M.; Mugunthan, S.P.; Kantwa, S.M.; et al. Current Challenges of Vaccination in Fish Health Management. Animals 2024, 14, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salonius, K.; Simard, N.; Harland, R.; Ulmer, J.B. The Road to Licensure of a DNA Vaccine. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 8, 635. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, C.; Lorenzen, N.; Collet, B. DNA Vaccination for Finfish Aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 85, 106–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruffo, M.; Maturana, C.; Kambalapally, S.; Larenas, J.; Tobar, J.A. Protective Oral Vaccination against Infectious Salmon Anaemia Virus in Salmo salar. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 54, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evensen, Ø. Immunization Strategies against Piscirickettsia Salmonis Infections: Review of Vaccination Approaches and Modalities and Their Associated Immune Response Profiles. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haatveit, H.M.; Hodneland, K.; Braaen, S.; Hansen, E.F.; Nyman, I.B.; Dahle, M.K.; Frost, P.; Rimstad, E. DNA Vaccine Expressing the Non-Structural Proteins of Piscine orthoreovirus Delay the Kinetics of PRV Infection and Induces Moderate Protection against Heart -and Skeletal Muscle Inflammation in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar). Vaccine 2018, 36, 7599–7608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, Ø.; Haugland, Ø.; Rode, M.; Fredriksen, B.N.; Dahle, M.K.; Rimstad, E. Inactivated Piscine orthoreovirus Vaccine Protects against Heart and Skeletal Muscle Inflammation in Atlantic Salmon. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Hodneland, K.; Frost, P.; Hoeijmakers, M.; Rimstad, E. Salmonid Alphavirus-Based Replicon Vaccine against Infectious Salmon Anemia (ISA): Impact of Immunization Route and Interactions of the Replicon Vector. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 36, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, C.M.; Pemula, A.K.; Braaen, S.; Sankaran, K.; Rimstad, E. Salmonid Alphavirus Replicon Is Functional in Fish, Mammalian and Insect Cells and in Vivo in Shrimps (Litopenaeus vannamei). Vaccine 2013, 31, 5672–5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Hodneland, K.; Frost, P.; Braaen, S.; Rimstad, E. A Hemagglutinin-Esterase-Expressing Salmonid Alphavirus Replicon Protects Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) against Infectious Salmon Anemia (ISA). Vaccine 2013, 31, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, M.S.; Bjørgen, H.; Nyman, I.B.; Wessel, Ø.; Koppang, E.O.; Dahle, M.K.; Rimstad, E. PRV-1 Infected Macrophages in Melanized Focal Changes in White Muscle of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Correlates With a Pro-Inflammatory Environment. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 664624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas-Aravena, A.; Sandino, A.M.; Spencer, E. Nanoparticles and Microparticles of Polymers and Polysaccharides to Administer Fish Vaccines. Biol. Res. 2013, 46, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Challenge | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fish | Vaccine | Cohabitation | Direct Injection | Vaccine Effect | |||||||||||||||
| PRV Genotype | Fish Species | Fish Weight (g) | Vaccine Molecule | Vaccine Dose | Adjuvant | Route of Administration | Time Post Vaccination | Inoculum Origin | Viral Load | Injection Route | Shedders % | Injection | Viral Load | Viral Load | HSMI Effect | Specific Response | Innate Response | Extra Observations | Reference |
| 1 | Atlantic salmon | 30–40 | DNA encoding viral proteins cloned into pcDNA3 or a SAV replicon. | 10 μg | NU | IM | 6 weeks | Blood from Atlantic salmon infected with PRV-1. | NI | IP | 20 | NA | NA | The pcDNA3.1/uNS + σNS + σ1 vaccine reduces the viral load from week 4, reaching statistical significance at week 8. | Reduction of lesions at all time points (significant at 8 wpc); lesions were almost absent at 8 wpc in fish vaccinated with pcDNA3.1/uNS + σNS + σ1. The groups vaccinated with pSAV/uNS + μ1 + σ2 + λ1 + λ3, pSAV/uNS + μ1 + σ3 + λ2, pSAV/uNS + μ1 + σ2 + σ3 + λ1 + λ2 + λ3, pcDNA3.1/uNS + σNS + σ3, pcDNA3.1/uNS + σNS, and pcDNA3.1/uNS showed a slight, non-significant attenuation in the kinetics of histopathological lesions. | The pcDNA3 uNS + σNS + σ1 vaccine slightly induces CD8, granzyme, CD4, and IgM, with significance reached only for CD4. The pSAV/uNS + μ1 + μ2 + σ1 + σ2 + σ3 + λ1 + λ2 + λ3 vaccine increases CD8α (not significant). | All vaccines slightly induce IFNγ, RIG-I, Mx, PKR, ISG15, and Viperin. | [78] | |
| 2 | Coho salmon | 18 | DNA encoding σ1 with different sequences linked at the N- or C-terminus. | 10 μg | NU | IM | 35 days | filtrated kidney and spleen homogenate from infected coho salmon. ** | NA | IP | 1 × 108 copies/mL 1:10 PBS (100 ul) | Significant reduction in the spleen at day 19 in TF-σ1 group. Non-significant reduction at day 27 in Disp-σ1 and Sec-σ1 | NE | TF-σ1 stimulates significant antibody response at 35 dpi. Sec-σ1 and Disp-σ1 increase not significantly at 35 dpi | NE | Sec-σ1 significantly increased the hematocrit at 27 dpi. | [62] | ||
| 22 | DNA encoding σ1 with different sequences linked at the N- or C-terminus. | 100 ng | NU | Not significant reduction at day 18 in TF-σ1 group. | NE | TF-σ1 significantly stimulates antibody response at 35 dpi. | NE | ||||||||||||
| 22 | Formalin-inactivated PRV-2 | 5 × 109 copies/mL (100 uL) | Water in oil Montanide ISA 763AVG 1:1 | NE | NE | NE | NE | ||||||||||||
| 1 | Atlantic salmon | 55 | PRV purified from blood of Atlantic salmon with clinical HSMI, followed by plasma formalin inactivation. | 6 × 109 particles per fish (100 uL) | Water in oil | IP | 6 weeks | Pelleted blood obtained from two independent HSMI outbreaks. | NA | One inoculum was administered IP, and the other IM | Ct 13.7 (1.2 ul; IP), Ct 11 (11.7 ul; IM) | Decrease from weeks 2 to 10 in plasma, heart, and blood | Reduction of heart lesions at weeks 4, 7, and 10. | NE | NE | Reduced detection of σ1 protein in blood from weeks 2 to 10. | [79] | ||
| Ct 13.7 (1.2 ul; IP), Ct 11 (11.7 ul;IM) | One inoculum was administered intraperitoneally, and the other intramuscularly | NSP | NA | Significant reduction at 2 weeks in blood, plasma, and heart. | Significant reduction of heart lesions at 7 weeks. | NE | NE | Reduced detection of σ1 protein in blood at week 2 | |||||||||||
| 1 | Atlantic salmon | 41.3 | formalin-inactivated PRV-1 | 6 × 109 particles per fish (200 uL) * | Water in oil | IP | 10 weeks | Two inocula of pelleted blood from differents outbreaks | Ct 17.6 and 16.4 (per inoculum) | IP | NSP | NA | A slight delay in viral load in spleen and heart. | At 5 wpi, no lesions were observed compared to the unvaccinated control. At 8 wpi, lesions were reduced and detected in only six out of eight fish. | No enhancement of the humoral response compared to unvaccinated infected fish. | Increase in IFNγ and granzymes at 5 and 8 wpi, respectively. | [26] | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Espinoza, D.; Rivas-Aravena, A. Toward Effective Vaccines Against Piscine Orthoreovirus: Challenges and Current Strategies. Viruses 2025, 17, 1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101372
Espinoza D, Rivas-Aravena A. Toward Effective Vaccines Against Piscine Orthoreovirus: Challenges and Current Strategies. Viruses. 2025; 17(10):1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101372
Chicago/Turabian StyleEspinoza, Daniela, and Andrea Rivas-Aravena. 2025. "Toward Effective Vaccines Against Piscine Orthoreovirus: Challenges and Current Strategies" Viruses 17, no. 10: 1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101372
APA StyleEspinoza, D., & Rivas-Aravena, A. (2025). Toward Effective Vaccines Against Piscine Orthoreovirus: Challenges and Current Strategies. Viruses, 17(10), 1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101372






