Abstract
Few studies have shown the presence of norovirus (NoV) RNA in blood circulation but there is no data on norovirus antigenemia. We examined both antigenemia and RNAemia from the sera of children with NoV infections and studied whether norovirus antigenemia is correlated with the levels of norovirus-specific antibodies and clinical severity of gastroenteritis. Both stool and serum samples were collected from 63 children admitted to Mie National Hospital with acute NoV gastroenteritis. Norovirus antigen and RNA were detected in sera by ELISA and real-time RT-PCR, respectively. NoV antigenemia was found in 54.8% (34/62) and RNAemia in 14.3% (9/63) of sera samples. Antigenemia was more common in the younger age group (0–2 years) than in the older age groups, and most patients were male. There was no correlation between stool viral load and norovirus antigen (NoV-Ag) levels (rs = −0.063; Cl −0.3150 to 0.1967; p = 0.6251). Higher levels of acute norovirus-specific IgG serum antibodies resulted in a lower antigenemia OD value (n = 61; r = −0.4258; CI −0.62 to −0.19; p = 0.0006). Norovirus antigenemia occurred more commonly in children under 2 years of age with NoV-associated acute gastroenteritis. The occurrence of antigenemia was not correlated with stool viral load or disease severity.
1. Introduction
Norovirus (NoV) is one of the leading causes of acute gastroenteritis (AGE) globally, causing both community-acquired and healthcare-associated outbreaks [1]. Noroviruses are single-stranded RNA viruses that are classified into ten genogroups (GI–GX) [2]. GI and GII have been implicated in most human infections [3]. For more than a decade, GII.4 has remained the predominant strain associated with major outbreaks worldwide [4]. Studies have shown that GII.4-associated diseases are accompanied by more severe symptoms compared with other genotypes [5].
The modes of transmission for norovirus are through the fecal–oral route, via direct person-to-person transmission, and through contaminated food or water. All age ranges are affected, with children experiencing the highest incidence. Severe outcomes, including hospitalization and death, occur primarily in children and the elderly [3,6]. The prevalence of NoV seropositivity increases rapidly before the age of 5 years, when the majority of the population has been exposed to the virus [7].
Norovirus virus-like particles (NoV VLPs) are used for studying immune responses against NoV. The expression of the norovirus capsid VP1 protein results in the formation of VLPs that are morphologically and antigenically similar to its endemic virions [8].
Norovirus is shed from infected cells into the intestinal lumen, but NoV-RNA can also be detected in serum and cerebrospinal fluid [6]. Improvements in methods for detecting norovirus have led to numerous reports of extraintestinal manifestations, other than gastroenteritis associated with NoV [9,10,11].
While viral gastroenteritis is generally confined to the intestines, rotavirus and norovirus can result in antigenemia and the presence of nucleic acid in the blood of ill patients without any extraintestinal infections [12,13]. Few studies have focused on norovirus RNA and we were unable to find any studies on antigenemia let alone its importance. In this study, we sought to determine whether the levels of NoV antigen in serum are correlated with the levels of norovirus-specific antibodies and clinical severity in NoV antigenemia patients. In addition, cross-reactivity of NoV antibodies between the predominant GII.4 and GII.17 Kawasaki 308 (predominant in winter 2014–2015) genotypes was investigated.
The determination of cross-reactivity allowed ascertaining whether patients may have pre-existing antibodies resulting from a strain that was predominant in the past.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
The study was conducted at Mie National Hospital, Tsu, Japan, from November 2018 to March 2021. Beginning in November 2018, stool and serum samples for clinical assessment were taken from hospitalized patients suspected of acute gastroenteritis, stored at −80 °C, and later tested for norovirus after receiving informed consent. From the stored samples, we detected NoV from stool specimens of 293 cases of acute gastroenteritis; of these, 63 NoV cases had both stool and serum samples available for use in this study (Figure S1). Moreover, cases were identified in the database, and their clinical information was extracted from the electronic medical chart system by a supervising clinician and confirmed for clinical cases. This included children between the ages of 0 years to 18 years. The study protocol was approved by the Ethical Review Board of Mie National Hospital (12/2020). As part of the clinical assessment, rotavirus and adenovirus were tested using the rapid antigen test kit [14]. In cases negative for enteric viruses, a stool culture was also performed for enteric pathogens.
2.2. Norovirus Detection in Stool and Serum
Viral RNA was extracted using the QIAamp® Viral RNA Minikit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Complementary DNA (cDNA) synthesis was conducted using SuperScript II Reverse Transcriptase for real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) (Table S2). For the detection of norovirus GI, primers COG1F and COG1R and probes RING1-TP(a) and RING1-TP(b) were used. For NoV GII, primers COG2F/ALPF and COG2R and probe RING2AL-Tb [15] were used in a StepOnePlus™ real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystem, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Foster City, California, CA, USA). The viral load was estimated in terms of PCR cycle threshold CT at which the amplicon was detected.
2.3. Norovirus Genomic Amplification and Genotyping
To analyze the genotype of the detected noroviruses, the capsid region C of ORF2 was amplified using the primer sets COG2F/G2SKR (first round) and G2SKF/G2SKR (second round), generating amplicons of ~387 and ~344 bp, respectively, for NoV GII [16]. For NoV GI, primers COG1F/G1SKR (first round) and G1SKF/G1SKR (second round) generated amplicons of ~381 and ~330 bp, respectively, all in a semi-nested PCR. In addition, we used the MON431/G2SKR that targets the ORF1/2 junction (~570 bp) in a single reaction. PCR was carried out using the TaKaRa Ex Taq® Hot Start Version. The PCR conditions were as follows: 94 °C for 3 min; 40 cycles of PCR at 94 °C for 30 s, 55 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 1 min; and a final incubation at 72 °C for 15 min. After amplification, the PCR products were visualized by gel electrophoresis. Positive norovirus samples were prepared as DNA and primer premixed templates and sent to Eurofins genomics for sequencing (Eurofins Genomics Co., Ltd., Ota City, Tokyo).
2.4. Detection of Norovirus Antigen in Serum
Norovirus antigen was detected in serum using the commercial Human Norovirus Antigen ELISA kit (MyBioresource, San Diego, Southern California, CA, USA), according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.5. Serum Antibody ELISA
Norovirus virus-like particles (VLPs) were used as antigens. The GII.4 VLP and GII.17 VLP were kindly provided by Prof. Kazuhiko Kaytayama, Kitasato University, in a baculovirus expression system as described by Hansman et al. [17]. These VLPs were produced by a recombinant baculovirus expression system using the GII.4 Sydney 2012 variant named Ni 1315 and GII.17 Kawasaki-308 (accession number LC037415). Briefly, the GII.4 Ni1315 strain capsid VP1 sequence originated from a patient sample collected in 2013 in Niigata Prefecture, Japan. A recombinant NoV VP1 capsid protein was expressed in the insect cell line High Five cells (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, California, CA, USA), and VLPs secreted into the cell medium were collected by ultracentrifugation at 100,000× g in an SW32 rotor (Beckman, Palo Alto, California, CA, USA). VLPs were purified by CsCl equilibrium gradient ultracentrifugation. Purified VLPs were applied to a carbon-coated electron microscopy grid, stained with 2% uranyl acetate, and examined and their identity verified by electron microscopy. Sera were tested for anti-GII.4 and anti-GII.17 IgG by ELISA, as previously described in [18,19], with some modifications. Serum samples were diluted two-fold starting at 1:100 and plated on GII.4 Ni 1315 and GII.17 Kawasaki-308 VLP-coated (0.1 μg/mL and 0.5 μg/mL phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)) 96-well half-area microtiter plates blocked with 5% skimmed milk. One known positive sample and one known negative sample (5% skimmed milk in PBS-T) were included in every plate as controls. Serum dilutions were incubated on the plates for 1 h at room temperature. The bound antibodies were detected with goat anti-human IgG-HRP (Invitrogen, California, CA, USA), followed by a KPL TMB 2-component microwell peroxidase substrate system; reactions were stopped with 1 N hydrochloric acid. All washes were performed with 0.1% Tween 20 in 1× phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). The optical density (OD) was measured at 450 nm using the victor2 1420 Multilabel counter (Wallac, Perkin Elmer, Turku, Finland) plate reader. The cut-off value was determined as two or three times the background signal.
2.6. Phylogenetic Analyses
Using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) available on the NCBI website (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, accessed on 1 December 2021), reference sequences for phylogenetic analysis were retrieved. Multiple sequence alignment was carried out in Bioedit and MEGA-X software, and the best-fit nucleotide sequence substitution model was determined using MEGA-X software [20]. Phylogenetic trees were constructed using the Maximum Likelihood algorithm with 1000 bootstrap replicates and a General Time Reversible plus Invariant site (GTR + I). Sequences derived in this study were deposited in GenBank under the accession numbers OK103809-OK103830, OK103833-OK103836, and OK103839-OK103840.
2.7. Statistical Analyses
All data were entered into Microsoft Access and Excel Windows Version 2020 (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA), and analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 9 and IBM SPSS 27. Differences between groups were analyzed using Fisher’s exact test (two-tailed) for categorical variables and Kruskal–Wallis test for differences in the antibody OD between the age groups. The Spearman correlation coefficient was used to determine the correlation between GII.4-specific antibodies and the serum antigen OD as well as the correlation between NoV-positive stool and antigenemia. Statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Detection of Norovirus RNA and Antigen in Serum
A total of 63 paired stool and serum samples were obtained from children reporting to the pediatric ward of Mie National Hospital with acute gastroenteritis. Of the 63 samples tested, the serum of one sample was completely exhausted after detection of NoV-RNA. Norovirus antigens (NoV antigenemia) were detected in 54.8% (34/62) by ELISA, whereas NoV-RNAs were detected in 14.3% (9/63) after RT-qPCR. Of the nine positive serum samples, five cases were not sequenced due to their low cDNA concentration.
There was also the presence of concomitant infection between norovirus and other pathogens (Table S1).
Estimation of NoV-RNA
The mean Ct values detected in the stool sample of patients with NoV-positive and -negative sera were 24.37 (range 18.9–39.8) and 26.78 (range 16–40.8), respectively. This difference was, however, not statistically significant (Figure 1A) (p = 0.4991). As demonstrated in (Figure 1B), there was no correlation between the stool viral load and norovirus antigen (NoV-Ag) levels expressed as optical densities (rs = −0.063; Cl −0.3150 to 0.1967; p = 0.6251, n = 62).
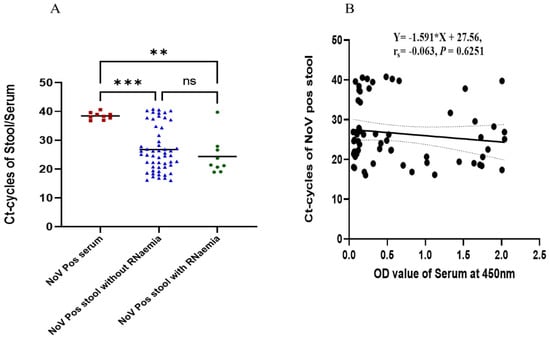
Figure 1.
Viral load estimation from RT-qPCR and its correlation with NoV-Ag levels in serum and stool samples. (A) The red square dots represent positive serum samples, the dotted blue triangles represent positive stool samples without RNA present in their serum, and the circular green dots represent positive stool samples with RNA present in the serum. (B) Correlation between positive stool and antigenemia based on serum OD at 450 nm. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
3.2. Clinical Features of NoV-Positive Cases
The age distribution of NoV-positive cases is shown in Table 1. Antigenemia was more often present in the younger age group (0–2 years) compared with the older age groups, and the majority of patients were males. There were no differences between the patients with antigenemia and patients without antigenemia with respect to the number of diarrheal stools, diarrhea duration and vomiting episodes. There was also no difference in transaminase levels, but CRP levels were higher in patients without antigenemia (Table 1). Children with NoV-Ag (as detected in serum) did not have more severe norovirus gastroenteritis episodes than those without NoV-Ag (Table 1).

Table 1.
Demographics and clinical features of children with/without the NoV-antigen in serum.
3.3. Responses Due to Pre-Existing NoV Antibodies
NoV-VLP-specific IgG antibody titration curves for sera from patients with acute infection are shown in Figure 2. Most of those infected with GII.4 Sydney/2012 (50.8%) had a high GII.4 Ni 1315 specific endpoint titer of ≤12,800 (Figure 2A), and all endpoint titers were ≤1,638,400. The same result was observed in those infected with other GII genotypes (GII.3, GII.2) as well as the G1.2 genotype (Figure 2B), and all endpoint titers were ≤409,600. Low endpoint titers (Figure 2C) were correspondingly obtained for GII.17 Kawasaki-308 in those infected with GII.4 Sydney/2012 as well as other genotypes (Figure 2D). There was also no significant difference in GII.4 Ni 1315 (p = 0.674) and GII.17 Kawasaki-308 (p = 0.068) specific titers in the acute phase between those infected with GII.4 Sydney/2012 and other genotypes.
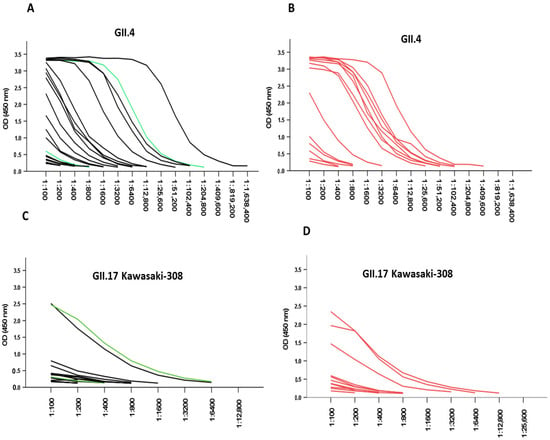
Figure 2.
NoV IgG titration curves in serum samples from acute infections. (A) Sera from children with GII.4 Sydney/2012 (black lines, n = 21) and GI.2 genotype (green line, n = 2). (B) Other GII genotypes (red lines, n = 14) were titrated with two-fold serial dilutions, and IgG antibodies were analyzed against GII.4 Ni 1315 and GII.17 Kawasaki-308 genotypes. For GII.17 Kawasaki-308, (C) black lines, n = 17; green lines, n = 2; and (D) red lines, n = 12.
Children in the age range of 0–2 years exhibited the lowest pre-existing antibody levels (median, 600), while those at 3–5 and 6–12 years had the highest pre-existing antibody level titers (median, 51,200 and 51,200, respectively) (0–2 vs. 3–5, p = 0.0476; 0–2 vs. 6–12, p = 0.0027) (Figure 3). Age was categorized into four groups: 0–2, 3–5, 6–12, and 13–18. The last age group had only one variable in the category and was therefore not included in the analysis for pre-existing NoV antibody titers.
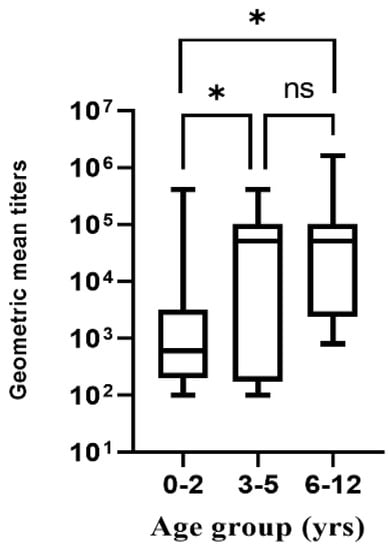
Figure 3.
NoV pre-existing antibody titer responses for different age groups. * p < 0.05, ns: not significant.
3.4. Correlation of Antigenemia with Acute Antibody Titers
We tested whether higher levels of acute norovirus-specific IgG serum antibodies resulted in lower antigenemia OD values and observed a moderate negative correlation with the OD value from EIA (n = 61, r = −0.4258, CI; −0.62 to −0.19; p = 0.0006) (Figure 4).
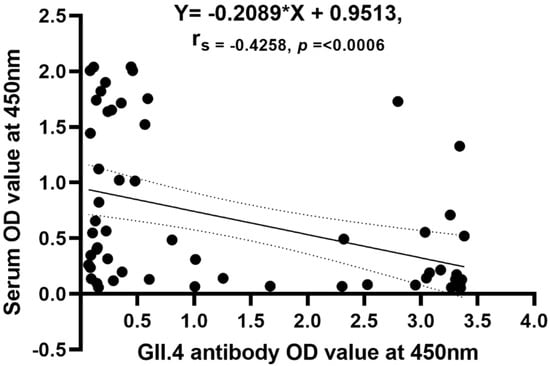
Figure 4.
Correlation of antigenemia to serum acute antibody titers.
3.5. Norovirus Genotypes and Phylogenetic Characteristics
Out of the 63 stool samples sequenced, the NoV genogroup GII was found in 54 cases and genogroup GI in 2 cases. However, seven cases were not sequenced because of the low concentration of cDNA. The genotypes detected from the stool samples were GII.4 (50.8%; 32/63), GII.3 (23.8%; 15/63), GII.2 (11.1%; 7/63), and GI.2 (3.2%; 2/63). The GII.4 had only one variant (Sydney/2012). Recombinant genotypes were also identified in this study, with GII.4 Sydney[P16] being the most predominant (n = 12) followed by GII.4 Sydney[P31] (n = 11), GII.3[P12] (n = 9), and GII.2[P16] (n = 6) (Table 2). GII.4 Sydney/2012 was the only genotype detected in the serum samples sequenced (Table 2) with identical homology to their paired stool samples (Figure 5). Most of the GII.4 Sydney/2012 sequences clustered with the GII.4[P16] virus detected in Brazil and India in 2018 as well as the other GII.4 Sydney[P16]. The same was observed for the serum samples.

Table 2.
NoV genotype distribution in infected children.
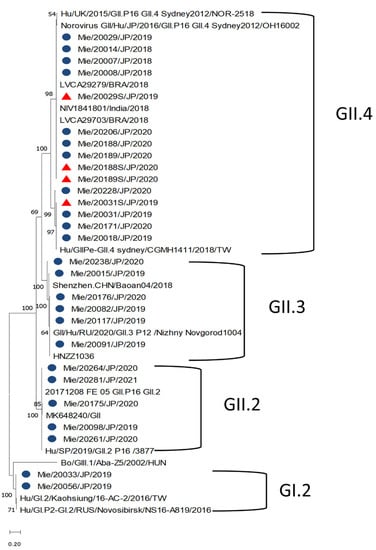
Figure 5.
Phylogenetic analyses generated by the maximum likelihood test using the partial nucleotide sequences (338, 302, and 342 bp) from the C region of the capsid of norovirus. The strains reported in this study are indicated with a blue circle (stool) and a red triangle (sera).
4. Discussion
Rotavirus antigenemia among pediatric patients has been well described [21,22,23]. However, this is the first NoV antigenic study of children in Japan. In this study, we found ~55% of children had NoV antigen in their sera (in Mie, Japan); this is consistent with reports from a rotavirus antigenemia study conducted elsewhere [21]. We were also able to detect NoV-RNA in 14.5% of sera screened, a rate higher than that reported in Finland (6.3%) [16] and lower than that reported in Brazil (20.4%) [24]. Of interest, our data suggest a higher prevalence of antigenemia than RNAemia, which may indicate the presence of infectious viruses in the blood.
It was observed that the Ct values detected in the sera of patients were significantly higher than those from stool samples (Figure 1A), similar to other study reports [13,24]. There was, however, no correlation between the stool Ct values and the likelihood of developing RNAemia, similar to that reported by Takanashi et al. [13]. Nonetheless, a study conducted in Brazil reported a positive correlation between stool Ct values and the likelihood of developing RNAemia [24].
It was reported that rotavirus antigenemia is inversely associated with baseline titers of serum rotaviral IgG [25]. Our results also show norovirus antigenemia to be negatively correlated with GII.4 acute antibody titers. Antigenemia was less likely to be detected in children with higher antibody titers; this might be due to the binding of the serum antibodies to the norovirus antigens present in blood and therefore precluding their detection by ELISA, or the serum antibodies may have prevented norovirus antigens from entering the blood.
One of our objectives was to assess the correlation of pre-existing serum IgG levels and the ability of antibodies to cross-react with VLPs of GII.17 Kawasaki-308 and the predominant GII.4 genotype. The majority of the children’s sera tested in this study recognized both GII.4 and GII.17 Kawasaki-308 VLPs using ELISA, with the level of responses more pronounced for GII.4. We also observed no differences in pre-existing GII.4-specific antibody responses when the IgG titers in patients infected with GII.4 Sydney/2012 were compared with those of patients with other GII/GI.2 infections. The low response to the GII.17 variant might be due to a lower circulation of the genotype in the population [26].
The children infected with NoV in this study were stratified into four age groups: 0–2, 3–5, 6–12, and 13–18 years. Those within the 0–2-year age group had the lowest pre-existing antibody levels. Studies have shown that IgG responses during the first year of life are relatively weak and short-lived; therefore, those in the 0–2 age group are more prone to multiple infections [27,28].
This study also sought to determine whether children with antigenemia presented with more severe clinical features of gastroenteritis than children without. We did not find any significant difference in clinical symptoms or disease severity. However, our laboratory results suggest that CRP levels were higher in those without antigenemia, which we could not explain. We also observed that antigenemia was more common in the younger age group (Table 2), which is likely to be associated with the lower antibody titer.
As observed in other studies, the partial genotyping of the positive samples showed a high detection rate of GII.4 variants [24,29]. The second most common circulating genotype was GII.3, which was detected at low frequency at schools in Shanghai, China [30]. The recombinant strains identified in this study have been well documented [31,32,33]. The GII.P16 polymerases were found to frequently recombine with the GII.4 and GII.2 capsid genotypes. Studies conducted in the past revealed that the P16 sequences that harbor the GII.4 Sydney capsids are almost identical to the P16 polymerase type associated with the GII.2 capsid [4,34]. The GII.4 Sydney/2012 variant identified in this study shared similarities with the GII.4 Sydney/2012 strain detected in Brazil and India in 2018.
This study was limited to only hospitalized children. Furthermore, we were unable to detect the presence of infectious viral particles in the serum.
5. Conclusions
Our results show that norovirus antigenemia occurred more often in children under 2 years of age with NoV-associated acute gastroenteritis. The occurrence of antigenemia did not correlate with stool viral load or disease severity. It could be hypothesized that the younger children had NoV-Ags in their serum due to their low pre-existing antibodies. This finding calls for an understanding of the levels of antigenemia and its correlation with extraintestinal infection, as well as vaccination.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/v14020173/s1. Figure S1: Summary of cases used in this study for statistical analyses, Table S1: Shows the distribution of Norovirus co-infection with other pathogens, Table S2: Reagents used in the reverse transcription (RT) reaction.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.T., J.X.A., K.S. and P.B.T.; methodology, J.X.A. and M.N.; software, J.X.A.; validation, K.T. and M.N.; formal analysis, J.X.A.; investigation, J.X.A., E.D.-M.K. and M.N.; resources, K.T.; data curation, M.N. and J.X.A.; writing—original draft preparation, J.X.A.; writing—review and editing, B.L.L., S.S. and K.T.; visualization, J.X.A. and K.T.; supervision, K.T.; project administration, K.T., J.X.A. and P.B.T.; funding acquisition, K.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Health Labor Sciences Research Grant, the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan, grant number 30140501 and 21HA1004.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethical review board of Mie National Hospital (protocol code 2020-12 and 22 May 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Sequences submitted in this study are available at NCBI GenBank with the accession numbers; OK103809-OK103830, OK103833-OK103836, and OK103839-OK103840.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the technical staff of the department of clinical research, Mie National Hospital, for their assistance and George Armah for his general advice.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rha, B.; Lopman, B.A.; Alcala, A.N.; Riddle, M.S.; Porter, C.K. Incidence of Norovirus-Associated Medical Encounters among Active Duty United States Military Personnel and Their Dependents. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, J.L.; Bonifacio, J.; Bucardo, F.; Buesa, J.; Bruggink, L.; Chan, M.C.; Fumian, T.M.; Giri, S.; Gonzalez, M.D.; Hewitt, J.; et al. Global Trends in Norovirus Genotype Distribution among Children with Acute Gastroenteritis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1438–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, R.I.; Parashar, U.D.; Estes, M.K. Norovirus gastroenteritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1776–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lun, J.H.; Hewitt, J.; Yan, G.J.H.; Enosi Tuipulotu, D.; Rawlinson, W.D.; White, P.A. Recombinant GII.P16/GII.4 Sydney 2012 Was the Dominant Norovirus Identified in Australia and New Zealand in 2017. Viruses 2018, 10, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebenga, J.J.; Vennema, H.; Zheng, D.P.; Vinje, J.; Lee, B.E.; Pang, X.L.; Ho, E.C.; Lim, W.; Choudekar, A.; Broor, S.; et al. Norovirus illness is a global problem: Emergence and spread of norovirus GII.4 variants, 2001–2007. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattner, F.; Sohr, D.; Heim, A.; Gastmeier, P.; Vennema, H.; Koopmans, M. Risk groups for clinical complications of norovirus infections: An outbreak investigation. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, S.M.; Greenberg, H.B. Immunity to calicivirus infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181 (Suppl. S2), S331–S335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Matson, D.O.; Ruiz-Palacios, G.M.; Hu, J.; Treanor, J.; Pickering, L.K. Expression, self-assembly, and antigenicity of a snow mountain agent-like calicivirus capsid protein. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 1452–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Takeshita, S.; Nezu, A.; Aihara, Y.; Usuku, S.; Noguchi, Y.; Yokota, S. Norovirus-associated encephalopathy. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2006, 25, 651–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, R.; Hembree, C.D.; Handel, A.; Matthews, J.E.; Dickey, B.W.; McDonald, S.; Hall, A.J.; Parashar, U.D.; Leon, J.S.; Lopman, B. Severe outcomes are associated with genogroup 2 genotype 4 norovirus outbreaks: A systematic literature review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, S.; Alansari, K.; Smatti, M.K.; Zaraket, H.; Al Thani, A.A.; Yassine, H.M. Epidemiological, Molecular, and Clinical Features of Norovirus Infections among Pediatric Patients in Qatar. Viruses 2019, 11, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, S.S.; Prober, C.G.; Fisher, M. (Eds.) Principles and Practice of Pediatric Infectious Diseases, 5th ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; p. 1907. [Google Scholar]
- Takanashi, S.; Hashira, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Yoshida, A.; Shiota, T.; Tung, P.G.; Khamrin, P.; Okitsu, S.; Mizuguchi, M.; Igarashi, T.; et al. Detection, genetic characterization, and quantification of norovirus RNA from sera of children with gastroenteritis. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 44, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsoum, Z. Rotavirus and adenovirus detecting method: Sensitivity and specificity of rapid antigen testing: Prospective study in one region of Ireland. VirusDisease 2020, 31, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishio, T.; Yonetani, R.; Ito, E.; Yoneta, M.; Maruo, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Sugimoto, T. Development of rhabdomyolysis in a child after norovirus gastroenteritis. BMC Pediatr. 2016, 16, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhti, L.; Hemming-Harlo, M.; Vesikari, T. Norovirus detection from sera of young children with acute norovirus gastroenteritis. J. Clin. Virol. 2016, 79, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansman, G.S.; Natori, K.; Shirato-Horikoshi, H.; Ogawa, S.; Oka, T.; Katayama, K.; Tanaka, T.; Miyoshi, T.; Sakae, K.; Kobayashi, S.; et al. Genetic and antigenic diversity among noroviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malm, M.; Uusi-Kerttula, H.; Vesikari, T.; Blazevic, V. High serum levels of norovirus genotype-specific blocking antibodies correlate with protection from infection in children. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 1755–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazevic, V.; Malm, M.; Honkanen, H.; Knip, M.; Hyöty, H.; Vesikari, T. Development and maturation of norovirus antibodies in childhood. Microbes Infect. 2016, 18, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramani, S.; Paul, A.; Saravanabavan, A.; Menon, V.K.; Arumugam, R.; Sowmyanarayanan, T.V.; Samuel, P.; Kang, G. Rotavirus antigenemia in Indian children with rotavirus gastroenteritis and asymptomatic infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 51, 1284–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemming, M.; Huhti, L.; Räsänen, S.; Salminen, M.; Vesikari, T. Rotavirus antigenemia in children is associated with more severe clinical manifestations of acute gastroenteritis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2014, 33, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justino, M.C.A.; Campos, E.A.; Mascarenhas, J.D.P.; Soares, L.S.; Guerra, S.F.S.; Furlaneto, I.P.; Pavão, M.J.C., Jr.; Maciel, T.S.; Farias, F.P.; Bezerra, O.M.; et al. Rotavirus antigenemia as a common event among children hospitalised for severe, acute gastroenteritis in Belém, northern Brazil. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reymão, T.K.A.; Fumian, T.M.; Justino, M.C.A.; Hernandez, J.M.; Bandeira, R.S.; Lucena, M.S.S.; Teixeira, D.M.; Farias, F.P.; Silva, L.D.; Linhares, A.C.; et al. Norovirus RNA in serum associated with increased fecal viral load in children: Detection, quantification and molecular analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.; Fenaux, M.; Sharma, S.; Malik, J.; Subodh, S.; Bhatnagar, S.; Greenberg, H.; Glass, R.I.; Gentsch, J.; Bhan, M.K. Quantitative evaluation of rotaviral antigenemia in children with acute rotaviral diarrhea. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 194, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morozov, V.; Hanisch, F.G.; Wegner, K.M.; Schroten, H. Pandemic GII.4 Sydney and Epidemic GII.17 Kawasaki308 Noroviruses Display Distinct Specificities for Histo-Blood Group Antigens Leading to Different Transmission Vector Dynamics in Pacific Oysters. Front Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegrist, C.A.; Aspinall, R. B-cell responses to vaccination at the extremes of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurminen, K.; Blazevic, V.; Huhti, L.; Rasanen, S.; Koho, T.; Hytonen, V.P.; Vesikari, T. Prevalence of norovirus GII-4 antibodies in Finnish children. J. Med. Virol. 2011, 83, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumazaki, M.; Usuku, S. Genetic Analysis of Norovirus GII.4 Variant Strains Detected in Outbreaks of Gastroenteritis in Yokohama, Japan, from the 2006–2007 to the 2013–2014 Seasons. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hao, L.; Pan, L.; Xue, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, W. Age, primary symptoms, and genotype characteristics of norovirus outbreaks in Shanghai schools in 2017. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Bao, C.; Huo, X.; Hu, J.; Shi, C.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, J.; Ai, J.; Xing, Z. Increasing Recombinant Strains Emerged in Norovirus Outbreaks in Jiangsu, China: 2015–2018. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wu, X.; Chen, L.; Fu, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhang, P.; Ji, L. Emergence of norovirus GII.P16-GII.2 strains in patients with acute gastroenteritis in Huzhou, China, 2016–2017. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, J.L.; Barclay, L.; Collins, N.R.; Wikswo, M.E.; Castro, C.J.; Magana, L.C.; Gregoricus, N.; Marine, R.L.; Chhabra, P.; Vinje, J. Genetic and Epidemiologic Trends of Norovirus Outbreaks in the United States from 2013 to 2016 Demonstrated Emergence of Novel GII.4 Recombinant Viruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2208–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Brewer-Jensen, P.D.; Mallory, M.L.; Debbink, K.; Swann, E.W.; Vinjé, J.; Baric, R.S. Antigenic Characterization of a Novel Recombinant GII.P16-GII.4 Sydney Norovirus Strain with Minor Sequence Variation Leading to Antibody Escape. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 217, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).