HBV-Integration Studies in the Clinic: Role in the Natural History of Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. HBV Integration in Acute B Infections
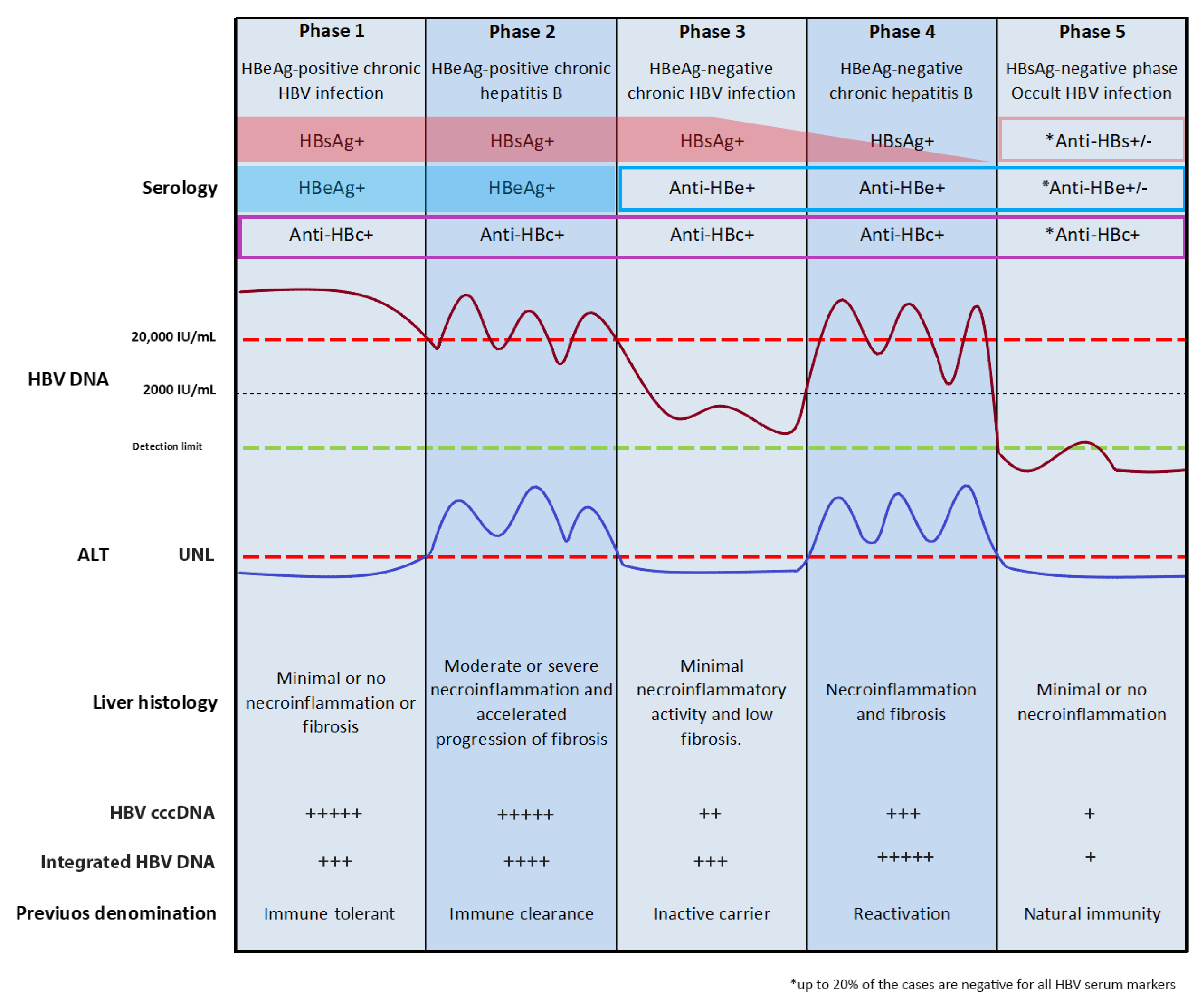
3. Natural History of Chronic HBV Infection
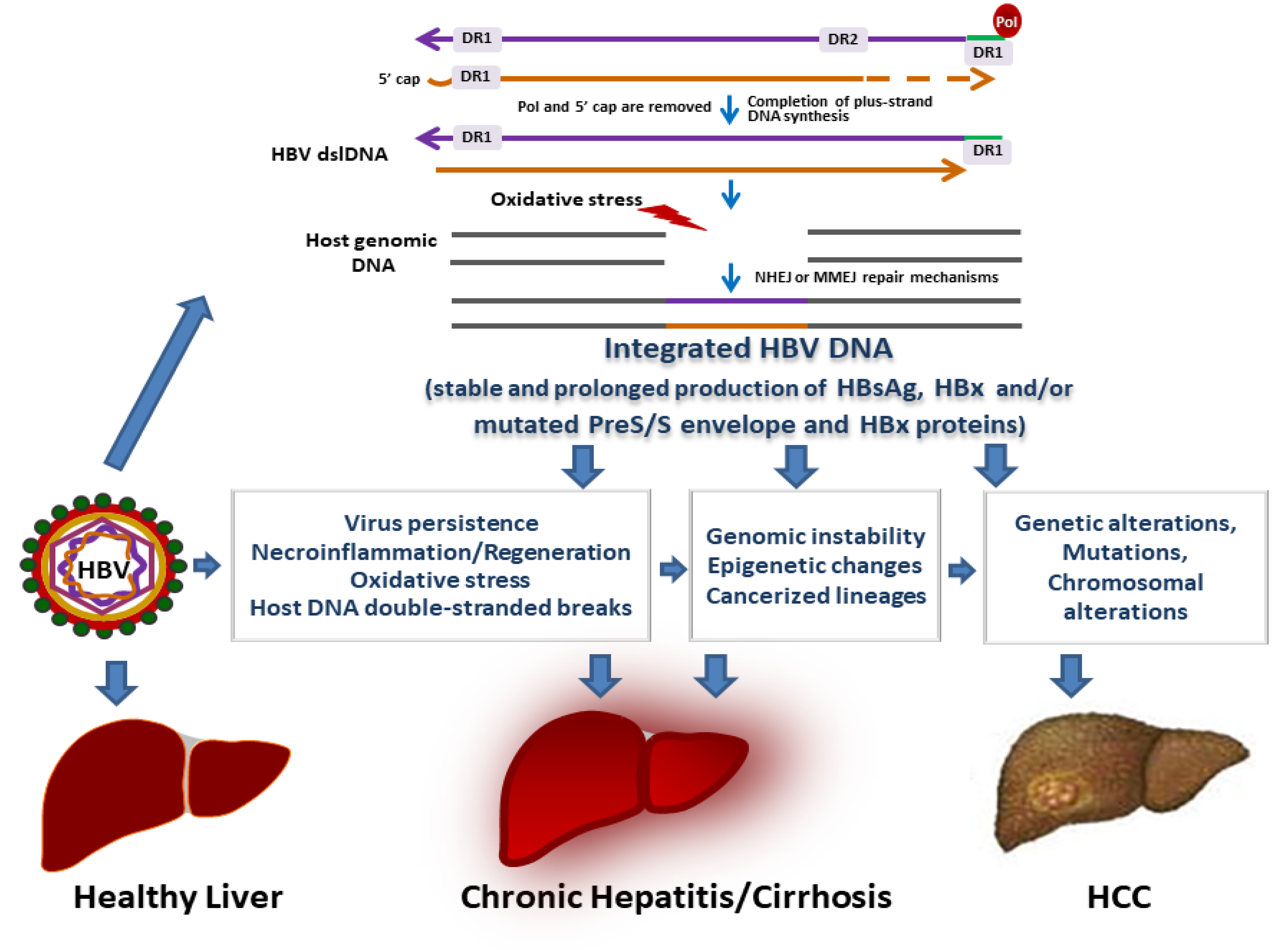
4. HBV Integration in Chronic B Infections
HBV Integration in Occult B Infection
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO (World Health Organization). Global Hepatitis Report 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/global-hepatitis-report2017/en/ (accessed on 4 April 2019).
- The Polaris Observatory Collaborators. Global prevalence, treatment, and prevention of hepatitis B virus infection in 2016: A modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 383–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1151–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.J. Hepatitis B: The virus and disease. Hepatology 2009, 49, S13–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likhitsup, A.; Lok, A.S. Understanding the Natural History of Hepatitis B Virus Infection and the New Definitions of Cure and the Endpoints of Clinical Trials. Clin. Liver Dis. 2019, 23, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, B.J. Natural History of Chronic Hepatitis B. Clin. Liver Dis. 2010, 14, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattovich, G.; Bortolotti, F.; Donato, F. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B: Special emphasis on disease progression and prognostic factors. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, P.T.F.; Litwin, S.; Dolman, G.E.; Bertoletti, A.; Mason, W.S. Immune Tolerant Chronic Hepatitis B: The Unrecognized Risks. Viruses 2017, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protzer, U.; Maini, M.K.; Knolle, P.A. Living in the liver: Hepatic infections. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knolle, P.A.; Thimme, R. Hepatic Immune Regulation and Its Involvement in Viral Hepatitis Infection. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1193–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utzschneider, D.T.; Alfei, F.; Roelli, P.; Barras, D.; Chennupati, V.; Darbre, S.; Delorenzi, M.; Pinschewer, D.D.; Zehn, D. High antigen levels induce an exhausted phenotype in a chronic infection without impairing T cell expansion and survival. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 1819–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.-F.; Chen, D.-S.; Dusheiko, G.M.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Lau, D.T.Y.; Locarnini, S.A.; Peters, M.G.; Lai, C.-L. Hepatitis B virus infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Isogawa, M.; Chisari, F.V. Host-virus interactions in hepatitis B virus infection. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2015, 36, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoletti, A.; Ferrari, C. Innate and adaptive immune responses in chronic hepatitis B virus infections: Towards restoration of immune control of viral infection. Gut 2012, 61, 1754–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 370–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, G.; Caccamo, G.; Filomia, R.; Pollicino, T. Occult HBV infection. Semin. Immunopathol. 2013, 35, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, T.I.; Pasquinelli, C.; Guilhot, S.; Chisari, F.V. Hepatitis B virus persistence after recovery from acute viral hepatitis. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehermann, B.; Ferrari, C.; Pasquinelli, C.; Chisari, F.V. The hepatitis B virus persists for decades after patients’ recovery from acute viral hepatitis despite active maintenance of a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 1104–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werle-Lapostolle, B.; Bowden, S.; Locarnini, S.; Wursthorn, K.; Petersen, J.; Lau, G.; Trepo, C.; Marcellin, P.; Goodman, Z.; Delaney, W.E., IV; et al. Persistence of cccDNA during the natural history of chronic hepatitis B and decline during adefovir dipivoxil therapy. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, G.; Locarnini, S.; Pollicino, T.; Levrero, M.; Zoulim, F.; Lok, A.S.; Taormina Workshop on Occult HBV Infection Faculty Members. Update of the statements on biology and clinical impact of occult hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seetharam, A.; Perrillo, R.; Gish, R. Immunosuppression in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B. Curr. Hepatol. Rep. 2014, 13, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, N.; Nagaoka, T.; Yamashiro, M.; Mochizuki, K.; Kaneko, A.; Yamamoto, K.; Omura, M.; Hikiji, K.; Kato, M. Long-term histologic and virologic outcomes of acute self-limited hepatitis B. Hepatology 2003, 37, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bläckberg, J.; Kidd-Ljunggren, K. Occult hepatitis B virus after acute self-limited infection persisting for 30 years without sequence variation. J. Hepatol. 2000, 33, 992–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, A.; Artini, M.; Cavalli, A.; Levrero, M.; Bertoletti, A.; Pilli, M.; Chisari, F.; Rehermann, B.; Del Prete, G.; Fiaccadori, F.; et al. Long-lasting memory T cell responses following self-limited acute hepatitis B. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbini, A.; Pilli, M.; Raimondo, G.; Ferrari, C.; Missale, G.; Boni, C.; Fisicaro, P.; Penna, A.; Di Vincenzo, P.; Giuberti, T.; et al. The Characteristics of the Cell-Mediated Immune Response Identify Different Profiles of Occult Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bes, M.; Vargas, V.; Piron, M.; Casamitjana, N.; Esteban, J.I.; Vilanova, N.; Pinacho, A.; Quer, J.; Puig, L.; Guardia, J.; et al. T cell responses and viral variability in blood donation candidates with occult hepatitis B infection. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanning, G.C.; Zoulim, F.; Hou, J.; Bertoletti, A. Therapeutic strategies for hepatitis B virus infection: Towards a cure. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, T.; Budzinska, M.A.; Shackel, N.A.; Urban, S. HBV DNA Integration: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Viruses 2017, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassal, M. HBV cccDNA: Viral persistence reservoir and key obstacle for a cure of chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2015, 64, 1972–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, C.; Mason, W.S. Molecular biology of hepatitis B virus infection. Virology 2015, 479–480, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levrero, M.; Pollicino, T.; Petersen, J.; Belloni, L.; Raimondo, G.; Dandri, M. Control of cccDNA function in hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, A.R.; Van Damme, P.; Shouval, D. The global impact of vaccination against hepatitis B: A historical overview. Vaccine 2008, 26, 6266–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, S. Hepatitis B virus X protein: A multifunctional viral regulator. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 36, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slagle, B.L.; Bouchard, M.J. Hepatitis B Virus X and Regulation of Viral Gene Expression. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a021402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Delgermaa, L.; Huang, F.; Oishi, N.; Liu, L.; He, F.; Zhao, L.; Murakami, S. The Transcriptional Transactivation Function of HBx Protein Is Important for Its Augmentation Role in Hepatitis B Virus Replication. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 5548–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivière, L.; Ducroux, A.; Buendia, M.A. The oncogenic role of hepatitis B virus. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2014, 193, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooddell, C.I.; Yuen, M.-F.; Chan, H.L.-Y.; Gish, R.G.; Locarnini, S.A.; Chavez, D.; Ferrari, C.; Given, B.D.; Hamilton, J.; Kanner, S.B.; et al. RNAi-based treatment of chronically infected patients and chimpanzees reveals that integrated hepatitis B virus DNA is a source of HBsAg. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaan0241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revill, P.A.; Tu, T.; Netter, H.J.; Yuen, L.K.W.; Locarnini, S.A.; Littlejohn, M. The evolution and clinical impact of hepatitis B virus genome diversity. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 618–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Summers, J. Integration of Hepadnavirus DNA in Infected Liver: Evidence for a Linear Precursor. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 9710–9717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bill, C.A.; Summers, J. Genomic DNA double-strand breaks are targets for hepadnaviral DNA integration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11135–11140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, T.; Budzinska, M.A.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Shackel, N.A.; Urban, S. Hepatitis B Virus DNA Integration Occurs Early in the Viral Life Cycle in anIn VitroInfection Model via Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide-Dependent Uptake of Enveloped Virus Particles. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02007-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péneau, C.; Imbeaud, S.; La Bella, T.; Hirsch, T.Z.; Caruso, S.; Calderaro, J.; Paradis, V.; Blanc, J.-F.; Letouzé, E.; Nault, J.-C.; et al. Hepatitis B virus integrations promote local and distant oncogenic driver alterations in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omata, M.; Yokosuka, O.; Imazeki, F.; Ito, Y.; Mori, J.; Uchiumi, K.; Okuda, K. Correlation of hepatitis B virus DNA and antigens in the liver. A study in chronic liver disease. Gastroenterology 1987, 92, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, R.; Van Buuren, N.; Suri, V.; Chan, H.; Buti, M.; Marcellin, P.; Mo, H.; Gaggar, A.; Li, L.; Feierbach, B. Targeted long read sequencing reveals the comprehensive architecture and expression patterns of integrated HBV DNA in CHB liver biopsies. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, S6–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, N.; Cunha, C.; Menne, S.; Gudima, S.O. Envelope Proteins Derived from Naturally Integrated Hepatitis B Virus DNA Support Assembly and Release of Infectious Hepatitis Delta Virus Particles. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 5742–5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budzinska, M.A.; Shackel, N.A.; Urban, S.; Tu, T. Cellular Genomic Sites of Hepatitis B Virus DNA Integration. Genes 2018, 9, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafritz, D.A.; Shouval, D.; Sherman, H.I.; Hadziyannis, S.J.; Kew, M.C. Integration of Hepatitis B Virus DNA into the Genome of Liver Cells in Chronic Liver Disease and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Studies in percutaneous liver biopsies and post-mortem tissue specimens. N. Engl. J. Med. 1981, 305, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, M.J.; Greenfield, C.; Chu, C.-M.; Karayiannis, P.; Dunk, A.; Lok, A.S.; Lai, C.L.; Yeoh, E.K.; Monjardino, J.P.; Wankya, B.M.; et al. Integration of HBV-DNA may not be a prerequisite for the maintenance of the state of malignant transformation:An analysis of 110 liver biopsies. J. Hepatol. 1986, 2, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-Y.; Harrison, T.J.; Lee, C.-S.; Chen, D.-S.; Zuckerman, A.J. Detection of hepatitis B virus dna in hepatocellular carcinoma: Analysis by hybridization with subgenomic dna fragments. Hepatology 1988, 8, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, S.; Gotoh, Y.; Hayashi, S.; Yoshida, M.; Koike, K. Structural rearrangement of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA as well as cellular flanking DNA is present in chronically infected hepatic tissues. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, K.-B.; Liu, M.-S.; Chang, P.-C.; Wu, S.-M.; Su, M.-W.; Pan, C.-C.; Han, S.-H. Analysis of six distinct integrated hepatitis B virus sequences cloned from the cellular DNA of a human hepatocellular carcinoma. Virology 1986, 154, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Saigo, K.; Takashima, H.; Minami, M.; Okanoue, T.; Bréchot, C.; Paterlini-Bréchot, P. Large scaled analysis of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA integration in HBV related hepatocellular carcinomas. Gut 2005, 54, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterlini-Bréchot, P.; Saigo, K.; Murakami, Y.; Chami, M.; Gozuacik, D.; Mugnier, C.; Lagorce, D.; Bréchot, C. Hepatitis B virus-related insertional mutagenesis occurs frequently in human liver cancers and recurrently targets human telomerase gene. Oncogene 2003, 22, 3911–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollicino, T.; Vegetti, A.; Saitta, C.; Ferrara, F.; Corradini, E.; Raffa, G.; Pietrangelo, A.; Raimondo, G. Hepatitis B virus DNA integration in tumour tissue of a non-cirrhotic HFE-haemochromatosis patient with hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitta, C.; Tripodi, G.; Barbera, A.; Bertuccio, A.; Smedile, A.; Ciancio, A.; Raffa, G.; SanGiovanni, A.; Navarra, G.; Raimondo, G.; et al. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA integration in patients with occult HBV infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 2311–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chami, M.; Gozuacik, D.; Saigo, K.; Capiod, T.; Falson, P.; Lecoeur, H.; Urashima, T.; Beckmann, J.; Gougeon, M.-L.; Claret, M.; et al. Hepatitis B virus-related insertional mutagenesis implicates SERCA1 gene in the control of apoptosis. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2877–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, M.; Poussin, K.; Bréchot, C.; Paterlini, P. A Novel PCR Technique UsingAlu-Specific Primers to Identify Unknown Flanking Sequences from the Human Genome. Genomics 1995, 29, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, W.S.; Liu, C.; Aldrich, C.E.; Litwin, S.; Yeh, M.M. Clonal Expansion of Normal-Appearing Human Hepatocytes during Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 8308–8315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, W.S.; Gill, U.S.; Kennedy, P.T.; Litwin, S.; Zhou, Y.; Peri, S.; Pop, O.; Hong, M.L.; Naik, S.; Quaglia, A.; et al. HBV DNA Integration and Clonal Hepatocyte Expansion in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Considered Immune Tolerant. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 986–998.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, T.; Mason, W.S.; Clouston, A.D.; Shackel, N.A.; McCaughan, G.W.; Yeh, M.M.; Schiff, E.R.; Ruszkiewicz, A.R.; Chen, J.W.; Harley, H.A.J.; et al. Clonal expansion of hepatocytes with a selective advantage occurs during all stages of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2015, 22, 737–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, W.-K.; Zheng, H.; Li, S.; Chen, R.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Lee, N.P.; Lee, W.H.; Ariyaratne, P.N.; Tennakoon, C.; et al. Genome-wide survey of recurrent HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, A.; Totoki, Y.; Abe, T.; Boroevich, K.A.; Hosoda, F.; Nguyen, H.H.; Aoki, M.; Hosono, N.; Kubo, M.; Miya, F.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing of liver cancers identifies etiological influences on mutation patterns and recurrent mutations in chromatin regulators. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, A.; Furuta, M.; Totoki, Y.; Tsunoda, T.; Kato, M.; Shiraishi, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Taniguchi, H.; Kawakami, Y.; Ueno, M.; et al. Whole-genome mutational landscape and characterization of noncoding and structural mutations in liver cancer. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Wu, L.; Lin, J.; Han, L.; Bian, J.; Wu, Y.; Robson, S.C.; Xue, L.; Ge, Y.; Sang, X.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing reveals the origin and evolution of hepato-cholangiocarcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svicher, V.; Salpini, R.; Piermatteo, L.; Carioti, L.; Battisti, A.; Colagrossi, L.; Scutari, R.; Surdo, M.; Cacciafesta, V.; Nuccitelli, A.; et al. Whole exome HBV DNA integration is independent of the intrahepatic HBV reservoir in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayard, Q.; Meunier, L.; Peneau, C.; Renault, V.; Shinde, J.; Nault, J.-C.; Mami, I.; Couchy, G.; Amaddeo, G.; Tubacher, E.; et al. Cyclin A2/E1 activation defines a hepatocellular carcinoma subclass with a rearrangement signature of replication stress. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Jhunjhunwala, S.; Liu, J.; Haverty, P.M.; Kennemer, M.I.; Guan, Y.; Lee, W.; Carnevali, P.; Stinson, J.; Johnson, S.; et al. The effects of hepatitis B virus integration into the genomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.-C.; Sun, T.; Ching, A.K.; He, M.; Li, J.-W.; Wong, A.M.; Co, N.N.; Chan, A.W.; Li, P.-S.; Lung, R.W.; et al. Viral-Human Chimeric Transcript Predisposes Risk to Liver Cancer Development and Progression. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.-H.; Liu, X.; Yan, H.-X.; Li, W.-Y.; Zeng, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, S.-P.; Zhuang, X.-H.; Lin, C.; et al. Genomic and oncogenic preference of HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugassy, C.; Bernuau, J.; Thiers, V.; Krosgaard, K.; Degott, C.; Wantzin, P.; Schalm, S.W.; Rueff, B.; Benhamou, J.P.; Tiollais, P.; et al. Sequences of Hepatitis B Virus DNA in the Serum and Liver of Patients with Acute Benign and Fulminant Hepatitis. J. Infect. Dis. 1987, 155, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bréchot, C.; Hadchouel, M.; Scotto, J.; Fonck, M.; Potet, F.; Vyas, G.N.; Tiollais, P. State of hepatitis B virus DNA in hepatocytes of patients with hepatitis B surface antigen-positive and -negative liver diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 3906–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotto, J.; Hadchouel, M.; Hery, C.; Alvarez, F.; Yvart, J.; Tiollais, P.; Bernard, O.; Brechot, C. Hepatitis B virus DNA in children’s liver diseases: Detection by blot hybridisation in liver and serum. Gut 1983, 24, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.M. Acute Liver Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1862–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Diaz, G.; De Battista, D.; Bock, K.W.; Moore, I.N.; Wollenberg, K.; Soto, C.; Govindarajan, S.; Kwong, P.D.; Kleiner, D.E.; et al. Role of humoral immunity against hepatitis B virus core antigen in the pathogenesis of acute liver failure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E11369–E11378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Minami, M.; Daimon, Y.; Okanoue, T. Hepatitis B virus DNA in liver, serum, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells after the clearance of serum hepatitis B virus surface antigen. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 72, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimbi, G.C.; Kramvis, A.; Kew, M.C. Integration of hepatitis B virus DNA into chromosomal DNA during acute hepatitis B. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 6416–6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summers, J.; Jilbert, A.R.; Yang, W.; Aldrich, C.E.; Saputelli, J.; Litwin, S.; Toll, E.; Mason, W.S. Hepatocyte turnover during resolution of a transient hepadnaviral infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11652–11659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allweiss, L.; Volz, T.; Giersch, K.; Kah, J.; Raffa, G.; Petersen, J.; Lohse, A.W.; Beninati, C.; Pollicino, T.; Urban, S.; et al. Proliferation of primary human hepatocytes and prevention of hepatitis B virus reinfection efficiently deplete nuclear cccDNA in vivo. Gut 2018, 67, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.; Shimizu, Y.; Watashi, K.; Wakita, T.; Fukasawa, M.; Michalak, T.I. Retrotransposon elements among initial sites of hepatitis B virus integration into human genome in the HepG2-NTCP cell infection model. Cancer Genet. 2019, 235–236, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summers, J.; Mason, W.S. Residual integrated viral DNA after hepadnavirus clearance by nucleoside analog therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 638–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazazian, H.H., Jr.; Moran, J.V. Mobile DNA in Health and Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero, R.B.; Roberts, L.R. The role of hepatitis B virus integrations in the pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 760–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaby, R.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, Y.; Zeng, X.; Li, G.; Wu, P.; Sung, W.-K. SurVirus: A repeat-aware virus integration caller. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. [Epub ahead of printing]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.-W.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Fu, Z.; Yan, X.; Zhu, H.; Diao, W.; Ding, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Hepatitis B virus-human chimeric transcript HBx-LINE1 promotes hepatic injury via sequestering cellular microRNA-122. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Imbeaud, S.; Datta, S.; Zucman-Rossi, J. Authors’ response: Virus-host interactions in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma: More to be revealed? Gut 2015, 64, 853–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshida, Y.; Nijman, S.M.; Kobayashi, M.; Chan, J.A.; Brunet, J.-P.; Chiang, D.Y.; Villanueva, A.; Newell, P.; Ikeda, K.; Hashimoto, M.; et al. Integrative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Common Molecular Subclasses of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7385–7392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, P.T.; Sandalova, E.; Jo, J.; Gill, U.; Ushiro–Lumb, I.; Tan, A.T.; Naik, S.; Foster, G.R.; Bertoletti, A. Preserved T-Cell Function in Children and Young Adults With Immune-Tolerant Chronic Hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-J.; Wong, D.K.; Wahed, A.S.; Lee, W.M.; Feld, J.J.; Terrault, N.A.; Khalili, M.; Sterling, R.K.; Kowdley, K.V.; Bzowej, N.H.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus–Specific and Global T-Cell Dysfunction in Chronic Hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 684–695.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milich, D.R.; Jones, J.; Hughes, J.; Maruyama, T. Role of T-Cell Tolerance in the Persistence of Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Immunother. Emphasis Tumor Immunol. 1993, 14, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Kuo, C.-F.; Akbari, O.; Ou, J.-H.J. Maternal-Derived Hepatitis B Virus e Antigen Alters Macrophage Function in Offspring to Drive Viral Persistence after Vertical Transmission. Immunity 2016, 44, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, G.; Stemler, M.; Schneider, R.; Wildner, G.; Squadrito, G.; Will, H. Latency and reactivation of a precore mutant hepatitis B virus in a chronically infected patient. J. Hepatol. 1990, 11, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-S.; Chien, R.-N.; Yeh, C.-T.; Sheen, I.-S.; Chiou, H.-Y.; Chu, C.-M.; Liaw, Y.-F. Long-term outcome after spontaneous HBeAg seroconversion in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2002, 35, 1522–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laras, A.; Koskinas, J.; Avgidis, K.; Hadziyannis, S.J. Incidence and clinical significance of hepatitis B virus precore gene translation initiation mutations in e antigen-negative patients. J. Viral Hepat. 1998, 5, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, W.-K.; Lai, C.-L.; Ip, P.P.C.; Fung, J.; Wong, D.K.-H.; Yuen, J.C.-H.; Hung, I.F.-N.; Yuen, M.-F. A Large Population Histology Study Showing the Lack of Association between ALT Elevation and Significant Fibrosis in Chronic Hepatitis B. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.J.; Hussain, M.; Lok, A.S.F. Quantitative serum HBV DNA levels during different stages of chronic hepatitis B infection. Hepatology 2002, 36, 1408–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, M.G.; Villeret, F.; Testoni, B.; Zoulim, F. Can we cure hepatitis B virus with novel direct-acting antivirals? Liver Int. 2020, 40 (Suppl. S1), 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornberg, M.; Lok, A.S.-F.; Terrault, N.A.; Zoulim, F. Guidance for design and endpoints of clinical trials in chronic hepatitis B—Report from the 2019 EASL-AASLD HBV Treatment Endpoints Conference. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimoda, R.; Nagashima, M.; Sakamoto, M.; Yamaguchi, N.; Hirohashi, S.; Yokota, J.; Kasai, H. Increased formation of ox-idative DNA damage, 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine, in human livers with chronic hepatitis. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 3171–3172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hagen, T.M.; Huang, S.; Curnutte, J.; Fowler, P.; Martinez, V.; Wehr, C.M.; Ames, B.N.; Chisari, F.V. Extensive oxidative DNA damage in hepatocytes of transgenic mice with chronic active hepatitis destined to develop hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 12808–12812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, J.; Dandri, M.; Bürkle, A.; Zhang, L.; Rogler, C.E. Increase in the frequency of hepadnavirus DNA integrations by oxidative DNA damage and inhibition of DNA repair. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 5455–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandri, M.; Burda, M.R.; Bürkle, A.; Zuckerman, D.M.; Will, H.; Rogler, C.E.; Greten, H.; Petersen, J. Increase in de novo HBV DNA integrations in response to oxidative DNA damage or inhibition of poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation. Hepatology 2002, 35, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.K.-H.; Cheng, S.C.Y.; Mak, L.L.-Y.; To, E.W.-P.; Lo, R.C.-L.; Cheung, T.-T.; Seto, W.-K.; Fung, J.; Man, K.; Lai, C.-L.; et al. Among Patients with Undetectable Hepatitis B Surface Antigen and Hepatocellular Carcinoma, a High Proportion Has Integration of HBV DNA into Hepatocyte DNA and No Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadziyannis, S.J.; Lieberman, H.M.; Karvountzis, G.G.; Shafritz, D.A. Analysis of Liver Disease, Nuclear HBcAg, Viral Replication, and Hepatitis B Virus DNA in Liver and Serum of HBcAg Vs. Anti-HBe Positive Carriers of Hepatitis B Virus. Hepatology 1983, 3, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budzinska, M.A.; Shackel, N.A.; Urban, S.; Tu, T. Sequence analysis of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA during HBeAg-seroconversion. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, S.B.; Tripodi, G.; Raimondo, G.; Saitta, C.; Norkrans, G.; Pollicino, T.; Lindh, M. Integration of hepatitis B virus DNA in chronically infected patients assessed by Alu-PCR. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 1568–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kam, W.; Rall, L.B.; Smuckler, E.A.; Schmid, R.; Rutter, W.J. Hepatitis B viral DNA in liver and serum of asymptomatic carriers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 7522–7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bréchot, C.; Gozuacik, D.; Murakami, Y.; Paterlini-Bréchot, P. Molecular bases for the development of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Semin. Cancer Biol. 2000, 10, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydell, G.E.; Larsson, S.B.; Prakash, K.; Andersson, M.; Norder, H.; Hellstrand, K.; Norkrans, G.; Lindh, M. Abundance of Noncircular Intrahepatic Hepatitis B Virus DNA May Reflect Frequent Integration into Human DNA in Chronically Infected Patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, U.S.; Pallett, L.J.; Kennedy, P.T.F.; Maini, M.K. Liver sampling: A vital window into HBV pathogenesis on the path to functional cure. Gut 2018, 67, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Oikawa, R.; Toyota, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Kokudo, N.; Tanaka, S.; Arii, S.; Yotsuyanagi, H.; Koike, K.; et al. DNA methylation at hepatitis B viral integrants is associated with methylation at flanking human genomic sequences. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Lou, X.; Hua, D.; Yu, W.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Gao, F.; Zhao, N.; Ren, G.; Li, L.; et al. Recurrent Targeted Genes of Hepatitis B Virus in the Liver Cancer Genomes Identified by a Next-Generation Sequencing–Based Approach. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1003065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podlaha, O.; Wu, G.; Downie, B.; Ramamurthy, R.; Gaggar, A.; Subramanian, M.; Ye, Z.; Jiang, Z. Genomic modeling of hepatitis B virus integration frequency in the human genome. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asabe, S.; Wieland, S.F.; Chattopadhyay, P.K.; Roederer, M.; Engle, R.E.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. The Size of the Viral Inoculum Contributes to the Outcome of Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 9652–9662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, W.S.; Litwin, S.; Jilbert, A.R. Immune selection during chronic hepadnavirus infection. Hepatol. Int. 2008, 2, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.L.-Y.; Thompson, A.; Martinot-Peignoux, M.; Piratvisuth, T.; Cornberg, M.; Brunetto, M.R.; Tillmann, H.L.; Kao, J.-H.; Jia, J.-D.; Wedemeyer, H.; et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen quantification: Why and how to use it in 2011—A core group report. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-L.; Wong, D.; Ip, P.; Kopaniszen, M.; Seto, W.-K.; Fung, J.; Huang, F.-Y.; Lee, B.; Cullaro, G.; Chong, C.K.; et al. Reduction of covalently closed circular DNA with long-term nucleos(t)ide analogue treatment in chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Thompson, A.J.; Bowden, S.; Croagh, C.; Bell, S.; Desmond, P.V.; Levy, M.; Locarnini, S.A. Hepatitis B surface antigen levels during the natural history of chronic hepatitis B: A perspective on Asia. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.Y.; Wong, V.W.; Zhou, H.J.; Chan, H.Y.; Gui, H.L.; Guo, S.M.; Wang, H.; Huang, L.; Bao, S.S.; Xie, Q.; et al. Relationship between serum hepatitis B virus DNA and surface antigen with covalently closed circular DNA in HBeAg-negative patients. J. Med. Virol. 2010, 82, 1494–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.J.; Nguyen, T.; Lau, G.K.; Lewin, S.R.; Visvanathan, K.; Desmond, P.V.; Locarnini, S.A.; Iser, D.; Ayres, A.; Jackson, K.; et al. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen titers: Disease phase influences correlation with viral load and intrahepatic hepatitis B virus markers. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1933–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manesis, E.K.; Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Tiniakos, D.G.; Hadziyannis, E.S.; Agelopoulou, O.P.; Syminelaki, T.; Papaioannou, C.; Nastos, T.; Karayiannis, P. Hepatitis B surface antigen: Relation to hepatitis B replication parameters in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Wang, R.; Fu, J.; Su, M.; Du, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Lu, F.; Jiang, J. Integration of hepatitis B virus S gene impacts on hepatitis B surface antigen levels in patients with antiviral therapy. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, Y.-F.; Seto, W.-K.; Wong, D.; Cheung, K.-S.; Fung, J.; Mak, L.-Y.; Yuen, J.; Chong, C.-K.; Lai, C.-L.; Yuen, M.-F. Seven-Year Treatment Outcome of Entecavir in a Real-World Cohort: Effects on Clinical Parameters, HBsAg and HBcrAg Levels. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2017, 8, e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, J.; Locarnini, S.; Zoulim, F. Direct-acting antivirals and viral RNA targeting for hepatitis B cure. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2020, 15, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamay, M.; Agami, R.; Shaul, Y. HBV integrants of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines contain an active enhancer. Oncogene 2001, 20, 6811–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Jayasuryan, N.; Kumar, R. A truncated mutant (residues 58-140) of the hepatitis B virus X protein retains transactivation function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 5647–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlüter, V.; Meyer, M.; Hofschneider, P.H.; Koshy, R.; Caselmann, W.H. Integrated hepatitis B virus X and 3′ truncated preS/S sequences derived from human hepatomas encode functionally active transactivators. Oncogene 1994, 9, 3335–3344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lucifora, J.; Arzberger, S.; Durantel, D.; Belloni, L.; Strubin, M.; Levrero, M.; Zoulim, F.; Hantz, O.; Protzer, U. Hepatitis B virus X protein is essential to initiate and maintain virus replication after infection. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leupin, O.; Bontron, S.; Schaeffer, C.; Strubin, M. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Stimulates Viral Genome Replication via a DDB1-Dependent Pathway Distinct from That Leading to Cell Death. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 4238–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloni, L.; Pollicino, T.; De Nicola, F.; Guerrieri, F.; Raffa, G.; Fanciulli, M.; Raimondo, G.; Levrero, M. Nuclear HBx binds the HBV minichromosome and modifies the epigenetic regulation of cccDNA function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19975–19979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decorsière, A.; Mueller, H.; Van Breugel, P.C.; Abdul, F.; Gerossier, L.; Beran, R.K.; Livingston, C.M.; Niu, C.; Fletcher, S.P.; Hantz, O.; et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein identifies the Smc5/6 complex as a host restriction factor. Nature 2016, 531, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-C.; Huang, W.; Lai, M.-D.; Su, I.-J. Hepatitis B virus pre-S mutants, endoplasmic reticulum stress and hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Sci. 2006, 97, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xia, Y.; Cheng, X.; Kleiner, D.E.; Hewitt, S.M.; Sproch, J.; Li, T.; Zhuang, H.; Liang, T.J. Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Activates Unfolded Protein Response in Forming Ground Glass Hepatocytes of Chronic Hepatitis B. Viruses 2019, 11, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.-H.; Su, I.-J.; Wang, H.-C.; Chang, W.-T.; Lei, H.-Y.; Lai, M.-D.; Huang, W. Pre-S mutant surface antigens in chronic hepatitis B virus infection induce oxidative stress and DNA damage. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 2023–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-C.; Wu, H.-C.; Chen, C.-F.; Fausto, N.; Lei, H.-Y.; Su, I.-J. Different Types of Ground Glass Hepatocytes in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Contain Specific Pre-S Mutants that May Induce Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 2441–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, I.-J.; Wang, H.-C.; Wu, H.-C.; Huang, W.-Y. Ground glass hepatocytes contain pre-S mutants and represent preneoplastic lesions in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollicino, T.; Amaddeo, G.; Restuccia, A.; Raffa, G.; Alibrandi, A.; Cutroneo, G.; Favaloro, A.; Maimone, S.; Squadrito, G.; Raimondo, G. Impact of hepatitis B virus (HBV) preS/S genomic variability on HBV surface antigen and HBV DNA serum levels. Hepatology 2012, 56, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.-H.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Su, I.-J.; Yen, C.-J.; Liu, Y.-R.; Liu, R.-J.; Hsieh, W.-C.; Tsai, H.-W.; Wang, L.H.-C.; Huang, W. Hepatitis B virus pre-S2 mutant large surface protein inhibits DNA double-strand break repair and leads to genome instability in hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Pathol. 2015, 236, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, L.-Y.; Wong, D.K.-H.; Pollicino, T.; Raimondo, G.; Hollinger, F.B.; Yuen, M.-F. Occult hepatitis B infection and hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology, virology, hepatocarcinogenesis and clinical significance. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollicino, T.; Saitta, C.; Raimondo, G. Hepatocellular carcinoma: The point of view of the hepatitis B virus. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 1122–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoda, H.; Kumada, T.; Kaneoka, Y.; Murakami, Y. Impact of hepatitis B virus (HBV) X gene integration in liver tissue on hepatocellular carcinoma development in serologically HBV-negative chronic hepatitis C patients. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamori, A.; Nishiguchi, S.; Kubo, S.; Enomoto, M.; Koh, N.; Takeda, T.; Shiomi, S.; Hirohashi, K.; Kinoshita, H.; Otani, S. Sequencing of human-viral DNA junctions in hepatocellular carcinoma from patients with HCV and occult HBV infection. J. Med. Virol. 2003, 69, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterlini, P.; Poussin, K.; Kew, M.; Franco, D.; Brechot, C. Selective accumulation of the X transcript of hepatitis B virus in patients negative for hepatitis B surface antigen with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 1995, 21, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poussin, K.; Dienes, H.; Sirma, H.; Urban, S.; Beaugrand, M.; Franco, D.; Schirmacher, P.; Brechot, C.; Paterlini Brechot, P. Expression of mutated hepatitis B virus X genes in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 80, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; London, W.T.; Duan, L.-X.; Feitelson, M.A. The value of hepatitis B x antigen as a prognostic marker in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 1993, 55, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kew, M.C. Hepatitis B virus x protein in the pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, T.-I.; Wang, X.W.; Forgues, M.; Wu, C.-G.; Spillare, E.A.; Giannini, C.; Bréchot, C.; Harris, C.C. Hepatitis B virus X mutants derived from human hepatocellular carcinoma retain the ability to abrogate p53-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 2001, 20, 3620–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.-F.; Lau, S.H.; Hu, L.; Xie, D.; Wu, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, M.-C.; Fung, J.; Bai, X.; et al. COOH-Terminal Truncated HBV X Protein Plays Key Role in Hepatocarcinogenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 5061–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizzano, R.A.; Yang, B.; Clippinger, A.J.; Bouchard, M.J. The C-terminal region of the hepatitis B virus X protein is essential for its stability and function. Virus Res. 2011, 155, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirma, H.; Giannini, C.; Poussin, K.; Paterlini, P.; Kremsdorf, D.; Bréchot, C. Hepatitis B virus X mutants, present in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue abrogate both the antiproliferative and transactivation effects of HBx. Oncogene 1999, 18, 4848–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtius, K.; Wright, N.A.; Graham, T.A. An evolutionary perspective on field cancerization. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, S. Molecular events in hepatic preneoplasia: A review. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2010, 88, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nault, J.C.; Calderaro, J.; Di Tommaso, L.; Balabaud, C.; Zafrani, E.S.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Roncalli, M.; Zucman-Rossi, J. Telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter mutation is an early somatic genetic alteration in the transformation of premalignant nodules in hepatocellular carcinoma on cirrhosis. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, D.; Saitta, C.; Giosa, D.; Di Tocco, F.C.; Musolino, C.; Caminiti, G.; Chines, V.; Franzè, M.S.; Alibrandi, A.; Navarra, G.; et al. Frequency of somatic mutations in TERT promoter, TP53 and CTNNB1 genes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma from Southern Italy. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 2368–2374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Technique | Suitable Uses | Advantages | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Southern blot hybridization | HBV DNA integration detection in liver samples with highly expanded hepatocyte clones | Low cost |
| [47,48,49,50] |
| Direct cloning and Sanger sequencing | Defining structure of HBV integration in liver samples with highly expanded hepatocyte clones | Definition of the sequences of integrated HBV DNA and the adjacent cellular DNA |
| [50,51] |
| Alu PCR | Detecting and sequencing of HBV integration in clonally expanded hepatocytes | Inexpensive |
| [52,53,54,55,56,57] |
| Inverse PCR | Detecting and quantifying HBV DNA integrations in small hepatocyte clones (single copy virus–cell junctions can be detected) |
|
| [39,41,58,59,60] |
| Whole genome sequencing (WGS) | Sensitive and comprehensive inthe identification of viral integrants across the human genome | Full genome coverage |
| [61,62,63] |
| Whole-exome sequencing | Detection of HBV integration in coding regions | Greater depth than WGS |
| [64,65,66,67] |
| RNA Sequencing | Sensitive and comprehensive in the identification of viral integrants across the human transcriptome |
|
| [42,65,66,67,68] |
| Capture-enriched next generation sequencing | High-throughput viral integration detection method |
|
| [42,69] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pollicino, T.; Caminiti, G. HBV-Integration Studies in the Clinic: Role in the Natural History of Infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030368
Pollicino T, Caminiti G. HBV-Integration Studies in the Clinic: Role in the Natural History of Infection. Viruses. 2021; 13(3):368. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030368
Chicago/Turabian StylePollicino, Teresa, and Giuseppe Caminiti. 2021. "HBV-Integration Studies in the Clinic: Role in the Natural History of Infection" Viruses 13, no. 3: 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030368
APA StylePollicino, T., & Caminiti, G. (2021). HBV-Integration Studies in the Clinic: Role in the Natural History of Infection. Viruses, 13(3), 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030368





