Abstract
Echinocandin antifungal drugs, including micafungin, anidulafungin, and caspofungin, have been recently reported to exhibit antiviral effects against various viruses such as flavivirus, alphavirus, and coronavirus. In this study, we focused on micafungin and its derivatives and analyzed their antiviral activities against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The micafungin derivatives Mi-2 and Mi-5 showed higher antiviral activity than micafungin, with 50% maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 5.25 and 6.51 µM, respectively (3.8 to 4.7-fold stronger than micafungin) and 50% cytotoxic concentration (CC50) of >64 µM in VeroE6/TMPRSS2 cells. This high anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity was also conserved in human lung epithelial cell-derived Calu-3 cells. Micafungin, Mi-2, and Mi-5 were suggested to inhibit the intracellular virus replication process; additionally, these compounds were active against SARS-CoV-2 variants, including Delta (AY.122, hCoV-19/Japan/TY11-927/2021), Omicron (BA.1.18, hCoV-19/Japan/TY38-873/2021), a variant resistant to remdesivir (R10/E796G C799F), and a variant resistant to casirivimab/imdevimab antibody cocktail (E406W); thus, our results provide basic evidence for the potential use of micafungin derivatives for developing antiviral agents.
1. Introduction
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), remains a global public health emergency with more than 648 million infections and 6.6 million deaths as of December 2022 (https://covid19.who.int/, accessed on 10 December 2022). In the past 20 years, SARS-CoV, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus, and SARS-CoV-2 have emerged as novel human coronaviruses, which indicates the potential threat of this viral group. There are currently several US Food and Drug Administration-approved anti-COVID-19 agents, including antiviral agents such as remdesivir (RDV), molnupiravir, and nirmatrelvir. RDV and molnupiravir are nucleoside analogues that target viral polymerases and show broad-spectrum antiviral effects; they were developed as drug candidates against viruses including ebola virus, hepatitis C viruses, and respiratory syncytia virus, before the COVID-19 pandemic [1,2,3,4,5]. Continuous development and studies on these antiviral agents enabled the rapid and successful application of these agents for treatment of COVID-19 within two years of the pandemic; thus, the identification and analysis of new classes of antiviral agents are important for not only developing a drug against the current infectious disease but also for developing a rapid response for managing new emerging infectious diseases, which should be stressed given the probable outbreaks of emerging viral infections in the future.
Micafungin (MCFG), anidulafungin, and caspofungin, belonging to the echinocandin class of antifungal drugs, are inhibitors of fungal cell wall synthesis. Fungal cell walls are composed of β-(1,3)-glucan, β-(1,4)-glucan, β-(1,6)-glucan, α-glucan, chitin, mannan, and various glycoproteins, the quantity and relative content of which vary depending on fungal species [6,7]. Echinocandins inhibit cell wall biosynthesis via noncompetitive inhibition of the β-(1,3)-glucan synthase complex [6,7,8], which is absent in mammalian cells, thereby providing a drug target with a favorable safety profile. The echinocandins are semi-synthetic lipopeptides originating from natural compounds; the original compounds of MCFG, anidulafungin, and caspofungin are FR901379 (WF11899A) [9] from Coleophoma empetri, echinocandin B from Aspergillus nidulans var. echinulatus, and pneumocandin B0 from Glarea lozoyensis, respectively [6]. Recently, echinocandin antifungal drugs have been reported to exert antiviral effects on several viruses [7,10,11,12,13,14]; MCFG and anidulafungin have been reported to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection [15,16]. In the present study, we focused on MCFG and its derivatives (see Figure S1) and analyzed their antiviral activities against SARS-CoV-2 and its variants. Our data present the antiviral potential of MCFG and its derivatives. The MCFG derivatives Mi-2 and Mi-5 showed higher antiviral activity than that of MCFG and may be used to develop antiviral agents.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Compounds
MCFG, anidulafungin, and caspofungin were obtained from Selleck Biotech (Tokyo, Japan). The MCFG derivative Mi-4 (ASP9726) was chemically synthesized as previously reported [17] and patented [18], and other derivatives (Mi-1, Mi-2, Mi-3, Mi-5, and Mi-6) were similarly synthesized as described previously [18,19,20,21]. RDV and cepharanthine (CEP) were purchased from Chemscene (Monmouth Junction, NJ, USA) and Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA), respectively.
2.2. Cell Culture
VeroE6/TMPRSS2 cells (transmembrane serine protease 2,-overexpressing VeroE6 cells [22]) were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical, Osaka, Japan) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Sigma-Aldrich), 100 units/mL penicillin, 100 µg/mL streptomycin, 10 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), and 1 mg/mL G418 (Nacalai Tesque, Kyoto, Japan) at 37 °C in 5% CO2. During the infection assay, G418 was removed and 10% FBS in the medium was replaced with 2% FBS. Calu-3 cells (human-derived lung epithelial cell line) were cultured in Eagle’s minimum essential medium (Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical), supplemented with 10% FBS, 100 units/mL penicillin, 100 μg/mL streptomycin, 10 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), and 1% GlutaMAXTM supplement (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.3. Infection Assay
SARS-CoV-2 was handled at biosafety level 3. We used the SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan strain (2019-hCoV/Japan/TY/WK-521/2020, GISAID ID: EPI_ISL_408667), Delta variant AY.122 (hCoV-19/Japan/TY11-927/2021, GISAID ID: EPI_ISL_2158617), Omicron variant BA.1.18 (hCoV-19/Japan/TY38-873/2021, GISAID ID: EPI_ISL_7418017), an E406W variant that is resistant to casirivimab/imdevimab (REGN-COV2) antibody cocktail (the complete sequence was shown in Table S1) [23], and RDV-escape mutant R10/E796G C799F (GenBank ID: LC742929) [23,24]. VeroE6/TMPRSS2 cells were inoculated with the viruses at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.003 for 1 h and unbound viruses were removed by washing, as previously described [25,26]. Cells were cultured for an additional 24 h and the extracellular viral RNA was quantified via real-time reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis. Compounds were added both during the virus inoculation (1 h) and after washing the inoculum (24 h), and 10 µM RDV was used as a positive control in these assays (see Figures S2A and S3A–D). In this experimental condition, nearly 100% population of cells was SARS-CoV-2 positive at 24 h post-inoculation [26,27].
The time-of-addition analysis was performed by adding compounds at three different time points to VeroE6/TMPRSS2 cells that were inoculated with SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan strain at an MOI of 0.1 (see Figure 1A): (a, whole life cycle, gray) present during the 1 h virus inoculation and maintained throughout the 24 h infection period; (b, entry, blue) treated during the 1 h virus inoculation and for an additional 2 h and then removed; (c, post-entry, green) added at 2 h after virus inoculation and treated for the remaining 22 h until harvest. Remdesivir and cepharanthine were used as positive controls for a replication and an entry inhibitor, respectively, as reported [28,29].
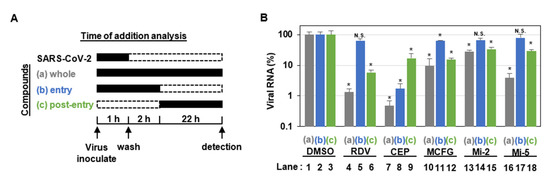
Figure 1.
MCFG and its derivatives inhibited the post-entry process of SARS-CoV-2. (A) Schematic representation of the time-of-addition analysis. Compounds were added at three different times: (a) whole: throughout the assay for 25 h, (b) entry: for the initial 3 h to evaluate the effect on the viral entry process, and (c) post-entry: for the last 22 h to evaluate the effect on viral replication/re-infection. (B) Extracellular viral RNA concentration of the cells treated as shown in (A) was quantified via real-time RT-PCR. The cells were treated with either 5 µM RDV, 3 µM CEP, 50 µM MCFG, 8 µM Mi-2, or 8 µM Mi-5 under the three experimental conditions (a–c), as shown in (A). These data were from hexaplicate experiments in DMSO and triplicate experiments in samples are presented as average values with error bars indicating standard deviation. * p < 0.05 vs. DMSO; N.S., not significant; with Mann–Whitney U test. RDV, remdesivir; CEP, cepharanthine; MCFG, micafungin; and DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide.
The Calu-3 cell infection assay was performed by inoculating the Wuhan strain for 3 h and incubating for an additional 21 h after which the extracellular viral RNA concentration was measured and 10 µM RDV was used as a positive control in the assay (see Figure S2C).
2.4. Quantification of Viral RNA
Viral RNA in the culture supernatant was extracted using a MagMAX Viral/Pathogen II Nucleic Acid Isolation kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and quantified via real-time RT-PCR analysis using a one-step quantitative RT-PCR kit (Thunderbird Probe One-step qRT-PCR kit; Toyobo, Osaka, Japan) using the SARS-CoV-2-specific primers (Forward: 5′-ACAGGTACGTTAATAGTTAATAGCGT-3′, Reverse: 5′-ATATTGCAGCAGTACGCACACA-3′) and probe (5′-FAM-ACACTAGCCATCCTTACTGCGCTTCG-TAMRA-3′) [30]. The quantification of viral RNA was calculated by ∆∆Ct methods [31].
2.5. Cell Viability
Cell viability was measured via a cytotoxicity assay using cell-counting kit-8 (Dojindo laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan) according to the manufacturer’s instructions (see Figure S2B,D). This examination evaluates the cellular dehydrogenase activities by treating tetrazolium salt, WST-8, which is reduced under dehydrogenase to produce a yellow formazan dye. VeroE6/TMPRSS2 and Calu-3 cells cultured for 24 h with the tested compounds were evaluated by this assay.
2.6. Calculation of IC50, IC90, IC99, and CC50
Inhibitory concentrations of 50, 90, and 99% maximum as well as 50% maximal cytotoxic concentration (IC50, IC90, IC99, and CC50) of each compound were determined from a regression line [Y = AX + B] of two values that sandwich 50, 90, or 99% inhibition at compound concentration (X) and inhibition value (Y). X (IC50, IC90, IC99, and CC50 values) was calculated when Y in the regression line was substituted with 50, 90, or 99.
2.7. Statistics
Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 9 software, and significance was determined using a non-parametric test (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01; N.S., not significant).
3. Results
3.1. MCFG and Its Derivatives Show Antiviral Activity against SARS-CoV-2 Infections
We used MCFG, anidulafungin, and caspofungin as approved echinocandin antifungal agents (see Figure S1) to evaluate anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity in a cell culture infection model [29]. Figure S2A,B show the viral RNA levels and cell viabilities, respectively, upon treatment with different concentrations of compounds. The IC50, IC90, IC99, and CC50 were calculated and are shown in Figure S2. MCFG and anidulafungin, among the three approved echinocandin antifungal agents, reduced the viral RNA levels in a dose-dependent manner (IC50 = 26.1 and 7.09 µM, respectively), while caspofungin did not show any antiviral effect up to a concentration of 64 µM (see Figure S2A). The cell viability assay showed a dose-dependent cytotoxicity of anidulafungin (CC50 = 24.6 µM) (see Figure S2B). Since anidulafungin had a narrow window between anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity and cytotoxicity, we focused on MCFG and synthesized derivatives. We synthesized six MCFG derivatives, Mi-1, Mi-2, Mi-3, Mi-4, Mi-5, and Mi-6 by changing the side chains of MCFG (see Materials and Methods, and Figure S1). In the SARS-CoV-2 infection assay, Mi-1, Mi-2, Mi-3, Mi-4, and Mi-5 reduced the viral RNA concentration without apparent cytotoxicity, while Mi-6 had no effect on viral RNA levels up to 64 µM (see Figure S2A,B). Among them, Mi-2 and Mi-5 showed lower IC50s than that of MCFG (IC50 = 5.25 and 6.51 µM, respectively; 3.8 to 4.7-fold lower than MCFG), but no remarkable reduction in cell viability (see Figure S2A,B); further, in Calu-3 cells, Mi-2 and Mi-5 showed stronger antiviral activity than MCFG (see Figure S2C, IC50 = 55.3, 10.1, and 5.71 µM for MCFG, Mi-2, and Mi-5, respectively), but with a detectable toxicity for Mi-5 (see Figure S2D, CC50 = 48.5 µM) (see Table 1); thus, we produced new derivatives of MCFG that have higher antiviral potencies.

Table 1.
The IC50 and CC50 of Micafungin and its derivatives against a SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan strain.
3.2. MCFG and Its Derivatives Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Replication
To determine the stages in the SARS-CoV-2 life cycle inhibited by MCFG, Mi-2, and Mi-5, we performed a time-of-addition assay in which antiviral activities were evaluated after treatment with the compounds at three different times (see Figure 1A, a–c). In this assay, RDV, a reported SARS-CoV-2 replication inhibitor [32], was used as a positive control and showed no inhibitory effect when added at the virus entry phase (see Figure 1B, lane 5), but showed remarkable antiviral activity at the post-entry phase (see Figure 1B, lane 6). We also confirmed the mode of action of CEP, a SARS-CoV-2 entry inhibitor that inhibits SARS-CoV-2 particle binding to cells [29], based on considerable inhibition of the virus entry phase (see Figure 1B, lane 8) as well as a lower viral activity at post-entry phase. This is likely to be obtained by inhibition of multiple rounds of viral re-infection (see Figure 1B, lane 9) [29]. In this assay, Mi-2 and Mi-5 clearly reduced viral RNA levels when added during the whole life cycle and the post-entry phase, but exhibited no inhibitory effect on the virus entry phase, similar to the effects of RDV (see Figure 1B, lanes 10–18). These data suggest that MCFG, Mi-2, and Mi-5 target virus replication, rather than the process for viral entry.
3.3. Antiviral Activity of MCFG and Its Derivatives against SARS-CoV-2 Variants
We further examined whether MCFG, Mi-2, and Mi-5 were effective against SARS-CoV-2 variants (see Figure S3). MCFG, Mi-2, and Mi-5 were effective in reducing viral RNA concentrations of Delta (IC50 = 11.8, <2, and <2 µM, respectively), Omicron (IC50 = 55.9, 13.0, and 7.56 µM, respectively), E406W (IC50 = 21.7, <2, and 4.48 µM, respectively), and R10/E796G C799F (IC50 = 31.3, 9.67, and 7.22 µM, respectively) (see Table 2). These data indicated that MCFG, Mi-2, and Mi-5 have wide antiviral effects on multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants, and Mi-2 and Mi-5 showed stronger antiviral activities than MCFG against all SARS-CoV-2 variants examined.

Table 2.
The IC50 against SARS-CoV-2 variants.
4. Discussion
Echinocandin antifungal drugs have been reported to show antiviral activities against multiple viruses. Kim et al. reported that MCFG inhibits Enterovirus 71 (EV71) infection in the first study describing the antiviral activity of an echinocandin compound [10]. This study suggested that MCFG targets virus replication and reported an estimated IC50 of 5–8 µM to a luciferase carrying EV71 replicon in Vero cells and weaker antiviral activity against coxsackievirus group B type 3-infected Hela cells and human rhinovirus-infected H1HeLa cells [10]. Recently, Ho et al. reported that MCFG inhibits the infection of Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) using U2OS or BHK-21 cells [11], Dengue virus serotype 2 (DENV-2) in Vero cells [12], and Zika virus (ZIKV) in Vero cells [14] (IC50 = 20.63, 10.23, and 7.35 µM, respectively). They also reported that anidulafungin inhibits DENV-2 [12] and ZIKV infections [14] (IC50 = 3.24 and 2.08 µM, respectively) and that caspofungin inhibits DENV-2 [12] and ZIKV [14] infections in the parallel infection assays (IC50 = 20.78 and 75.75 µM, respectively). MCFG and anidulafungin have also been reported to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection in Vero cells with IC50 = 5.5–12.9 µM [15] and 4.64 µM [16], respectively, consistent with the anti-SARS-CoV-2 activities shown in the present study (see Figure S2A and Table 1). Regarding the target of antiviral action of these echinocandin drugs, MCFG inhibits the replication of CHIKV [11] and the entry of DENV-2 [12], while anidulafungin inhibits ZIKV entry [14], which is mainly demonstrated in time-of-addition assays; also, MCFG was reported to inhibit the helicase enzymatic activity of DENV-2 in vitro (IC50 = 4.98 µM) [13], in addition to its anti-DENV entry activity [12], speculating that MCFG may potentially have multiple targets for antiviral activity. In a structural computer modeling of SARS-CoV-2 proteins, MCFG has been predicted to interact with 3CLpro [33,34] and was shown to inhibit 3CLpro enzymatic activity in vitro (IC50 = 47.63 µM) [33]. It should be clarified whether 3CLpro is an actual target for MCFG, Mi-2, and Mi-5 in the future. Additionally, anidulafungin inhibits angiotensin converting enzyme 2-spike protein interaction in SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus entry assay [35]; thus, MCFG and the related echinocandins may have multiple targets as broad-spectrum antiviral agents. Given the possible reduced efficacy of antiviral activity against emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants, development of additional anti-SARS-CoV-2 drugs with new mode of action is demanded. Identification of the target molecule of MCFG and its derivatives would be needed in the future.
In this study, we summarized the structure–activity relationship of the MCFG derivatives in Figure 2. Comparison of MCFG (IC50 = 26.1 µM), Mi-5 (IC50 = 6.51 µM), and Mi-6 (IC50 > 64 µM), which share the same basic skeleton, R2, and R3 with different structure in R1, indicated the importance of the R1 structure for anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity. Since Mi-2, Mi-5, Mi-4, and Mi-1 had higher anti-SARS-CoV-2 activities than that of MCFG, replacement of the R1 moiety of MCFG with structures containing two six-membered rings (cyclohexane, piperidine, or piperazine) might increase its activity. By comparing Mi-2 and Mi-4 that have identical R2 and similar R1, the SO3H group in R3 seems preferable for high anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity. Further derivative analysis based on the aforementioned structure–activity relationship is expected to yield more potent antiviral compounds.
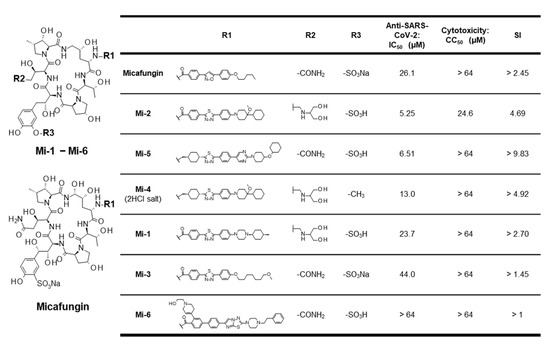
Figure 2.
Structure–activity relationship of micafungin derivatives with anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity, cytotoxicity, and selectivity index (SI = CC50/IC50) observed in VeroE6/TMPRSS2 cells. The base structure (left) and the moieties at R1, R2, and R3 (right) are shown.
The pharmacokinetics of MCFG for human adults indicate that the Cmax and half-life are, reportedly, 7.2 mg/L (5.67 µM) and 11–17 h upon administration at 100 mg daily, respectively; 100 mg/d is the approved dose for anti-fungal treatment [7]. The exposure concentration of MCFG in serum in treated adults is lower than the anti-SARS-CoV-2 IC50 calculated in this study, but that in the human lung has not been well determined. In addition, the pharmacokinetics profiles of the MCFG derivatives are needed to predict the antiviral potency in an in vivo setting. Further development of MCFG derivatives may be useful not only for developing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drugs but also as broad-spectrum antiviral drugs, which are helpful for developing a rapid response to probable new virus pandemics in the future.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/v15020452/s1, Figure S1: Chemical structures of micafungin, caspofungin, anidulafungin, and the micafungin derivatives; Figure S2: Anti-SARS-CoV-2 activities of micafungin and its derivatives; Figure S3: Activities of micafungin and its derivatives against SARS-CoV-2 variants; Table S1: The complete sequence of SARS-CoV-2 E406W variant.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.N. and K.W.; investigation, S.N., H.O. and K.W.; analysis, S.N., H.O., D.A., S.T., R.S., T.F. and K.W.; resources, S.T., R.S. and T.F.; writing—original draft preparation, S.N. and K.W.; supervision, K.W.; and funding acquisition, K.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) (JP21fk0108589, JP22fk0310504, JP22jm0210068, and JP22wm0325007), the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI (JP20H03499, JP20K16267, and JP21H02449), JST MIRAI program (JPMJMI22G1), and the Takeda Science Foundation.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Astellas Pharma Inc. for providing micafungin derivatives (six compounds, including Mi-1 to Mi-6). VeroE6/TMPRSS2 cells were kindly provided by Makoto Takeda at the University of Tokyo Graduate School of Medicine. We are grateful for the isolation of the SARS-CoV-2 clinical strains performed by the Department of Virology I, the Department of Veterinary Science, Center for Influenza and Respiratory Virus Research, and the Department of Pathology at the National Institute of Infectious Diseases.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Siegel, D.; Hui, H.C.; Doerffler, E.; Clarke, M.O.; Chun, K.; Zhang, L.; Neville, S.; Carra, E.; Lew, W.; Ross, B.; et al. Discovery and Synthesis of a Phosphoramidate Prodrug of a Pyrrolo[2,1-f][triazin-4-amino] Adenine C-Nucleoside (GS-5734) for the Treatment of Ebola and Emerging Viruses. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1648–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, T.K.; Jordan, R.; Lo, M.K.; Ray, A.S.; Mackman, R.L.; Soloveva, V.; Siegel, D.; Perron, M.; Bannister, R.; Hui, H.C.; et al. Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys. Nature 2016, 531, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheahan, T.P.; Sims, A.C.; Graham, R.L.; Menachery, V.D.; Gralinski, L.E.; Case, J.B.; Leist, S.R.; Pyrc, K.; Feng, J.Y.; Trantcheva, I.; et al. Broad-spectrum antiviral GS-5734 inhibits both epidemic and zoonotic coronaviruses. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Pang, Z.; Li, M.; Lou, F.; An, X.; Zhu, S.; Song, L.; Tong, Y.; Fan, H.; Fan, J. Molnupiravir and Its Antiviral Activity Against COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 855496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardo, J.; Shukla, A.M.; Chamarthi, G.; Gupte, A. The journey of remdesivir: From Ebola to COVID-19. Drugs Context 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, S. Micafungin: A sulfated echinocandin. J. Antibiot. 2009, 62, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymanski, M.; Chmielewska, S.; Czyzewska, U.; Malinowska, M.; Tylicki, A. Echinocandins–structure, mechanism of action and use in antifungal therapy. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2022, 37, 876–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Zapata, D.; Petraitiene, R.; Petraitis, V. Echinocandins: The Expanding Antifungal Armamentarium. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61 (Suppl. 6), S604–S611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, T.; Fujie, A.; Sakamoto, K.; Tsurumi, Y.; Shigematsu, N.; Yamashita, M.; Hashimoto, S.; Okuhara, M.; Kohsaka, M. WF11899A, B and C, novel antifungal lipopeptides. I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and physico-chemical properties. J. Antibiot. 1994, 47, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Kang, H.; Kim, D.E.; Song, J.H.; Choi, M.; Kang, M.; Lee, K.; Kim, H.S.; Shin, J.S.; Jeong, H.; et al. Antiviral activity of micafungin against enterovirus 71. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.J.; Liu, F.C.; Yeh, C.T.; Yang, C.M.; Lin, C.C.; Lin, T.Y.; Hsieh, P.S.; Hu, M.K.; Gong, Z.; Lu, J.W. Micafungin is a novel anti-viral agent of chikungunya virus through multiple mechanisms. Antivir. Res. 2018, 159, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Lu, J.W.; Yeh, C.T.; Lin, T.Y.; Liu, F.C.; Ho, Y.J. Micafungin Inhibits Dengue Virus Infection through the Disruption of Virus Binding, Entry, and Stability. Pharmacy 2021, 14, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Park, S.-J.; Park, J.; Shin, H.; Jang, Y.-S.; Woo, J.-S.; Min, D.-H. Identification of a Direct-Acting Antiviral Agent Targeting RNA Helicase via a Graphene Oxide Nanobiosensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 25715–25726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.W.; Chen, Y.C.; Huang, C.K.; Lin, K.C.; Ho, Y.J. Synergistic in-vitro antiviral effects of combination treatment using anidulafungin and T-1105 against Zika virus infection. Antivir. Res. 2021, 195, 105188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, K.B.; Shin, H.J.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, B.T.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, C. Repurposing Screens of FDA-Approved Drugs Identify 29 Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 1843–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.; Ko, M.; Lee, J.; Choi, I.; Byun, S.Y.; Park, S.; Shum, D.; Kim, S. Identification of Antiviral Drug Candidates against SARS-CoV-2 from FDA-Approved Drugs. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e00819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, H.; Tomishima, M.; Kayakiri, N.; Araki, T.; Barrett, D.; Akamatsu, S.; Matsumoto, S.; Uchida, S.; Nakai, T.; Takeda, S.; et al. Synthesis and antifungal activity of ASP9726, a novel echinocandin with potent Aspergillus hyphal growth inhibition. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 1172–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomishima, M.; Morikawa, H.; Makino, T.; Imanishi, M.; Kayakiri, N.; Asano, T.; Araki, T.; Nakagawa, T. Polypeptide Compound. WO 2009/057568, 7 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Toda, A.; Matsuya, T.; Mizuno, H.; Matsuda, H.; Murano, K.; Barrett, D.; Ogino, T.; Matsuda, K. Cyclic Hexapeptide Derivatives. PCT Patent WO 01/60846, 23 August 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kayakiri, N.; Araki, T.; Makino, T.; Tomishima, M.; Harayama, Y.; Tanabe, D.; Tojo, T.; Nagai, Y. Polypeptide Compound. WO 2012/115159, 30 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ohki, H.; Murano, K.; Tojo, T.; Shiraishi, N.; Matsuya, T.; Matsuda, H.; Mizuno, H.; Barrett, D.; Matsuda, K.; Kawabata, K. New Compound. WO 99/40108, 12 August 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama, S.; Nao, N.; Shirato, K.; Kawase, M.; Saito, S.; Takayama, I.; Nagata, N.; Sekizuka, T.; Katoh, H.; Kato, F.; et al. Enhanced isolation of SARS-CoV-2 by TMPRSS2-expressing cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 7001–7003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, G.; Nakajima, S.; Watashi, K.; Torii, S.; Suzuki, R.; Fukuhara, T.; Ohoka, N.; Inoue, T.; Demizu, Y. Antiviral activity of ciclesonide acetal derivatives blocking SARS-CoV-2 RNA replication. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 149, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torii, S.; Kim, K.S.; Koseki, J.; Suzuki, R.; Iwanami, S.; Fujita, Y.; Jeong, Y.D.; Matsuura, Y.; Shimamura, T.; Iwami, S.; et al. Characterization of various remdesivir-resistant mutations of SARS-CoV-2 by mathematical modeling and molecular dynamics simulation. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, H.; Hishiki, T.; Akazawa, D.; Kim, K.S.; Woo, J.; Shionoya, K.; Tsuchimoto, K.; Iwanami, S.; Moriyama, S.; Kinoshita, H.; et al. Different efficacies of neutralizing antibodies and antiviral drugs on SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants, BA.1 and BA.2. Antivir. Res. 2022, 205, 105372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saso, W.; Yamasaki, M.; Nakakita, S.I.; Fukushi, S.; Tsuchimoto, K.; Watanabe, N.; Sriwilaijaroen, N.; Kanie, O.; Muramatsu, M.; Takahashi, Y.; et al. Significant role of host sialylated glycans in the infection and spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, H.; Wang, F.; Stappenbeck, F.; Tsuchimoto, K.; Kobayashi, C.; Saso, W.; Kataoka, M.; Yamasaki, M.; Kuramochi, K.; Muramatsu, M.; et al. Identification of Anti-Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Related Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Oxysterol Derivatives In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Mao, C.; Luan, X.; Shen, D.D.; Shen, Q.; Su, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, W.; Gao, M.; et al. Structural basis for inhibition of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from SARS-CoV-2 by remdesivir. Science 2020, 368, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, H.; Watashi, K.; Saso, W.; Shionoya, K.; Iwanami, S.; Hirokawa, T.; Shirai, T.; Kanaya, S.; Ito, Y.; Kim, K.S.; et al. Potential anti-COVID-19 agents, cepharanthine and nelfinavir, and their usage for combination treatment. iScience 2021, 24, 102367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.; Bleicker, T.; Brunink, S.; Schneider, J.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokic, G.; Hillen, H.S.; Tegunov, D.; Dienemann, C.; Seitz, F.; Schmitzova, J.; Farnung, L.; Siewert, A.; Hobartner, C.; Cramer, P. Mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 polymerase stalling by remdesivir. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mody, V.; Ho, J.; Wills, S.; Mawri, A.; Lawson, L.; Ebert, M.; Fortin, G.M.; Rayalam, S.; Taval, S. Identification of 3-chymotrypsin like protease (3CLPro) inhibitors as potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergoten, G.; Bailly, C. In silico analysis of echinocandins binding to the main proteases of coronaviruses PEDV (3CL(pro)) and SARS-CoV-2 (M(pro)). Silico Pharm. 2021, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahamad, S.; Ali, H.; Secco, I.; Giacca, M.; Gupta, D. Anti-Fungal Drug Anidulafungin Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Induced Syncytia Formation by Targeting ACE2-Spike Protein Interaction. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 866474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).